The life cycle of a star: Space physics: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
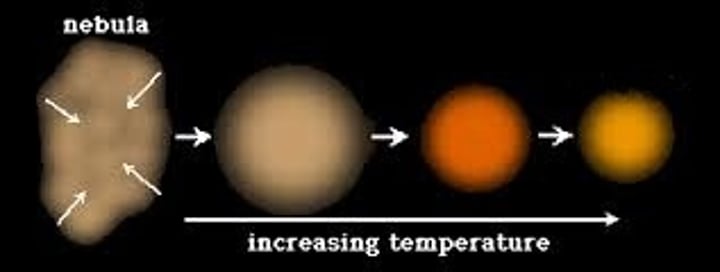
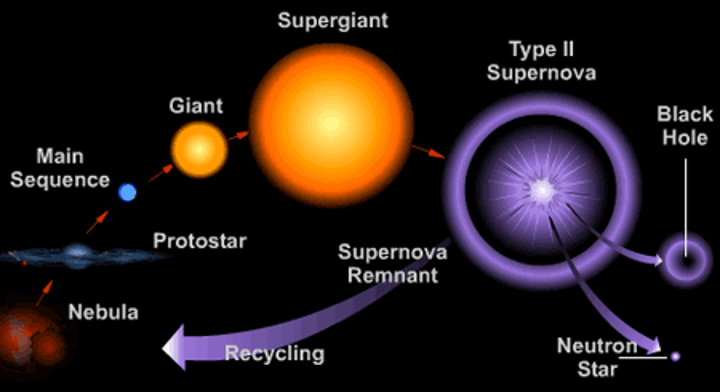
Nebula
A large cloud of dust and gas in space

Protostar
Formed from the core of a nebula after it collapses under its own gravity
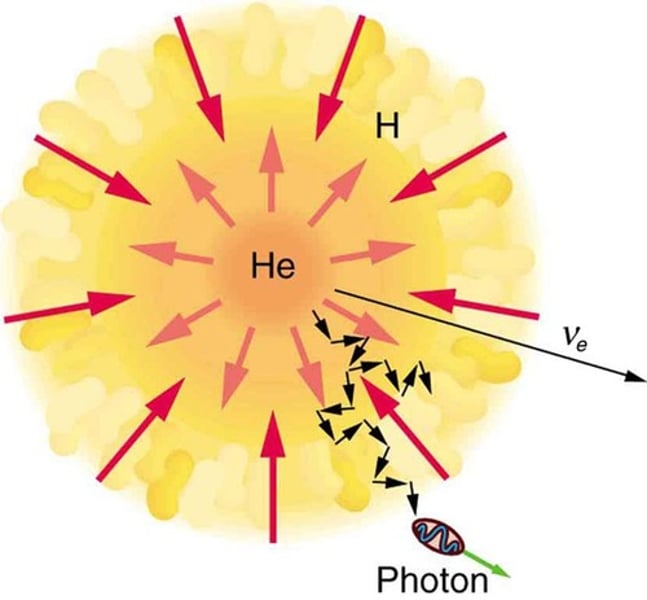
Nuclear fusion (stars)
Begins when the core of a protostar becomes hot and dense enough for fusion to start
Main sequence star
A star that is in equilibrium and remains in this phase for most of its lifetime
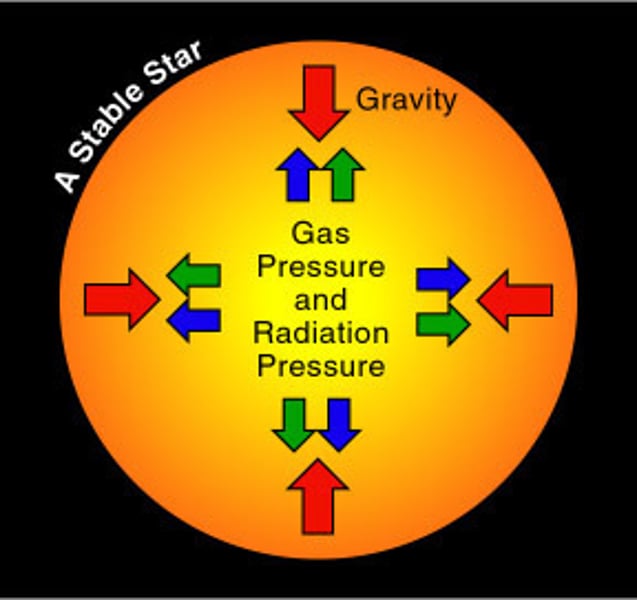
Equilibrium (stars)
When the gravitational collapse of a star is balanced by the expansion due to the energy released by fusion
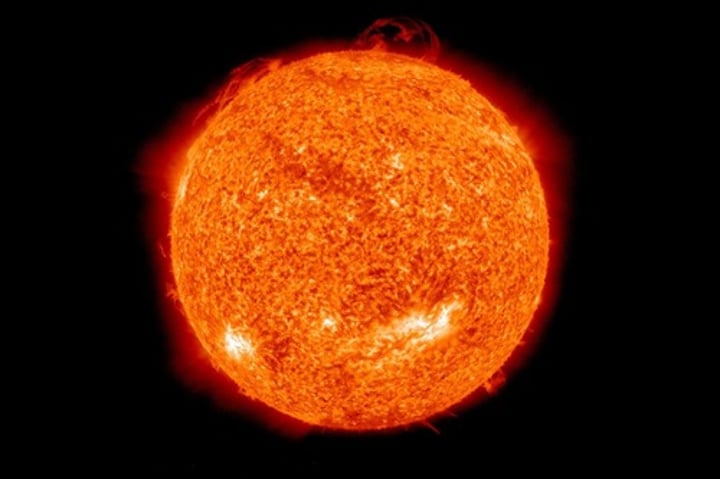
The Sun
A relatively small, main sequence star that is roughly in the middle of its life cycle
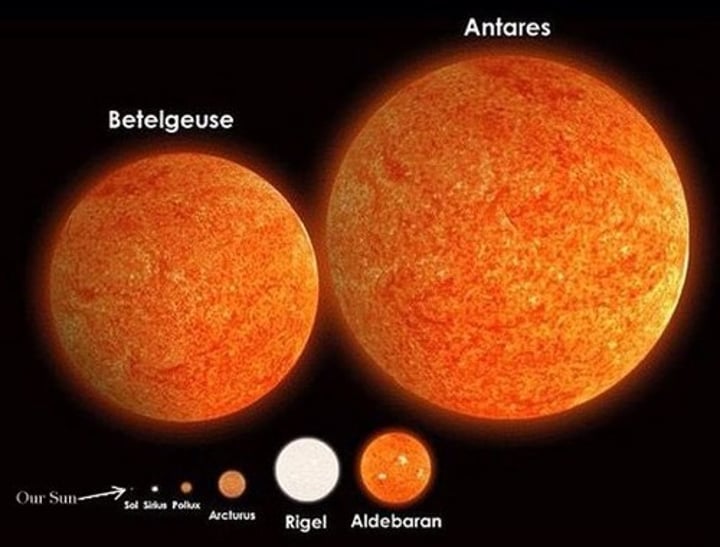
Red giant
Formed when a star about the same size as the Sun runs out of hydrogen so larger nuclei form and the star expands

White dwarf
Formed when the nuclear reactions in a red giant stop and it starts to contract due to its own pull of gravity

Black dwarf
Formed when a white dwarf cools until it no longer emits any radiation

Red super giant
Formed when star much larger than the Sun runs out of hydrogen so larger nuclei form and the star expands
Supernova
Occurs when a red super giant expands until it explodes, throwing hot gas into space

Neutron star or black hole
Left behind after a supernova and depends on the mass of the star at the start of its life
Forming elements in stars
All the naturally occurring elements are produced by fusion reactions in stars
How the lighter elements (up to iron) form
Formed in main sequence stars when the hydrogen runs out, so helium nuclei start to fuse etc
How the heavier elements (heavier than iron) form
Formed when a supernova explodes and are thrown out into the universe