Elasticities
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
price elasticity of demand
how responsive the change in QD is to a change in price
calculating PED
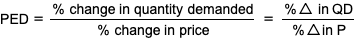
0 PED value
perfectly inelastic
QD is completely unresponsive to the change in price
this is usually a very theoretical value
0-1 PED value
relatively inelastic
% change in QD is lower than the % change in price
1 PED value
unitary elasticity
% change in QD is equal to % change in price
1-∞ PED value
relatively elastic
% change in QD is greater than % change in price
∞ PED value
perfectly elastic
% change in QD will fall to zero with any % change in price
highly theoretical
determinants of PED
SPLAT
substitutes
good availability of substitutes results in higher PED (relatively elastic)
price of product as a proportion of income
the lower the proportion of income the price of the product represents, the lower the PED will be
consumers are less responsive to price changes on cheaper products
luxury
luxury products are elastic
necessities are inelastic
addictiveness
if product is addictive, low PED value
time period
in short term: consumers are less responsive to price INCREASES resulting in a low value of PED
in long term: consumers may feel the price increase more and will then look for substitutes, resulting in a high value of PED
total revenue rule
in order to maximise revenue, producers must increase prices on products that are inelastic in demand, and decrease prices on products that are elastic in demand
diagram of revenue when tax on elastic vs. inelastic (govs)
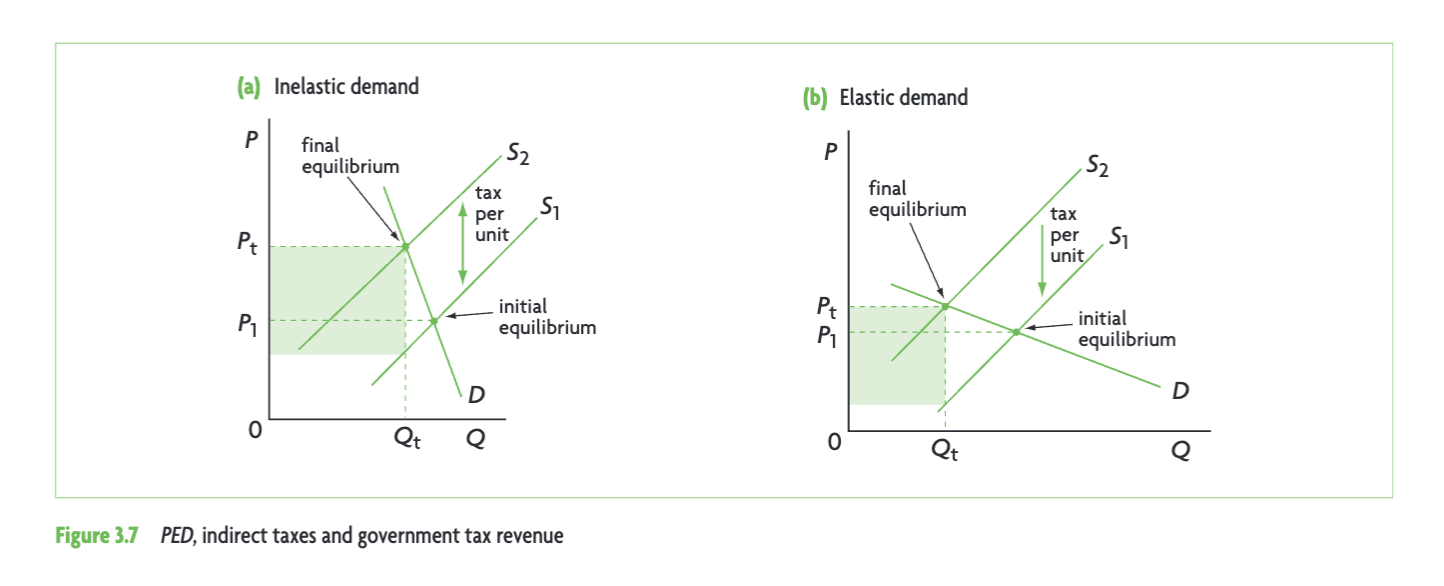
diagram of good that is price elastic in demand
shallow curve
there is a greater than proportional increase in QD in response to a decrease in price
a small decrease in price leads to a large increase in QD
total revenue is higher once price is decreased
diagram of good that is price inelastic in demand
steep curve
there is a smaller than proportional decrease in QD in response to an increase in price
a large increase in price leads to a smaller decrease in QD
TR is higher once price is increased
implications of PED for firms and governments
knowledge of PED is important to maximise revenue
knowledge of PED is important to governments for taxes and subsidies
if they tax price inelastic in demand goods, they can raise tax revenue without harming firms excessively
if they subsidise price elastic in demand goods, there can be a greater than proportional increase in QD
income elasticity of demand (YED)
how responsive the change in QD is to a change in income
engel curves are used to represent this relationship
YED formula
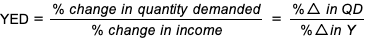
interpreting YED values
a positive YED value means it’s a normal good (luxury or necessity)
a negative YED value means it’s an inferior good
YED<0 value
inferior good
e.g cheap cereal
0-1 YED value
necessity
normal good
income inelastic, which means it’s relatively unresponsive to a change in income
e.g loaf of bread
YED>1 value
luxury
normal good
income elastic, which means it’s relatively responsive to a change in income
YED determinants
influenced by any factors in an economy that will change wages of workers
e.g during a recession wages usually fall, and demand for inferior goods increase swhilst demand for luxury goods falls
price elasticity of supply
how responsive the change in QS is to a change in price
PES formula
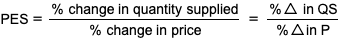
0 PES value
perfectly inelastic
QS is completely unresponsive to a change in P
e.f fixed number of seats in a theatre
0-1 PES value
relatively inelastic
the % change in QS is less than proportional to the % change in P
1-∞ PES
relatively elastic
% change in QS is more than proportional to the % change in P
∞ PES value
perfectly elastic
the % change in QS will fall to zero with any % change in P
very theoretical
determinants of PES
MATUR
mobility of FOP
if producers can quickly switch their resources between products, then PES will be more elastic
e.g if prices for hiking boots increase, shoe manufacturers can switch resources from trainers to boots
ability to store goods
if products can be easily stored, then PES will be higher as producers can quickly increase supply (e.g canned goods)
inability to store products results in lower PES
time period
in short term: producers may find it harder to respond to an increase in prices as it takes time to produce the product e.g avocados
in long term: they can change any of their factors of production so as to produce more
unused capacity
if price increase for a product and there is a capacity to produce more in the factories that make those products, then supply is elastic
if there is no spare capacity to increase production, supply will be inelastic
rate at which cost of production increase
it costs more to produce each additional unit of output
if the rate of the marginal cost increase is low, then the QS will be more elastic
if marginal costs rise quickly, QS will be more inelastic