Unit 1 Quiz 1 - Lessons 1-4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:39 PM on 2/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
1
New cards
Father of Psychology said…
“The unconscious is the true physical reality”
2
New cards
Three Structures of personality
* Id (devil)
* Ego (self)
* Superego (angel)
* Ego (self)
* Superego (angel)
3
New cards
Id
* Totally unconscious: has no contact with reality.
* Consists of instincts: our reservoir of psychic energy.
* Has no morality.
* Consists of instincts: our reservoir of psychic energy.
* Has no morality.
4
New cards
Ego
* Deals with the demands of reality.
* Called the “executive branch” of personality: uses reasoning to make decisions
* Has no morality.
* Called the “executive branch” of personality: uses reasoning to make decisions
* Has no morality.
5
New cards
Superego
* The moral branch of personality.
* Takes into account the values and morals of society which are learned from one's parents and others.
* The superego's function is to control the id's impulses
* Takes into account the values and morals of society which are learned from one's parents and others.
* The superego's function is to control the id's impulses
6
New cards
**5 Stages of Psychosocial Development- Frued**
* Oral Stage (birth- 18 months)
* Anal Stage (18 months- 3 years)
* Phallic Stage (3-6 years)
* Latent Stage (6 years - puberty)
* Genital Stage (puberty on)
* Anal Stage (18 months- 3 years)
* Phallic Stage (3-6 years)
* Latent Stage (6 years - puberty)
* Genital Stage (puberty on)
7
New cards
Oral Stage
* Pleasure centers around the mouth.
* Chewing, sucking, and biting are sources of pleasure.
* Chewing, sucking, and biting are sources of pleasure.
8
New cards
Anal Stage
* Pleasure centers around the anus.
* Elimination functions are sources of pleasure.
* Elimination functions are sources of pleasure.
9
New cards
Phallic Stage
* Pleasure focuses on the genitals.
* Self- manipulation is a source of pleasure.
* Self- manipulation is a source of pleasure.
10
New cards
Latent Stage
* Child represses all interest in sexuality.
* Child develops social and intellectual skills.
* Energy is channeled into emotionally safe areas.
* Child forgets the highly stressful conflicts of the phallic stage.
* Child develops social and intellectual skills.
* Energy is channeled into emotionally safe areas.
* Child forgets the highly stressful conflicts of the phallic stage.
11
New cards
Genital Stage
* This is a time of sexual reawakening.
* The source of sexual pleasure comes from outside the family.
* The source of sexual pleasure comes from outside the family.
12
New cards
Oedipus Complex
Young child’s development of an intense desire to replace the same-sex parent and enjoy the affection of the opposite-sex parent.
13
New cards
Fixation
When the individual remains locked in an earlier developmental stage because needs are under or over-gratified.
14
New cards
Oral Fixation
Weaning too early = smoking, drinking, chewing gum etc.
15
New cards
Anal Fixation
Too strict with potty training= Excessively neat and orderly.
16
New cards
Phallic Fixation
Punishing masturbation= Seeking pornography.
17
New cards
Genital Fixation
Smothering children with too much affection= difficulty with romantic relationships.
18
New cards
Chronological Age
Number of years lapsed since birth.
19
New cards
Biological Age
Individual’s age in terms of biological health. Knowing the functional capacities of a person’s vital organ system.
20
New cards
Mental Age
Individual’s ability to solve problems on a standardized instrument compared with others of the same chronological age.
21
New cards
Psychological Age
Individual’s adaptive capacities compared with those of other individuals of the same chronological age
22
New cards
Social Age
Social roles and expectations related to a person’s age.
23
New cards
Erik Erikson
* Trust vs. Mistrust
* Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
* Initiative vs. Guilt
* Industry vs. Inferiority
* Identity vs. Identity Confusion
* Intimacy vs. Isolation
* Generativity vs. Stagnation
* Integrity vs. Despair
* Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
* Initiative vs. Guilt
* Industry vs. Inferiority
* Identity vs. Identity Confusion
* Intimacy vs. Isolation
* Generativity vs. Stagnation
* Integrity vs. Despair
24
New cards
Trust vs. Mistrust (1st year)
• Physical comfort and minimal fear about the future are both required for a sense of trust.
• Trust in infancy sets the stage for a lifelong expectation that the world will be a good and pleasant place.
• Trust in infancy sets the stage for a lifelong expectation that the world will be a good and pleasant place.
25
New cards
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (2nd year)
• Infants begin to discover that their behaviour is their own.
• They start to assert their sense of independence or autonomy and realize their will.
•Restraining and punishing leads to a sense of shame and doubt.
• They start to assert their sense of independence or autonomy and realize their will.
•Restraining and punishing leads to a sense of shame and doubt.
26
New cards
Initiative vs. Guilt (Preschool years)
• As preschool children encounter a widening social world, they are
challenged more, and purposeful behaviour is needed to cope with these challenges.
• Children are asked to assume responsibility for their bodies,
behaviour, toys, and pets.
• Guilt may arise if the child is irresponsible and made to feel anxious.
challenged more, and purposeful behaviour is needed to cope with these challenges.
• Children are asked to assume responsibility for their bodies,
behaviour, toys, and pets.
• Guilt may arise if the child is irresponsible and made to feel anxious.
27
New cards
Industry vs. Inferiority (Elementary years)
• Children direct their energy towards mastering knowledge and intellectual skills.
• The danger during this time is the development of a sense of
inferiority – feeling incompetent and unproductive.
• Teachers have special responsibility for children’s development of industry.
• The danger during this time is the development of a sense of
inferiority – feeling incompetent and unproductive.
• Teachers have special responsibility for children’s development of industry.
28
New cards
Identity vs. Identity Confusion (Adolescence)
• Individuals are faced with finding out who they are, what they are all
about, and where they are going in life.
• Confronted with many new roles and adult status.
• If the adolescent explores roles in a healthy manner and arrives at a
positive path in life, then positive identity will be achieved.
• If an identity is pushed on the adolescent by parents, if the adolescent
does not adequately explore many roles then identity confusion
reigns.
about, and where they are going in life.
• Confronted with many new roles and adult status.
• If the adolescent explores roles in a healthy manner and arrives at a
positive path in life, then positive identity will be achieved.
• If an identity is pushed on the adolescent by parents, if the adolescent
does not adequately explore many roles then identity confusion
reigns.
29
New cards
Intimacy vs. Isolation (Early Adulthood)
• Task of forming intimate relationships with others.
• Intimacy is defined as finding oneself yet losing oneself in another.
• Achieved through the formation of healthy friendships and an intimate relationship with another individual.
• Isolation results from failure to achieve the above.
• Intimacy is defined as finding oneself yet losing oneself in another.
• Achieved through the formation of healthy friendships and an intimate relationship with another individual.
• Isolation results from failure to achieve the above.
30
New cards
Generativity vs. Stagnation (Middle Adulthood)
• A chief concern is to assist the younger generation in developing and
leading useful lives (generativity).
• The feeling of having done nothing to help the next generation is
(stagnation.)
leading useful lives (generativity).
• The feeling of having done nothing to help the next generation is
(stagnation.)
31
New cards
Integrity vs. Despair (Late Adulthood)
• This involves reflecting on the past and either piecing together a
positive review or concluding that one’s life has been well spent.
• Integrity is achieved through reflecting on a past deemed worthwhile.
• If the older adult resolved many of the earlier stages of negativity,
looking back will lead to doubt or gloom (despair).
positive review or concluding that one’s life has been well spent.
• Integrity is achieved through reflecting on a past deemed worthwhile.
• If the older adult resolved many of the earlier stages of negativity,
looking back will lead to doubt or gloom (despair).
32
New cards
Jean Piaget said…
“The goal of education is to create men and women who are capable of doing new things”
33
New cards
Piaget’s Theory
* Children actively construct their understanding of the world.
* Children progress through four stages of cognitive development.
* Children progress through four stages of cognitive development.
34
New cards
Assimilation
* Incorporating new information into their existing knowledge.
35
New cards
Accommodation
Adapting one’s existing knowledge to new information.
36
New cards
Piaget Stages
* Sensorimotor Stage (0 – 2 years)
* Preoperational Stage (2 – 7 years)
* Concrete Operational Stage (7 – 11 years)
* Formal Operational Stage (11 and up)
* Preoperational Stage (2 – 7 years)
* Concrete Operational Stage (7 – 11 years)
* Formal Operational Stage (11 and up)
37
New cards
**Sensorimotor Stage (0 – 2 years)**
* Infants construct an understanding of the world by coordinating sensory experiences with physical motor actions.
* Brain development through the 5 senses.
* Working memory is developed.
* Egocentric
* Brain development through the 5 senses.
* Working memory is developed.
* Egocentric
38
New cards
Object permanence
* Understanding that items and people still exist even when you can't see or hear them.
39
New cards
**Preoperational Stage (2 – 7 years)**
* Children begin to represent the world with words, images, and drawings.
* Intuitive thoughts and fantasies.
* Age 4: The age of questioning. (Intuitive thinking)
* Intuitive thoughts and fantasies.
* Age 4: The age of questioning. (Intuitive thinking)
40
New cards
**Concrete Operational Stage (7 – 11 years)**
* Children can perform mental operations.
* Logical reasoning replaces intuitive thought, as long as reasoning can be applied to concrete examples.
* Ability to empathize.
* Logical reasoning replaces intuitive thought, as long as reasoning can be applied to concrete examples.
* Ability to empathize.
41
New cards
Inductive reasoning
* A method of drawing conclusions by going from the specific to the general.
42
New cards
Concept of conservation
* Ability that allows a person to determine that a certain quantity will remain the same despite adjustment of the container, shape, or apparent size.
43
New cards
**Formal Operational Stage (12 and up)**
* Individuals move beyond concrete experiences and think in abstract, more logical terms.
* Problem-solving and hypothesizing.
* Understand and develop identity.
* Morality+ compassion.
* Philosophize.
* Problem-solving and hypothesizing.
* Understand and develop identity.
* Morality+ compassion.
* Philosophize.
44
New cards
Deductive reasoning
* A logical approach where you progress from general ideas to specific conclusions.
45
New cards
**Erogenous zone**
Parts of the body that have especially strong pleasure-giving qualities at a particular stage of development.
46
New cards
Jung
Psyche: the ego, the personal unconscious, and the collective unconscious.
Archetypes: The nature of an archetype is such that we recognize it instantly and are able to attach to it a specific emotional meaning. (the wise old man, the hero etc.)
The persona: The self that we present to the world.
Animus: Real man
Anima: Woman, virgin, seductress.
Archetypes: The nature of an archetype is such that we recognize it instantly and are able to attach to it a specific emotional meaning. (the wise old man, the hero etc.)
The persona: The self that we present to the world.
Animus: Real man
Anima: Woman, virgin, seductress.
47
New cards
Adler
Every person has a sense of inferiority.
From childhood, people work to try to overcome this inferiority.
This drive was the motivating force behind behaviours, emotions, and thoughts.
From childhood, people work to try to overcome this inferiority.
This drive was the motivating force behind behaviours, emotions, and thoughts.
48
New cards
Anna Freud
Made significant contributions to the fields of child psychoanalysis and child development.
Concerned with the ego, its conflicts with reality, and the defense mechanisms.
Concerned with the ego, its conflicts with reality, and the defense mechanisms.
49
New cards
Karen Horney
Criticized Freud’s argument on the grounds of gender and cultural differences.
**Neurosis.** 10 neurotic trends, which she believed resulted from parental indifference, basic hostility, and basic anxiety leads the child to develop coping strategies and as the individual matures neurosis may develop.
Individuals could benefit from self-analysis.
**Neurosis.** 10 neurotic trends, which she believed resulted from parental indifference, basic hostility, and basic anxiety leads the child to develop coping strategies and as the individual matures neurosis may develop.
Individuals could benefit from self-analysis.
50
New cards
Erich Fromm
Human nature is influenced by dysfunctional social patterns i.e poverty, war etc.
Feminism.
Men had to prove themselves in the world and thus were driven to acquire wealth and power at the expense of people and the environment. Women, on the other hand, feared being abandoned and submitted to male power.
Considered the influence of racism, sexism, and economic inequalities on personality growth.
Feminism.
Men had to prove themselves in the world and thus were driven to acquire wealth and power at the expense of people and the environment. Women, on the other hand, feared being abandoned and submitted to male power.
Considered the influence of racism, sexism, and economic inequalities on personality growth.
51
New cards
Descriptive research
Has the purpose of observing and recording behavior
52
New cards
Laboratory research
Controlled setting in which many of the complex factors of the 'real world' are removed
53
New cards
Naturalist observation
Observing behavior in the real world settings
54
New cards
Standardized tests
Test with uniform procedures for administration and scoring. Many standardized tests allow a person's performance to be compared with the performance of other individuals.
55
New cards
Case study
An in-depth look at a single individual
56
New cards
Life-History records
Records of information about a lifetime. Chronology of events and activities that often involve a combination of data records on education, work, family, and residence.
57
New cards
Correlational research
Goal is to describe the strength of the relationship between two or more events or characteristics.
58
New cards
Experimental research
Carefully regulated procedure in which one or more of the factors believed to influence the behavior being studies are manipulated, while all other factors are constant.
59
New cards
Cross-sectional
Research strategy in which individuals of different ages are compared at one time.
60
New cards
Longitudinal
Research strategy in which the same individuals are studied over a period of time, usually several years or more.
61
New cards
*Lev Vygotsky said…*
“We become ourselves through others”
62
New cards
Lev Vygostsky’s Theory
* Shares Piaget’s view that children actively construct their knowledge.
* Emphasizes developmental analysis, the role of language, and social relations.
* Emphasizes developmental analysis, the role of language, and social relations.
63
New cards
Zone of Proximal Development
The space between what a learner can do without assistance and what a learner can do with adult guidance or in collaboration with more capable peers.
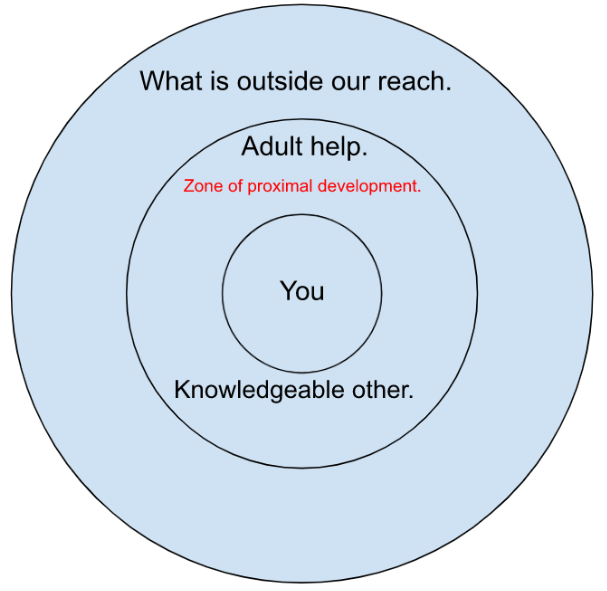
64
New cards
MCAT
Medical school exam.
65
New cards
LSAT
Law school exam.
66
New cards
LSAT and MCAT
Examples of standardized tests.
67
New cards
Structuralism
* Breaking down the mental processes to the most basic components
* The major tool of structuralism is introspection, a careful set of observations made under controlled conditions.
* The major tool of structuralism is introspection, a careful set of observations made under controlled conditions.
68
New cards
Functionalism
* Reaction to sturcturalism
* Influenced by Darwin’s theory of evolution
* Outside the lab into everyday life to study behaviour and development
* (ADAPTING)
* Influenced by Darwin’s theory of evolution
* Outside the lab into everyday life to study behaviour and development
* (ADAPTING)
69
New cards
Behaviourism
* Observing how we react through our behaviours
* The mind cannot be observed, we must observe behaviours. As this will give us insight.
* (REACTING)
* The mind cannot be observed, we must observe behaviours. As this will give us insight.
* (REACTING)