2.2 Intramolecular force and Potential Energy
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Covalent bonds are the bonds between ______ when they ______
two nonmetals; share valence electrons.
Different types of covalent bonds:
Polar or nonpolar
In polar covalent bonds, electrons are shared equally/unequally
unequally
In nonpolar covalent bonds, electrons are shared equally/unequally
equally
Covalent bonds can what three types of bonds?
single, double, triple bonds
What type of bond do covalent bonds have if there are resonance structures?
Average of single, double, triple bonds
Covalent bonds occur at the highest/lowest energy state.
lowest
The low energy state of covalent bonds happens when:
the attraction between the nuclei is greatest for the shared electrons, but the repulsions between electrons and between the nuclei is the least.
What happens when atoms in covalent bonds are too close together?
The nuclei will repel each other
What happens when atoms in covalent bonds are too far apart?
the attraction will not be enough to hold them together
Bond energy is the energy required when:
breaking a bond
the energy released when a bond is formed
bond energy
Compare the magnitude and sign of energy required when breaking a bond vs energy released when forming a bond:
Same magnitude but different sign
Larger atomic radii increase/decreases the bond length.
increases
Longer bond length increases/decreases the bond energy
decreases
Increasing the bond order increases/decreases the bond energy
increases
Why does increasing the bond order increase the bond energy?
there are more electrons involved and therefore greater coulombic attraction and the bond length has decreased.
The energy to separate ions in ionic compounds is their:
lattice energy
The change in energy that takes place when gaseous ions are combined to form an ionic solid.
Lattice energy
Combining ions will absorb/release energy.
release
Lattice energy can be represented using:
a modification of Coulomb’s law where the energy is proportional to the charges and inversely proportional to the distances between the nuclei.
Why is energy proportional to the charges in terms of lattice energy?
Larger charges = more attraction = more energy required to separate the ions
Why is energy inversely proportional to distance between the nuclei in terms of lattice energy?
Smaller radii = more attraction = more energy required to separate the ions
What is a useful representation for describing the interactions between atoms?
A graph of potential energy vs distance between atoms
Graphs of potential energy vs distance between atoms illustrate:
Equilibrium bond length and bond energy
The separation between atoms at which the potential energy is lowest:
Equilibrium bond length
The energy required to separate the atoms:
Bond energy
In a covalent bond, the bond length is influenced by:
Size of the atom’s core and the bond order
Examples of bond order:
Single, double, triple
Bonds with a higher bond order are longer/shorter
Shorter
Shorter bond have larger/smaller bond energies
Larger
What can be used to understand the strength of interactions between cations and anions?
Coulomb’s law
Larger charges lead to stronger/weaker interactions
Stronger
Why do larger charges lead to stronger interactions?
Interaction strength is proportional to the charge on each ion
Smaller ions lead to stronger/weaker interactions
Stronger
Why do smaller ions lead to stronger interactions?
The interaction strength increases as the distance between the centers of the ions (nuclei) decreases
A chemical bond involves a balance between:
Attractions and repulsions
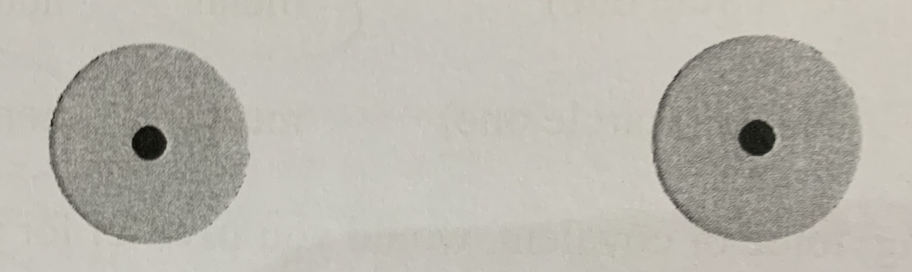
Is this a covalent bond?
No
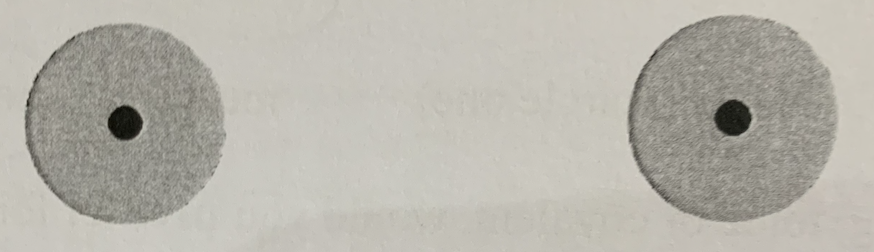
Why is this not a covalent bond?
The atoms are too far apart and they do not interact with each other
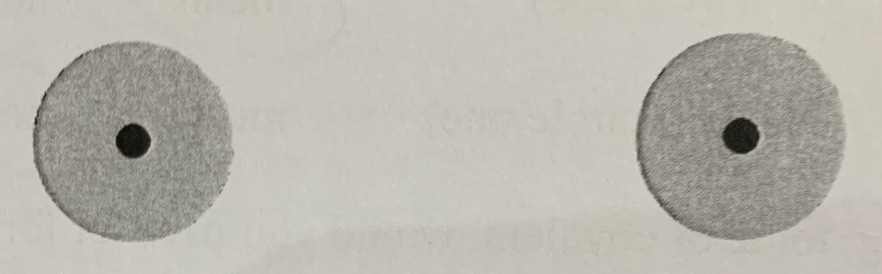
The potential energy between the atoms is equal to:
Zero
This is a ______ bond
Stable covalent
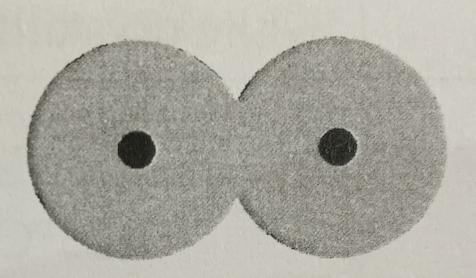
There is a balance between:
Attractions between the proton of one atom and the electron of the other atom, repulsions between protons, and repulsions between electrons
Is this a stable arrangement?
No
Why is this not a stable arangement?
The atoms are too close together, so there is too much repulsion between the protons of each atom
The potential energy between the atoms is very high/low
High
Internuclear distance vs potential energy graph with atoms that are far apart, touching, and overlapping:
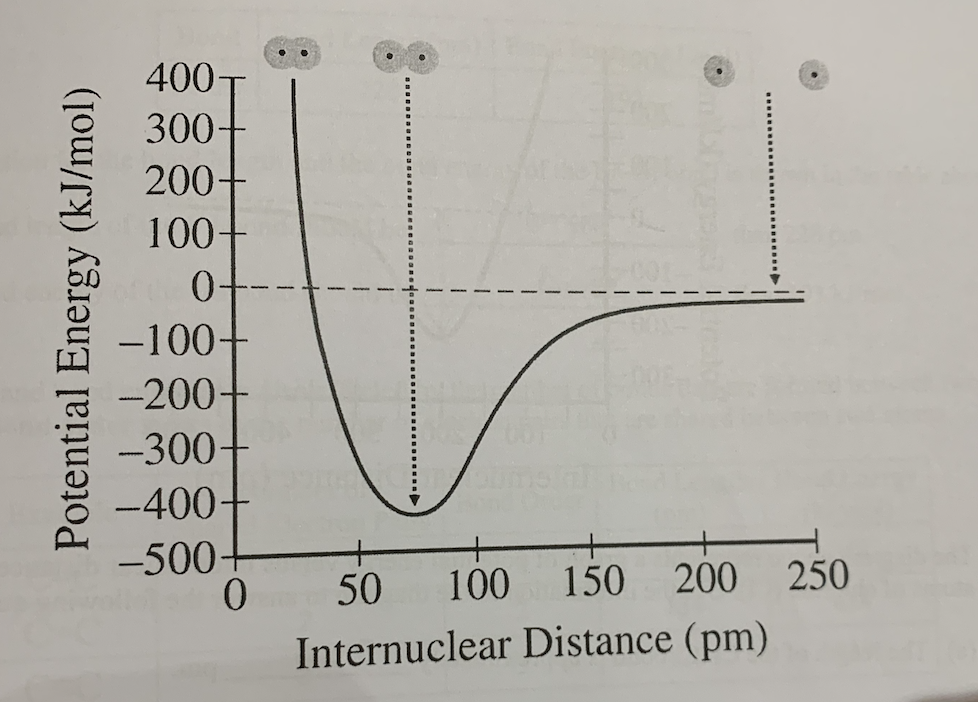
Label bond length on internuclear distance vs potential energy graph:
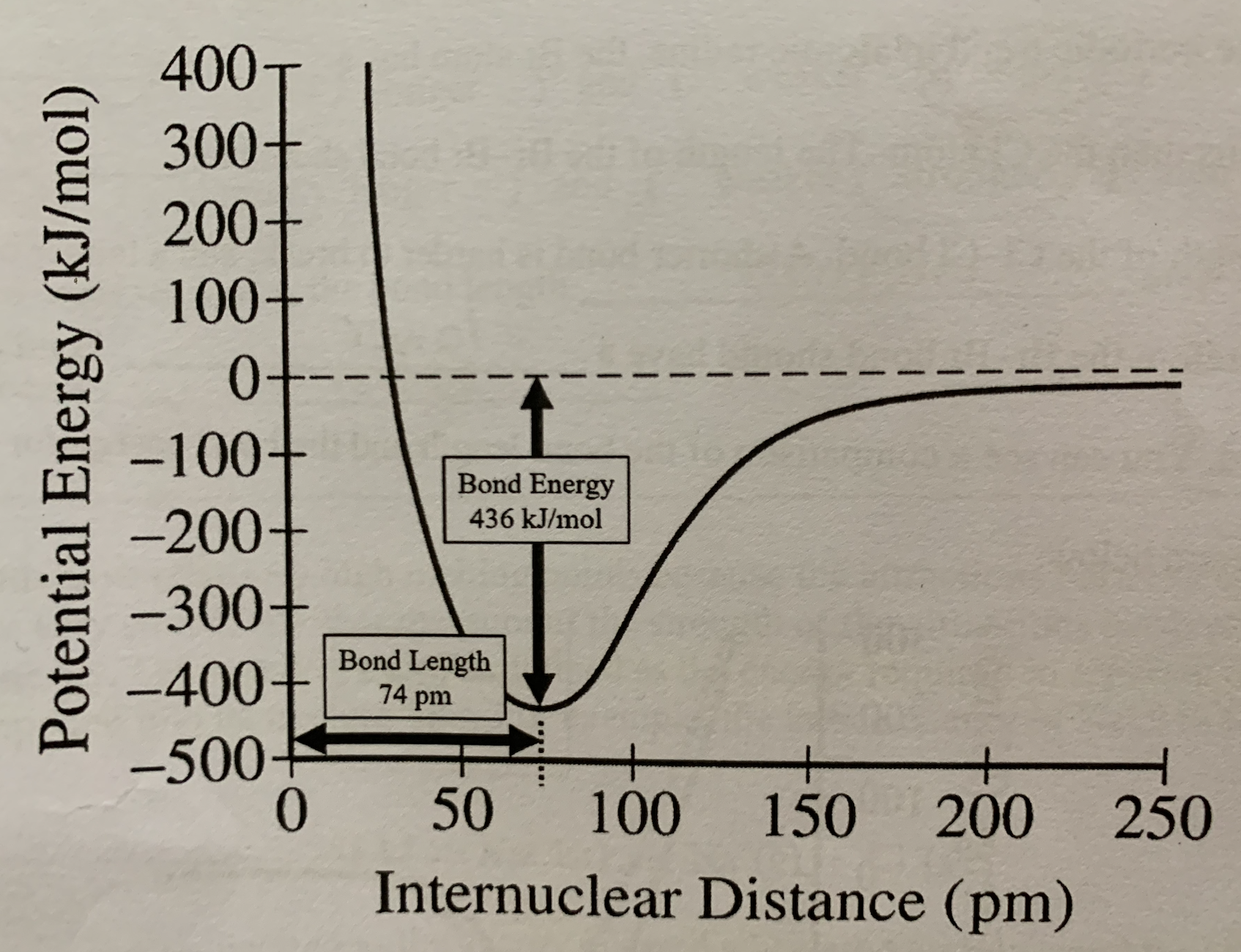
Label bond energy on internuclear distance vs potential energy graph:

The bond energy represents the energy that is:
Released when the bond is formed and absorbed when the bond is broken
The number of bonds that are formed between two atoms affect the:
Bond length and bond energy
The number of electron pairs that are shared between two atoms
Bond order
A double bond is shorter/longer than a single bond
Shorter
A double bond is weaker/stronger than a single bond
Stronger
A triple bond is shorter/longer than a double bond
Shorter
A triple bond is weaker/stronger than a double bond
Stronger
As the bond order increases, the bond length increases/decreases
Decreases
As the bond order increases, the bond energy increases/decreases
Increases
Ionic compounds have relatively high/low melting points
High
Why do ionic compounds have relatively high melting points?
The attractions between the ions in the solid crystal are very strong
Measure of the strength of the attractions between ions
Lattice energy
The energy required to separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions
Lattice energy
The energy released when gaseous ions combine to form one mole of a solid ionic compound
Lattice energy
The greater the magnitude of the lattice energy, the stronger/weaker the attraction between the ions in the crystal lattice of an ionic compound
Stronger
Coulomb’s law describes the:
Attractive (or repulsive) force between two charged particles
Coulomb’s law:
F is proportional to q1q2/r²
The magnitude of the lattice energy of an ionic solid depends on:
Magnitude of the charges on the ions and the distance between the ions in the crystal lattice
The magnitude of the lattice energy of an ionic compound tends to increases as the magnitude of the charges on the ions increases/decreases
Increases
The magnitude of the lattice energy of an ionic compound tends to increases as the distance between the ions in the crystal lattice increases/decreases
Decreases
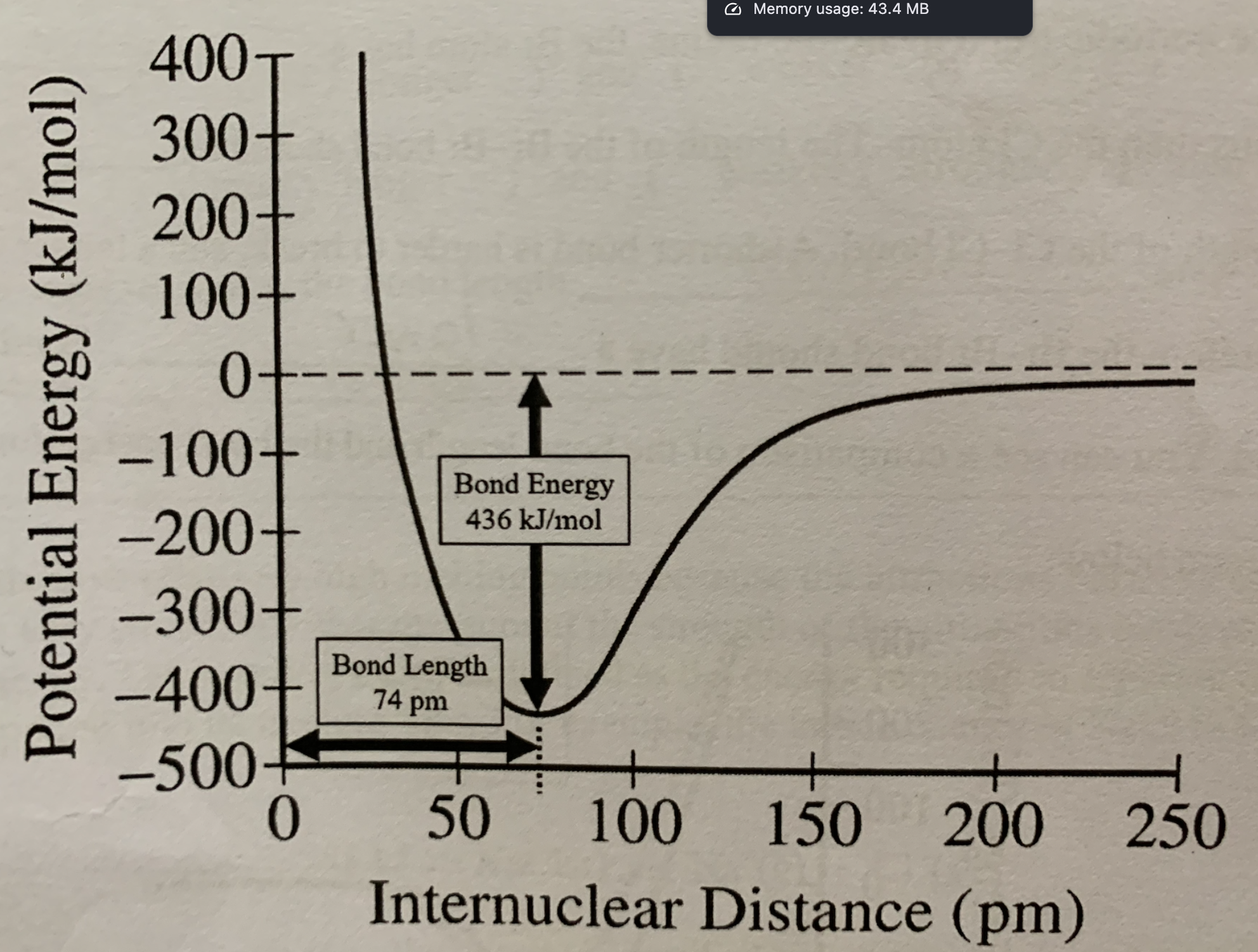
From bond length of 0 to 74 pm, is repulsion less than, greater than, or equal to attraction?
Greater than
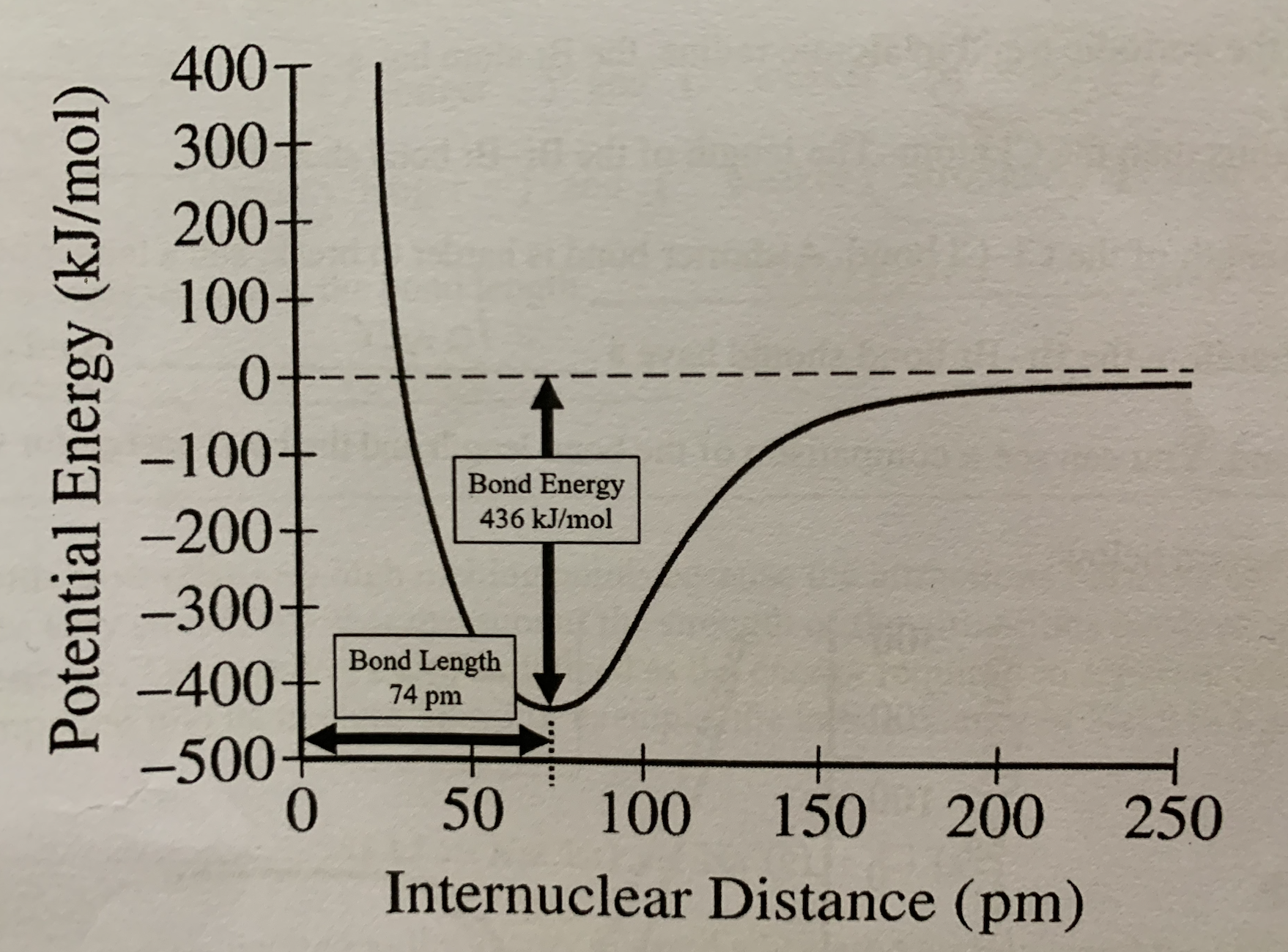
At bond length of 74 pm, is attraction less than, greater than, or equal to repulsion?
Equal to
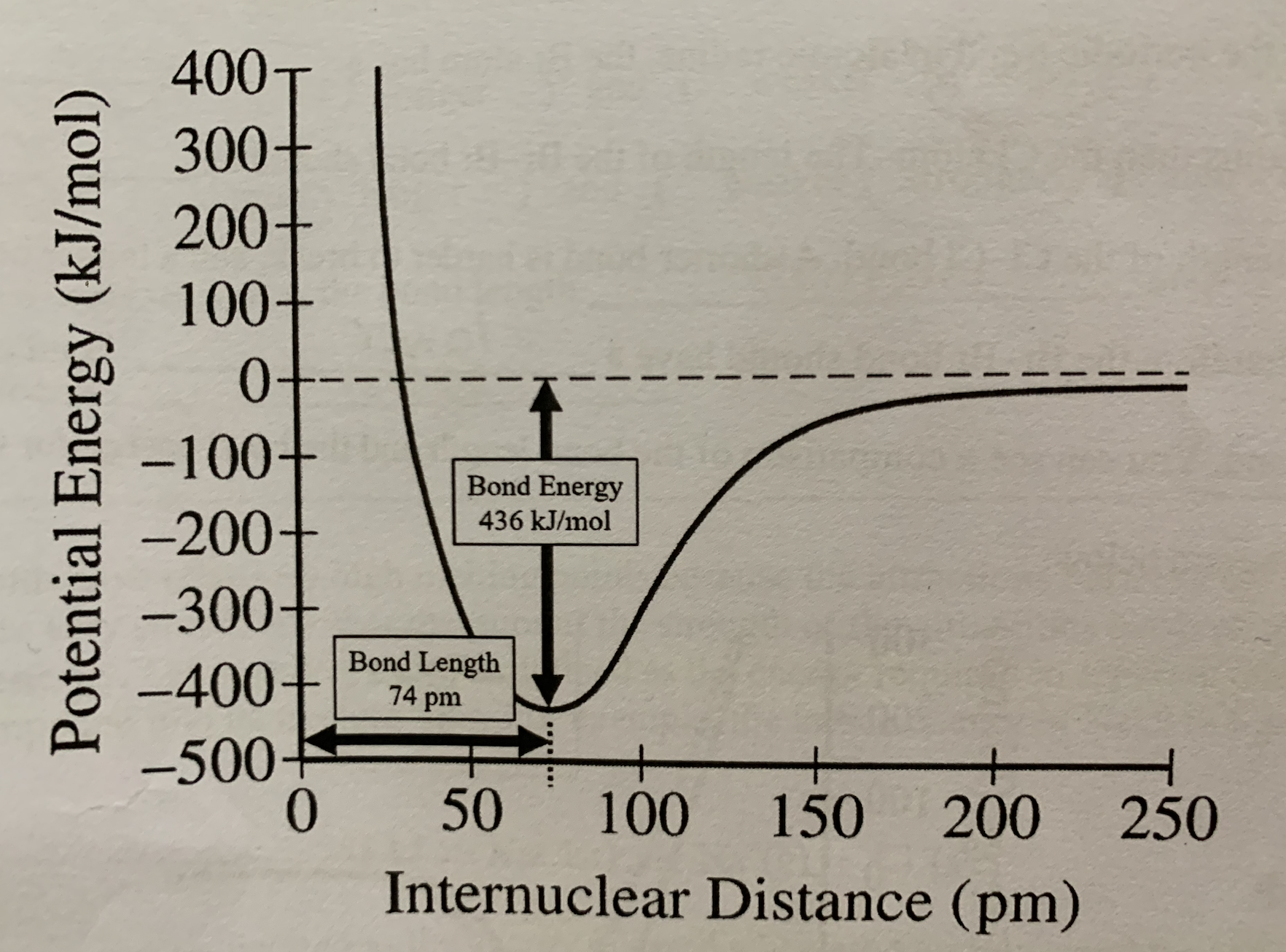
From bond length of 74 to 250 pm, is attraction greater than, less than, or equal to repulsion
Greater than
Energy released is exothermic/endothermic
Exothermic
Energy gained is exothermic/endothermic
Endothermic
Bond length is directly/inversely proportional to bond energy
Inversely