Semester Exam Review - Diagram Anatomy
1/177
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy vocabulary flashcards for semester exam review.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

178 Terms
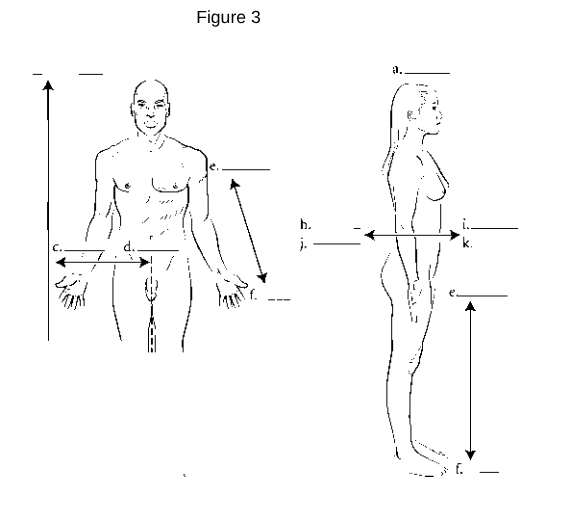
a
Superior: Refers to a position above or higher than another part of the body.
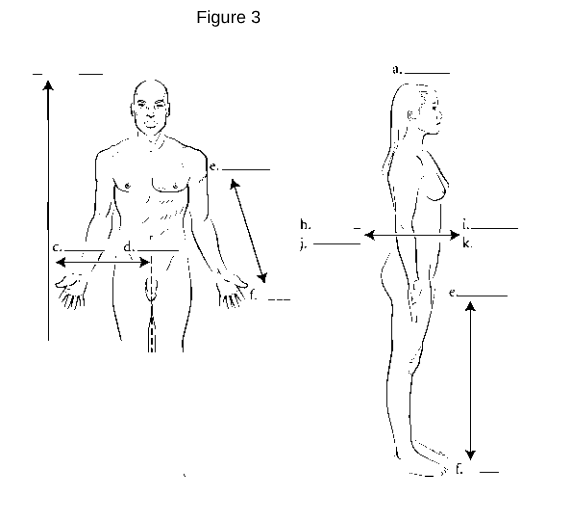
z
Inferior: Refers to a position below or lower than another part of the body.
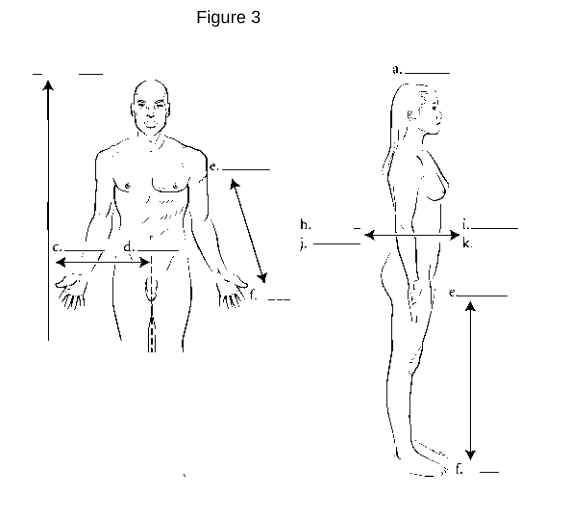
i/k
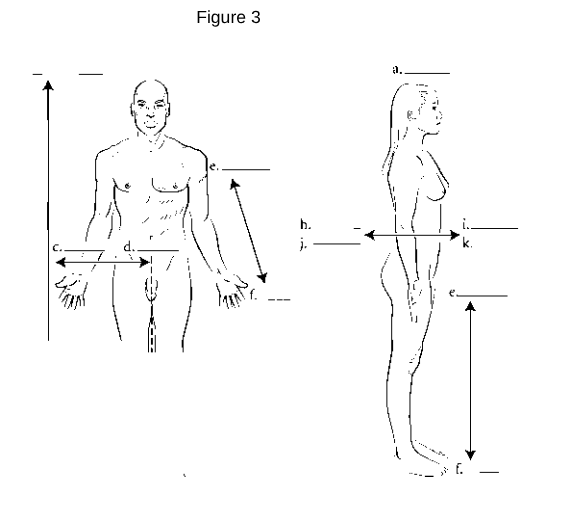
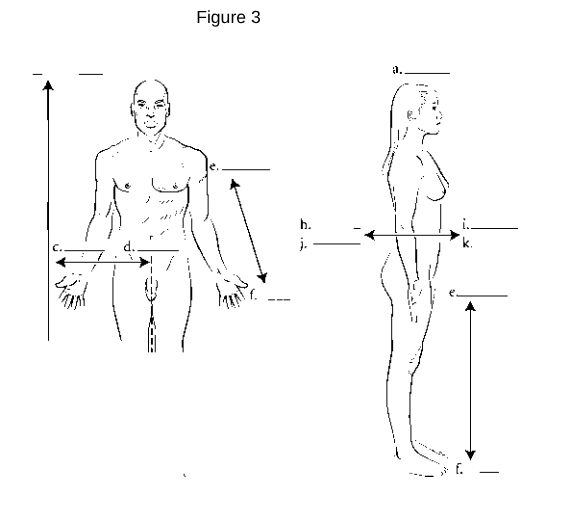
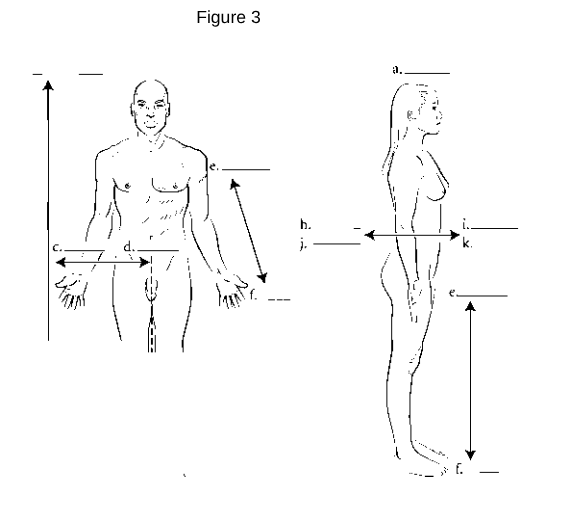
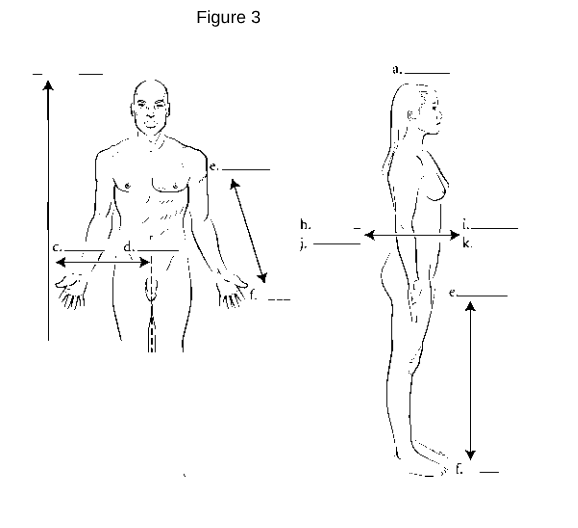
Anterior (Ventral): Refers to the front of the body.
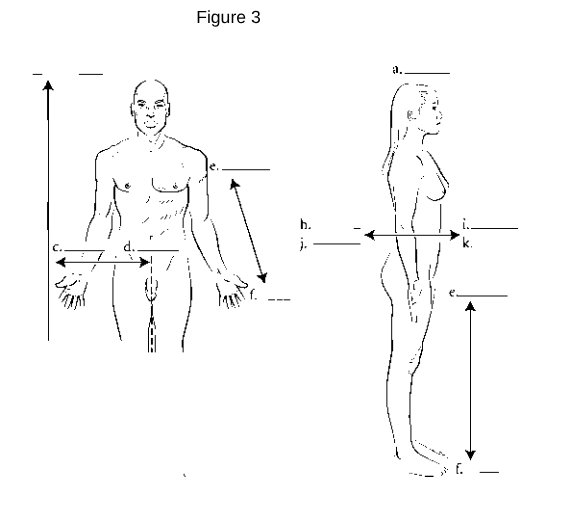
h/j
Posterior (Dorsal): Refers to the back of the body.
d
Medial: Refers to being closer to the midline of the body.
c
Lateral: Refers to being further away from the midline of the body.
e
Proximal: Refers to being closer to the point of attachment or origin.
f
Distal: Refers to being further away from the point of attachment or origin.
Superficial
Refers to a structure located near the surface of the body.
Deep
Refers to a structure located further away from the surface of the body.
Sagittal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts.
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
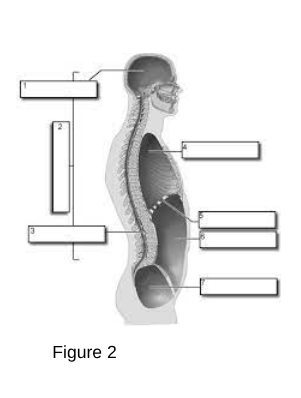
1
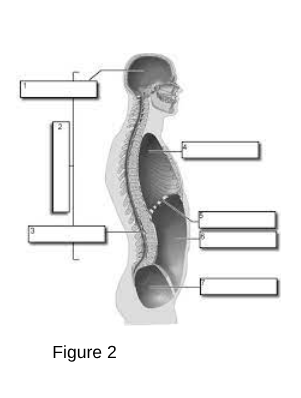
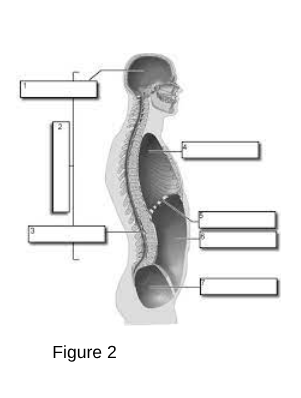
Cranial Cavity: The space within the skull that houses the brain.
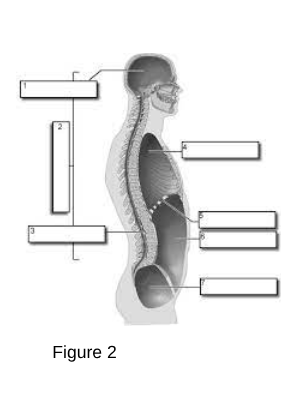
3
Vertebral (Spinal) Cavity: The space within the vertebral column that houses the spinal cord.
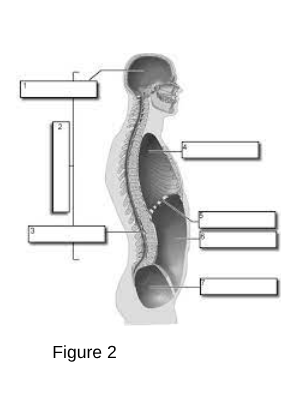
4
Thoracic Cavity: The chamber of the body that lies between the neck and the diaphragm.
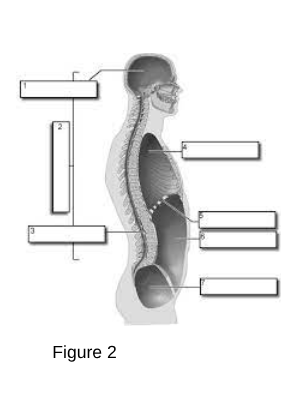
5
Diaphragm
A dome-shaped muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity, playing a critical role in respiration by contracting and relaxing to facilitate breathing.
6
Abdominal Cavity: The area of the body that contains the digestive organs.
7
Pelvic Cavity: The space bounded by the bones of the pelvis.
a/b
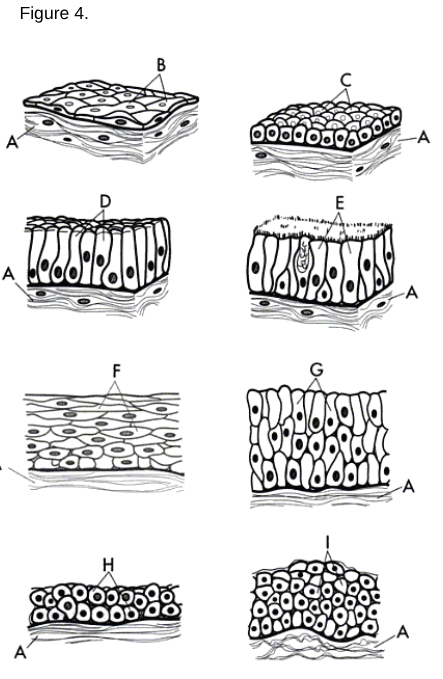
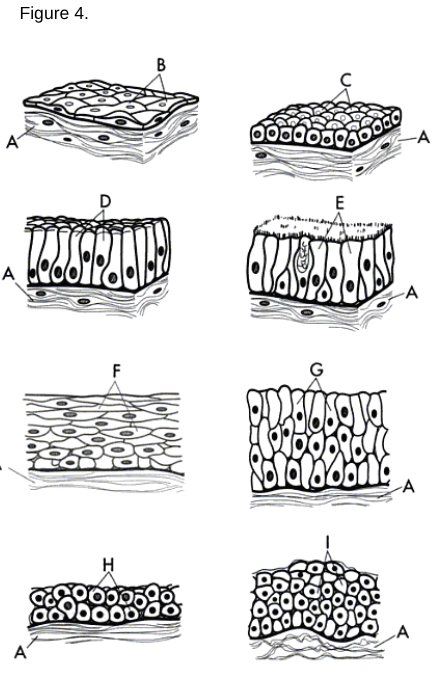
Simple Squamous Epithelium: A single layer of flat cells found in areas where diffusion or filtration occurs.
a/c
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: A single layer of cube-shaped cells used for secretion and absorption.
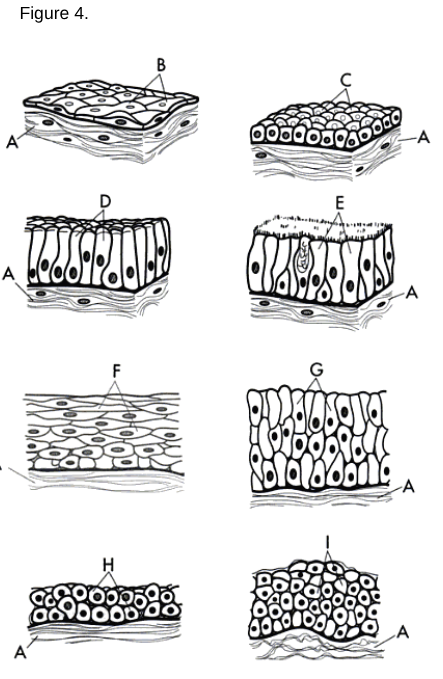
a/d
Simple Columnar Epithelium: A single layer of tall, column-like cells that may have microvilli or cilia.
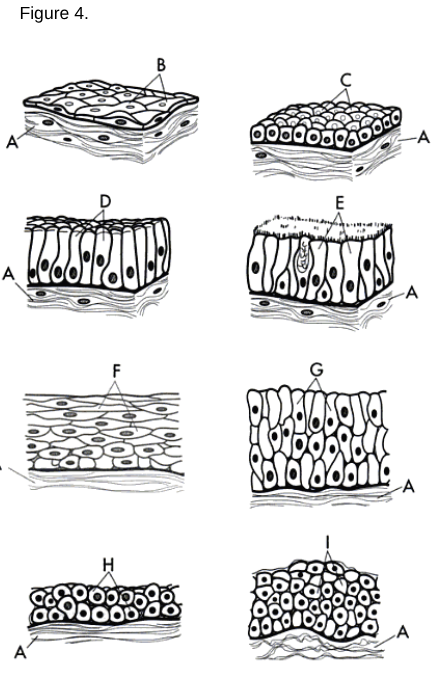
a/f
Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Multiple layers of cells where the uppermost cells are flat.
Bone
A type of dense connective tissue that makes up the skeleton.
Cartilage
A flexible connective tissue found in various parts of the body.
Blood
A specialized connective tissue that transports nutrients and waste.
Skull
The bony structure that forms the head and protects the brain.
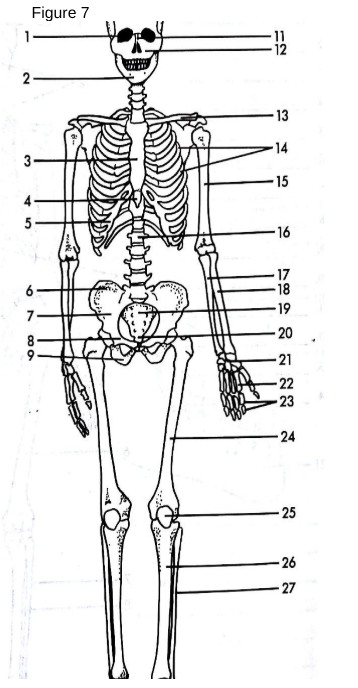
13
Clavicle: The collarbone, connecting the arm to the body.
Also known as the shoulder blade.
Scapula
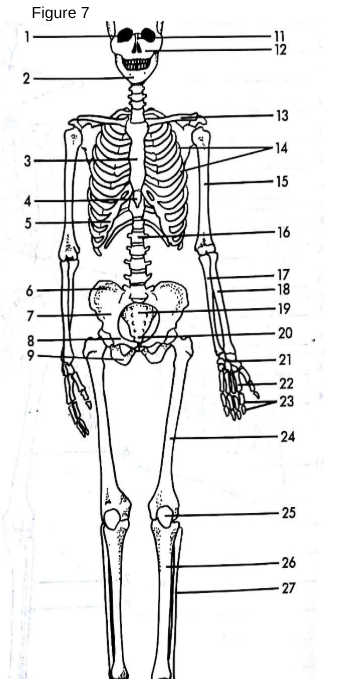
3
Sternum
The breastbone located in the center of the chest.
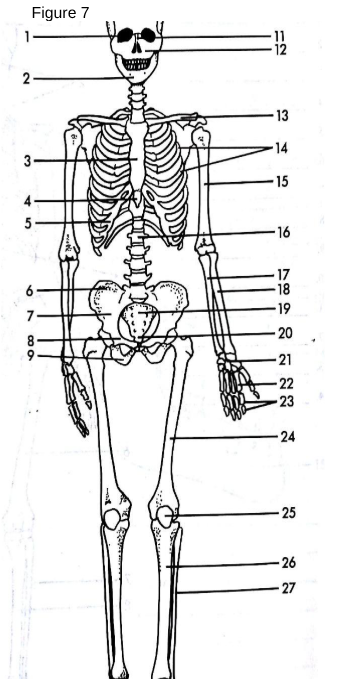
5
False Ribs
The bones that form the rib cage around the thoracic cavity.
15
Humerus
The long bone of the upper arm.
18
Radius
One of the two bones of the forearm, located on the thumb side.
17
Ulna
One of the two bones of the forearm, located on the pinky side.
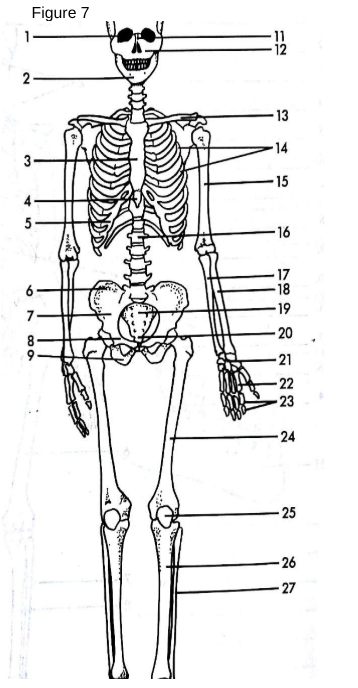
21
Carpals
The wrist bones.
22
Metacarpals
The bones of the hand.
23
Phalanges (hand)
The bones of the fingers.
Axial Skeleton
The part of the skeleton that consists of the skull, vertebrae, and rib cage.
Appendicular Skeleton
The part of the skeleton that includes the limbs and girdles.
Epiphysis
The end part of a long bone.
Diaphysis
The shaft or central part of a long bone.
8
Compact Bone
The denser, outer layer of bone.
9
Spongy Bone
The lighter, inner layer of bone that contains trabecular.
The central cavity of a bone that houses bone marrow.
Medullary Cavity
Bones that are longer than they are wide.
Long Bone
Bones that are approximately cuboidal in shape.
Short Bone
Bones that are thin and flat.
Flat Bone
Bones that do not fit into any of the other categories.
Irregular Bone
Bones that are embedded within tendons.
Sesamoid Bone
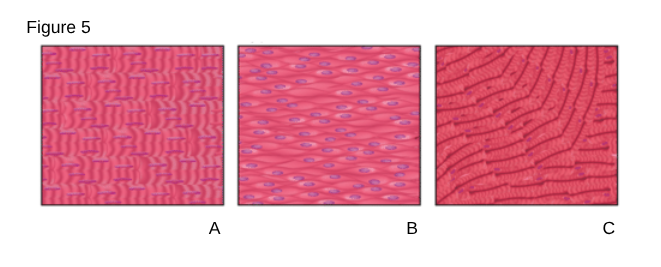
A
Skeletal Muscle
Striated muscle tissue that is under voluntary control.
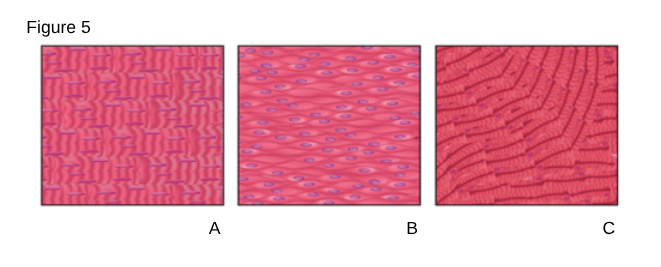
B
Smooth Muscle
Non-striated muscle tissue that is under involuntary control.
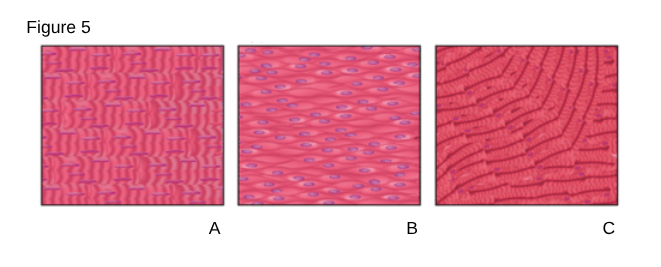
C
Cardiac Muscle
Striated muscle tissue of the heart.
Part of the nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Part of the nervous system that includes all nerves outside the CNS.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The organ of the body that serves as the control center.
Brain
Spinal Cord
The main pathway for information connecting the brain and peripheral nervous system.
Fibers that transmit signals between the brain and body.
Nerves
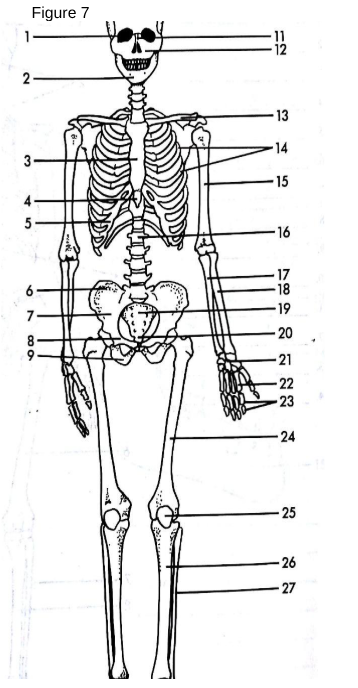
14
True ribs
connected directly to sternum
4
xiphoid process
lower part of sternum
6
Ilium uppermost flared portion of the pelvis
8
pubis
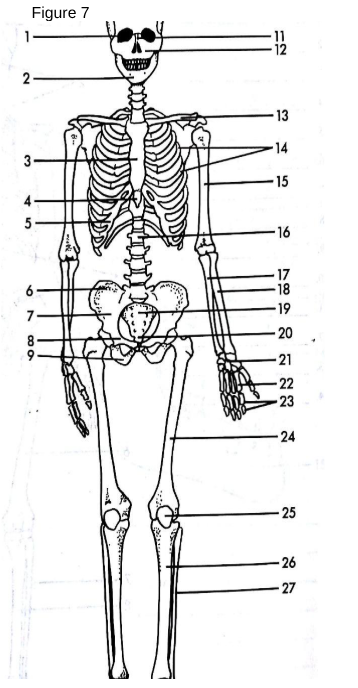
27
Fibula
“a tiny fib” The slender bone located alongside the tibia in the lower leg, providing stability to the ankle and supporting muscles.
9
Ischium
19
Sacrum
triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms the back part of the pelvis.
20
Coccyx
The small, triangular bone at the base of the vertebral column, formed by the fusion of four vertebrae.
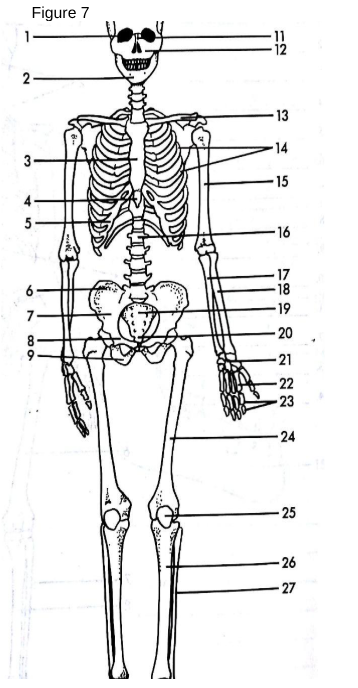
24
Femur
the longest bone in the human body, located in the thigh and connecting to the pelvis.
25
Patella
The small, flat, circular bone located at the front of the knee joint, commonly known as the kneecap. Universal sesamoid bone.
26
Tibia
The second largest bone in the lower leg, commonly known as the shinbone, it bears weight and connects the knee to the ankle.
1
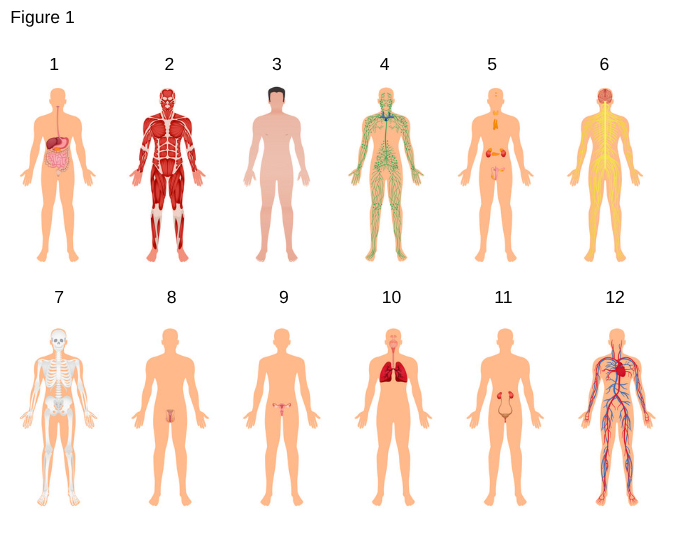
Digestive System
the system responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and expelling waste from the body.
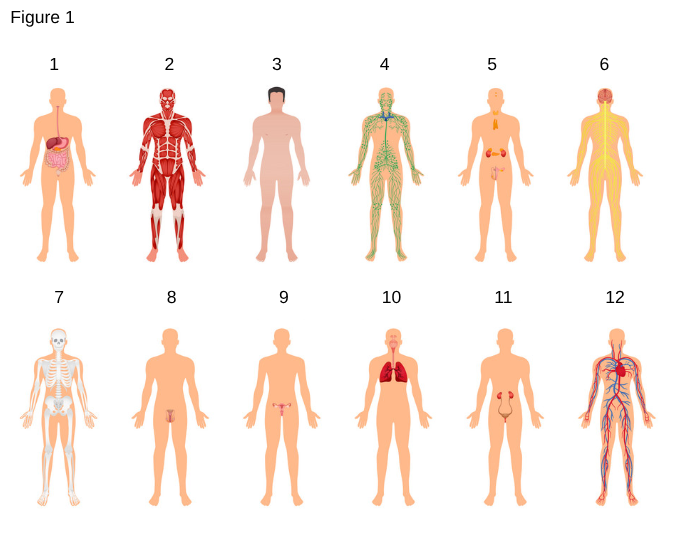
2
Muscular System
the system that enables movement, maintains posture, and produces heat through muscle contractions.
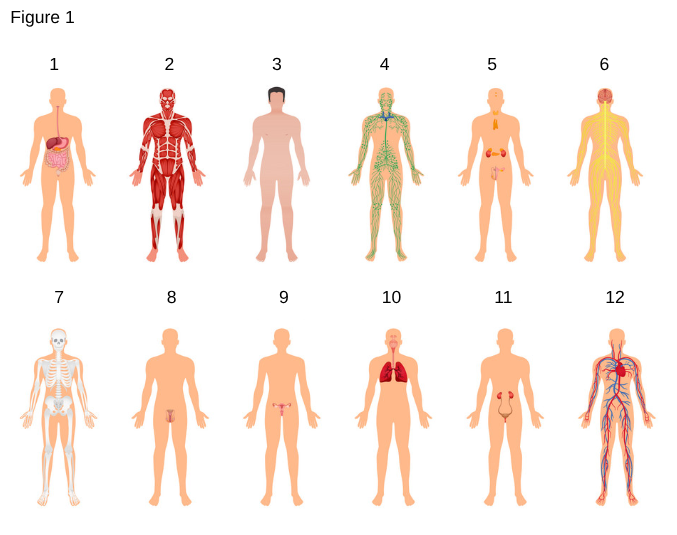
3
Integumentary System
the body's outer covering that protects internal organs, regulates body temperature, and provides sensory information.
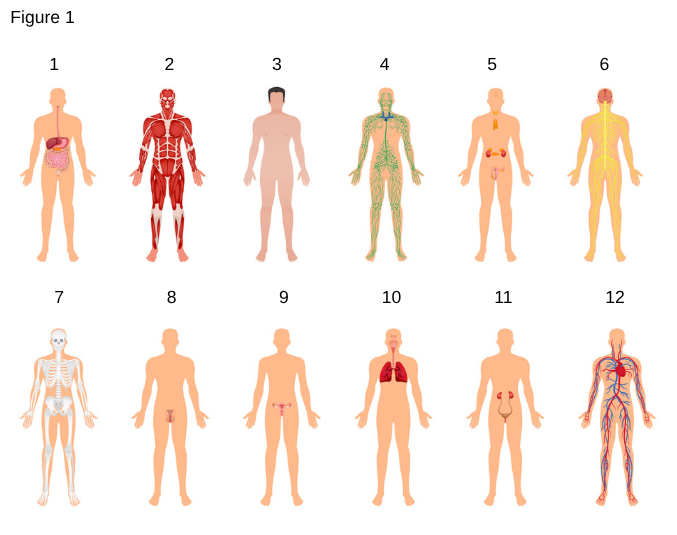
4
Lymphatic System
the system that helps protect and maintain the fluid environment of the body by filtering and draining lymph away from each region of the body.
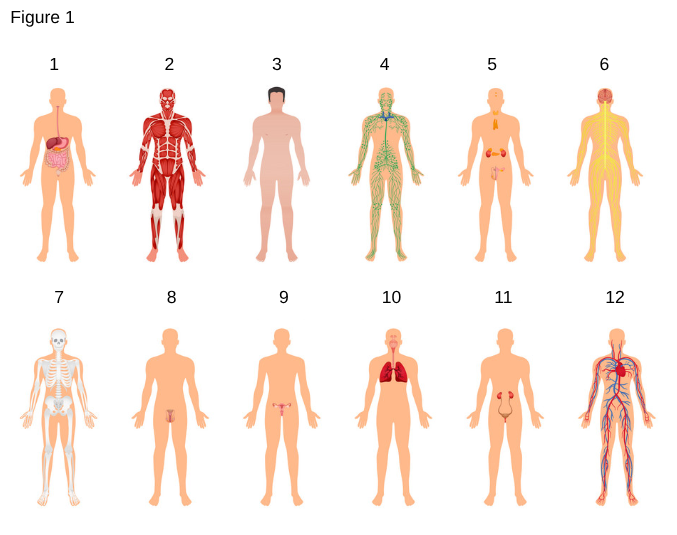
5
Endocrine System
the system of glands that secrete hormones to regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
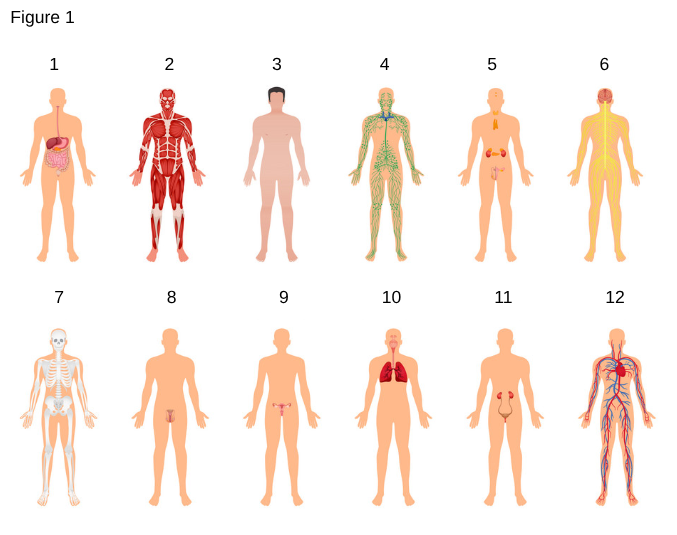
6
Nervous System
the network of nerves and cells that coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions by transmitting signals between different parts of the body.
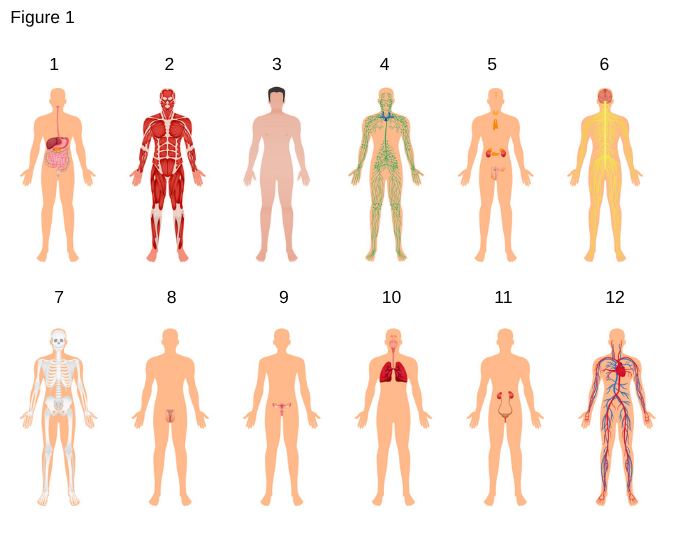
7
Skeletal System
the system that provides structural support, protection for internal organs, and facilitates movement by serving as an attachment point for muscles.
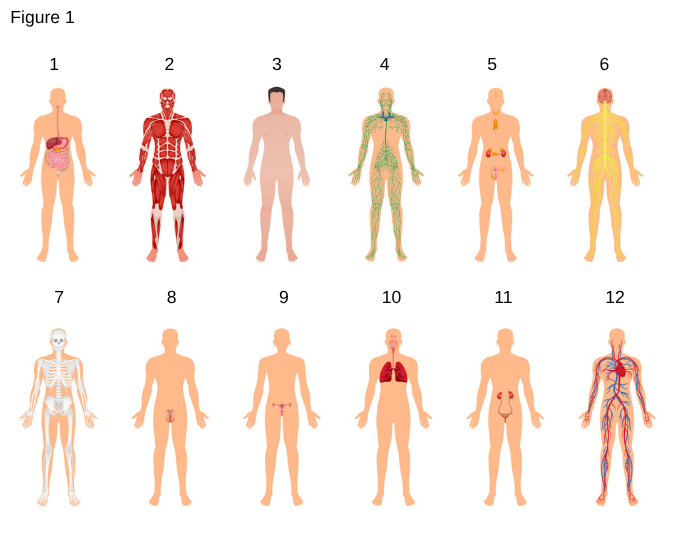
8
Male Reproductive System
the system responsible for the production of sperm and production of hormones such as testosterone, including organs like the testes, prostate gland, and penis.
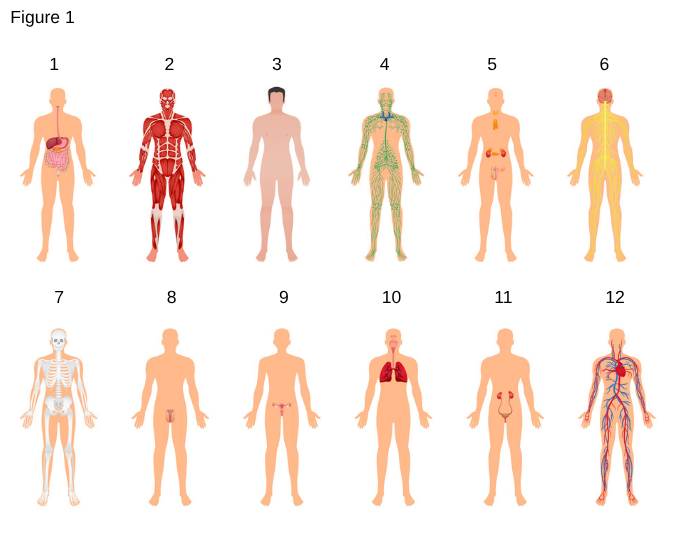
9
Female Reproductive System
the system responsible for the production of ova and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone, including organs like the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
10
Repiratory System
the system responsible for the exchange of gases, primarily oxygen and carbon dioxide, through organs such as the lungs, trachea, and bronchi.
11
Urinary System
the system responsible for the production, storage, and excretion of urine, including organs like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
12
Cardiovascular System
the system responsible for the circulation of blood and lymph throughout the body, including the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
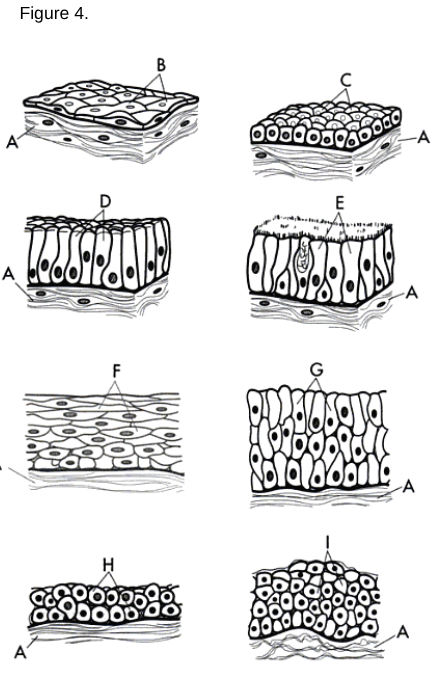
a/g
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
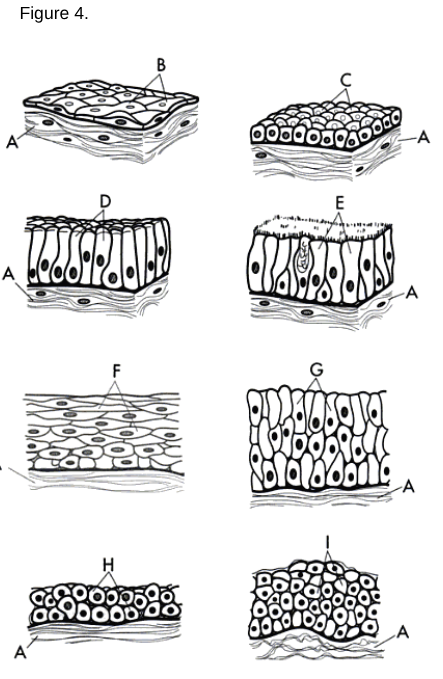
a/h
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
a type of tissue composed of multiple layers of cube-shaped cells, primarily found in glandular ducts and some areas of the reproductive system.
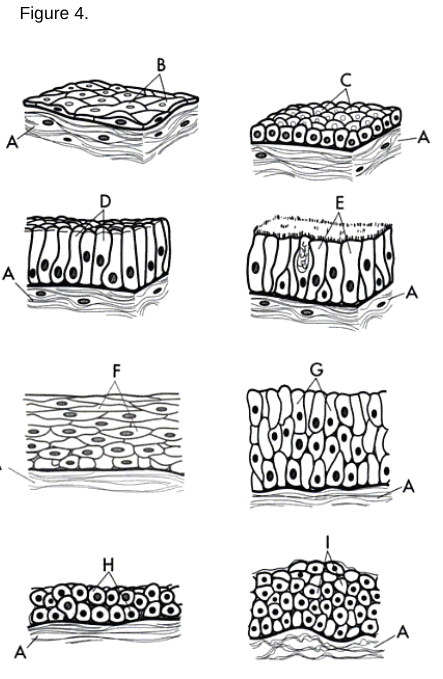
a/i
Transitional Epithelium
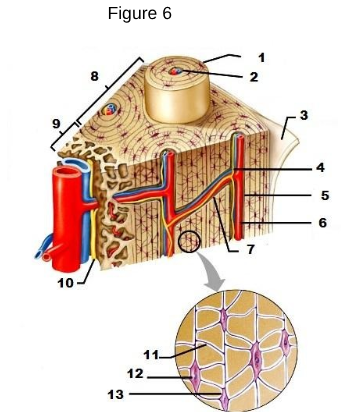
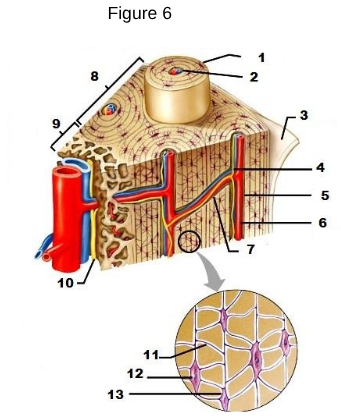
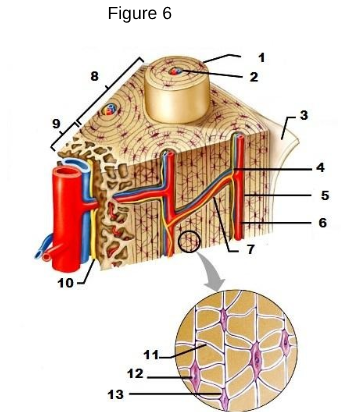
1
osteon
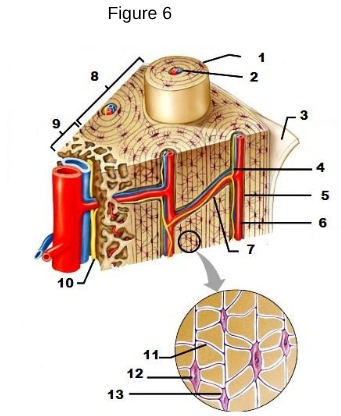
2
Lamellae
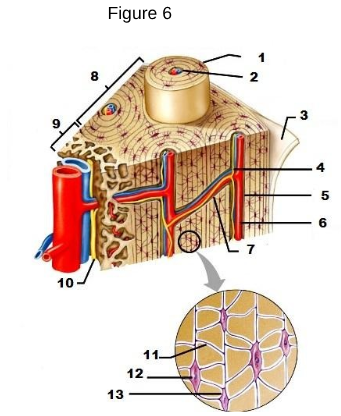
3
Periosteum
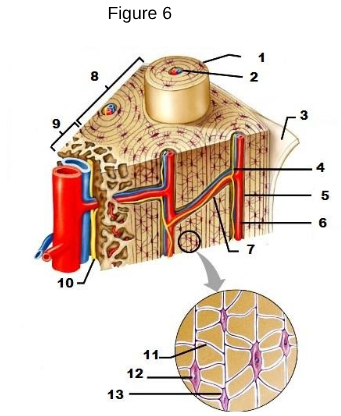
4/5/6
Central/Haversian Canal
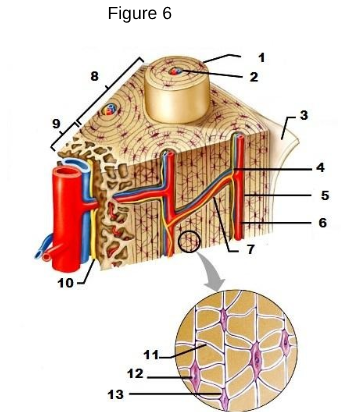
7
Volkman’s Canal
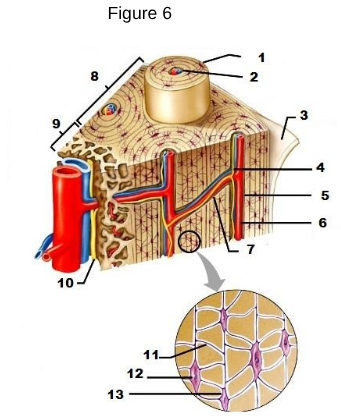
11
Canaliculi
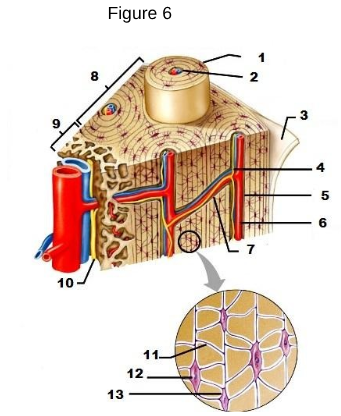
12
Osteocyte
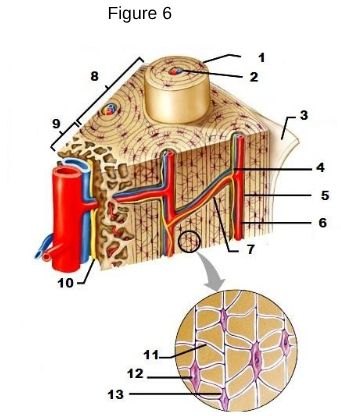
13
Lacunae “lakes between osteocytes”
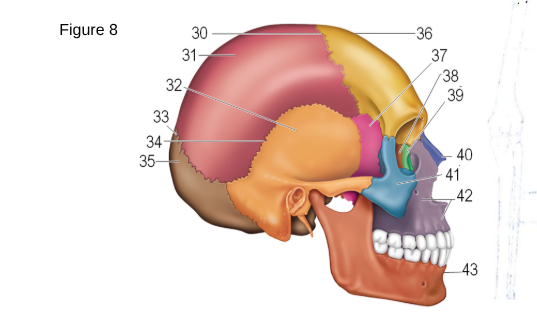
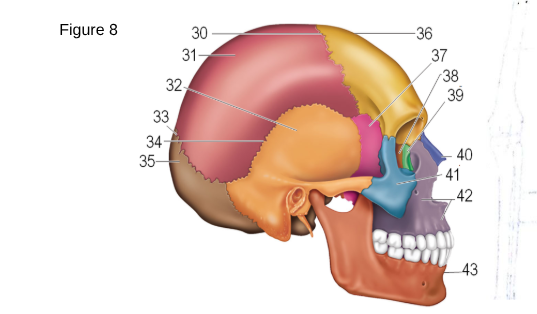
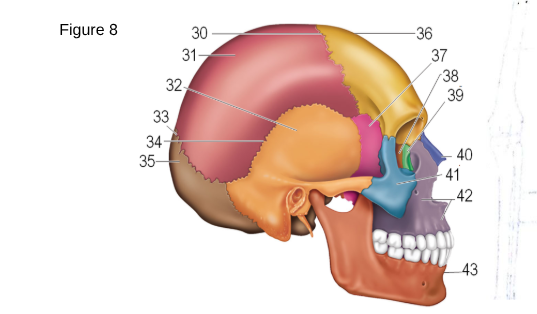
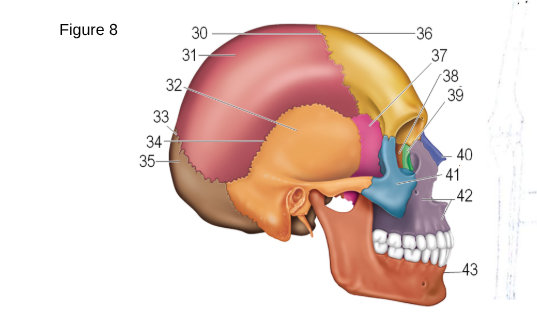
36
Frontal
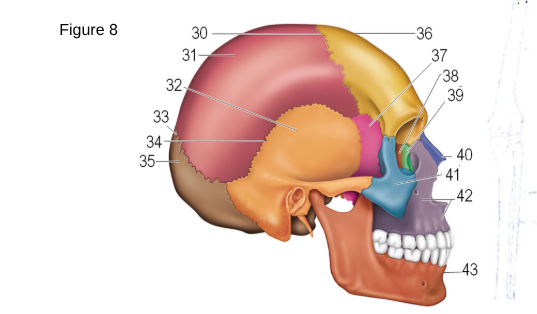
37
Sphenoid
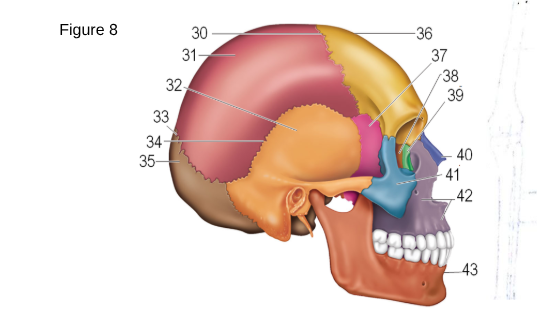
38
ethmoid
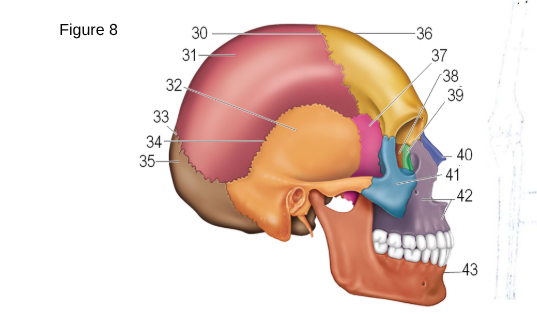
41
zygomatic
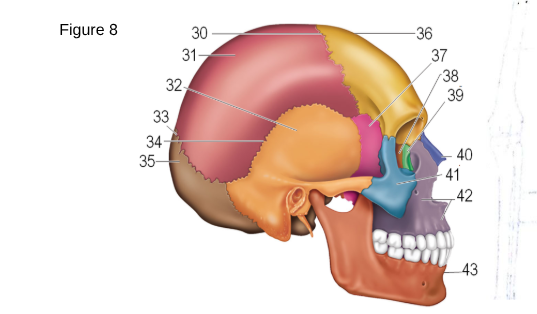
42
maxilla
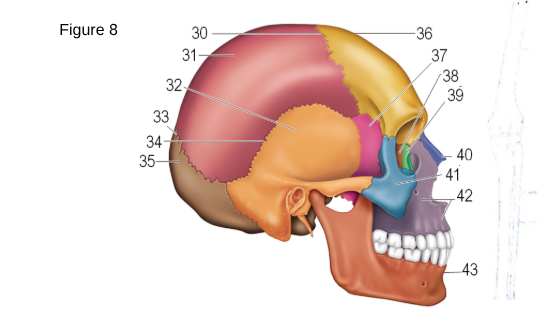
43
mandible
35
occipital
32
temporal
31
parietal
a
transverse