CNIT 17600 Exam 1 Flashcards
1/209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
210 Terms
A Model
One way of breaking down the layers of a computing system and thinking about how computers function
Task
Find something that we want to do
Algorithm
Break the problem down into steps
Program
This is the full set of instructions you write in a programming language (like Python or C++) to tell the computer what to do. Think of it like writing a recipe for making a cake. The program is the complete recipe with all the steps listed.*
Instruction Set Architecture
This is the limited set of basic commands that the computer's processor can understand directly. It's like a list of very simple tasks the processor knows how to do, such as "add two numbers" or "store this data
Microarchitecture
Connects all the small hardware components, like registers, memory units, and arithmetic units, to make sure those ISA instructions can be processed efficiently.*
Logic Gates
simplest building blocks of a computer, performing basic binary like 1s and 0s, so every component of the microarchitecture can be implemented using logic gates.
Devices
Computing system is a series of switches considered transistors. These transistors have a charge which is manipulated by electrons and can be interpreted as either 1 or 0.
An abstraction
a mental model that removes complex details.
Top Down
Program that has a knight touch every square once, Kinda goes in a sequence-like motion
A system
is a collection of components linked together and organized in such a way as to be recognizable as a single unit.
The boundary of a system defines
what is inside the system (the components like CPU, memory and hard drive) and what is outside (the environment). It helps us understand what belongs to the system.
The environment
is anything outside of the system, like sound ways like your voice and hearing, stuff outside of the system things will affect it heat, how much space does it have and other computers in its enviornment that it can talk with
System Architecture
The fundamental properties, and the patterns of relationships,connections, constraints, and linkages among the components and between the system and its environment are known collectively as the architecture of the system
Client server computing
A program on a client computer requests services from a program on a server computer
Distributed Processing Systems
2-tier,3-tier,N-tier
Cloud computing
the cloud is someone else's computer
Peer to peer computing
client-server computer must request a computer
Centralization of services permits
easier administration of services by IT
professionals
easier availability and location by
users
consistency of resources, such as files
and data, can be managed and assured
more efficient and cost-effective
hardware procurement through purchasing
a small number of very powerful
computers
Two-tier architecture
Two computers are involved in a service
Three-tier architecture
Three computers are involved in a service
N-tier architecture
Extends the three-tier model by adding more layers (or tiers) to separate different functions further.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
applications run on a server or processing may be divided on server and client.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
tools for a developer to create and run applications
on a cloud platform
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
cloud-based hardware emulation of virtual
machines and networking
Cloud Computing Advantages
• Client’s datacenter needs are simplified; reduced costs
• Supports collaboration
• Scalable to a variety of host platforms
• Reduced maintenance downtime
• Lower investment for short-term projects
Cloud computing disadvantages
• Quality of security is critical and questionable
• Outages or loss of connectivity may prevent users from
working
• Requires long-term commitment and viability of cloud
service
• Changes in operating procedures can result in data loss
PEER-TO-PEER COMPUTING advantages
• Sharing files between personal computers
• Internet file sharing
PEER-TO-PEER COMPUTING disadvantages
• Difficult to establish centralized control of services
• Difficult to locate services
• Difficult to synchronize versions of files or software
• Difficult to secure network from unauthorized access
and from viruses
Gen 0: Hobbies, What were the first devices
Mechanical Calculating Machines
What years was Gen 0
1642-1945
Who made the calculating clock
Wilhelm Schinckard
Who made the pascaline
Blaise Pascal
Who made the difference Engine
Charles Babbage
Who made the punches card tabulating machine
Herman Hollerith
Who was the first programmer?
Ada Lovelace
What is a pascaline
Adds and subtracts only, you have to manually control the switches
What is a difference engine
A comples design of gears and pulleys that does manual calculations
What was the punched card tabulating machine built for?
The census
What did Alan turning do?
developed many core concepts to computing as we understand it today.
First generation was
More of a university project
First generation had
vaccum tube computers
Vaccum computer years
(1945-1953)
What did the Atanasoff Berry Computer Do
solved systems of linear equations
what did ATANASOFF BERRY COMPUTER (ABC) implement
There were vacuum tubes - electron tubes, thermionic valves, or simply valves, are electronic devices that control the flow of electric current in a vacuum.
Magnetic drum for kilobytes
Not random access, have to turn them until you get the bits and turn to the right spot
What was the first general computer?
The ENIAC
The second generation device
Transistorized Computers
Second generation years
(1954 - 1965)
What did Transistorized computers have
small vacuum tubes, smaller transistors, nanometers, so small for electrons then get confused and not get over them
Transistorized computer example
univac 1100
What is a transistor
Replaced vacuum tube, fast, small,
More durable, cheap
What is a magnetic core
Replaced magnetic drums, information available instantly, replace our drums and first ability to have random access
what is Magnetic Disks
Replaced magnetic tape, data can be accessed directly, can go backwards and forward
what is core memory module
sewing like project - thread put in it, expensive to produce
The third generation…
integrated circuit computers
Third generation years
1965-1980
The third generation had
hundreds of transistors smashed together
Did the third generation have short or long term storage
short term
What are Integrated Circuits
Replaced circuit boards, smaller, cheaper, faster, more reliable
what are transistors now used for
memory construction
What is a terminal
An input/output device with a keyboard and screen
What is the IBM 360
Typewriter like
Using paper as our screen
Fourth generation years
1980-??
Fourth generation had
large scale integration, advances in chip technology
Fourth generation computer
VLSI computers
Moores law
The density of transistors in an integrated circuit will double every year
Floppy disks
used for storage, 1.22 gb, larger and hold less for floppy disks,
Moore's Law means that…
computers get better and cheaper over time because we can fit more tiny switches (transistors) onto computer chips
Rock's law
The cost of capital equipment to build semiconductors will double every four years
Quantum Computing
Not very well researched- will likely be in the next generation
Optical Computing/Photonic Computing is
Moving data at the speed of light
With this new tech, we have the potential to
upgrade from gigahertz speeds of CPUs to terabits speeds (1000x faster)
Definition of an Operating
System
A collection of computer programs that
integrate the hardware resources of the
computer and make those resources
available to a user and the user’s
programs, in a way that allows the user
access to the computer in a productive,
timely, and efficient manner.
How did users interact with the ENIAC?
plugboards
Signed and Unsigned Binary numbers
Signed binary starts with a 1 unsigned starts with 0
Bit
(short for binary digit) is the smallest unit of data in a computer.
Nibble/Nybble
a four-bit aggregation, or half an octet. It is also known as half-byte or tetrade.
Byte
a group of binary digits or bits (usually eight) operated on as a unit.
A gibibyte is most accuratley used to measure what
data storage
how does rgb define a color
using floating point representation
What is the main memory?
RAM
A hardware platform may support …
a variety of operating systems
An operating system may support…
many platforms
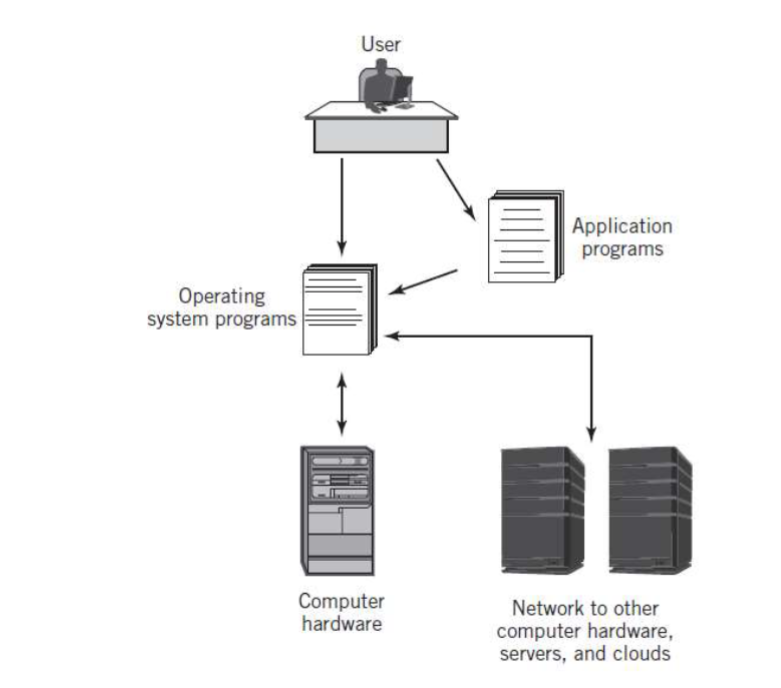
integrated computer enviroment
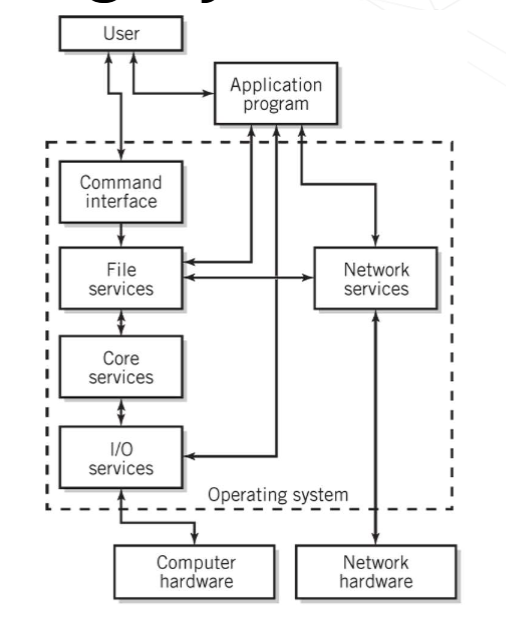
Simplified Diagram of
Operating System Services
memory resident
Always loaded in memory
• Commonly called the kernel
• Contains essential services required by other
parts of the operating system and applications.
• Typically responsible for managing memory,
processes and tasks, and secondary storage
memory non resident
Infrequently used programs
• Software tools
• Commands
unix has what kind of configuration
Monolithic configuration
windows has qhat kind of configuration
Hierarchical (layered) configuration
MAC OS has what kind of configuration
microkernal
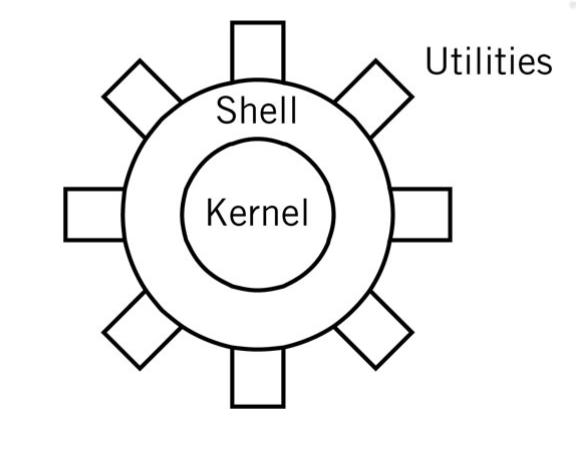
monolithic kernal
monolithic drawbacks
stability and integrity must be
managed carefully
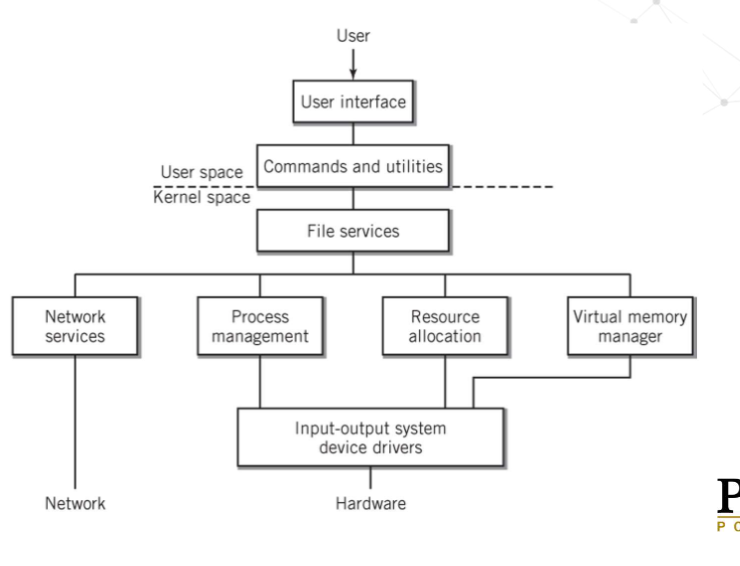
hierarchical model of an OS
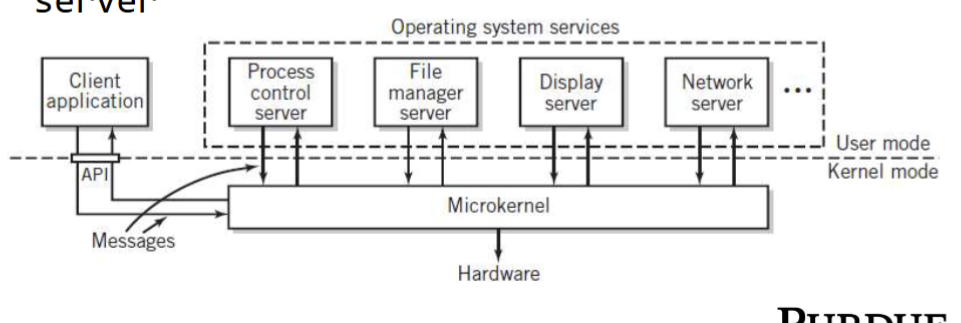
microkernal
microkernal has
minimum essential functionality
operating systems can …
Manages, loads, and executes programs
CLI
Command Line Interface
GUI
graphical user interface
what is a shell?
User interface and command processor that
interacts with the kernel
File
local unit of storage