Tablet formulation and excipients
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
what are tablets
Solid dosage forms containing medicinal substances with/without suitable diluents
have many shapes and designs, which depend on a die set
die set consists of two punches: upper punch and lower punch, and a die cavity
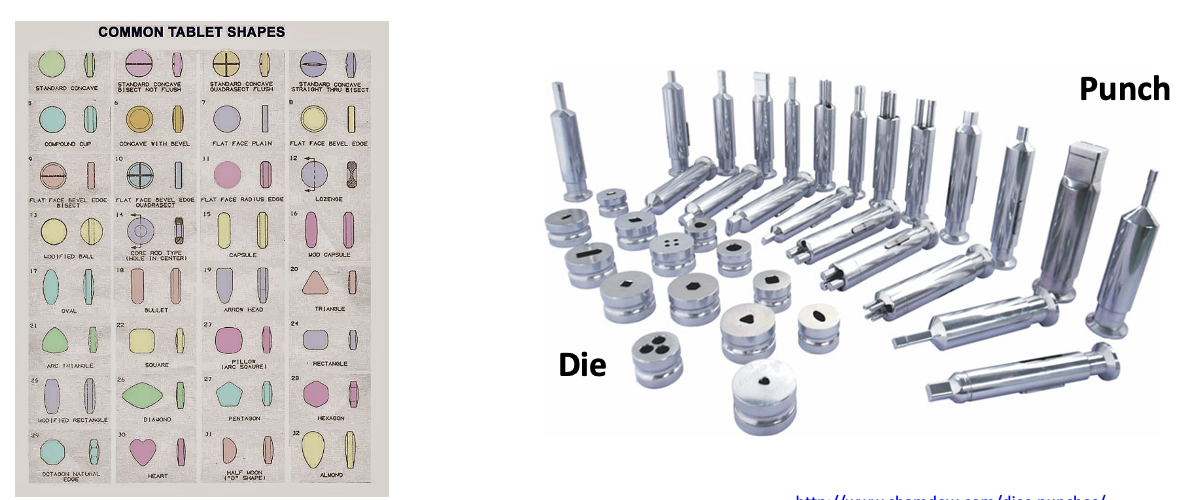

what are the advantages of a tablet to a patient
Accurate dosage/minimum variability
Ease of administration
Elegance
Convenience (Light & compact)
what are the advantages of a tablet to a manufacturer
Suited for large-scale production
Variation & low cost.
Special release profiles possible
Easy/cheap to package & ship
what are the disadvantages of tablets
Swallowing
Poor wetting / slow dissolving drugs
Dosage
Bitter taste
Oxygen/moisture sensitive may require coating
how are tablets formed
powder formulation
compressions
the manufacturing of tablets is hard as it involves different components/excipients like diluent, binder, glidant and disintegrant
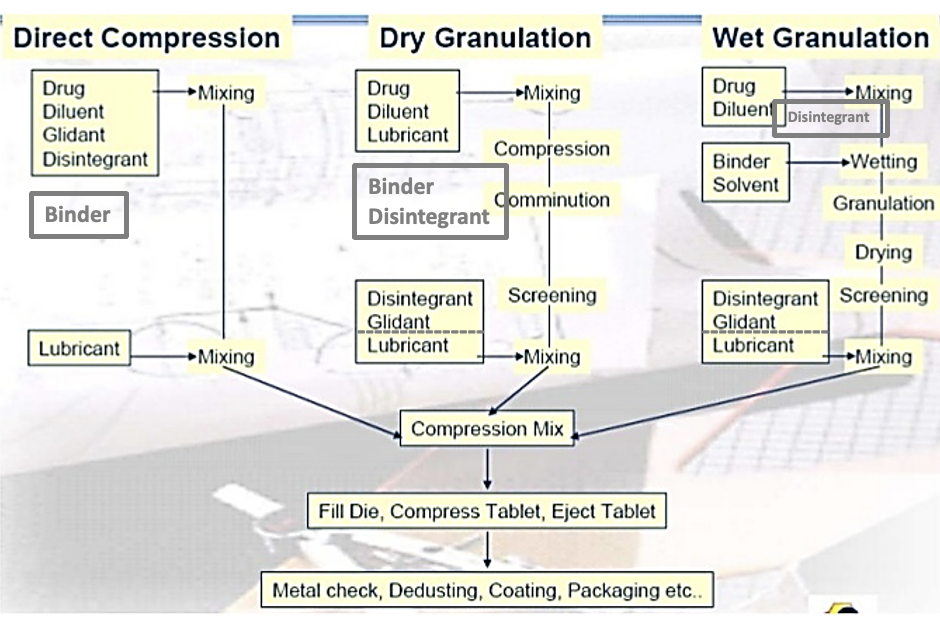
what are the three methods of tablet manufacturing
dry compression
dry granulation
wet granulation
each method consists of a different number of steps
what components are needed for a good tablet
API (active pharmaceutical ingredient)
excipients
what are examples of excipients
Diluent
Binder/Adhesive
Glidant/lubricants
Disintegrants
Coloring agents
Flavoring agents
Coating agent
what are the minimum characteristics for the design and formulation of compressed tablets
Compactibility → ability of excipients to compress well + maintain strong VDW forces (aids binder/adhesive)
Fluidity → abiility of a substance to flow (aids granulation+flow)
Lubricity → for Ejection of Tablets and prevent sticking to the walls of the dye/punches (aids lubricants)
what are diluents (fillers)
Bulking agent that mainly consist of carbohydrates and some inorganic salts
consist of 10-50% of powder formulation
Must meet criteria of good compressibility
physically and chemically stable
inert (won’t interact with drugs)
Must be biocompatible (no allergic reactions)

what are common diluents
lactose
glucose
sucrose
starch
sugar alcohols: sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol
cellulose
Dicalcium Phosphate dihydrate (Emcompress)
what is cellulose and why is it used as a diluent
polysaccharide consisting of linear chain of many glucose molecules linked by glycosidic linkage
biocompatible (no allergic reactions)
chemically inert
good compactability and disintegration properties → used as a binder and disintegrant
(but hydroscopic so can go through hydrolysis)
most common example of cellulose is MCC
why is Dicalcium Phosphate dihydrate (Emcompress) used as a diluent
their particles tend to break to increase the size of granules and improve flowability
this is helpful in mixing and tablet formation
what are disintegrants
substances routinely included in tablet formulations and many hard shell capsule formulations
promote moisture penetration and dispersion of the matrix of the dosage form in dissolution fluids to expose primary drug particles
can break tablet to expose the particles for therapeutic action
what is the disintegration process
if tablet made from granules, it will disintegrate from granules into individual particles
If made by direct compression method, they will break into individual components as powders are directly compressed into tablets, without granulation process
therefore, dissolution is generally quicker with direct compression tablets
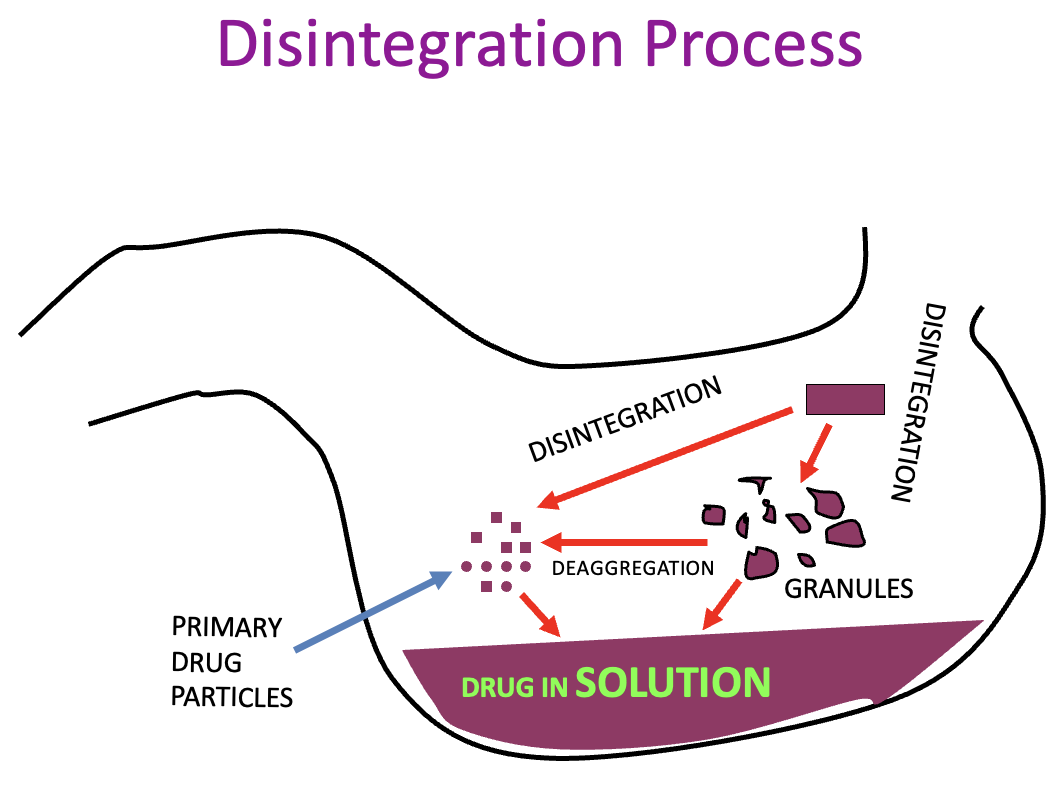
what does it mean if all disintegrants are hydroscopic
they absorb moisture, drawing liquid into the tablet
usually swell and disintegrate, breaking the tablet into pieces
give examples of disintegrants
Starch
Modified Cellulose or Super Disintegrant
Cros-carmellose sodium
Sodium Starch glycolate
why is starch used as a disintegrant
it is effective when used up to 10%
mode of mechanism is through swelling properties → starch is considered as elastic in nature
de-form under pressure
energy-rich → energy is released when in contact with water, which breaks the tablet
why is modified cellulose or super disintegrants like cros-carmellose sodium and Sodium Starch glycolate used as disintehrants
they swell due to cross linking, which breaks the tablet
they don’t dissolve but absorb water due to cross linkages
generally used from 1-5% in tablet formation
when more than 8% of super disintegrant used, disintegration time increases because above 8% they make jelly/jelling→ viscosity increases
when using wet or dry granulation methods, when are disintegrants added
we add half before granulation (intrangular) and half after granulation (extrangular)
half will break the tablets, other half will break granules individually
what are the three main roles of lubricants in tablet formation
true lubricant (reduce friction during tablet compression/ejection)
anti-adhesion (prevent tablet/particles sticking to surfaces)
glidant (improves flow of particles)
what will happen if lubricant isn’t present in powder formulation
it may cause capping and fragmentation of tablets
Capping → either upper or lower part of tablet separates horizontally from main body of tablet upon ejection during compression process
fragmentation/elimination → tablet is horizontally fractured into many distinct layers upon ejection
what three phases does tablet compression consist of
filling
compression
ejection
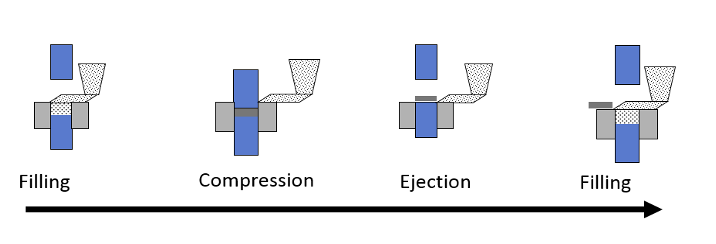
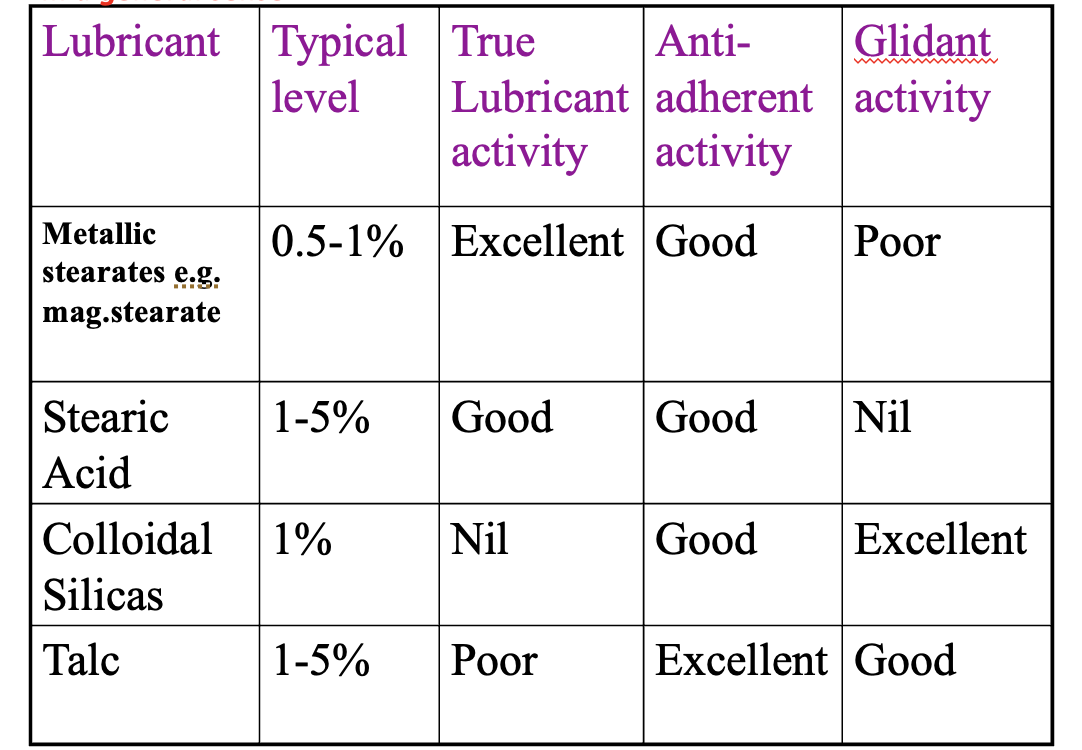
types of lubricants
metallic stearates is the best lubricant due to its excellent true lubricant activity → prevents friction between surfaces of particles
but has poor glidant activity → can be fixed by adding a separate excipient as a glidant
why are lubricants effective
they are hydrophobic (not water soluble) e.g. magnesium stearate
what are the issues with lubricants
mixing for too long increases disintegration and dissolution time
powder mixing causes slight heat generation so hydrophobic layer over the particles/granules, prevents moisture penetration
high amount of lubricant can interfere with bonding and soften tablets
particles of lubricants adhere to surfaces of large particles and reduce bonding between particles during compaction, forming tablets of lower strength
what are glidants
improve flowability of granules or particles from hoppers and into die cavity during compression
enhances flowability of direct compression mixtures, but can be used in granulation for high production speed
poor powder/flowability can cause weight variation among tablets
the optimum concentration is related to the amount needed to just coat the bulk powder particles
traditionally, talc used in tablet formulation as a glidant in conc of 1-2%, but now most commonly used is colloidal silica in a very low conc of less than 1%
what is a binder
adhesive agents which glue a number of various particles to each other to make a granule
helps hold tablet together and improves compactability
this size enlargement process improves flowability
used before wet granulation (binders are dissolved in a suitable solution either (water or alcohol), the liquid binder is referred to as granulation liquid
in dry granulation, we use them as a dry binder before compaction (slugging/compact mass/tableting)
what are flavouring agents
for pleasant taste to mask unpleasant taste
coats the tablets/granules.
are thermolabile (heat-sensitive)
often mixed with the granules as an alcohol solution
can be added with powder formulations using direct compression methods
what are colorants
used to dress up the tablets to make it more attractive
helps with Identification e.g. for older patients
can help with patient compliance
what are the two main manufacturing methods
Direct Compression (DC) method
Granulation method
Wet Granulation
Dry Granulation
what is Direct Compression (DC) method
simple method to reduce production time and cost as it only contains two major steps: mixing/blending and compression
mix/blend all the excipients together containing diluents, glidants, disintegrants in the drug
sieve
then before compression, lubricant can be mixed
followed by direct compression
blend → sieve → blend → compress
what is the starting point for making a new tablet formulation
the size of the dose
low doses
<25 mg
most of the tablet will be excipients
API should equally mix with excipients to give required dose in each tablet → important to achieve a content of uniformity
high dose
>250 mg
Most of the tablet will be drug/API
good compatibility and flowability properties
what manufacturing method is preferred for low dose drugs
direct compression method
because we blend/mix all the excipients with the drug/API and compress it straight away
If there are any problems in compression e.g. lack of compactibility/flowability, direct compression fillers (DC filler or DC excipients) can be used
what are the advantages of direct compression over granulation
more economical due to less time
avoids heat and moisture due to no solvent
when made from mostly MCC (diluent), better flowability due to large particles and high compressibility
what are the disadvantages of direct compression
segregation → content of uniformity/distribution of active ingredient can be affected in low dose drugs, causing segregation (the process when one of the ingredients based on their size, shape or density can be separated out from the rest of the powder formulation)
not practical for large doses → if drug possesses poor flowability/compactability, then granulation method is better
requires tight control over excipients → in terms of properties like flowability, disintegration and compactability etc. If excipients don’t possess these properties, its expensive to produce new DC excipients
punch wear → DC may damage the punches as powders are directly compressed into tablets using high compression
dust
what is granulation
size-enlargement process in which primary powder particles adhere to form larger, multi-particle entities called granules
what is the need for granulation
prevent segregation (the separation of one ingredient from the rest of the formulation)
flow improved (as increase in particle size reduces particle interaction)
improve the compaction characteristics (as addition of binder produces tablets of required mechanical strength)
reduces dust (as no fine particles present in granules)
what are the similarities between dry and wet granulation
improve flowability, particle size, and die filling
both contain many steps and so are time consuming compared to direct compression
what is the traditional granulation method
wet granulation
involves wetting the powders with binder solution (glue) and drying
two main methods of wet granulation
wet massing techniques
fluid bed granulation
not suitable for heat/water sensitive drugs → DC is used
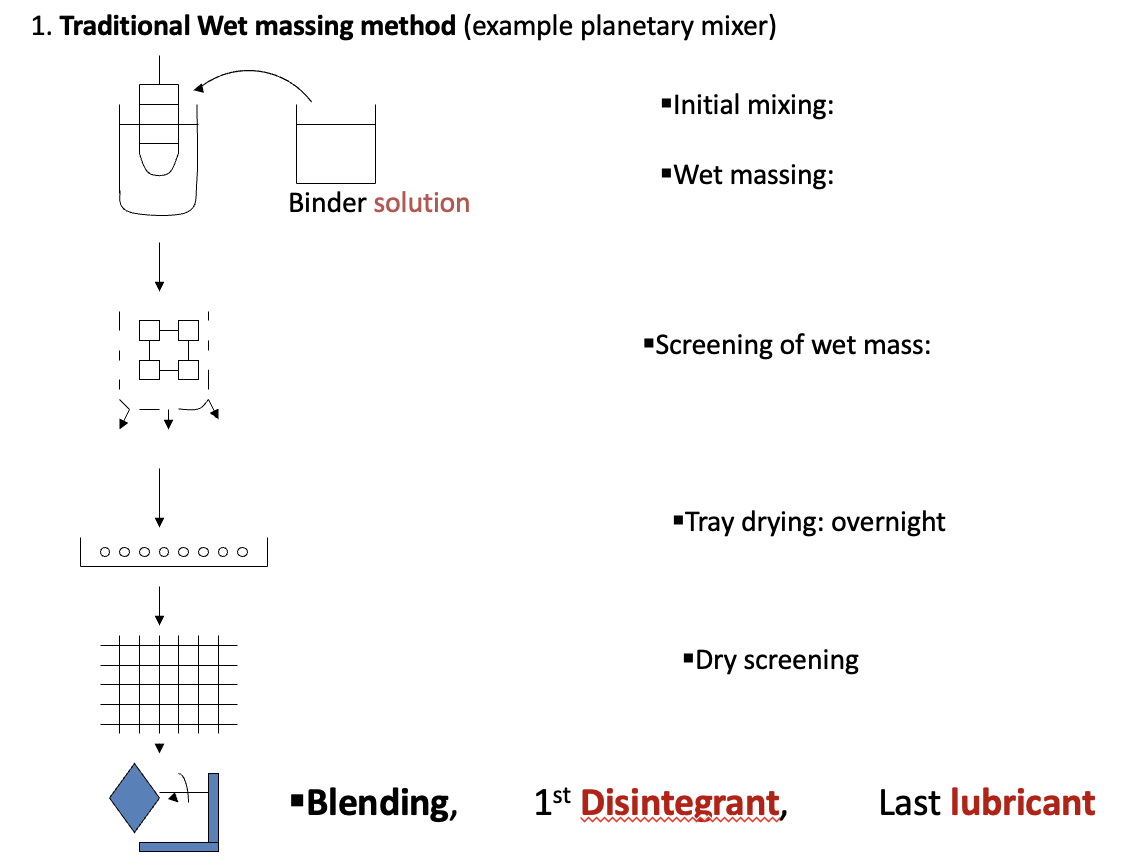
what are the steps of traditional wet massing method
initial mixing of drug and diluent using a planetary mixer
wet massing formed by addition of binder solution
screening of wet mass by passing through a mesh-sieve to make granules
tray drying overnight: granules transferred to trays/dried in oven for few hours depending on temperature conditions
wet can checked from time to time until no further increase in mass
dry screening: dry granules passed through sieve/mesh again for potential sticking of granules to each other
blending/mixing with disintegrant, then lubricant
granules are then ready for compression
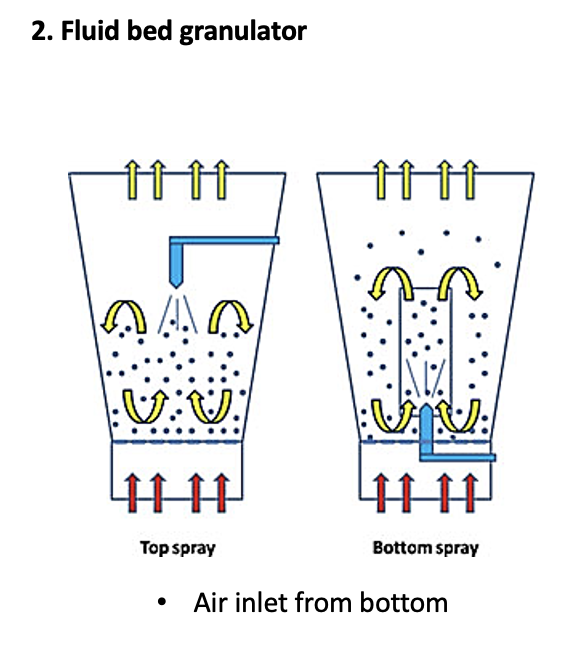
what is the fluid bed granulator
a multi-purpose, processing equipment commonly used in pharmaceutical industries
mixing, granulation and drying are carried out simultaneously
how does the fluid bed granulator work
powder material placed over perforated plate
hot, filtered air blown through perforated plate to fluidise particles and mix powder
granulating fluid pumped from a reservoir through spray nozzle positioned over the bed of particles.
the fluid causes the primary particles to adhere when the droplets and powders collide
escape of material from granulation chamber prevented by exhaust filters, which are agitated to reintroduce the collected material into the fluidised bed
sufficient liquid of binder solution is sprayed to produce granules, hot air makes granules dry uniformly to give uniformed granules
the spray is turned off but the fluidizing air continue to dry the granules.
what are the advantages and disadvantages of wet granulation
advantages
spherical shapes made
binder keeps particles in a uniformed form → easier to compress
granules prevent segregation and eliminate dust formation
disadvantages
heat and moisture sensitive due to use of solvent
longer disintegration time as tablets disintegrate into granules, then individual particles
many steps so labour intensive and time-consuming
what is dry granulation
converts primary powder particles using pressure, without the intermediate use of a liquid (dry binder used, not solvent)
avoids liquid-heat combinations that might cause degradation of heat-sensitive materials
what are the two major steps for dry granulation
in first step after mixing , powder formulation compressed in compact mass/flakes/slugs
slugs/flakes converted intr granules and pass through mesh/sieve, followed by mixing with disintegrant and finally lubricant
granules compressed into tablets
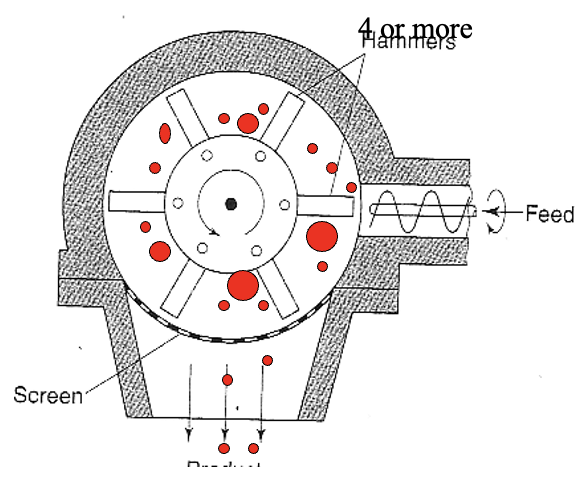
what is slugging in dry granulation
dry powders compressed using a conventional tablet machine or a large heavy-duty rotary press
the compact made in the process (typically 25 mm diameter, 10-15 mm thick) is termed a ‘slug’ → bigger tablets
hammer mill is suitable for breaking the compacts (convert slugs into granules)
high velocity of hammer causes brittle fracture (small granules are less prone to fracture than larger granules)
granules retained by screen/mesh at bottom to allow only granules of required size through
what are roller compactors
alternative gentler method to making slugs
powder mix is squeezed between two rollers to form a compressed sheet
sheet is weak and breaks into flakes
flakes broken using gentler treatment (screening alone) to form granules
what are the two equipments necessary for dry granulation
machine for compressing the dry powders into compacts mass or flakes
mill for breaking up the compacts mass or flakes into granules.
summary of the different manufacturing methods
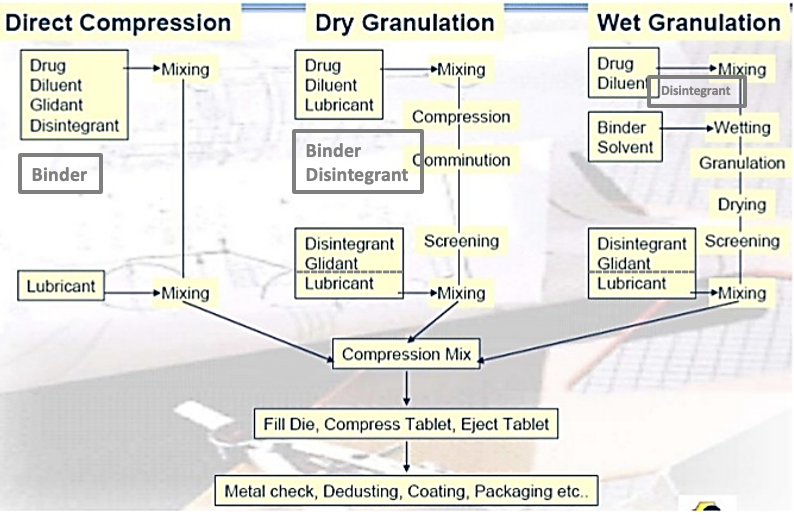
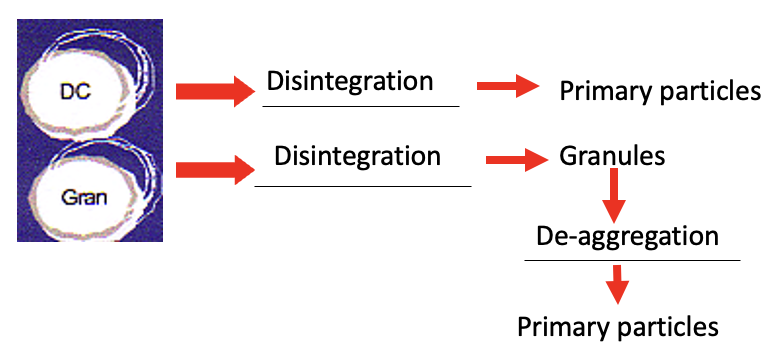
diagram showing the stages of DC and granulation to give primary particles
tablets from DC exposes primary particles (active ingredients) much quicker than tablets manufactured form granules
summary steps for wet granulation
1. Milling of drugs & excipients
2. Mixing of milled powders
3. Preparation of binder solution
4. Mixing of binder solution with powder mixture to form wet mass
5. Coarse screening of wet mass using 6 to 12 mesh screen
6. drying of moist granules
7. Screening of dry granules through 14 to 20 mesh screen
8. Mixing of screened granules with disintegrate + mixing with lubricant
9. Tablet compression
summary steps for dry granulation
1. Milling of drugs & excipients
2. Mixing of milled powders
3. Compression into large, hard tablets, to make slugs
4. Screening of slugs
5. Mixing with disintegrant + Mixing with lubricant
6. Tablet compression
summary steps for direct compression
1. Milling of drugs & excipients
2. Mixing of mill powder
3. Tablet compression