SHS 427 semantics
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
A semantic feature is..
The most basic meaning-bearing component of a word
What is a semantic features role in semantic categories
Used to distinguish between two similar things
Where do object concepts appear to be stored in the brain
Anywhere and everywhere
According to the grounded cognition model…
Object concepts are made up of fragments of semantic info that is widely distributed and is recalled by activating brain regions related to how the object is perceived.
What part of the brain is activated when manipulating a tool
Left Supramaringal gyrus
What evidence is there for the grounded cognition model
When thinking about a manipulable object the Left Supramaringal gyrus activates
Top-down effect
How your brains predictions influences your interpretation
Bottom-up effect
How the acoustic signal influences your interpretation
How are bottom-up effects measured
Use of eye tracking when asked to look at a specific object
What were the four types of words used to measure bottom up processing
Target word, Cohort (same beginning as target), Rhyme, unrelated
What is the ganong effect
When an ambiguous sound is produced within a word a listener will subconsciously perceive the sound as one that makes the most sense in their language. I.e. Gift instead of kift and Kiss instead of giss
What is the phoneme restoration effect
When part of a word is replaced by white noise the listener subconsciously fills in the missing part with the phoneme that makes the most sense given the context
Describe what makes swearing different than speaking
Some of the only words used for infixation
Describe the parts of the brain involved in swearing
Limbic system
What is coprolalia
Involuntary utterance of objectionable words
What is infixation
Like prefix and suffix but in the middle of a word
In english where are infixes typically located
right before the stressed syllable
What is a lexical decision task
Participants are asked “is this a word?” and respond yes or no
What are the typical results of a lexical decision task
Decisions are made about 90 ms faster for high frequency words
Describe how children break the acoustic signal into individual words
Sounds that are within the same words are likely to appear together more frequently than sounds that cross word boundaries
Word segmentation is a precursor to…
Developing vocabulary
When do children typically have their first word
Around 1 year
How does vocabulary grow early on
Exponentially
By 2 years old children should have around…
120 words
By seven years old children should have around…
5.000 words
Adults have more than…
20,000 words
What is the most critical factor in vocabulary growth
Exposure to language
What is code switching
The act of choosing to switch between languages or dialects
Describe some explanations for why it is used
Translation is unknown or not straightforward, expressing solidarity
What is circumlocution
Defining a word instead of using it outright
Describe anomia
A severe issue naming object concepts
What is anomia a symptom of
All types of aphasia
What causes anomia
Broad damage to the brain as is typical of alzheimer's disease
What is Primary progressive Aphasia (PPA)
A neurodegenerative disease that causes progressive atrophy in the left cortex which causes a progressive language disorder
Semantic variant of PPA (svPPA)
Gradual loss of semantic/conceptual knowledge while sparing grammatical and phonological aspects of language
Describe Broca’s aphasia
Language disorder causing difficulty expressing language and understanding complex topics
Describe the evidence for separation of an individual’s multiple languages in the brain
Electro cortical stimulation often only affects one language at a time
Describe the evidence for interaction between an individual’s multiple languages in the brain
Aphasia can target both languages
Describe different types of bilingual aphasia patterns
Can target both languages or just one of them
What is parallel language recovery
Both languages are recovered together while maintaining relative proficiency levels
What is differential language recovery
Both languages are recovered but one has a much higher relative proficiency level than it had before the aphasia
What is antagonistic language recovery
One language is initially preserved but is lost as the second language is recovered
What is blended language recovery
Patient mixes words an syntax from both languages
What is the difference between blended language recovery and code-switching
Code switching is under the speakers control
What is selective aphasia
When not all languages are recovered
What is successive recovery
One language fully recovers and then the second language recovers
Describe what classifiers are
Indicate a property of a word (in ASL the Park handshape and feeling fingers)
Describe the role of space in sign languages
Can be used for emphasis and also to place referents in a conversation
Do babies produce sign faster than spoken language
Potentially but it is more a reflection of motor development than it is of linguistic development
Describe suprasegmentals
Parts of speech that can influence the meaning beyond phonemes and syllables
Describe lexical stress
The relative prominence or emphasis on a syllable
Describe emotional prosody
How the tone and rhythm of a sentence can change perception of the emotion behind it
What is an example of pitch on emotional prosody
Excited has a higher pitch than sad
What is an example of pitch changes on emotional prosody
Happy has larger changes in pitch
What is an example of speed on emotional prosody
Angry is fast sad is slow
What is an example of stress patterns on emotional prosody
Angry tends to have more stress
Describe lexical tones
A change in tone that changes the meaning of a word
Describe where lexical stress is processed in the brain
Primarily Left hemisphere with some right hemisphere interaction
Describe where emotional prosody is processed in the brain
Primarily in the right hemishpere
Describe where tones for tonal languages are processed in the brains of people who do not speak tonal languages
Processed in the right hemisphere much like prosodic information
Describe where tones for tonal languages are processed in the brains of people who do speak tonal languages
Processed in the left hemisphere
What does segmentation refer to as used on the Antovich and Graf Estes article
The ability to divide the speech stream into “words”
Bilingual infants receive … exposure to each of their language than monolingual infants do in theirs
Less
In research prior to the Antovich and Graf Estes article it was suggested that monolingual adults … to segment artificial languages that had over-lapping or non-overlapping syllables
Relied on different speaker voices
What did the two languages in the Antovich and Graf Estes article have in common
Overlapping syllables
What was different between the two languages in the Antovich and Graf Estes article
L1 was presented in a male voice while L2 was presented in a female voice
According to Rosenblau et al. what predicted accuracy for the control group
Greater connectivity between the Superior temporal sulcus and the anterior cingulate cortex
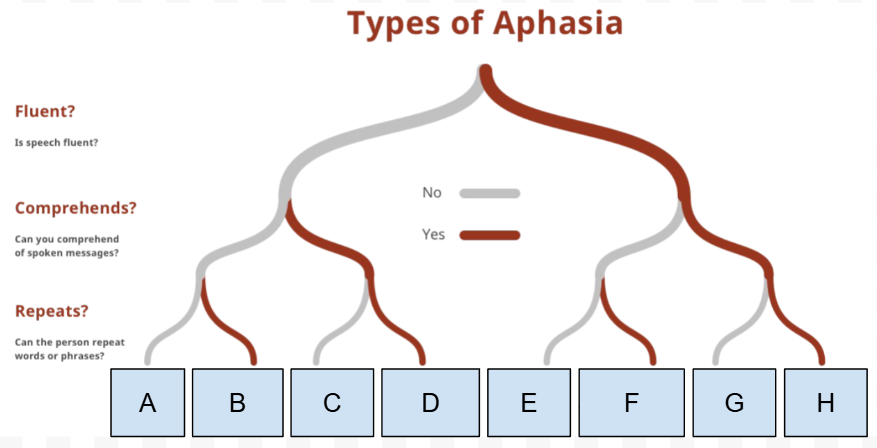
What Type of Aphasia is A
Global aphasia
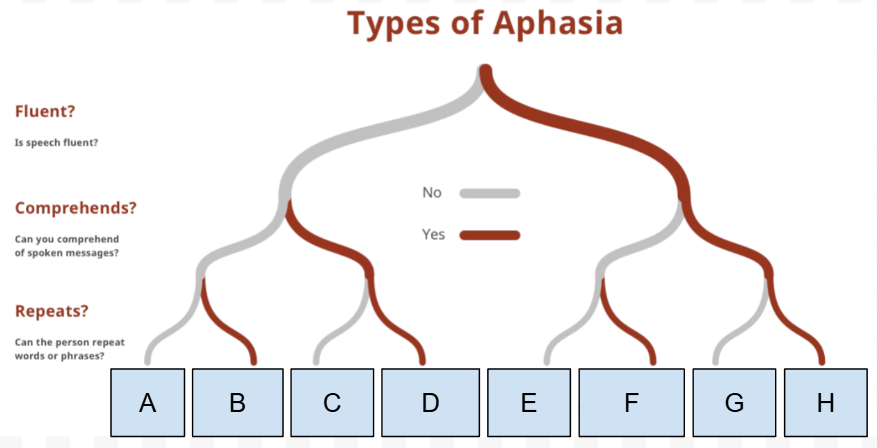
What Type of Aphasia is B
Mixed transcortical aphasia
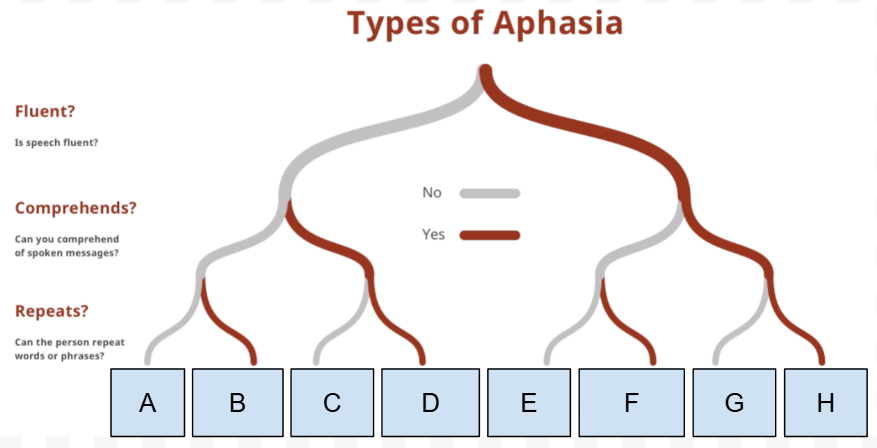
What Type of Aphasia is C
Broca’s Aphasia
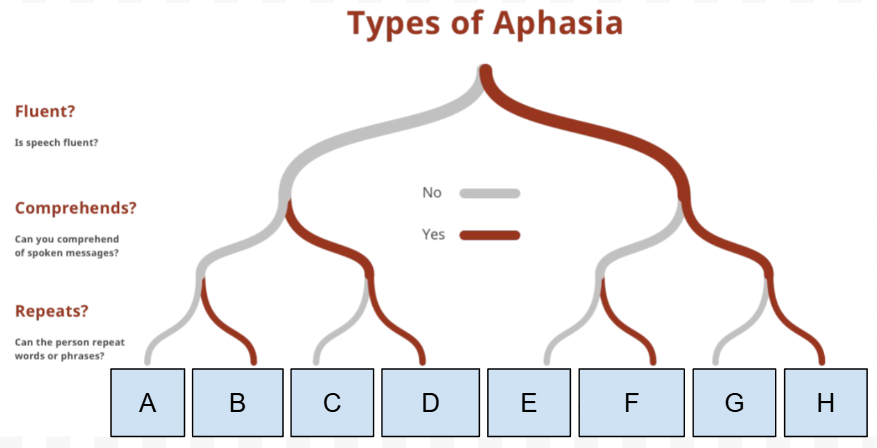
What Type of Aphasia is D
Transcortical motor aphasia
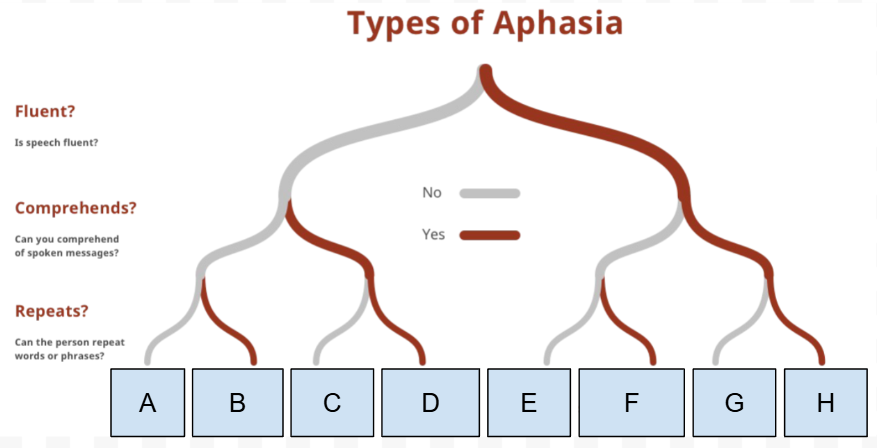
What Type of Aphasia is E
Wernike’s Aphasia
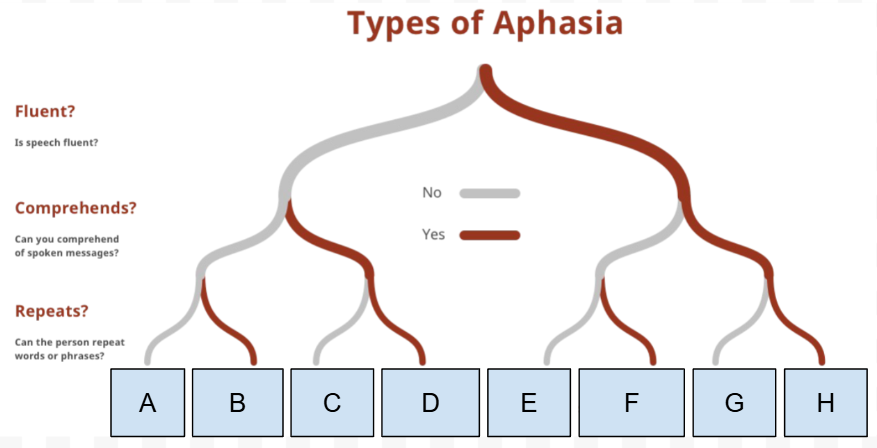
What Type of Aphasia is F
Transcortical sensory aphasia
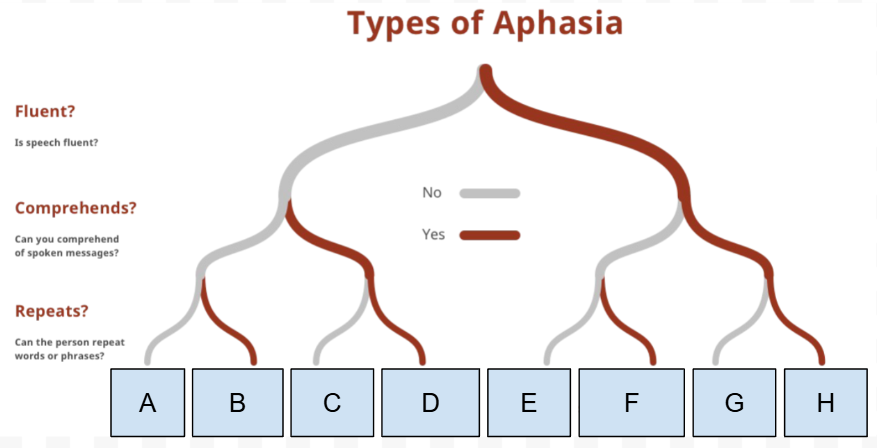
What Type of Aphasia is G
Conduction aphasia
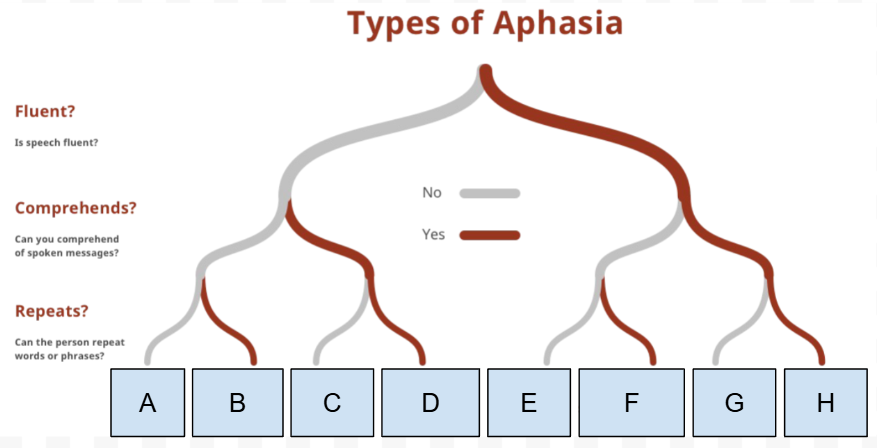
What Type of Aphasia is H
Anomic Aphasia
What is the first Question on the “types of Aphasia” chart
Is speech Fluent
What is the Second question on the “types of Aphasia” chart
Can they comprehend spoken messages
What is the third question on the “types of Aphasia“ chart
Can they repeat words/phrases