Pig Dissection Part 1-D
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Mouth
Entry of digestive tract; mechanical and chemical digestion (amylase).
Pharynx
Shared food / air passage behind mouth.
Esophagus
Muscular tube moving food to stomach via peristalsis.
Stomach
Stores / digests proteins using HCl and pepsin.
Cardiac Sphincter
Valve between esophagus → stomach; prevents reflux.
Pyloric Sphincter
Valve between stomach → duodenum; controls chyme flow.
Chyme
Semi-liquid food mixture in stomach.
Cardiac Stomach
Upper stomach near esophagus.
Pyloric
Stomach Lower stomach leading to small intestine.A section of the stomach that connects to the duodenum, regulating the exit of chyme.
Small Intestine
Major site of digestion / nutrient absorption.
Duodenum
First section; receives bile & pancreatic enzymes.
Jejunum
Middle section; absorbs nutrients.The second segment of the small intestine, responsible for further digestion and absorption of nutrients after the duodenum.
Ileum
Final section; absorbs vitamins & bile salts.It is the last part of the small intestine, crucial for absorbing vitamin B12 and various nutrients before waste enters the large intestine.
Mesentery
Thin membrane anchoring intestines & carrying blood vessels.
Large Intestine (Colon)
Absorbs water / electrolytes; forms feces.
Caecum
Pouch between small & large intestines; digests cellulose.
Rectum
Stores feces before elimination.
Anus
Exit opening for waste; controlled by sphincters.
Liver
Produces bile; stores glycogen; detoxifies blood.
Bile
Fluid that emulsifies fats.
Gall Bladder
Stores & releases bile to duodenum. It is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver, essential for digestion.
Bile Duct
Tube carrying bile from liver / gall bladder to intestine.
Pancreas
Secretes digestive enzymes & bicarbonate; regulates blood sugar. It plays a crucial role in digestion and metabolism.
Spleen
Filters blood; recycles red cells; immune function (produces white blood cells).
Diaphragm
Muscle aiding breathing & abdominal pressure. It separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities, playing a key role in respiration.
Peristalsis
Wave-like motion pushes food through the tract. It occurs in the digestive tract and involves the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles.
Pepsin
The stomach enzyme breaks down proteins. It is secreted as pepsinogen and activated by stomach acid.
Amylase
Enzyme digesting starch into sugars. It is produced in the saliva and pancreas, playing a crucial role in carbohydrate digestion.
Lipase
Enzyme breaking down fats. It is produced in the pancreas and works in the small intestine to hydrolyze triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol.
Trypsin
Pancreatic enzymes digest proteins. It works in the small intestine and activates other digestive enzymes. It is secreted as trypsinogen and activated by the action of intestinal juices.
Maltase / Sucrase / Lactase
Enzymes split sugars into monosaccharides. They facilitate the digestion of carbohydrates into simpler forms. Maltase splits maltose, sucrase splits sucrose, and lactase splits lactose.
Gastrin
Hormone triggering acid secretion in stomach. It stimulates the production of gastric acid to aid digestion.
Secretin
Hormone prompting pancreas to release bicarbonate. It helps neutralize stomach acid in the small intestine.
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Hormone causing gall bladder & pancreas to secrete. Digestive enzymes for fat and protein.
Umbilical Vein
Brings nutrient-rich blood from placenta → fetus.It is one of the two blood vessels in the umbilical cord that supplies oxygen and nutrients to the developing fetus.
Umbilical Arteries
Carry waste / deoxygenated blood from fetus → placenta.They are two blood vessels in the umbilical cord that transport carbon dioxide and metabolic waste back to the placenta for elimination.
Peritoneum
The lining membrane of the abdominal cavity covers the abdominal organs.
Which organ lies anterior to the stomach?
Liver
Which organ is posterior to the stomach and connects by a sphincter?
Small intestine (duodenum)
Which organ is under the liver and stores bile?
Gall bladder
Which organ is attached to the left side of the stomach?
Spleen
What structure lies between the stomach and duodenum?
Pyloric sphincter
Which thin membrane holds the intestines in place and carries blood vessels?
Mesentery
Which muscular sheet separates thoracic and abdominal cavities?
Diaphragm
Which vessel runs along the umbilical cord carrying nutrient-rich blood to the fetus?
Umbilical vein
Which organ lies beneath the stomach and releases digestive enzymes?
Pancreas
Why is the fetal liver proportionally larger than an adult’s?
It stores glycogen and filters maternal blood from the placenta.
Why is bile necessary for fat digestion?
It emulsifies large fat droplets into smaller ones, increasing enzyme efficiency.
Why is the stomach lined with mucus?
To protect stomach tissue from acid and pepsin damage.
What advantage do villi provide in the small intestine?
They greatly increase surface area for nutrient absorption.
Why is peristalsis important even when lying down?
It moves food through the tract independent of gravity.
How does the mesentery assist the digestive system?
It suspends the intestines and delivers absorbed nutrients via blood vessels.
Why doesn’t the stomach constantly secrete acid?
Acid production is controlled by hormones (like gastrin) and only occurs when food is present.
What two hormones regulate pancreatic and gall-bladder secretions?
Secretin and cholecystokinin (CCK).These hormones coordinate the digestive process by stimulating the pancreas to release digestive enzymes and the gallbladder to release bile.
What would happen if the pyloric sphincter failed to close properly?
Chyme could reflux into the stomach or move too quickly, reducing digestion efficiency.
What are the two main regions of the small intestine where absorption occurs?
Jejunum and ileum.
What structure prevents food from entering the trachea?
Epiglottis.
What connects the fetal pig to the placenta?
Umbilical cord (contains one vein and two arteries).
Which two organs release fluids into the duodenum
Gall bladder (bile) and pancreas (enzymes + bicarbonate).
What connects the small intestine to the large intestine?
Caecum.
What is the purpose of the pyloric sphincter?
To regulate passage of chyme from stomach to duodenum.
Which organ both detoxifies blood and produces bile?
Liver.
What is the function of the spleen in digestion?
It isn’t directly digestive; it filters blood and supports immunity.
Why is the duodenum crucial to digestion?
It receives bile and pancreatic enzymes—site of most chemical digestion.
What gas-exchange muscle indirectly aids digestion by pressure changes?
Diaphragm.
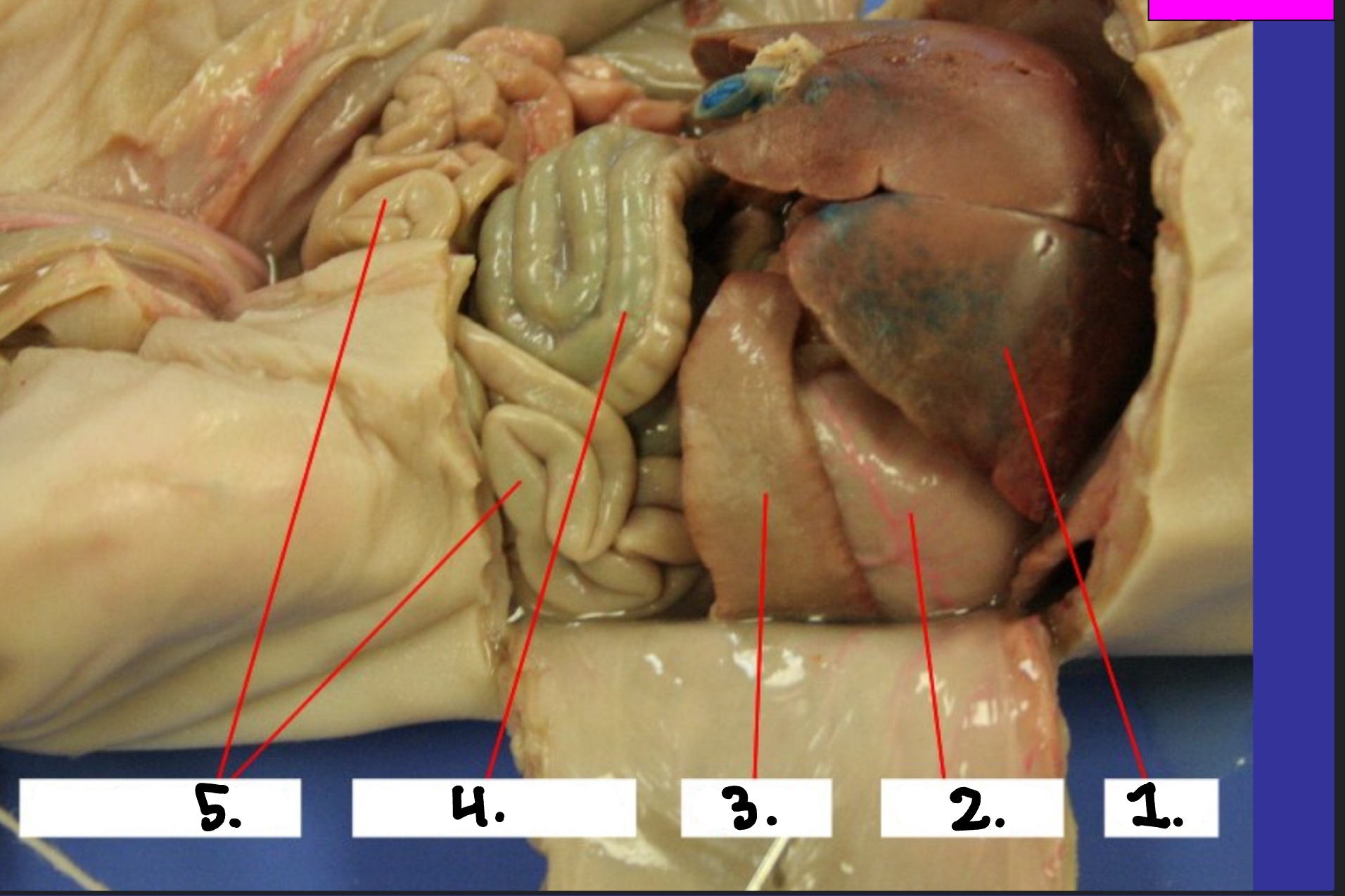
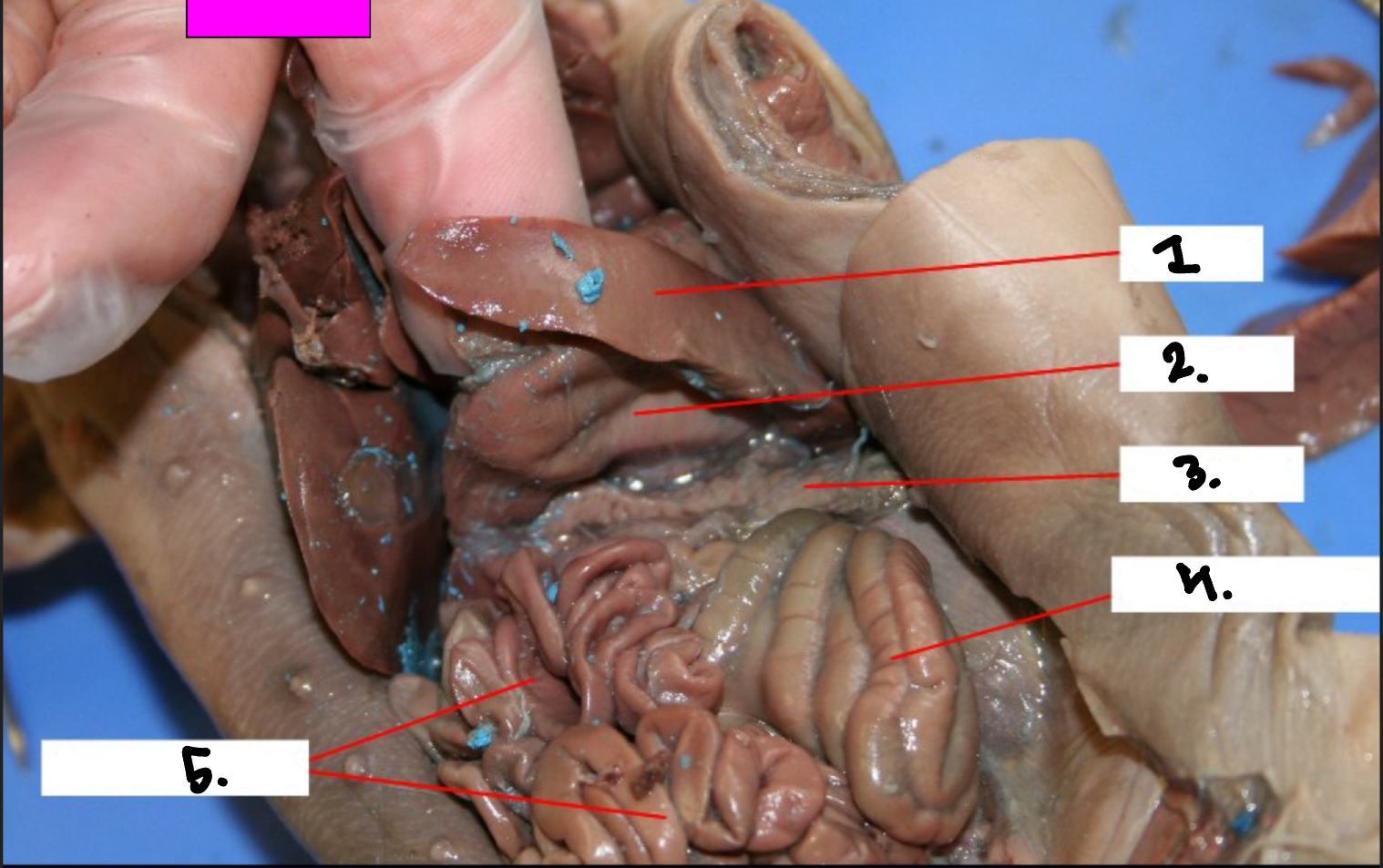
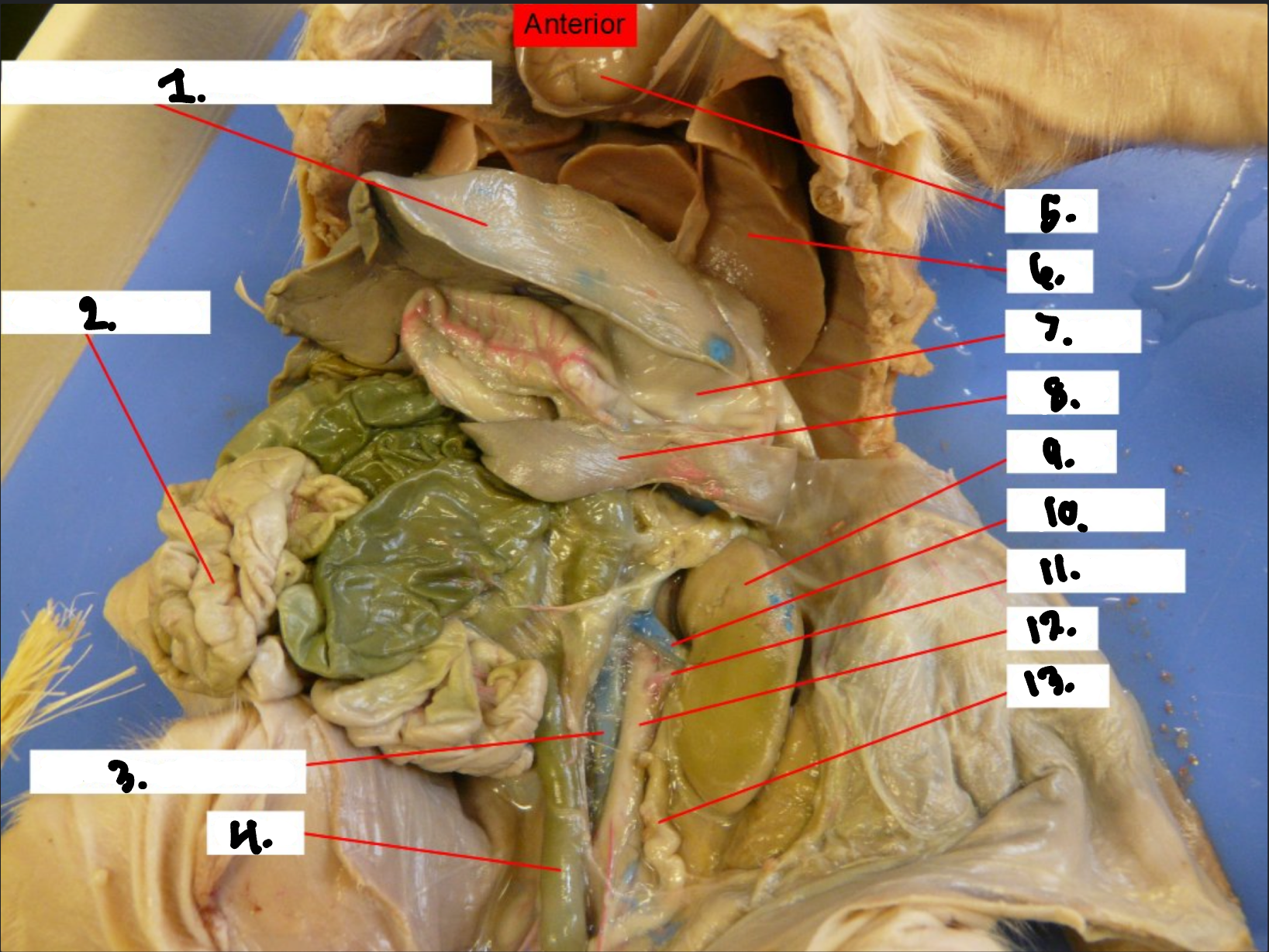
What is 1?
Liver
What is 2?
Stomach
What is 3?
Spleen
What is 4?
Large intestine
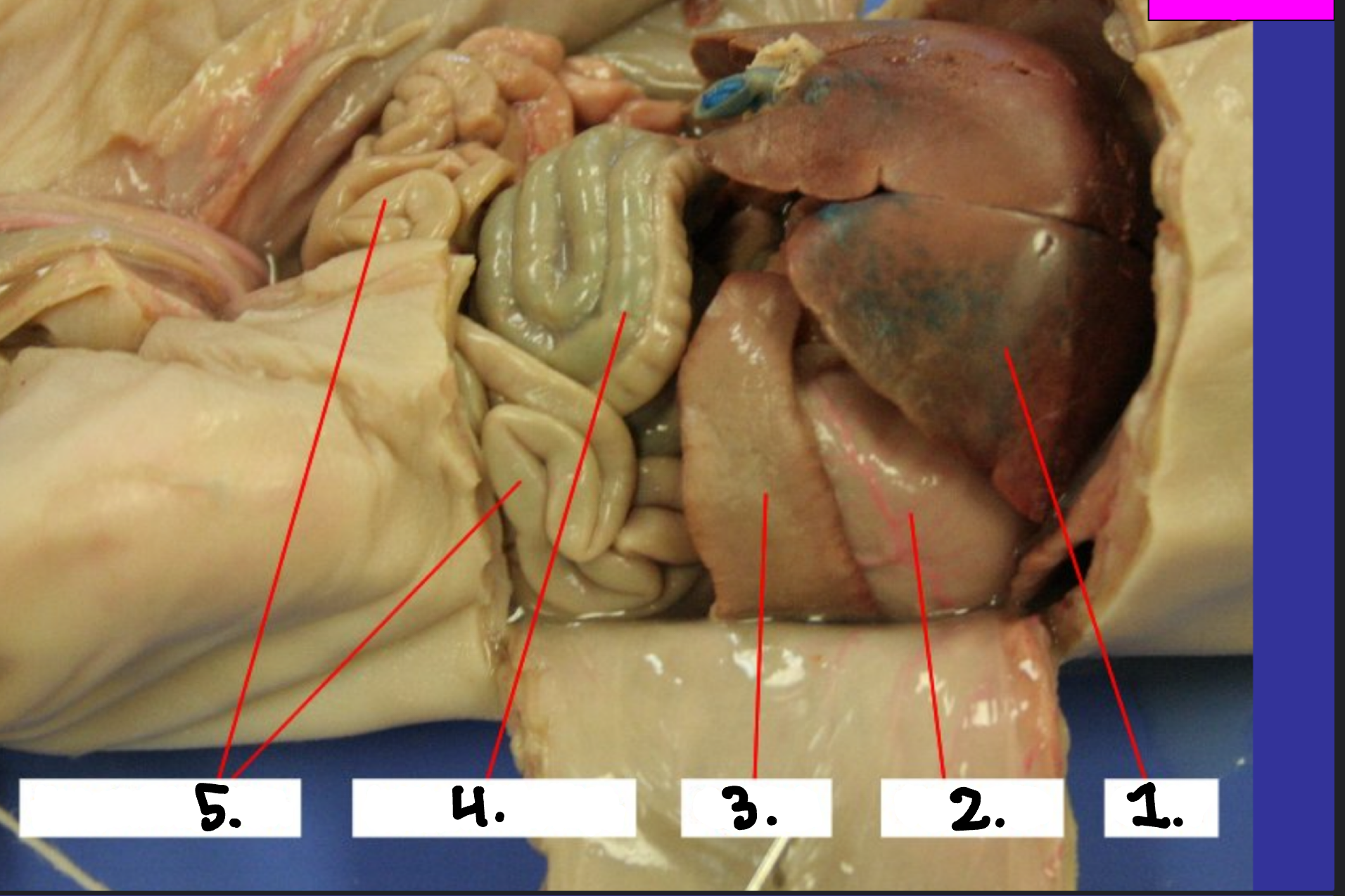
What is 5?
Small intestine
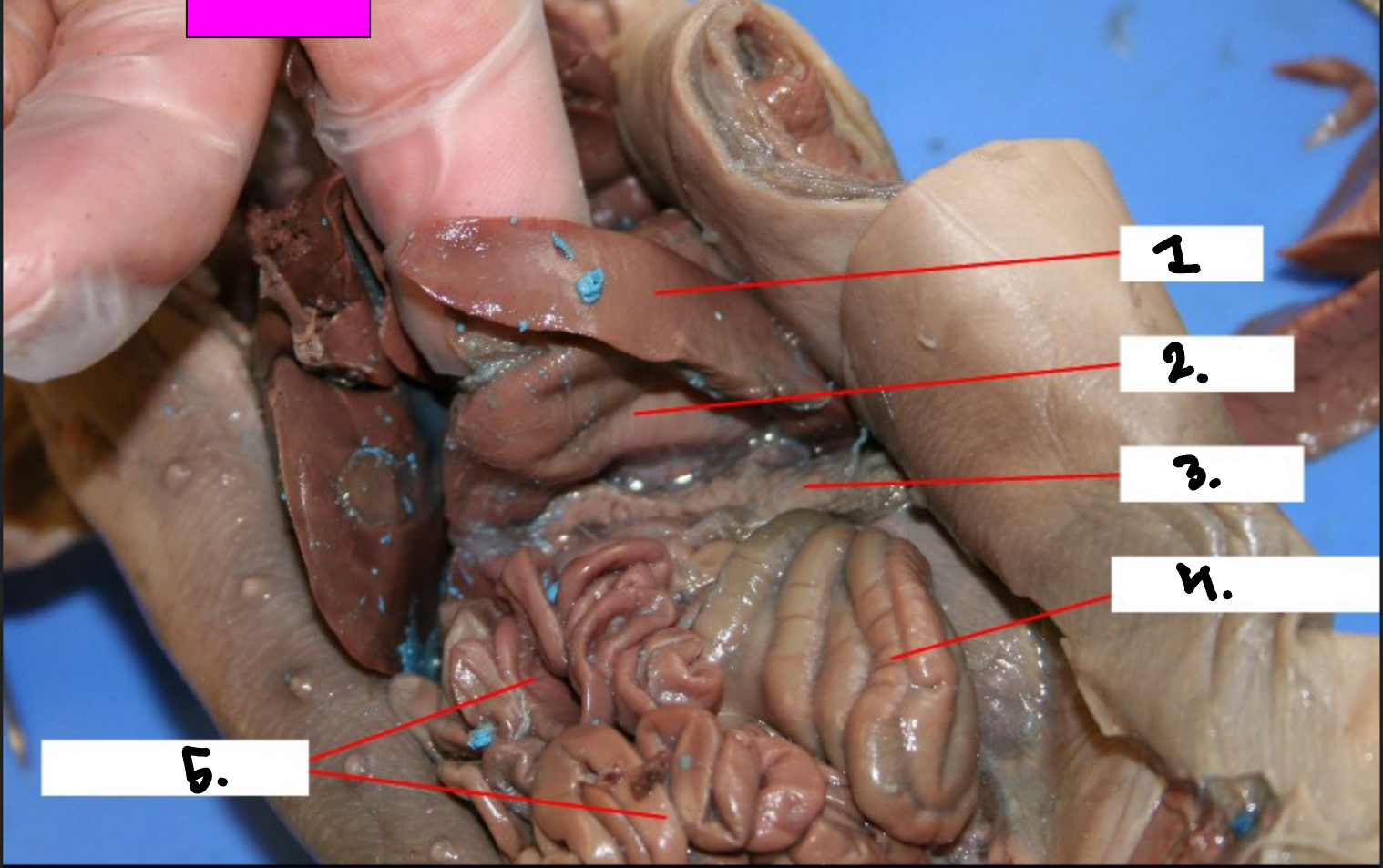
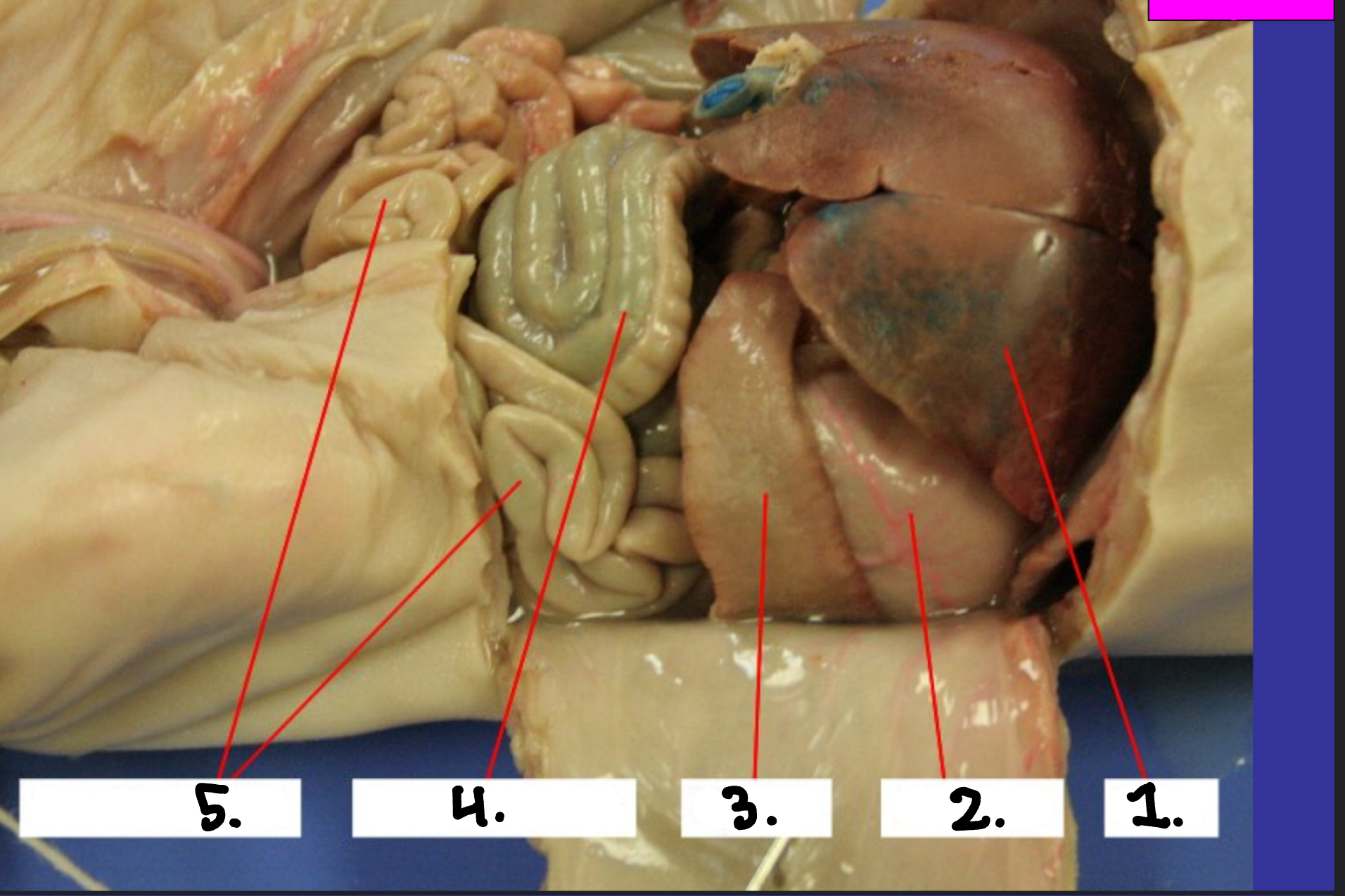
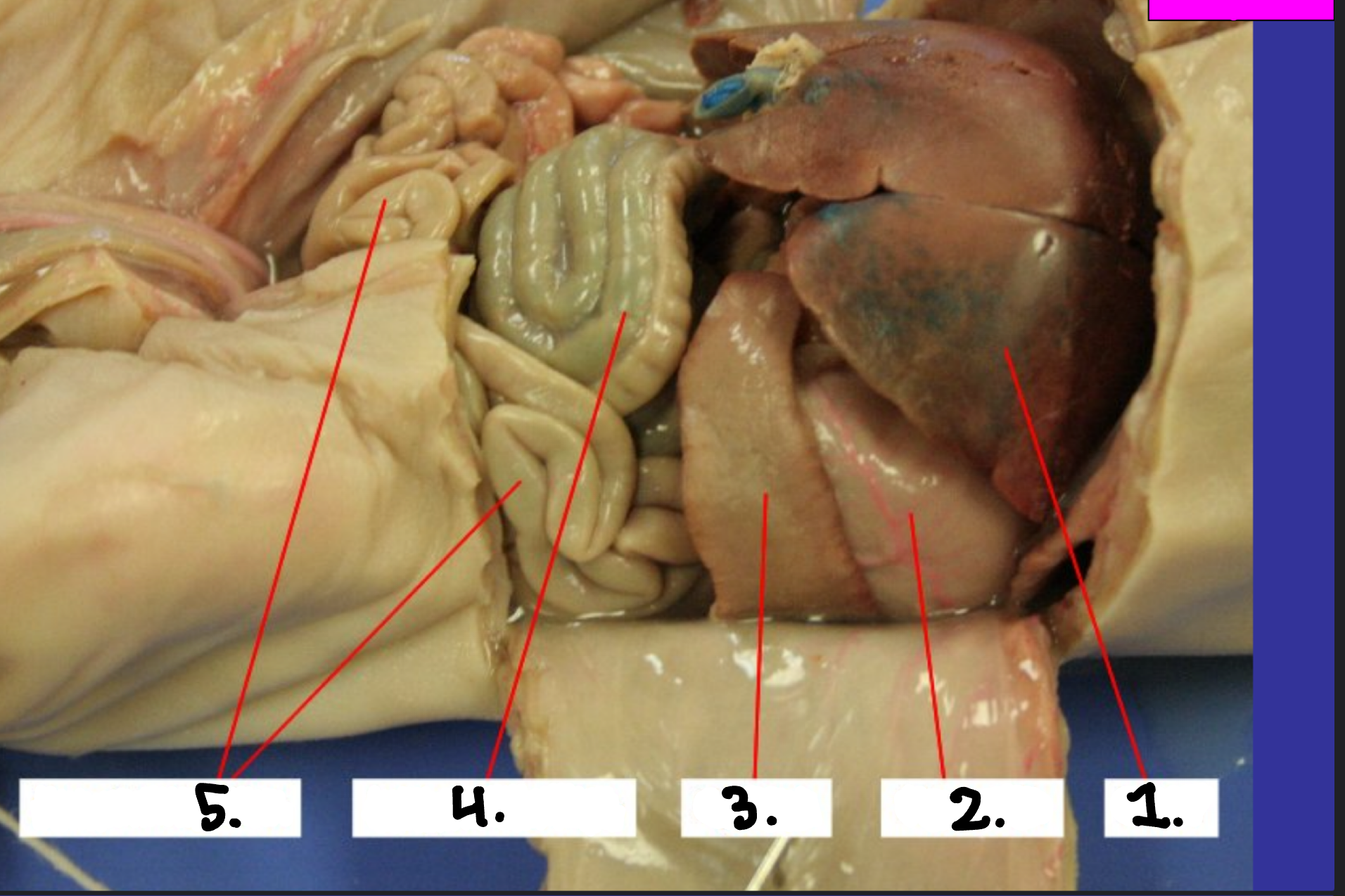
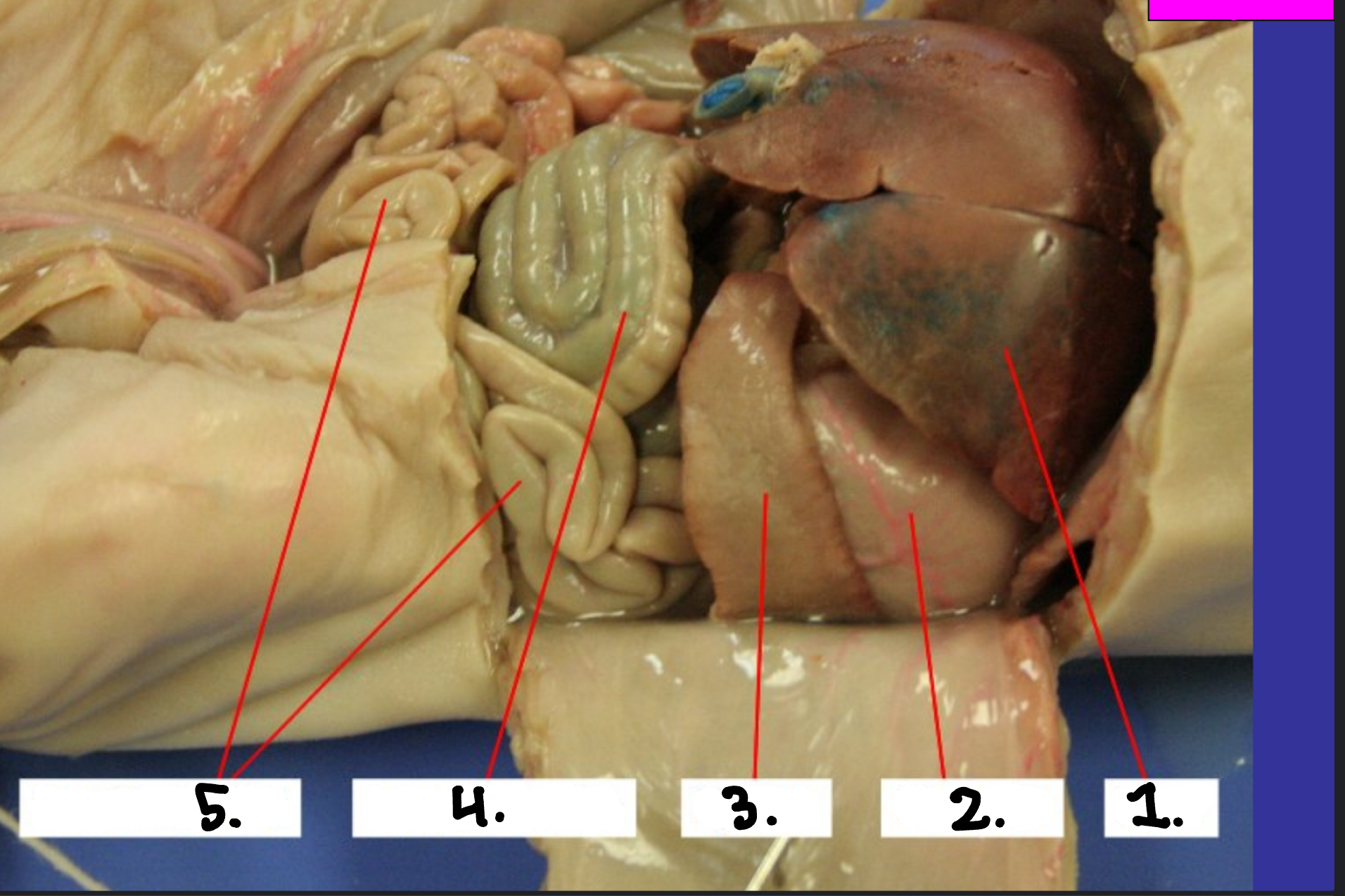
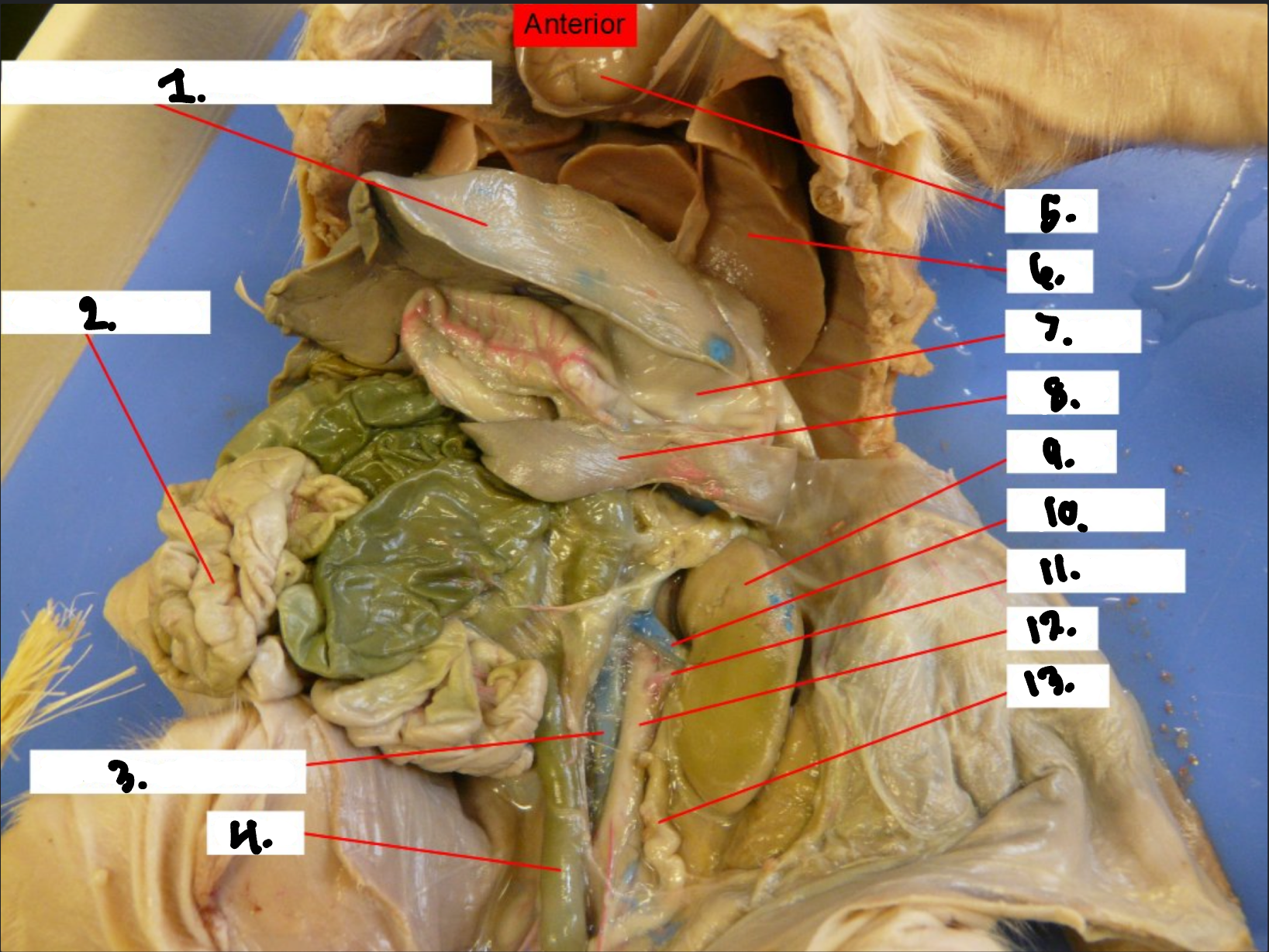
What is 1?
Spleen
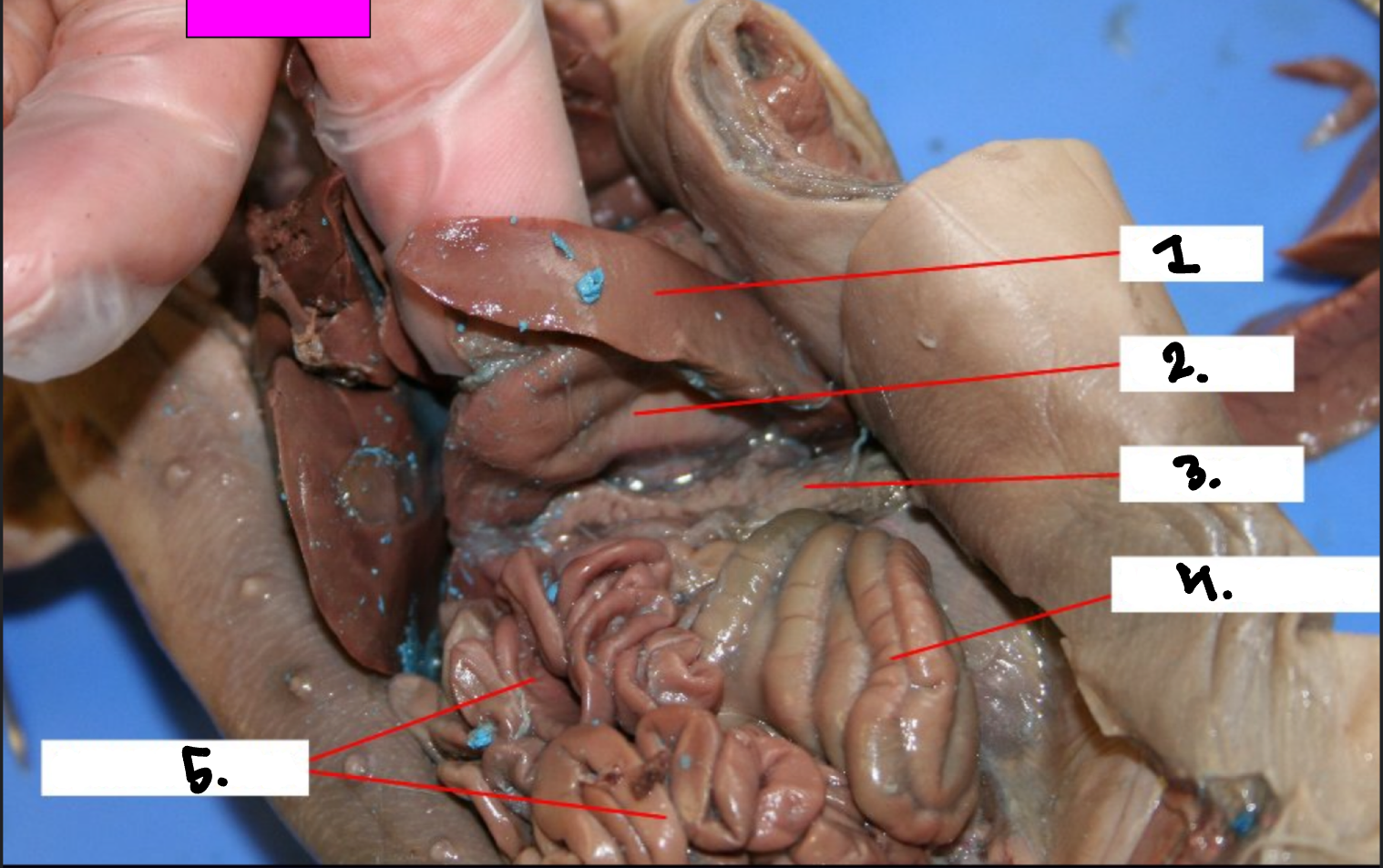
What is 2?
Stomach
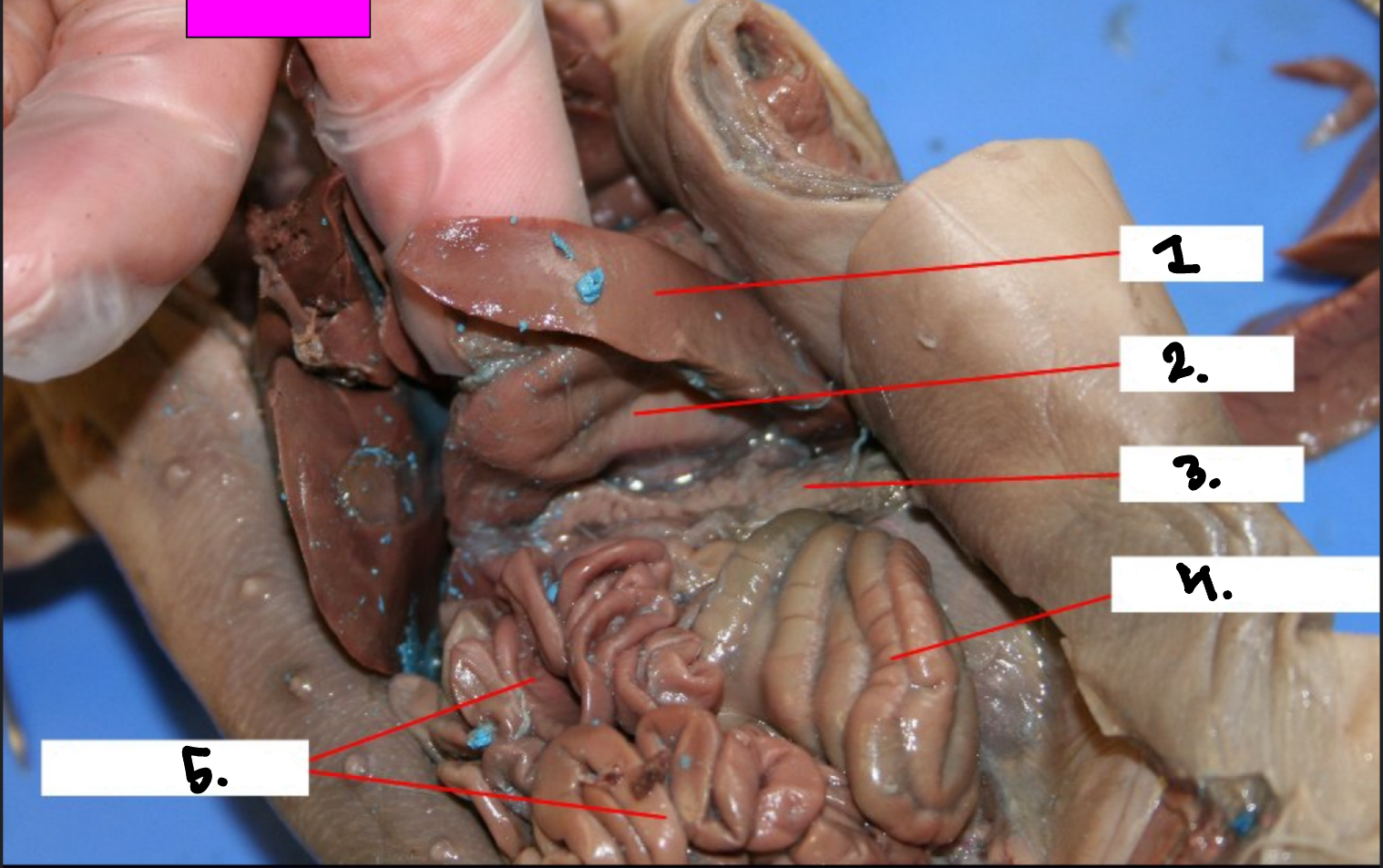
What is 3?
Pancreas
What is 4?
Large intestine
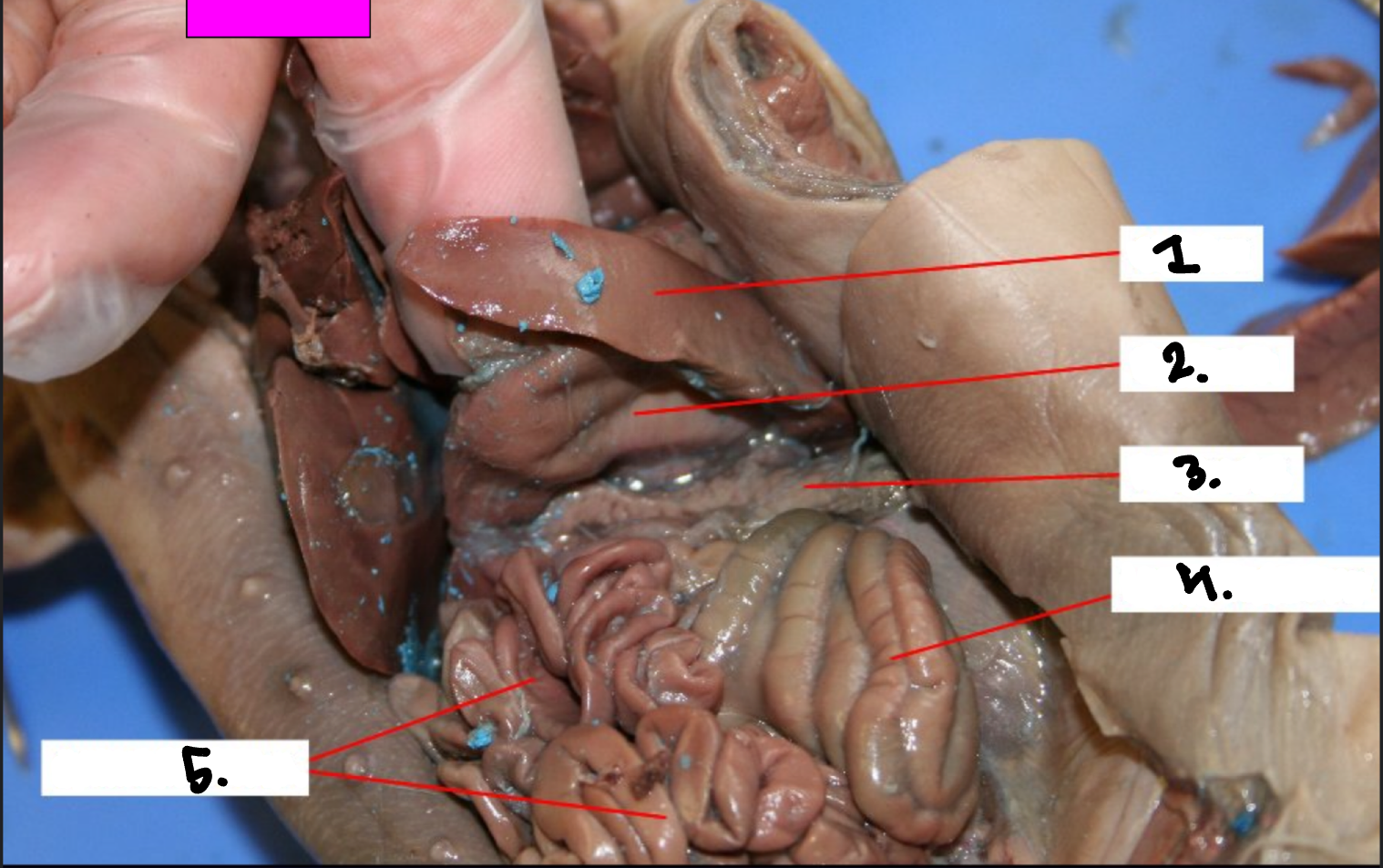
What is 5?
Small intestine
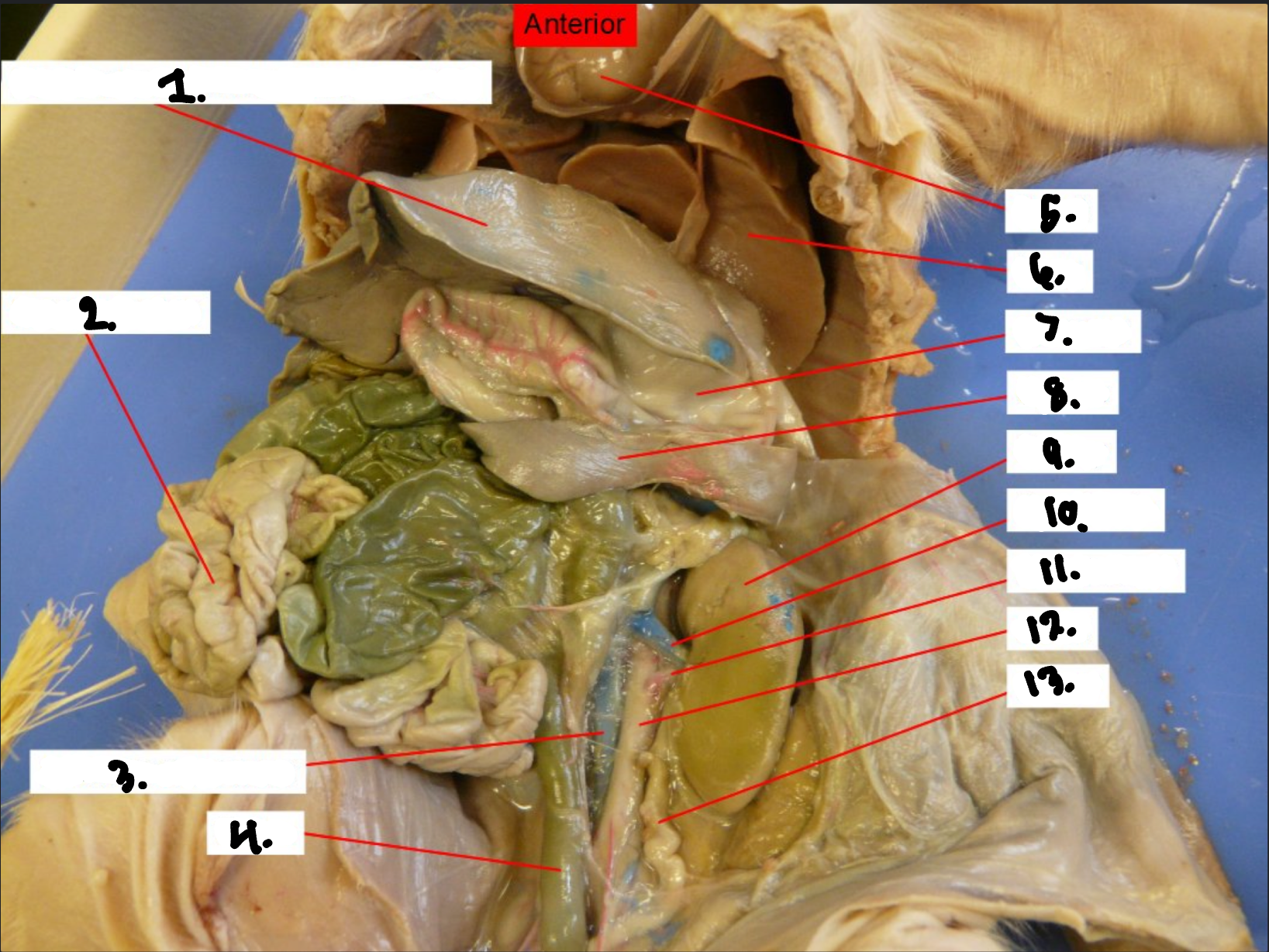
what is 1?
Diaphragm
what is 2?
Small intestine
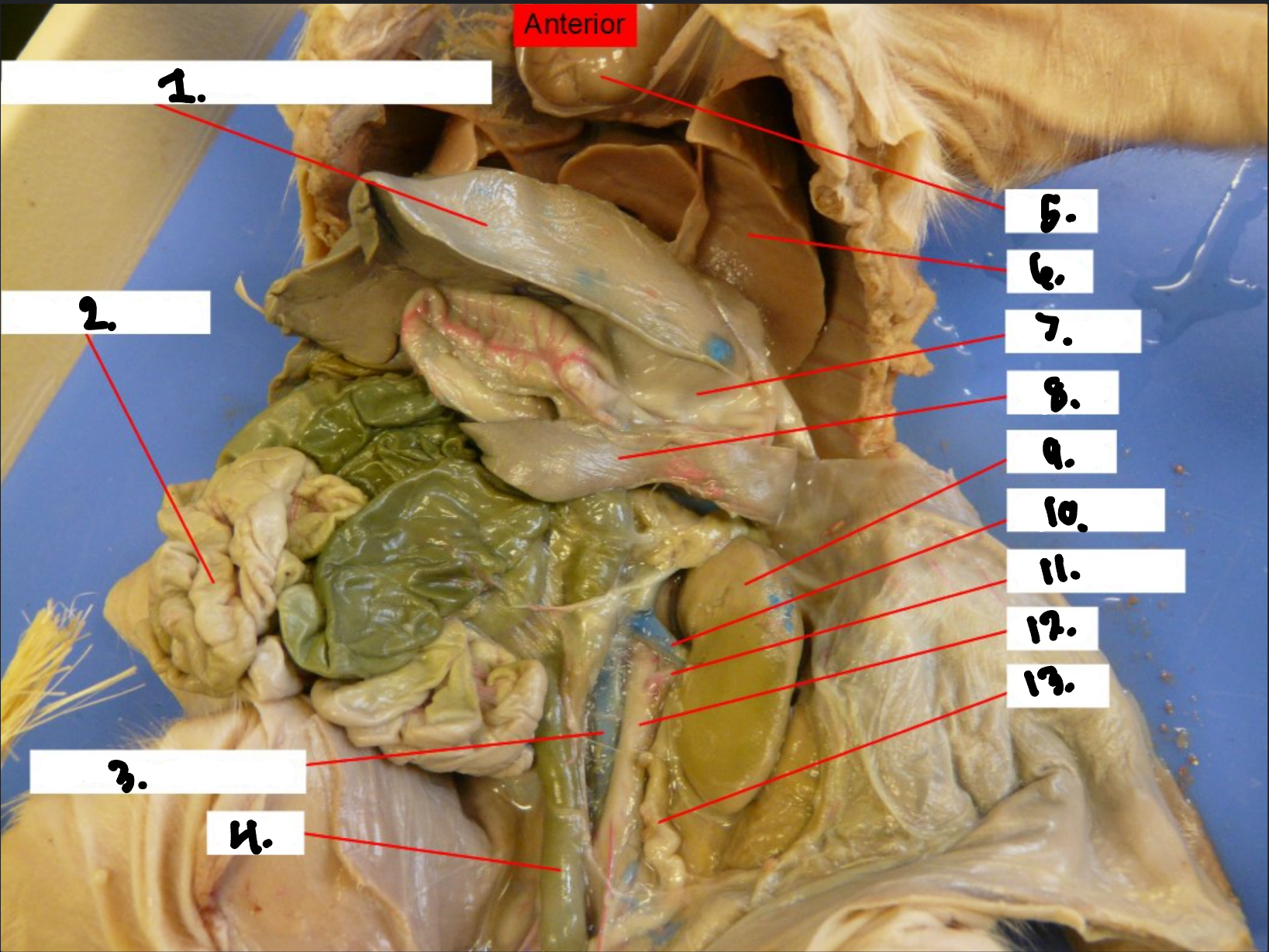
what is 3?
Posterior vena cava
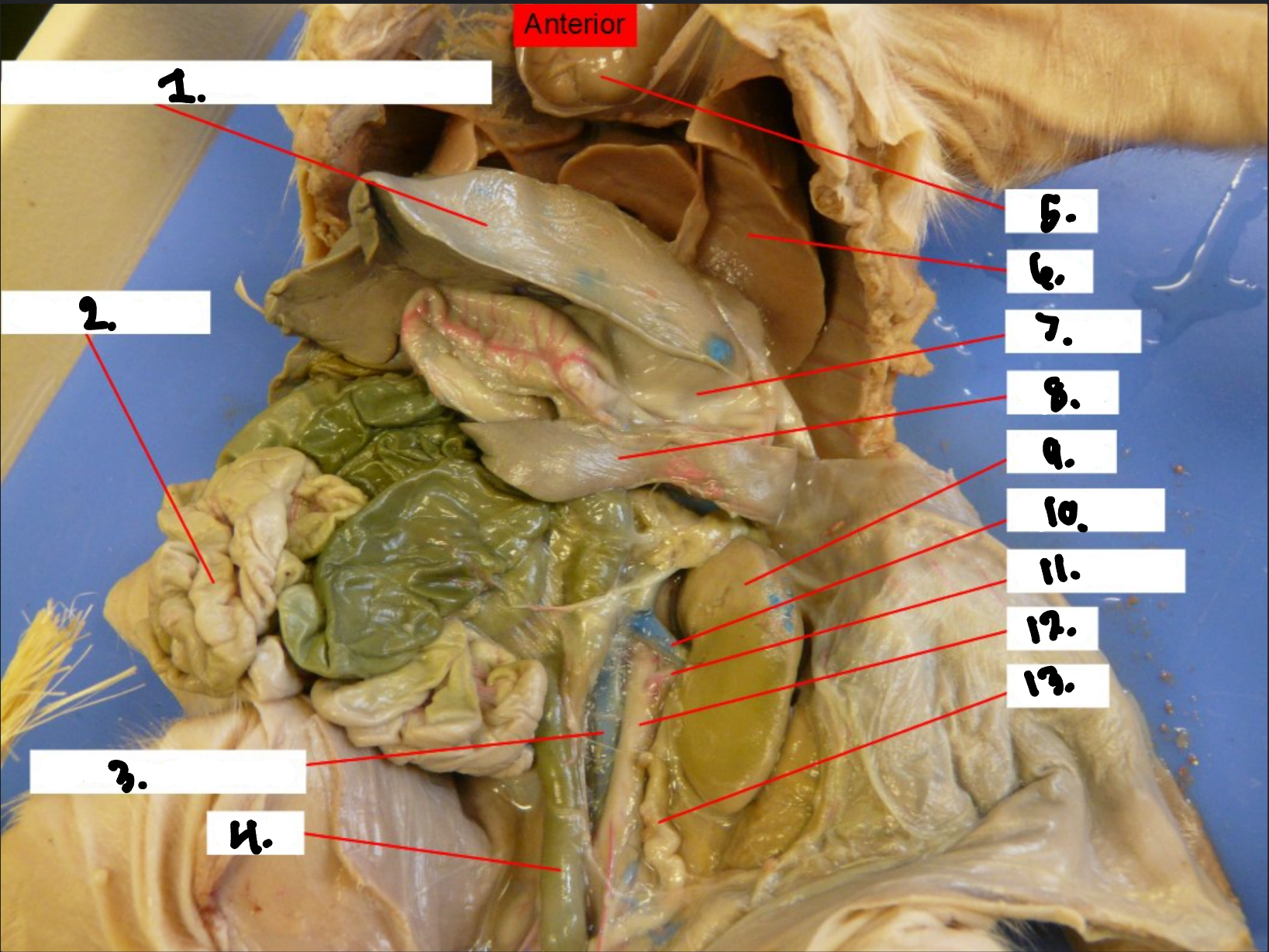
what is 4?
Colon
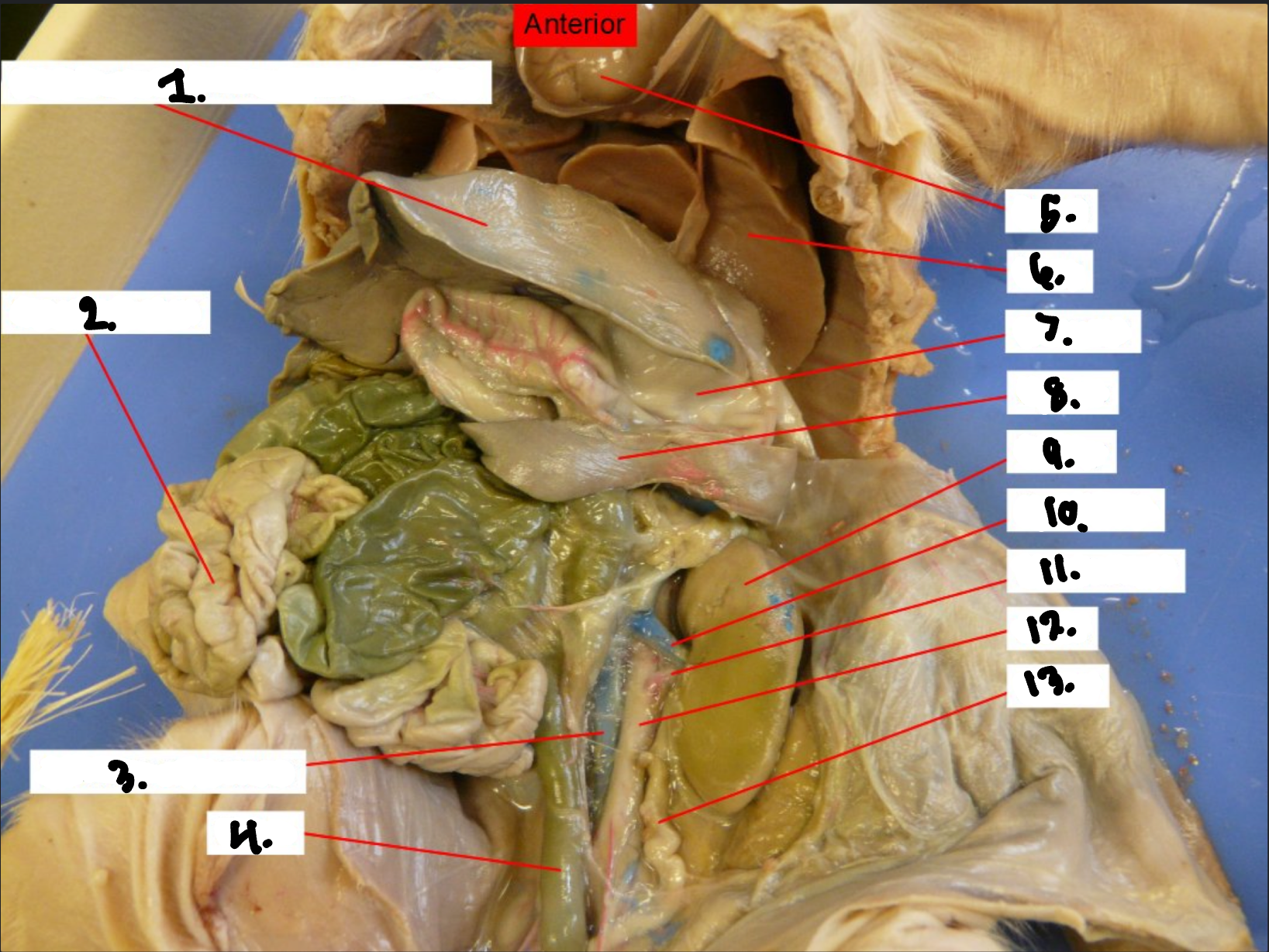
what is 5?
Heart
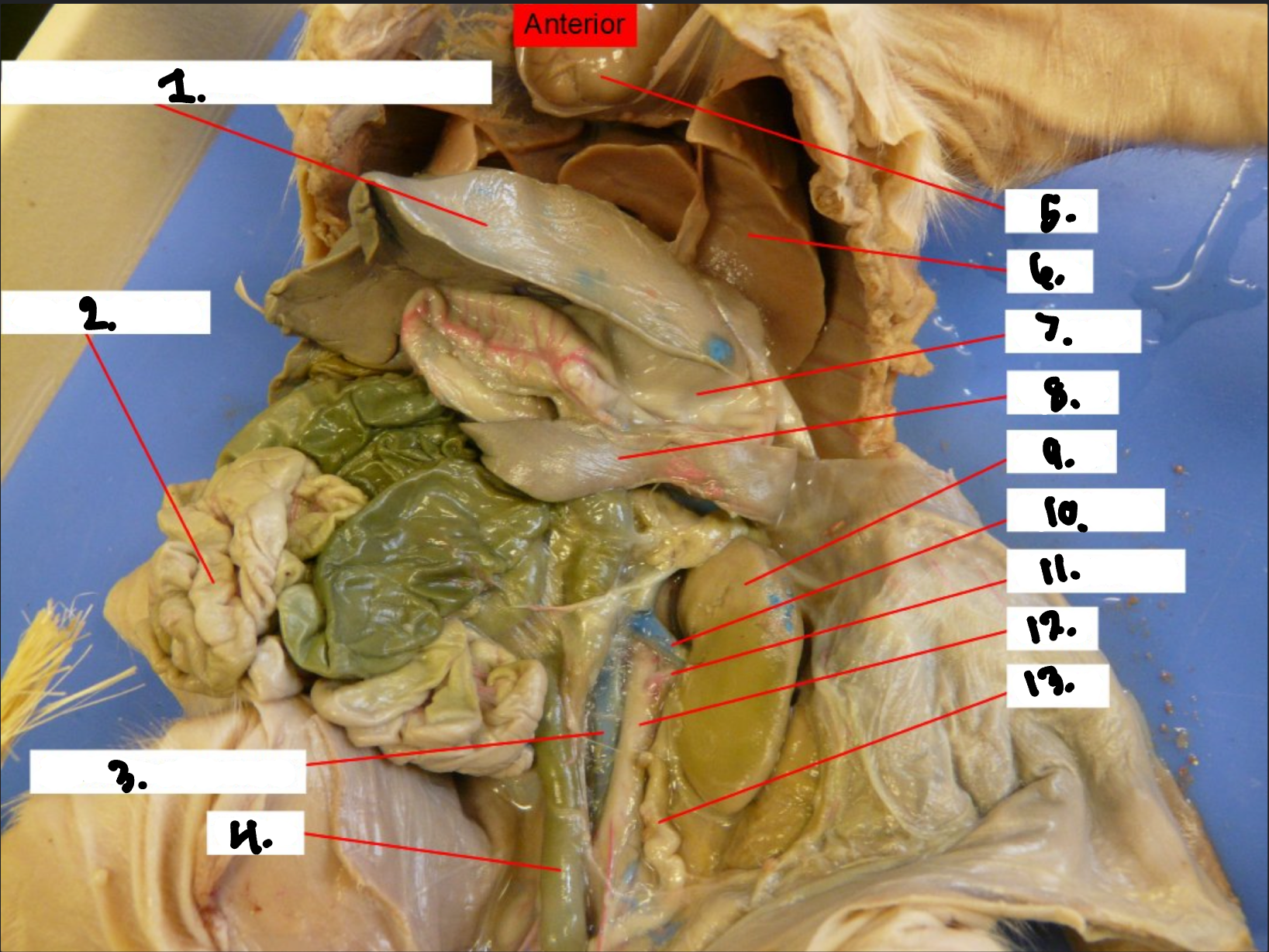
what is 6?
Lung
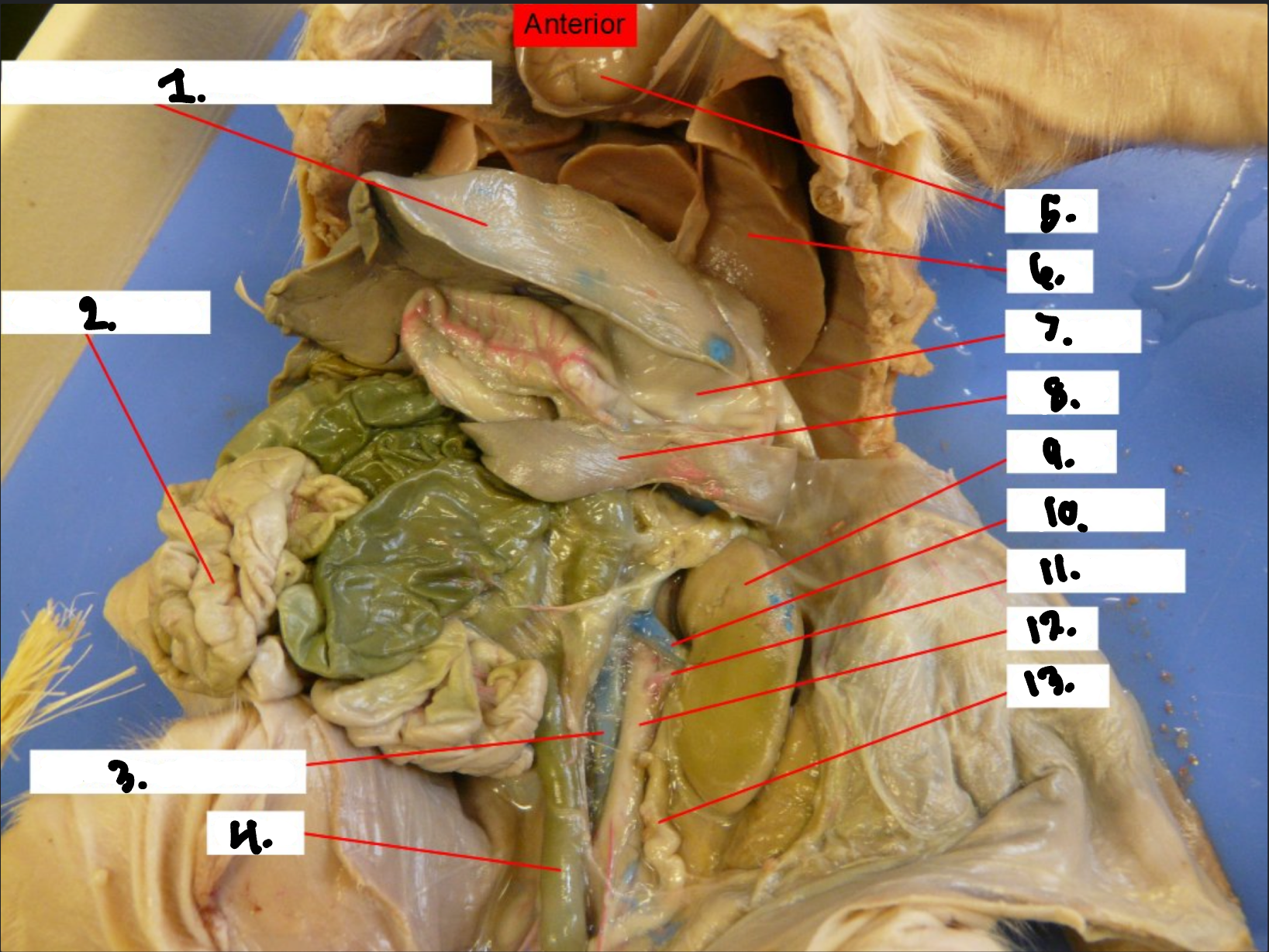
what is 7?
Stomach
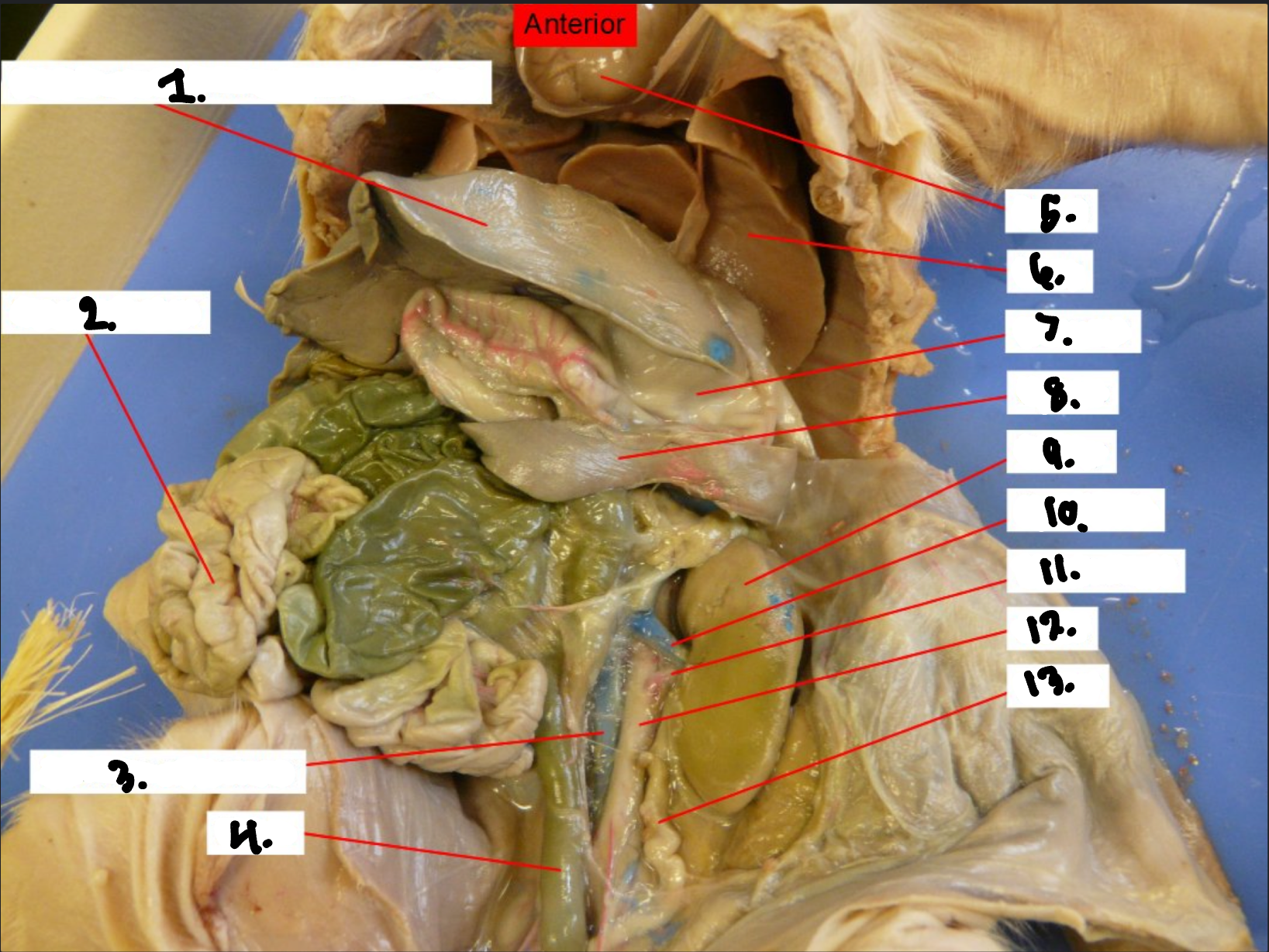
what is 8?
Spleen
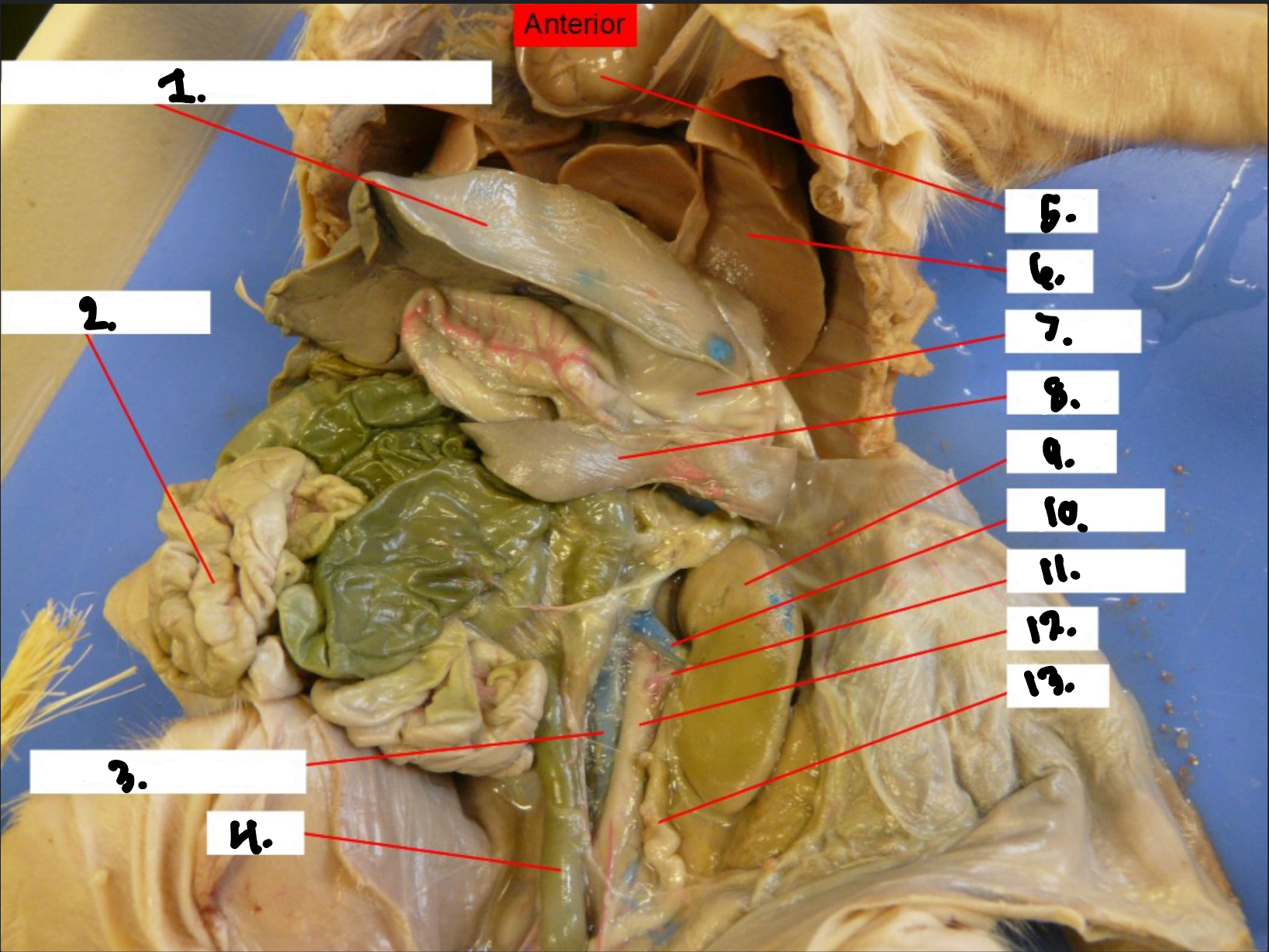
what is 9?
Kidney
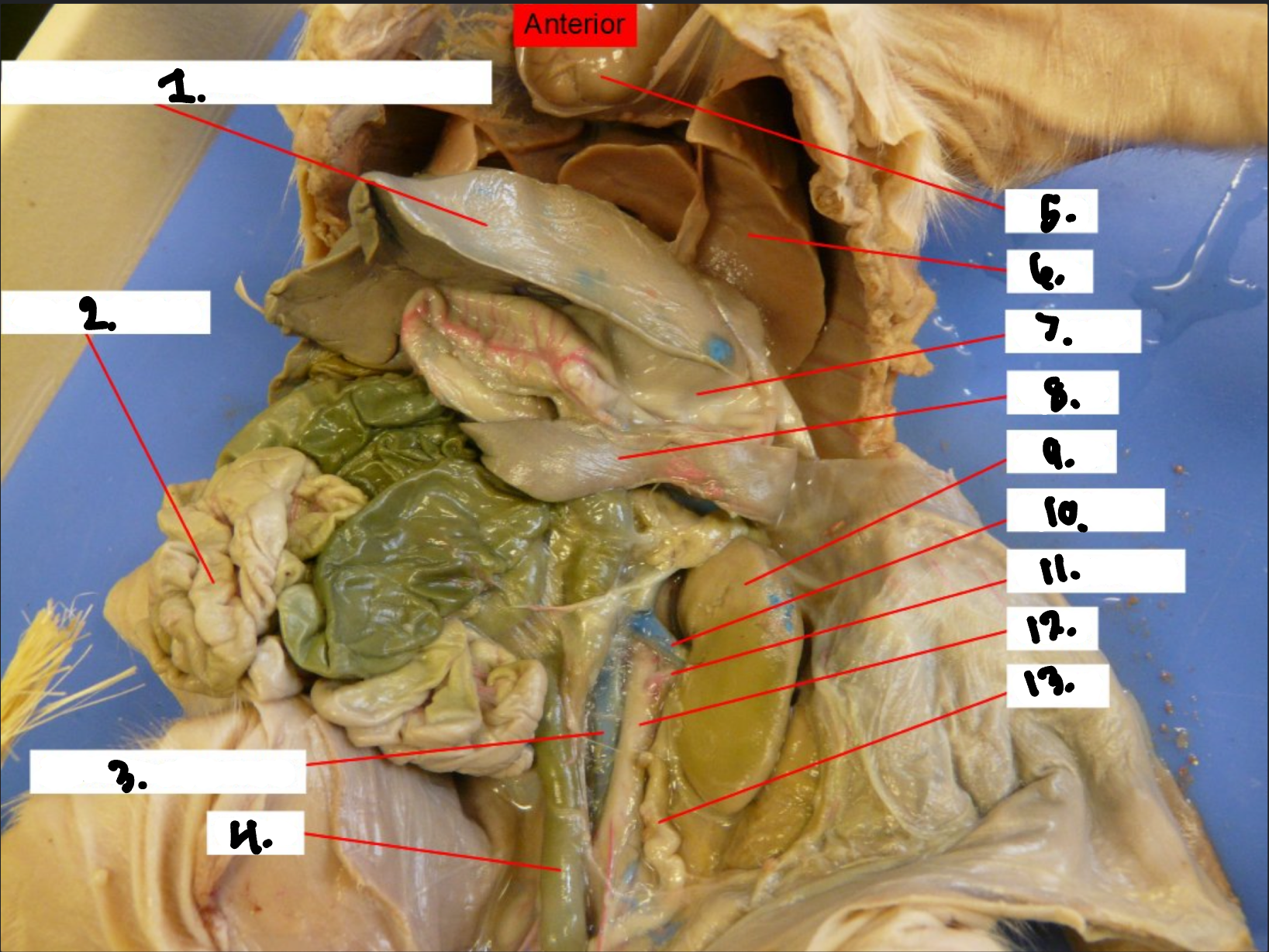
what is 10?
Renal vien
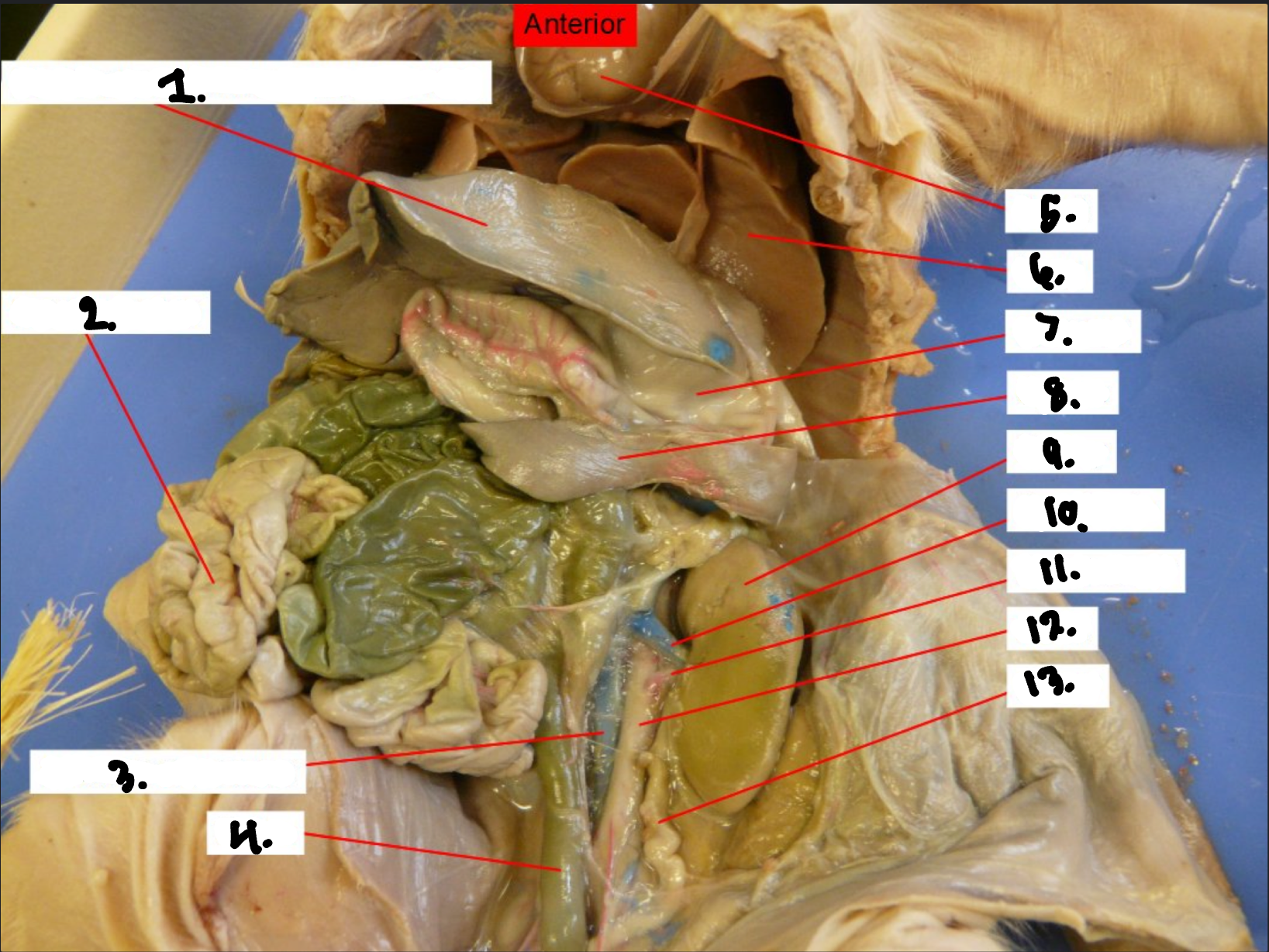
what is 11?
Renal artery
what is 12?
Aorta
what is 13?
Ureter
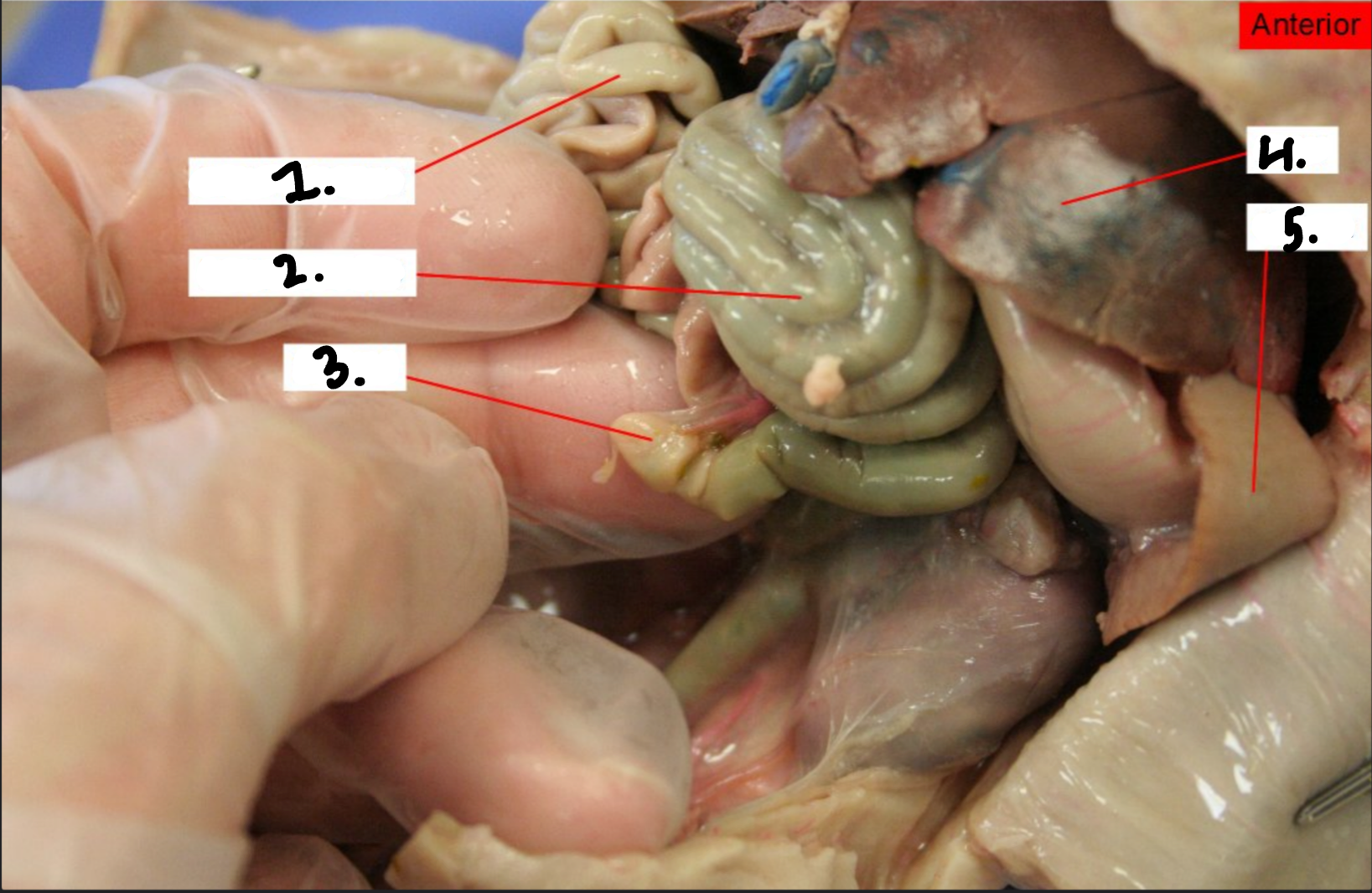
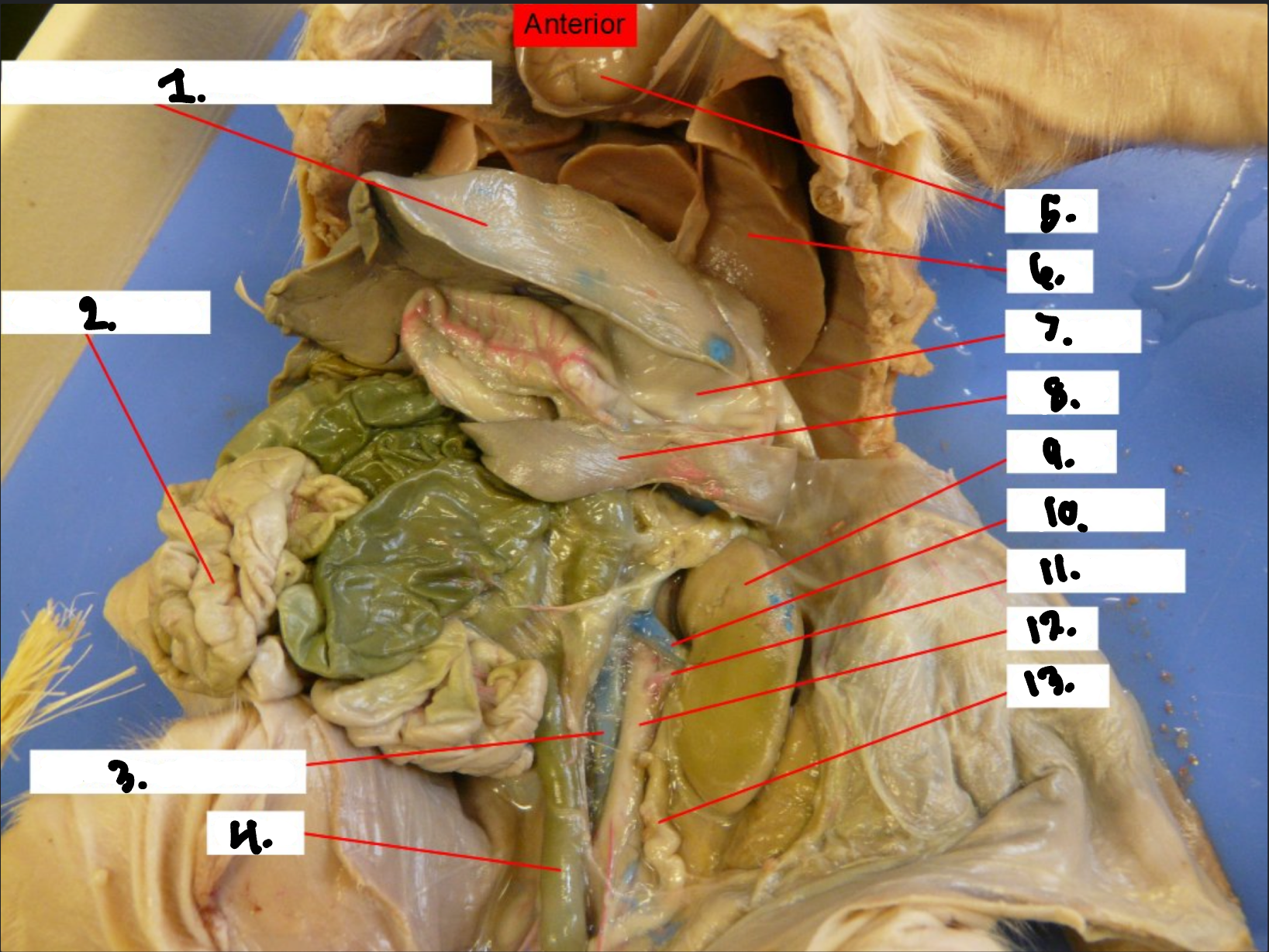
what is 1?
Small intestine
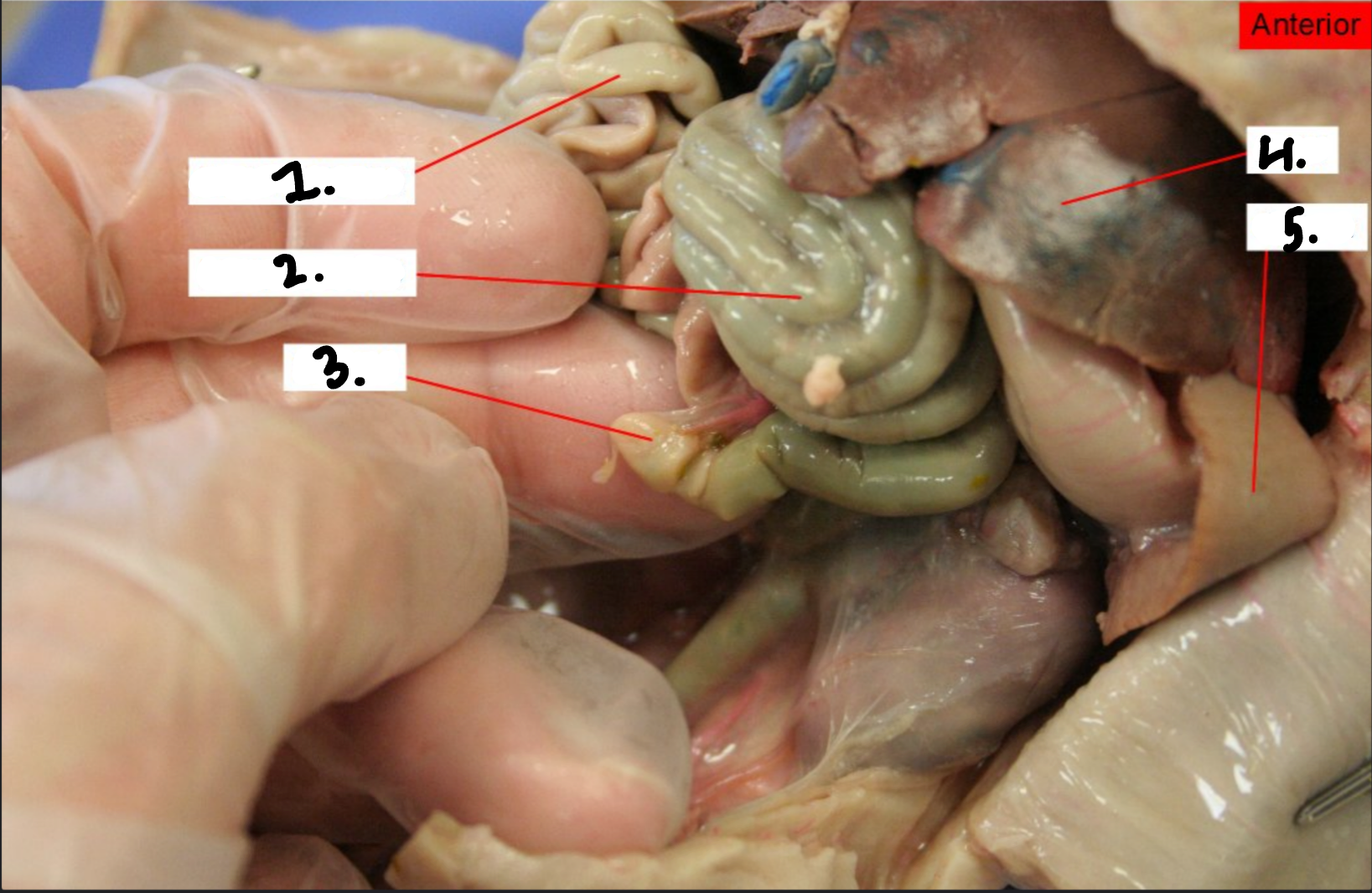
What is 2?
Large intestine
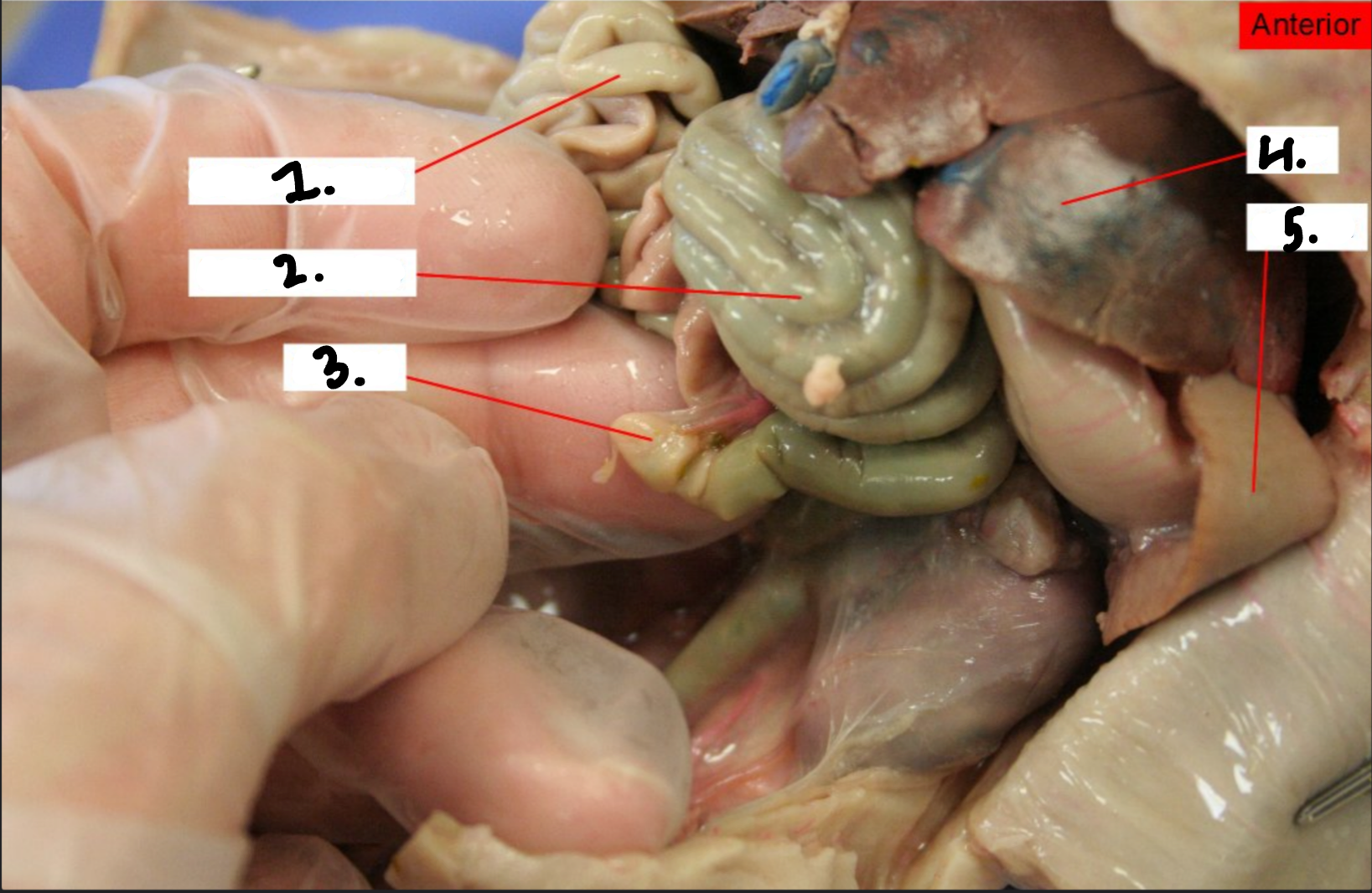
what is 3?
Cecum
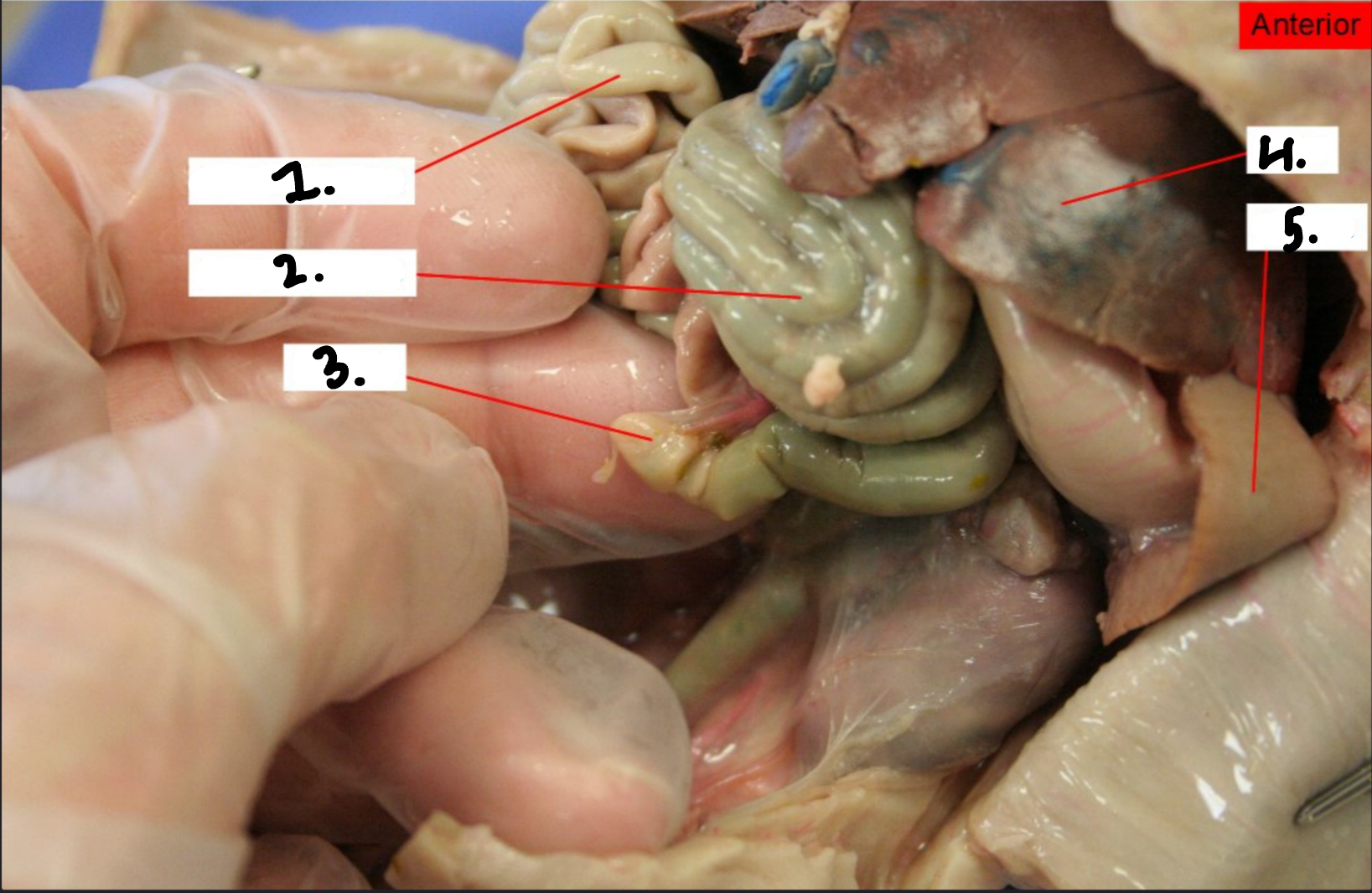
what is 4?
Liver
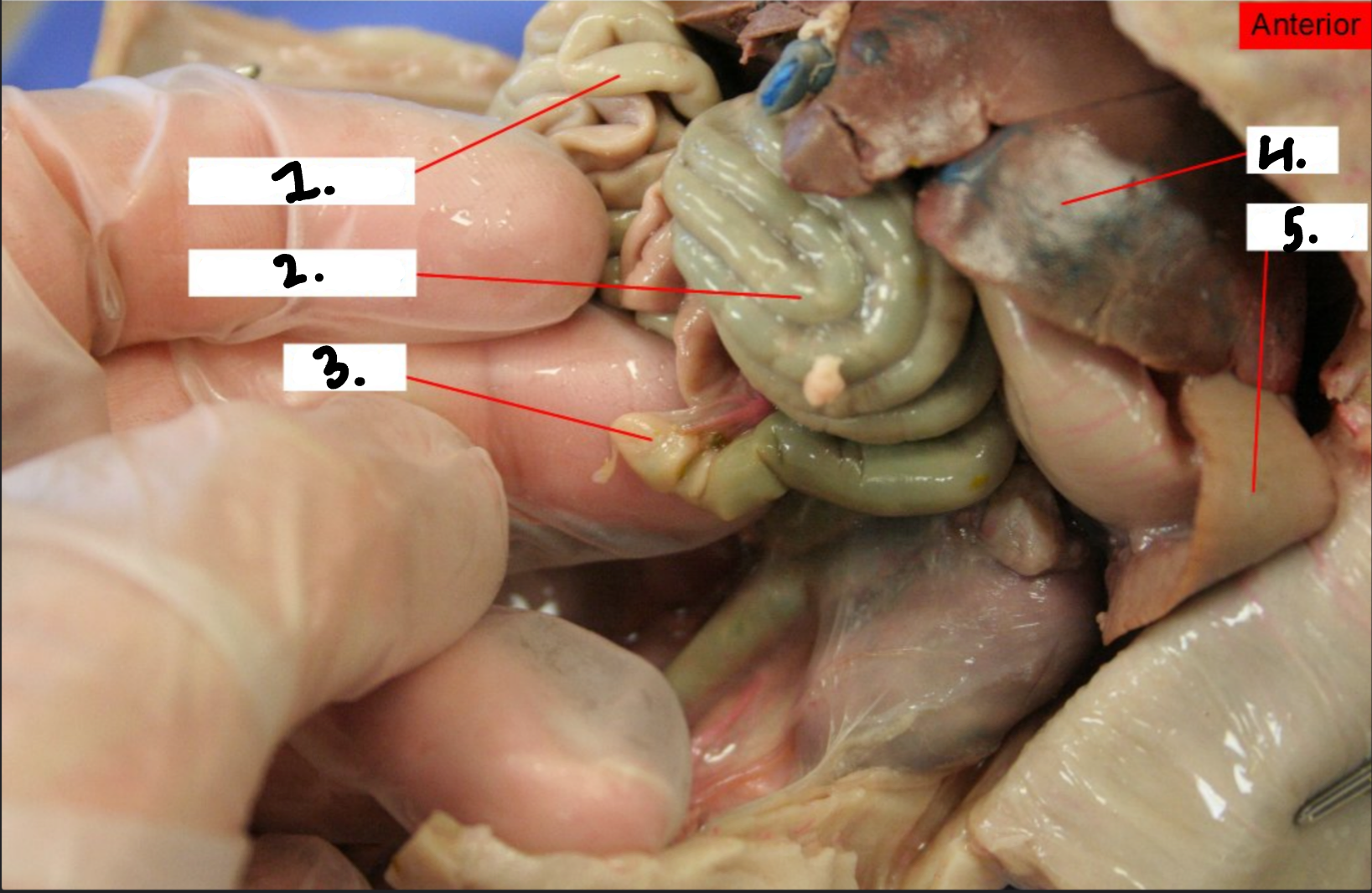
what is 5?
Spleen