Chapter 4 and 5 Biology Test
1/93
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Isomer Types
Structural, Geometric, Enatiomers
Isomers
Compounds that have the same formulas but different functions.
Structural Isomer
Different in covalent arrangements of their atoms
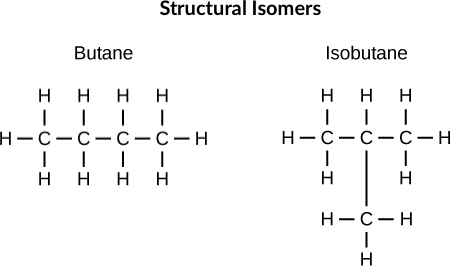
Geometric Isomer
Same covalent partnership but different in spatial arrangements. Arise from the flexibility of double bonds.
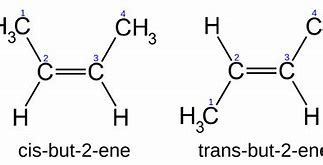
Enantiomers Isomers
Molecules that are mirror images of each other. Usually an asymmetric carbon.
Functional Groups
Groups that alter the function of molecules
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen
Hydrolysis
Dehydration process allowing for chemical breakdown
Organic
relating to or derived from living matter
Hydrocarbon Uses
Fuel, high energy
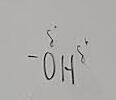
What functional group is this?
Hydroxyl
What does a hydroxyl do when added to a molecule
It makes it polar, or an alcohol if it is on a carbon chain
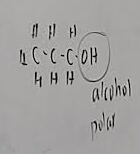
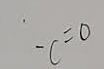
What functional group is this?
Carbonyl
What are the types of carbonyl groups and how are they different?
When the carbonyl is added to the end of a molecule it forms an aldehyde and if it is added to the middle it forms a ketone

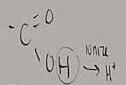
What functional group is this?
Carboxyl
What does a carboxl do when added to a molecuel
It makes it acidic because it is an H+ donor and polar
What functional group is this?
Amino
What does an amino do when added to a molecule
It makes it basic (h+ acceptor)
What functional group is this?
Sulfhydryl
What does a sulfhydryl do when added to a molecule
Creates thiols (compounds that possess a sulfhydryl)
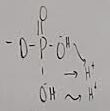
What functional group is this?
Phosphate
What does a phosphate do when added to a molecule
It turns it to a weak acid and is used for energy transfers
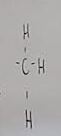
What functional group is this?
Methyl
What does a methyl do when added to a molecule
Makes it nonpolar and hydrophobic
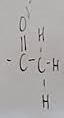
What functional group is this?
Acetyl
What does a acetyl do when added to a molecule
Makes it polar and hydrophilic
Macromolecules
Large molecules formed by joining many subunits together. Aka polymers.
Monomer
A building block of a polymer
Dehydration Synthesis
The chemical reaction that joins monomers into polymers. Covalent bonds are formed by the removal of water molecule between the monomers.
Hydrolysis
Reverse of dehydration synthesis. Breaks polymers into monomers by adding water.
Main types of macromolecules
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids
What is the monomer of nucleic acids
Nucleotides
Elements in nucleic acids
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus (CHONP)
Food sources for nucleic acids
All foods!
Examples of Nucleic Acids
DNA, RNA, ATP
Polymer of nucleotide
Nucleic acid
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, 1 less H+ than RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid
Strands of DNA?
Double Stranded
Strands of RNA?
Single Stranded
Parts of Nucleotide?
nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, phosphate
pentose sugar
5-C sugar, ex ribose, deoxyribose
Pyrimidines
Cytosine(C) Thyme(T) Uracil(U) 1 ring
Purines
Adenine(A) Guanine(G) 2 ring
Pyrimidines and purines in DNA
Cytosine(C) Thyme(T) Adenine(A) Guanine(G)
Pyrimidines and purines in RNA
Cytosine(C) Uracil(U) Adenine(A) Guanine(G)
Adenine(A) pairs with ____
Thyme(T) in DNA and Uracil(U) in RNA
Guanine(G) pairs with ____
Cytosine(C)
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level
Nucleic Acids
Polymers that contain information
Lipids
Broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others.
Monomer of lipids
Glycerol
Elements in lipids
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (CHO)
Function of lipids
Store energy, cushion and insulate organs, material used for cell membrane
Food source for lipids
Butter, nuts, oil
Example of lipids
Fats, Oils, Waxes
Structure of lipids
long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl on the end
Name of link between lipids
Ester bonds/linkage(covalent bonds)
Do lipids link together?
No, lipids stack on top of each other. Not true macromolecules.
Saturated fatty acid
All single bonds in the fatty acid tail. Solid at room temp. C5H12
Unsaturated fatty acid
At least one double bond between carbons in fatty acid tail. Liquid at room temp. C5H10
Polysaturated
More than one double bond.
Hydrogenated Oils
Added hydrogen to fatty acid tail.
Elements in carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (CHO). 1C:2H:1O
Monomer of carbohydrate
Monosaccharides
Function of carbohydrate
Provide material to build cell membrane. Quick energy for cells.
Foods for carbohydrates
Pastas, breads, fruits, vegetables
Example of carbohydrates
Glucose, Fructose, Lactose, Cellulose
Polymer of Carbohydrate
Polysaccharide
Shape of carbohydrate
Hexagon
Disaccharide
2 monosaccharides linked together
Oligosaccharides
3 to 10 monosaccharides. Used for cell identification and communication
Polysaccharides
100 to 1000 monosaccharides.
Alpha glucose in plants
Starch (Potato), large chains
Alpha glucose in animals
glycogen ( the stored form of glucose that's made up of many connected glucose molecules)
Beta glucose in plants
Cellulose, cell walls
Beta glucose in animals
Chitin, exoskeletons
Steroids
4 fused hydrocarbon rings. Differ by attached functional groups. Ex estrogen, testosterone, cholesterol
Elements in proteins
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (CHON)
Monomer of proteins
Amino acid
Function of proteins
Provide structure, aid in muscle movement, provide immunity
Proteins food source
Seafood, milk, eggs, cheese, meat
Examples of proteins
Insulin, hemoglobin, antibodies, enzymes
Polymer of proteins
polypeptide/proteins
Stages of proteins folding
Primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
Polypeptide
Multiple amino acids linked together
Dipeptide
Two amino acids linked together
What dictates amino acid order in a polypeptide?
DNA that tells RNA how to make the polypeptide
How many changes does a protein need to go through to become functional?
4, the quaternary stage
Primary protein folding stage
2d line of amino acids made by peptide bonds
Secondary protein folding stage
3d structure formed by hydrogen bonding between the R groups. Two main secondary structures. Either forms an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet, determined by the hydrogen bonding pattern of the amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
Tertiary protein folding stage
Bonding between the R groups. Possible bonds: Ionic bonds, disulfur bridges, vanderwaal’s bonds, hydrophobic interactions.
Quaternary protein folding stage
When two or more polypeptides bond together. The molecule becomes functional.
Events causing a proteins to lose it’s shape
Ph shifts, high salt concentrations, heat