Real poop v2
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Define Absolute Threshold
the minimum amount of stimulation needed for a person to detect a particular stimulus half of the time.
What would be the absolute threshold for a hearing test?
x
Sensation
occurs when our sensory organs receive stimulus energies from the environment and convert them into the electrical energy of the nervous system.
Transduction
transformation of sensory stimulus energy from the environment into neutral impulses
Perception
including organizing, constructing, and interpreting sensory information—all to form a representation inside the brain of what it thinks is on the outside.
What are sensory and perceptual adaptations?
Sensory - wearing clothes all-day
Perceptual - ability to adjust to an inverted perception field
Examples of sensory and perceptual adaptation
nose blindness, itchy sweater in the morning
Wavelength
Amplitude
Purity
Three physical properties of light
Law of effect
actions that are followed by positive outcomes are strengthened, and behaviors followed by negative outcomes are weakened.
wavelength
width of wave and hue
amplitude
height of wave and brightness
purity
how many different wavelengths comprise the light.
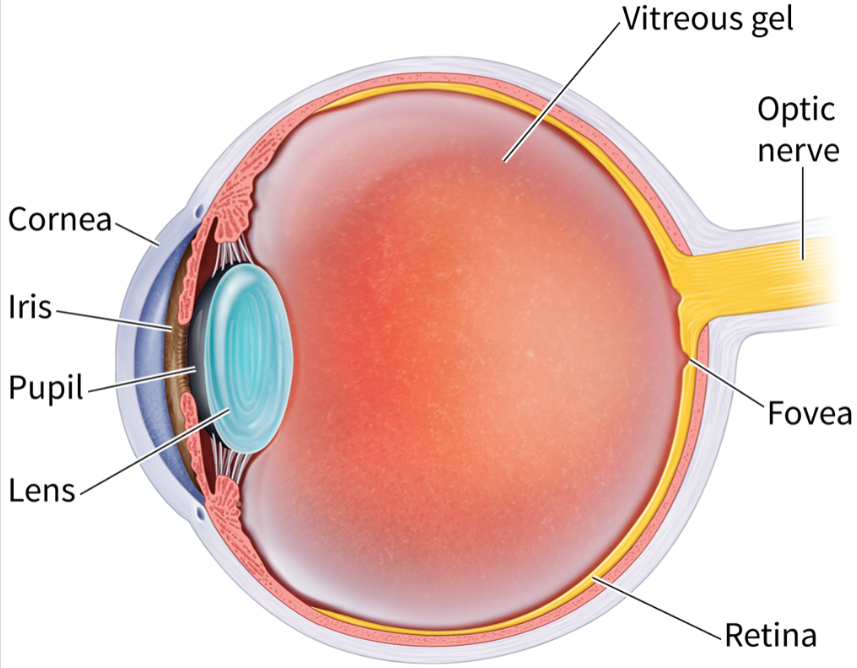
major structures of the eye
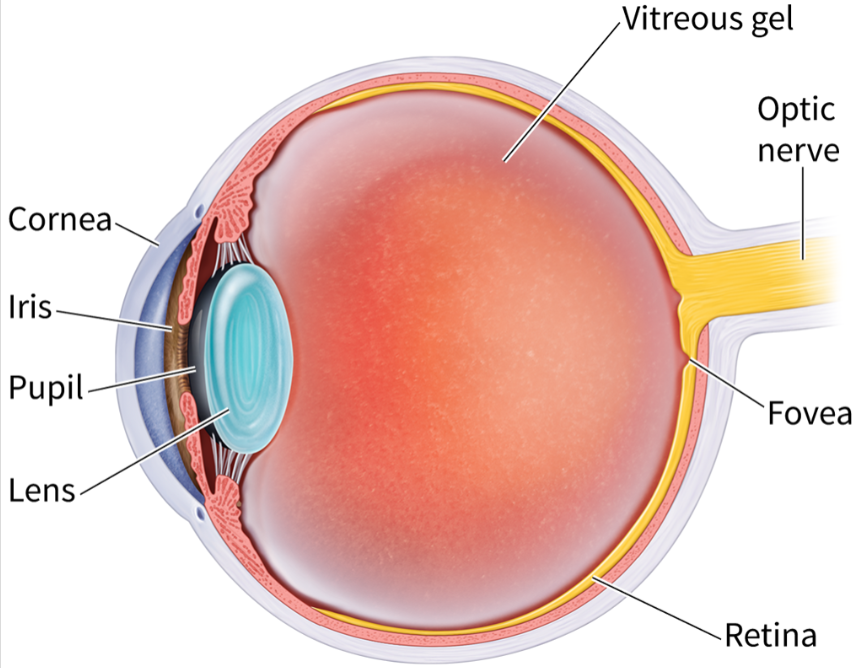
The order light enters the eye
Cornea
Pupil/Iris
Lens
Retina
Trichromatic theory
(Humans are trichromatic) proposes that our ability to perceive color is based on the presence of three types of cone cells in the retina. Each type of cone is sensitive to a different range of wavelengths corresponding to red, green, and blue light
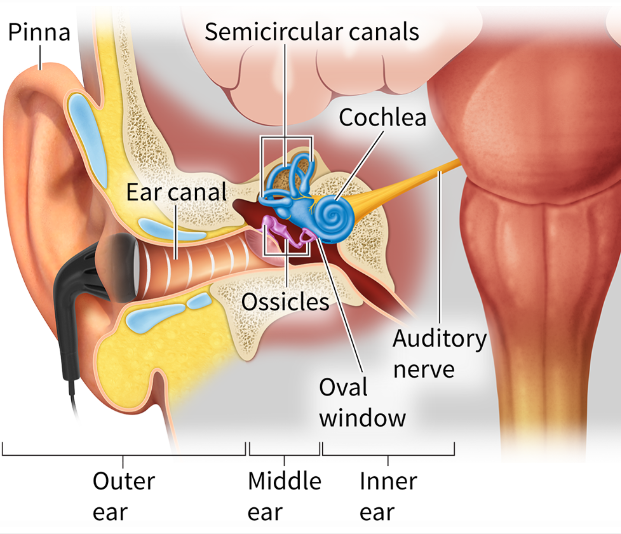
Know the major structures of the ear
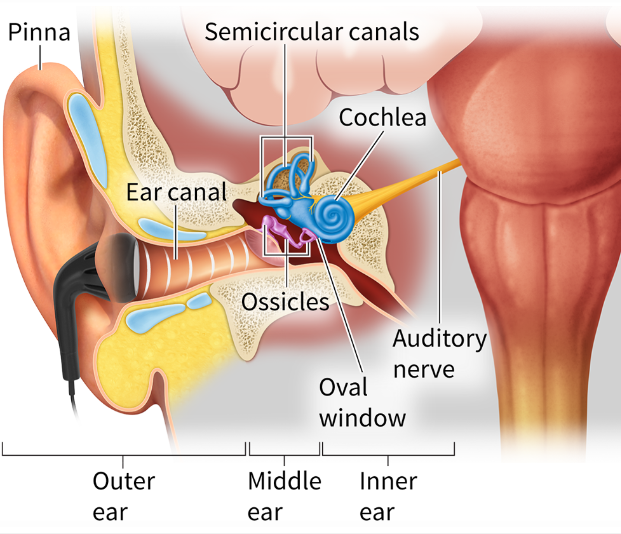
Rather than using a mallet to strike a drum, in your ear, the drum moves a mallet to amplify the air pressure waves.
Pay special attention to the anatomy and function of the
middle ear: how might the eardrum respond to changes in altitude or air pressure?
How does the
eardrum connect to and move the ossicles
These three bones—the hammer, anvil, and stirrup—form a bridge between the eardrum and another membrane called the oval window.
What is the tactile sense?
Touch sense
What are the 4 different types of tactile receptors that give rise to skin sensations?
somatosensory system
nociceptor
thermoreceptors
primary somatosensory cortex
Consciousness
The moment-by-moment awareness of the external environment as well as one’s thoughts, feelings, etc.
What is the Inverted Spectrum Problem?
Experiencing consciousness in another way
Selective Attention
Act of focusing one’s awareness onto a particular aspect of one’s experience, excluding everything else.
Examples in selective attention
tuning out distractions while focusing on an exam.
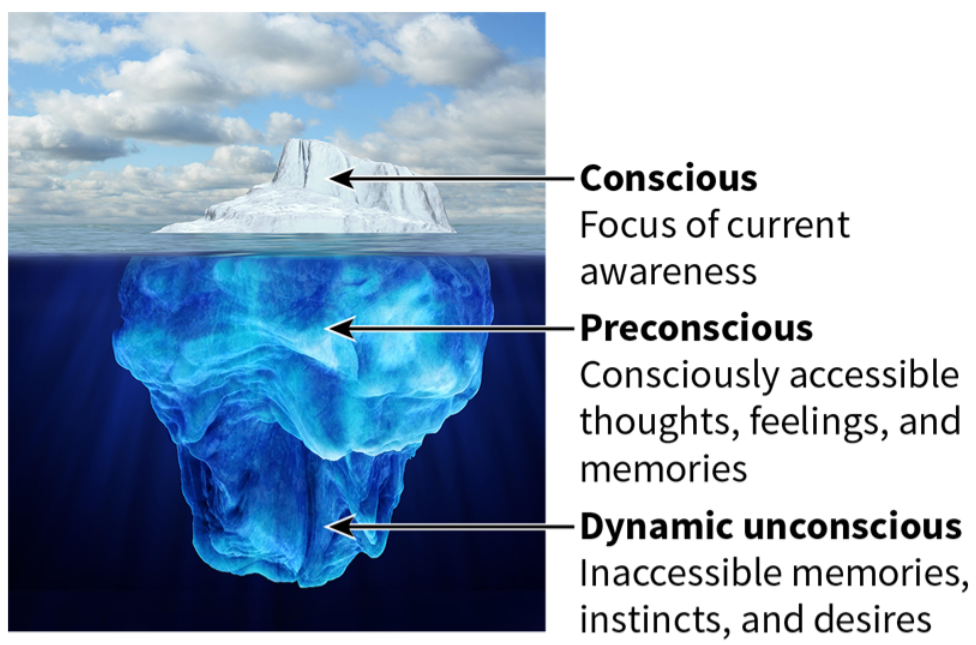
Sigmund Freud’s model of human consciousness as compared to an iceberg.
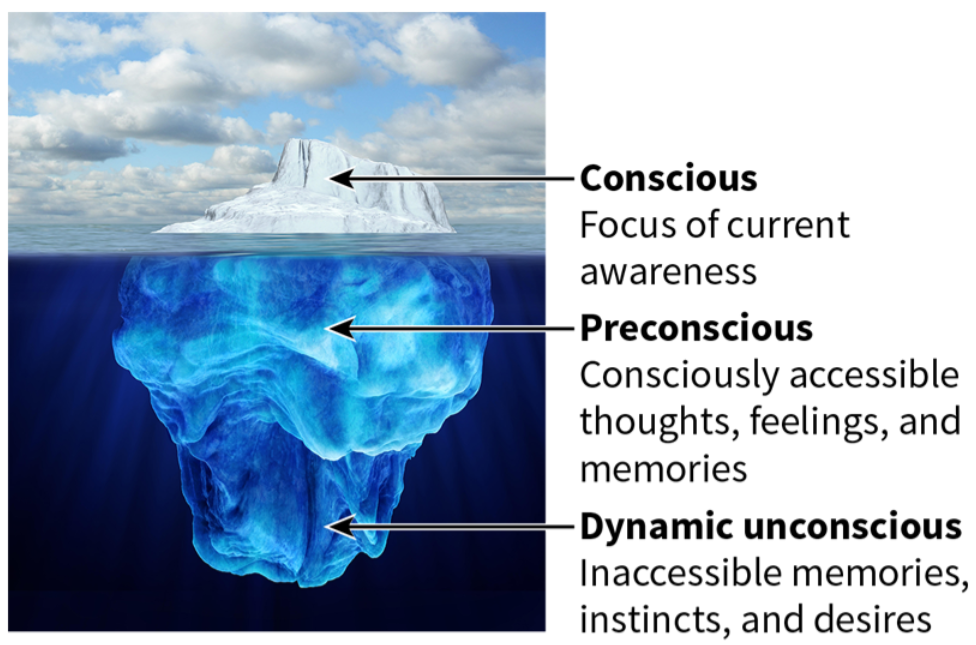
Conscious in Sigmund Freud’s Model
Focus of current awareness
Preconscious in Sigmund Freud’s Mode
Consciously accessible thoughts, feelings, and memories
Dynamic Unconscious in Sigmund Freud’s Model
Inaccessible memories, desires, and instincts
Change Blindness
when you fail to notice a change in visual stimulus
What is the Default Mode Network of the brain? When is it likely to be active?
A region of the brain that is alert and aware but not focused on anything particular, mind wandering
What does the global workspace hypothesis state?
conscious awareness arises from synchronized activity, from across various brain regions, that is integrated into coherent representations of an experience
Define REM Sleep
rapid eye movement, similar brain activity to being awake, faster breathing and heart, can’t move skeletal muscles, dreams
What is REM rebound?
The tendency to spend more time in REM sleep if deprived of it on previous nights
Why is REM sleep sometimes called Paradoxical Sleep?
because, despite the heightened activity in the brain’s motor cortex, the muscles of the body are completely relaxed
What does it mean that humans are diurnal animals?
Most aroused during the day
What was Freud’s theory of dreaming?
believed that dreams were thus a window into unconscious conflicts and could be analyzed to help people with psychological problems.
Define Manifest
According to Sigmund’s theory, the visible surface content of a dream or behavior disguises the hidden content
Latent Content
The hidden drives and wishes expressed in dreams and behaviors but it in a disguised form
Depressants –
decrease arousal, reducing activity of the CNS. Alcohol is most commonly used.
Define Withdrawal
a set of unpleasant symptoms caused by the sudden stoppage or dosage drop of long-term drug use
What are some symptoms of withdrawal?
E.g. headache, irritability, anxiety.
3 parts of the ossicles
hammer,
anvil
stirrup
Associative Learning
involves making connections between different events and our behavioral responses to them—dark clouds lead to rain and umbrellas keep us dry.
Habitual Learning
an organism’s reflexive response to a repeated stimulus becomes weaker
Sensitization Learning
an organism’s reflexive response to a repeated stimulus becomes stronger.
Classical Conditioning
a passive form of associative learning where an involuntary response—such as a reflex—becomes associated with a new stimulus
Operant Conditioning
a second form of associative learning in which a learner makes associations between a voluntary behavior and its consequences and makes a behavioral change as a result.
Primary Reinforcers (w examples)
tend to be innately satisfying because they meet some biological need and are effective regardless of a person’s prior experience. They include food, a drink when thirsty, warmth when cold, or even sex
Secondary Reinforcers (w examples)
acquiring value through experience because of their association with primary reinforcers (When you give your dog a food treat and tell him "good boy, treat is primary and the verbal expression is secondary)
Social learning theory
Observational learning extends beyond the imitation of simple actions to the learning of complex skills and social behaviors.
4 components of Social Learning Theory
Attention
Retention
Motor reproduction
reinforcement
What did Albert Bandura observe during the Bobo Doll Study? What was the outcome of this
study?
Bandura observed that children who watched an adult model behave aggressively towards a Bobo doll were more likely to imitate that aggressive behavior themselves.
What is meant by Insight learning….the “ah ha!” moment?
occurs when a solution to a problem suddenly comes to mind. Chimpanzees, like humans, appear to be able to learn by insight
Neutral Stimulus (NS)
A stimulus that initially does not elicit any intrinsic response. For example, a bell ringing before conditioning.
Acquisition
s the initial learning of the US-CS link in classical conditioning. This is the phase where the pairing of the US and the neutral stimulus is introduced, such as the pairing of the food and the bell.
Extinction
whereby the CR is weakened in response to the CS if it is frequently presented in the absence of the US.
bell rung but no food would be brought out, no more salivating
Spontaneous
recovery is the reappearance of an extinguished conditioned response after an interval of time.
; for what type of associations is the amygdala important for?
is critical for learning fear responses. It brings together information regarding a CS (sound) and US (e.g., painful shock) and connects with other brain regions that control various behavioral and endocrine responses of the unconditioned response.
Non-Associative Learning
which involves changes in how much or how little we respond to a single event or stimulus with experience
Unconditioned Stimulus (US):
A stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a response without any prior learning. For instance, food causing a dog to salivate.
Unconditioned Response (UR):
The natural, unlearned reaction to the unconditioned stimulus. In the example above, the dog’s salivation in response to the food.
Conditioned Stimulus (CS):
A previously neutral stimulus that, after being associated with the unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response. For example, the bell ringing after it has been paired with the presentation of food.
Conditioned Response (CR):
The learned response to the previously neutral stimulus, which is now the conditioned stimulus. In this case, the dog’s salivation in response to the bell ringing