L 3 tissues
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
what are the common set of functions of a cell?
Nutrient uptake
Energy metabolism
Division (replication)
tissues
Groups of cells in multicellular organisms that have a specific function that distinguishes them from other groups of cells in a whole organism.
These groups of cells have some common function
What is the extracellular matrix?
The ECM is the non-cellular part within all tissues
it is the stuff in the spaces in and around the cells.
what does the extracellular matrix provide?
It provides essential physical scaffolding for the cells and is involved in other tissue processes including homeostasis.
what is the extracellular matrix composed of?
The ECM is typically composed of water, proteins, minerals or salts, and polysaccharides. Each tissue's ECM has a unique composition
what does thee extra cellular matrix contain?
The matrix may contain salts (bone) and structural molecules (collagen, elastin) help to hold the cells of the tissue together. Some extracellular matrix will be more fluid, some will be more solid.
Epithelial tissue description
The cells in epithelial tissues are tightly packed together with a small amount of extracellular matrix between cells.
connective tissue description
Connective tissues have only a relatively small number of cells but have a large amount of extracellular matrix between cells.
name the 7 different types of epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Stratified columnar epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
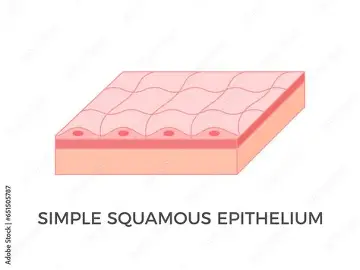
function of simple squamous epithelium
enable diffusion
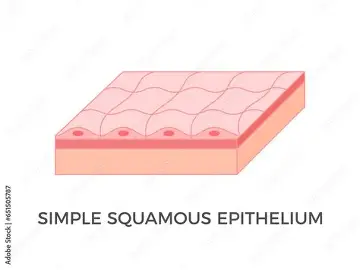
where is simple squamous epithelium found?
inner lining of blood vessels, air sacs of lungs, inner lining of heart
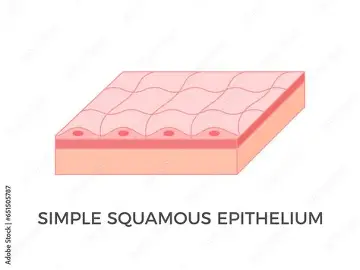
explain the Simple Squamous epithelium.
a single layer of squamous cells- the structure is specially adapted to primary function.
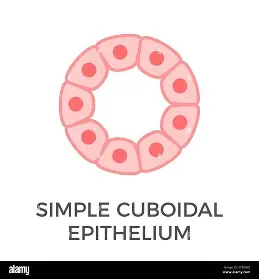
explain the Simple Cuboidal epithelium
A single layer of cube shaped cells These types of cells are found in the inner linings of ducts and tubules.
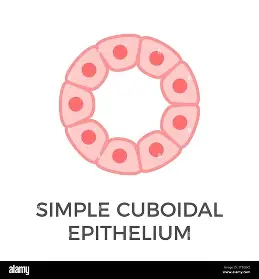
function of the Simple Cuboidal epithelium
absorbing and secreting materials into ducts or tubules
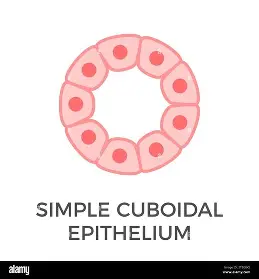
where is the Simple Cuboidal epithelium found?
kidney tubules
pancreatic ducts
salivary ducts.
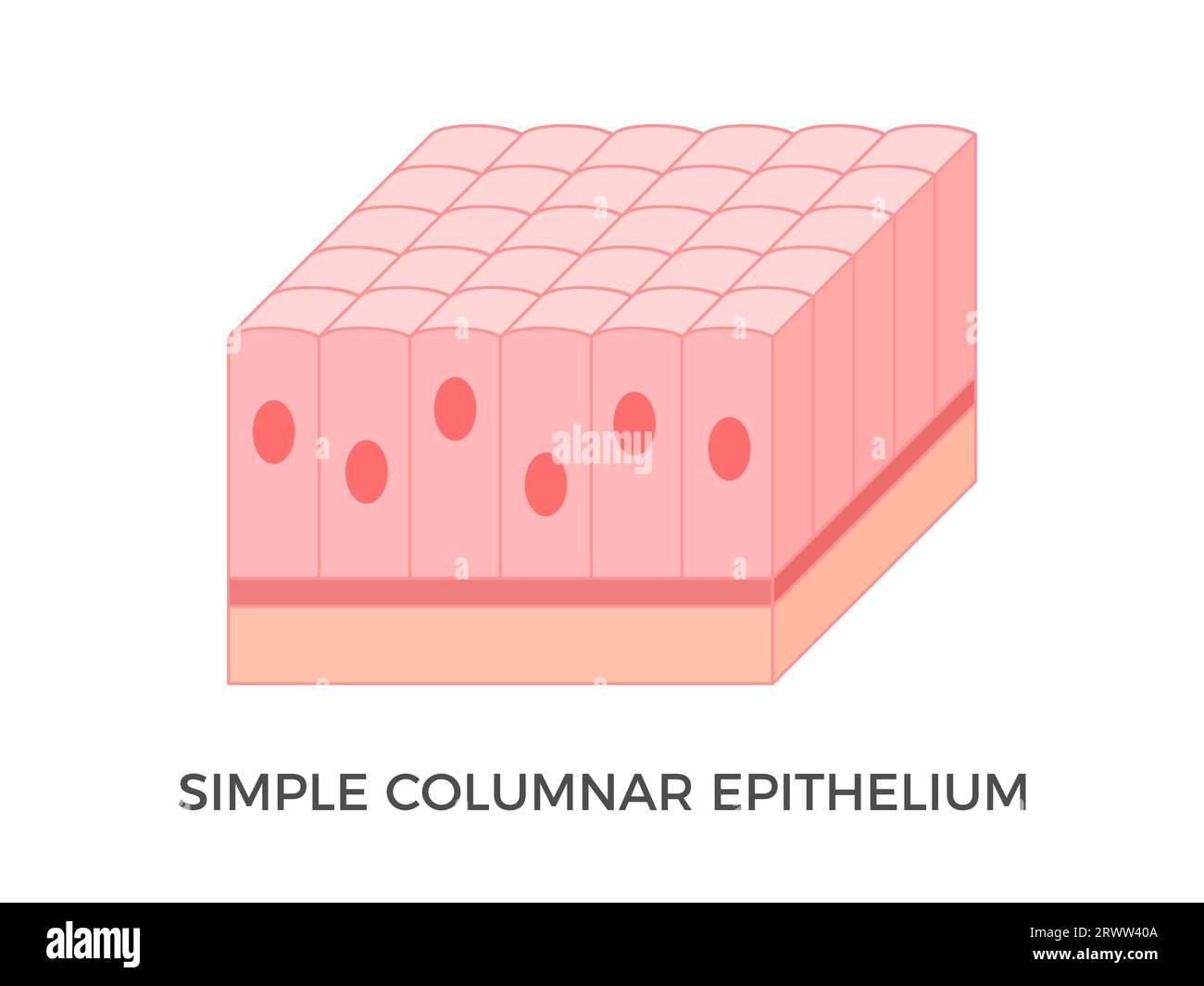
explain the Simple Columnar epithelium
Single layer of tall narrow cells with a nucleus near the base of the cell
These cells will often have specialised extensions (cilia or microvilli) to support their function
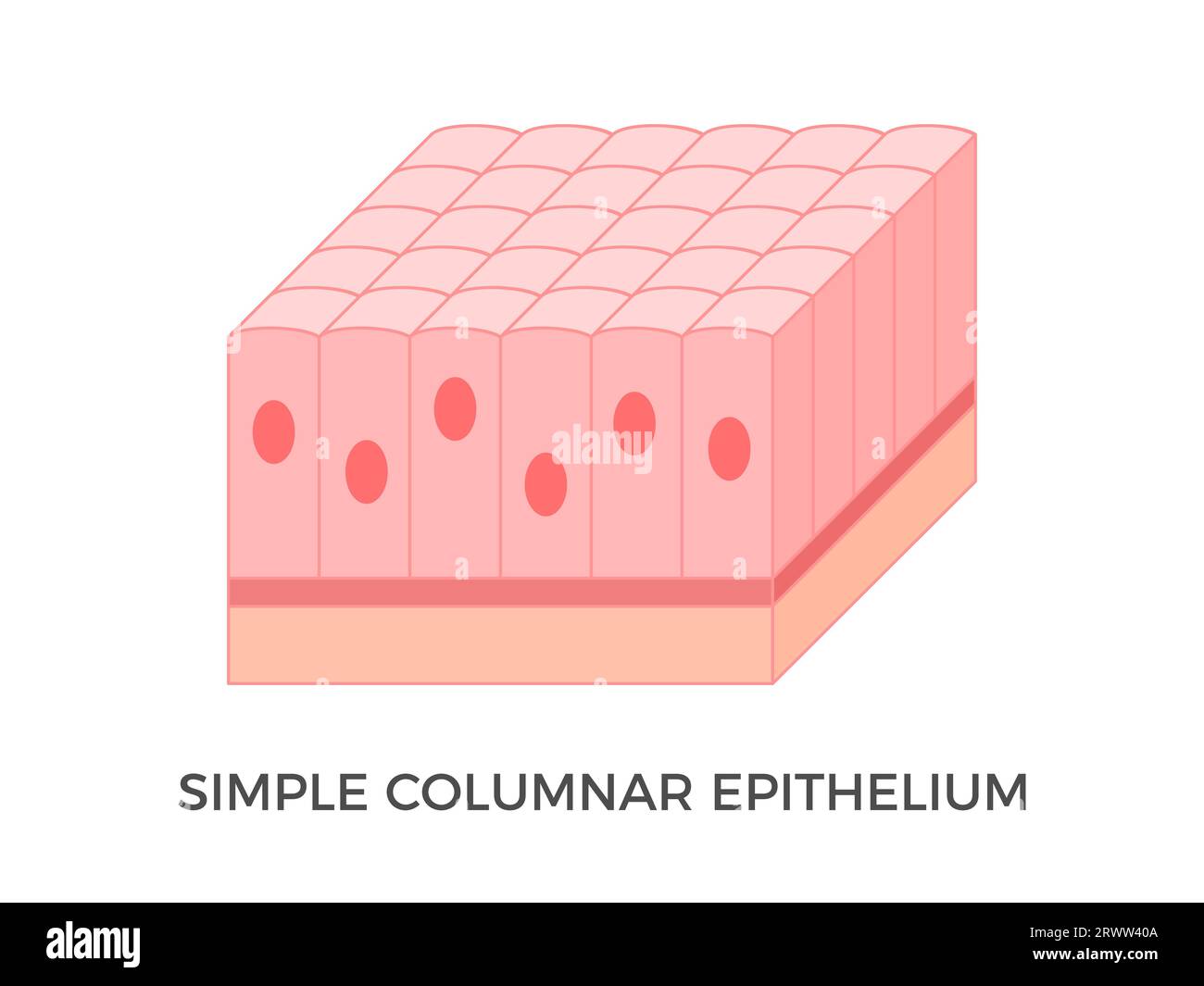
what is the function of the Simple Columnar epithelium?
adapted for secretory and absorptive activity:
it is specialised to function primarily in the gastrointestinal tract.(but can be found elsewhere)
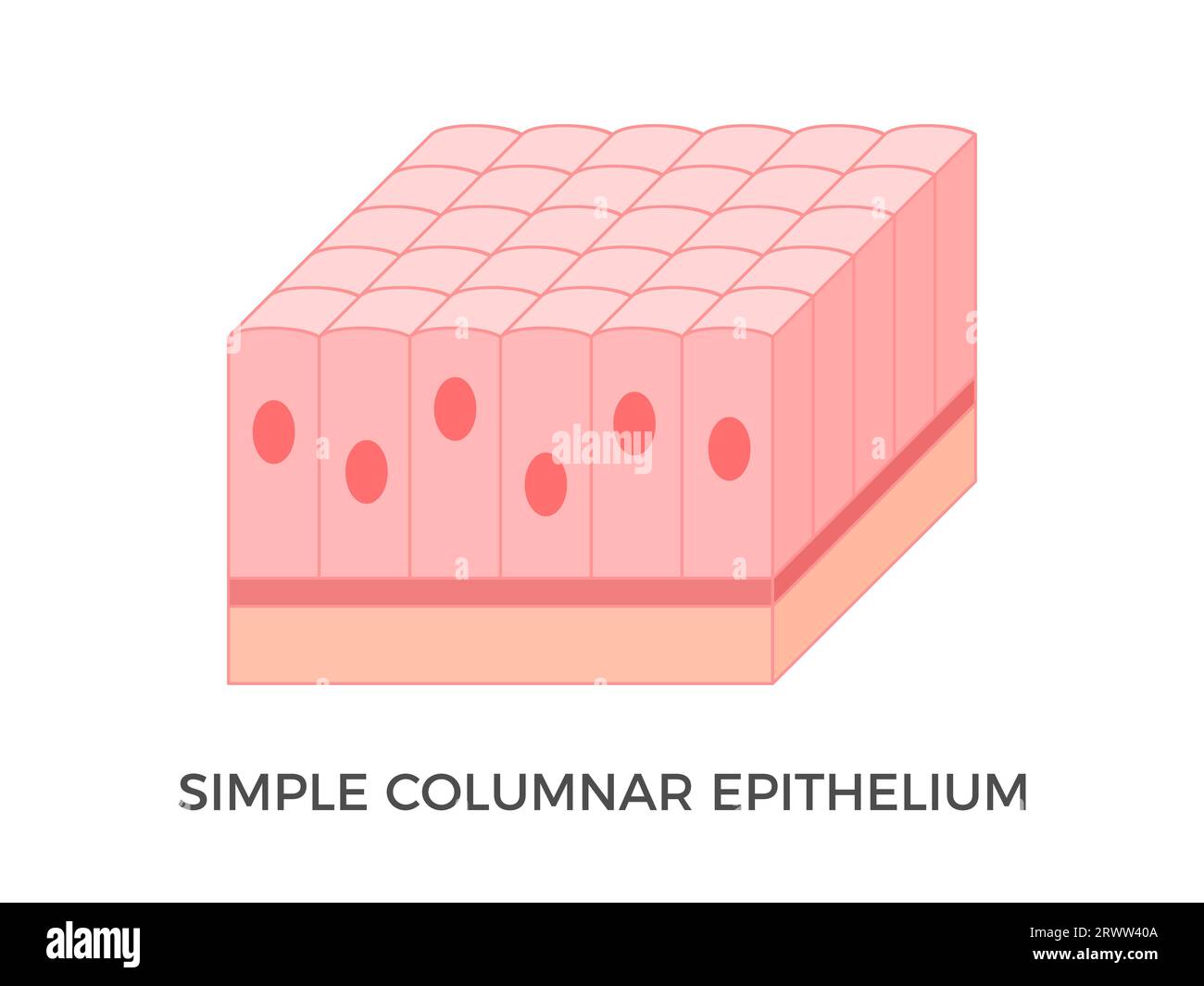
where is the Simple Columnar epithelium found?
stomach
duodenum
ileum
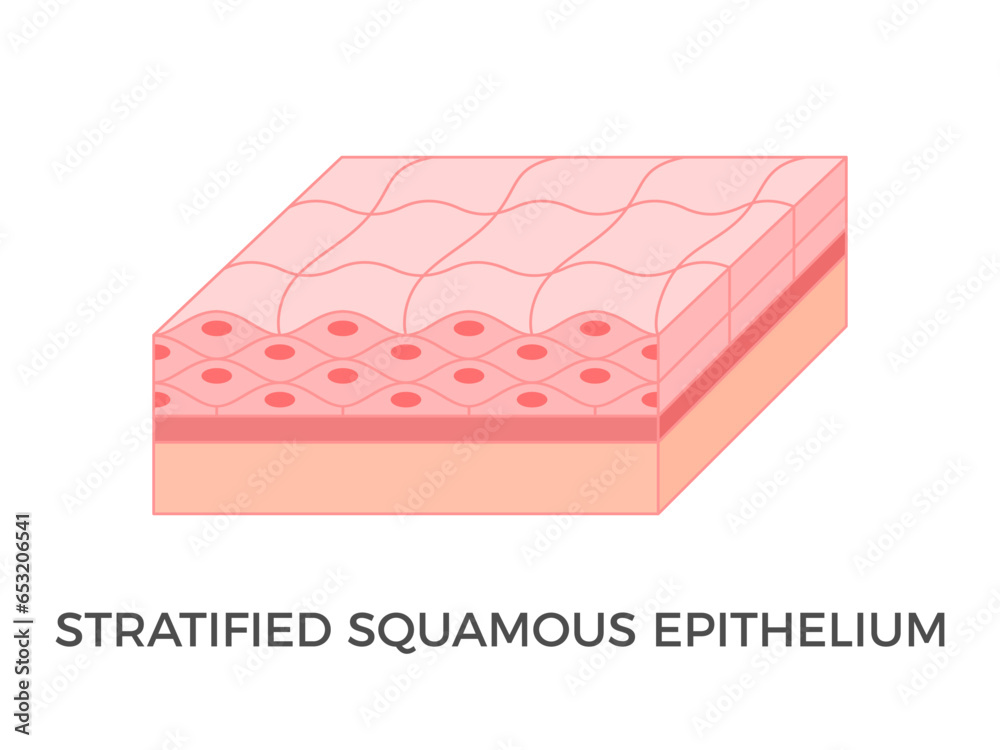
explain the Stratified squamous epithelium?
A thick tissue composed of multiple layers of squamous cells.
Human skin stratified epithelial cells have a special protein in them called keratin which keeps them dry and impermeable
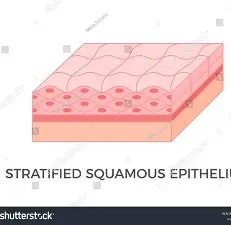
what is the function of the the Stratified squamous epithelium?
primarily to act as a protective physical barrier
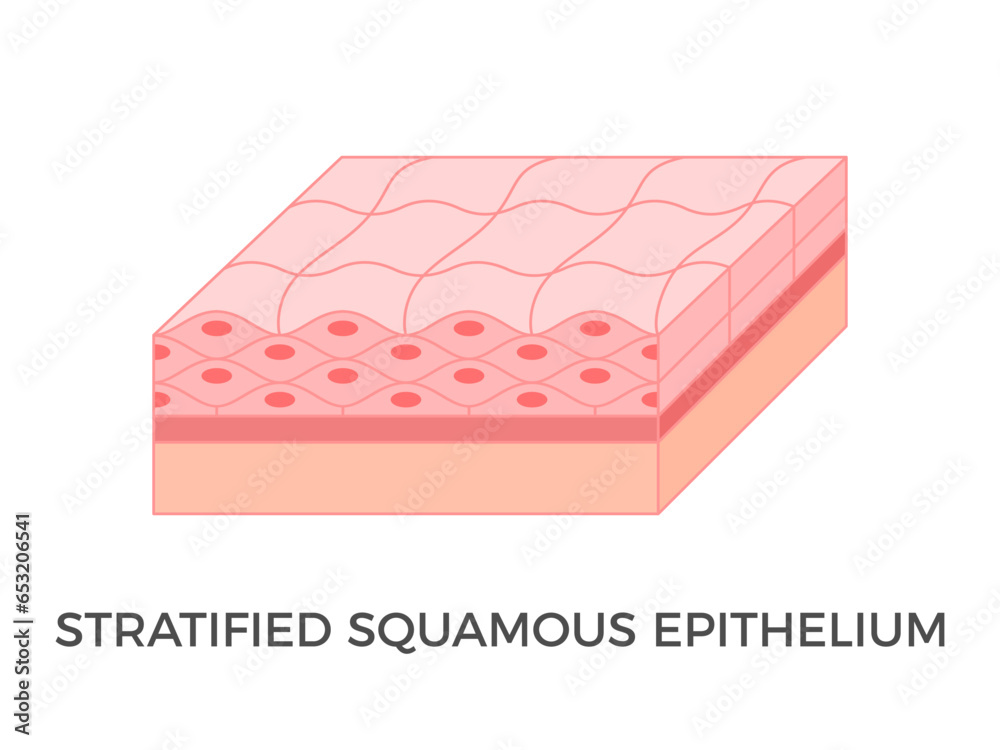
where is the Stratified squamous epithelium found?
skin inside mouth oesophagus

how many layer does the Stratified cuboidal epithelium have?
Only 2 layers the top most layer is cuboidal but the 2nd layer can often be a different cell type and different shape

function of the the Stratified cuboidal epithelium?
protection

where is the the Stratified cuboidal epithelium found?
inner linings of sweat glands
mammary glands
salivary glands

explain the Stratified columnar epithelium.
Tissue with multiple layers of columnar cells.

function of the Stratified columnar epithelium.
provides protection and supports secretion-secretion of waste materials inot the ducts and out of the body

where is the Stratified columnar epithelium found?
linings of pharynx
urethra
salivary gland ducts
mammary gland ducts
it is a rare type of epithelial tissue
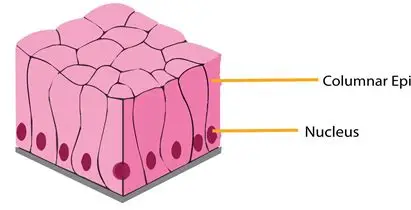
explain Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
A type of epithelium that seems to be stratified but is not: consists of a single layer of irregularly shaped and differently sized columnar cells.
In pseudostratified epithelium, the nuclei of adjacent cells appear at different levels and gives the appearance of stratification
- but all cells touch the bottom and therefore only one layer of cells exists
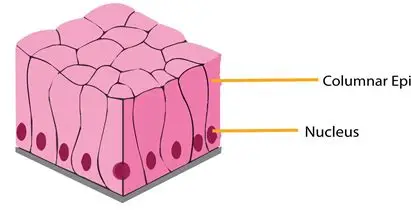
where is Pseudostratified columnar epithelium found?
inner lining of trachea near cells that secrete mucous
inner lining of the epididymis (tube that carries sperm)
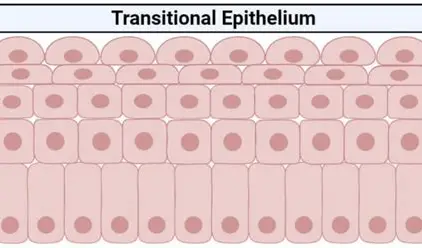
what does transitional epithelium consist of ?
Consists of multiple layers of cuboidal or columnar cells that can contract and expand.
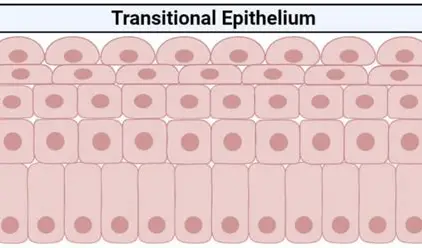
functions of transitional epithelium
distension- it can expand or contact to adapt to the level of stretching needed
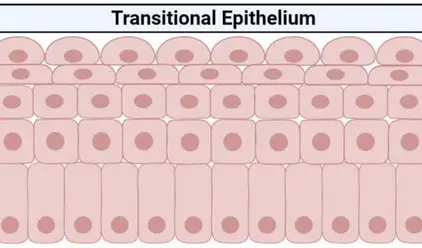
where is transitional epithelium found?
urinary bladder
ureters- tissues that need to stretch
what kind of cells are in the bladder?
it has several layers of large dome-shaped cells on its surface
what are the 4 major tissue types
1. epithelial tissue
2.connective tissue
3. muscular tissue
4. nerve/nervous tissue
what is a fibre?(general)
any long strand of material
what is a fibre? (anatomy)
any elongated, thread-like structure
what are the main types of fibre
collagen and elastic fibre
what us the most common tissue type in the body
connective tissue
what is the most widely distributed form of tissue in the body
connective tissue
what does connective tissue refer to
several different tissues of the body that function to Connect, Support, and Bind other tissues
how much extracellular matrix does connective tissues have?
a large amount within which cells and fibres are located
what do most connective tissues have?
cells
extracellular matrix
fibres
forms of connective tissue
solid
semi-solid
fluid
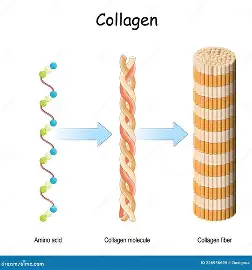
collagen fibres
contain Collagen (white in colour)-
a protein chain that provides the dual qualities of strength
& flexibility Collagen fibres are usually straight and thick.
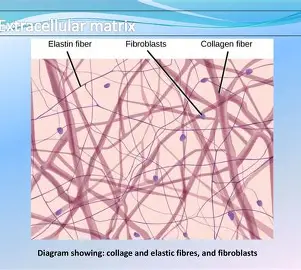
elastic fibres
contains Elastin, another protein chain (yellow in colour)
- that is not as strong as collagen
but is more flexible (elastic)
Elastic fibres are branched
loose fibrous connective tissue
1. Loose fibrous connective tissue contains many blood cells: fibroblast cells, fat cells, and white blood cells
2. Its Extracellular Matrix contains a lot of soft jelly-like ground substance with mainly 2 types of protein fibres running through it:
- Collagen
- Elastin
3. Found in lungs, arteries, muscle, and bladder and supports the expansion and contraction of these organs Loose connective tissue can also contain reticular fibres
dense fibrous connective tissue
1. Dense fibrous connective tissue contains Fibroblast cells
2. Its Extracellular Matrix has much less ground substance and is tightly packed with Collagen fibres
3. Found in Tendons and Ligaments where it forms the key part of these tissues
what does cartilage provide
structure
shape
protection in and around bones and other structures in the body
how is cartilage similar to bone
Cartilage has a large amount of ECM.
Cartilage is very similar to bone but is less hard and more flexible.
This is because its ECM does not have minerals (it is not mineralised like bone).
are there fibroblasts in cartilage
In cartilage, there are a small number of cells including Fibroblasts,
and specially differentiated fibroblasts called Chondroblasts and Chondrocytes
does cartilage vary
Cartilage varies according to the fibre types it contains
does cartilage have a direct blood supply
Cartilage tissue does not have a direct blood supply.
what are the 3 types of cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Elastic cartilage
what is the most common type of cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
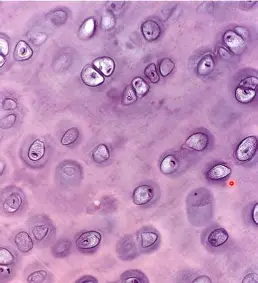
describe Hyaline Cartilage
most common, contains a small number of fine collagen fibres,
ECM is clear, cells are found scattered in small holes called lacunae.
Found in nose, ends of bones, ribs, rings around trachea.
describe Fibrocartilage
has an ECM containing a large amount of collagen fibres densely layered together.
Cells are smaller and often organised in rows inside lacunae.
Found in the discs between the vertebrae of the spine and in the knee joint
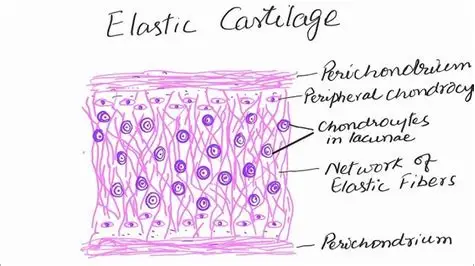
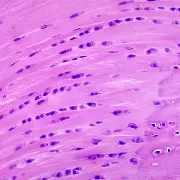
describe Elastic cartilage
has an ECM containing a large number of elastic fibres and is flexible.
Cells are found scattered in holes called lacunae.
Found in the outer ear and epiglottis.
what are the 2 types of bone
compact
spongy
what forms the skeletal system
Bones form the skeletal system that broadly connects the body together.
what consists of mineralised salts
bones ECM is very hard and consists of mineralised salts
deposited around collagen fibres with some elastin
cells in bones
osteoclasts
osteoblasts
osteocytes
what is blood made up of?
Blood consists of red blood cells and white blood cells and platelets
and a fluid extracellular matrix called plasma.
Blood is mostly plasma -fluid
what is blood responsible for?
Blood is responsible for transporting O2 and nutrients into the extracellular fluid
which surrounds the cells in tissues and enables removal of waste products including CO2
Blood also is involved in transport, immunity, fluid balance, endocrine gland communications and pH balance
what connects the cells of the body
Blood serves as the connector among all cells of the body.
Blood does not contain fibres
what is lymph
Lymph is the second form of fluid connective tissue.
what does lymph contain
It has a clear fluid ECM and contains several white blood cell types
lymph is non-blood fluid that drains into lymph vessels from the interstitial fluid around cells
Lymph is mostly fluid
what does lymph connect
Connects multiple organs and tissues:
Lymph transports absorbed fat from the intestine into the blood
and has an important role in transporting lymph for filtration at the lymph nodes.
Lymph does not contain fibres.
what are the 3 types of muscle
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
what are muscle cells known as
They are known as fibres because of their elongated shape.
shape of a muscle cell
They are like long tubes/pipes in Skeletal and Cardiac muscle.
These cells are structured specially to enable contraction
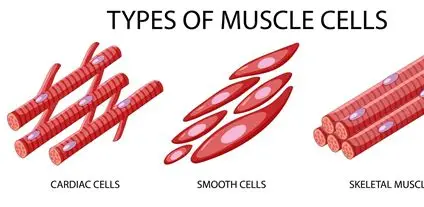
muscle tissue cells
In muscle tissue the cells have a unique structure and are known as muscle fibres
what is inside a muscle cell
Packed inside tightly inside the cell are long bundles of protein chains called myofibrils.
filaments
The protein chains that make up the myofibrils
what do the interactions between filaments enable?
enables muscle contraction & relaxation
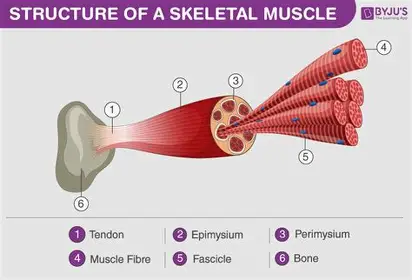
Skeletal muscle cells
1. Cylindrical and long (hence known as fibres)
2. They are densely packed with protein filaments.
3. They also have a striated appearance (light and dark bands) because of the way the filaments line up inside the cell.
4. ECM is fluid-based with structural proteins in and around the cells.
5. Function: movement under voluntary control
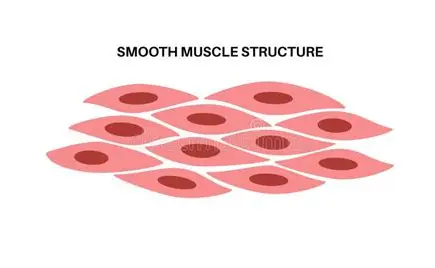
Smooth muscle
1. Smooth muscle cells are named this way as they have no striations.
2. Cell is less elongated and not tube/pipe-like in structure.
3. They contain a smaller number of protein filaments and do not have striations
4. ECM is fluid-based with structural proteins.
5. Found on the walls of the intestines and other organs.
6. Smooth muscle contracts more slowly but can stay contracted for longer- responsible for peristalsis, constriction of blood vessels, and other involuntary tissue movements.
Cardiac Muscle
1. Cardiac muscle: found only in the walls of the heart.
2. Cardiac cells are branched and appear fused together (they are not).
3. They are similar in structure to skeletal muscle cells in that they are elongated and tube-like (but have branches connecting them).
4. They are densely packed with protein filaments.
5. ECM is fluid-based with proteins in and around the cells.
6. Contraction & relaxation of this muscle is responsible for cardiac systole and diastole: it has features of both smooth and skeletal muscle: it has striations but is involuntary.
where is nervous tissue found?
brain
spinal cord
peripheral nerves
what is the ECM of nervous tissue composed of
The ECM of nervous tissue is composed of a fluid base substance along with many structural proteins providing support to the neurons and other cells.
3 key parts of a neuron
dendrites
cell bodies
axon
what are axons covered in?
myeline
what does the cell bodies contain?
nucleus
cytosol
organelles
what do cells support and service
neurons called neuroglia
neuroglia
10 times more of these cells than neurons in the human brain
types of neuroglia in the CNS
ependymal cells
oligodendrocytes
astrocytes
microglia
where is the cardiac muscle found
in the walls of the heart
shape of cardiac cells
Cardiac cells are branched and appear fused together but they are not
They are similar in structure to skeletal muscle cells in that they are elongated
and tube-like but have branches connecting them
what is responsible for cardiac systole and diastole?
Contraction & relaxation of cardiac muscle
it has features of both smooth and skeletal muscle
it has striations but is involuntary