CMS II Geriatrics: E2
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1. Pressure Injury (Ulcers)
1. Pressure Injury (Ulcers)
What is the pathophysiology of pressure injuries?
Pressure → Friction (breaks in skin surface) → Shearing forces (demoepidermal junction separates resulting in decreased tissue perfusion) → moisture (tissue breakdown)
What are the 4 most susceptible bony prominences for pressure injuries?
- Sacrum
- Heel
- Greater trochanter
- Ischial tuberosity
What are the normal changes in elderly skin?
- Thinning dermis and decreased vascularity
- Decreased elastin
- Loss of subQ fat
- Dec dermis/epidermal turnover
Qhat is included in wound assessment for pressure injury?
Location
Class/stage
Size
Base tissues
Exudates
Odor
Edge/perimeter
Pain
Infection evaluation
A ___% reduction in size over 2 weeks is a reliable predictive indicator of healing
20%
Which stage of pressure injury:
Intact skin with localized area of non-blanchable erythrema
Stage 1
ID a Stage 1 Pressure Ulcer
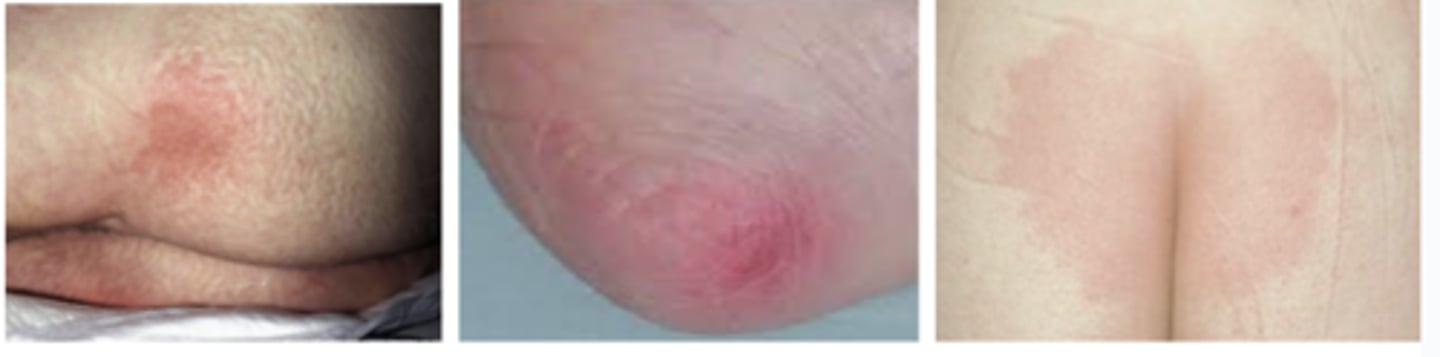
Which stage of pressure injury:
Partial thickness skin loss, no subQ exposure
Note: May include intact/ruptured blisters
Stage 2
ID a Stage 2 Pressure Ulcer
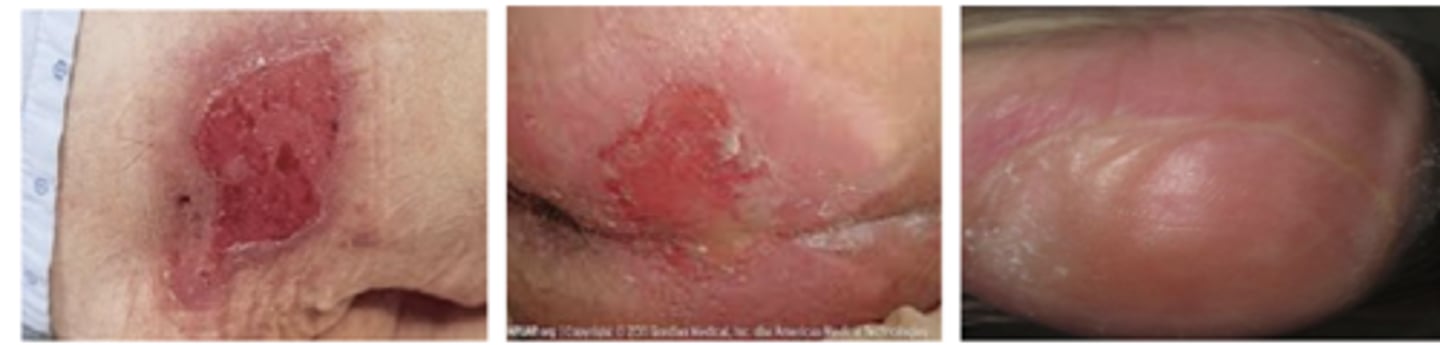
Which stage of pressure injury:
Full thickness skin loss that extends to the subQ tissue
Stage 3
ID a Stage 3 Pressure Ulcer
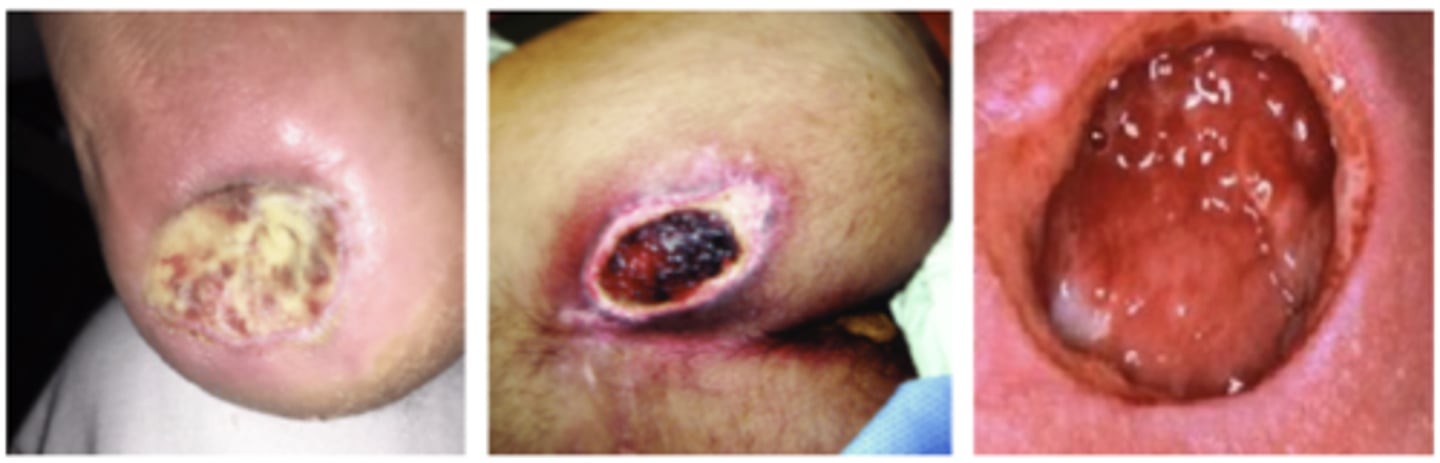
Which stage of pressure injury:
Full thickness skin loss w/ extensive destruction exposing muscle, tendon, cartilage, or bone
Stage 4
ID a Stage 4 Pressure Ulcer
What is a reliable predictor of healing for stage 3/4 pressure injuries?
Granulation tissue
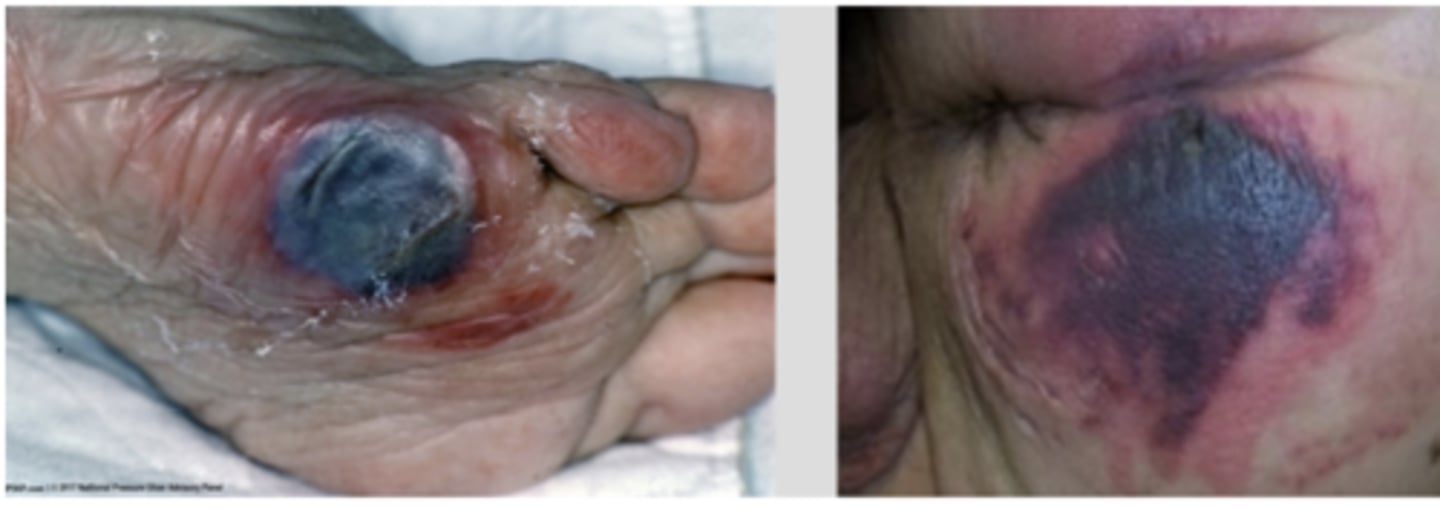
What is a Deep Tissue Pressure Injury?
Persistent non-blanchable deep red or purple skin which can be intact or non-intact → can present as blood filled blisters
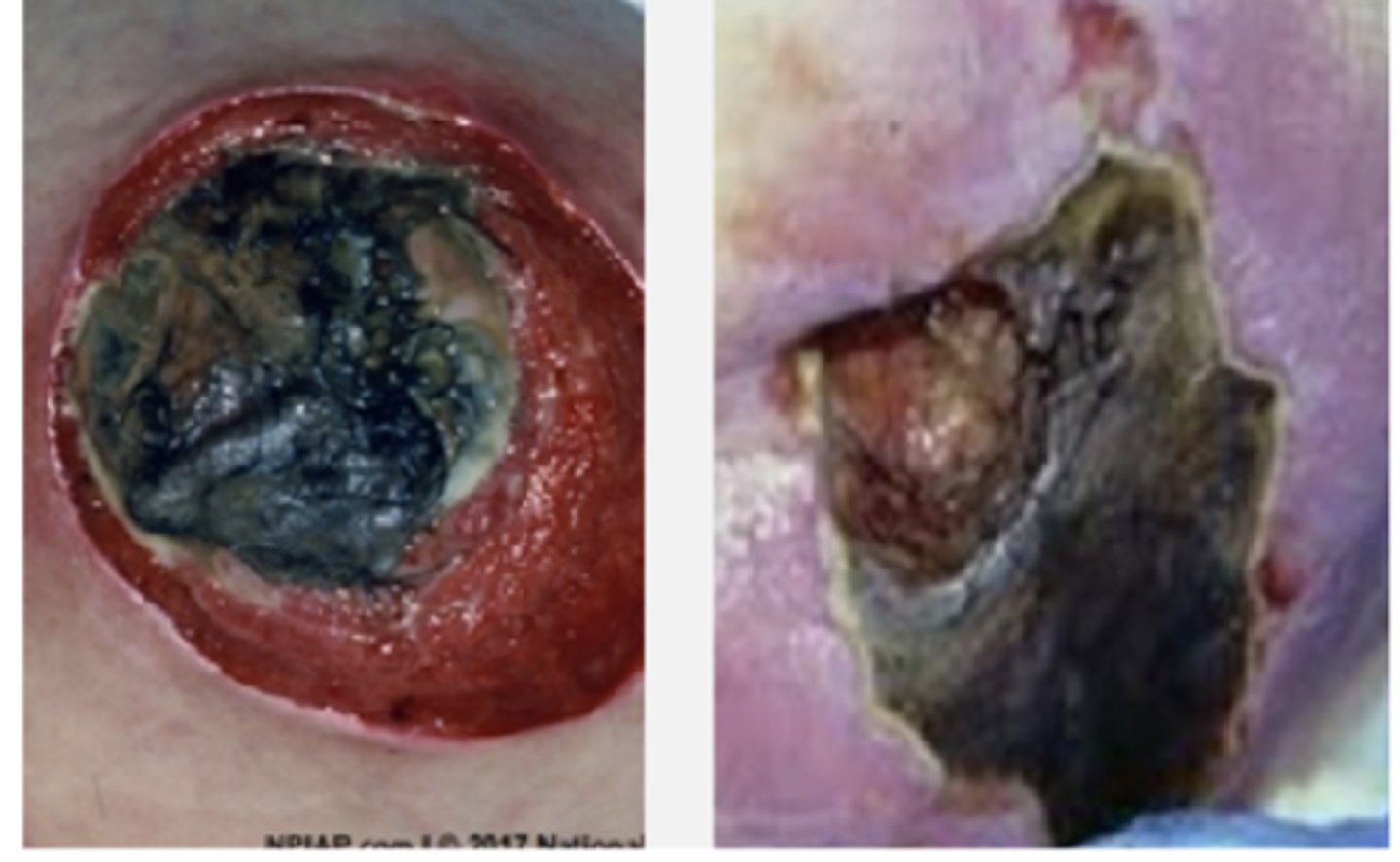
What is an unstageable ulcer?
Localized area of tissue necrosis covered with slough or escar
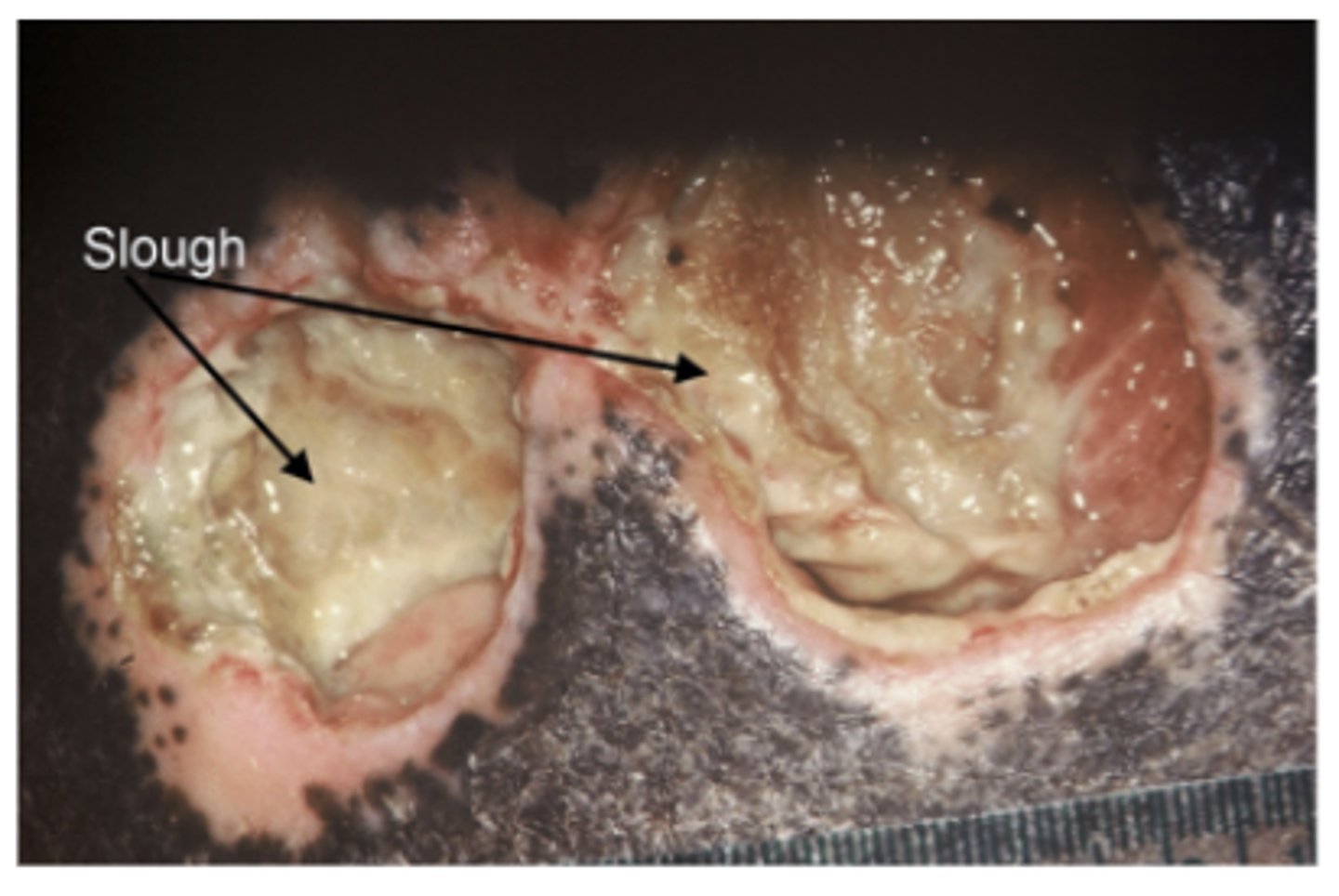
What is a collection of viscous fibrinous dead tissue (pale, yellow to tan)?
Note: soft, moist avascular tissue
Slough
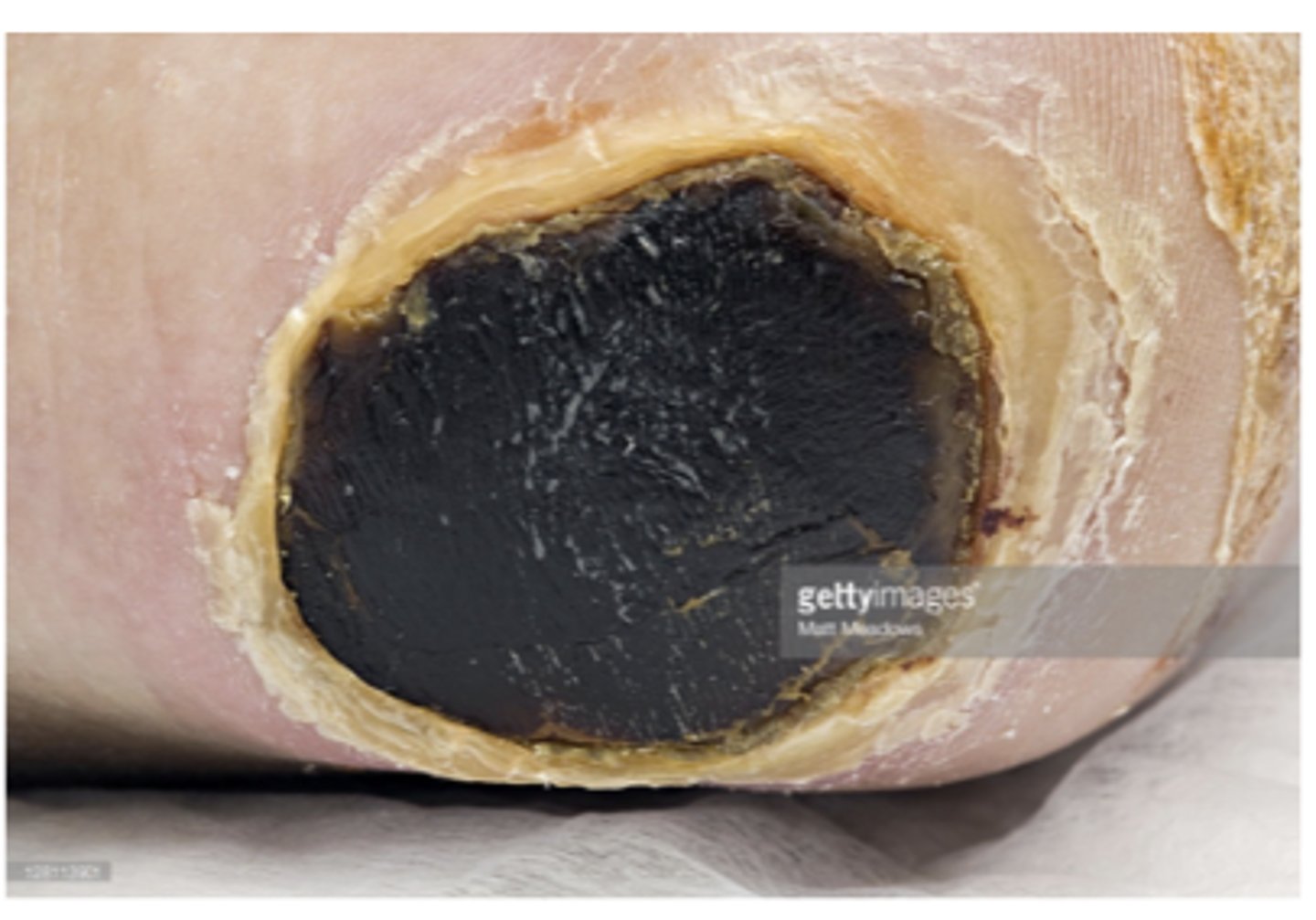
What is a collection of dead tissue that presents as a dry, dark scab?
Eschar
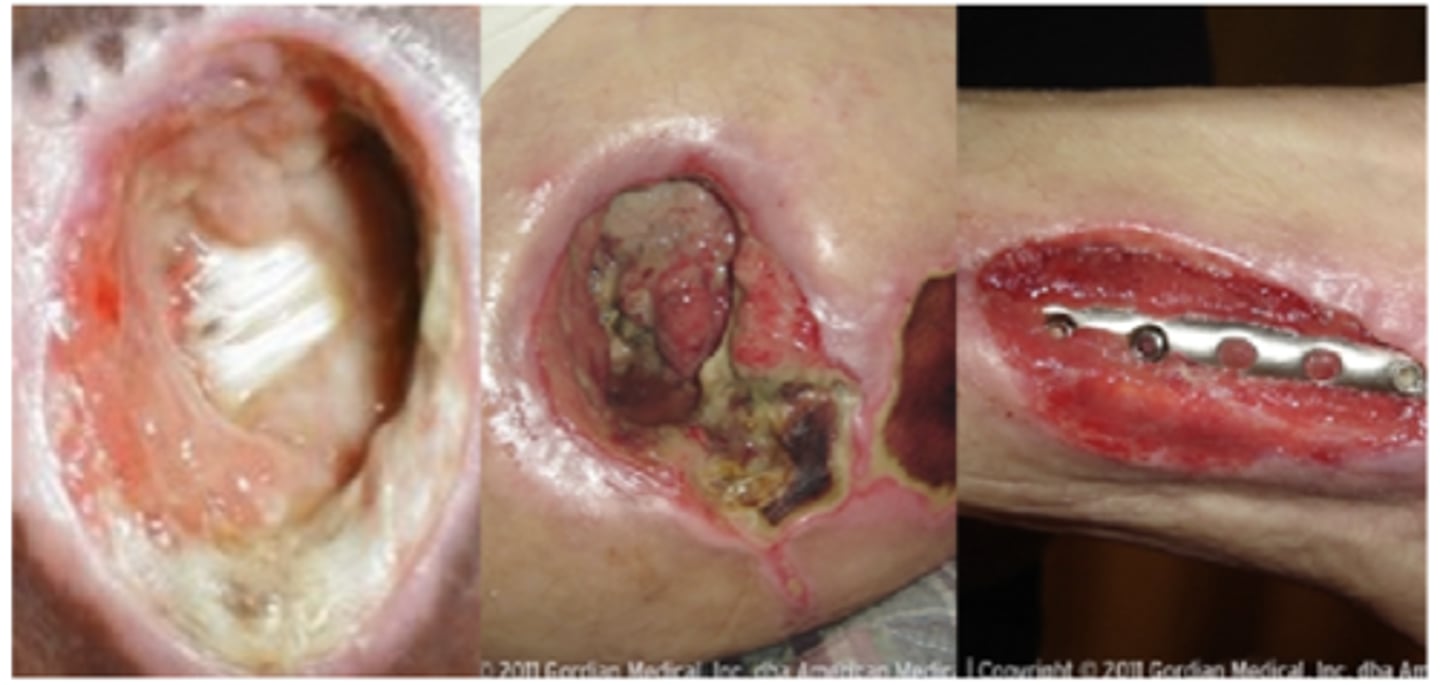
Deep Tissue Pressure Injury vs. Unstageable Pressure Injury:
Appearance:
→ Persistent localized area of non-blanchabledeep red or purple skin.
→ Can also present as blood-filled blisters. (Can have epidermal separation → dark wound bed or blood-filled blister.)
→ Can be intact or non-intact.
Features:
→ Pain/temperature changes oftenprecede skin color changes.
→ Can evolve rapidly to reveal the actual extent of tissue injury -or- may resolve without tissue loss.
Cause:
** Caused by damage to underlying soft tissues.**
Intense and/or prolonged pressure and shear forces at the bone-muscle interface.
Deep Tissue Pressure Injury
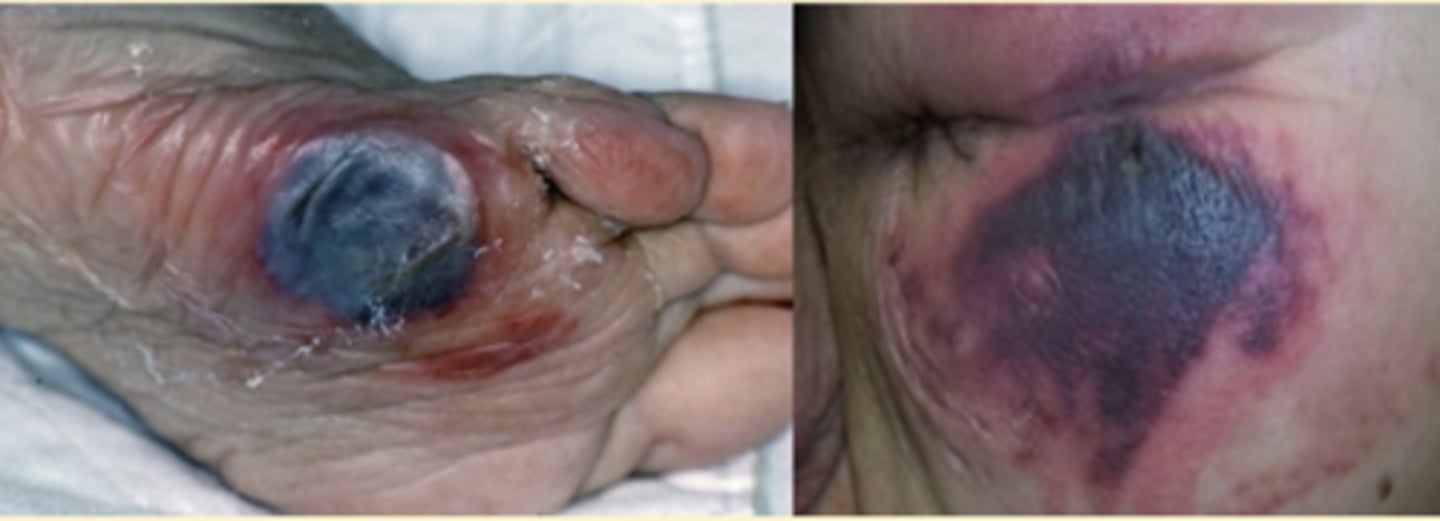
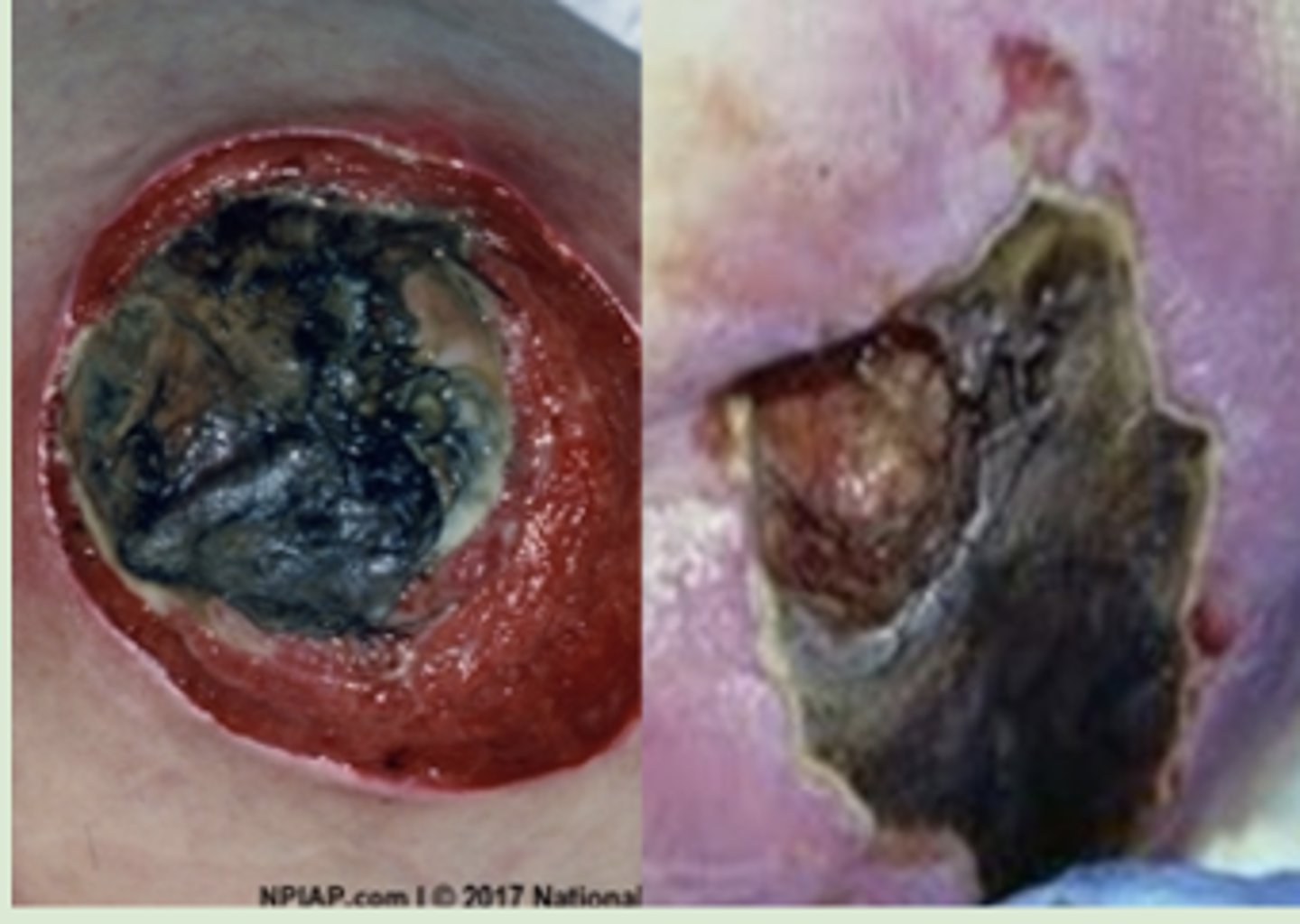
Deep Tissue Pressure Injury vs. Unstageable Pressure Injury:
Appearance:
→ Localized area of tissue necrosis covered with slough or eschar.
(AKA: debris/eschar covers the pressure ulcer.)
NOTES:
→ NEVER debride stable lesions.
→ The base of the ulcer needs to be visible in order to properly assess the stage… but it is not visible in this case, thus unstageable.
→ (It is possible for skin edges to be rolled w/ these, seen with the example photos.)
→ Slough = collection of viscous fibrinous dead tissue (pale yellow to tan in color).
→ Eschar = a collection of dead tissue that presents as a dry, dark scab.
Unstageable Pressure Injury
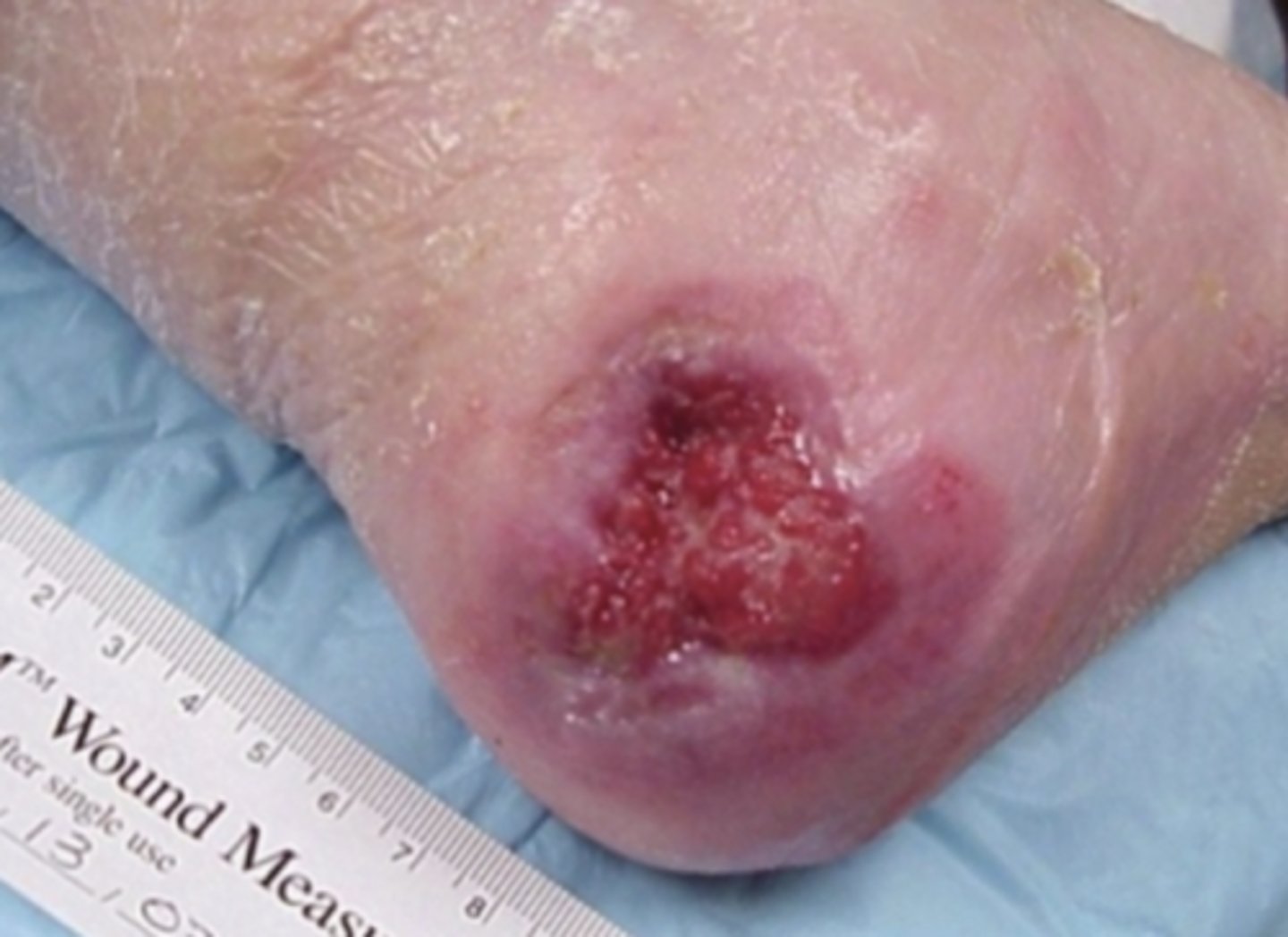
What is pink/red moist tissue comprised of new blood vessels, collagen fibers, and fibroblasts?
Note: Appears Shiny and Moist
Granulation tissue
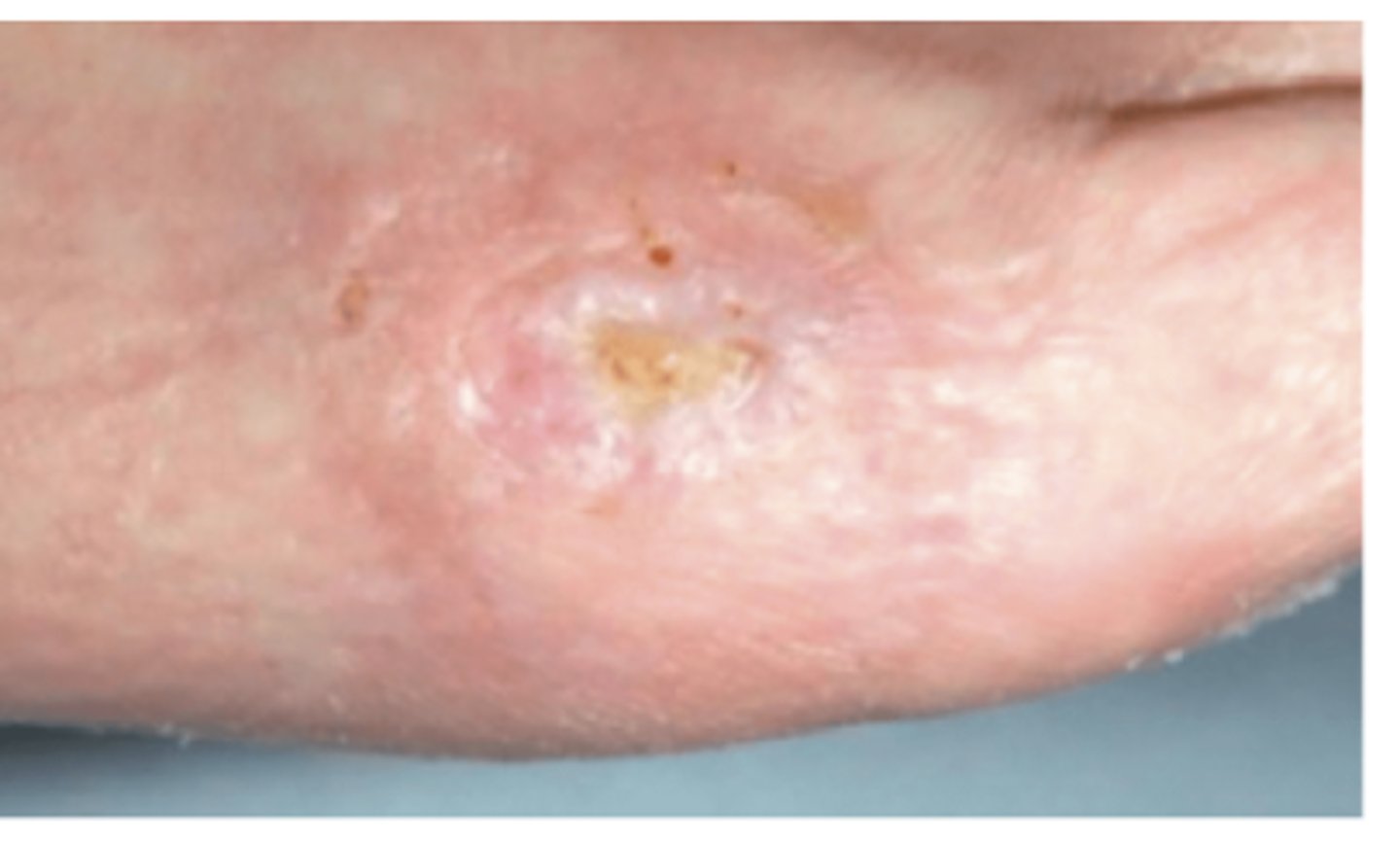
What is shiny, new, pink tissue/skin that grows in from the edges or as islands on a wound surface?
Epithelium
What is a dead space in a wound caused by erosion under the wound edges?
Note: Large wound with small opening
Undermining
What effects the fascial planes and is a narrow passageway deep within a wound?
Tunneling
What is the recommended solution when irrigating a pressure injury?
Normal Saline
What is thin, watery, clear/straw colored fluid?
Serous
What is thin, pale red/pink colored fluid?
Serosanguinous
What is thick, opaque, yellow/green fluid with an offensive odor?
Purulent
What amount of exudate: Small amount in center?
Slight
What amount of exudate: Contained within dressing?
Moderate
What amount of exudate: Extends beyond dressing on onto clothes?
Copious
What is defined as multiplication of organisms without invasion but interfering with wound healing?
Note: Wounds stagnate without obvious signs of infection
Critical colonization
Why is critical colonization concerning?
Can result in failure to heal, poor quality tissue, increased friability and increased drainage
What are the 4 phases of wound healing and their timing?
1. Hemostasis → immediately
2. Inflammatory → wound development up to 6 days
3. Proliferation → 4-24 days
4. Maturation (remodeling) → 21 days-2 yrs
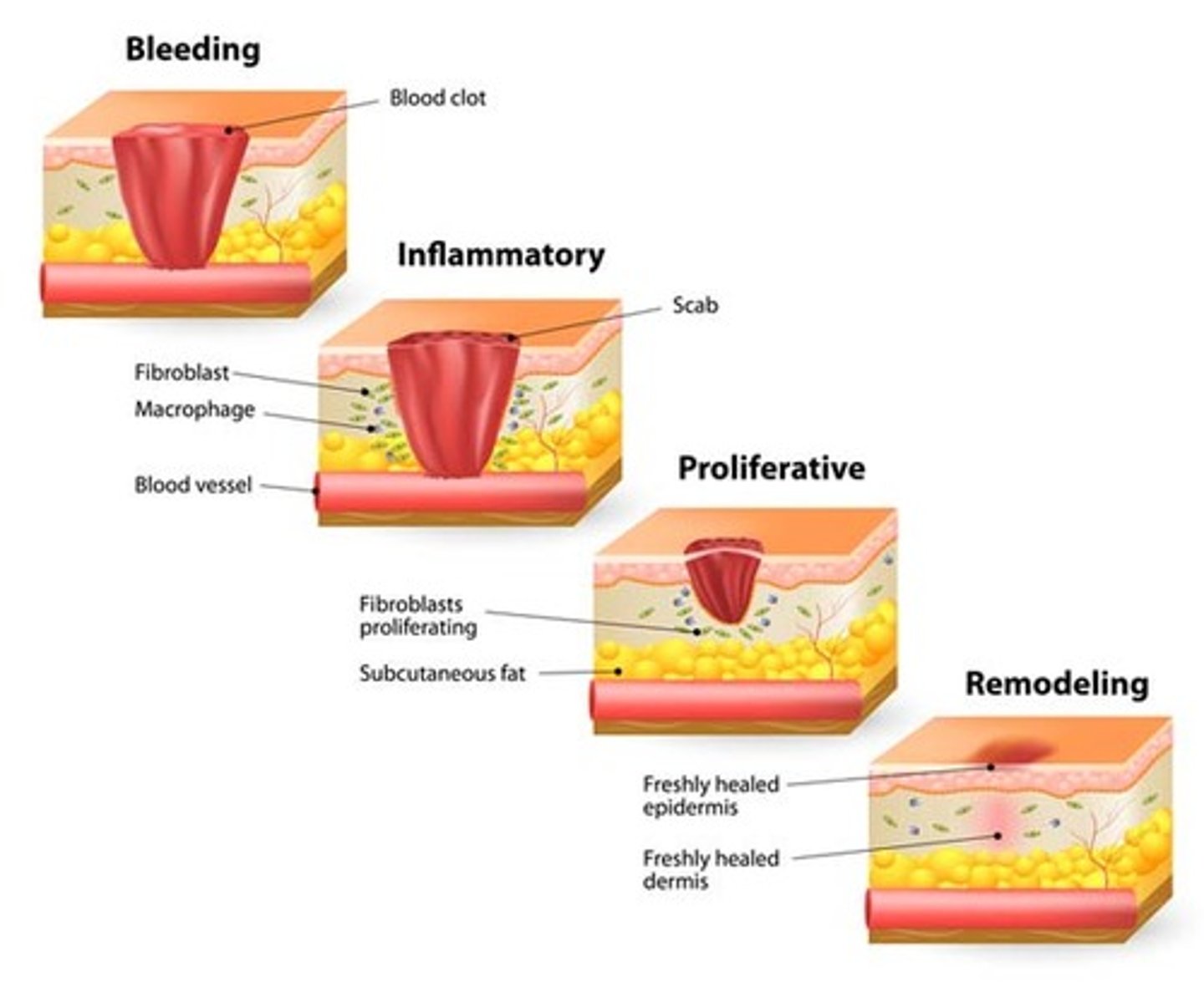
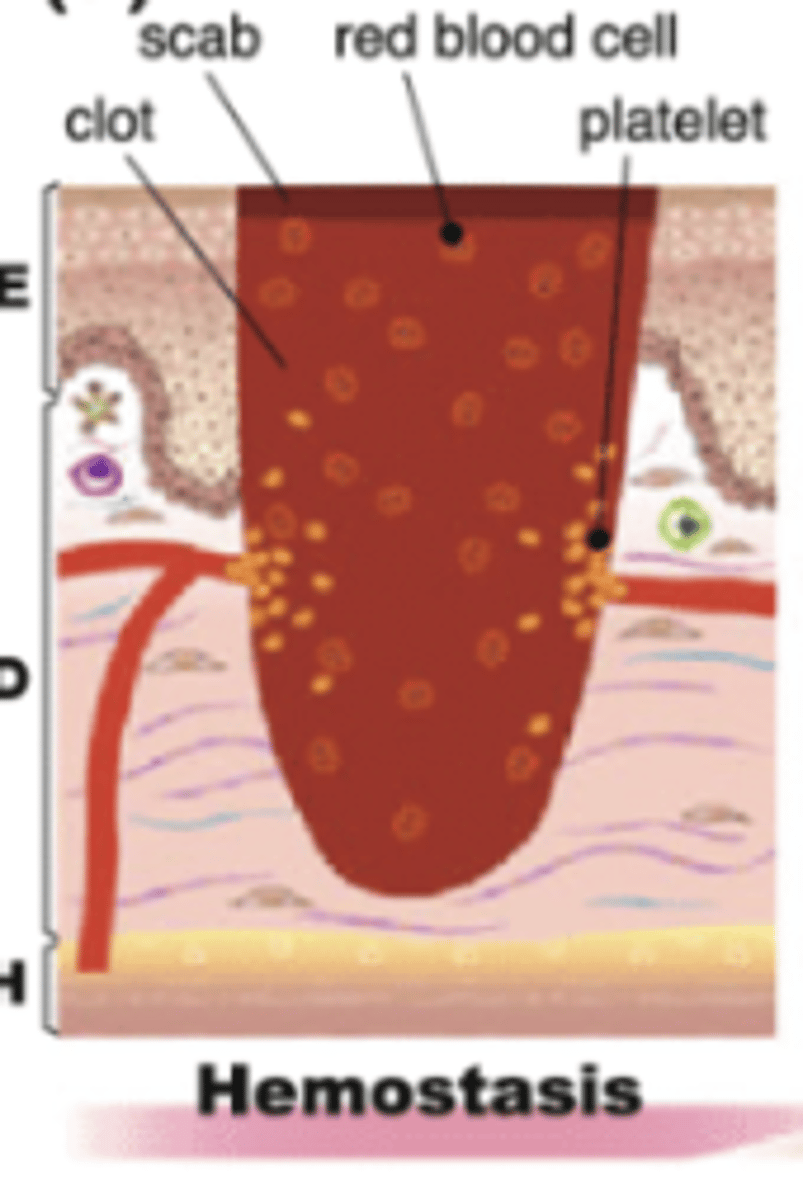
Which phase of wound healing is characterized by local vasoconstriction, formation of a platelet plug, clot formation and retraction, and fibrinolysis?
Note: Immediately after injury- minutes - hours
Hemostasis → when bleeding stops
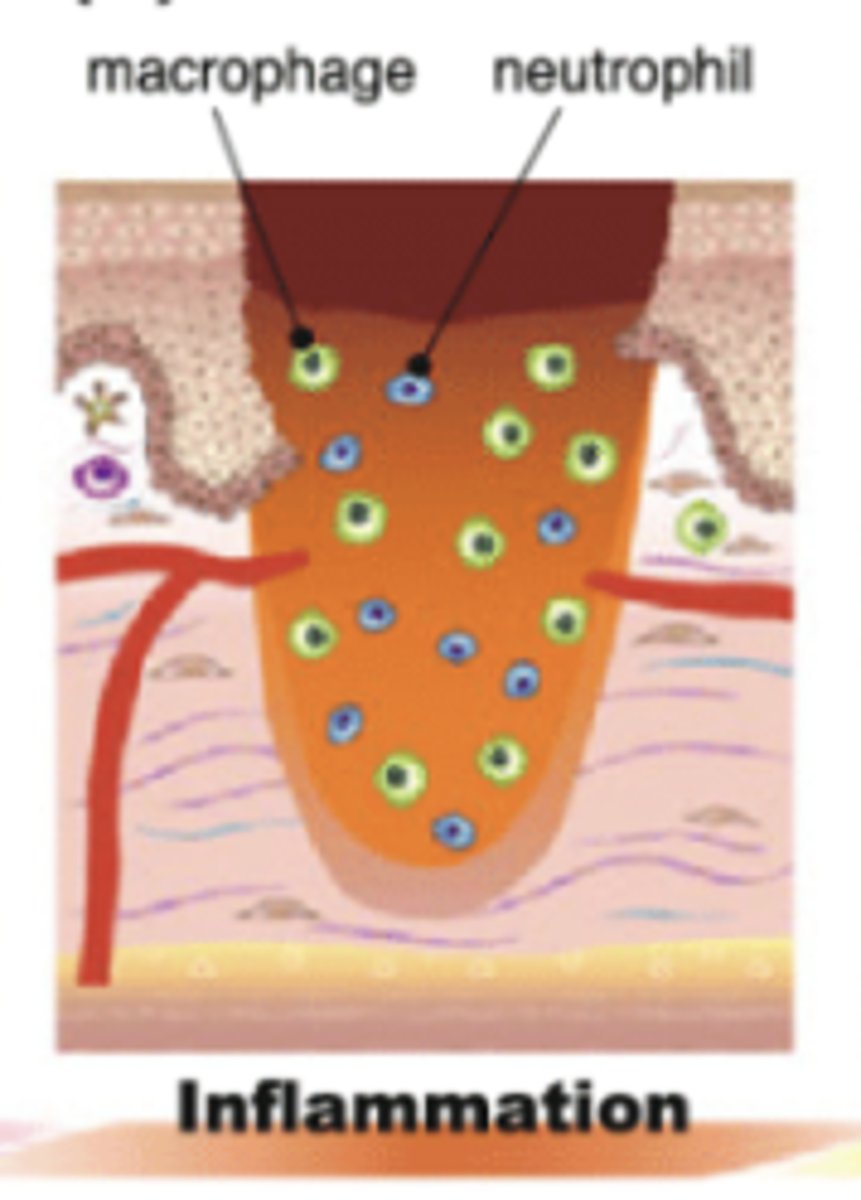
Which phase of wound healing is characterized by redness, swelling, warmth, phagocytosis and stimulation of growth factor?
Note: Beginning immediately, last up to 6 days
Inflammatory → chronic wounds can get stuck in this phase
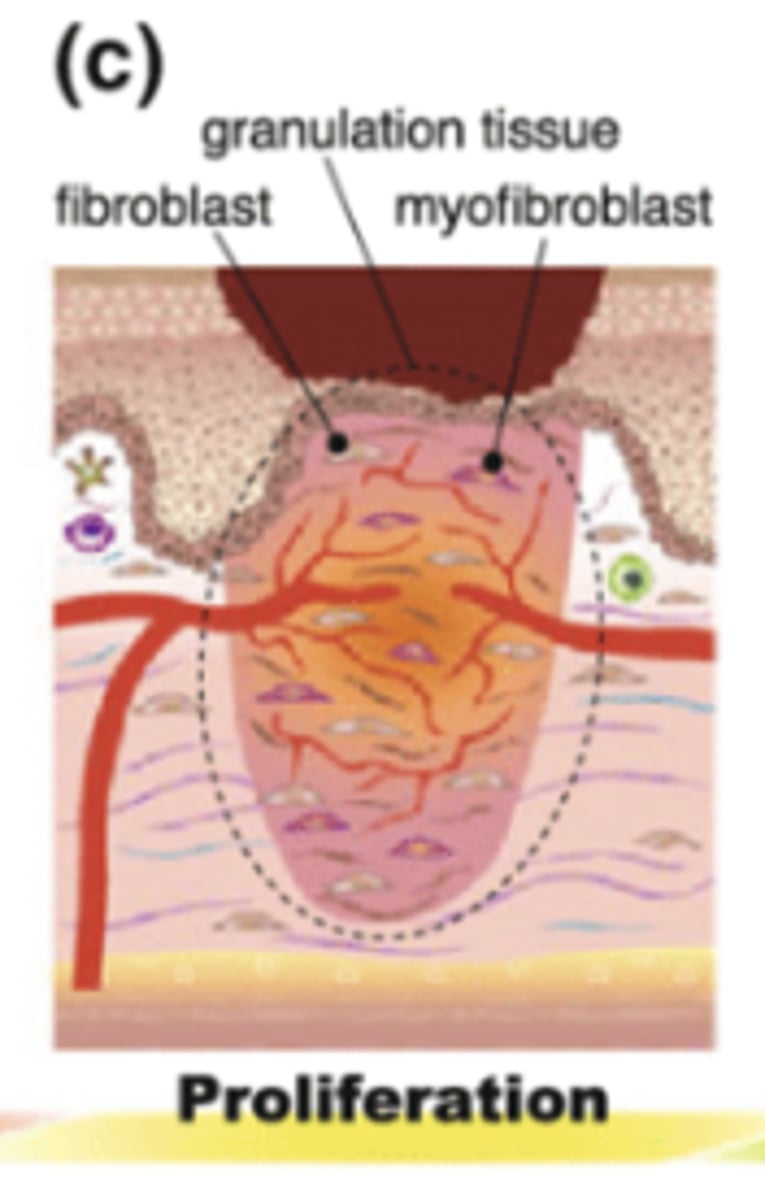
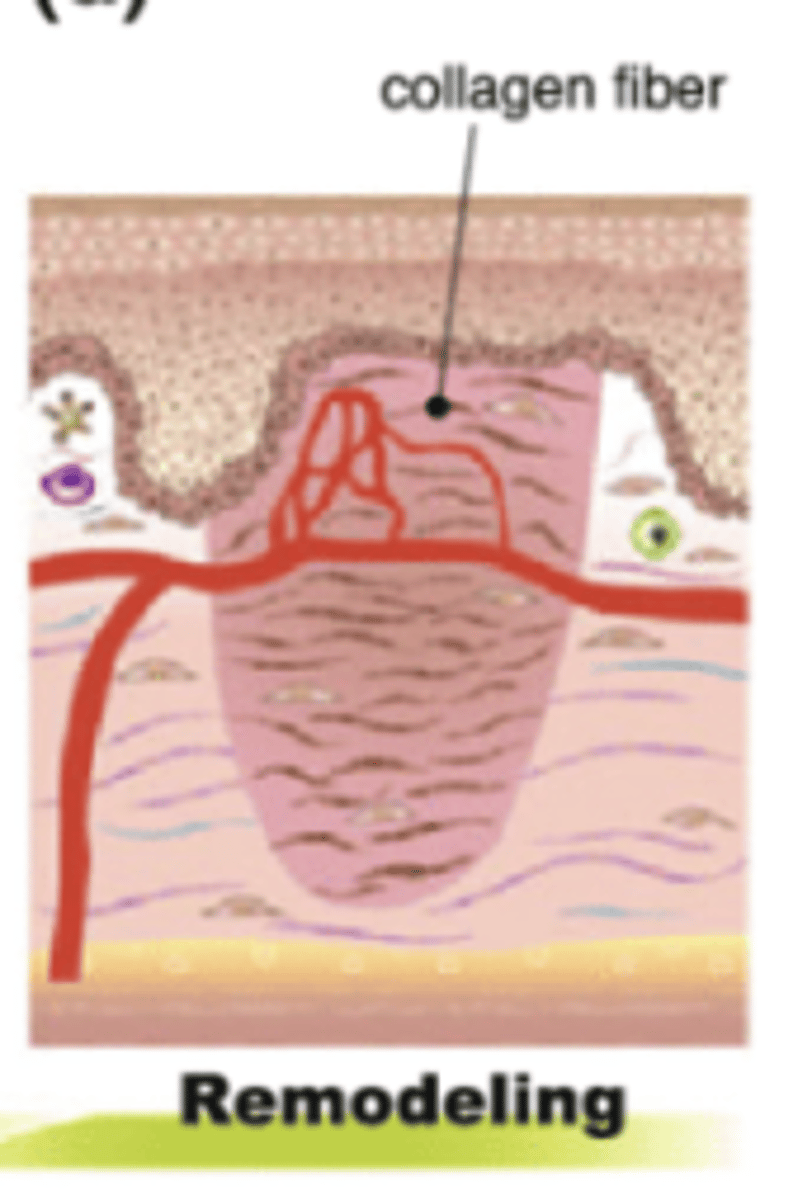
Which phase of wound healing is characterized by granulation formation, angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, epithelialization, and contraction of wound edges?
Note: Day 4-24
Proliferation
Which phase of wound healing is characterized by scarring, reorganization of collagen, and improvement of tensile strength?
Note: Begins - Day 21, can last up to 2 years
Maturation
Which dietary recommendations should be made to pts with wounds?
Encourage protein, calorie-dense foods and fluids
2. Dizziness and Syncope
2. Dizziness and Syncope
Vertigo vs. Pre-Syncope vs. Disequilibrium vs. Syncope:
Rotational Sensation
Vertigo
Vertigo vs. Pre-Syncope vs. Disequilibrium vs. Syncope:
Impending faint
Pre-Syncope
Vertigo vs. Pre-Syncope vs. Disequilibrium vs. Syncope:
Feeling of imbalance of standing or walking
Diseuilibrium
Vertigo vs. Pre-Syncope vs. Disequilibrium vs. Syncope:
Sudden, transient loss of postural tone & consciousness (not d/t trauma); spontaneous full recovery
- Loss of postural tone and consciousness with spontaneous recovery
Syncope
What is the MC Peripheral Vestibular Disorder?
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)→ brief spells brought on by changes in position
calcium debris (canalithiasis) within semicircular canals causes movement of endolymph and results in spinning sensation
How is Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis → Dix-Hallpike
Treatment → Epley maneuver
What is a positive Dix-Hallpike?
Nystagmus
Vertigo
Fatiguing of sx
Confirming BPPV
What is a positive Head Thrust?
Eyes cannot remained fixated
What is a positive Fukunda?
Sway >30 degrees toward affected side indicates unilateral vestibular lesion or acoustic neuroma
Which dx is characterized by repeated episodes of tinnitus, fluctuating hearing loss with sensation of fullness in ears, and severe vertigo?
Meniere's disease → tx w salt restriction and diuretics
Which stage of Meniere's:
Sudden unpredictable vertigo, hearing loss and tinnitus with hearing returning between attacks?
Early
Which stage of Meniere's:
Vertigo attacks are less severe, hearing loss and tinnitus worsening with periods of remission?
Middle
Which stage of Meniere's:
Less frequent vertigo with worsening hearing loss and tinnitus and problems with balance?
Late
What is the MC brain tumor associated with dizziness?
Acoustic Neuroma
What are the s/sx of Acoustic Neuromas?
Unilateral cochlear symptoms (tinnitus and hearing loss)
What are the MCC of presuncope?
Cerebral Ischemia secondary to:
-Orthostatic hypotension
-Cardiac causes
-Dehydration
-Medications
-Vasovagal attack
-Autonomic dysfunction secondary to diabetes
-Parkinsonism
Postprandial hypotension
What are the MCC of syncope?
- Cardiac
- Electrical
- Structural
- Vascular causes
- Postural change
- Post-prandial hypotension → decreased in systolic BP >20 mmHg 1-2 hrs after a meal
What factors are associated with Disequilibrium?
- Proprioceptive disorders → Peripheral Neuropathies
- Visual probs → cataracts, macular degeneration
- MSK disorders → RA, OA, weakness
- Gait disorders → Stroke, Parkinson's
What med classes are most associated with dizziness in the elderly?
Antihypertensives
Psychotropic meds
Aminoglycosides
NSAIDs
What are the 3 provocative tests of the vestibular system?
1. Dix-Hallpike
2. Head-thrust test
3. Fukuda stepping test → difficult if weakness or gait disorder present
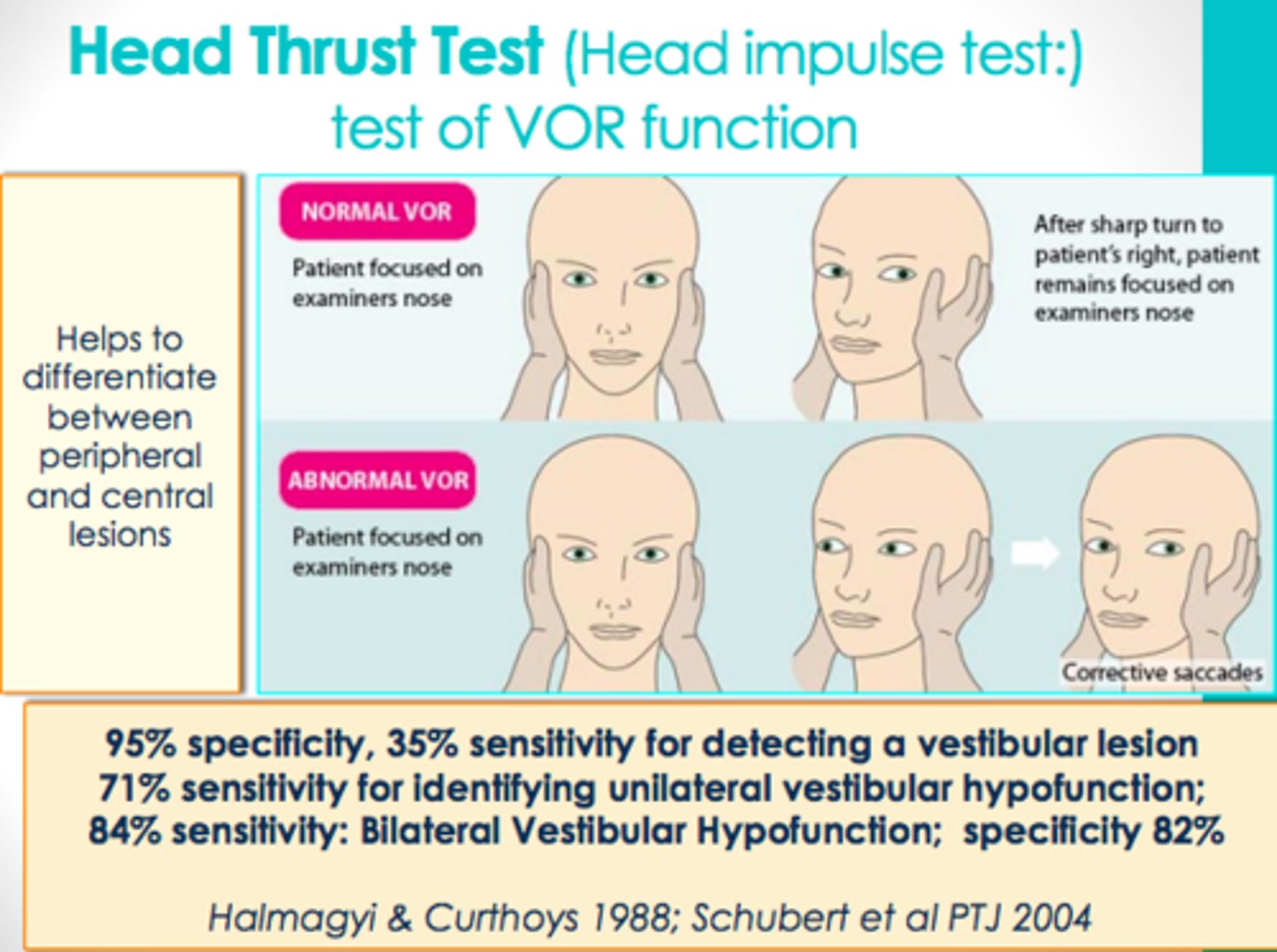
Other than provocative tests should always be performed on PE when evaluating dizziness?
BP
Cardiac exam
Balance and gait
Audiometry
Tilt table test
Lab testing
If dizziness is long-standing and lasts more than several months, what other conditions should you consider?
Psychological
How does aging affect the baroreflex?
Decreased ability to increase HR in response to sympathetic stimulation → Syncope
What is the pathophys of syncope?
reflex mechanisms are less responsive → decreased ability to increase HR in response to sympathetic stimulation and increased sensitivity to effects of dehydration and vasodilator drugs
Which comorbidities affect postural responses?
DM
Arrhythmia
AS
MI
Which drugs can impair postural reflexes?
Vasodilators
Antidepressants
Alpha/beta blockers
TCAs
Which cause of syncope:
Sudden, occurs in any position, no precipitant, blue/ashen skin, faint/absent pulses, rapid recovery?
Syncope caused by Arrhythmia
Which cause of syncope:
Aborted if person lies flat, nausea/diaphoresis precipitant, visual changes, pale and motionless, fatigue/nausea/diaphoresis on recovery without retrograde amnesia?
Vasovagal Syncope
Which cause of syncope:
Occurs in any position without warning, rigid tone, rapid pulse and high BP, tonic eye deviation, frothing at mouth, incontinence, slow recovery?
Seizure
Why do we obtain an EKG in all adults with syncope?
Assess for:
- Acute or remote MI
- Conduction abnormalities and pre-excitation
- Sinus bradycardia
- Prolonged QT
What is the tx for syncope caused by Orthostatic HypOtension?
Adjust meds
Ensure adequate volume
Other conservative measures (stockings)
What is the tx for vasovagal syncope?
Avoidance of triggers; medical therapy is somewhat controversial (BB, clonidine, paroxetine, midodrine)
What is the tx for Carotid Sinus Hypersensitivity induced syncope?
Avoid stimulating factors (tight collars or rapid neck movements); pacemaker
What is the tx for syncope due to Post Prandial Hypotension?
Avoid alcohol and high carb meals
Remain recumbent after meals
What is the tx for syncope due to ventricular tachyarrhythmia?
Implanted defribrillator or medical tx
What is the tx for syncope due to bradyarrhythmia?
Pacemaker
3. Urinary Incontinence
3. Urinary Incontinence
What is the sympathetic control of normal micturition?
Urine storage → inhibits detrusor contraction and increases sphincter contraction
What is the parasympathetic control of normal micturition?
Voiding → induces detrusor contraction and sphincter relaxation
What are the age-related urinary tract changes?
Detrusor muscle function decreases → fibrosis of bladder wall and increased sensitivity to neurotransmitter
Leads to →
Decreased bladder capacity
Detrusor instability
Decreased urinary flow rate
Decreased voided volume
Increased PVR
What are the transient causes of urinary incontinence?
Hint: DIAPPERS:
- Delirium
- Infection
- Atrophic vaginitis/urethritis
- Pharmaceuticals
- Psych probs
- Excessive urine output
- Restricted mobility
- Stool impaction
What is the MC type of incontinence in the geriatric population?
Urge incontinence
What is the leakage of urine along w/ or before the urge to void (MC in older population)?
Urge incontinence
What is the leakage of urine w/ increased intra-abdominal pressure in absence of bladder contraction?
Stress incontinence
What is the continuous leakage of urine, dribbling, incomplete emptying, "bedwetting"?
Overflow incontinence
What type of incontinence is where the patient is physically unable to toilet themselves in a timely fashion despite intact storage and emptying function?
Functional incontinence
What nonpharm treatments for incontinence have high rates of satisfaction?
- Bladder training
- Biofeedback
- Pelvic muscle exercises
What are the primary causative mechanisms associated with Stress incontinence?
- Weak pelvic floor muscles
- ntrinsic sphincter deficiency
Who is Overflow Incontinence MC in?
Men → due to outlet obstruction and detrusor underactivity
PVR > 200 mL = inadequate emptying
Which Antimuscarinic needs dose adjustment in renal insuff?
Trospium
Which drugs are Antimuscarinincs? What are their side effects?
- Oxybutynin
- Tolterodine
- Trospium
- Darifenacin
- Solifenacin
- Fesoterodine
- Dry mouth, blurry vision, constipation, dental caries, cognitive
Which drug is a Beta 3 agonist? What are common SE?
Mirabegron (Myrebetriq)
Constipation, Diarrhea, HA, Dizziness, Nausea, Tachycardia, HTN, UTI
Urine storage is under what control?
Sympathetic
Voiding is under what control?
Parasympathetic
What is indwelling catheterization reserved for?
1. Short term decompression of acute urine retention
2. Chronic retention not surgically/medically remediable
3. Patients with wounds that must be kept clean of urine
4. Very ill/end of life pts
Why should catheterization be done with caution?
Significant morbidity → polymicrobial bacteriuria
4. Palliative Care
4. Palliative Care
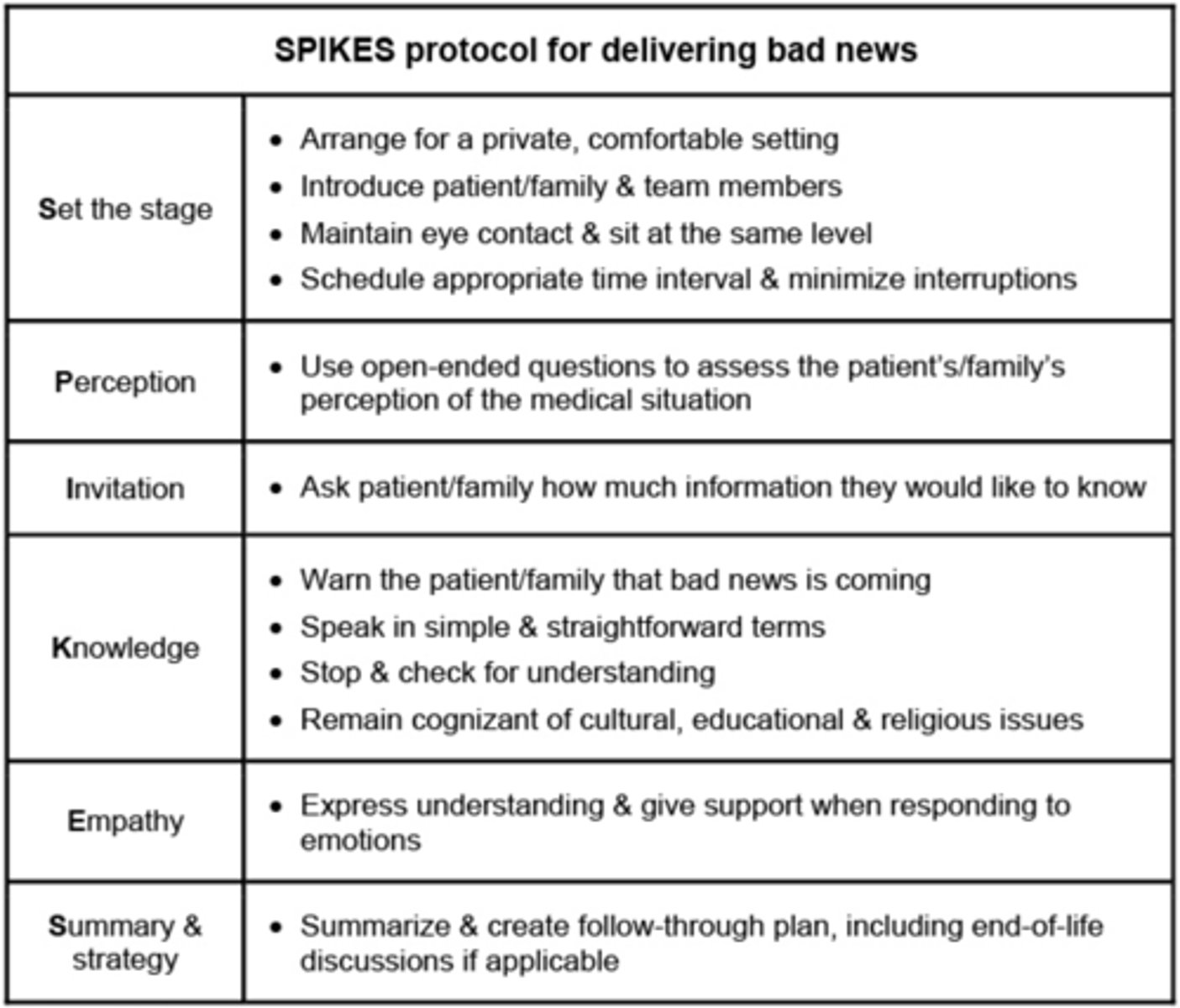
Which protocol provides a framework for difficult discussions?
SPIKE
What is the main goal of palliative care? Which dx is it used for?
improve quality of life
Cancer, Failure to thrive, COPD/emphysema/ILD/IPF, advanced liver dz, stroke, CHF 3+, dementia, HIV/AIDS, parkinsons, ALS