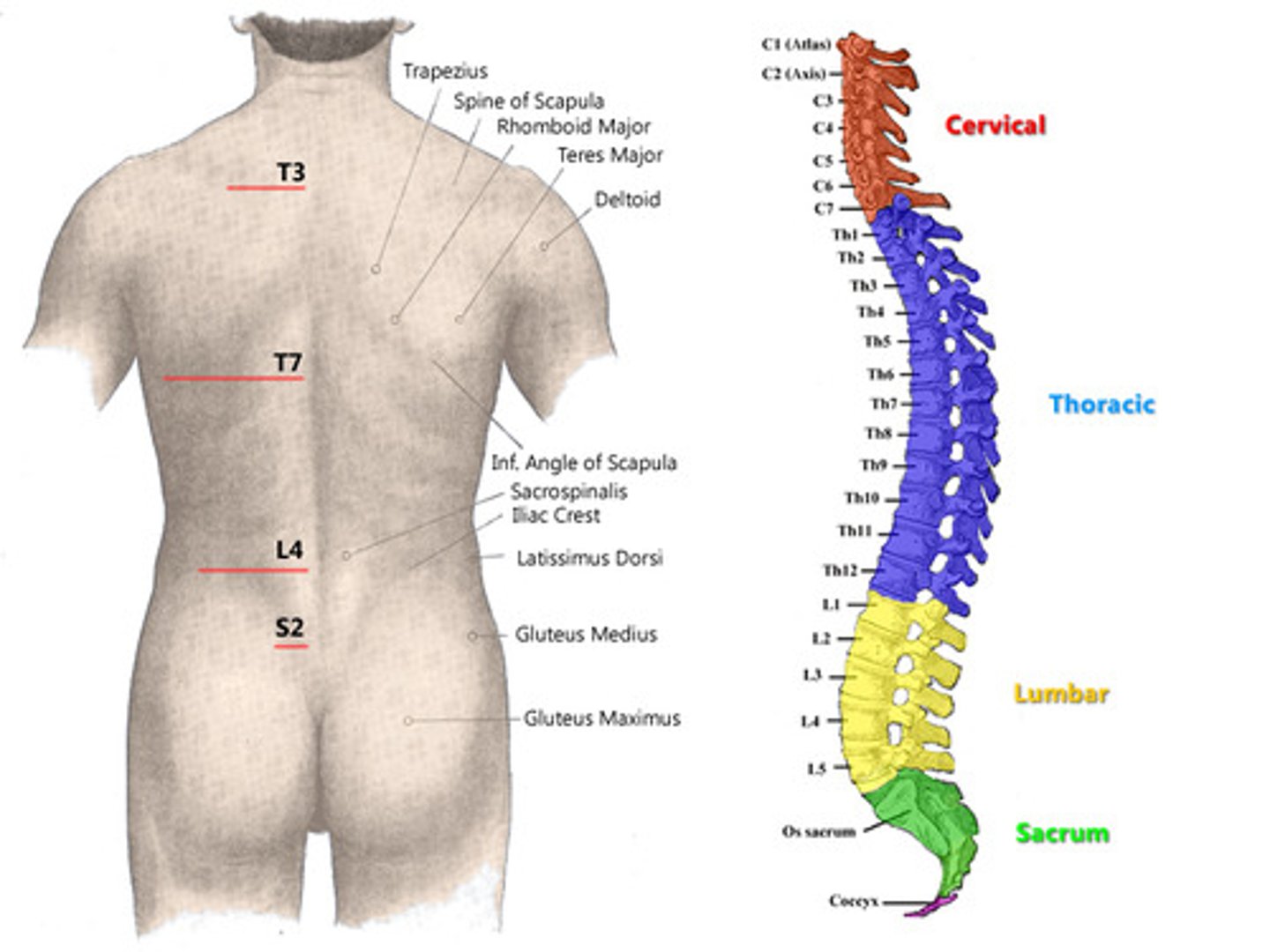
Vertebral Column
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
The vertebral column is a region of the ______ skeleton
Axial
Ther vertebral column consists of _____, ______ and ______ that connect the adjacent vertebrae
vertebrae, intervertebral discs, ligaments
Number of cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal vertebrae?
7, 12, 5, 5, 4
Vertebrae become progressively _____ from cervical to lumbar regions since more weight is supported by inferior vertebrae
Larger
The ____ is the cylindrical, anterior part of the vertebra
body
The superior and inferior surfaces of the body are covered by ______ cartilage end plates
hyaline
______ ____ lies posterior to the vertebral body and each ____ consists of 2 pedicles and 2 laminae.
Vertebral Arch, arch

Short, stout cylindrical processes projecting posteriorly from the vertebral body
Pedicles
Broad, flat plates of bone attaching laterally to the pedicles and on the midline
Laminae

The space bounded laterally and posteriorly by the vertebral arch and anteriorly by the posterior border of the vertebral body.
Vertebral Foramen
Succesive vertebral foramen forms the ____ ____ which contains the spinal cord, spinal roots, meninges, fat, blood vessels and nerves
vertebral canal

Indentations on vertebral pedicles
Vertebral notches
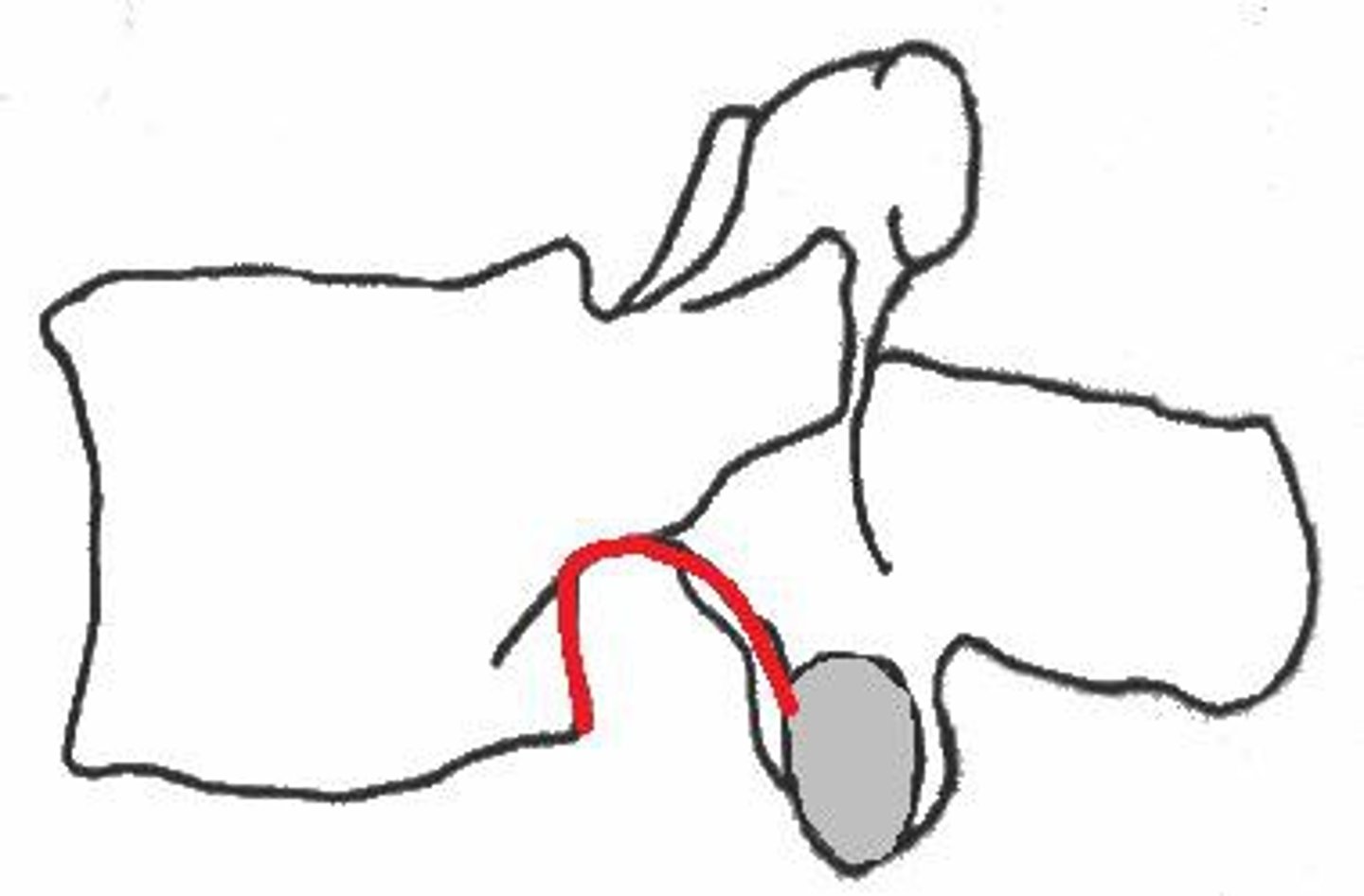
_____ _____ are formed by an inferior vertebral notch of a superior vertebra and the superior vertebral notch of the inferior vertebra.
Intervertebral Foramen
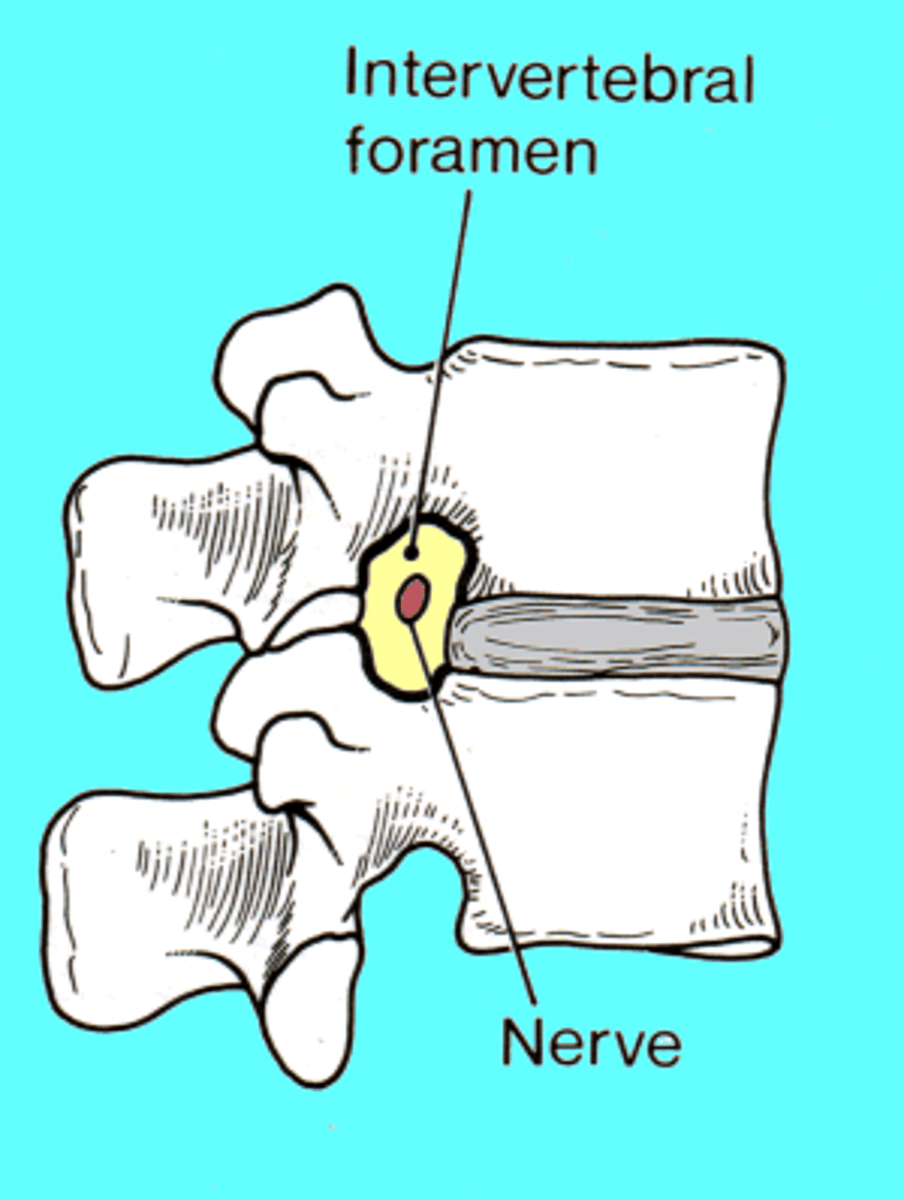
Passing through the intervertebral foramen are _____ ____ and ____ ____ associated with the vertebrae and spinal cord.
Spinal Nerves, blood vessels
Single, median process which projects posteriorly and arises where the two lamina meet, site of muscle attachment
Spinous Process

Bilateral processes arising from the junction of the pedicles and laminae, site of muscle attachment
Transverse Process
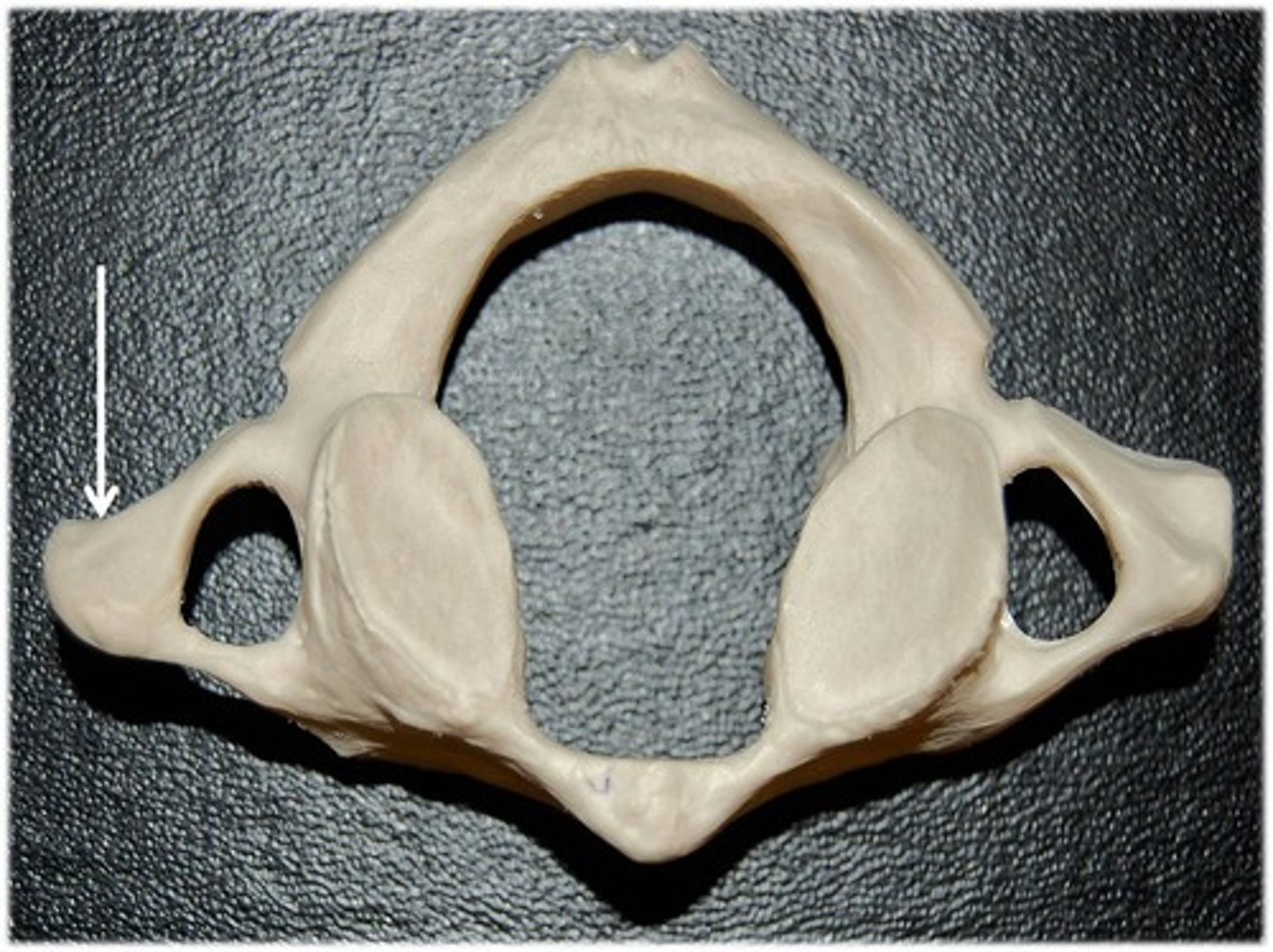
2 superior and 2 inferior processes, each with a region where articuation occurs
Articular Processes
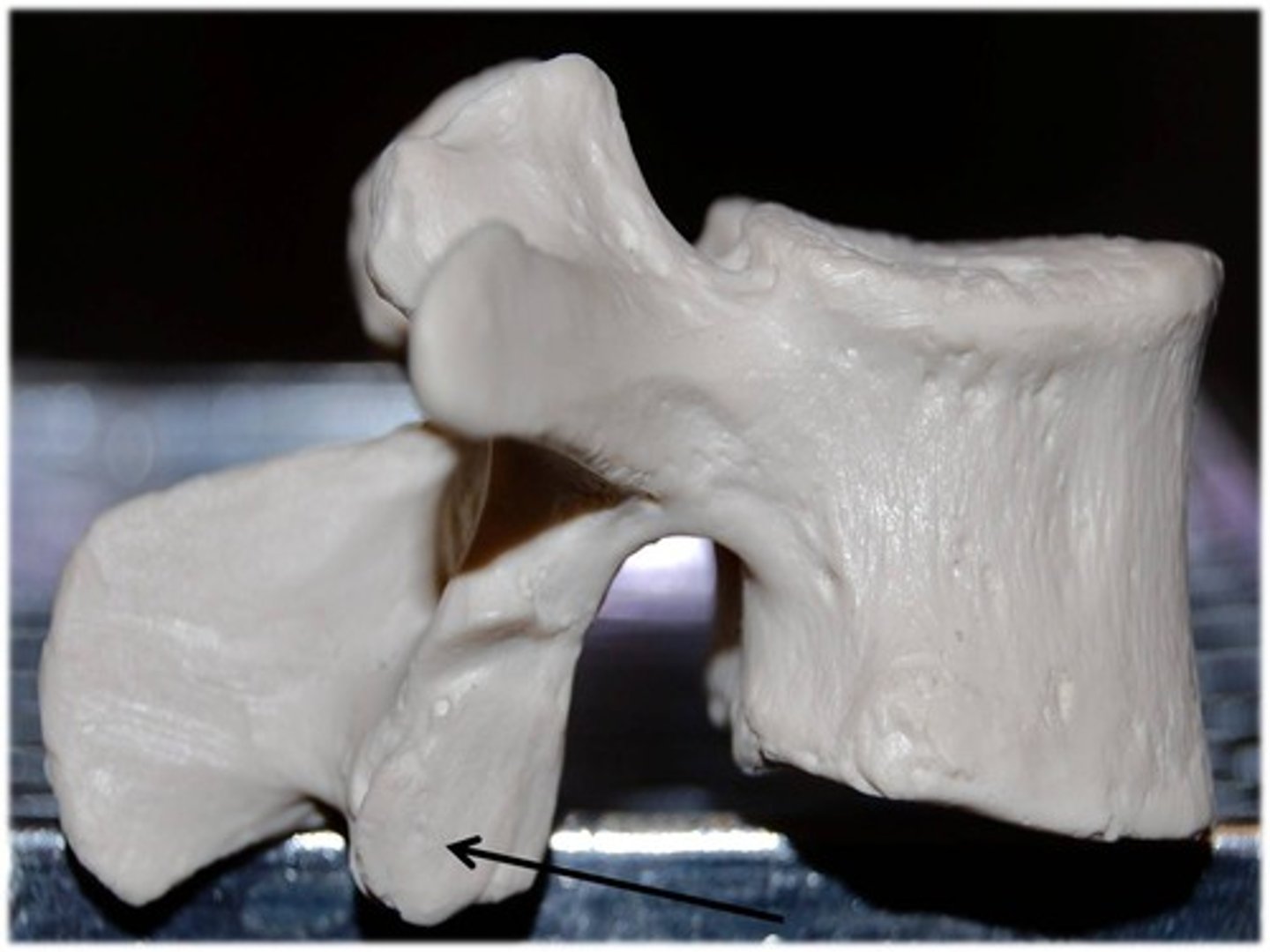
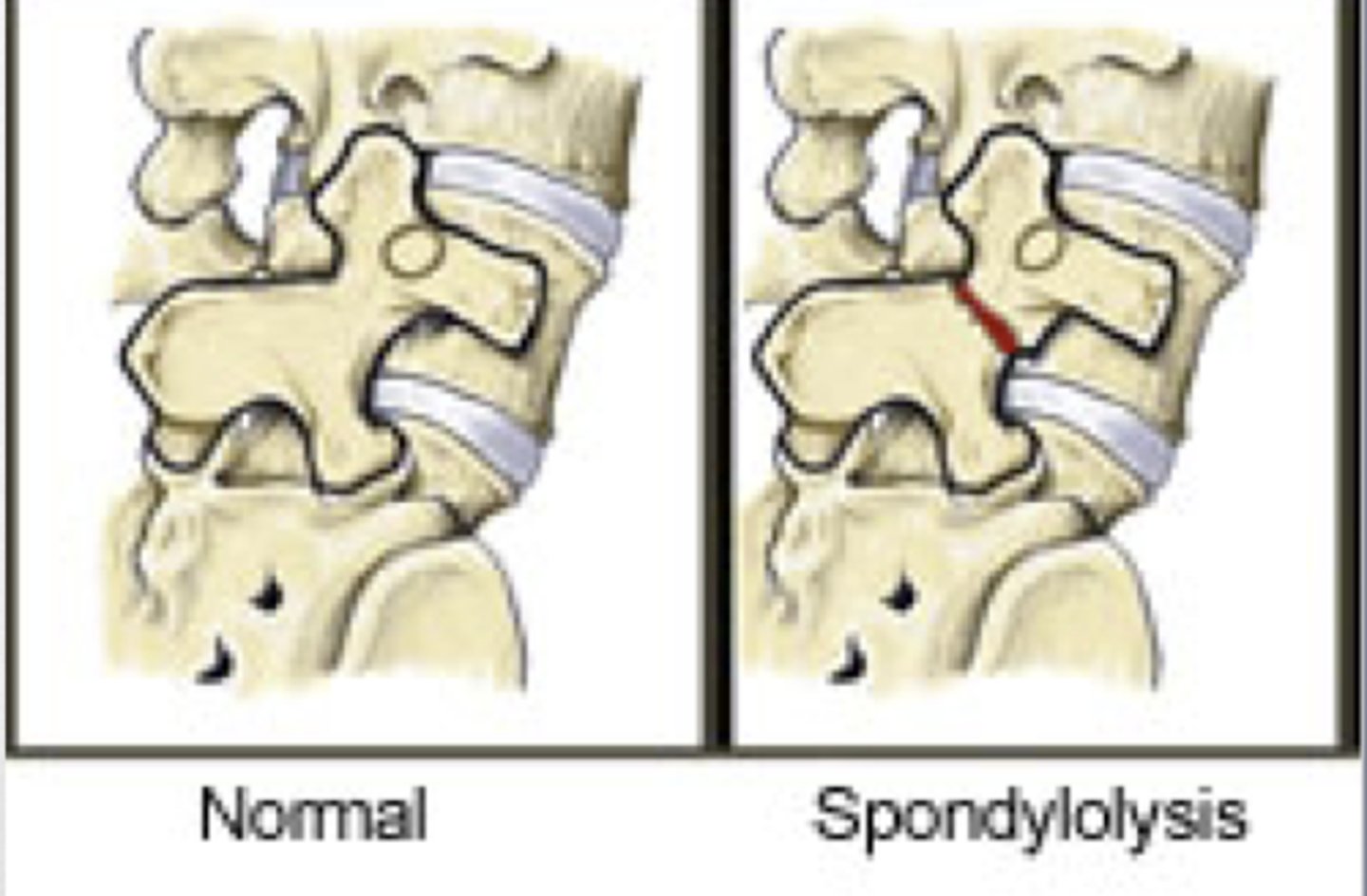
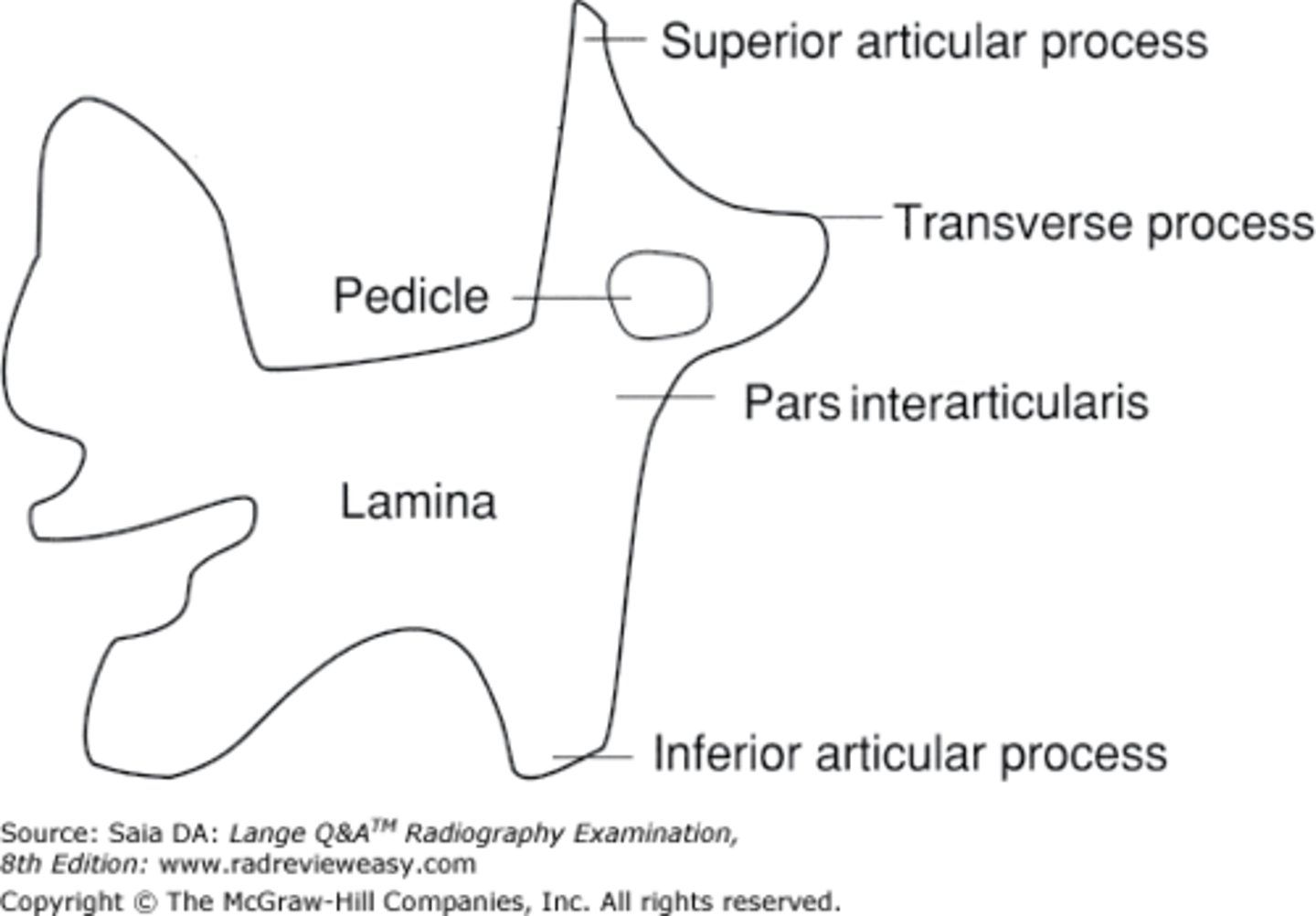
The bone between the superior and inferior articular processes
Pars Interarticularis
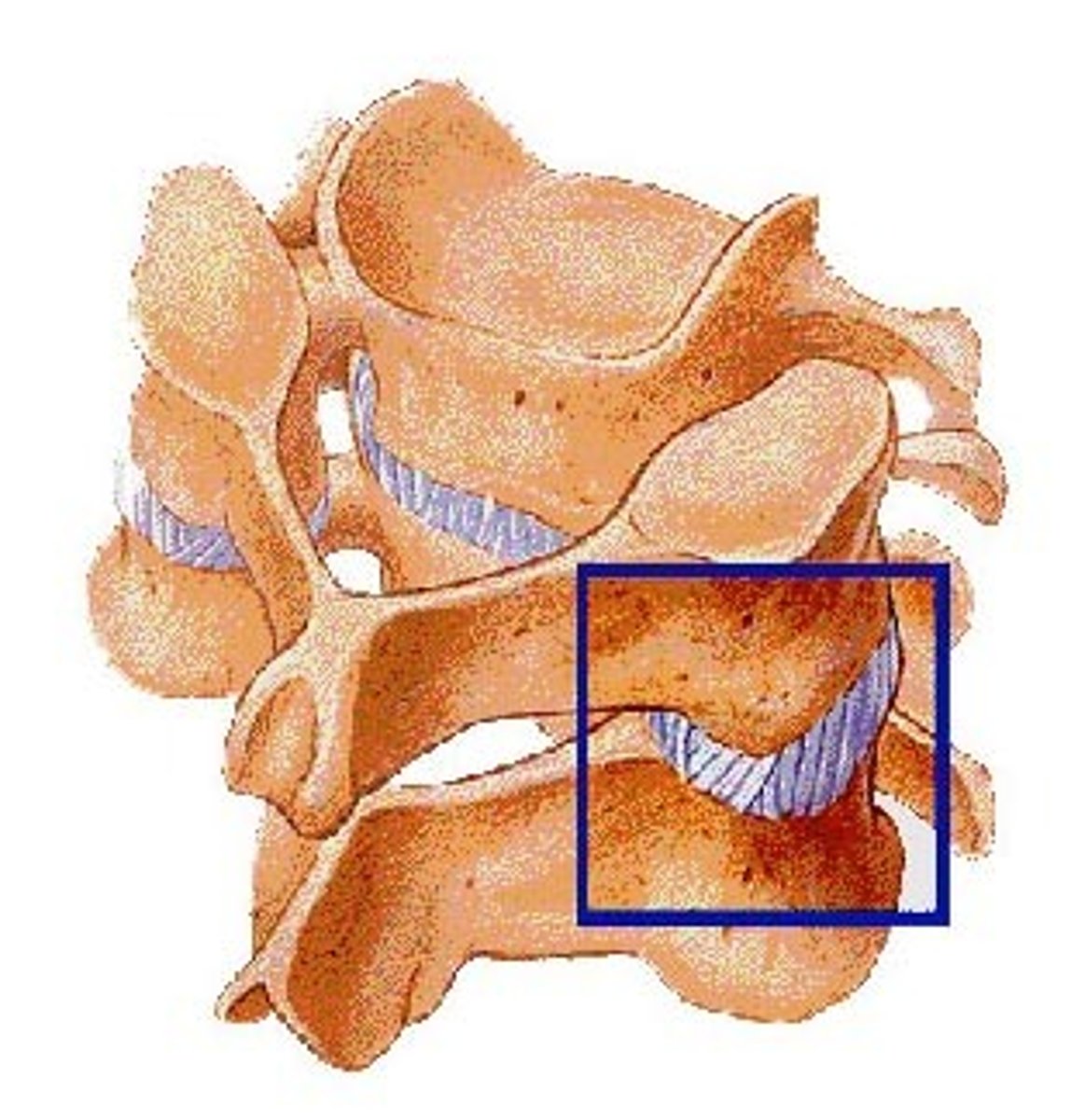
The pars interarticularis is fractured in ______ also known as a "______ fracture"
Spondylolysis, hangman
During fetal life, the primary center that forms the body of the vertebra
Centrum
This connects to the centrum via neurocentral joints
neural arches
Connects centrum to the neural arches
neurocentral joints
Secondary ossification occurs after _____ and begins at the tips of the _____ _____ and the _____ _____ and the superior and inferior surfaces of the vertebral bodies
spinous process, transverse process
All vertebrae contain a ____ ____ during development that typically only becomes a rib in the thoracic region.
Costal Element
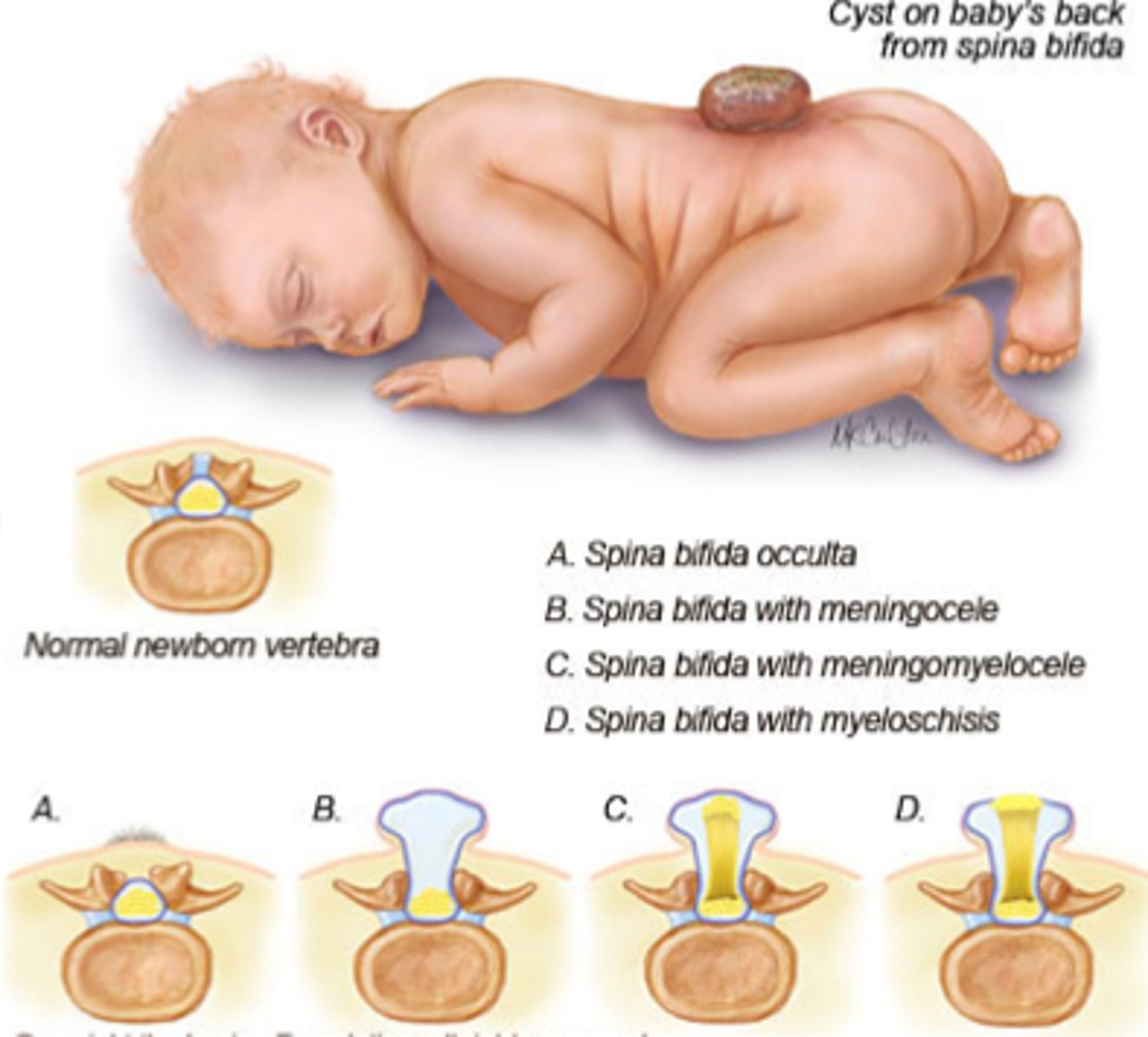
Failure of the neural arch to fuse on the posterior midline results in?
Spina Bifida
Greatest movement occurs in which region of the vertebral column?
Cervical region
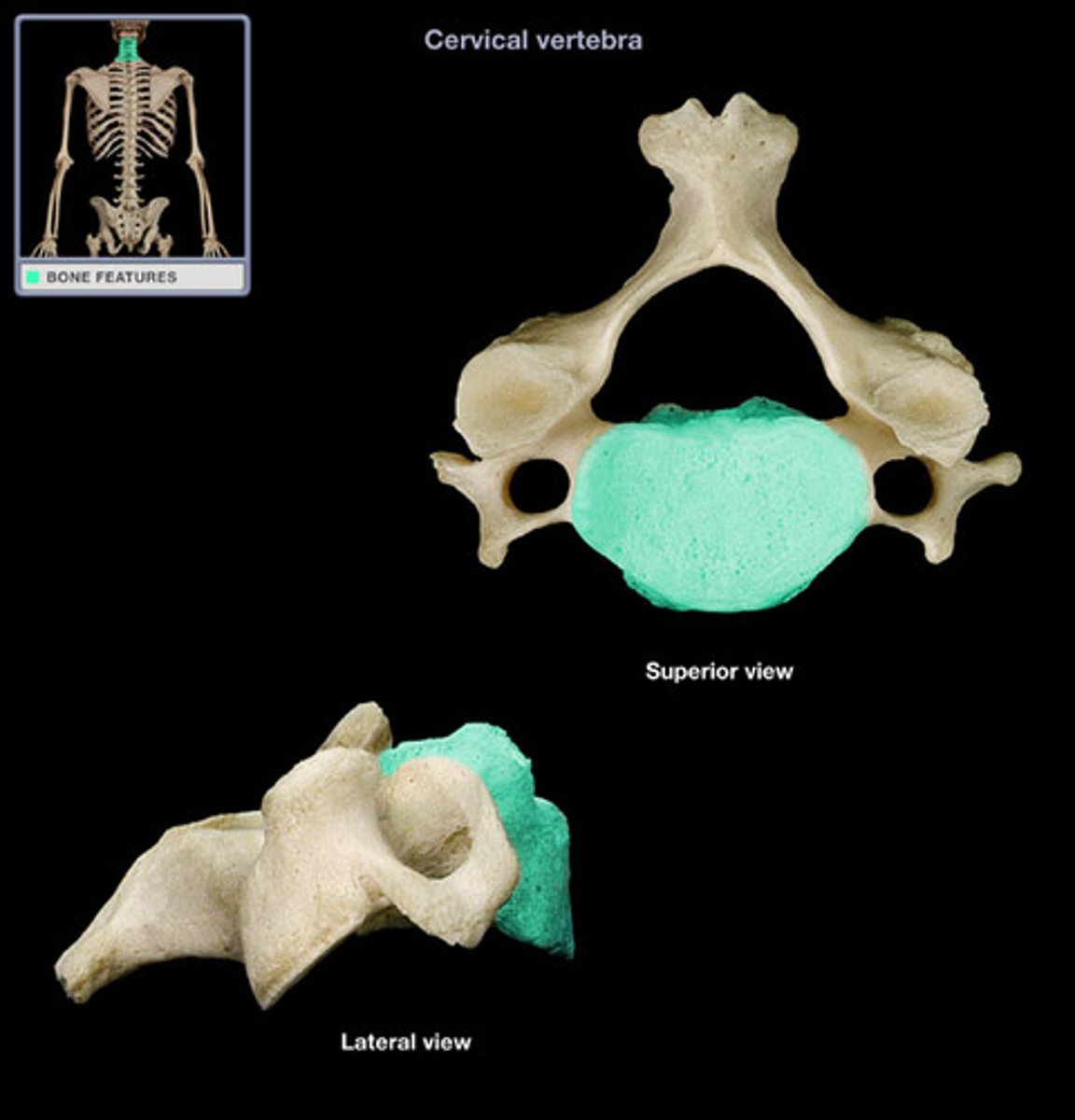
True or False, vertebral foramen are small in cervical vertebrae?
False, large in order to accommodate the large spinal cord diameter in this region of the spinal column
Intervertebral Foramen of the cervical region are _____ thus, nerves and blood vessels are susceptible to compression
narrow
Transverse Processes have _____ _____ through which passes the vertebral artery and vein
Foramen Transversarium
Anterior tubercle of C6 is named the ______ and the _____ artery lies anterior to it
Carotid Tubercle, Carotid
Transverse processes have anterior and posterior _____ which have arisen from the costal element
Tubercle
True or False, cervical vertebrae have a bifid spinous process?
True
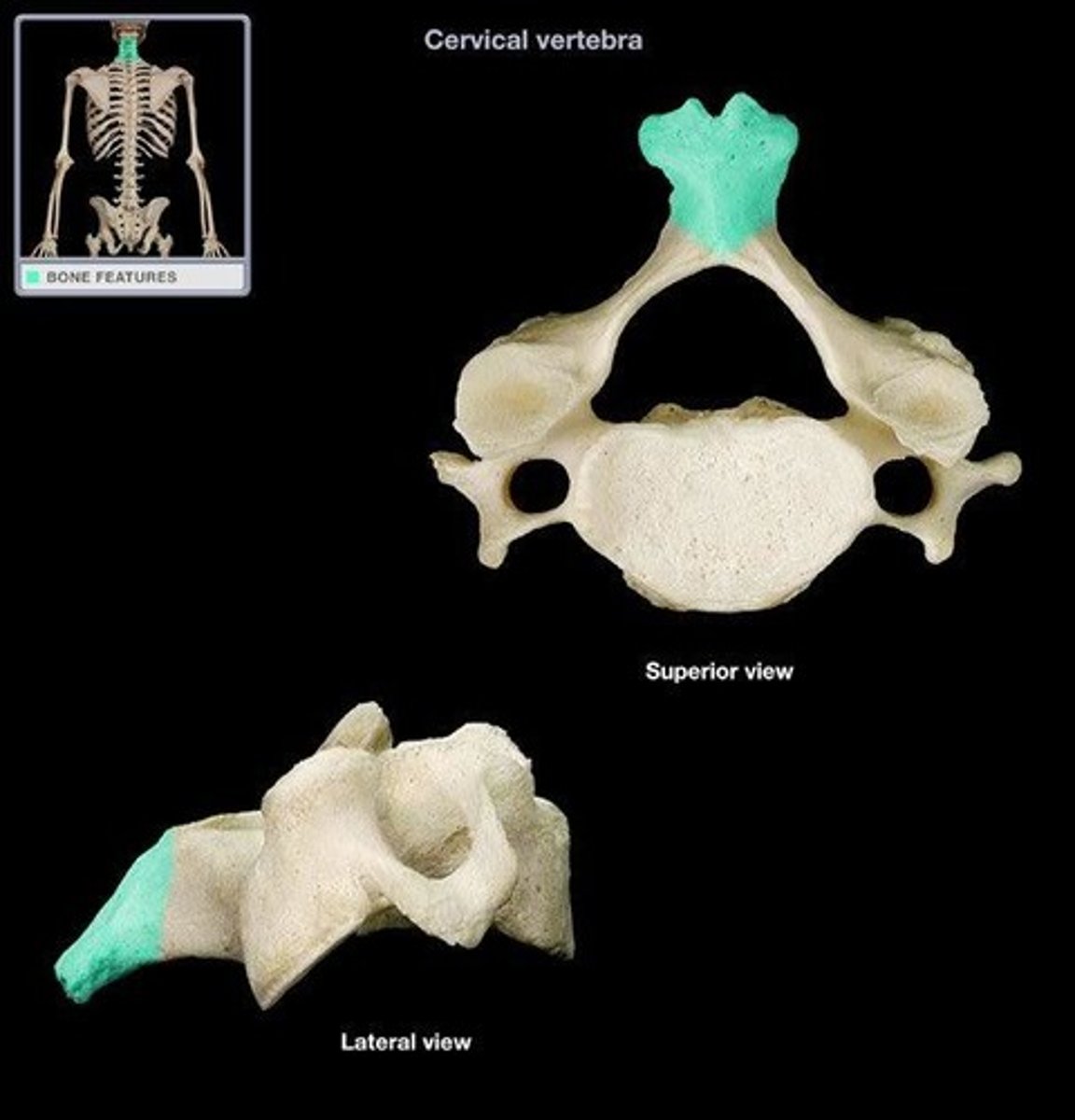
Spinous process of C7
Vertebra Prominens
C3-C7 have projection from the posterolateral aspect of body termed an _____
uncus
Articular facets allow for _____ and _____ of the neck
flexion and extension
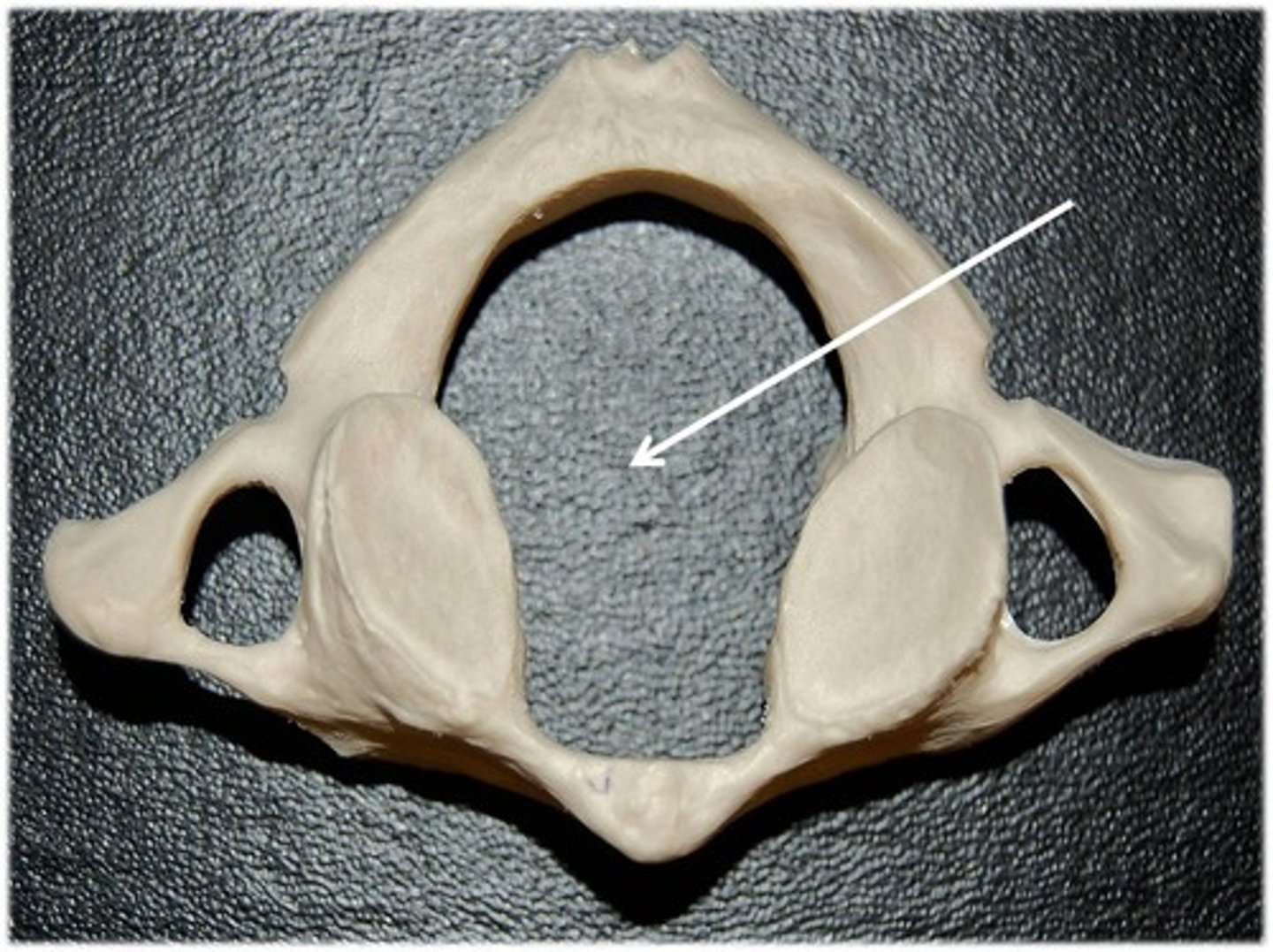
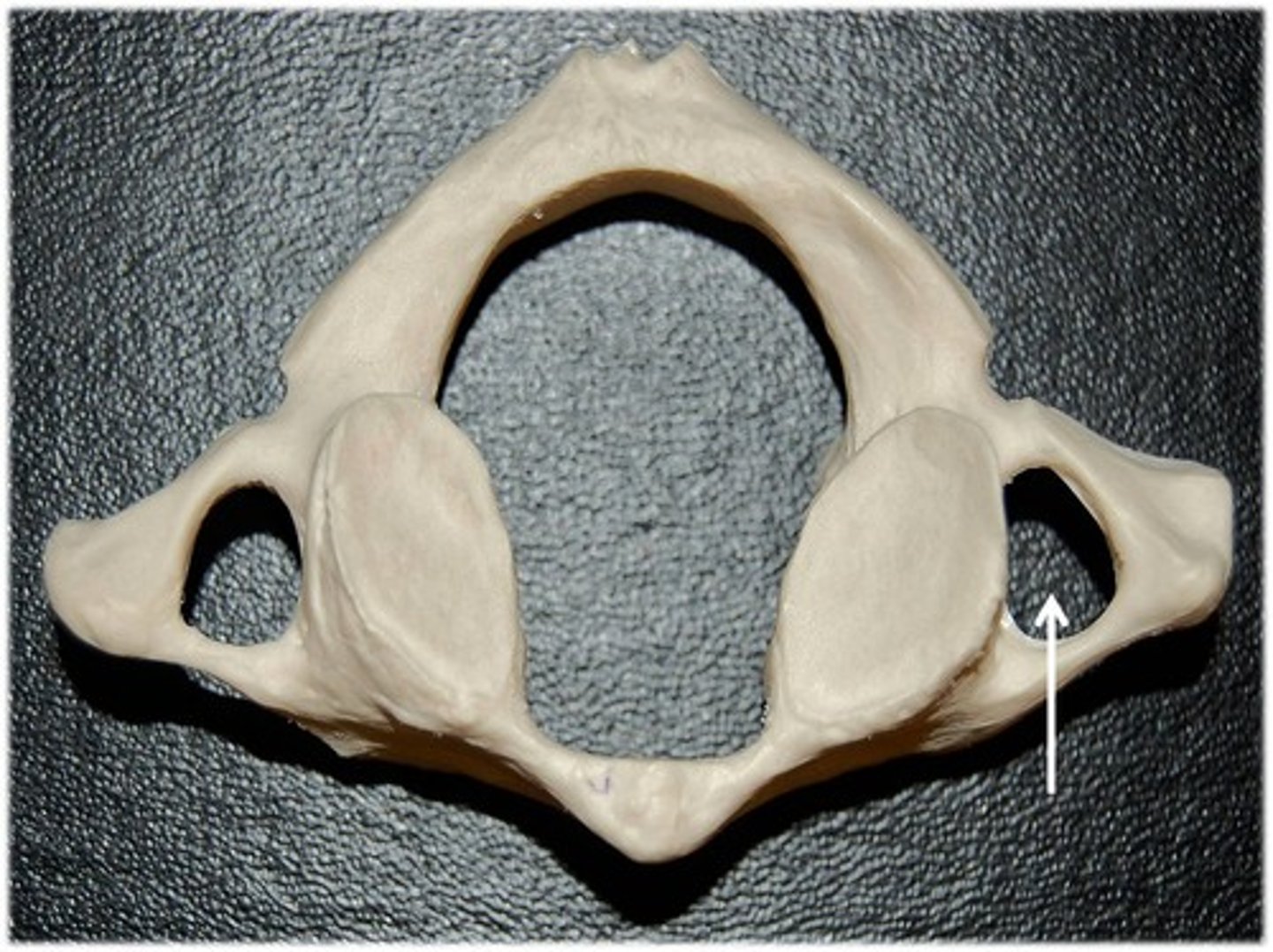
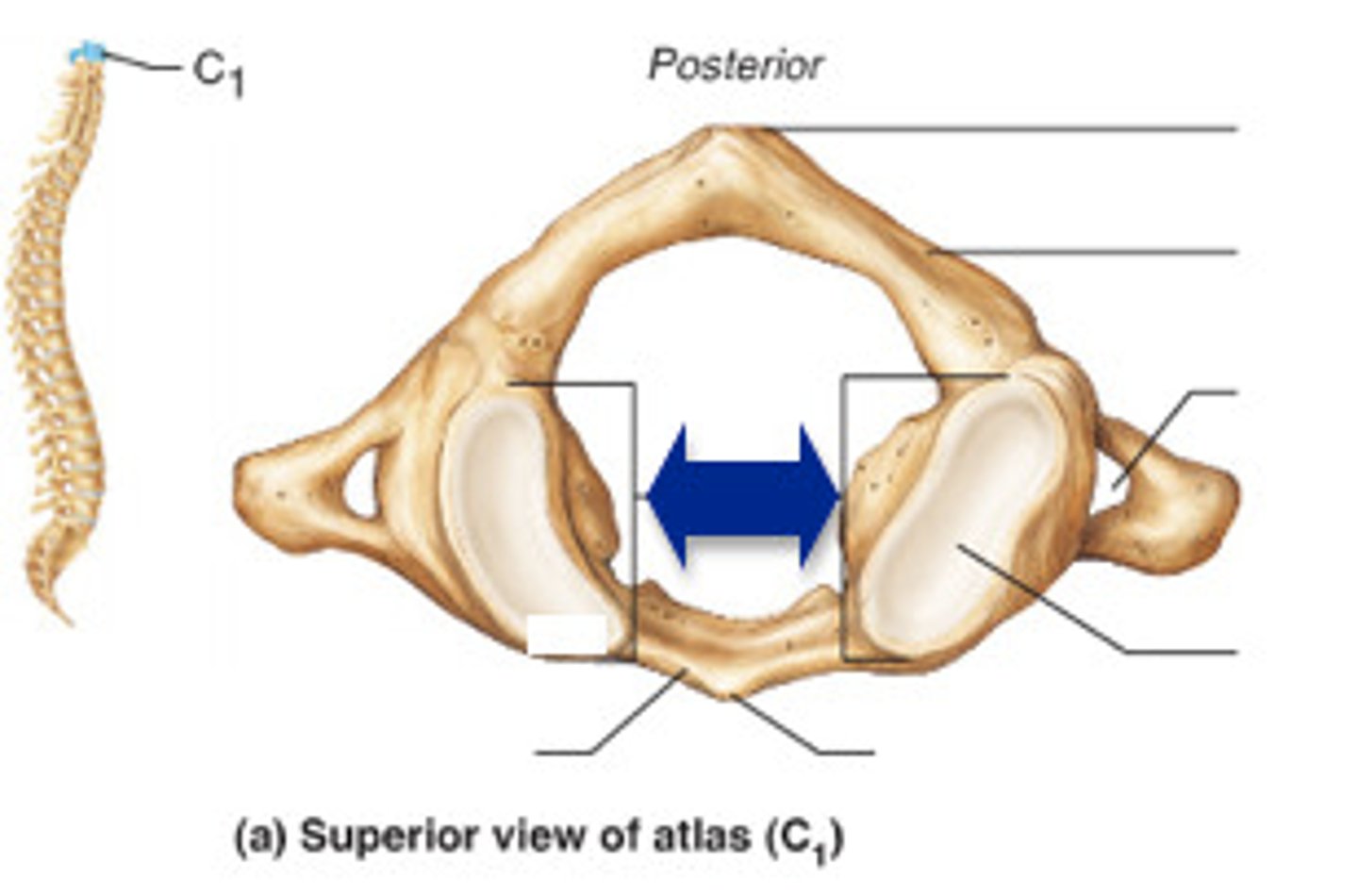
True or False, atlas has a spinous process?
False
The Atlas vertebrae has an _____ _____ with an anterior tubercle and a posterior arch with a _____ _____
anterior arch, posterior tubercle
Superior surface of the posterior arch of Atlas
Vertebral Artery Grooves
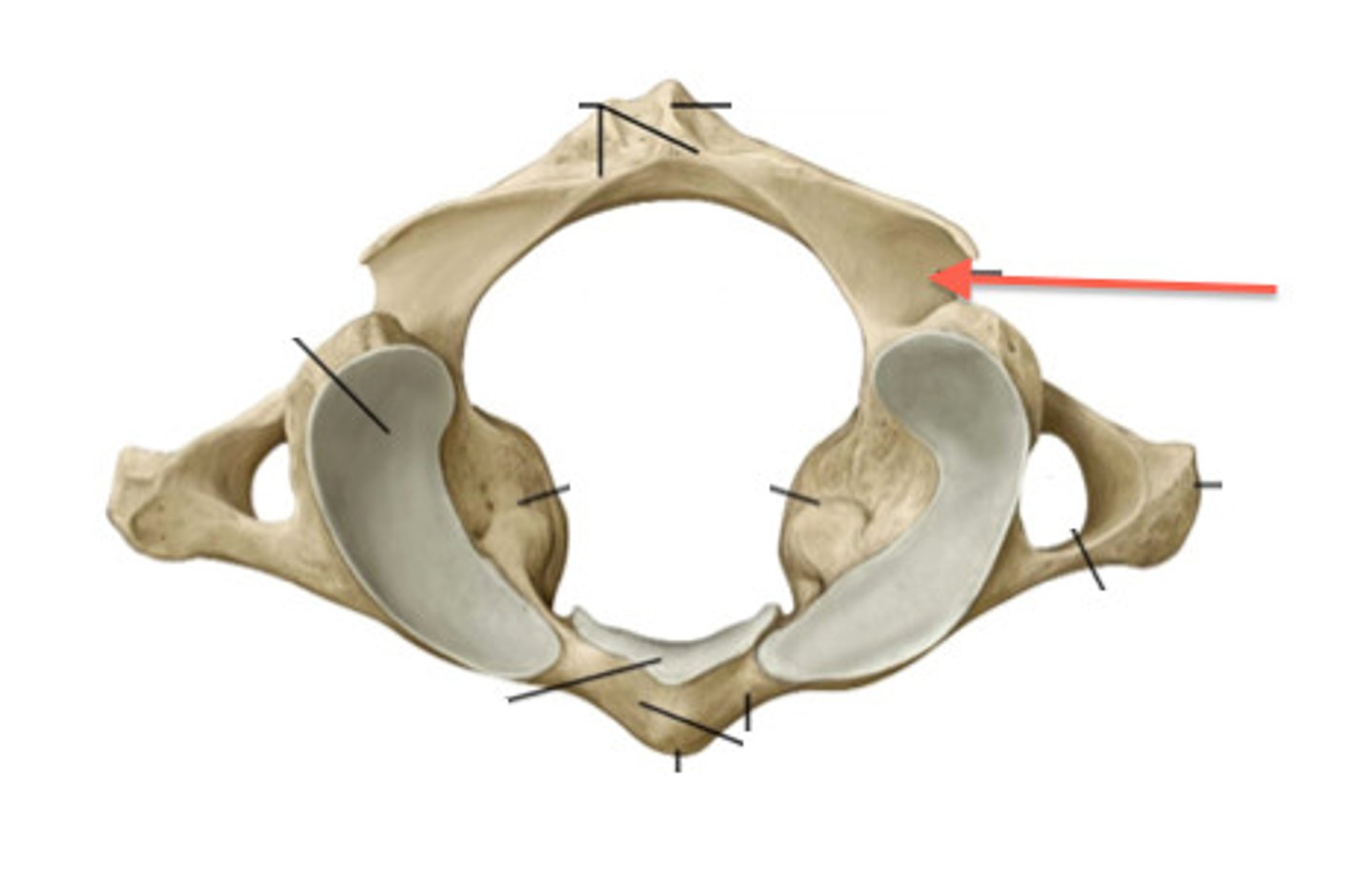
The ___ ____ lie beteween the anterior and posterior arches and support the superior and inferior articular surfaces
lateral masses
Axis most distinguishing feature
Dens

Transverse processes of spinous processes contain _____ ____
costal facets

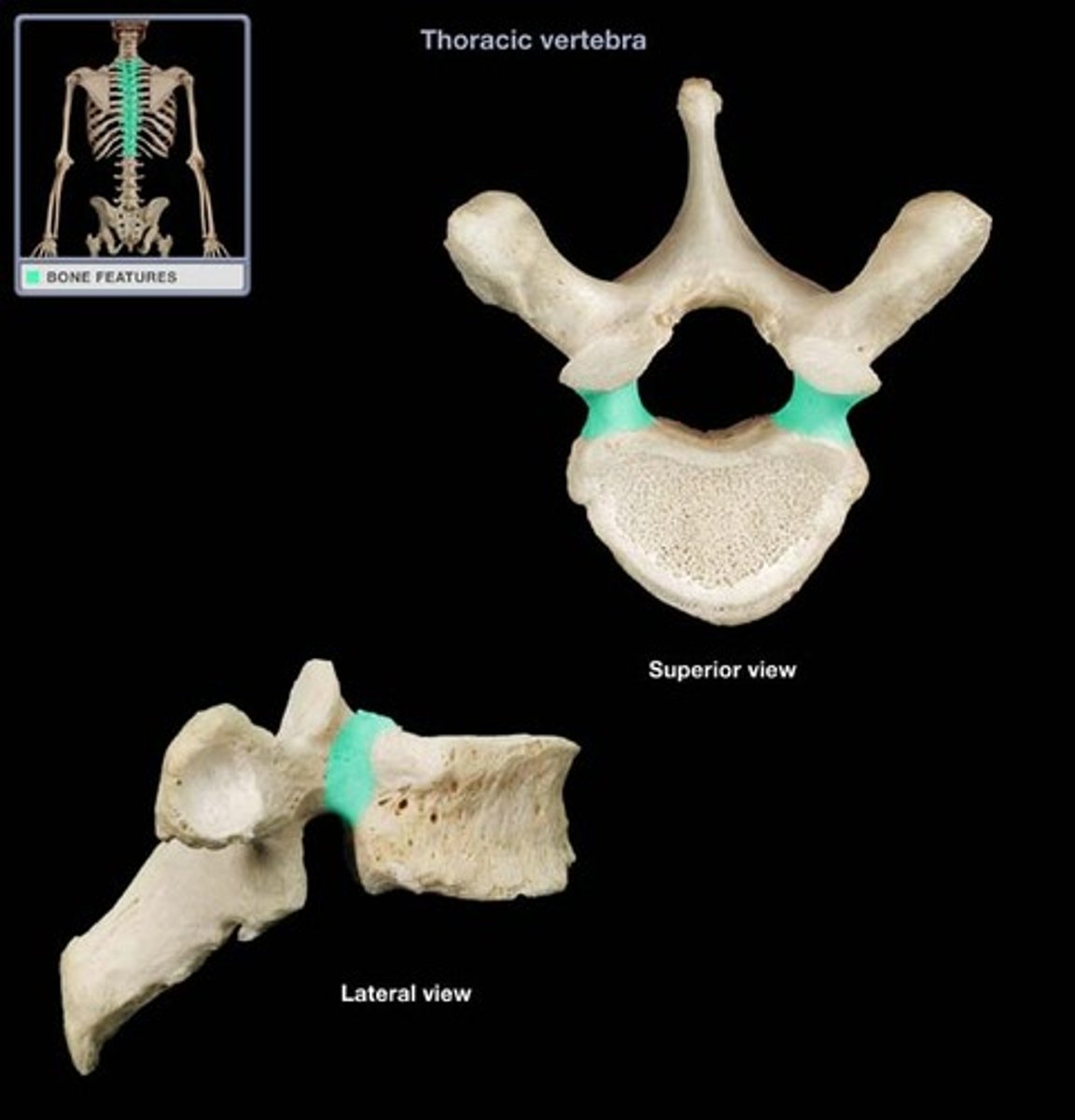
The preferred movement around thoracic vertebrae
Rotation
What features of thoracic vertebrae limit flexion and extension?
Spinous process, rib attachments
Lumbar vertebrae have relatively long and slender transverse processes with ______ _____ at posterior surface. Base of this for muscle attachment
Accessory Process
Tubercles on posterior surface of superior articular processes of lumbar vertebrae are called _____ _____ and are for muscle attachment
Mammillary Processes
What angle of X-Ray must be taken to see the "Scotty Dog" in Lumbar vertebrae
Oblique
Scotty Dog Features
Superior articular process- Ear, Transverse process- Nose, Pedicle- Eye, Inferior articular process- Front Leg, Pars Interarticularis- Neck
Sacrum is united to the hip bones at the _____ ____ via the _____ ____
sacroiliac joint, auricular surface
Wide region of sacrum
Base
Prominent Anterior edge of sacral base
Sacral Promontory
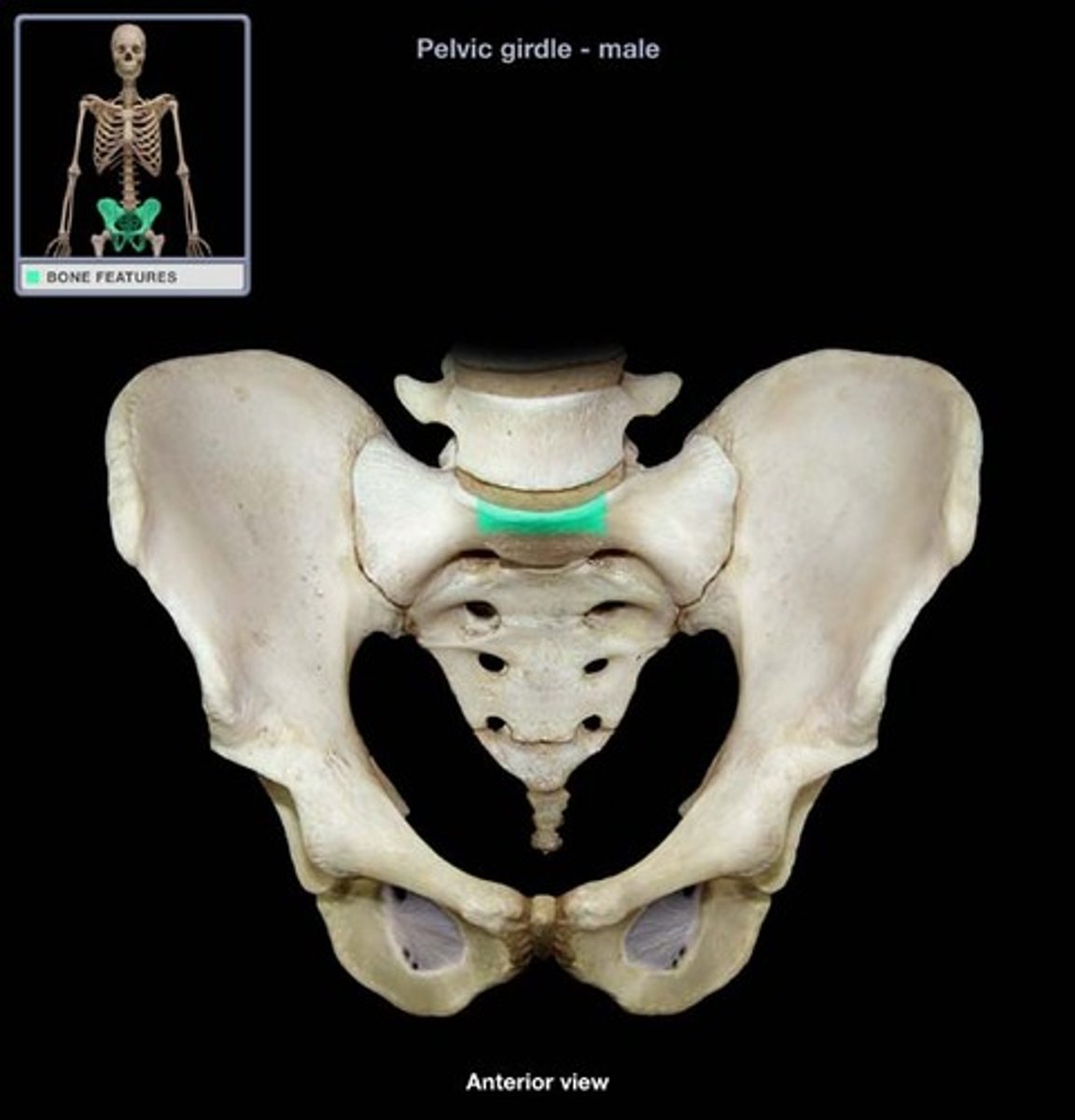
Wings of sacrum
alae
Superior articular processes articulate with inferior articular processes of L5 and form the _____ _____
lumbosacral angle
Inferior, narrow end of sacrum that articulates with coccyx
Apex
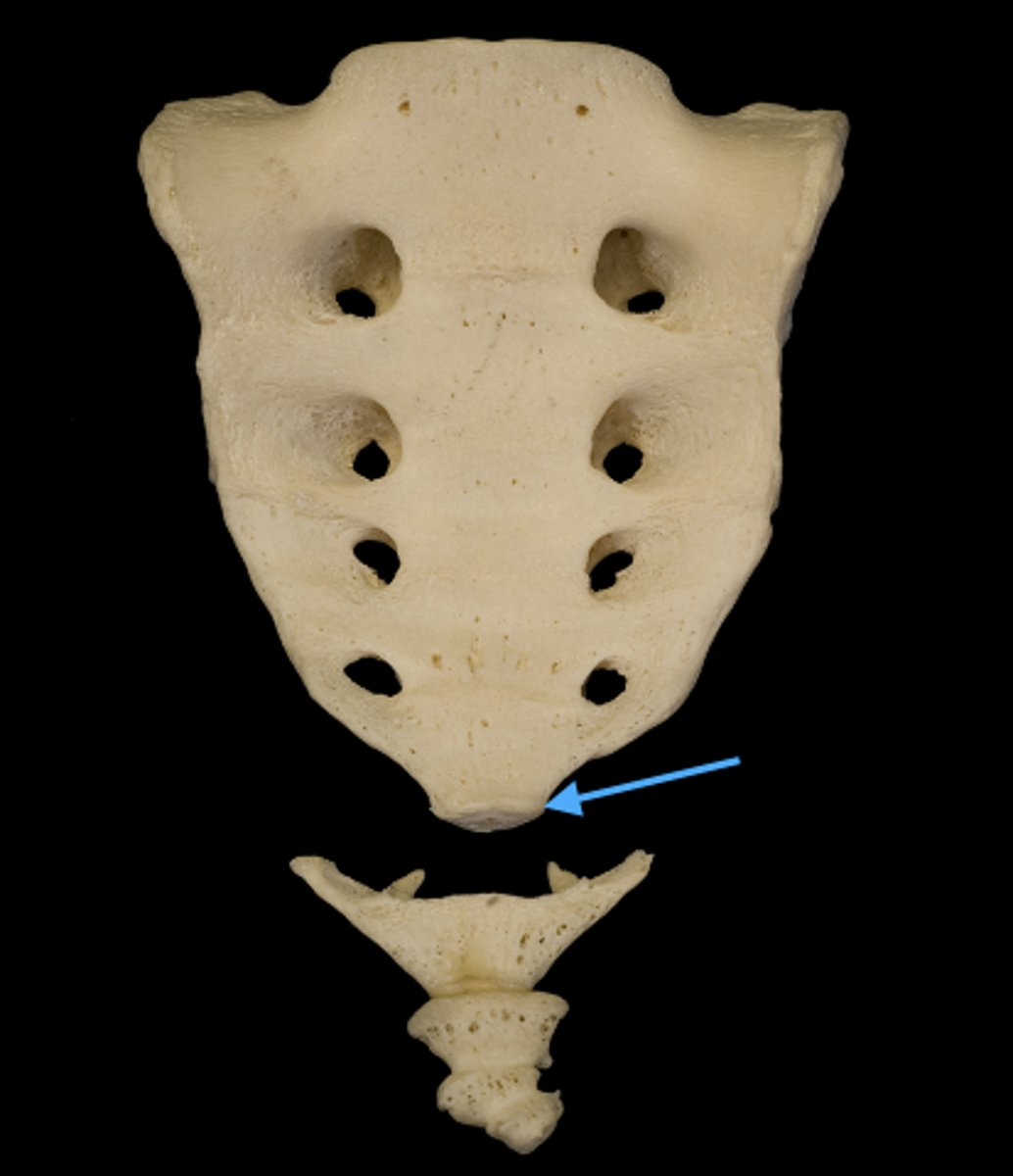
Inferior articular process of the sacrum
Sacral Cornua
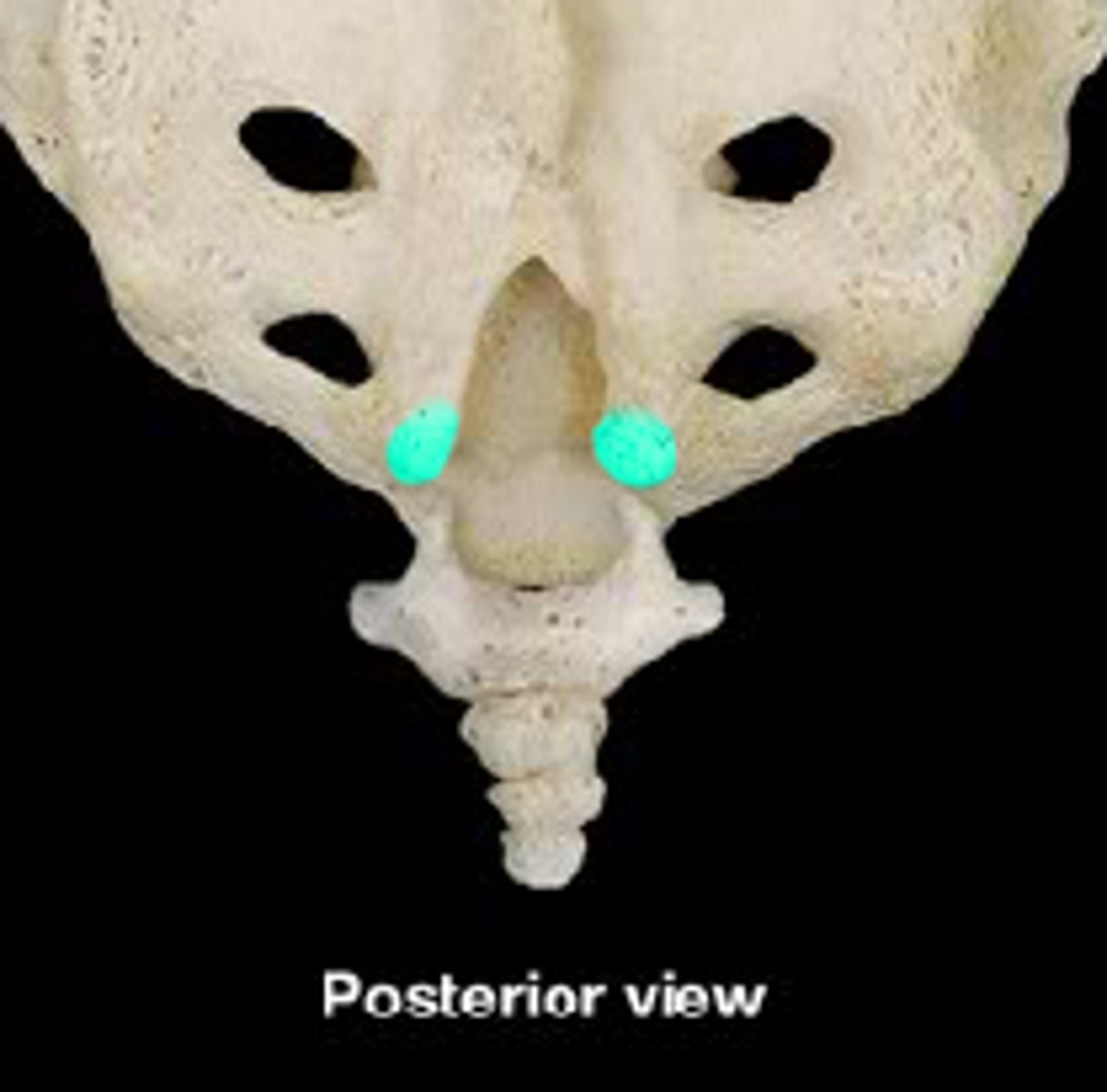
Continuation of the vertebral canal enclosed within fused vertebrae
Sacral canal
Sacral Canal contains which region of the spinal cord?
Cauda Equina
Pelvic/Anterior surface of sacrum is concave and has 4 _____ ____ located at the site of fusion
Transverse ridges
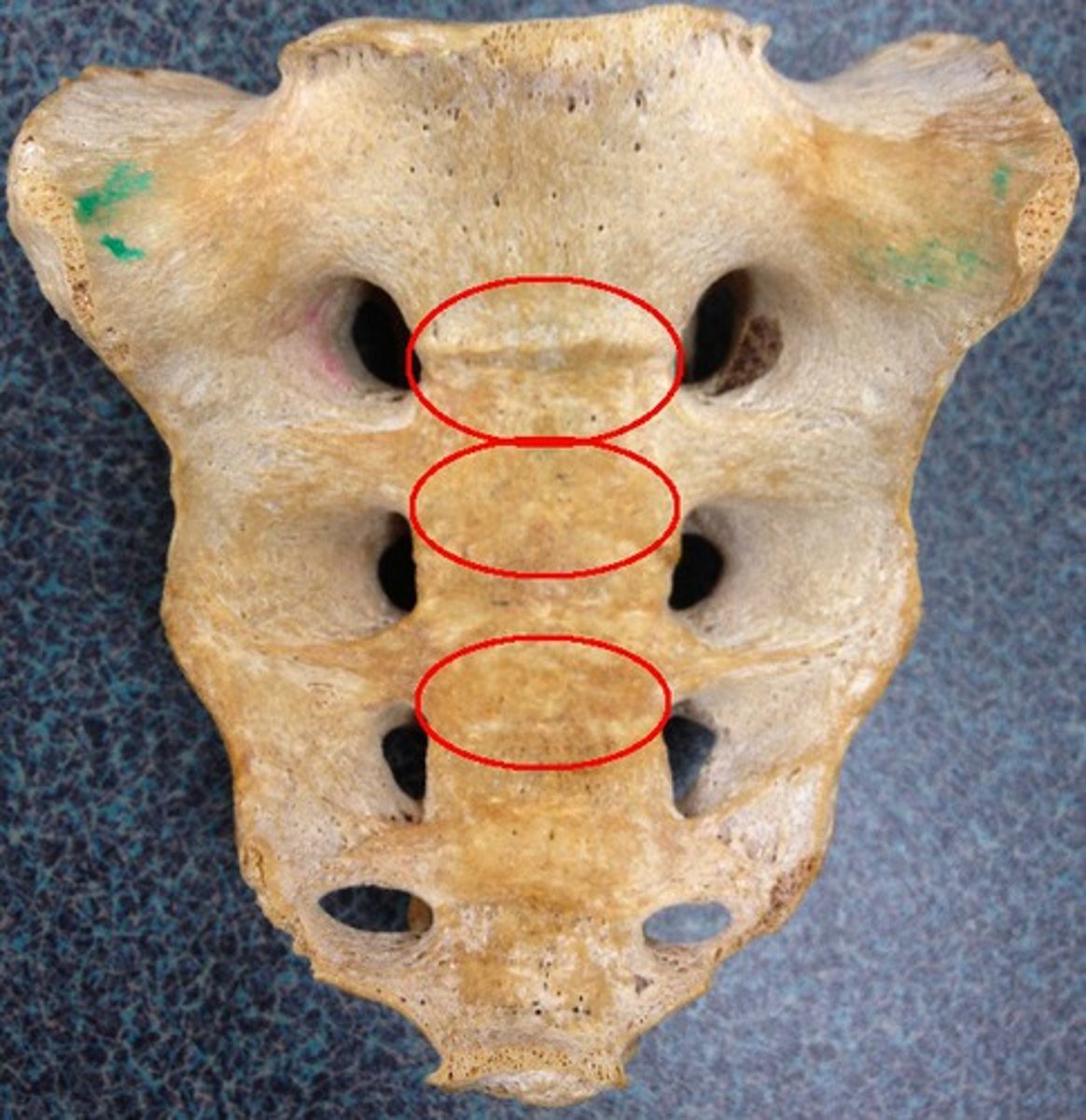
_____ _____ _____ allow passage of anterior/ventral rami of sacral spinal nerves S1-S4
Anterior Sacral Foramina
Formed by fusion of spinous processes of sacral vertebrae
Median sacral Crest
Formed by fusion of articular processes of sacral vertebrae
Intermediate Crest

Formed by fusion of transverse processes of sacral vertebrae
Lateral Crest
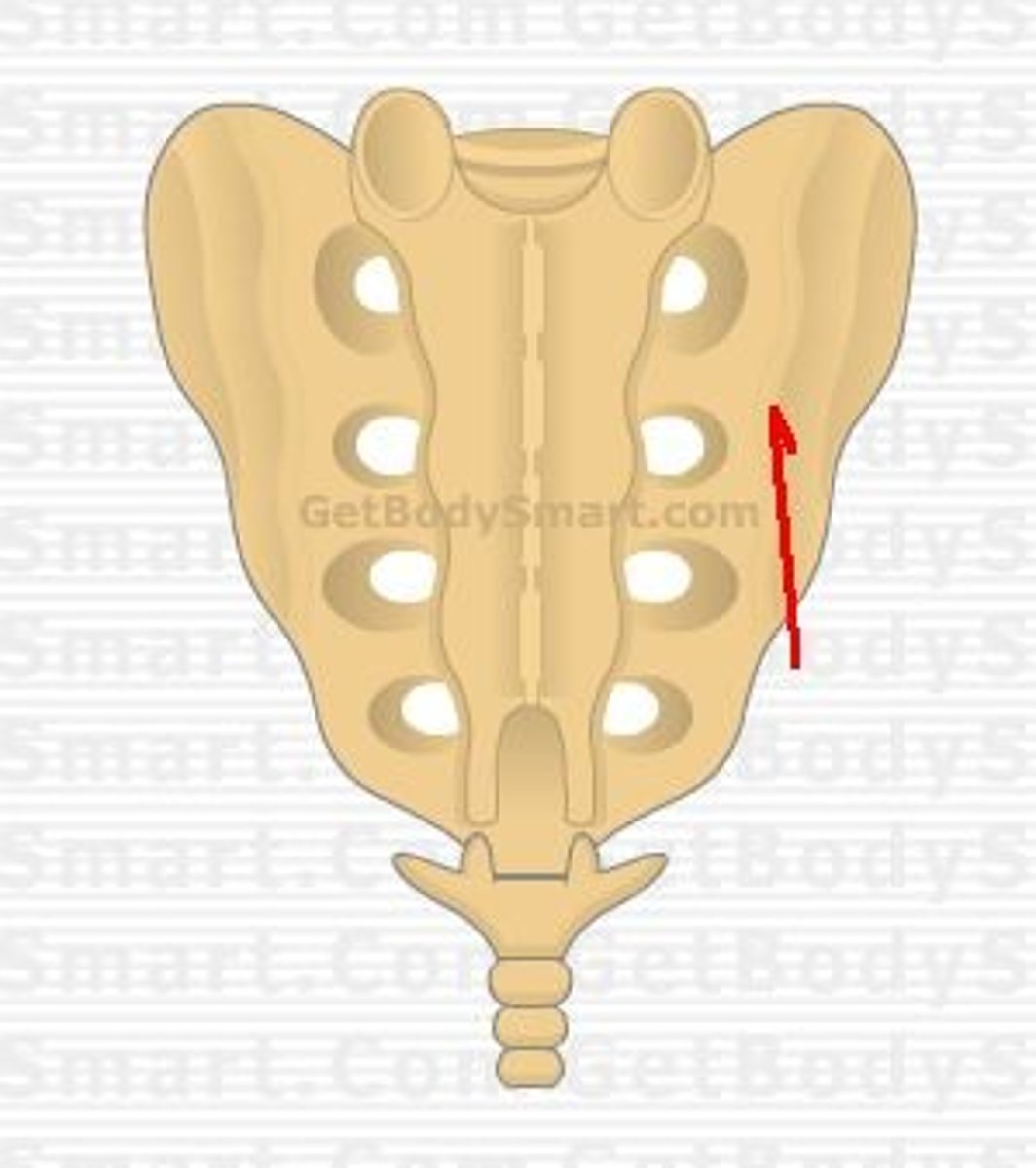
U shaped defect in the distal part of dorsal surface of sacrum due to failure of lamina S5 to develop
Sacral Hiatus

Four paired ____ ____ ___ allows passage of posterior/dorsal rami of S1-S4 spinal nerves
Posterior Sacral Foramina
CO1 has ____ ____ that articulate with the sacral cornua and help close off the intervertebral foramen for the 5th sacral nerves
Coccygeal Cornua

Which regions of the spine concave posteriorly?
Cervical, Lumbar
Which regions of the spine concave anteriorly?
Thoracic, Sacral
A fetus has all regions concave ____ thus, this type of curve is called a primary curve
Anteriorly, Primary Curves
These curves develop as a child.
Secondary Curves
Name for normal anterior concave
Kyphosis
Abnormal pronounced posterior convex curvature of the thoracic spine
Hunchback
Name for normal posterior concave
lordosis
Lordosis of the lumbar paired with anterior tilting pelvis=?
swayback
Abnormal lateral curvature of the vertebral column with associated rotation of vertebrae
Scoliosis
Condition where L5 is completely or partially fused with sacrum
Sacrilization
Condition where S1 is completely of partially separate from the sacrum
Lumbarization
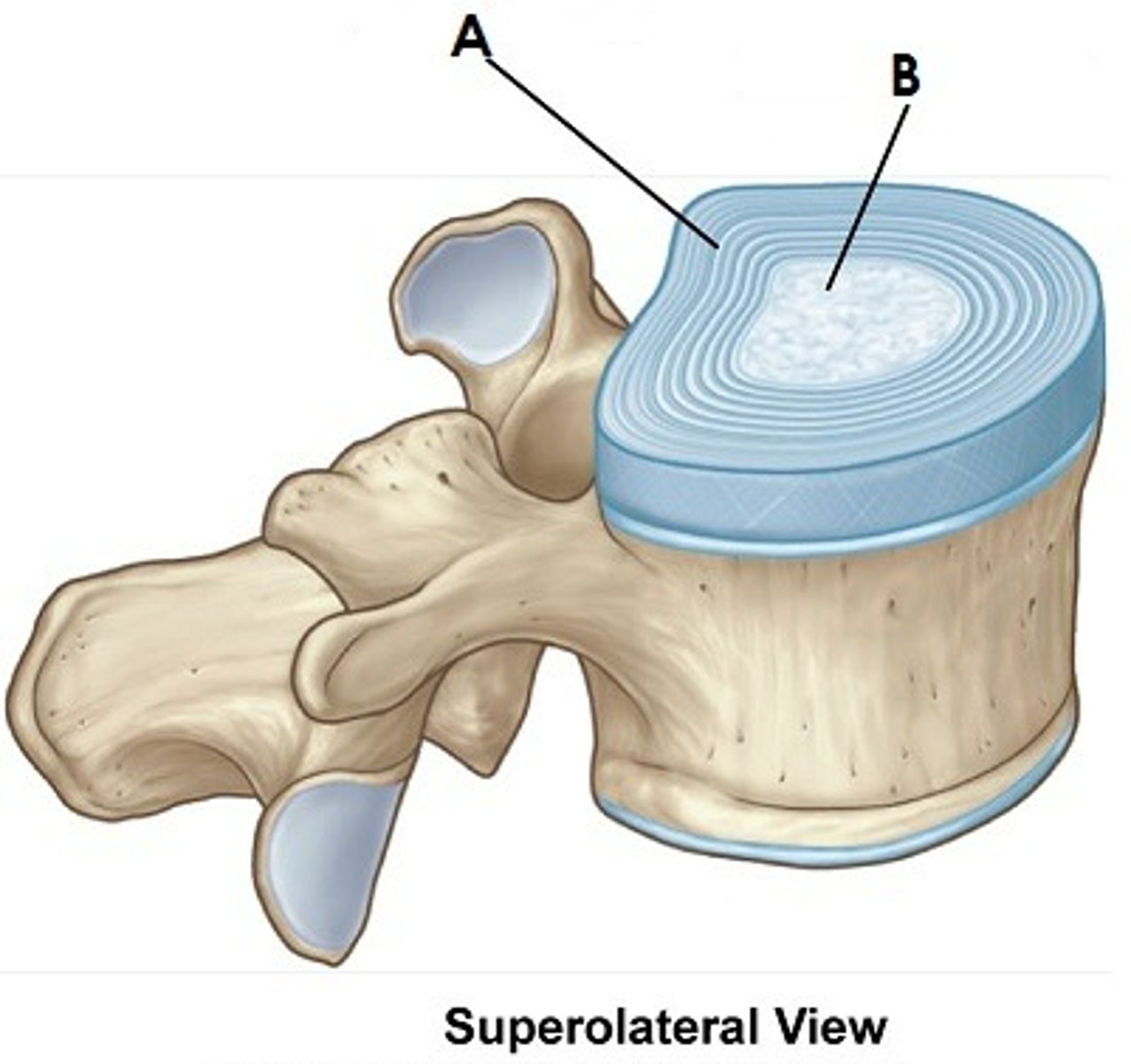
Outer Ring of IVD
anulus fibrosis
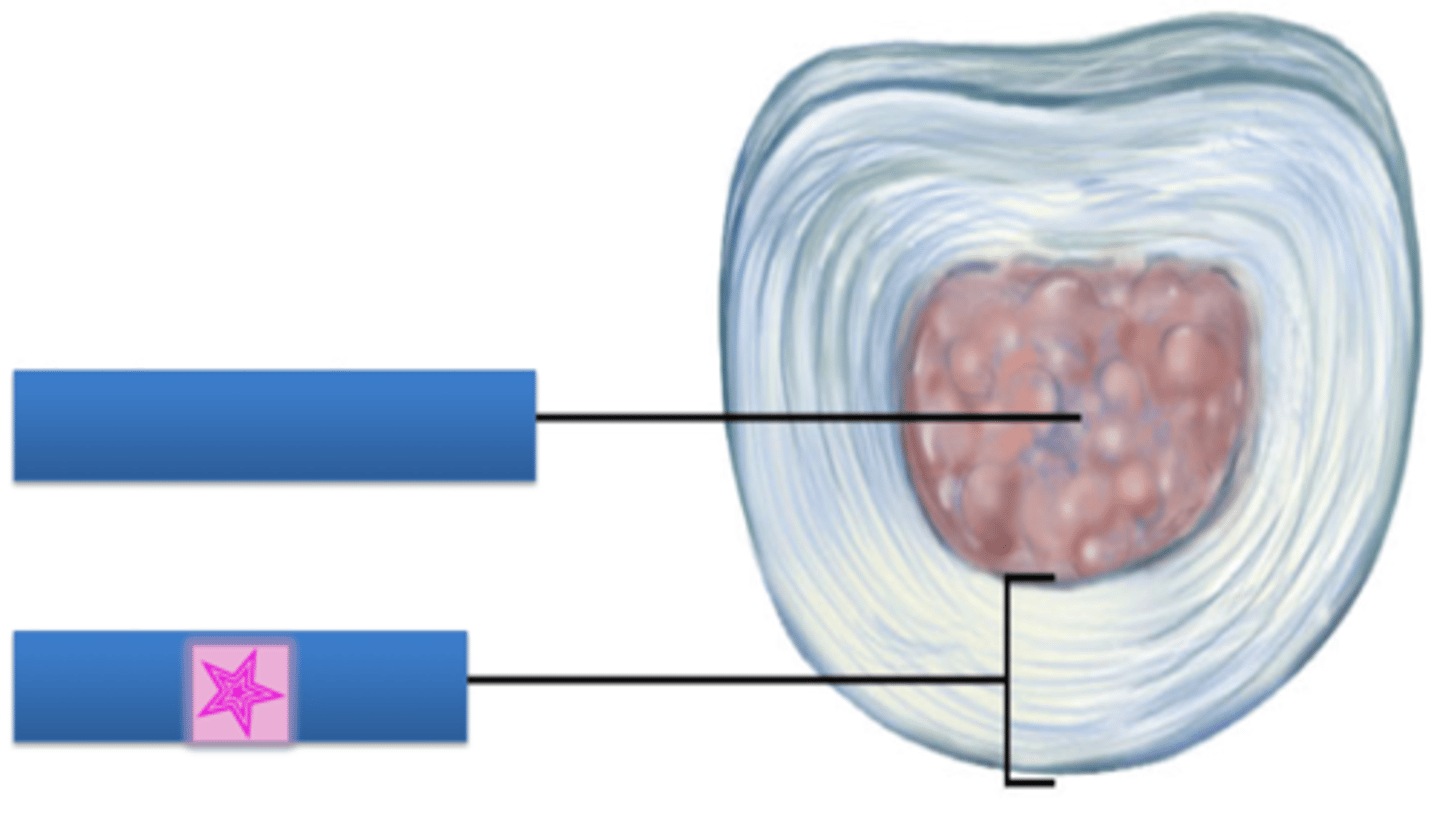
Inner core of IVD
Nucleus Pulposus
Rupture of what feature results in a herniated disk?
Nucleus Pulposus
Protrusion of IVD into an adjacent vertebral body
Schmorl's Node

These connect vertebral arches of adjacent vertebrae via plane synovial joints between superior and inferior articular processes
Zygapophysial Joints
Small synovial joints associated with C3-C7 vertebrae, between the uncus on the posterior lateral surface of inferior surfaces of the vertebral body above
Unconvertebral Joints
Condyloid, synovial joints between the convex occipital condyles at the base of the skull at the anterio-lateral side of the foramen magnum and the concave superior articular facet of C1.
Atlanto Occiptial Joints
True or False, movement allowed by Atlanto Occipital Joints is rotation?
False, flexion and extension
Joints between the inferior facet of lateral mass of C1 and the superior articular facets of C2
Lateral Atlanto-Axial Joints
Single pivot synovial joint between the dens of C2 and the anterior arch of C1
Median Atlanto Axial Joint
Ligament that covers the anterior and lateral surfaces, vertebral bodies and IVD. C1 all the way down
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
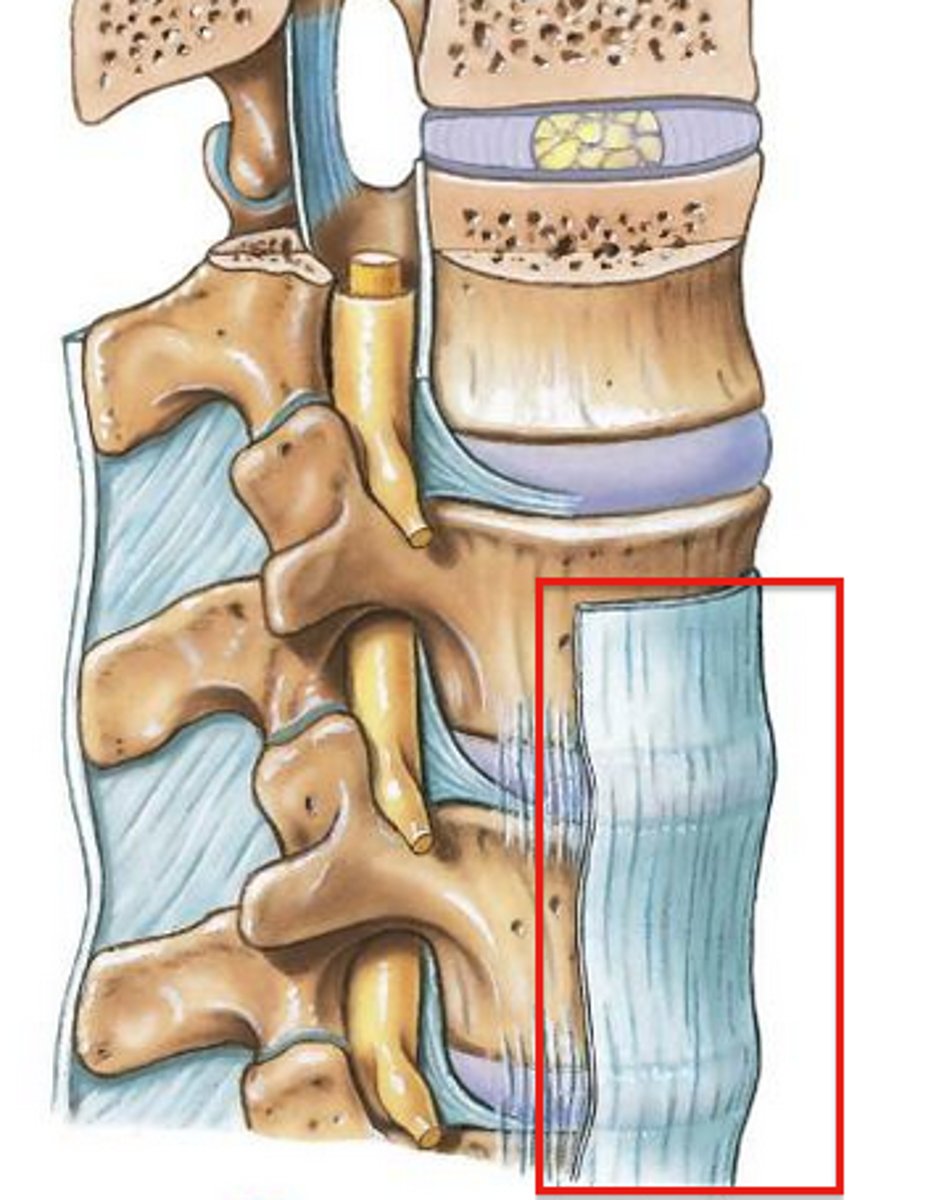
Ligament that lies on the posterior surface of the vertebral bodies, IVD and is WITHIN the vertebral canal from C2 to sacrum
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
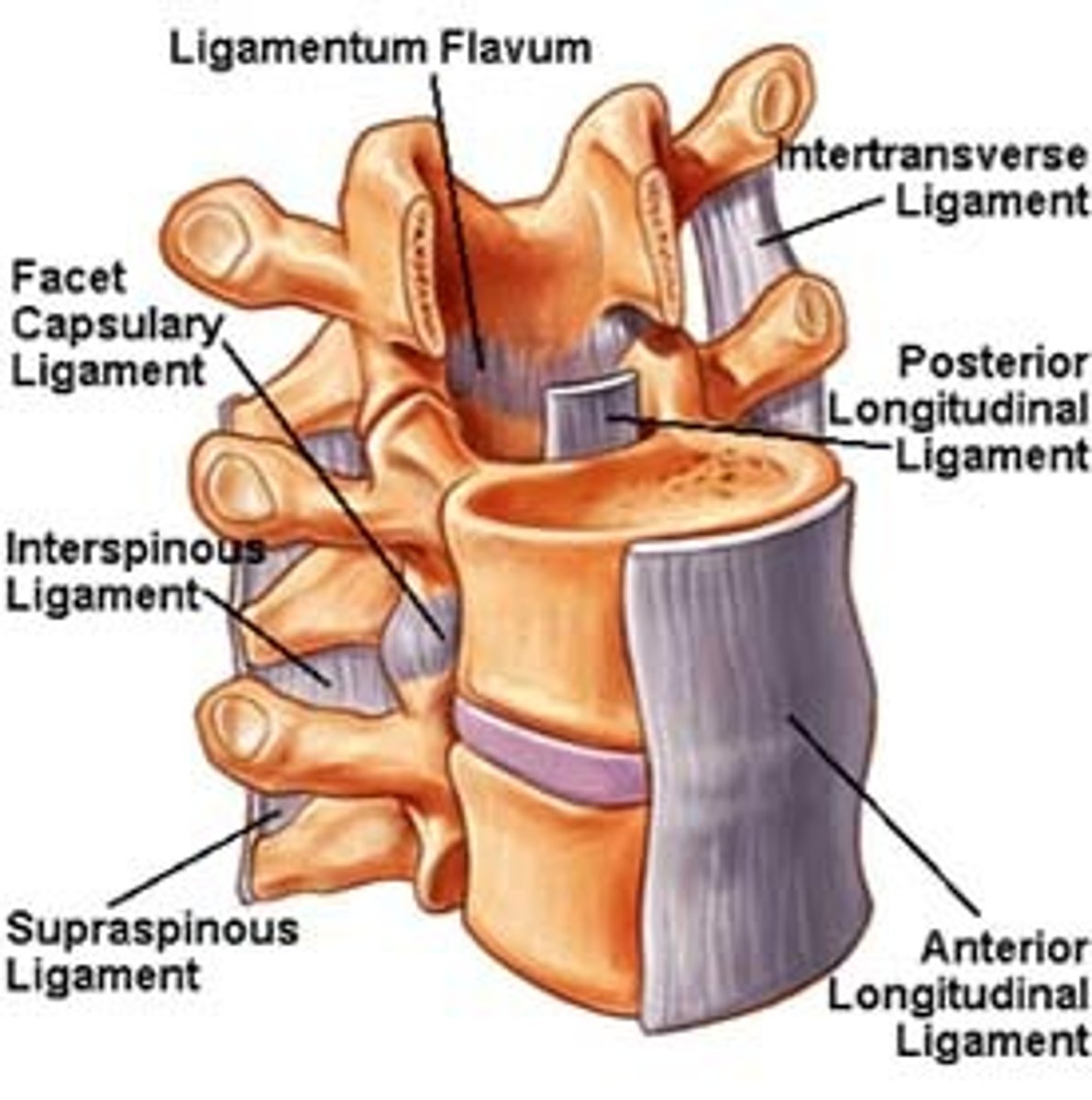
Ligament that is yellow in color that connects laminae of adjacent vertebrae. Prevents excessive separation
Ligamentum Flava

Ligament attaching tips of spinous processes
Supraspinous ligament
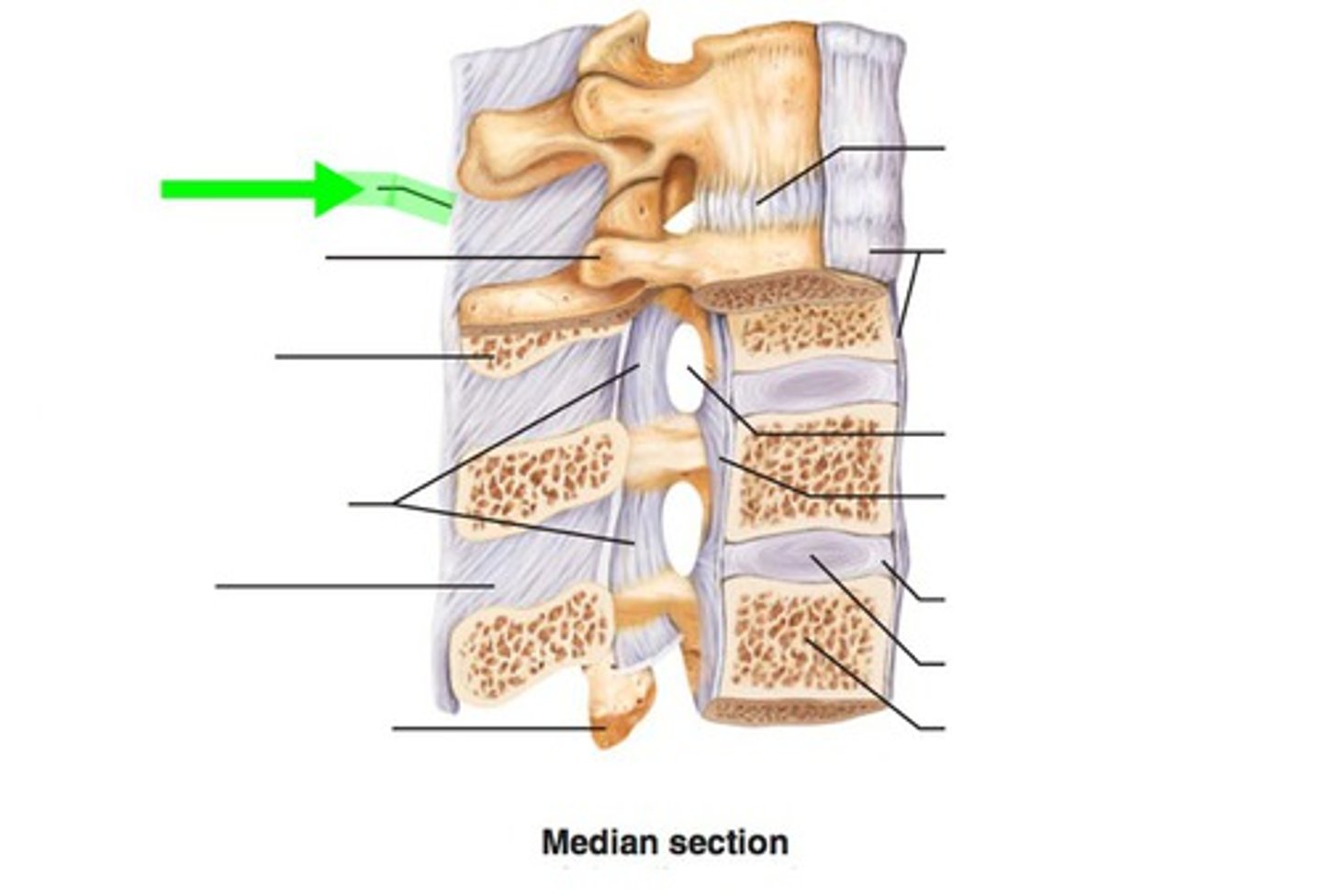
Extension of supraspinous ligament in cervical region as a sheet of fibroelastic tissue that attaches to external occipital protrubence of skill and to tips of all cervical spinous processes
Nuchal Ligament

Membranous bands of ligament that lie deep to supraspinous ligaments, filling space between spinous processes
Interspinous Ligament
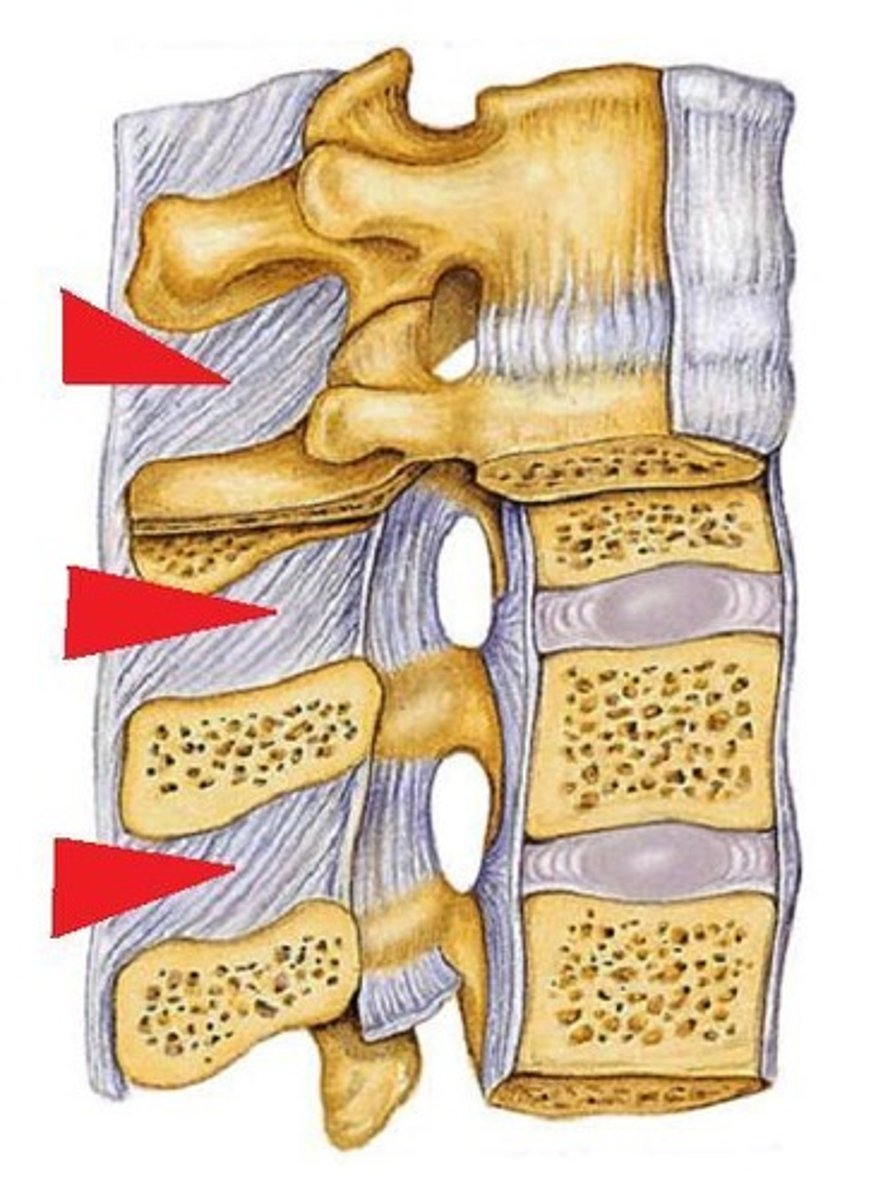
Ligament that connects adjacent transverse ligaments
Intertransverse Ligaments
Ligament that lies posterior to dens and attaches either side to medial tubercles on lateral masses of atlas
Transverse ligament of atlas
Three ligaments comprising the cruciate ligament of atlas
transverse ligament of atlas, superior longitudinal band and inferior longitudinal band
Bilateral, thick cord like ligament that connects tip of dens to the occipital bone on the internal, lateral side of the foramen magnum
alar ligament
Superior continuation of the posterior longitudinal ligament that runs from C2, through the foramen magnum and attaches to the internal surface of the occipital bone. Posterior to cruciate ligament and the median atlantoaxial joint
Tectorial membrane
Attach the anterior and posterior arches of C1 respectively to the margins of the foramen magnum.
Anterior and posterior atlanto-occipital membrane
Provide sensory innervation for pain and proprioception to various parts of the vertebral column including the bones, joints, and ligaments. _______ ______ ___ __ _____ ______ of spinal nerves convey sensory information from the zygapophysial joints. The _____ _____ ______ of spinal nerves convey sensory information from the vertebral bodies, the annulus fibrosus, and the various ligaments of the vertebral column.
Articular branches off the posterior rami, recurrent meningeal branches
The _____ _____ ______ lies in the epidural space (between the dura mater and the vertebral bone) and is formed by paired and interconnected ______ and ______ _____ _____ _____ ___. The relatively large ______ _____ that drains each vertebral body, passes through a foramen in the posterior aspect of the vertebral body and empties into the anterior longitudinal internal vertebral veins. The _____ _____ ____ ____surrounds the external surfaces of the vertebrae and is smaller than the internal plexus, to which it is connected by veins that pass through the intervertebral foramen
internal vertebral plexus,
anterior and posterior longitudinal internal vertebral veins, basivertebral vein, external vertebral venous plexus
Blood supply for thoracic and lumbar regions come from? What about cervical region?
Blood supply branches off from the aorta (posterior intercostal and lumbar arteries). Cervical region is cervical arteries, sacral region is sacral arteries