BMEN 207
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What type of prototyping fabrication method produces the highest fidelity and strong, functional parts?
Computer controlled machining/milling (CNC) and laser cutting
What type of prototyping fabrication method is the quickest and lowest cost?
3D Printing
Stereolithography (SLA)
Fused filament fabrication (FFF)/Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Selective laser sintering (SLS) including direct metal laser sintering (DMLS)
Polyjet
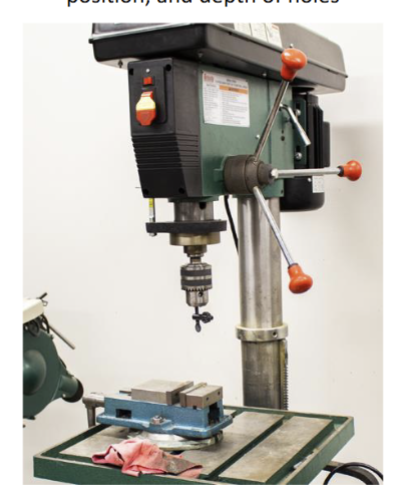
What’s a drill press good for?
Better control of angle, position, and depth of holes

What’s a table saw good for?
Precise ripping and cross cutting wood and plastic

Bandsaw (vertical)
Precise cutting of metal (including steel), plastic, and wood

Horizontal bandsaw
Cross cutting of mostly metal (including steel) and plastic (better options for wood)
Unlike vertical band saw, you can cut arbitrarily long pieces

Mill
Precise machining of metal (including steel) and plastic using changeable tools
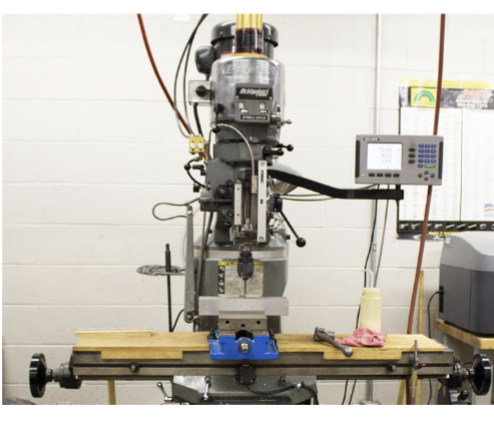
Grinder
Grinding of ferrous metals (steel), for example, sharpening a drill bit. No Aluminum!!

Combination Sander
Sanding smooth materials like wood, plastic, and metals

Miter saw
great for quick precise cross-cutting of wood, plastic and nonferrous metals (like extruded aluminum (with an appropriate blade)

Cordless drill
great for less precise hole drilling
Rotary tool
grinding, sanding, buffing small parts, cutting small steel pieces (cutting off a rusting bolt for example)

Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)/Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Heated filament is extruded into fine bead and used to build up layers that fuse and cool
• Most common low-cost desktop system for printing plastics
• Low resolution and poor surface characteristics but can be functional (for light duty)
SLA (stereolithography)
• A laser or projected light (digital light processing) is used to solidify selected areas on a layer
of photosensitive polymer
• High resolution and good surface characteristics
Polyjet
• Inkjet deposited photopolymers are solidified with UV light
• Good resolution and surface finish
• Good material selection
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) including Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
• Heat (usually laser generated) is used to sinter selected volumes in the part
• Potentially high resolution and mechanically robust and functional prototypes
SLA/FDM Fabrication Differences
SLA
• Layer by layer
• Smaller scale products
• High resolution (Thinner layers)
FFF/FDM
• Layer by layer
• Larger scale products
• Low resolution (Thicker layers)
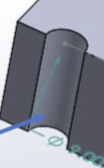
Thru hole
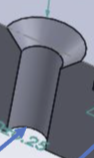
Counter sunk hole (thru)
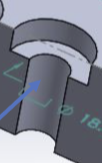
Counter bored hole (thru)

Tapped hole (thru)
Threaded to fit a bolt or machine screw
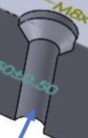
Counter drilled hole (thru)

Blind hole
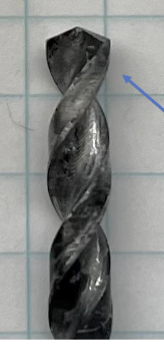
Common high speed steel (HSS) drills
Good general use drill for metals and
even wood and plastic. Use at lower
speeds for harder material and larger
diameters. Best to use lubrication for
drilling metal.
Sometimes coated for extra hardness
(gold colored for example)
Can be resharpened
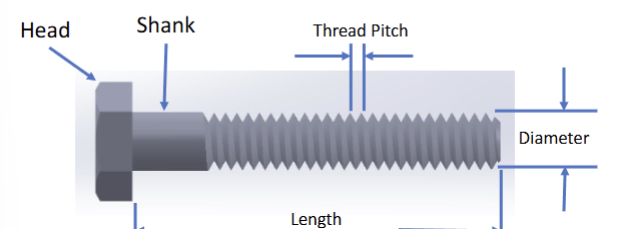
What do these dimensions mean in metric notation for screws? M6 x 1.0 x 10 mm
Diameter (mm) x Distance between threads (mm) x Length (mm)
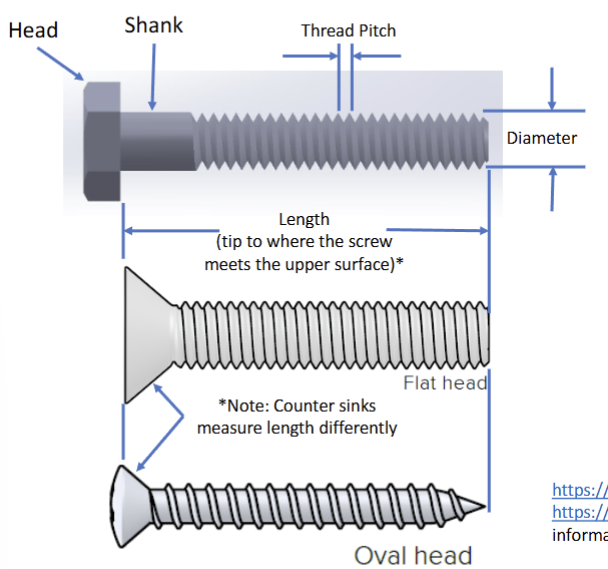
What do these dimensions mean in english notation for screws? #4 – 40 x 1 in
Diameter # (bigger number = bigger diam.) x Thread Count (threads per inch or
TPI) x Length (inch)
Draw three types of screws and label their parts
What happens when diameters are above size 12 in English bolt notation?
They are given in fractions











































