Week 9/10 Asynchronous Work: Immune, Integumentary, & Musculoskeletal
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
HIV
A virus that attacks and destroys the human immune system
-causes immune dysfunction, cant fight pathogens
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA):
-autoimmune disease which effects the synovial joints and erodes bone and cartilage
-unknown etiology
Congenital Hypothyroidism
thyroid hormone deficiency present at birth
Anaphylaxis
-hyper reaction
-A severe and life-threatening allergic reaction that causes extreme inflammation
Non-specific immune response:
-none specific, innate
-inflammation (cytokines, sound alarm)
-faster (24 hrs)
-physical barriers
-chemical barriers
-Phagocytosis, macrophages
Specific immune response:
-Active immunity, memory
-B and T cells
-antibodies mount the immune response against pathogens
-takes longer
What is IgA?
-local immunity passed from breast milk to infant
What is IgG?
-responsible for Rh reactions
What is IgE?
-responsible for allergic response and parasites
How long do antibodies take to react to specific antigens?
3 days
Risk factors for HIV:
-perinatal exposure (delivery and breastmilk)
-blood product exposure
-assault survivor
-STI w/o knowing
Nursing considerations for HIV:
-treat to reduce viral load
-monitor CDC, WBC, liver function test
-optimize nutrition
-prevent infection
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE):
-auto immune, inflammation
-rash and arthritis
-pain, altered image
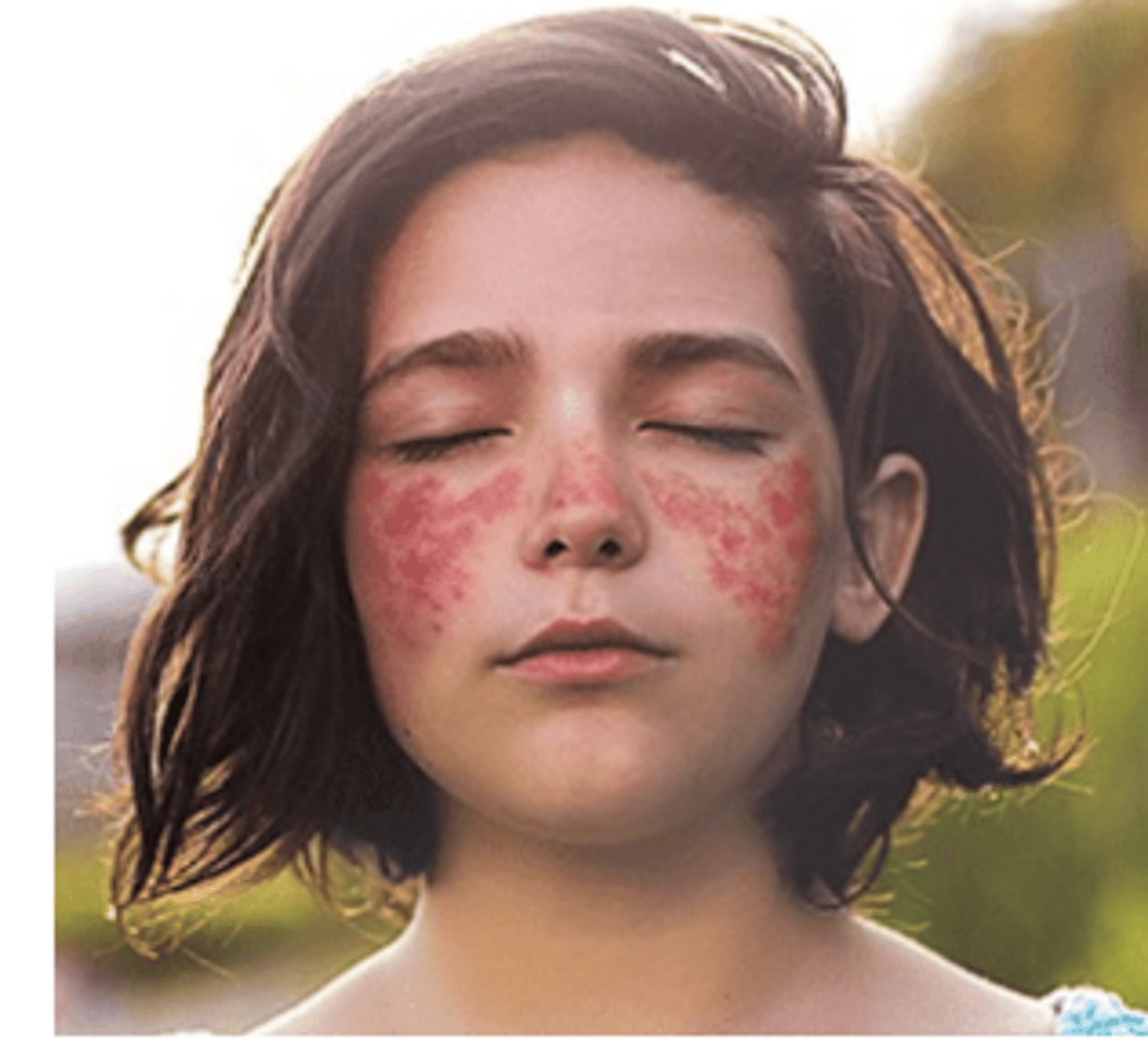

Nursing considerations for SLE:
-comfort patients
-administer medication
-emotional support
-avoid sun/UV light
S/s of JIA:
-swelling in at least 1 joint for longer than 6 weeks AND
-2 of the following: decreased ROM, pain, warmth over joints
Medications to treat JIA:
NSAID and methotrexate
What is methotrexate:
stops the inflammatory process that causes damage in the joints and body tissues
Nursing considerations for JIA:
-educate on continuing to be mobile
-medications are immune suppressants, educate on side effects of this
-manage pain
S/s of Anaphylaxis
-rash
-hives, swelling
-redness, flushing
-itching
-wheal and flare (IgE mediated reaction)
-bronchospasm
-severe: narrowing airways, stridor
Atopic triangle:
-food allergies
-asthma
-eczema
Nursing considerations for anaphlaxis:
-administer epinephrine
-educate on epipen
-educate on hydration importance for eczema
S/s of Congenital Hypothyroidism
-poor or slow growth
-weak or floppy muscle tone
-swelling around the eyes
-difficulty feeding
Club foot
A birth defect in which the foot is twisted out of shape or position
-3 categories
-needs to be corrected before child starts to walk
Fracture
break or disruption in the bones
-excessive or traumatic force exceeds strength of the bone
Osteogenesis imperfecta
brittle bone disease
-faulty bone mineralization resulting in frequent fractures and bone deformities
Osteomyelitis
bacterial infection of the bone that causes abscesses on bone
-can occur due to open fracture
-can occur due to blood source
Immobilization effect on muscular system:
-decreased muscle strength and endurance
-atrophy
-contractures and loss of joint mobility
Immobilization effect on skeletal system:
bone demineralization
Immobilization effect on cardiovascular syetem:
-altered distribution of blood volume
-increased risk of DVT due to increased clotting
-dependent edema
Immobilization effect on respiratory system:
-decreased need for oxygen
-loss of respiratory muscle strength
Immobilization effect on gastrointestinal system:
-distention caused by poor abdominal muscle tone
-difficulty feeding in prone position
-peristalsis slowed, constipation/anorexia
Immobilization effect on metabolism:
-decreased metabolic rate
-negative nitrogen balance
-hypercalcemia (due to demineralization)
Immobilization effect on integumentary system:
-decreased circulation and pressure leading to decreased healing capacity
Immobilization effect on urinary system:
-difficulty voiding in supine position
-urinary retention
Immobilization effect on psychologic:
-altered perception of self and environment
-dependence on others creates frustration, helplessness, anxiety
-social isolation creates anger, regression
Nursing considerations for immobility:
-assess skin color, capillary refill time, temp, sensation, movement of digits, pulse
-ensure padding
-assess for skin redness or breakdown
What is talipes equinovarus?
toes faing inward and lower than heel
-MOST COMMON
-treated: weekly foot stretching prior to new cast

S/s of osteogenesis imperfecta:
-multiple bone fractures
-blue sclera
-early heading loss
-bowed legs and arms
-kyphosis/scoliosis
Nursing considerations for osteogenesis imperfecta:
-supportive care and rehabilitation to prevent further contractures or deformities
-medications to increase bone density
What is achondroplasia?
Dwarfism
-obesity, hydrocephalus, skeletal issues, bowed legs
Nursing considerations for soft tissue injuries:
RICE
-rest, ice (30 mins max), compression, elevate
ICES
-immobilize, compression, elevation, support
How common are fractures in infants? Children?
common in children
-rare in infants (under 1), warrants investigation
Complete fracture
bone fragments are seperated
Incomplete fracture
bone fragments are still attached
Closed or simple fracture
fracture occurs without a break in the skin
Open or compound fracture
fractured bone protrudes through the skin
S/s of fractures:
-generalized swelling
-pain or tenderness
-deformity
-diminished functional use
-may have bruising or muscular rigidity
-edema
-warmth or redness
6 P's assessment of fracture:
-pain and point of tenderness
-pallor
-pulselessness (diminished, late sign)
-Paresthesia (numbness, late sign)
-Paralysis
-pressure
Compartment syndrome:
medical emergency
-first 48 hrs of fracture
-bleeding and swelling into tissues, arm expands, tissue cant keep up
S/s of compartment syndrome:
-pain, pallor
-poikilothermia (coolness)
-paresthesia (numb)
-pulselessness
-paralysis (late finding)
-cast comes off/fasiotomy
What is traction for fracture?
Pulling force to part of body to position and hold bone fragments in correct alignment
-immobilizes fracture site, reduces muscle spasms
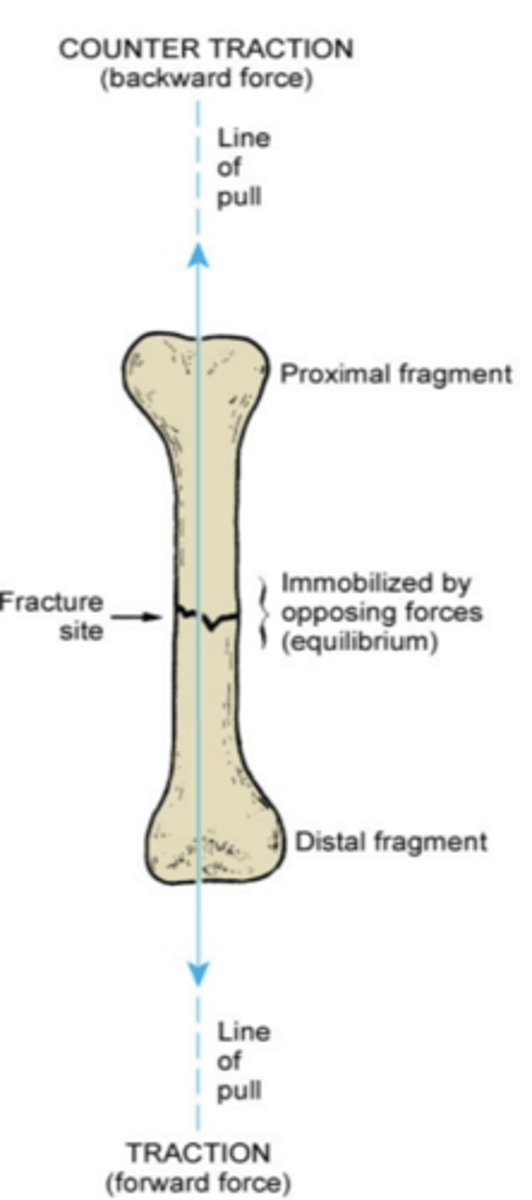
What is distraction of fracture:
-process of separating opposing bone to encourage regeneration of new bone in created space
-used when limbs are unequal in length and new bone is needed to elongate shorter limb
S/s of osteomyelitis:
-2 to 7 days of pain
-warmth, fever
-tenderness
-decreased ROM in affected limb
-marked (increased) WBC
-irritability, lethargy
Nursing considerations for Osetomyletis:
-administer IV antibiotics
-place PICC line (due to length of treatment)
-teach family about PICC line care
-promote bed rest and immobility of limb (watch for DCT)
Name two goals for fracture management or JIA?
preserve function
preventing deformity
relieve symptoms