Plant Hormones and External Factors
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
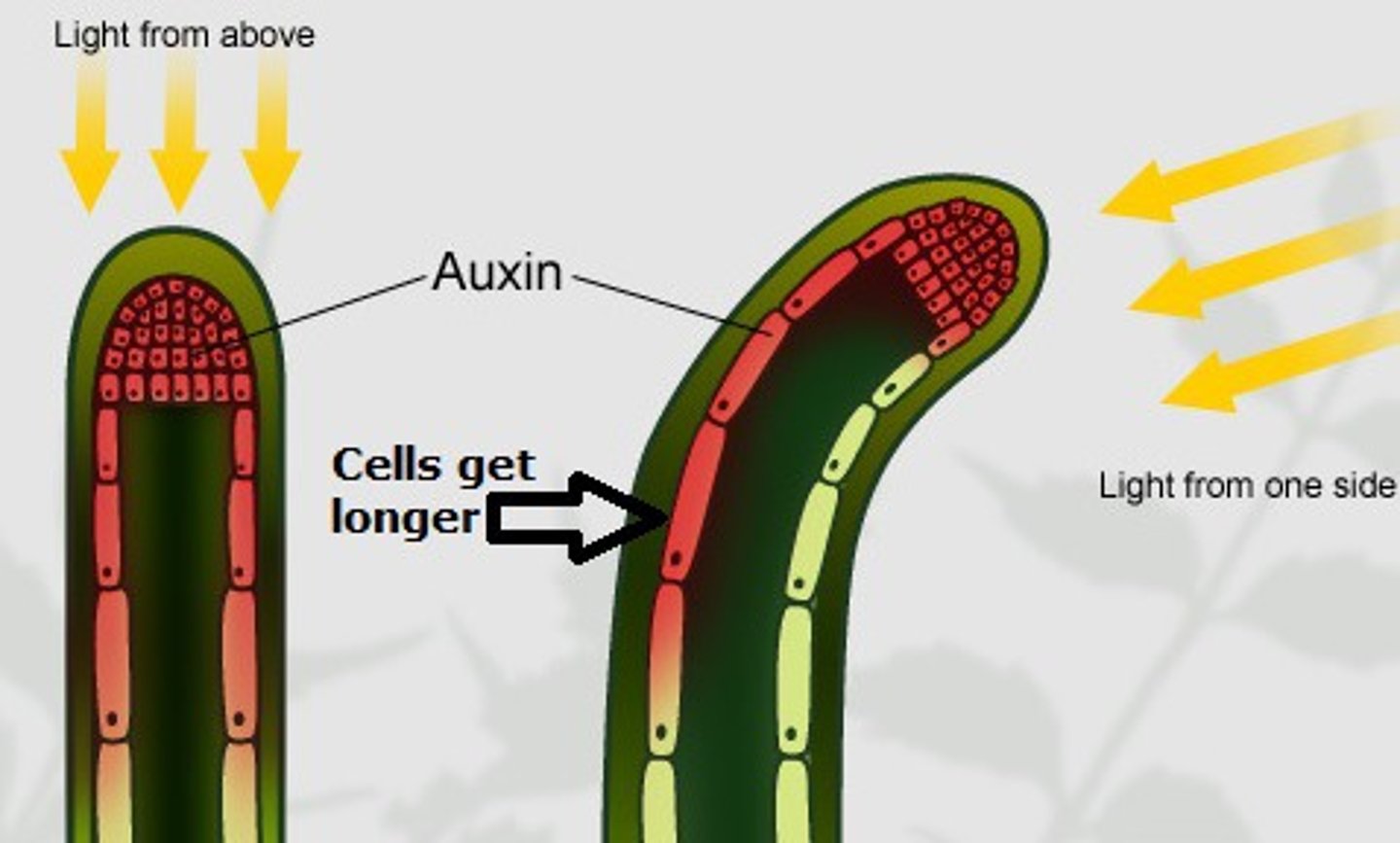
Roles of Auxin
Cell elongation, apical dominance, lateral root formation, tropisms
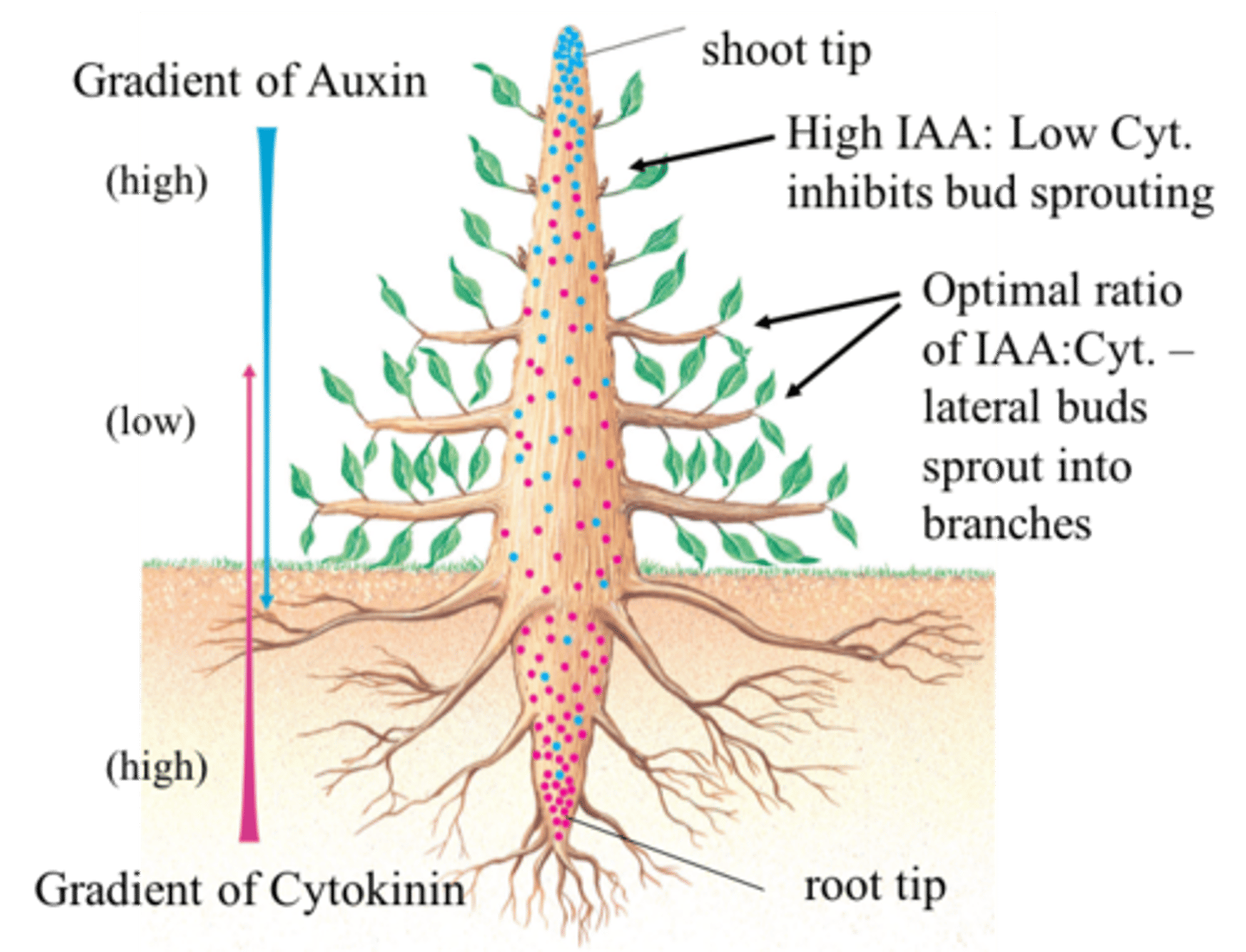
Roles of Cytokinin
Regulate cell division, modify apical dominance (inhibits auxin), delay leaf aging, used in tissue culture, cell differentiation
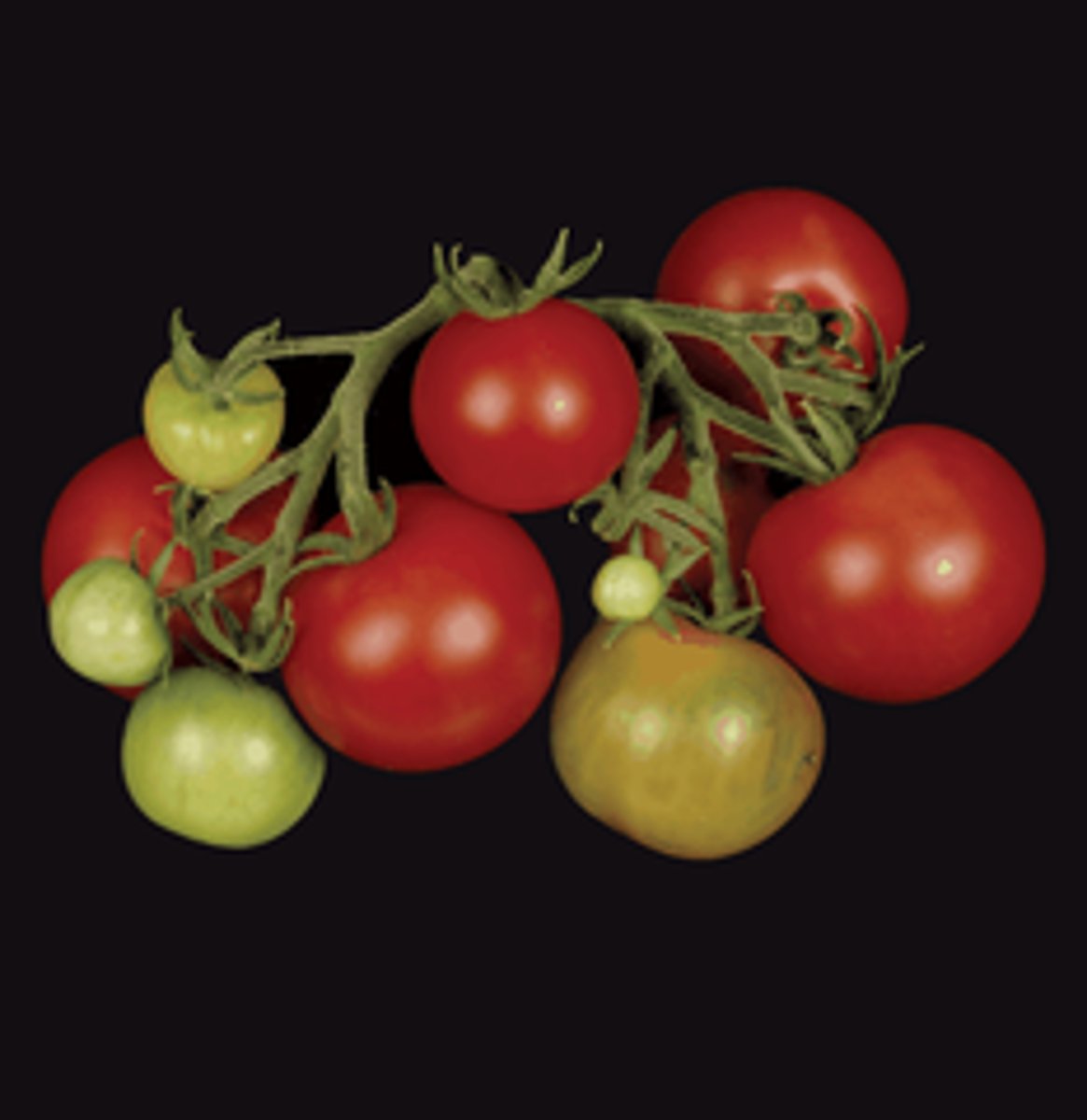
Roles of Ethylene
Promote leaf/fruit abscission, cause fruit ripening

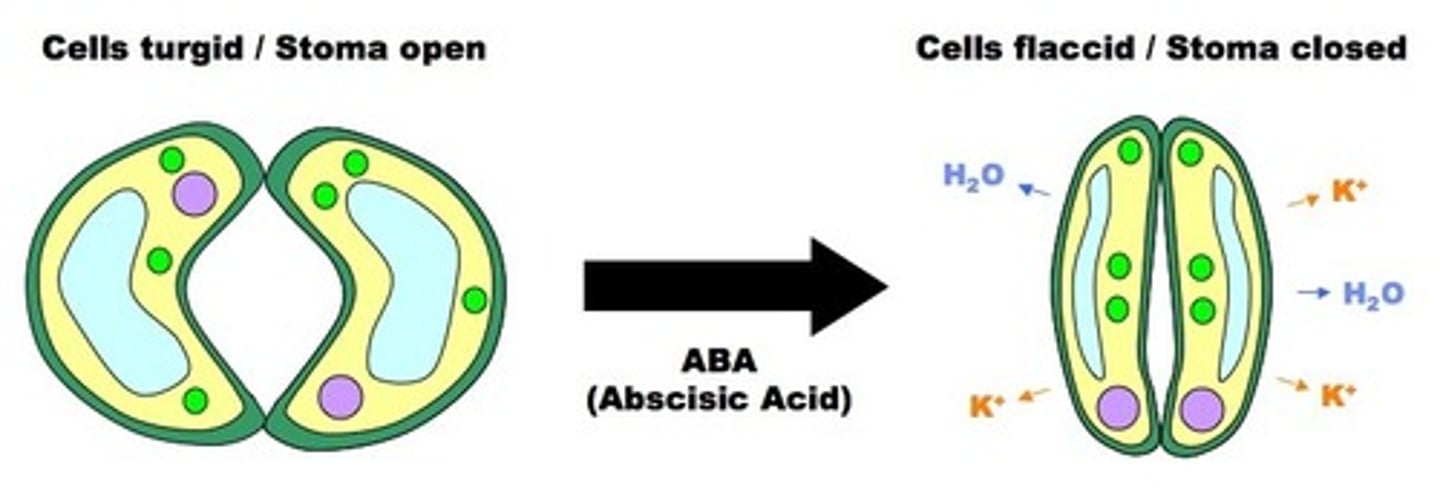
Roles of Abscisic Acid
prevents premature seed germination, induces stomatal closing
Roles of Gibberellins
stimulates cell elongation+division, hastens seed germination

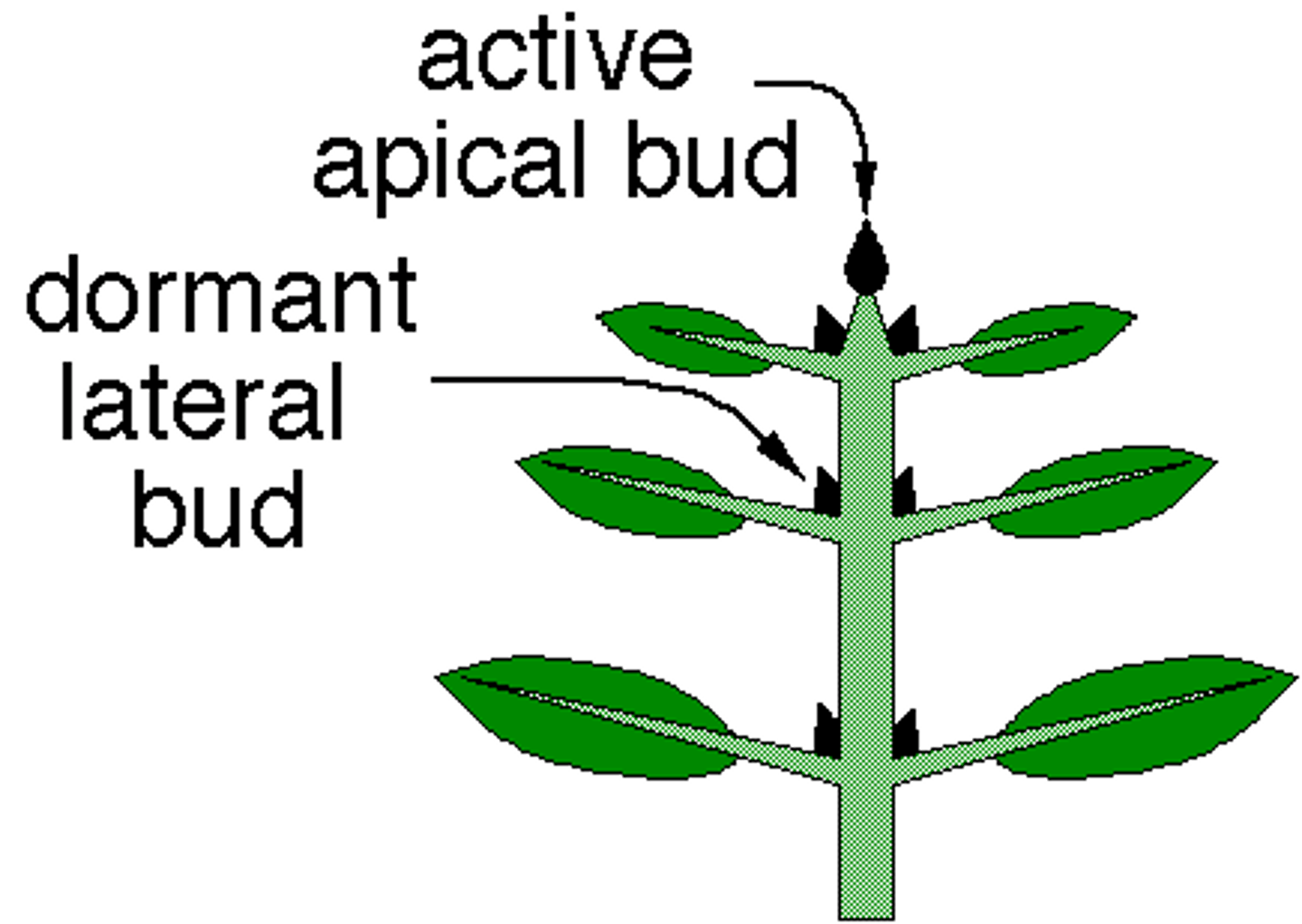
Apical Dominance
phenomenon in which the closer a bud is to the stem's tip, the more its growth is inhibited; controlled by auxin
Roles of Brassinosteroids
steroid hormones in plants that have a variety of effects, including cell elongation, retarding leaf abscission, and promoting xylem differentiation.
Tropism
A growth response of a plant toward or away from a stimulus
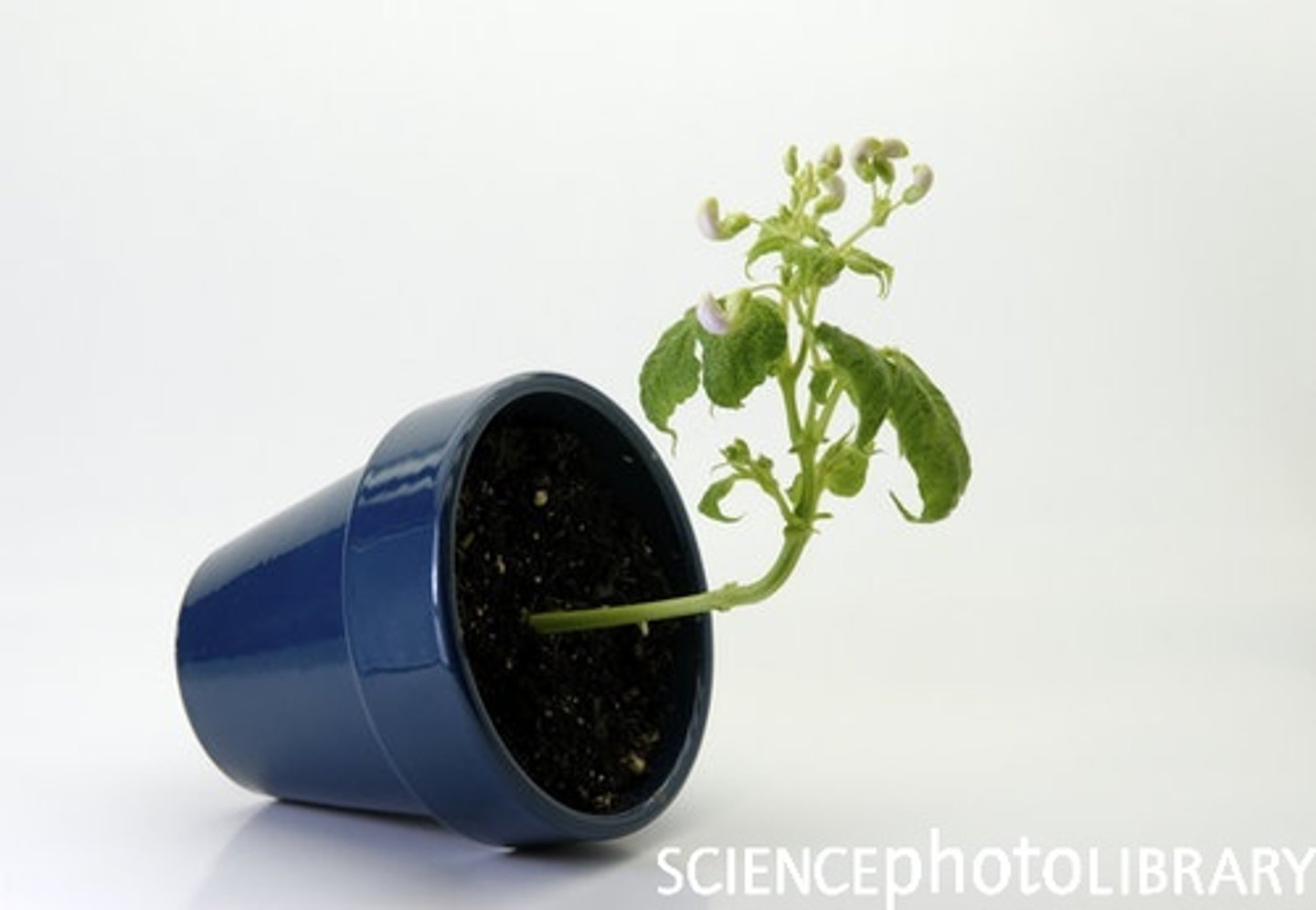

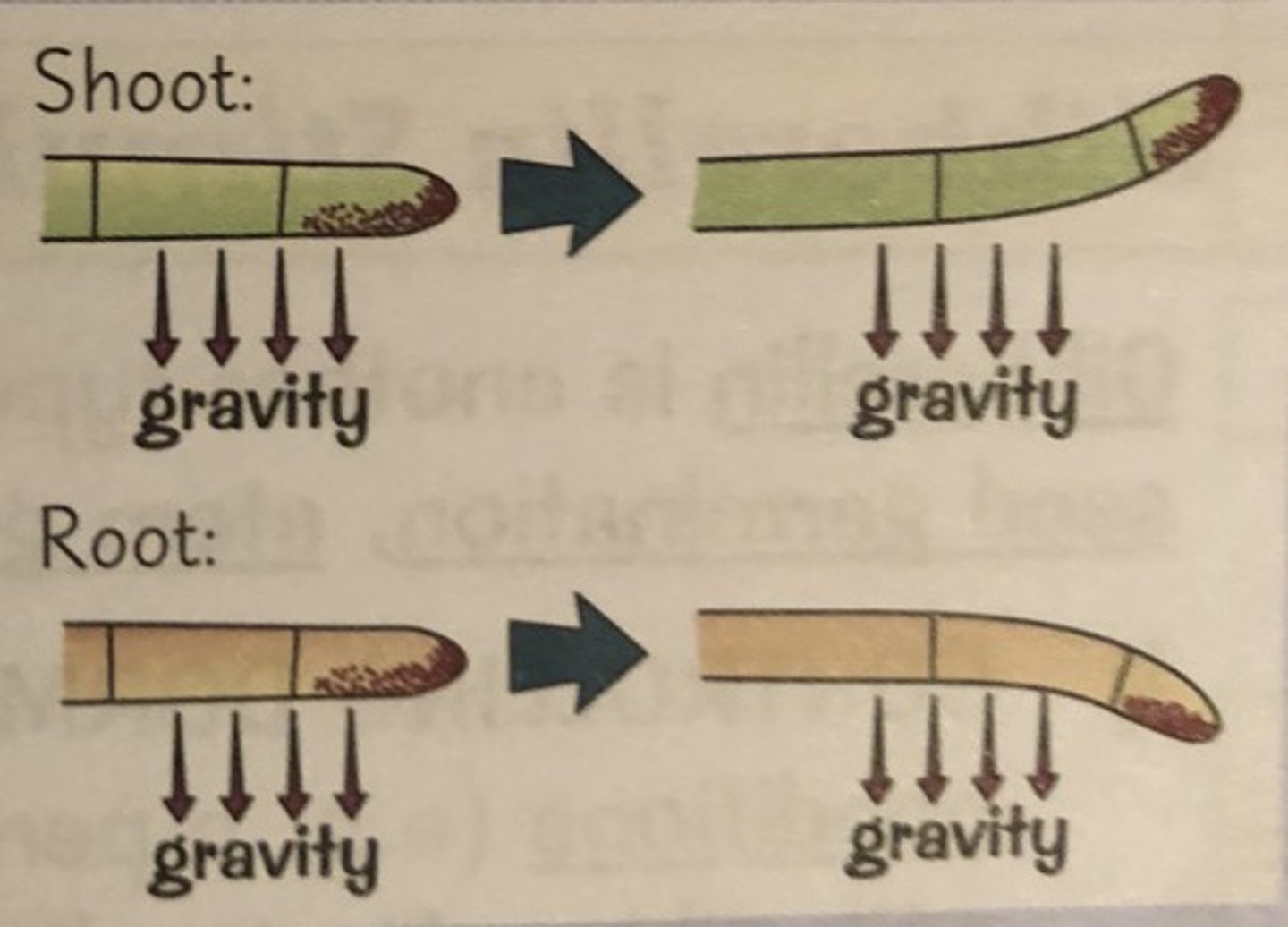
Gravitropism (roots)
Growth towards (positive) gravity; amyloplasts sense gravity at bottom of cell, auxin inhibits elongation on lower side of cell
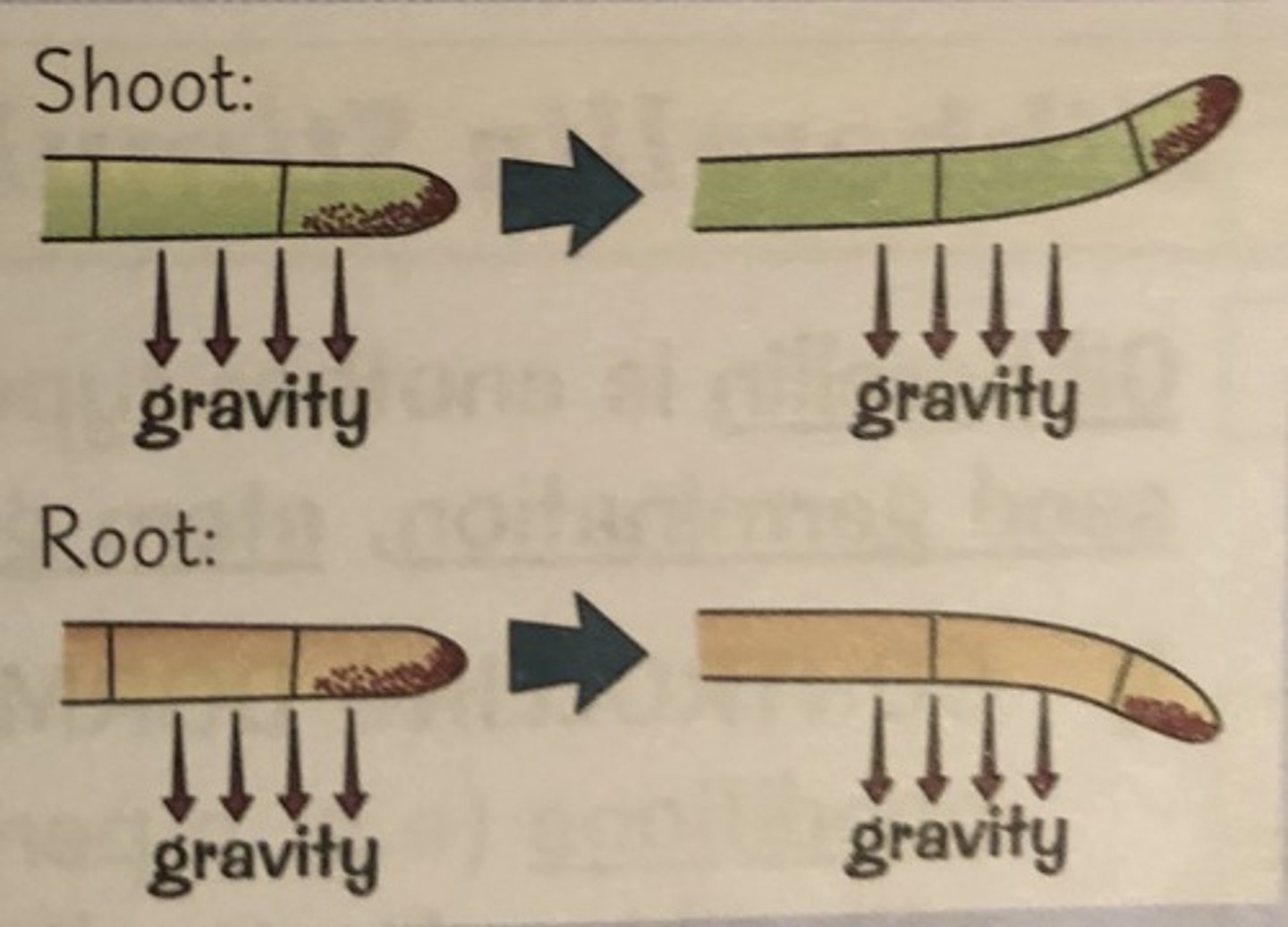
Gravitropism (shoots)
Growth away (negative) from gravity, auxin promotes elongation on lower side
Hydrotropism
a plants growth response to water; root grows towards the water
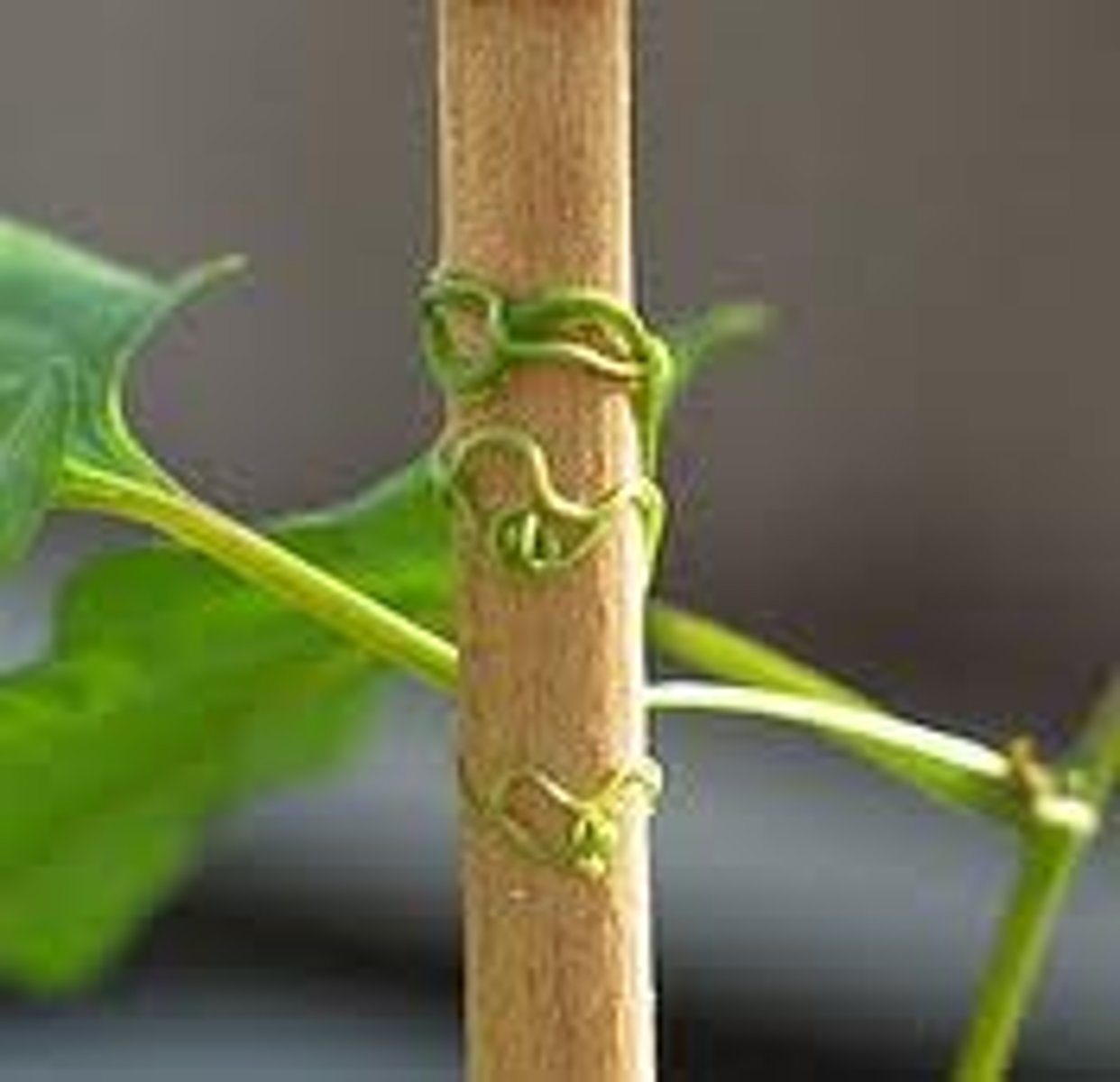
Thigmotropism
A growth response to touch

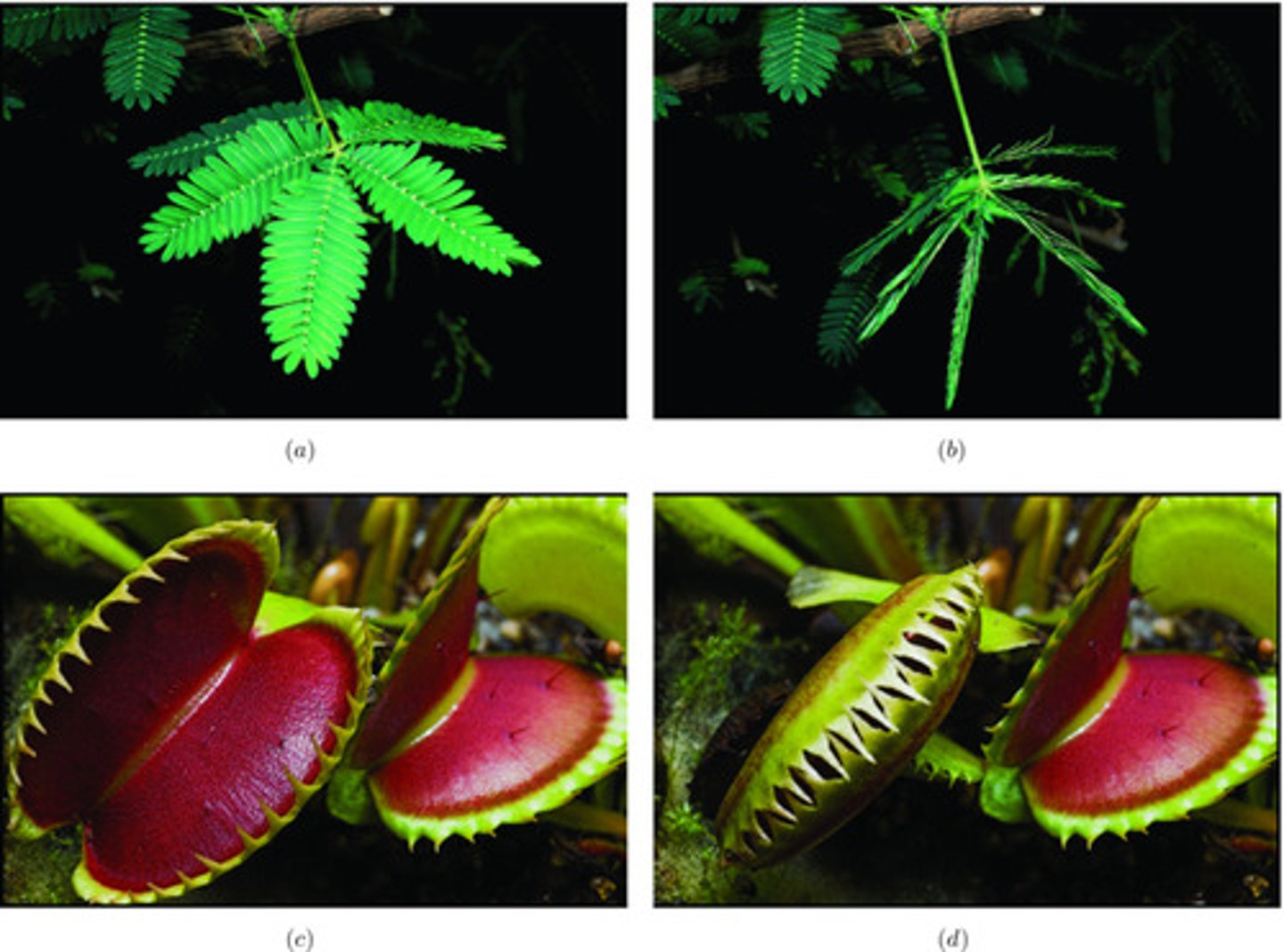
Nastic movement
Response of plant to stimulus; its direction of growth is independent of stimulus; can be due to turgor pressure
Sleep mvmts = leaves droop at night (turgor pressure)

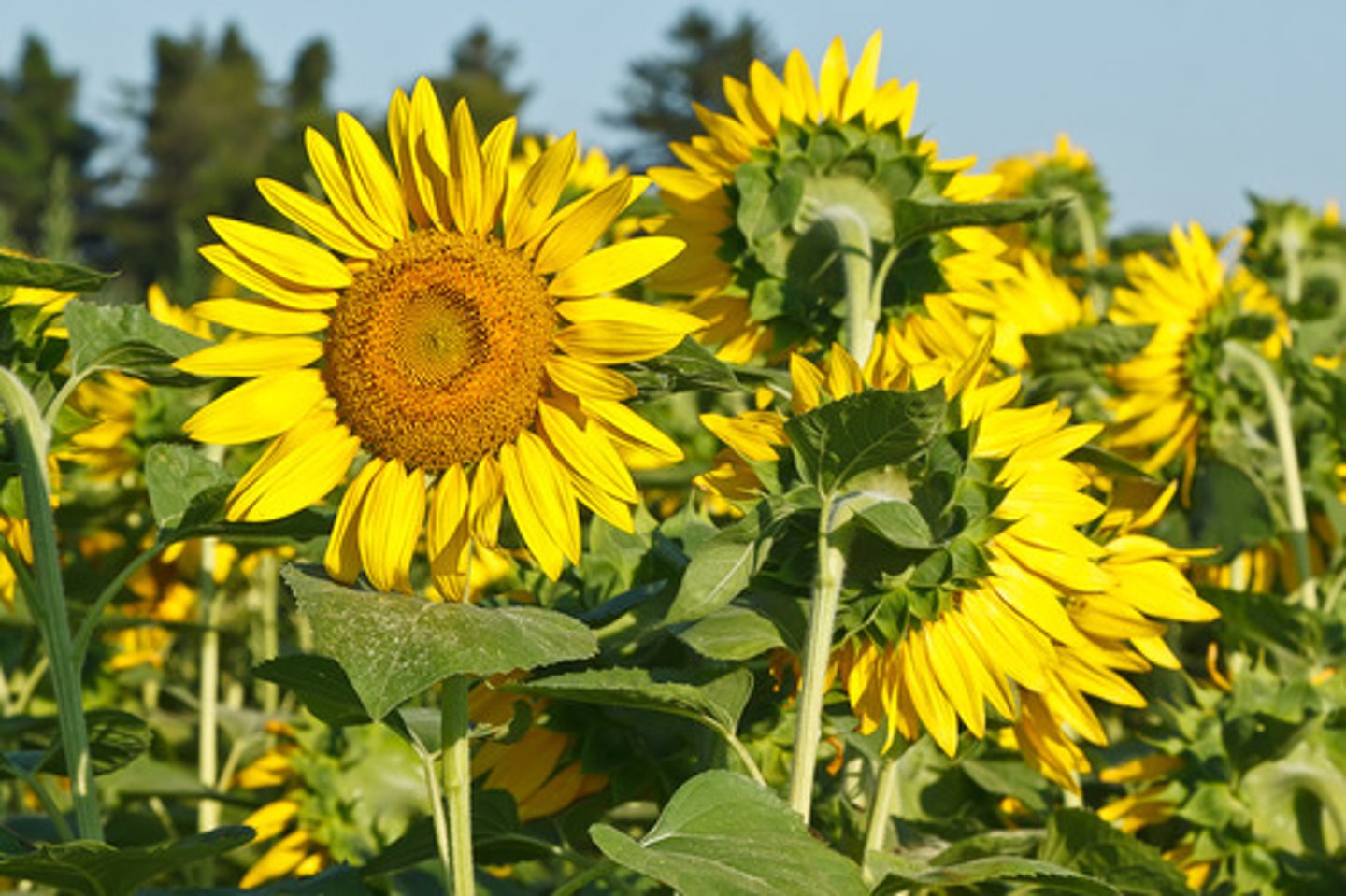
Heliotropism
tropism + nastic movement; tracking of sun via turgor pressure

Photoperiodism
Flowering response due to changes in day length
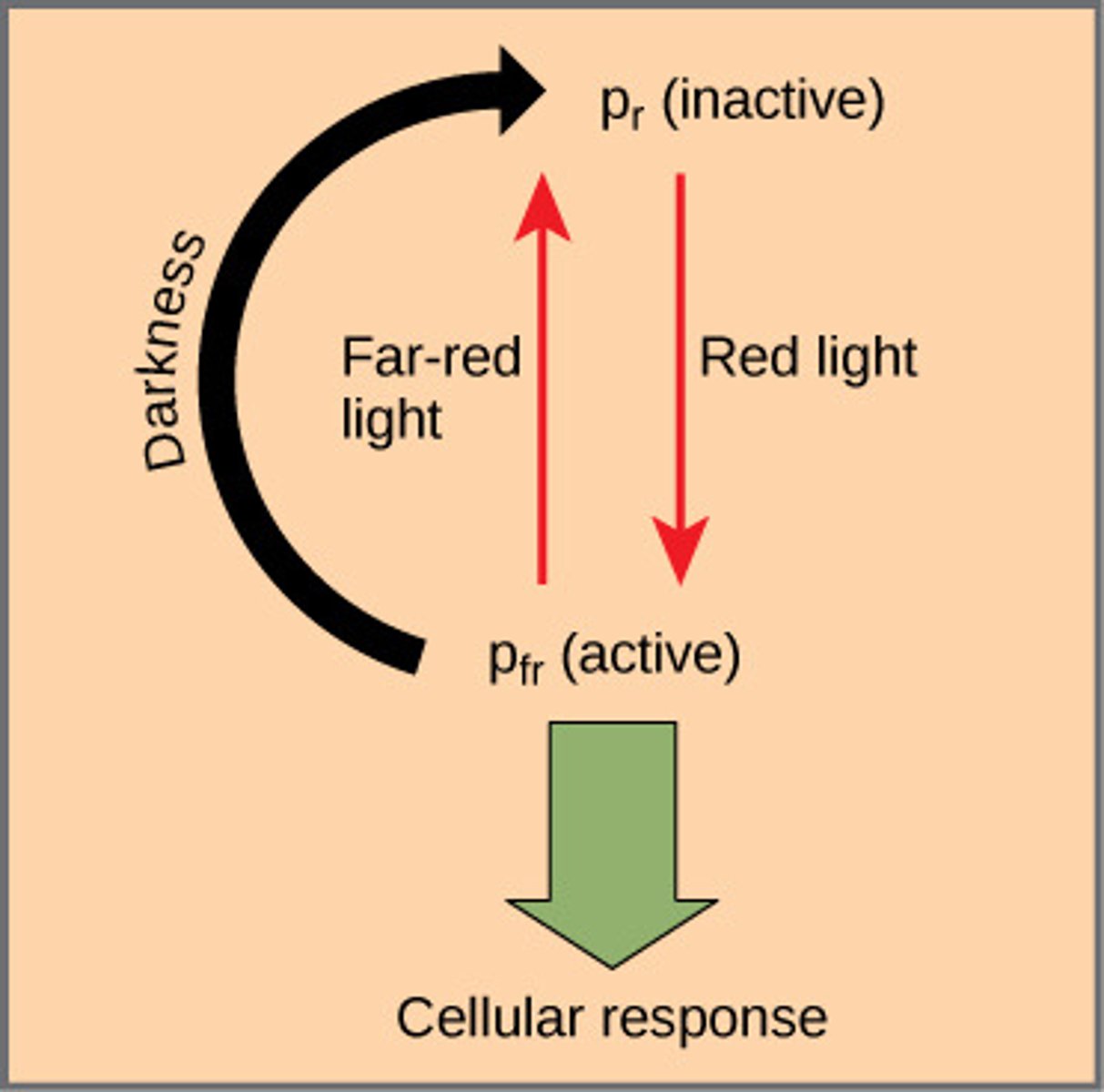
Phytochrome
responsible for photoperiodism
Pr= inactive, absorbs red light, converted to Pfr
Pfr= active, absorbs far red light, converted to Pr
Pr=Pfr during day, flashes of far red light at night will reverse flowering behavior
circadian rhythm
24hr clock reset by phytochrome system, helps plant tell what time of day