Control of Gene Expression in Bacteria: Lac Operon Mechanisms and Regulation bio112 lect 9
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is gene expression?
Gene expression occurs when a protein or other gene products is synthesized and is active in the cell.
What are the three main mechanisms of gene regulation?
Transcriptional control, translational control, and post-translational control.
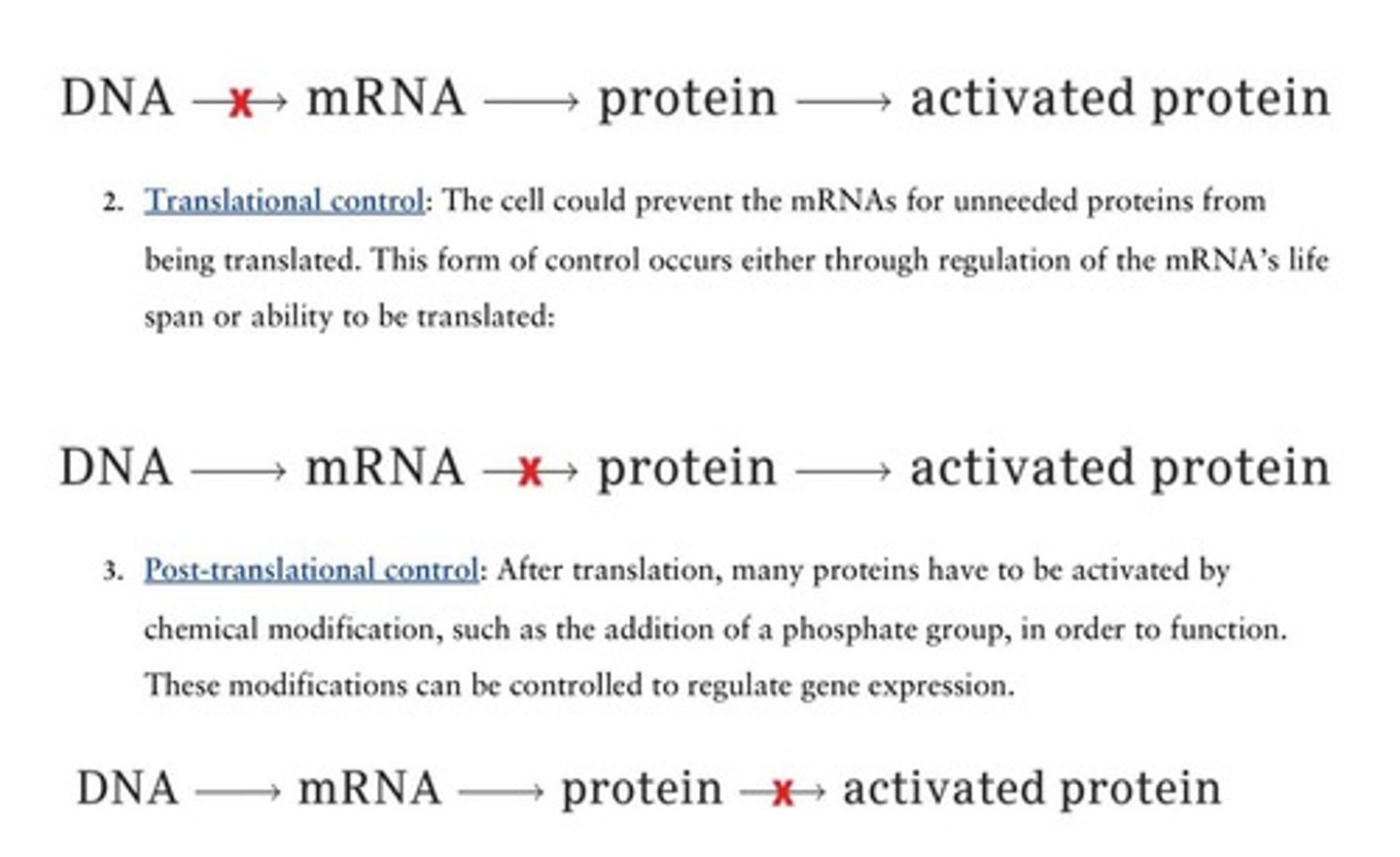
What is transcriptional control?
Control of gene expression at the DNA to mRNA stage, preventing mRNA synthesis.
What is translational control?
Control of gene expression at the mRNA to protein stage, preventing translation.
What is post-translational control?
Control of gene expression at the protein stage, activating or inactivating existing proteins.
Which mechanism of gene regulation is the most efficient in resource use?
Transcriptional control is the most efficient because it stops the process at the earliest point.
Which mechanism of gene regulation provides the fastest response?
Post-translational control provides the most rapid response.
What are constitutive genes?
Genes that are transcribed at all times.
What are regulated genes?
Genes that can be either induced or repressed, with variable levels of expression.
Who studied the regulation of lactose metabolism in E. coli?
Jacob and Monod in the 1950s and 60s.
What is the preferred sugar for E. coli for ATP production?
Glucose is preferred over lactose.
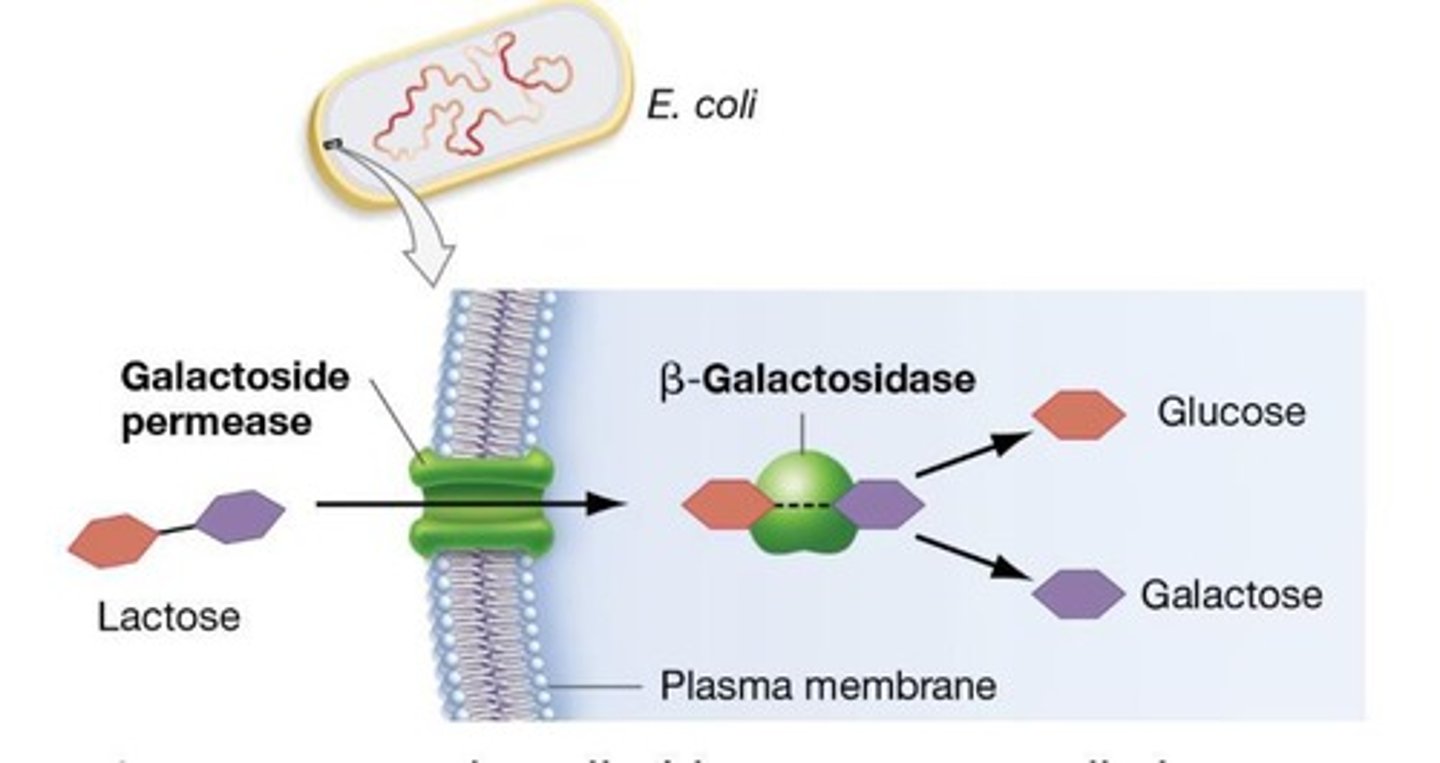
What enzyme is produced when lactose is present in E. coli?
β-galactosidase is produced when lactose is present.
How does glucose affect the regulation of the β-galactosidase gene?
Glucose inhibits the expression of the β-galactosidase gene when it is present.
What are the three types of lactose metabolism mutants in E. coli?
Mutants that affect lactose transport (galactoside permease), lactose breakdown (β-galactosidase), and regulatory functions (LacI).
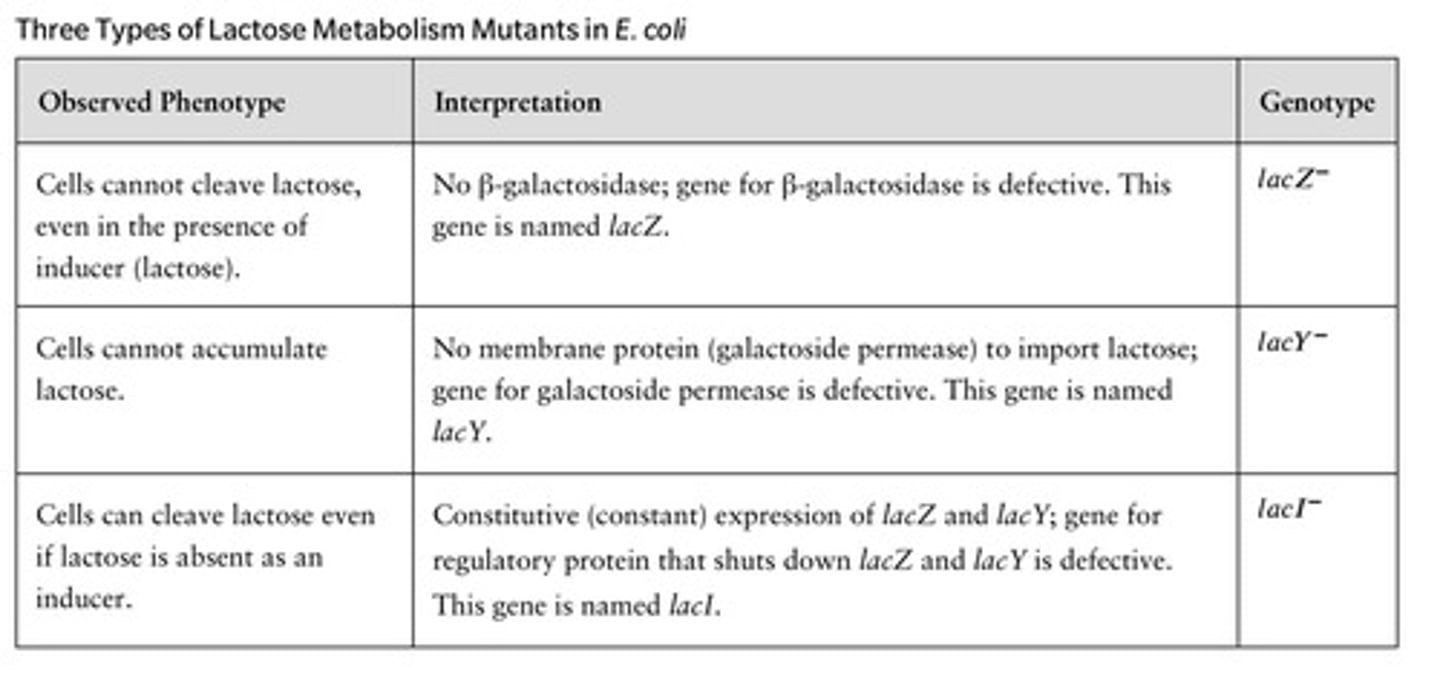
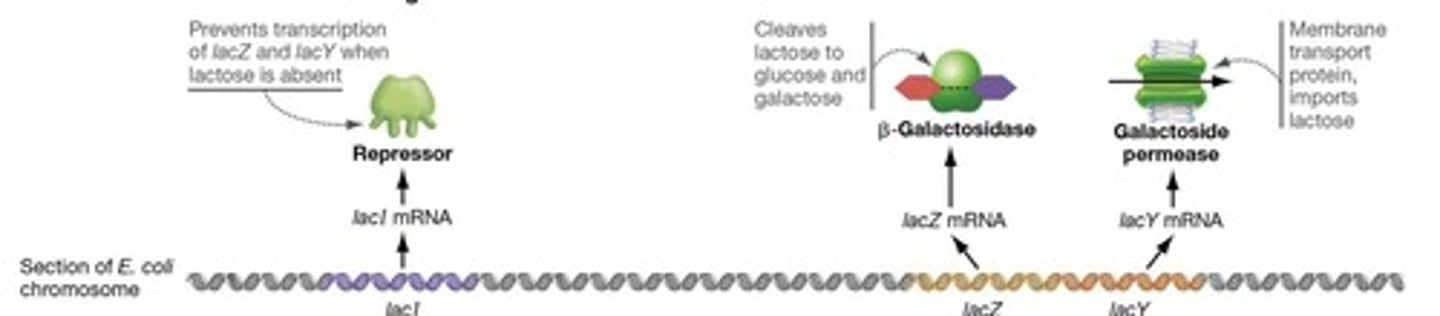
What is the function of the LacZ gene?
LacZ codes for the enzyme β-galactosidase involved in lactose metabolism.
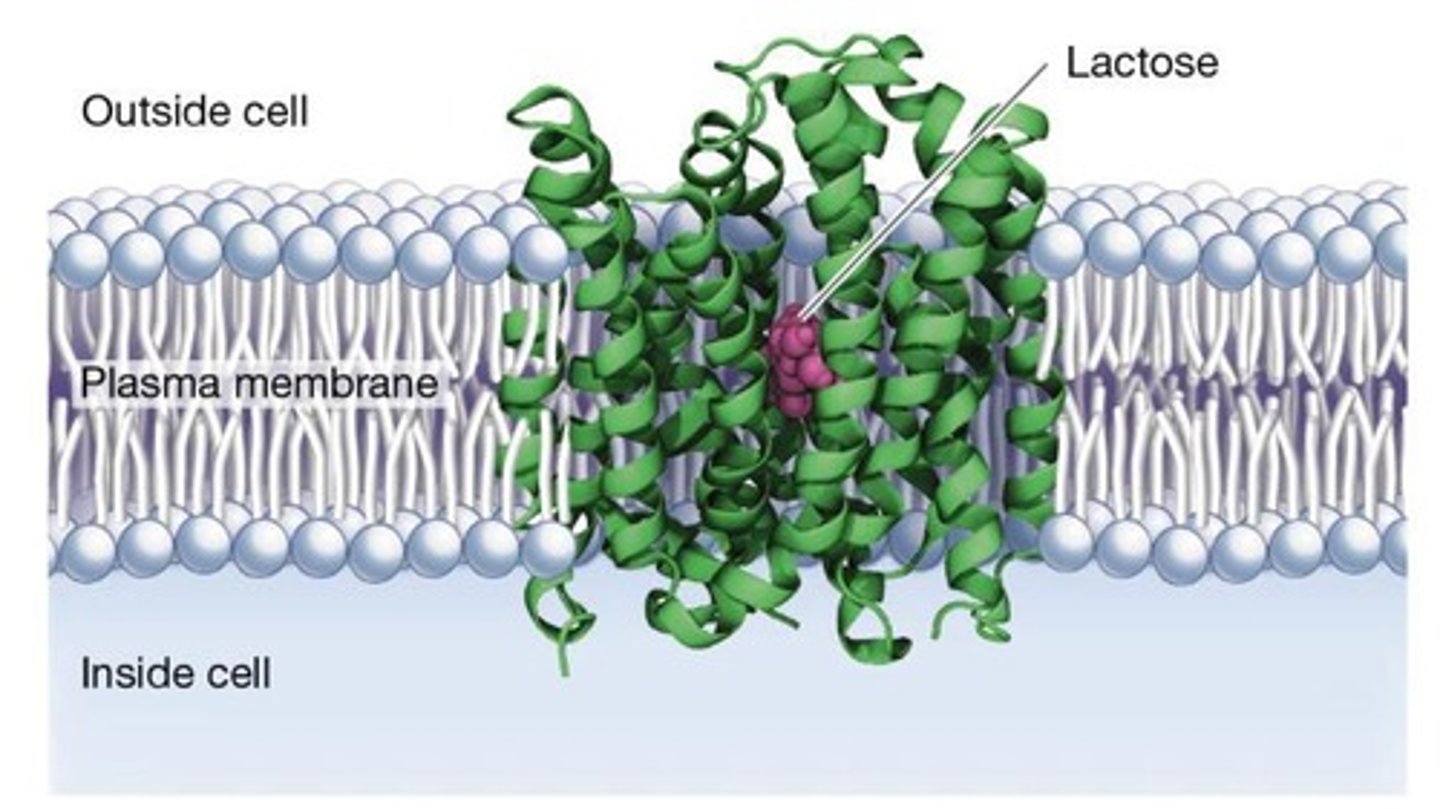
What is the function of the LacY gene?
LacY codes for the membrane protein galactoside permease, which transports lactose into the cell.
What role does the LacI gene play in gene regulation?
LacI produces a repressor protein that inhibits the expression of LacZ and LacY when lactose is absent.
What happens to LacZ and LacY expression when lactose is present?
The expression of LacZ and LacY is induced when lactose is present.
What is negative control in gene regulation?
Negative control occurs when a repressor protein binds to DNA and shuts down transcription.
What is positive control in gene regulation?
Positive control occurs when a regulatory protein enhances transcription.
What is the significance of variations in gene expression?
Variations allow cells to respond to changes in their environment.
What is the role of environmental signals in gene expression?
Environmental signals such as pH, temperature, and nutrients trigger transcription and translation.
What is the process of genetic screening?
Genetic screening involves identifying mutants that cannot grow well in a specific environment.
What is replica plating?
A method used to identify mutant cells by transferring them to a new agar medium.
What is the role of β-galactosidase in lactose metabolism?
β-galactosidase catalyzes the breakdown of lactose into glucose and galactose.
What is the relationship between lactose and the lac operon?
Lactose acts as an inducer that stimulates the expression of genes in the lac operon.
How does the presence of glucose affect lactose metabolism in E. coli?
Lactose is only used for metabolism when glucose is depleted.
What is positive control in transcription regulation?
Positive control occurs when a regulatory protein called an activator binds to DNA and switches on transcription.
What are the two general ways to regulate transcription?
Transcription can be regulated by negative control or positive control.
What are operons?
Operons are gene clusters in bacteria and archaea that are transcribed together as a single mRNA from one promoter.
What is the Lac operon?
The Lac operon is a group of genes involved in lactose metabolism, including lacZ, lacY, and lacA, which are transcribed together.
Who coined the term 'operon'?
Jacob and Monod coined the term operon to describe a set of coordinately regulated bacterial genes.
What is the role of the lacI gene in the Lac operon?
The lacI gene produces a repressor protein that binds to DNA and blocks transcription of the lacZ and lacY genes.
How does the repressor protein affect transcription in the Lac operon?
The repressor binds to the operator region, preventing RNA polymerase from initiating transcription.
What happens when lactose is present in relation to the repressor?
Lactose binds to the repressor, causing it to change shape and detach from the DNA, allowing transcription to occur.
What is allosteric regulation?
Allosteric regulation is when a small molecule binds to a protein and causes it to change its shape and activity.
What is catabolite repression?
Catabolite repression is a mechanism where the presence of glucose inhibits the expression of the lac operon.
What is the role of CAP in the Lac operon?
CAP (catabolite activator protein) exerts positive control by binding to a regulatory sequence and enhancing RNA polymerase binding to the promoter.
How does glucose influence CAP binding to DNA?
High glucose levels inhibit cAMP synthesis, preventing CAP from binding to DNA and thus reducing transcription.
What is the effect of low glucose levels on CAP and transcription?
Low glucose levels increase cAMP synthesis, allowing CAP to bind to DNA and stimulate transcription of the lac operon.
What is inducer exclusion?
Inducer exclusion is when glucose inhibits the transport of other sugars, preventing lactose from entering the cell and keeping the repressor bound.
What are the three genes involved in the Lac operon?
The three genes are lacZ, lacY, and lacA.
What does the lacA gene code for?
The lacA gene codes for the enzyme transacetylase, which helps export certain sugars when they are too abundant.
What is co-transcription in the context of the Lac operon?
Co-transcription refers to the coordinated expression of multiple genes from a single mRNA transcript.
What happens to transcription when glucose is low and lactose is high?
Transcription of the lac operon is stimulated due to low glucose levels and the presence of lactose.
What happens to transcription when glucose is high and lactose is high?
Transcription of the lac operon is still not stimulated because glucose presence inhibits the necessary regulatory mechanisms.
What happens to transcription when glucose is low and lactose is low?
Transcription of the lac operon is not stimulated due to the absence of both glucose and lactose.
What is the significance of the operator in the Lac operon?
The operator is the DNA segment where the repressor binds to block transcription of the operon genes.
What is the function of the enzyme β-galactosidase in the Lac operon?
β-galactosidase is produced to metabolize lactose when it is present in the environment.
How does the presence of lactose affect the repressor's activity?
The presence of lactose causes the repressor to detach from the operator, allowing transcription to proceed.
What is the relationship between the lac operon and glucose levels?
Glucose levels inversely affect the transcription of the lac operon; high glucose reduces transcription while low glucose promotes it.
What happens to transcription when glucose is high and lactose is low?
Transcription of the lac operon is not stimulated due to high glucose levels and lack of lactose.