Competitive Markets: Price, Entry, and Profit Dynamics in Microeconomics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the primary goal of Chapter 9?
To explain how competitive markets are formulated.
What are the key learning objectives of this chapter?
1. Market characteristics of perfect competition. 2. How prices are established in competitive markets. 3. Why economic profits approach zero in competitive markets. 4. How society benefits from market competition.
What does each firm's supply curve represent in a competitive market?
Each firm's supply curve is its marginal cost (MC) curve.
What factors determine the market supply curve?
The price of factor inputs, technology, expectations, taxes and subsidies, and the number of firms in the industry.
What happens to the market supply curve when an industry is profitable?
New firms enter and existing firms expand, causing the supply curve to shift right.
What is the significance of economic profits in a competitive market?
Economic profits attract new firms, which increases supply and lowers prices until profits approach zero.
What occurs when firms exit an industry due to economic losses?
The market supply curve shifts left, causing prices to rise and economic losses to decrease.
What are the characteristics of perfect competition?
Many small firms, identical products, perfect information, profit maximization at MC = P (= MR), low barriers to entry and exit, and zero economic profit.
How do competitive forces affect product prices?
They drive prices down, making products more affordable and expanding the market.
What is allocative efficiency in the context of competitive markets?
It occurs when the industry produces the right output mix based on consumer demand.
What happens to economic profits in a competitive market over time?
Competition drives economic profits to zero as firms produce at maximum productive efficiency.
What is the relationship between economic profits and consumer demand?
High economic profits signal strong consumer demand, leading producers to increase output.
What occurs when economic profits are negative?
It signals that consumers want fewer goods from that industry, prompting producers to reduce output.
What is the outcome of a competitive market in terms of prices and output?
The market stabilizes at higher output, lower price, minimum average total cost (ATC), and zero economic profit.
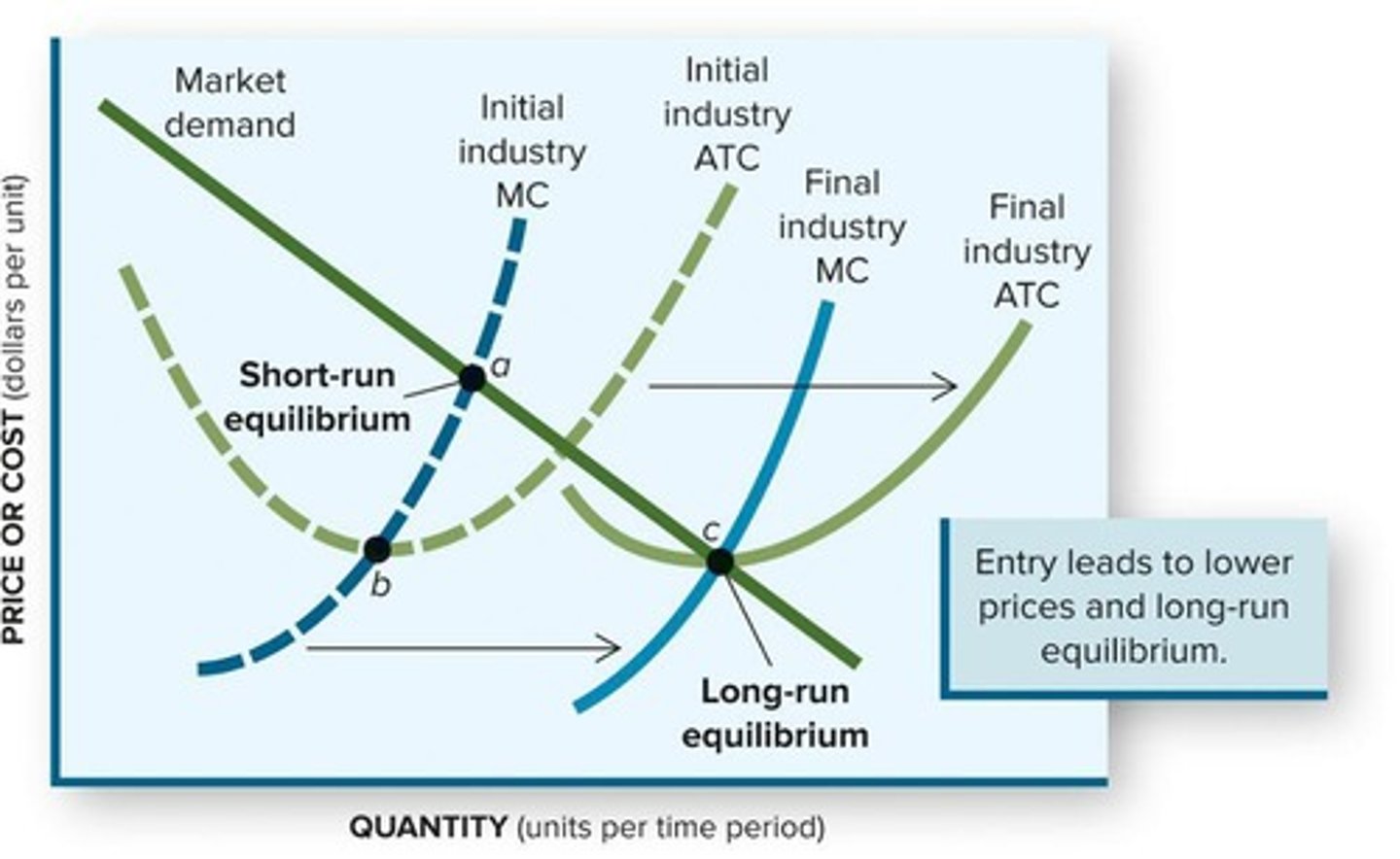
What happens if a firm lowers its production costs?
It encourages increases in output, shifting the marginal cost curve right.
What is the impact of a firm shutting down due to low prices?
It may dump inventory at reduced prices, causing further price drops in the industry.
How does competition drive innovation in markets?
Firms must improve product quality and lower costs to remain competitive.
What is the role of new entrants in a competitive market?
New entrants increase supply, which can lead to a decrease in prices and profits.
What does the term 'relentless profit squeeze' refer to?
The continuous pressure on profits due to new entrants and increased competition.
What is the significance of the market mechanism?
It uses market prices and sales to signal desired outputs or resource allocations.
How do firms respond to economic losses?
They reduce production or exit the industry to align supply with declining consumer demand.
What happens to the market when economic profits are high?
It attracts new suppliers, shifting the supply curve right and lowering prices.
What is the effect of continuous new product introductions in competitive markets?
They maintain consumer interest and drive competition among firms.
What does zero economic profit indicate for firms?
It means firms earn normal profit, covering opportunity costs but no excess profits.
What is the impact of competition on consumer prices?
Competition typically lowers prices, making goods more accessible to consumers.