Lecture 7: Reflexes
1/271
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
272 Terms
What is the integrating center of the nervous system?
The brain and spinal cord (CNS)
What are the two divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
Afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor)
What does the autonomic nervous system primarily regulate?
Internal environment and visceral functions
What is rheostasis?
It described the dynamic adjustment of physiological "set points" to adapt to changing internal or external conditions
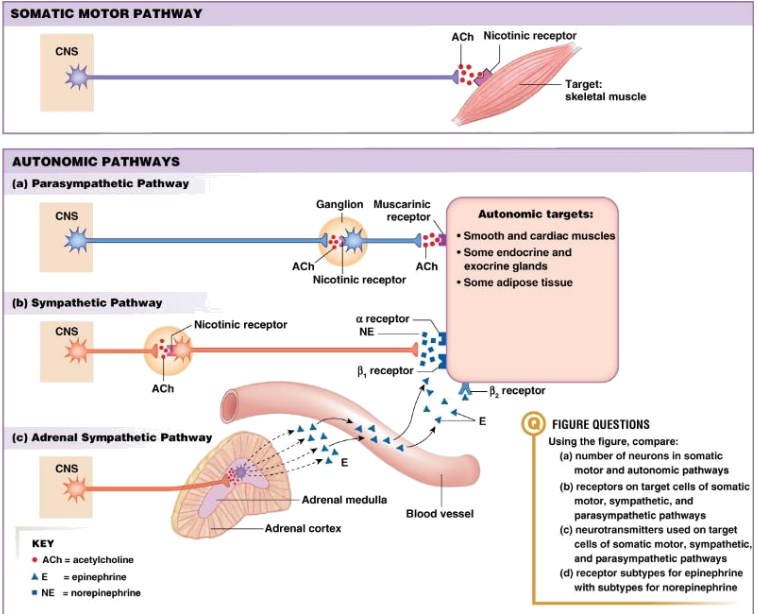
How many different neurons are in the efferent pathway of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
Two: preganglionic and postganglionic
Where are sympathetic preganglionic cell bodies located?
Intermediolateral gray column of thoracic and upper lumbar spinal cord
Where are parasympathetic preganglionic cell bodies located?
Brainstem nuclei and sacral spinal cord (S2–S4).
What organs are innervated by the ANS?
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, secretory epithelia
What is the general function of the sympathetic nervous system?
Prepares the body for fight-or-flight
What is the general function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Supports vegetative and resting functions
What nerve carries the largest number of visceral afferents?
Vagus nerve (CN X)
Where are visceral afferent cell bodies located?
Dorsal root ganglia or cranial nerve ganglia
What neurotransmitter is released by all preganglionic autonomic neurons?
Acetylcholine
What receptor type is on postganglionic parasympathetic targets?
Muscarinic receptors (G-protein coupled receptor that bind acetylcholine to regulate the PSNS)
What receptors are found at the neuromuscular junction?
Nicotinic N1 receptors
What cells of the adrenal medulla are modified postganglionic neurons?
Chromaffin cells
What hormones are released from the adrenal medulla?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
What is a mixed (neuroendocrine) reflex pathway?
A reflex using both neural and hormonal output
What is the stimulus of the myotatic reflex?
Muscle stretch
What is the function of the myotatic reflex?
Maintenance of muscle length
What fibers carry the afferent limb of the myotatic reflex?
A1 afferents
What reflex causes ipsilateral flexion and contralateral extension?
Flexion-crossed extension reflex
What is the main function of the baroreflex?
Blood pressure regulation
What receptors detect blood pressure?
Stretch receptors in the carotid sinus
Where is the baroreflex integrated?
Medullary cardiovascular centers
What type of reflex controls urination?
Autonomic (micturition reflex)
Which system allows voluntary control of the external urethral sphincter?
Somatic nervous system (pudendal nerve).
Somatic motor neurons innervate __________ muscle
skeletal
Autonomic motor neurons innervate __________, __________, and glands.
smooth muscle; cardiac muscle
The sympathetic division is also called the __________ division.
thoracolumbar
The parasympathetic division is also called the __________ division.
craniosacral
Postganglionic sympathetic neurons usually use __________ receptors on target cells.
adrenergic
Sweat glands are innervated by sympathetic neurons that release __________.
acetylcholine
Nicotinic N2 receptors are located on __________ neurons.
postganglionic autonomic (both symp and parasymp)
Acetylcholine is synthesized from __________ and __________.
acetyl-CoA; choline
Catecholamines are synthesized from the amino acid __________.
tyrosine
α₁ receptors cause __________ of blood vessels.
vasoconstriction
β₁ receptors increase __________.
heart rate
Baroreceptor afferents travel in cranial nerve __________.
IX (glossopharyngeal)
Reflex pathways can be __________, __________, or __________.
nervous; endocrine; mixed
During micturition, parasympathetic activity causes bladder __________.
contraction
In the flexion-crossed extension reflex, the contralateral limb undergoes __________.
extension
True or false: Somatic reflexes use two neurons in the efferent pathway
False: somatic reflexes use only one efferent neuron; autonomic reflexes use two
True or false: Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons are usually short.
True! Terminal ganglia are near or within target organs
True or false: Visceral pain is poorly localized
True
True or false: α₂ receptors are primarily presynaptic and inhibitory
True
True or false: The adrenal medulla only affects innervated tissues
False: Hormones released into blood affect non-innervated tissues.
True or false: Increased blood pressure decreases parasympathetic discharge.
False: Increased BP increases parasympathetic activity to lower heart rate
True or false: Myotatic reflex inhibitory effects are disynaptic
True
True or false: flexion-crossed extension reflex is monosynaptic.
False: it’s POLYsynaptic
True or false: baroreceptors respond to chemical changes in blood.
False: They respond to stretch (pressure)
True or false: Rheostasis allows regulated variables to change with demand.
True
What is a reflex?
A rapid, automatic, stereotyped response to a stimulus
What are the five components of a reflex arc?
• Receptor
• Afferent neuron
• Integrating center
• Efferent neuron
• Effector
What determines whether a reflex is somatic or autonomic?
The type of effector organ
What effectors are used in somatic reflexes?
Skeletal muscle
What effectors are used in autonomic reflexes?
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
What is reciprocal inhibition?
Inhibition of antagonistic muscles during contraction of agonists
What is the stimulus for the Golgi tendon reflex?
Increased muscle tension
What is the function of the Golgi tendon reflex?
Prevents excessive force and muscle damage
What type of sensory receptor is in the Golgi tendon organ?
Ib afferent endings
What is the difference between monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes?
Monosynaptic reflexes have one synapse; polysynaptic reflexes have multiple synapses
Which reflex uses muscle spindles as receptors?
Stretch (myotatic) reflex
What type of receptor detects muscle length?
Muscle spindle
What is gamma motor neuron function?
Adjusting muscle spindle sensitivity
What is central integration in reflexes?
Processing of sensory input in the spinal cord or brainstem
What reflex helps maintain posture?
Stretch (myotatic) reflex
A reflex is an __________ and __________ response to a stimulus.
automatic; stereotyped
The sensory limb of a reflex is called the __________ limb.
afferent
The motor limb of a reflex is called the __________ limb
efferent
The integrating center of spinal reflexes is the __________.
spinal cord
Golgi tendon organs monitor muscle __________
tension
Gamma motor neurons innervate __________ fibers of muscle spindles.
intrafusal
In reciprocal inhibition, the __________ muscle is inhibited
antagonist
Monosynaptic reflexes involve __________ synapse(s).
one
Polysynaptic reflexes involve __________ synapse(s).
multiple
Autonomic reflex effectors include __________ and glands
smooth muscle
True or false: Reflexes don’t require conscious processing
true
True or false: The Golgi tendon reflex causes muscle contraction when tension increases
False: it causes muscle relaxation to prevent damage from excessive tension
True or false: gamma motor neurons increase spindle sensitivity
True
True or false: Reciprocal inhibition enhances co-contraction of antagonistic muscles.
False: it inhibits antagonists to allow smooth agonist contraction
True or false: Monosynaptic reflexes are faster than polysynaptic reflexes.
True: they have fewer synapses
True or false: Muscle spindles detect changes in muscle force
False: Muscle spindles detect muscle length; Golgi tendon organs detect force.
True or false: Autonomic reflexes can regulate glandular secretion
True
True or false: The stretch reflex is important for maintaining upright posture
True
What is summation in reflex pathways?
The combined effect of multiple excitatory or inhibitory inputs on a neuron
What is temporal summation in reflexes?
Summation caused by repeated input from the same synapse over time
What is spatial summation in reflexes?
Summation caused by input from multiple presynaptic neurons
What is afterdischarge in a reflex?
Continued response after the stimulus ends due to interneuron circuits
What is divergence in a reflex pathway?
One afferent neuron synapsing with multiple interneurons or motor neurons
What is convergence in reflex pathways?
Multiple afferent neurons synapsing on a single interneuron or motor neuron
What is the withdrawal (flexor) reflex designed to protect against?
Painful or damaging stimuli
What type of receptor initiates the withdrawal reflex?
Nociceptor
What happens to extensor muscles on the stimulated side during withdrawal?
They are inhibited
What happens to flexor muscles on the stimulated side during withdrawal?
They contract
What is the role of interneurons in reflexes?
To process and distribute sensory information within the CNS
What type of reflex is the corneal blink reflex?
Brainstem reflex
What is the purpose of the pupillary light reflex?
Regulates the amount of light entering the eye
What spinal cord level mediates the patellar reflex?
L2–L4
What is the clinical purpose of reflex testing?
To assess integrity of sensory and motor pathways