Muscle Physiology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
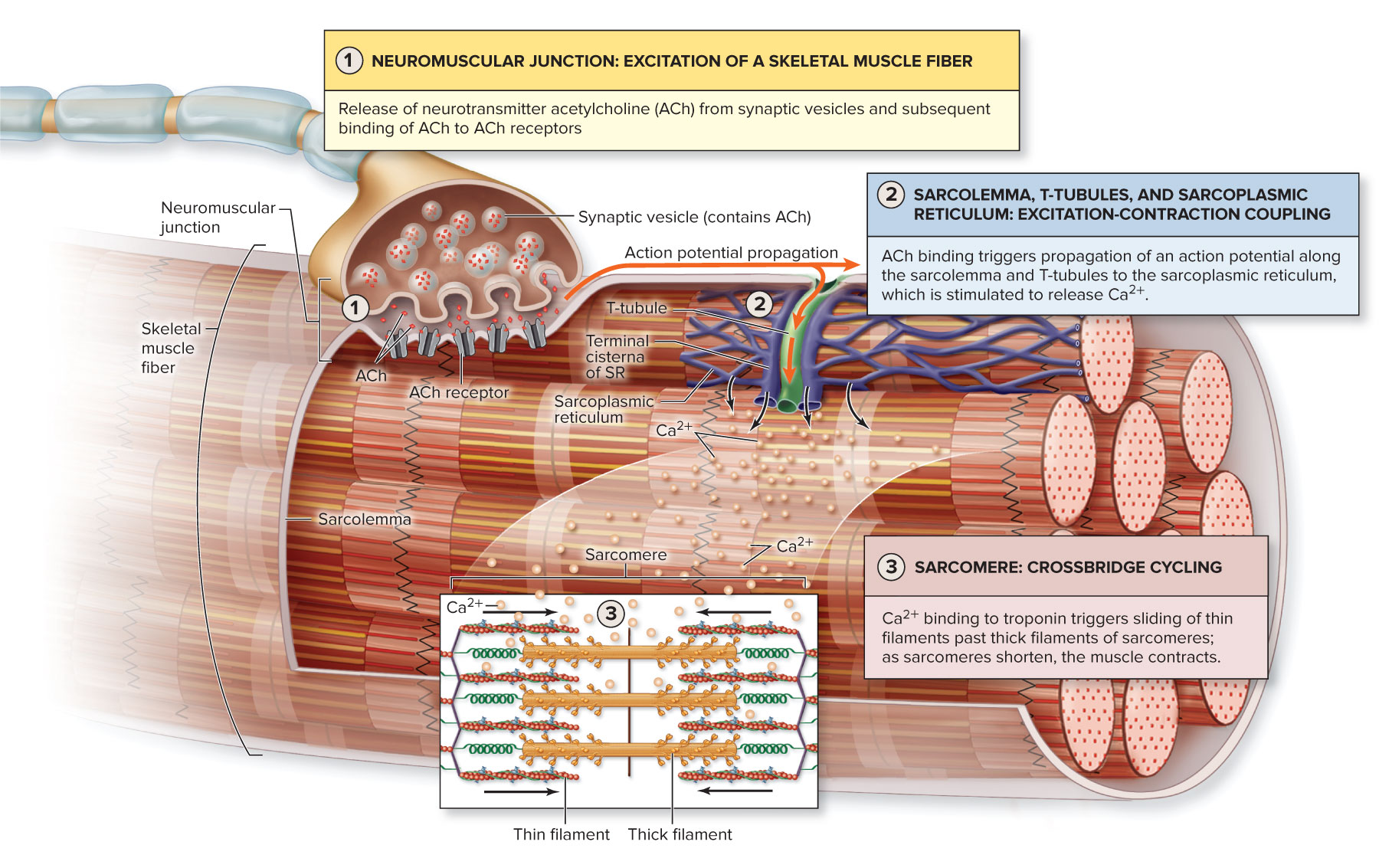
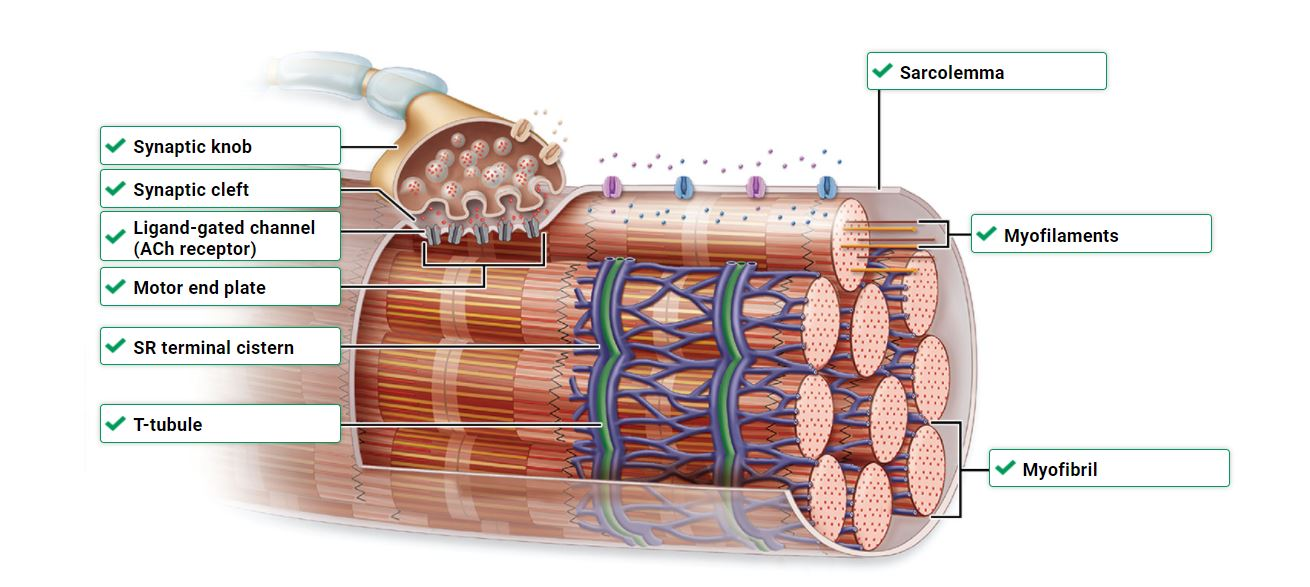
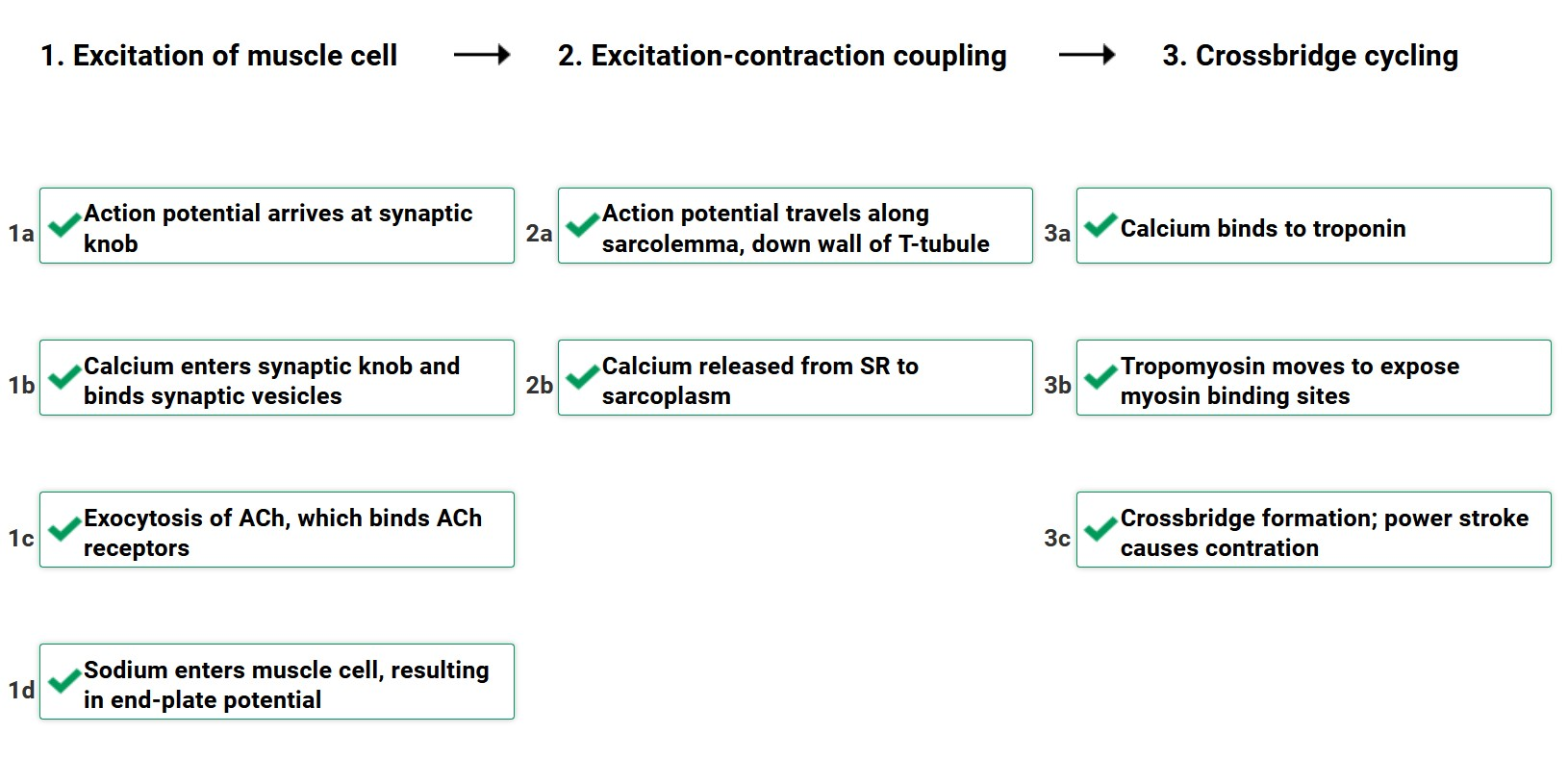
Neuromuscular junction:
1) __ __ travels down axon
2) in axon terminal: __ __ channels open & _ ions diffusion into _
3) __ __ inside axon terminal release _ into motor end plate of muscle fiber
4) ACh diffuses through synaptic cleft of ACh receptors of _ _ ion channels in postsynaptic cell
5) Ligand gated ion channel opens
6) Na+ flows ___, K+ flows __, (more Na+ goes _ than K+ goes _) membrane potential becomes less negative
7) Once membrane potential reaches absolute threshold, an action potential spreads throughout __
action potential, voltage gated Ca+, Ca+, terminal, synaptic vessels, ACh, ligand gated, in, out, sarcolemma
end plate potential
triggering opening of ligand gated Na+ channel
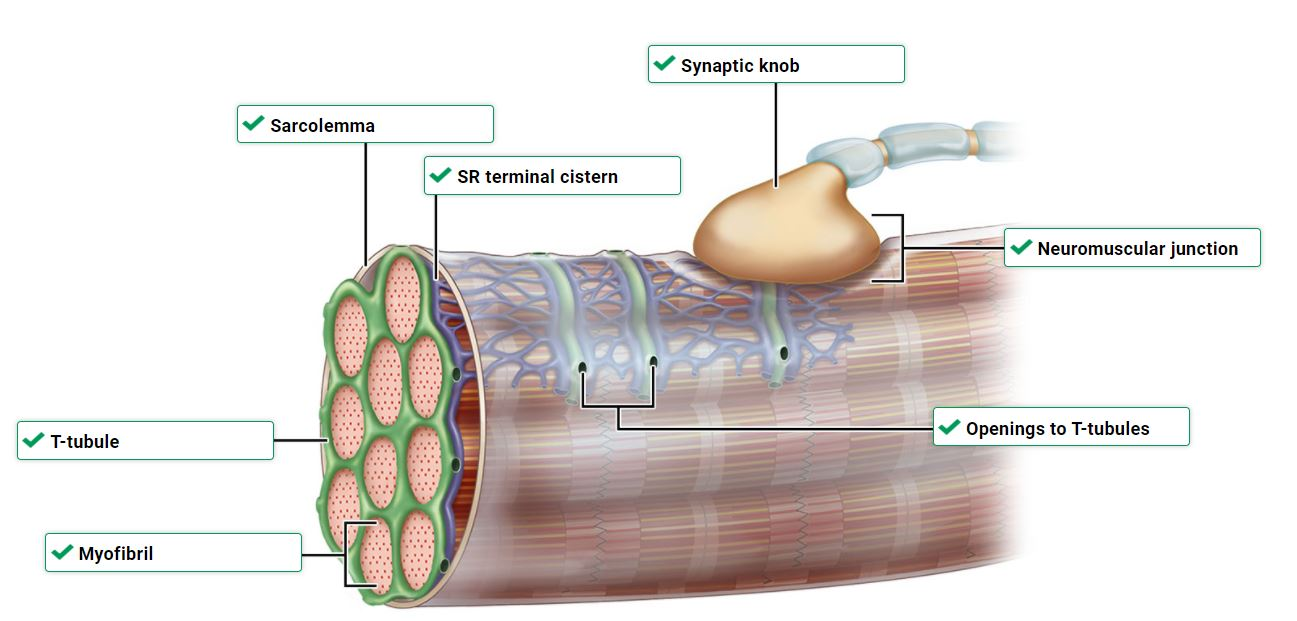
Excitation contraction coupling: when __ ___ spreads through __ and throughout ____ __
SR forms bulges, terminal cisternae. 2 terminal cisternae + 1 t tubule = triad
action potential, sarcolemma, tranverse (t) tubules
Cross bridge cycle:
-takes place in the ___, where thin & thick filaments are located
-release of ___ from SR bind to ___, causing it to change shape. this removes ___, and moves away from actin, revealing actin binding sites
-myosin binds to actin binding site
-myosin performs power stroke with ____ of ATP
-ATP required to ___ binding between myosin head & actin
-ATP on myosin head makes it go back into cocked position
relaxation = _____
sarcoplasmatic reticulum, Ca+, troponin, tropomyosin, removal, break, reuptake of Ca+ back into SR
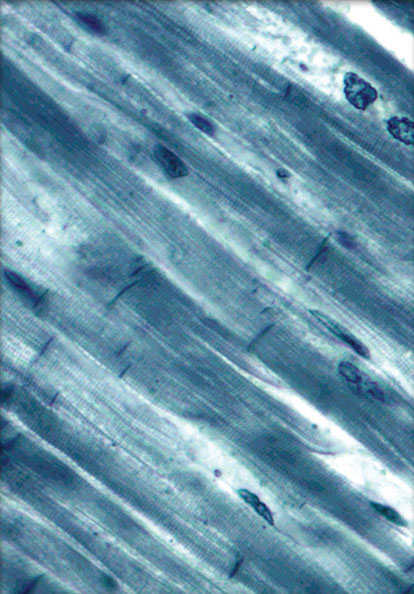
what type of muscle is this?
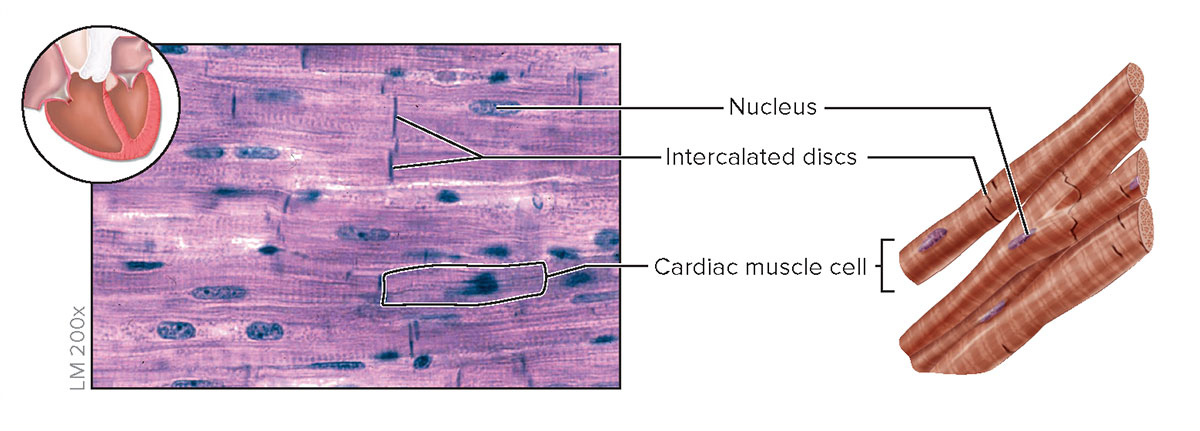
cardiac: short, branched, striated, uninucleated, involuntary
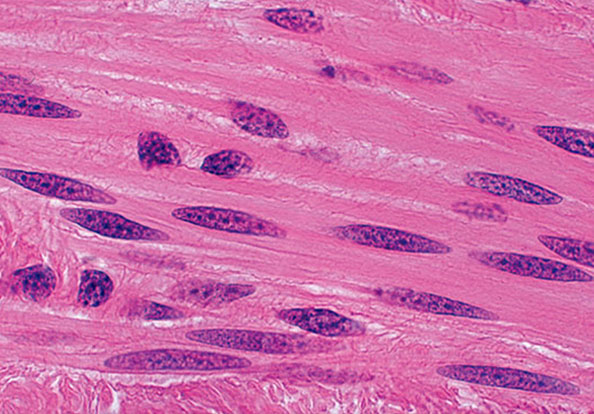
which type of muscle is this?
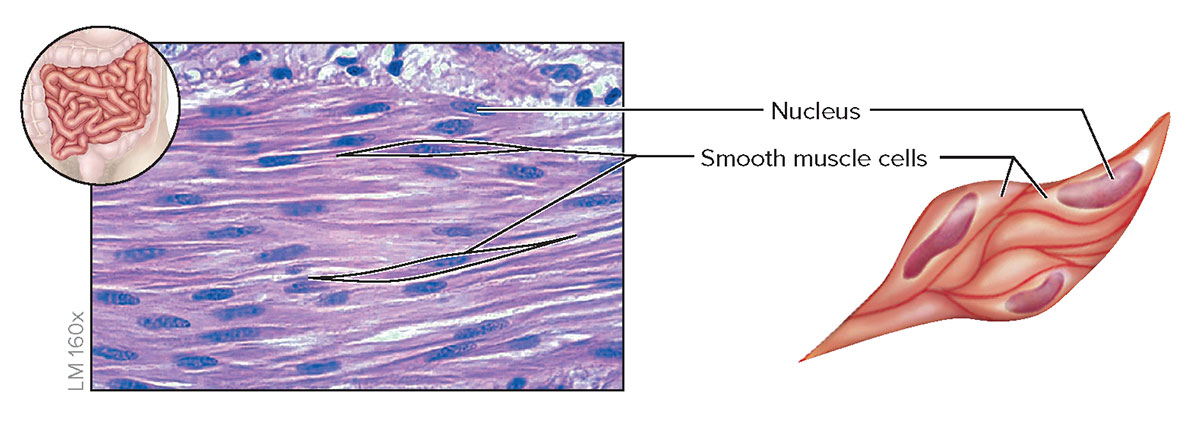
smooth: short, fusiform shape, nonstriated, uninucleated, for involuntary movement
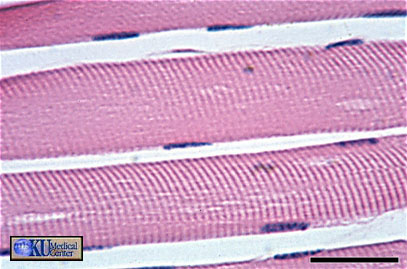
which type of muscle is this?
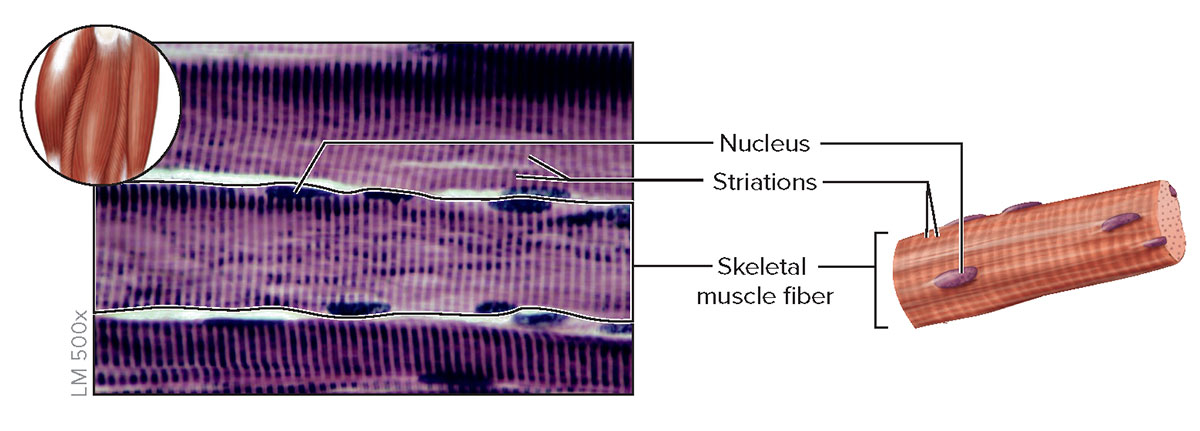
skeletal: long, cylindrical, striated, multinucleated, voluntary movement
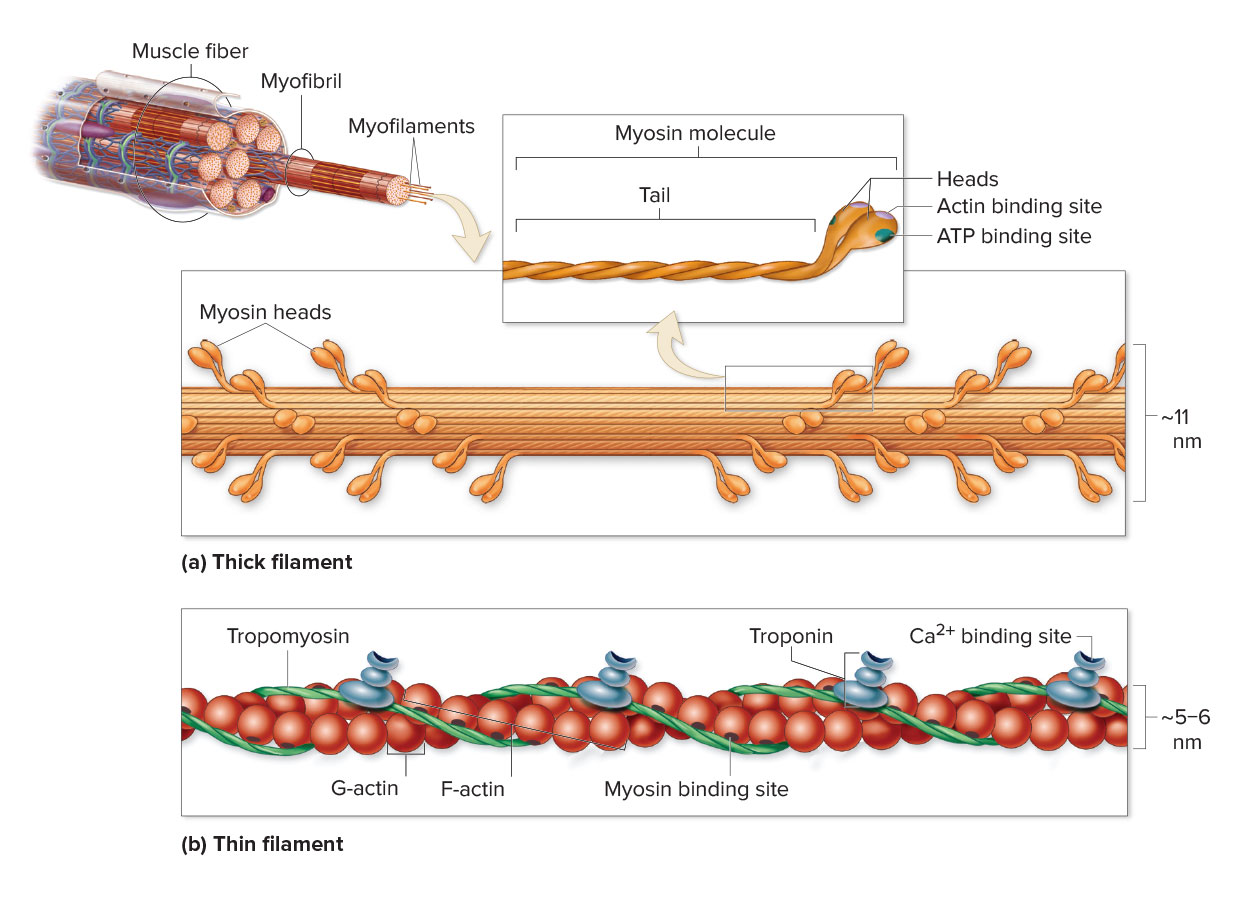
anatomy of muscle fiber:
a band:
z line:
h zone:
i band:
entirety of thick filaments, entirety of thin filaments, only thick filaments (no overlap with thin filaments), only thin filaments
*The end-plate potential causes ____ near the NMJ to reach threshold, generating an action potential (AP) that propagates across the ___.
voltage/ ligand-gated channels, sarcolemma
The network of T-tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum ensures ____.
all myofibrils respond in unison
What would happen if, during cross bridge cycling, ATP "ran out" but sarcoplasmic calcium concentration remained high?
myosin heads would be unable to detach from actin & muscle cell would be unable to relax
Botulinum neurotoxin blocks exocytosis (release) of ACh at the neuromuscular junction. As a result, what event cannot occur?
Formation of an end-plate potential (depolarization of muscle fiber membrane at neuromuscular junction)
Electrical stimulation:
Role of electrode: ___
Role of transducter: ___
At 0.2 volts, 0 g of force was elicited bc threshold was not reached
electrically stimulate muscle, measure force of muscle contraction,
what’s the difference between threshold stimulus & maximum stimulus?
Threshold stimulus elicits ___ muscle response
then, from threshold to maximum stimulus, _____
Maximum stimulus elicits ____
weak, muscle will increase in response until the max, same amount of force (even when stimulus is surpassed)
Effects of stretch on muscle tension: stabilizing proteins:
elastic filaments made of protein called titin, that run through core of thick filaments and attach them to z disks on either end. titin resists overstretching
*The amount of tension generated by a contracting muscle is influenced by the: ___ & ___
-length of muscle or how much it was stretched just before stimulation
-frequency of stimulus, with stimuli arriving close together producing stronger contractions than less frequent stimuli
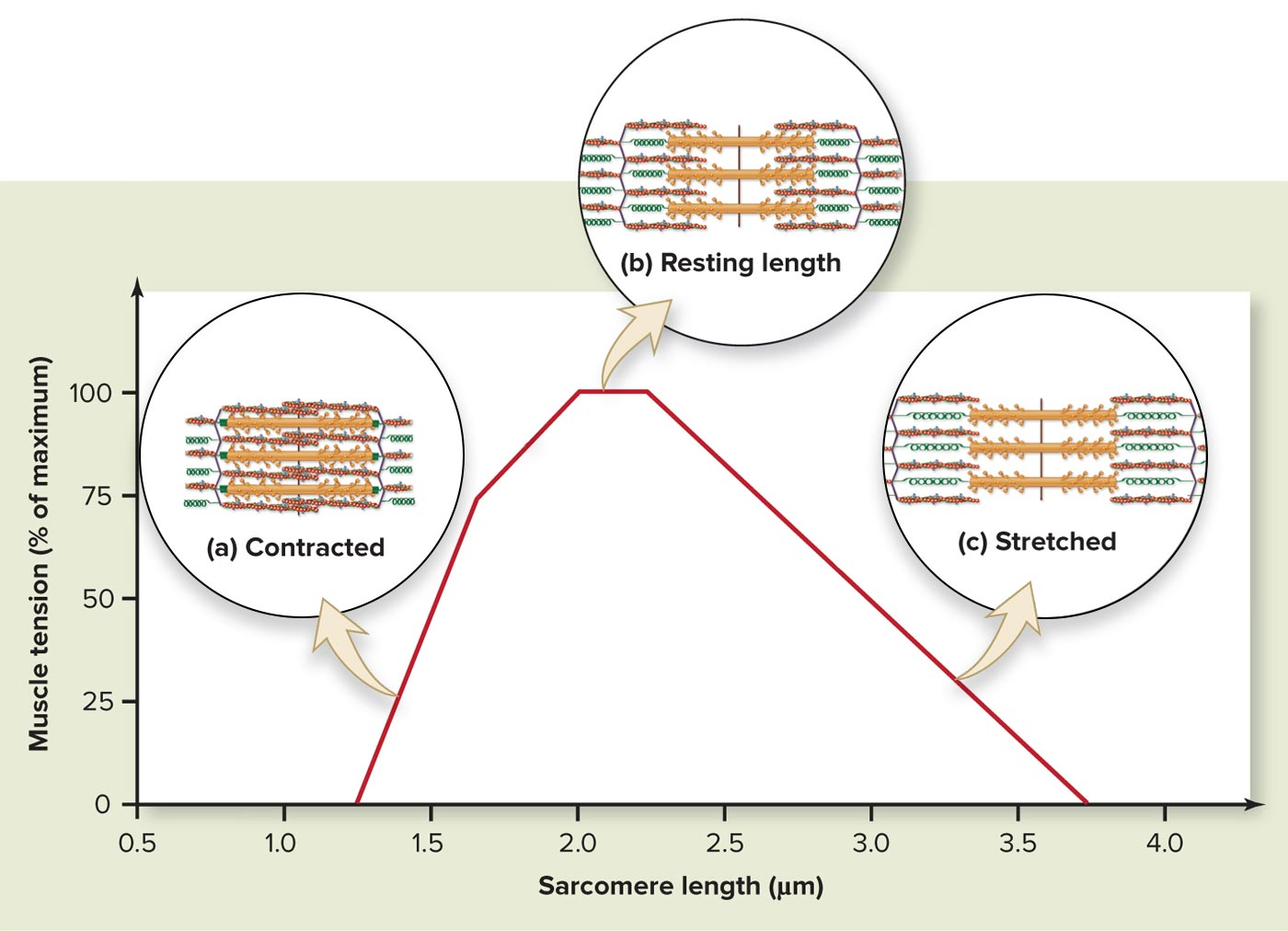
Muscle Length-Tension Relationship
-If a muscle is already contracted, ___
-There is an optimal length where overlap is maximized. This length is where a muscle can generate the most tension.
-If a muscle is overstretched, ____
-it cannot contract much farther before thick filaments butt up against the Z discs and stop. The contraction would be brief and weak
-there is little overlap between the thick and thin filaments. Myosin cannot get a grip on the thin filaments and the contraction is weak
Muscle Length-Tension Relationship:
x axis should be:
y axis should be:
length, tension
*Active vs passive tension:
-Active tension: ____
-Passive tension: ___
-force generated by the thick filaments pulling on the thin filaments (cross-bridge cycling)
-occurs during stretch beyond the normal range of motion, use of titin, collagen, and elastin in sarcomere (essentially stretch using connective tissue & elastin proteins)
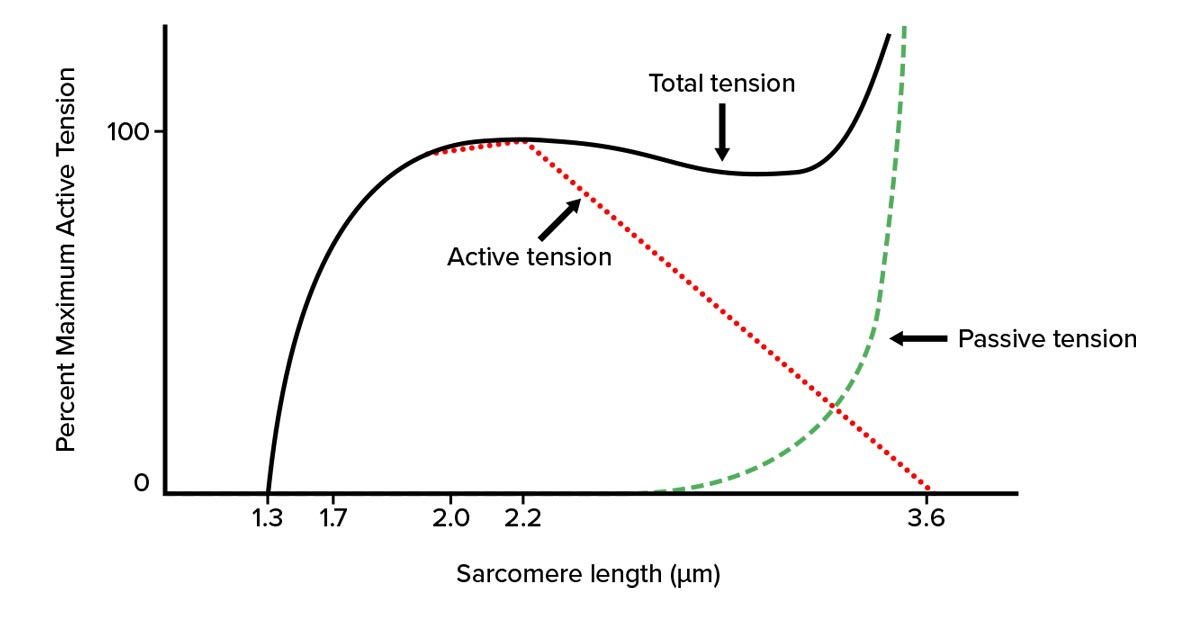
*At sarcomere length 2.0, __ __ is responsible for total tension produced.
At sarcomere length where thick & thin filament overlap is minimal/ absent, ___
active tension, passive tension (stretch using connective tissue & elastin proteins) contributes significantly to total tension
Stimulus Frequency and Muscle Tension:
-In skeletal muscle, the refractory period is brief (a few milliseconds) and the muscle can be stimulated in quick succession. The amount of tension generated depends on the __ ___ ___.
-A single stimulation results in a __ ___ –one cycle of __ followed by ____.
-If another signal arrives before the muscle has completely relaxed, the next twitch "rides piggyback" on the previous one and their contractile forces are combined. This response is called ___.
-As the frequency of stimulation increases, a fluttering, sustained contraction called __ ___ occurs.
-Further increases in frequency result in __ ___ –a smooth, sustained, maximal contraction. This is achieved at unnaturally high stimulus frequencies produced only in the lab.
frequency of stimulation, muscle twitch, contraction, relaxation, summation, incomplete tetanus, complete tetanus
.
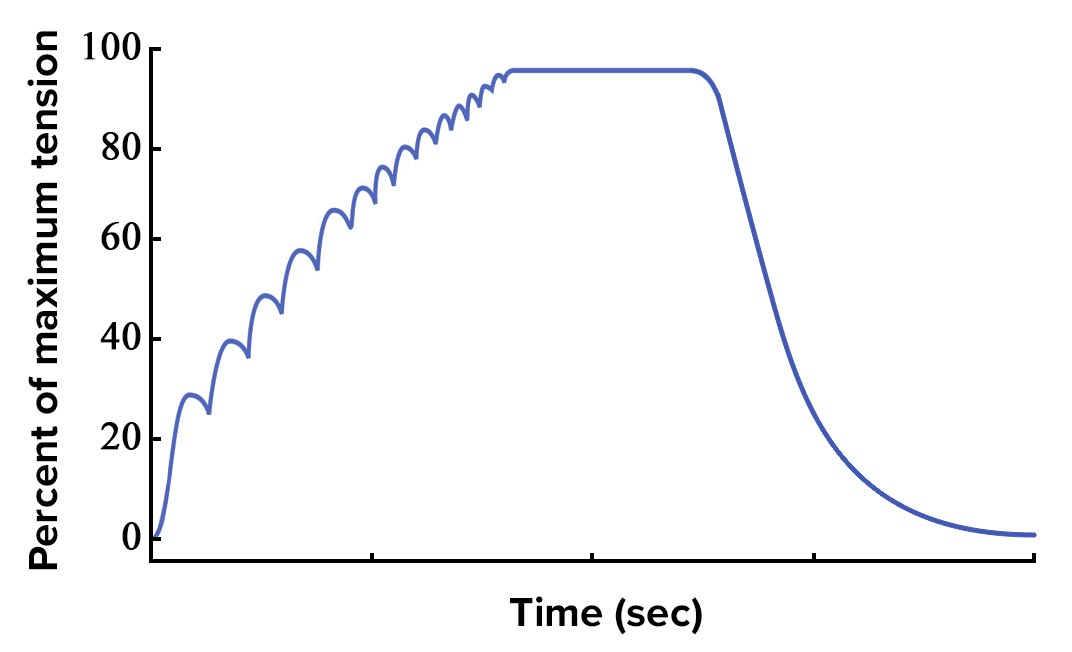
what does this graph represent?
slowly and steadily increasing rate of stimulation generated higher percentage of muscle tension
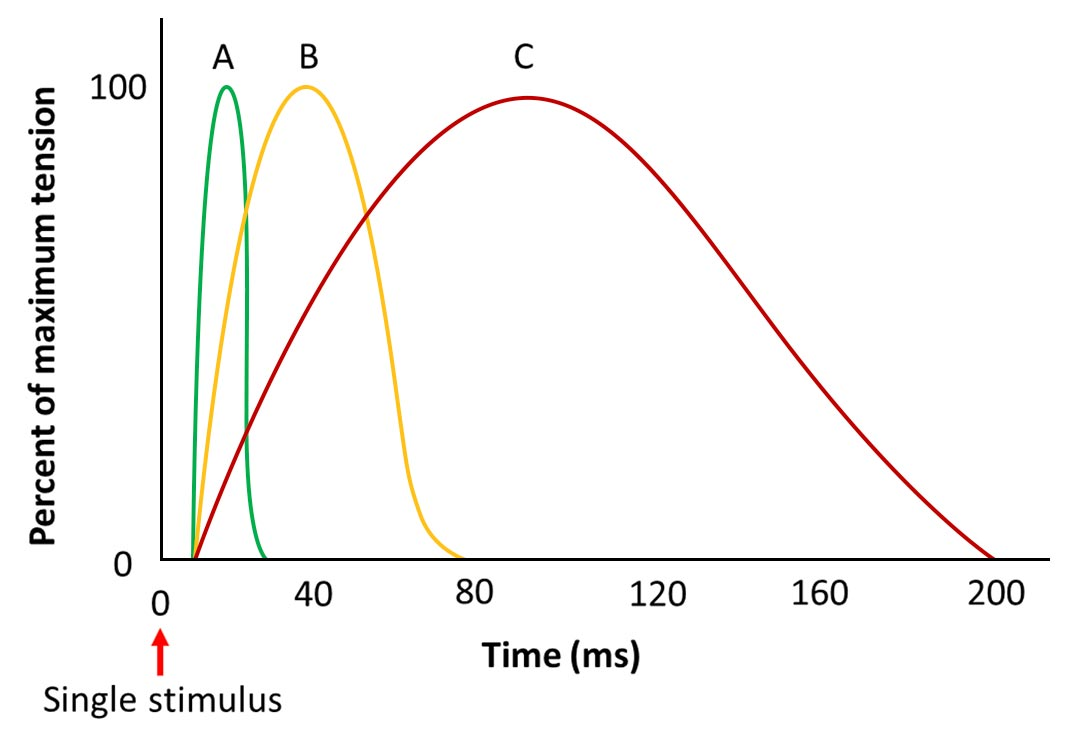
which will be able to reach complete tetanus?
muscle c: The one that reaches complete tetanus will be the one that has the longest recovery time because the longer they take to recover, the more incomplete tetanus they’ll complete and eventually reach complete tetanus
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
t tubule
Membranous channel extending inward from muscle fiber membrane
sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm of a muscle fiber
perimysium
Layer of connective tissue that separates a muscle into small bundles called fascicles
sarcolemma
Plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
epimysium
Layer of connective tissue that surrounds a skeletal muscle