Exam IV Ortho w/Instruments
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
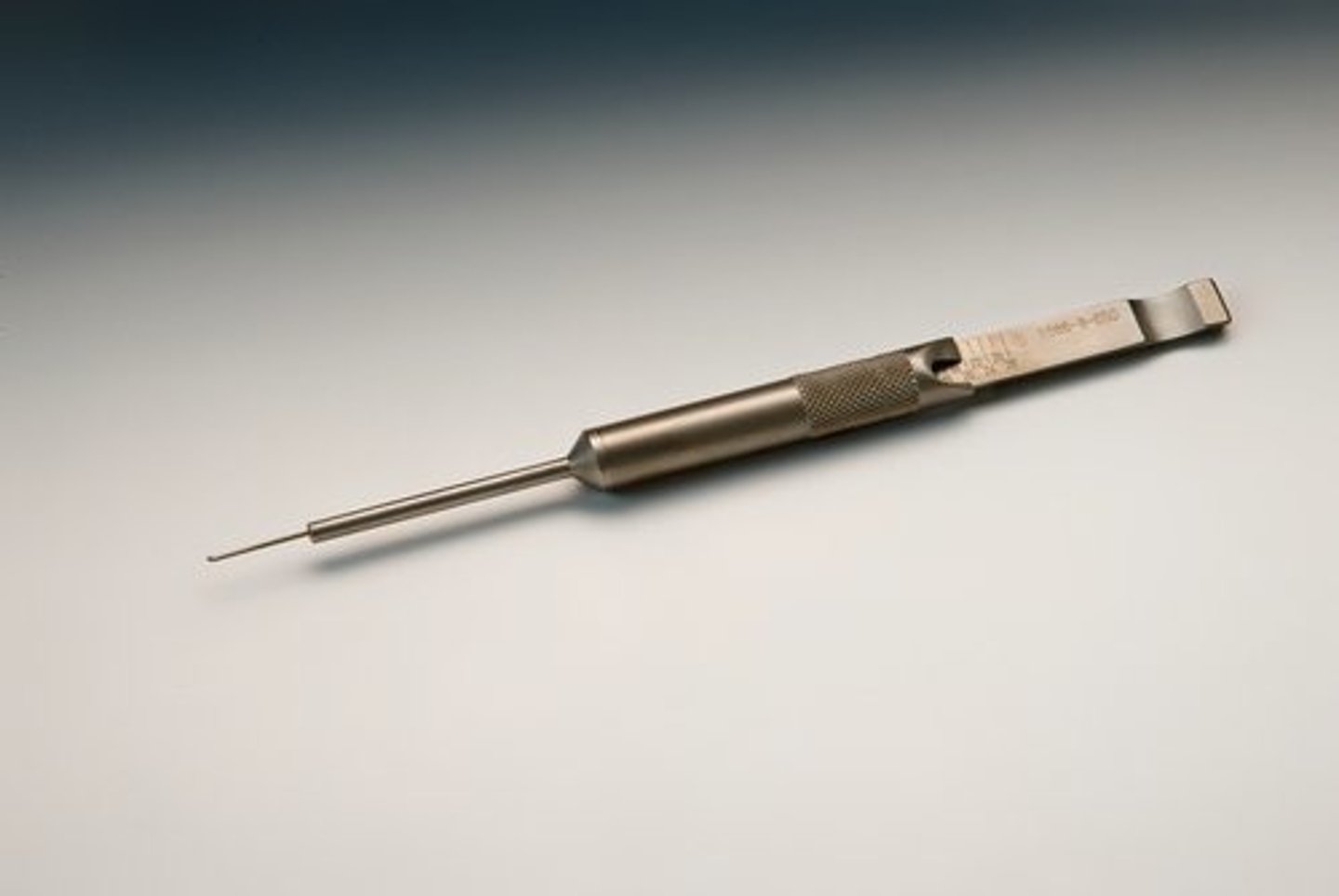
Depth Gauge
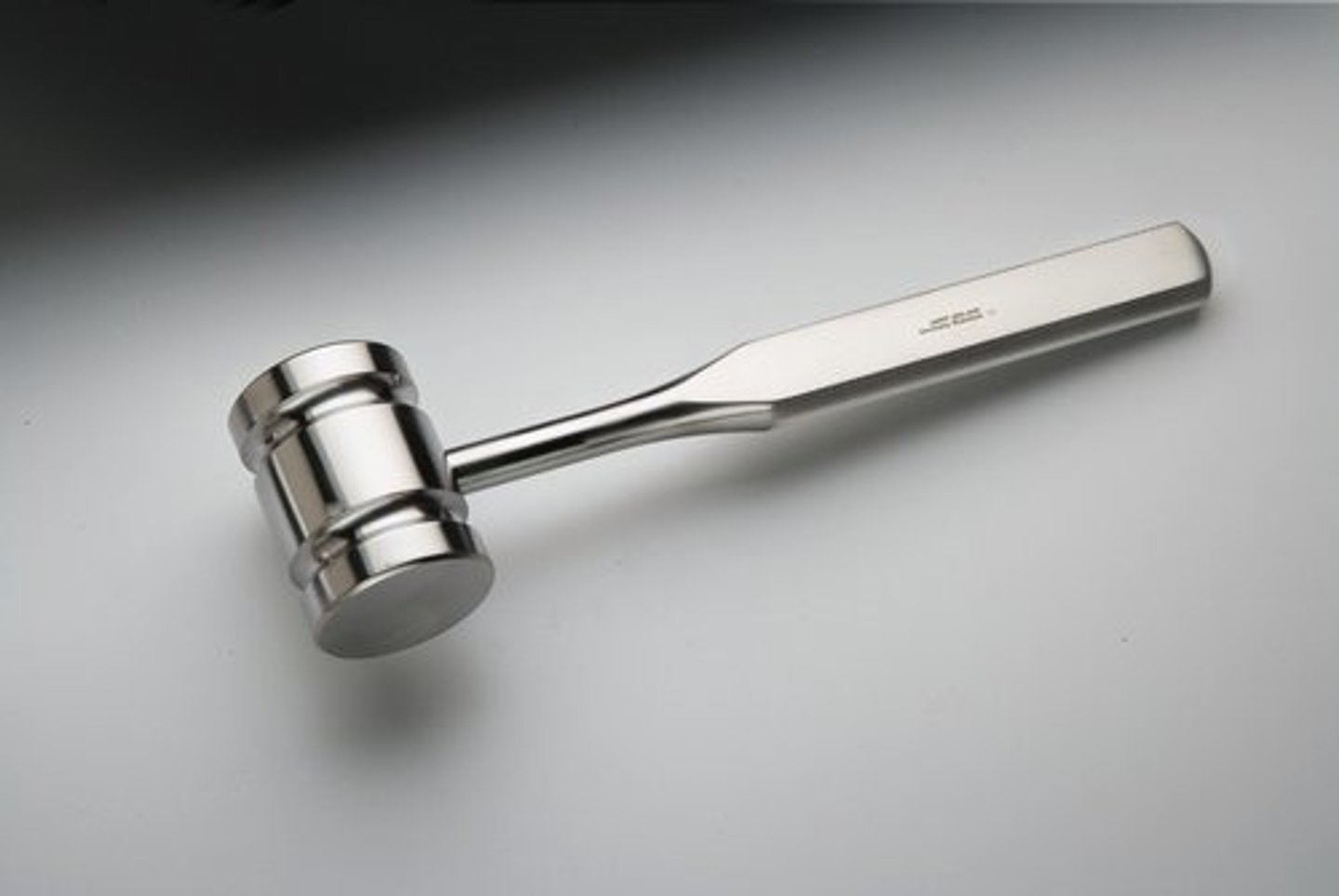

Mallet
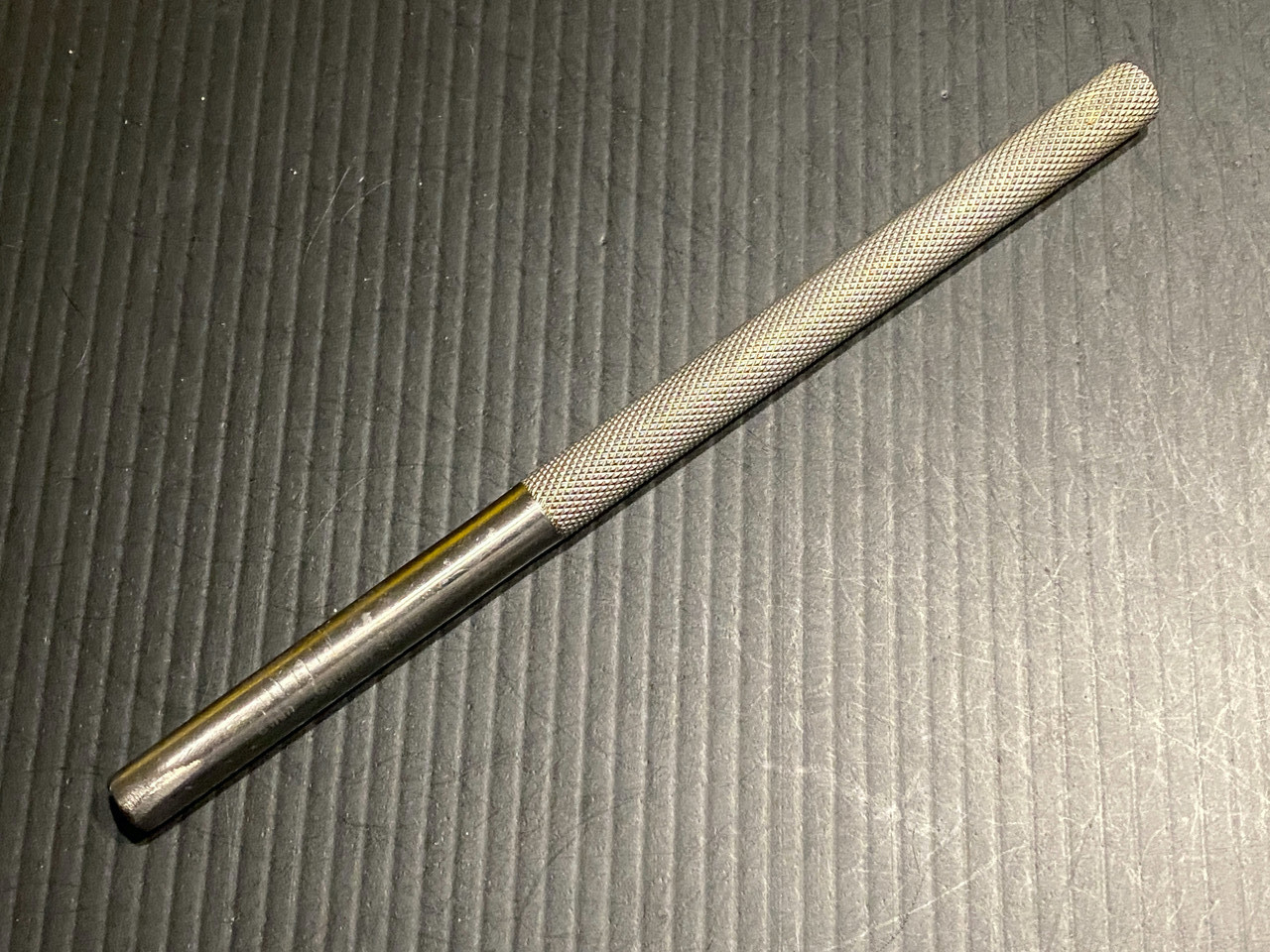

Bone Tamp
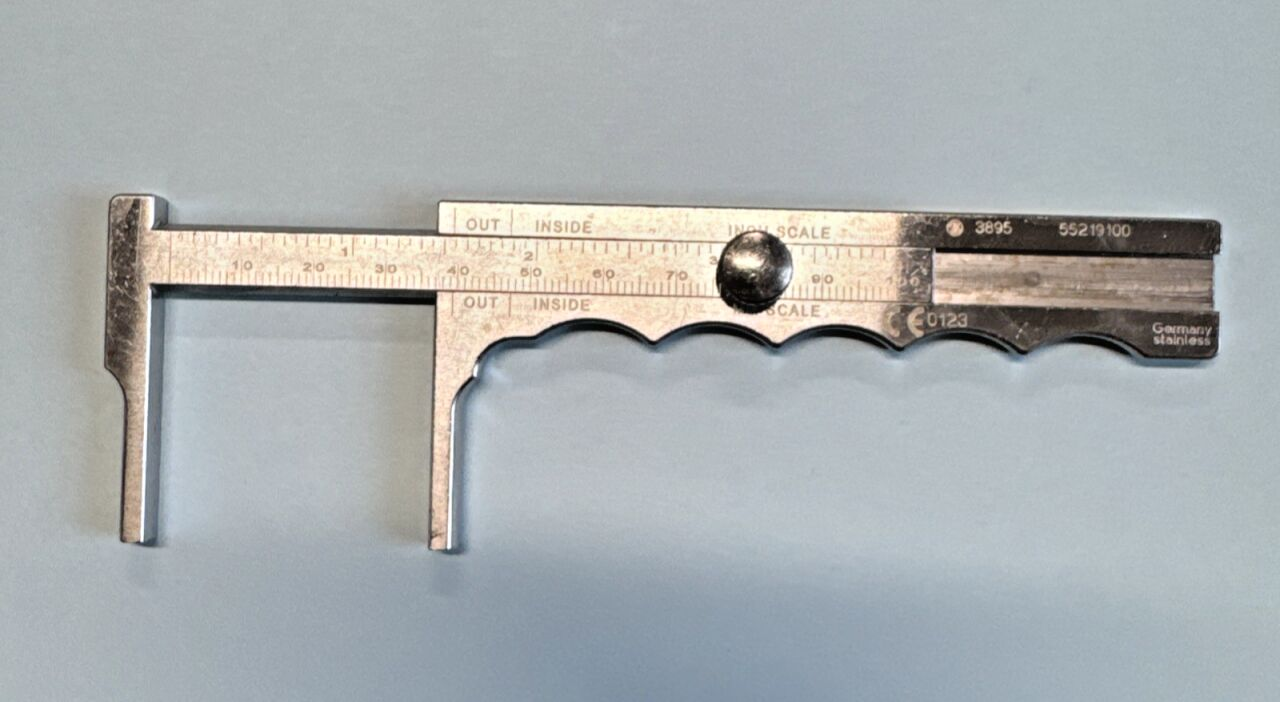

Townley Caliper
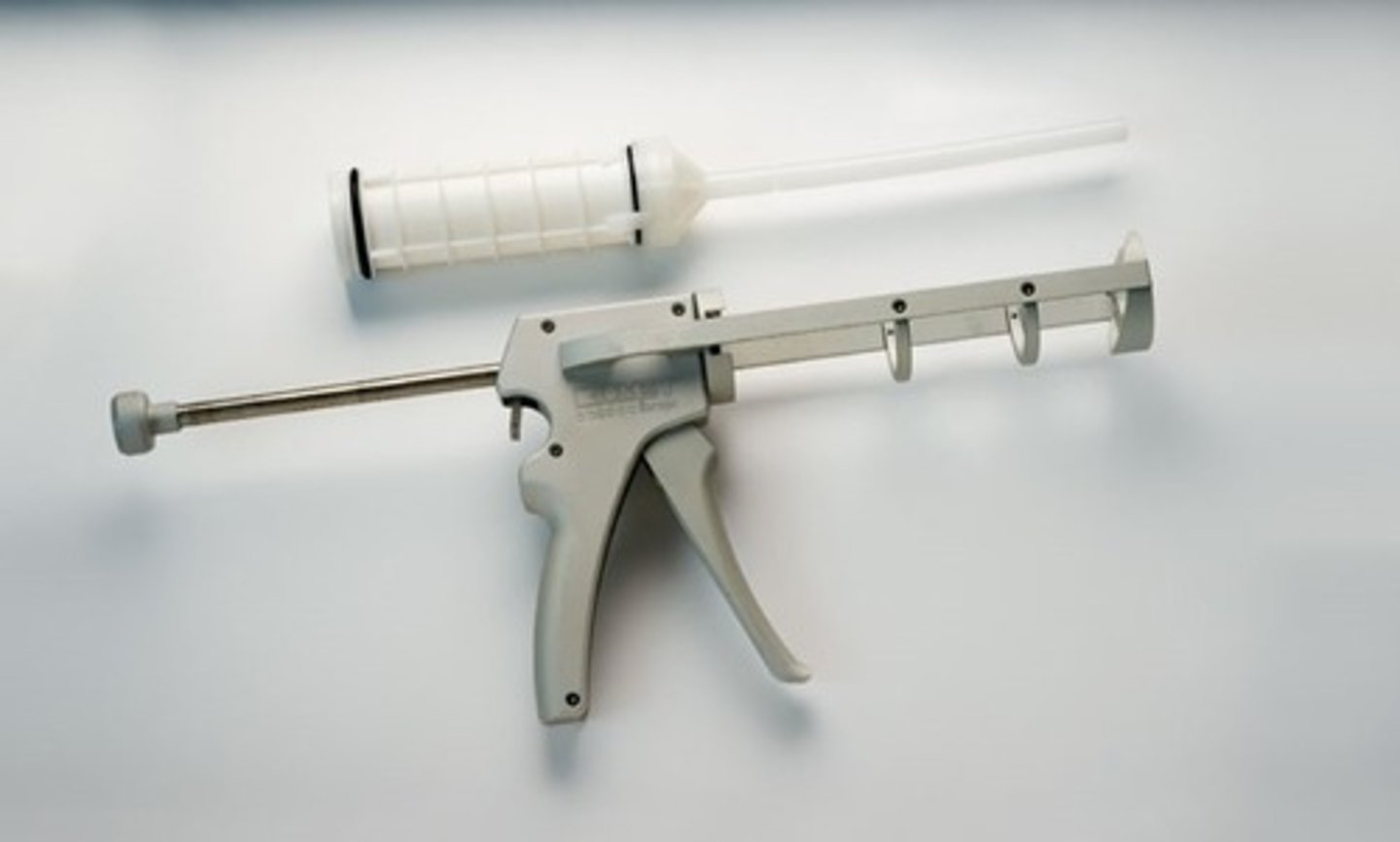

Bone Cement Injector
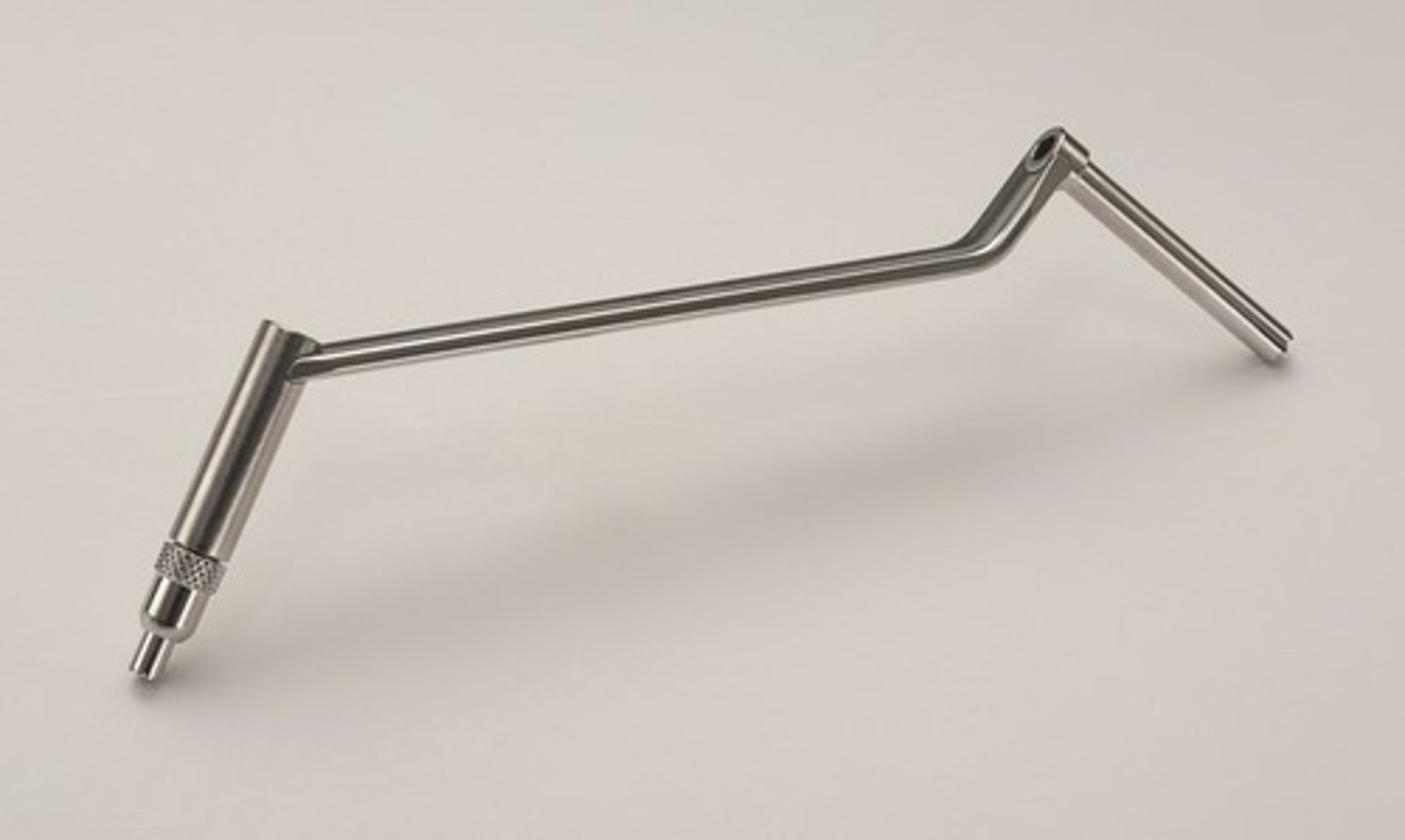

Drill Guide
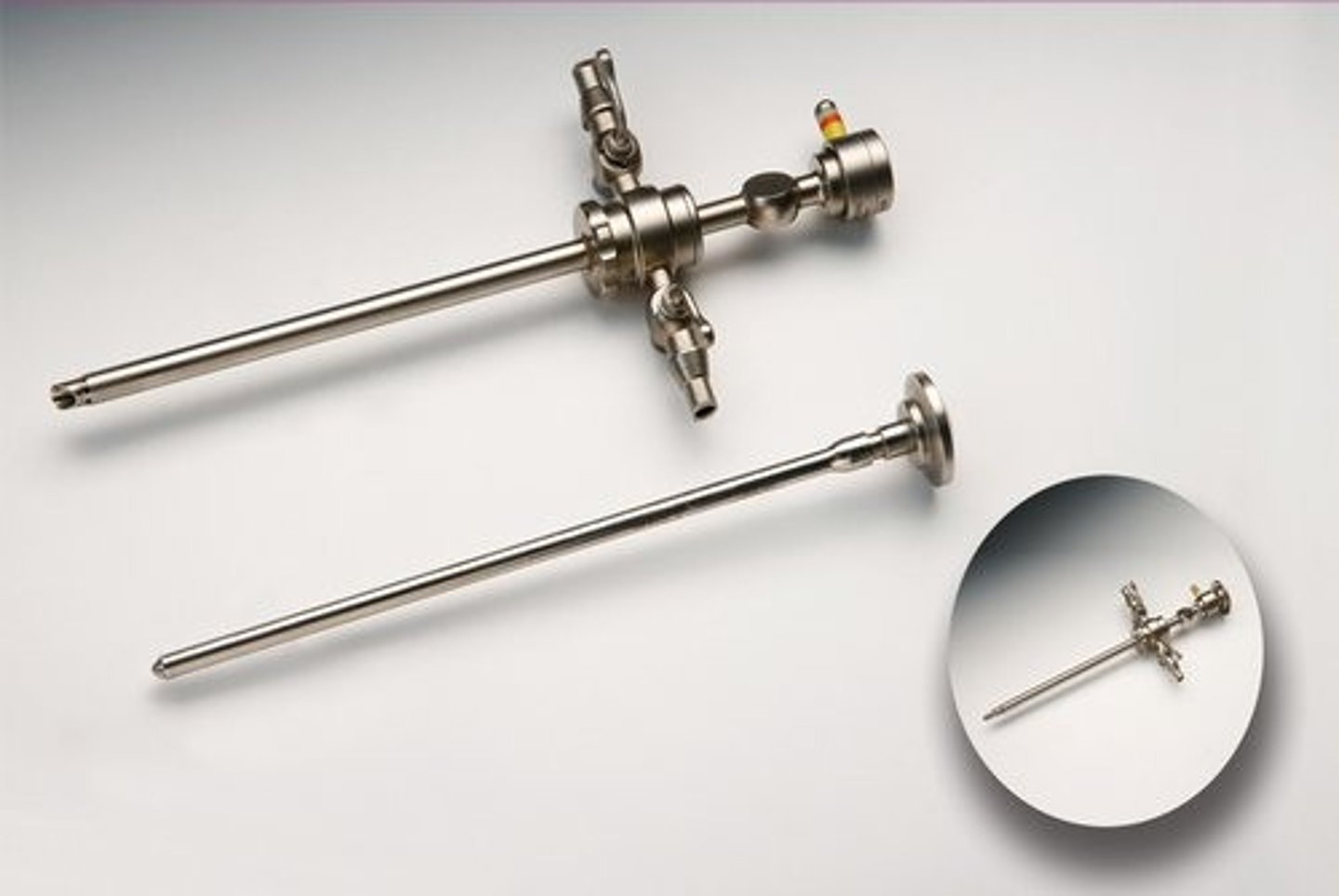

4-mm Sheath with Obturator
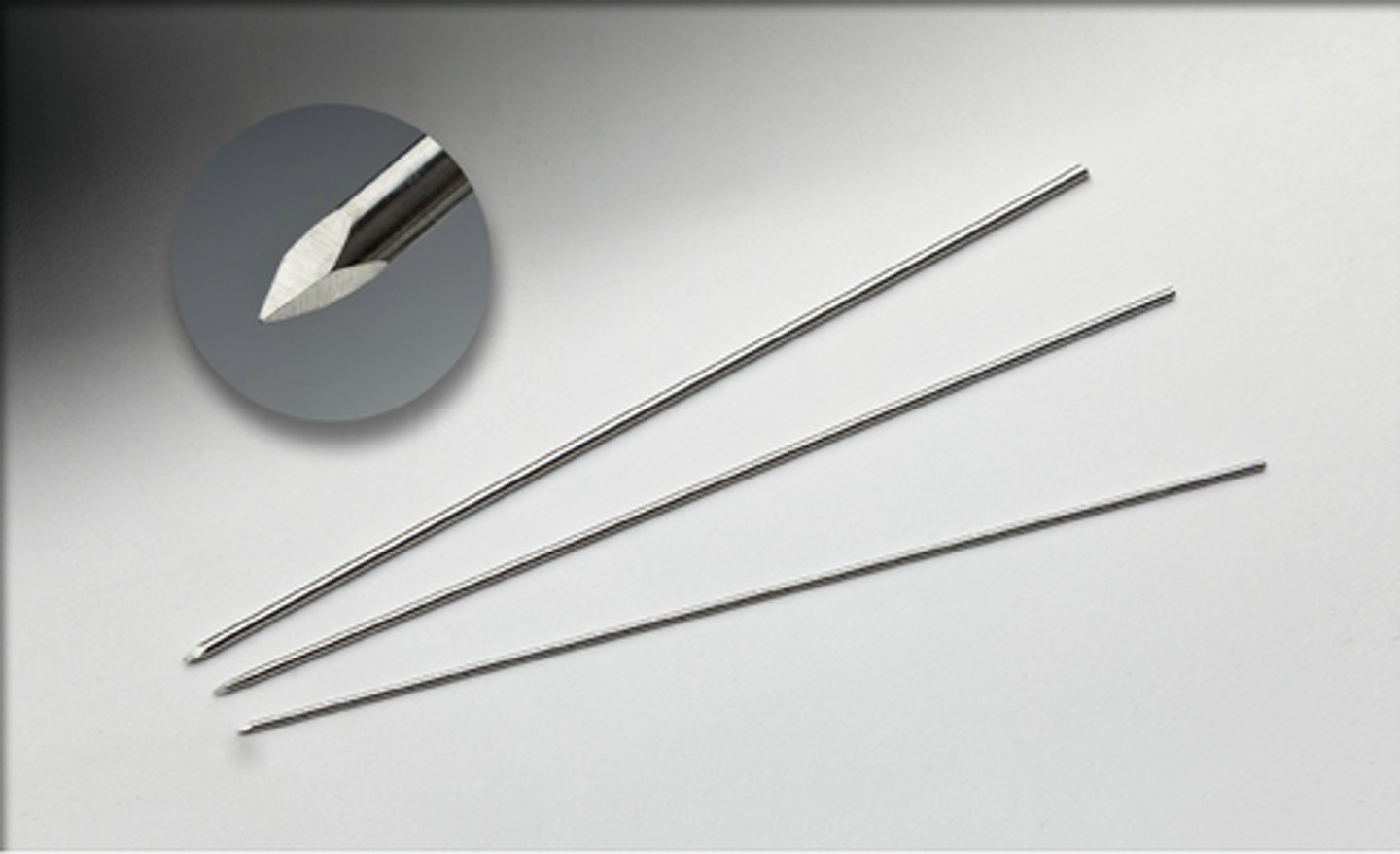
Kirschner Wires
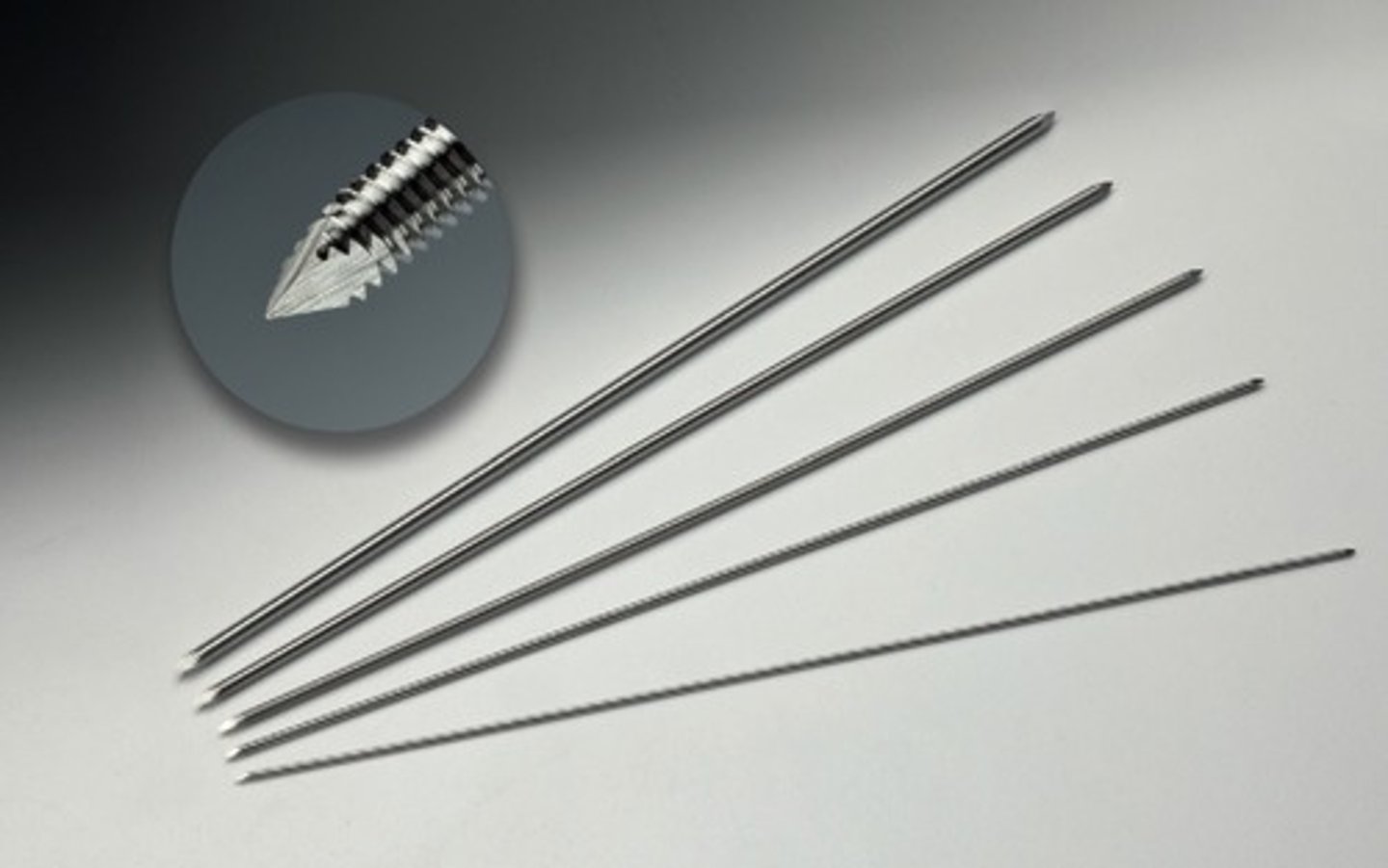
Steinman Pins
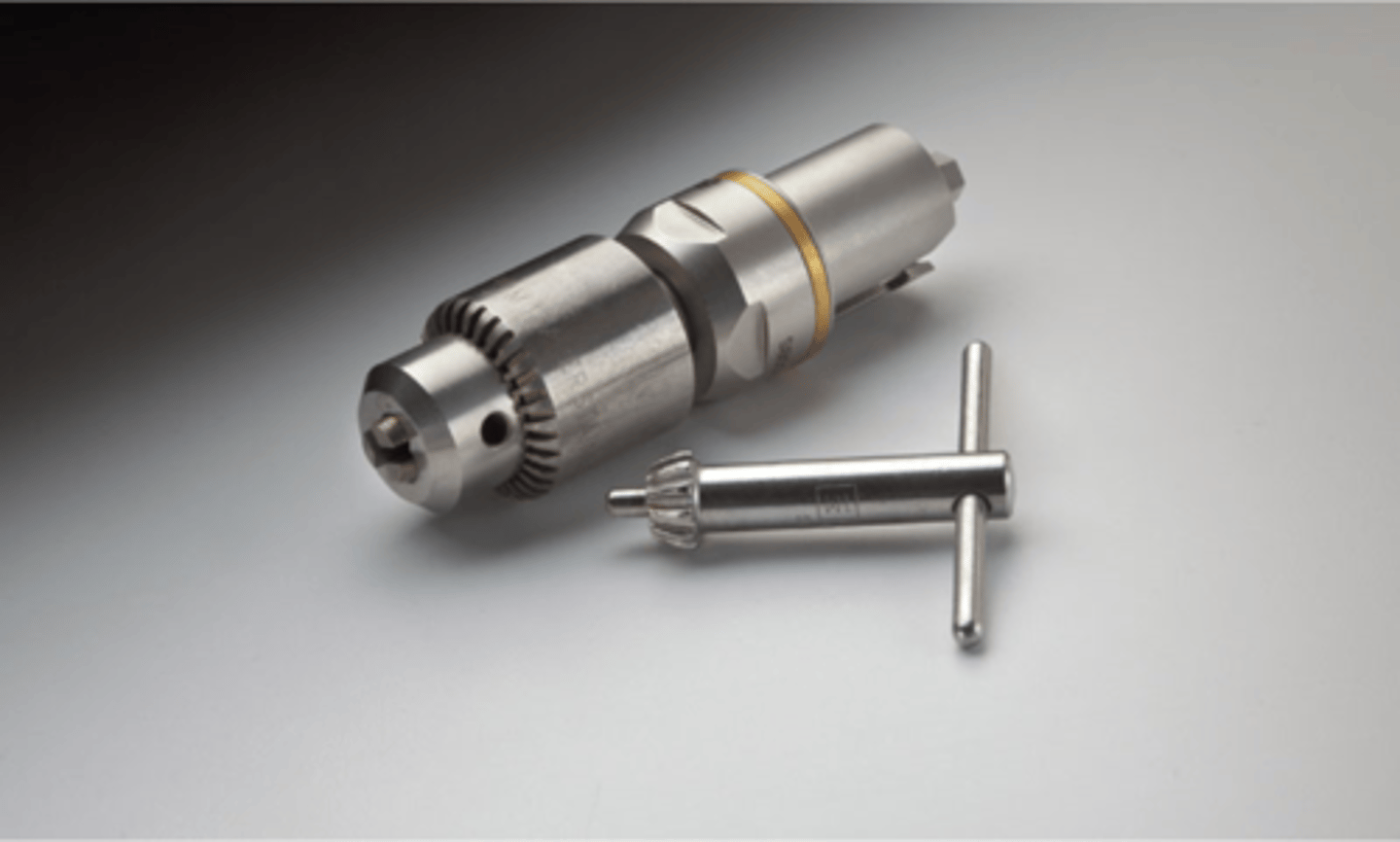

Jacobs Chuck & Key
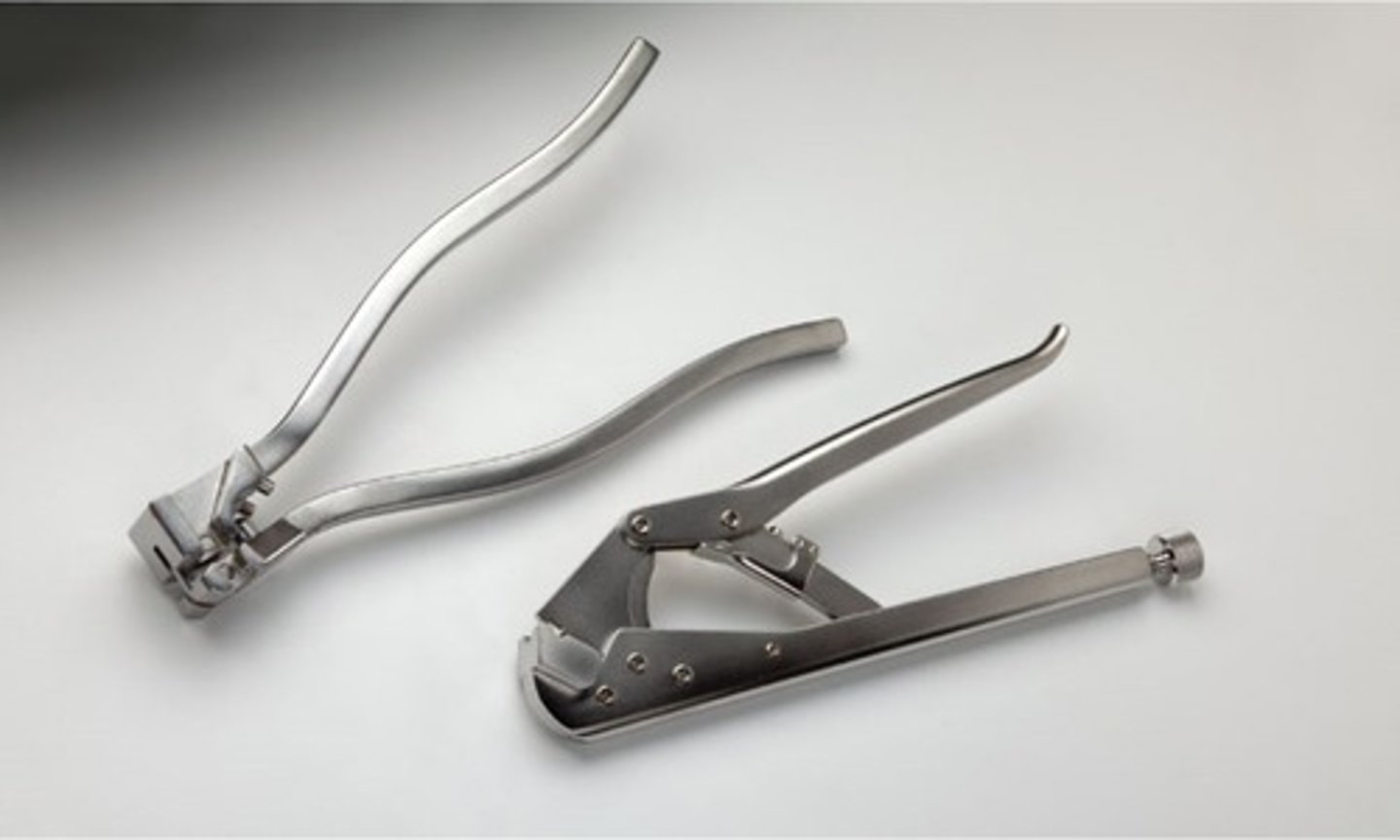
Plate Bending Pliers
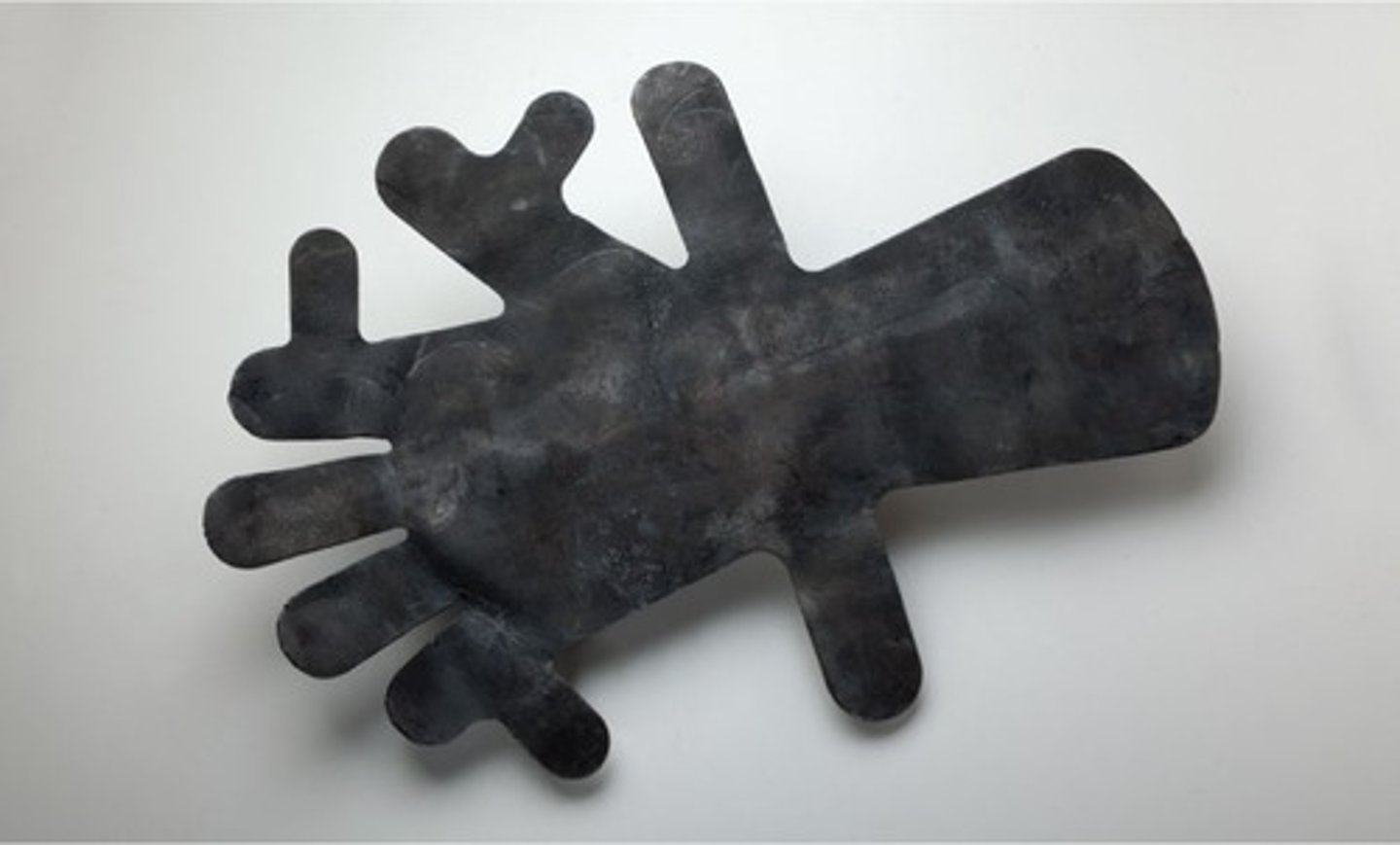

Lead Hand
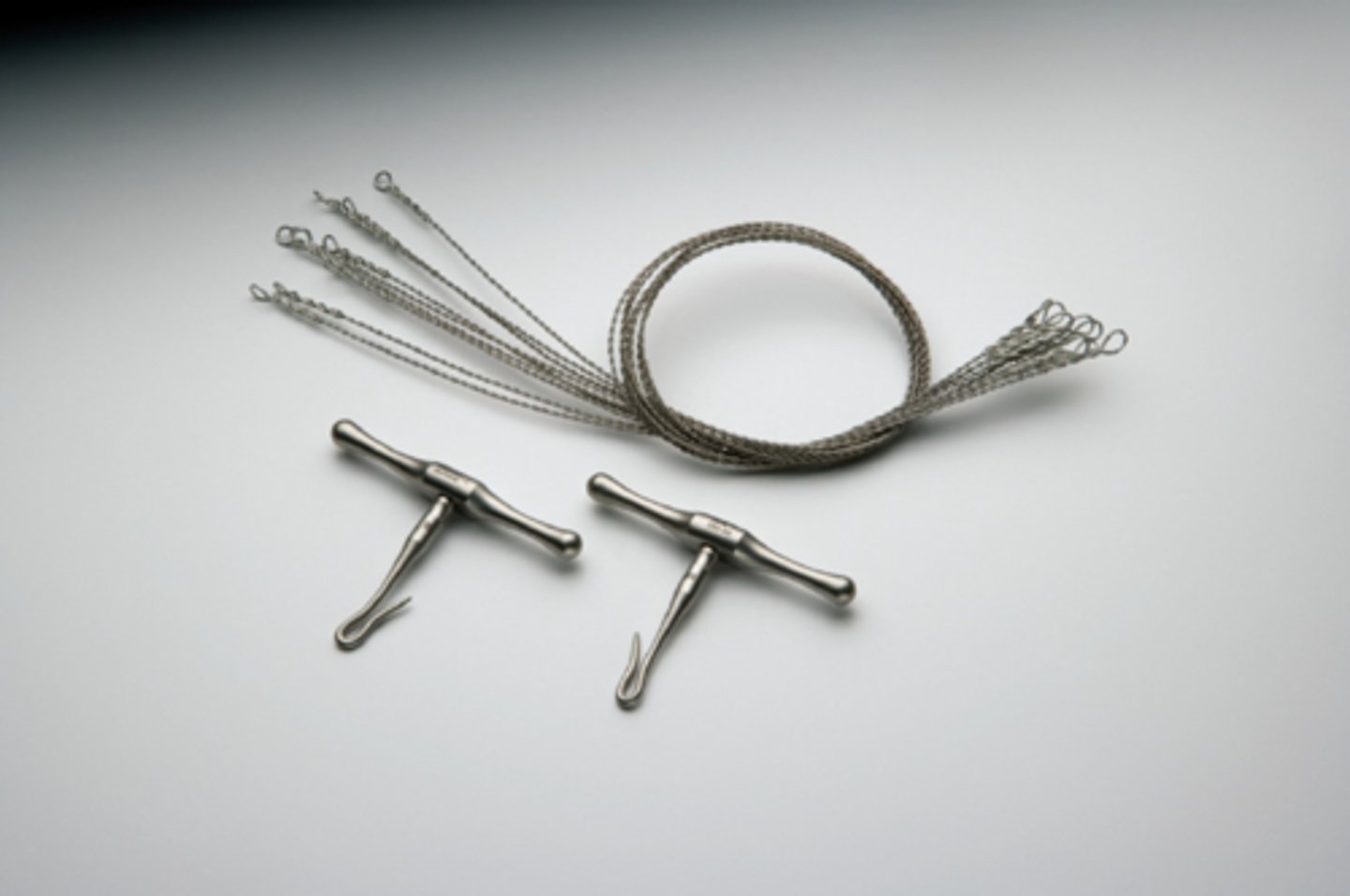

Gigli Saw
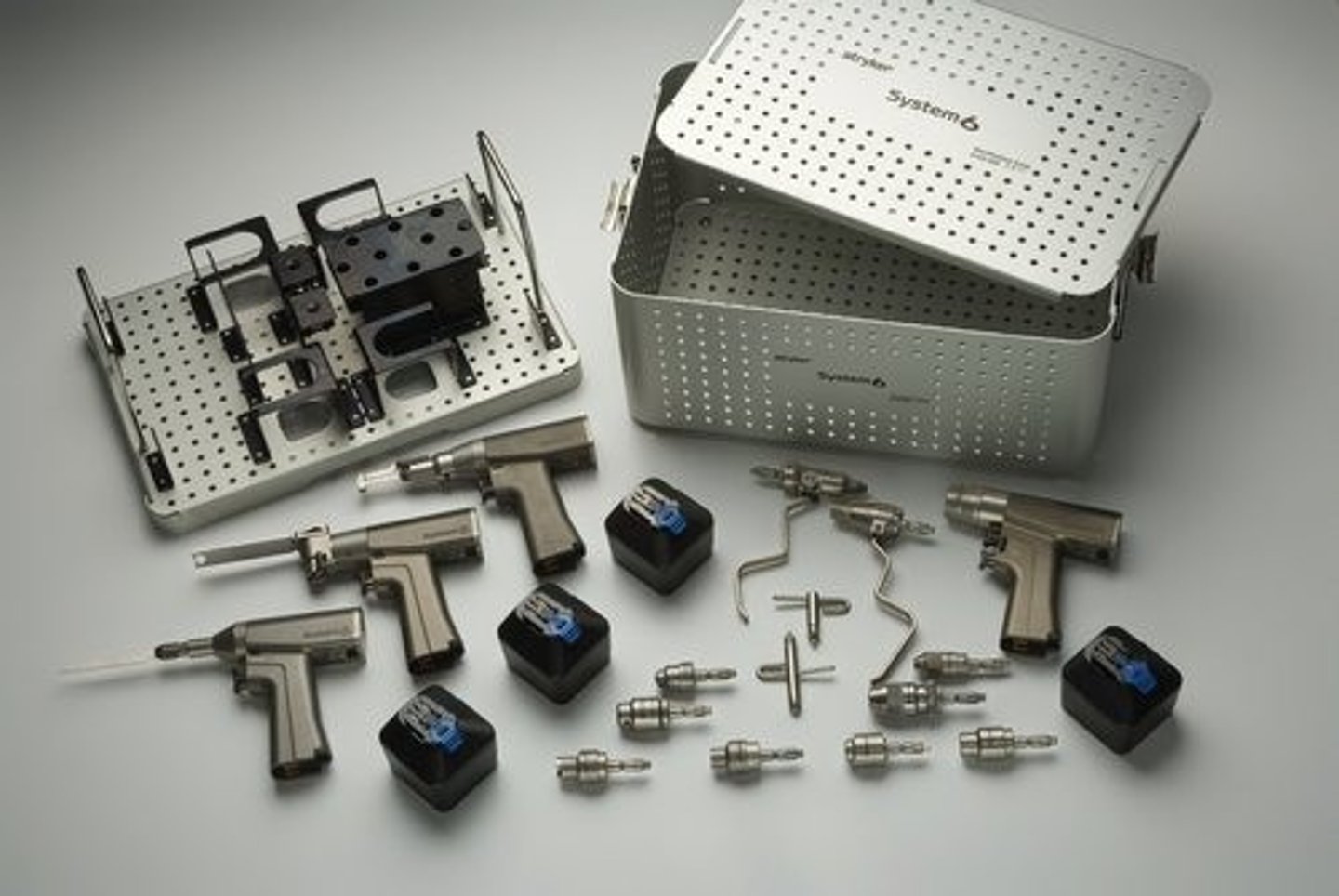

Stryker System 6 Power
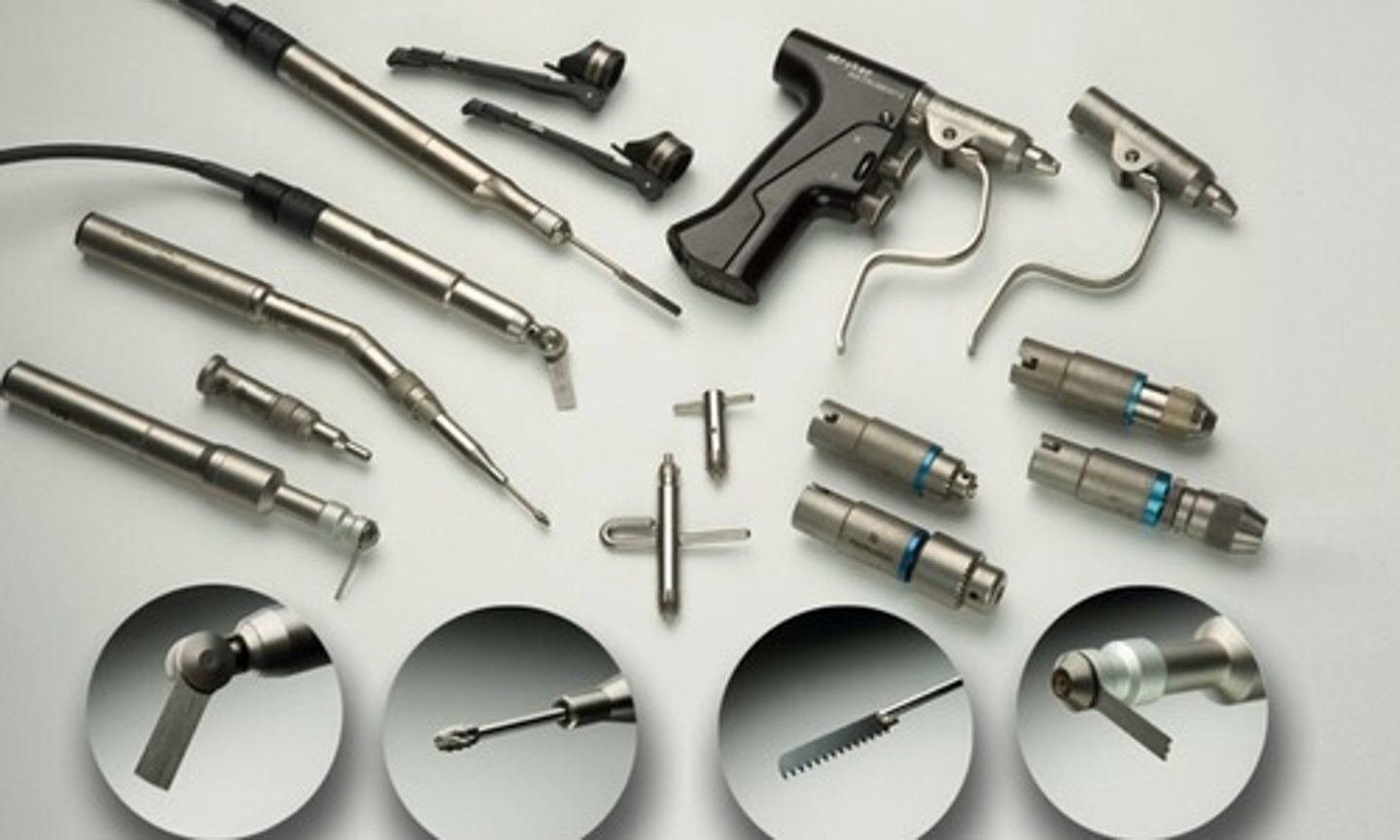

Stryker Core System
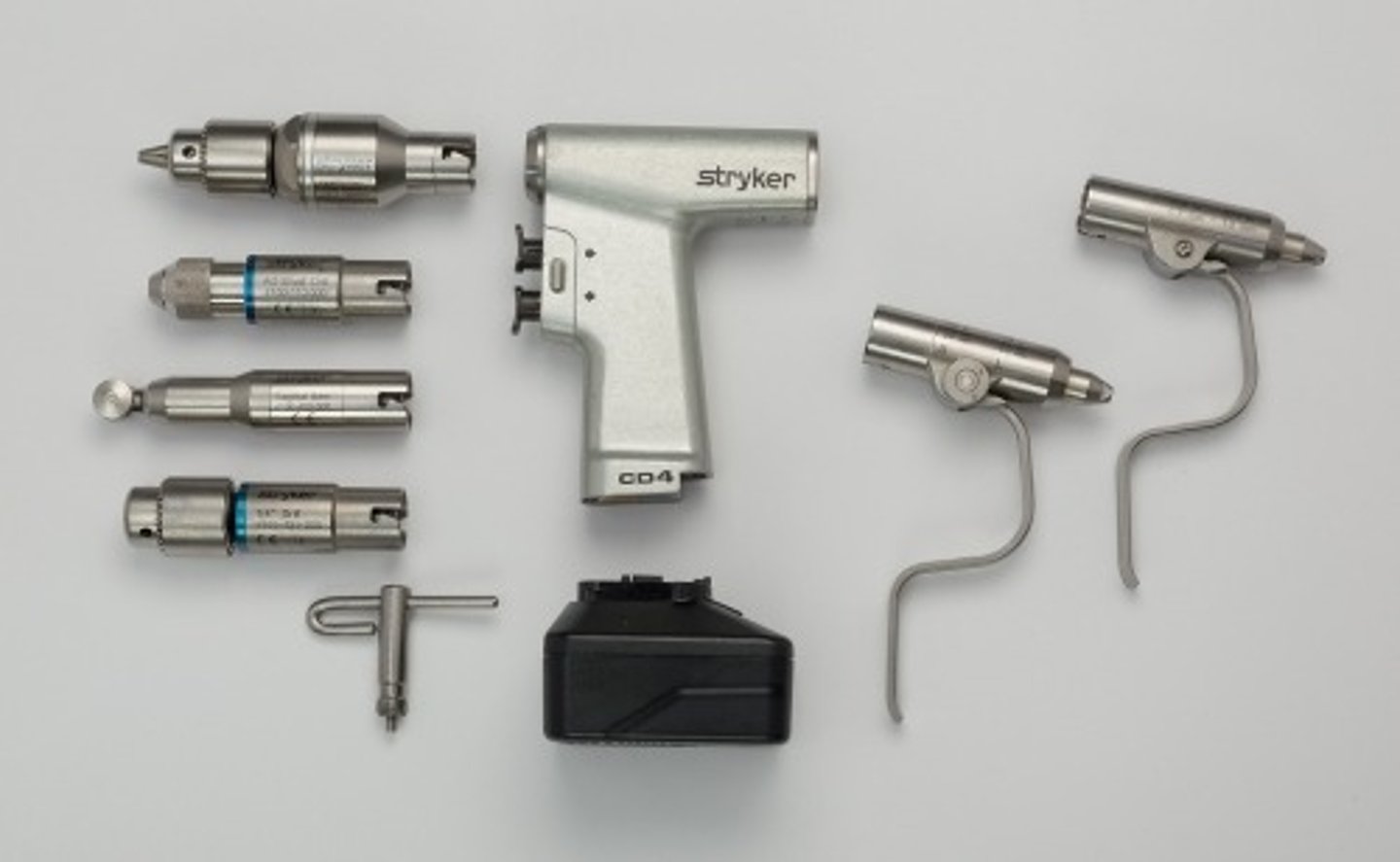

Cordless Driver 4
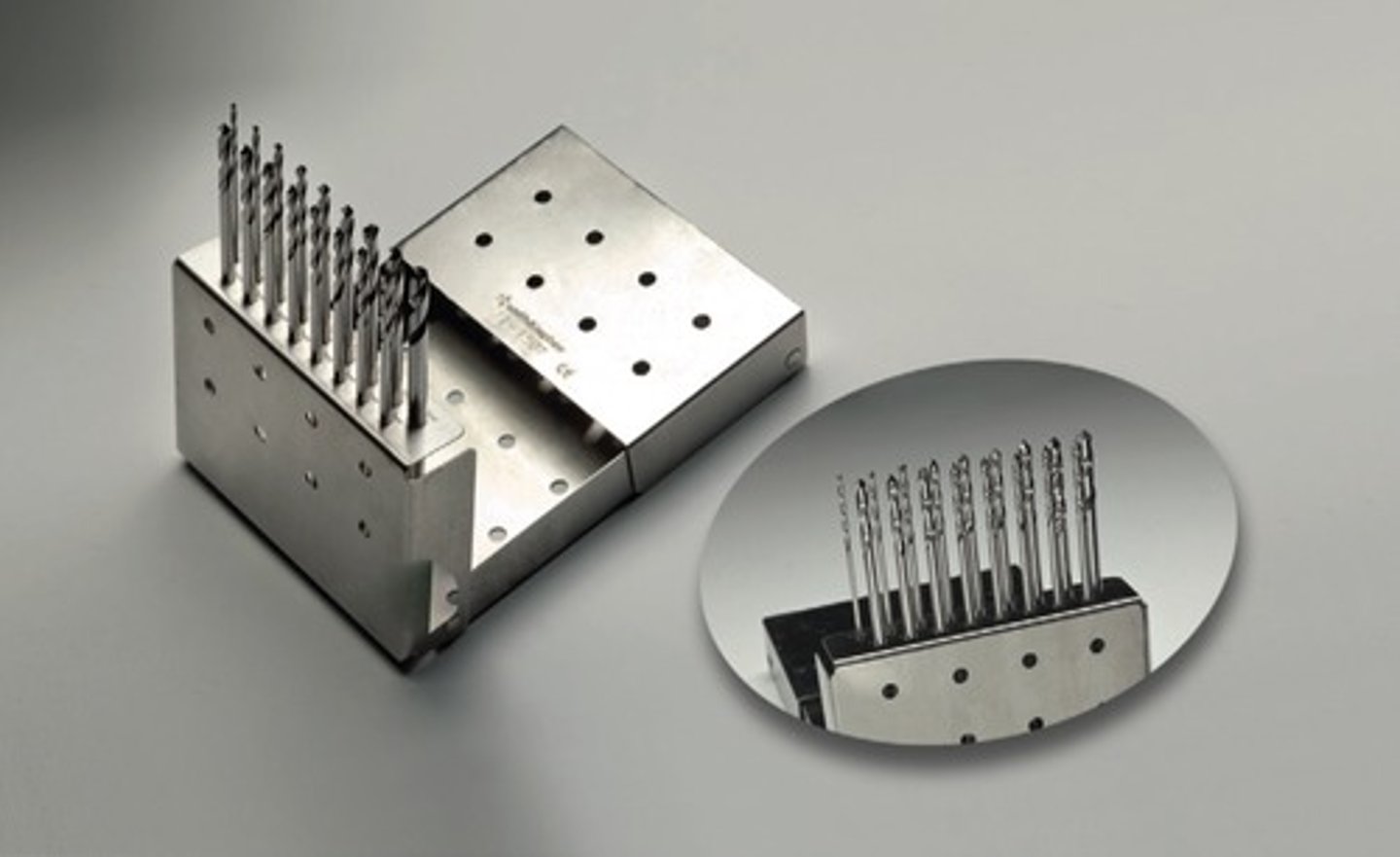

Drill Bit Set
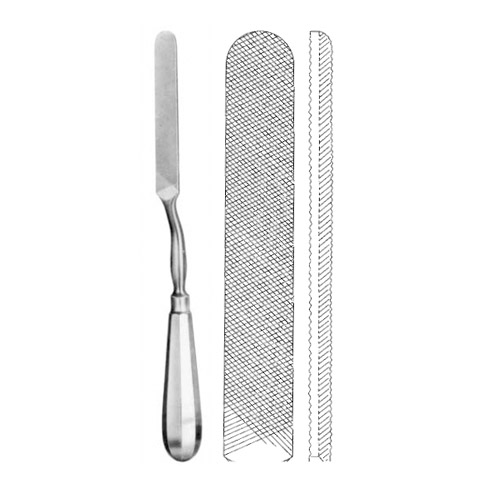

Bone File
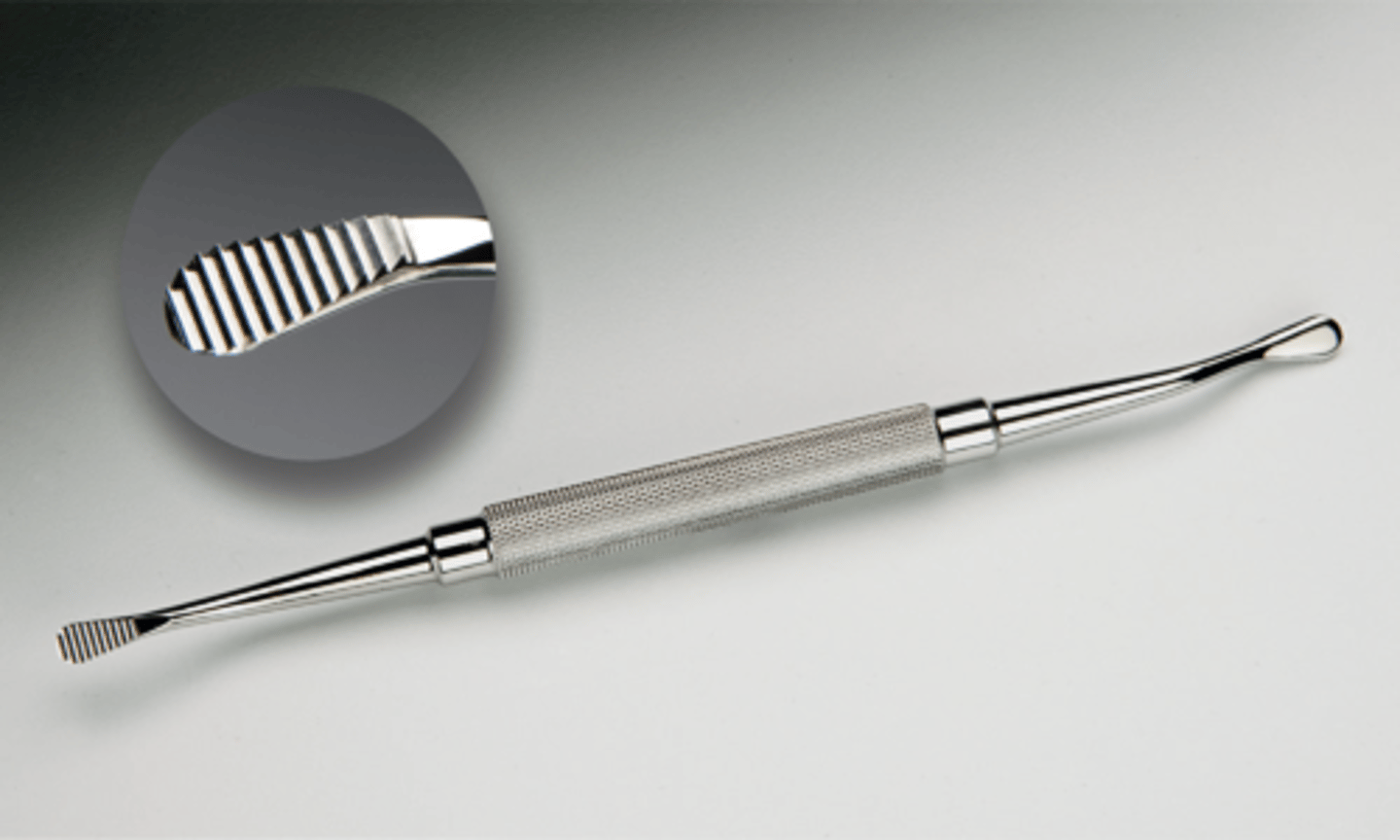
Miller Rasp
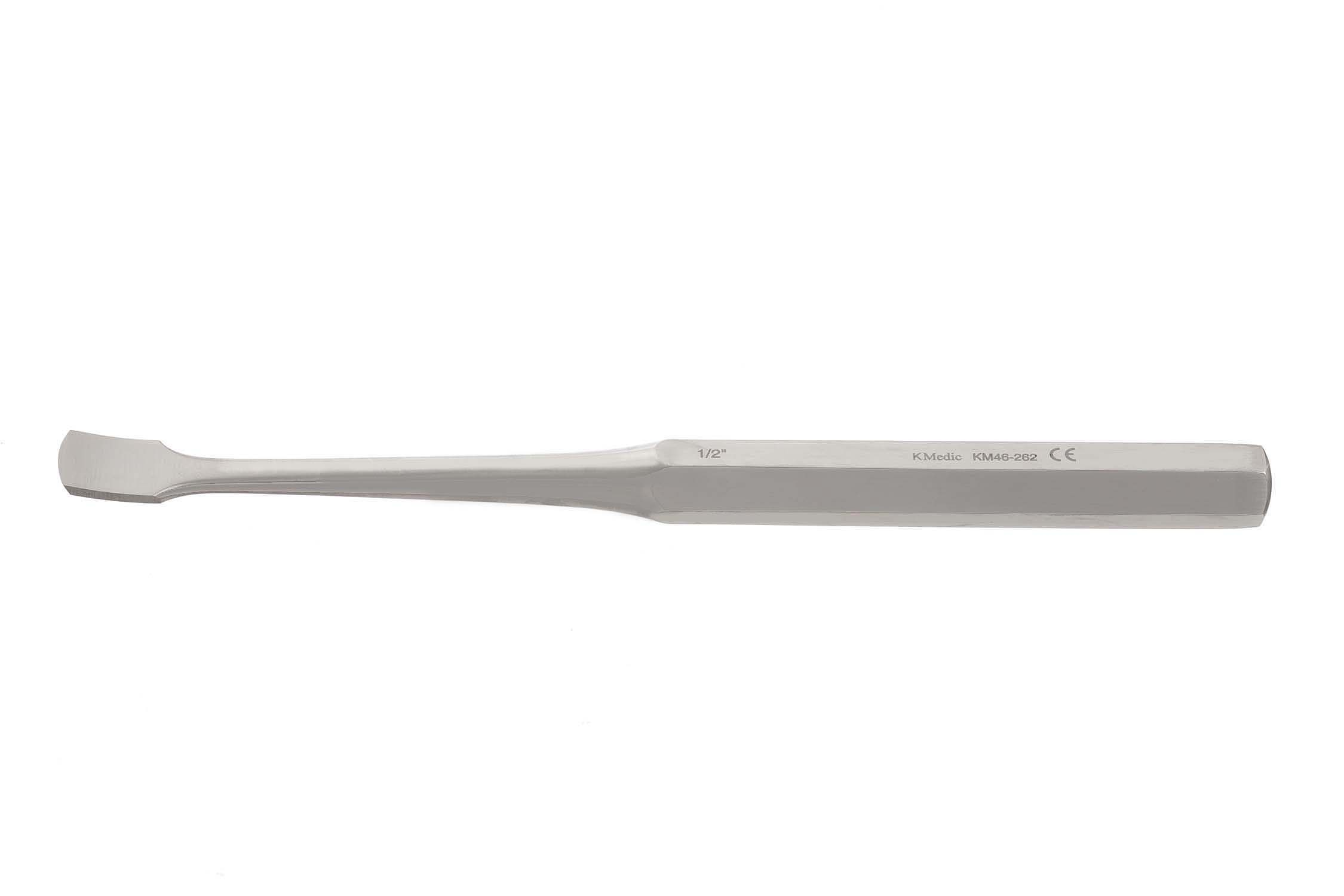
Key Periosteal Elevator
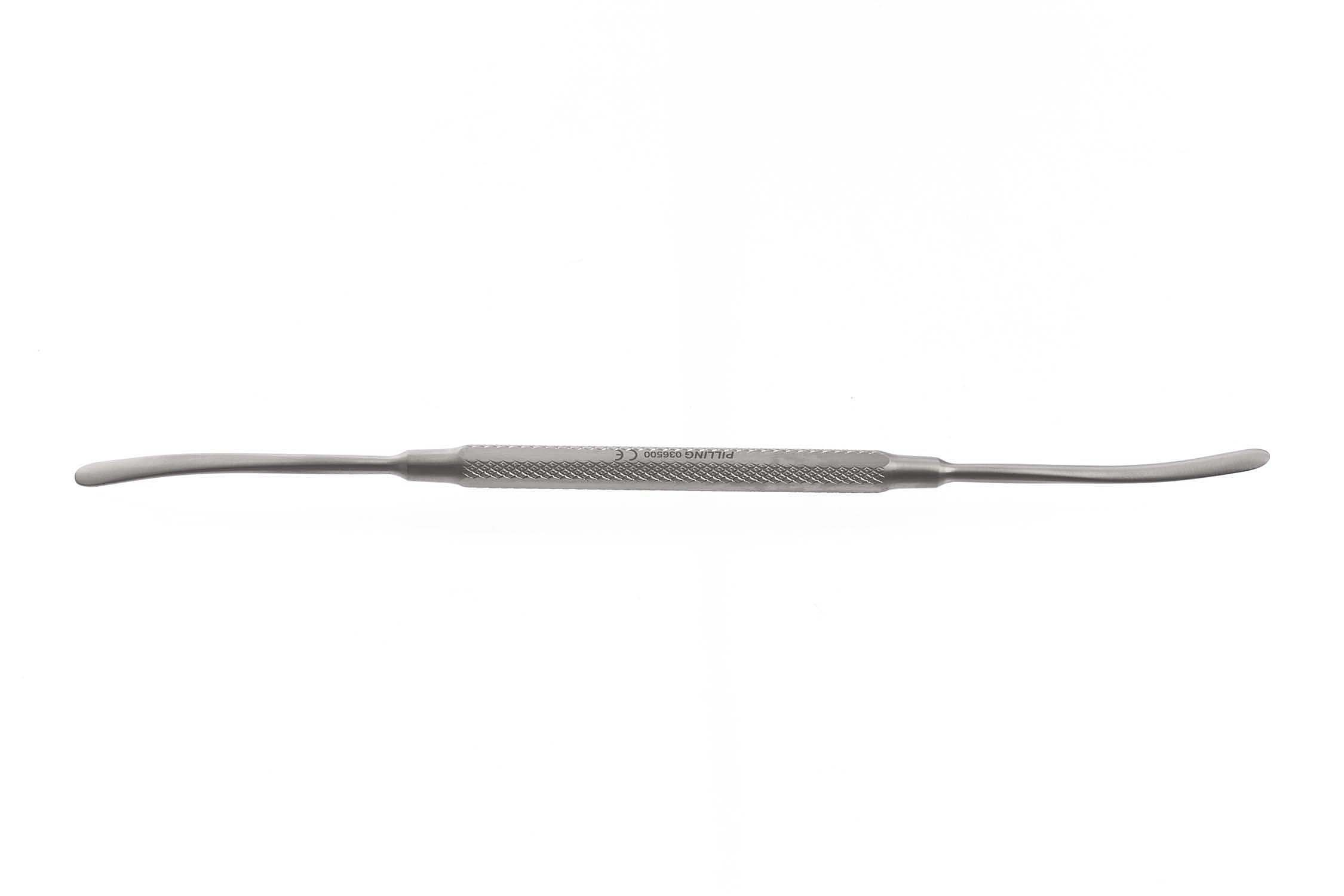

Freer Elevator
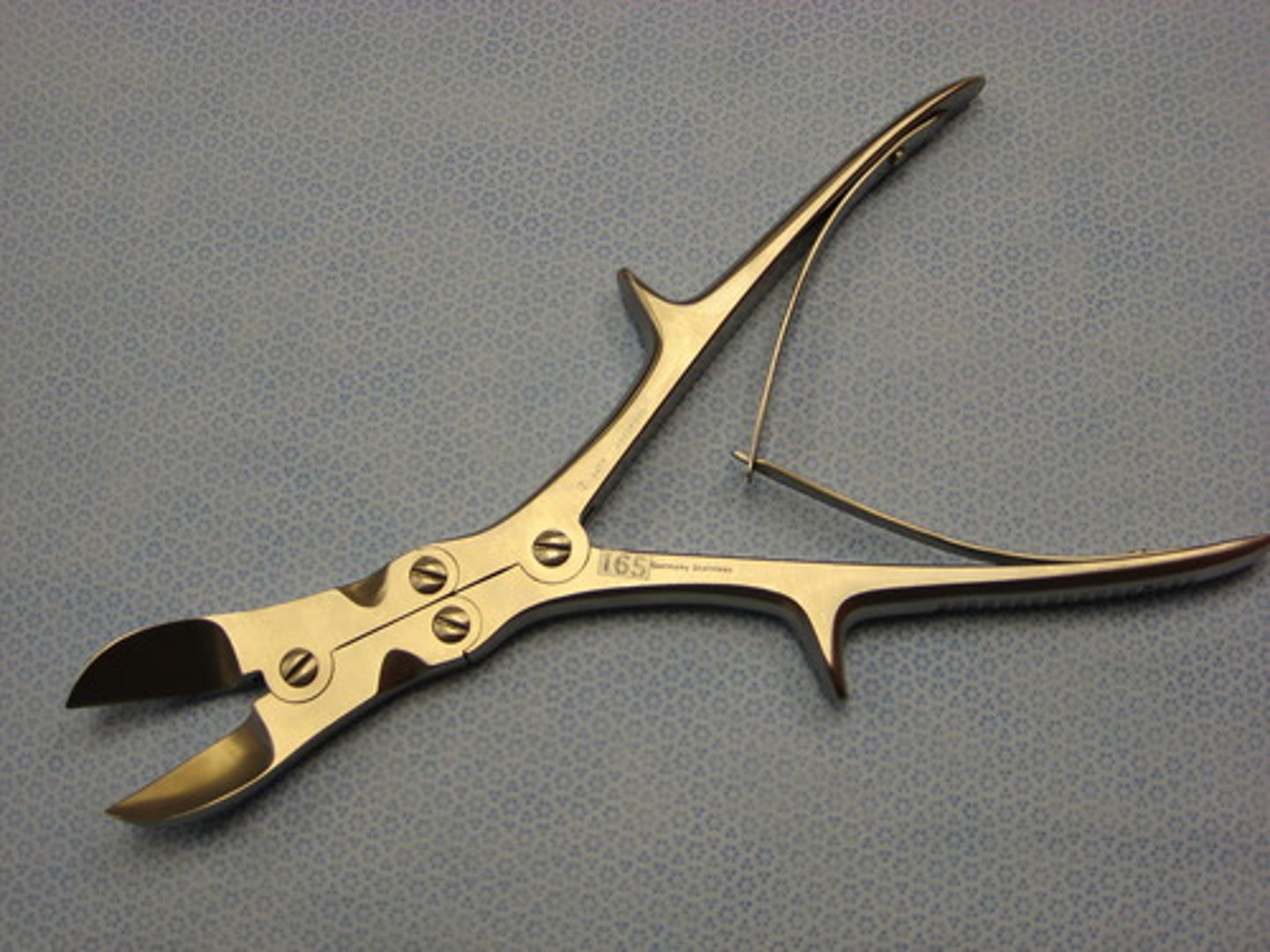
Liston Bone Cutter
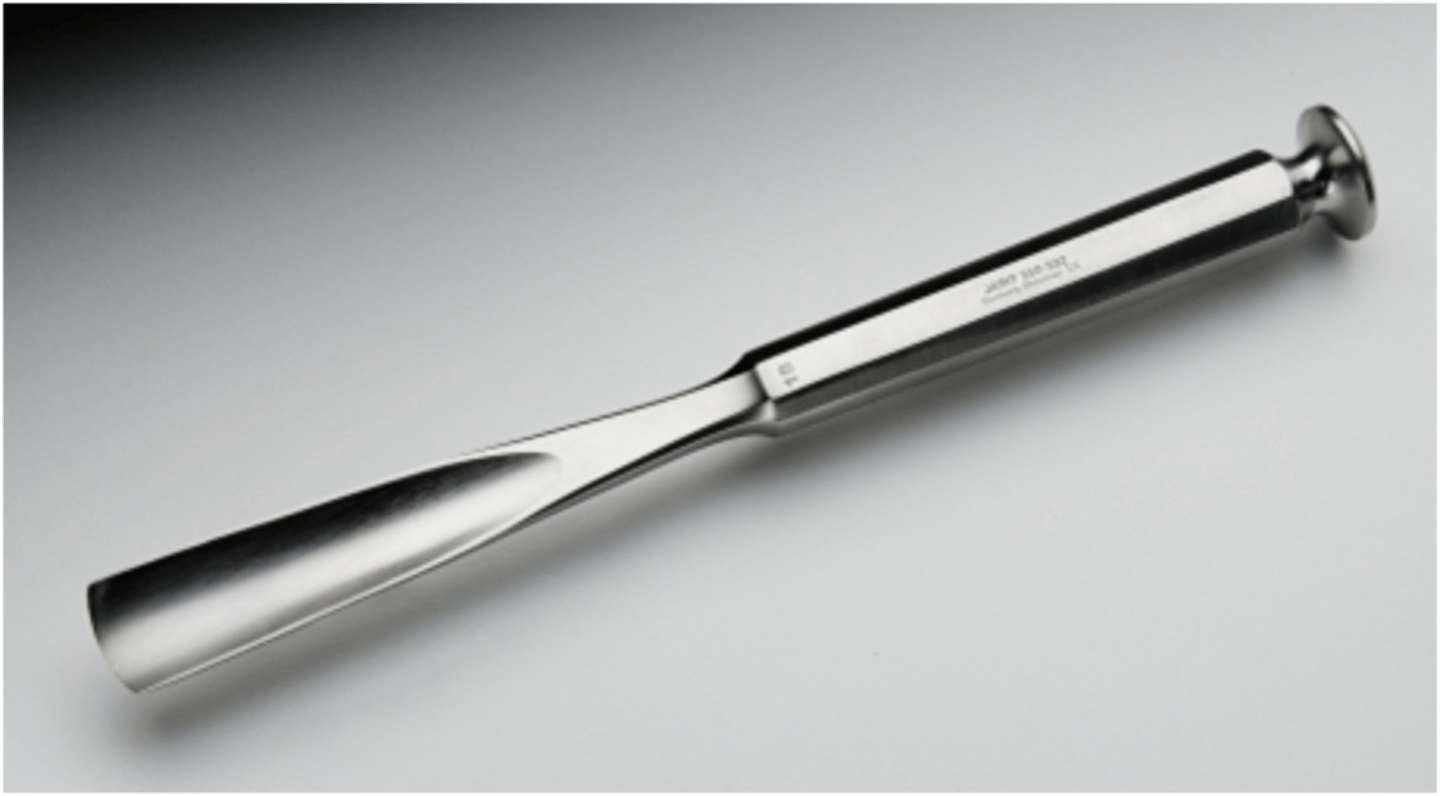

Stille Bone Gouge
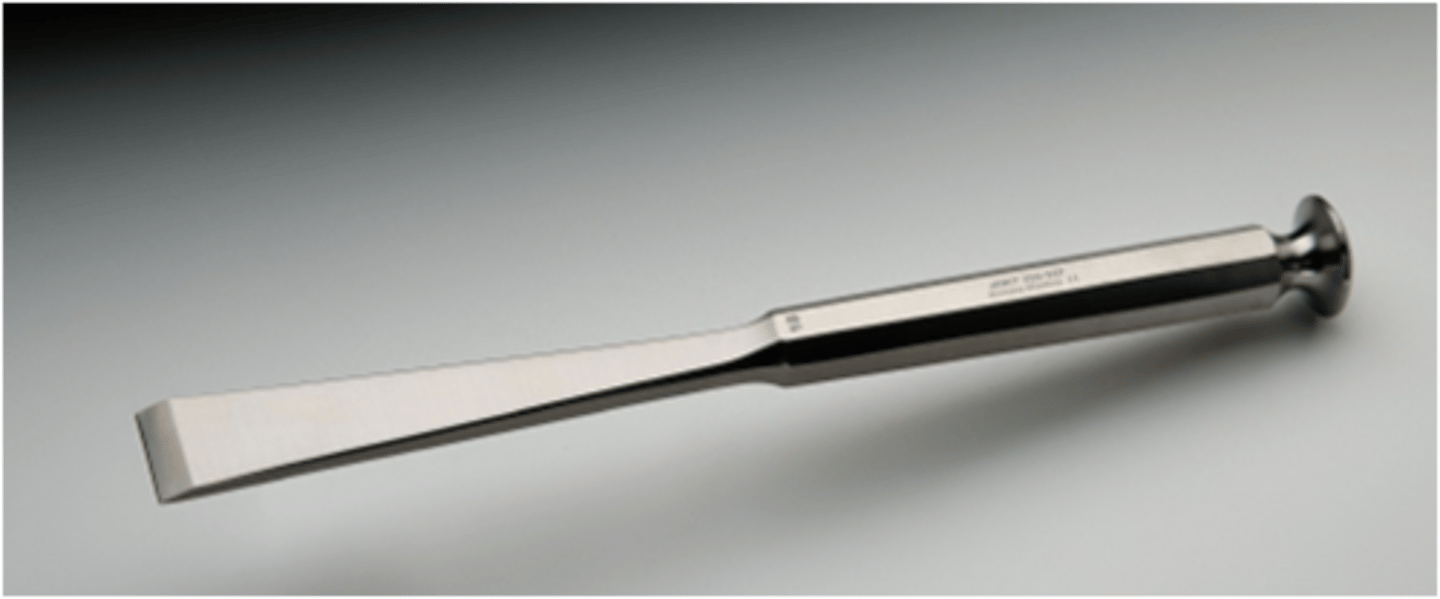
Stille Bone Chisel

Stille Bone Osteotome
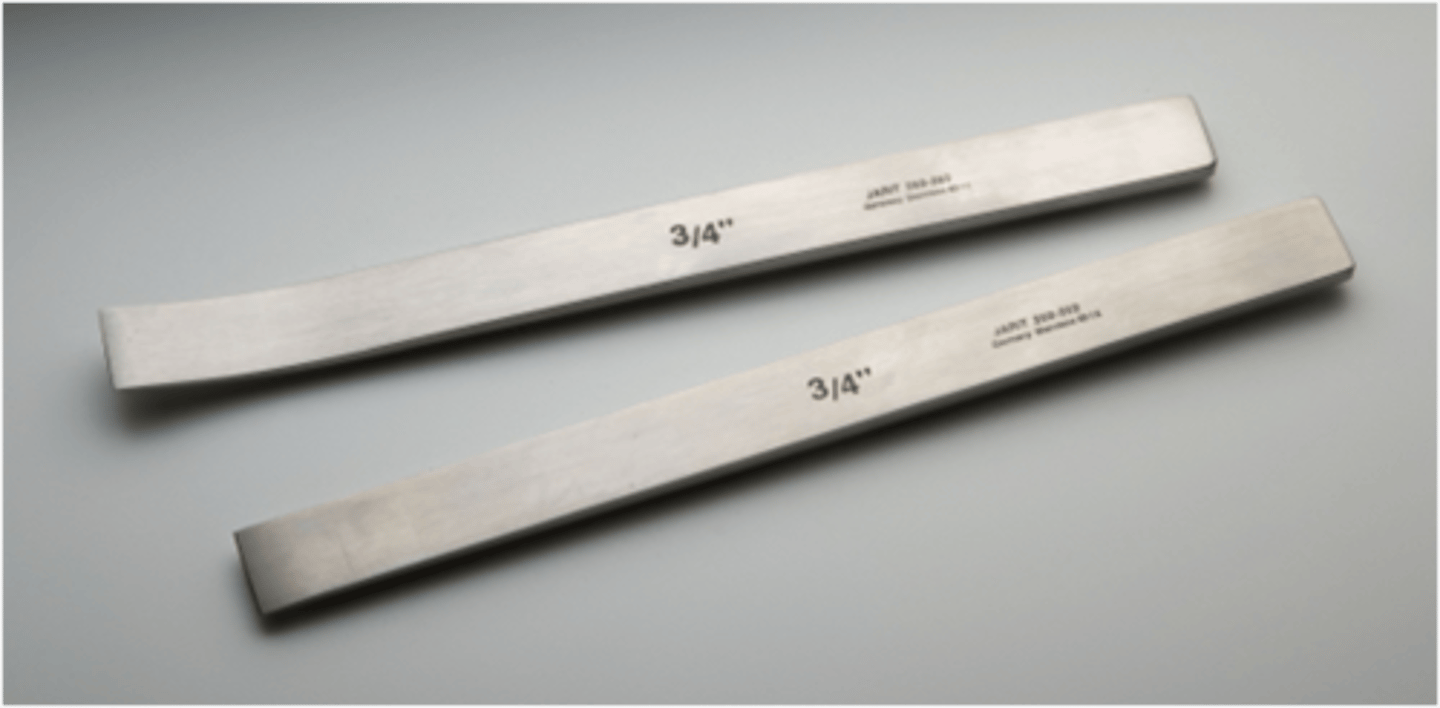

Lambotte Osteotome
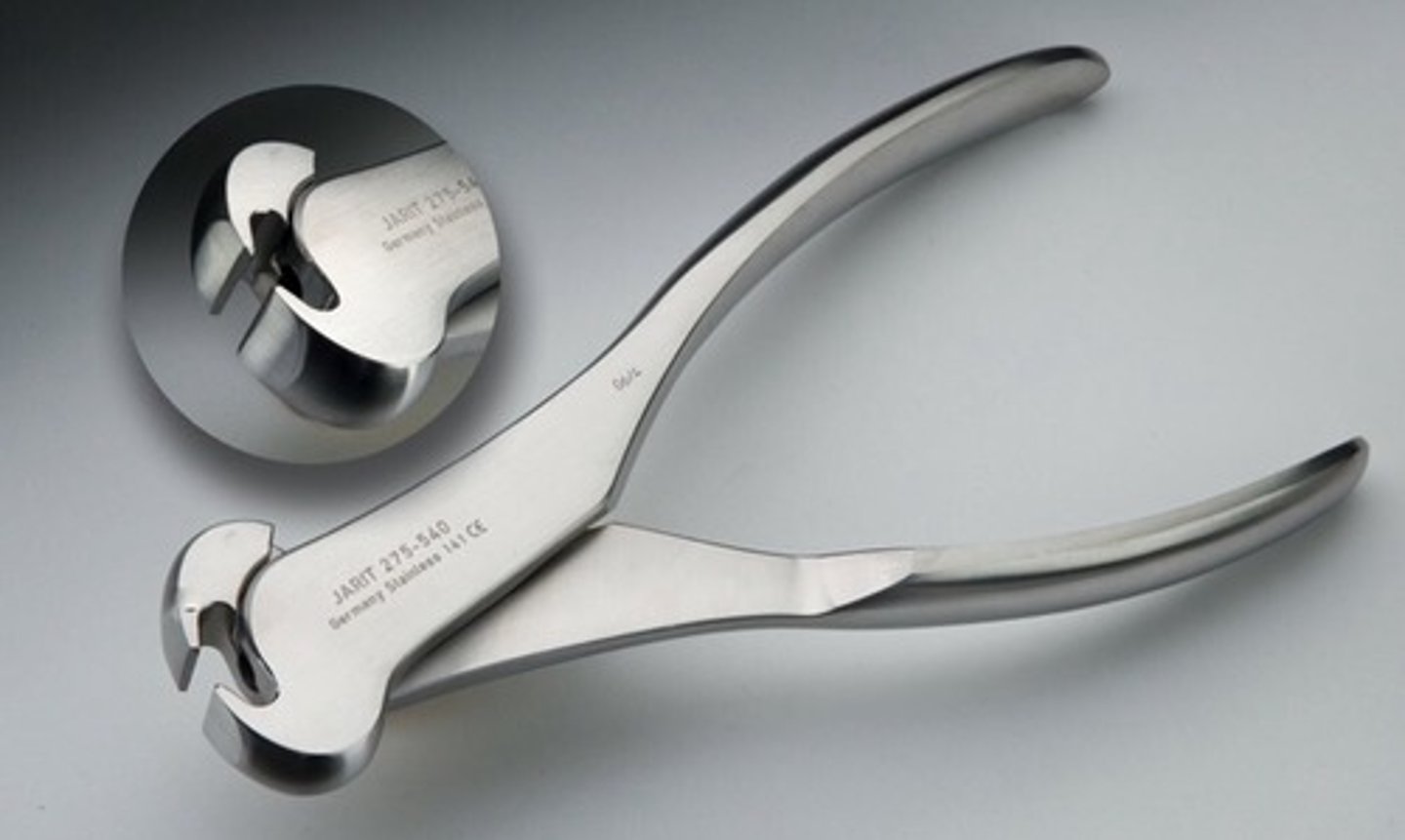
Pin Cutter
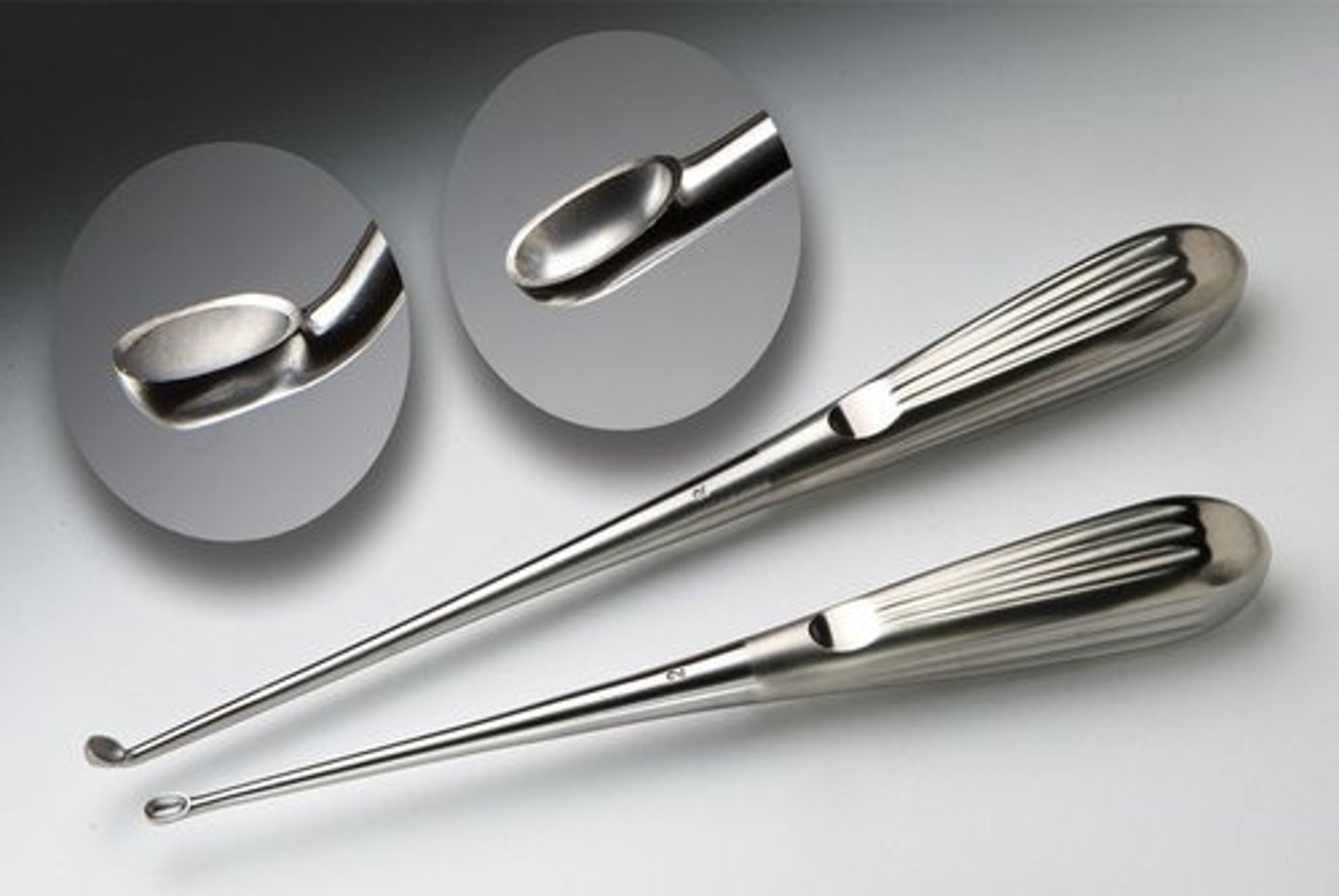

Bruns Oval Curettes
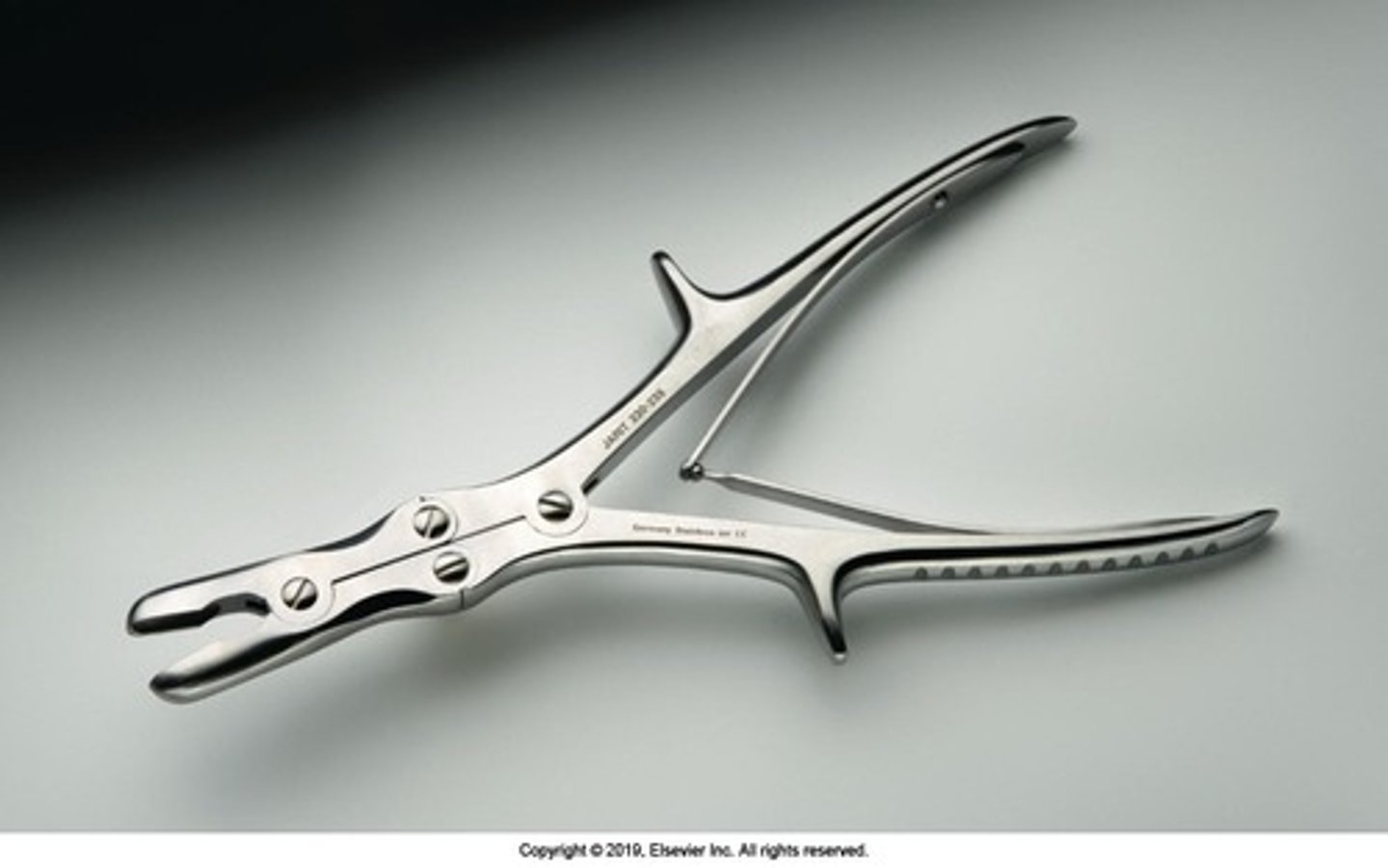
Stille-Leur Rongeur
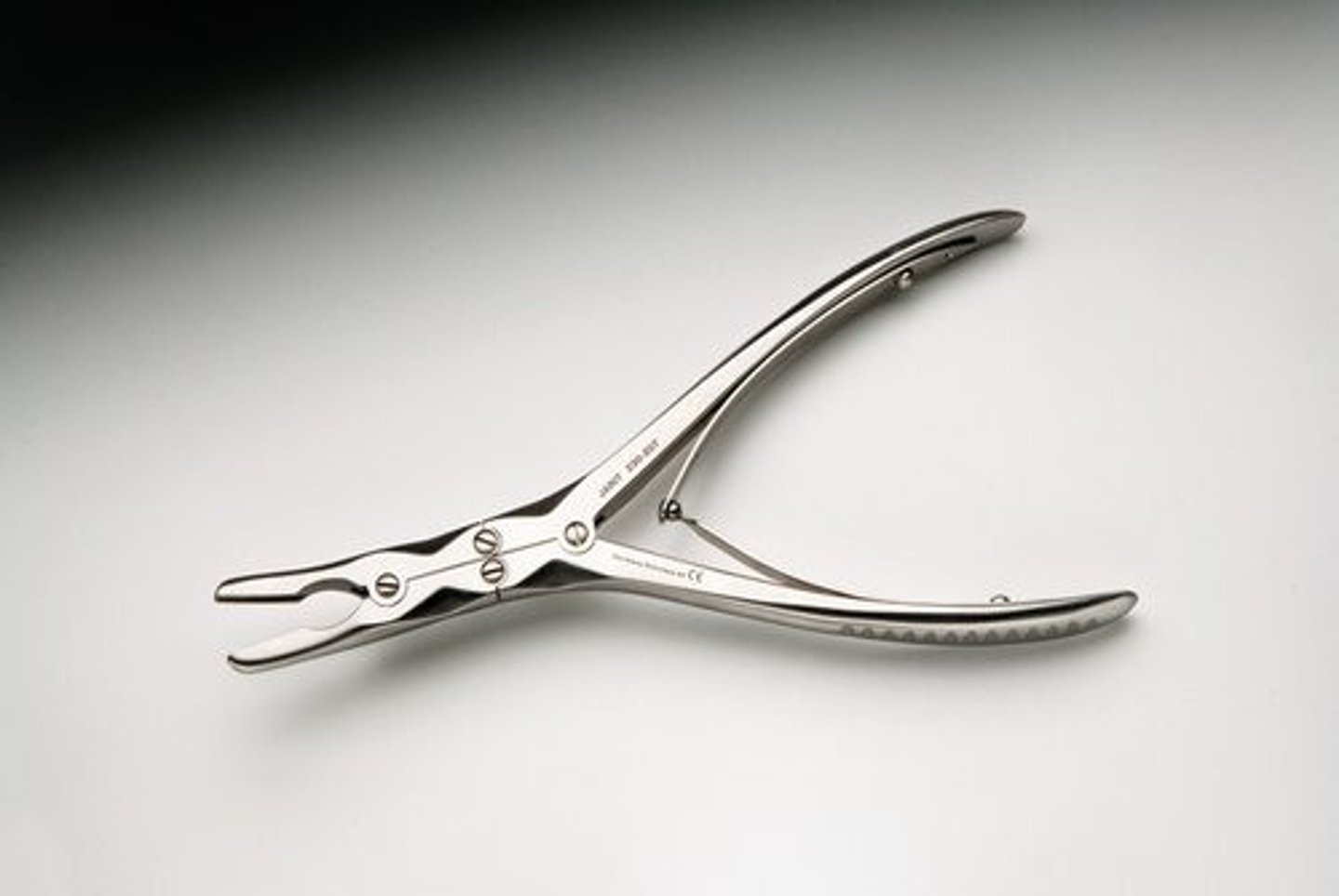
Zaufel-Jansen Rongeur
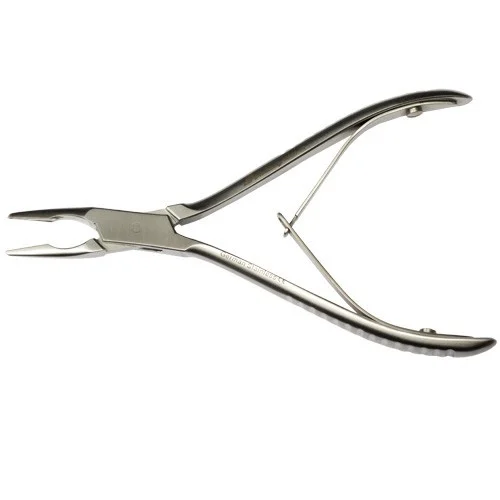

Cushing Rongeur
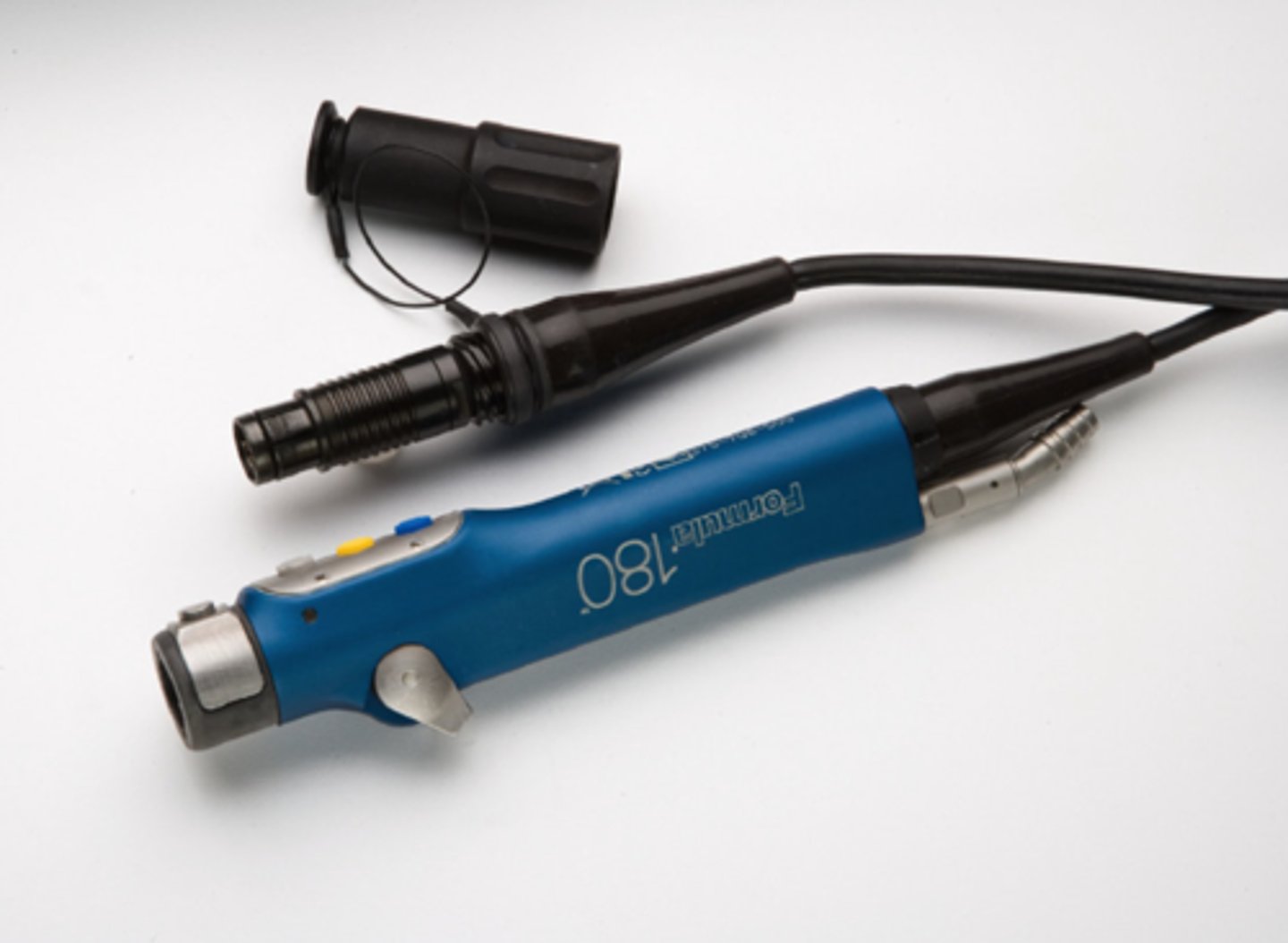

Shaver
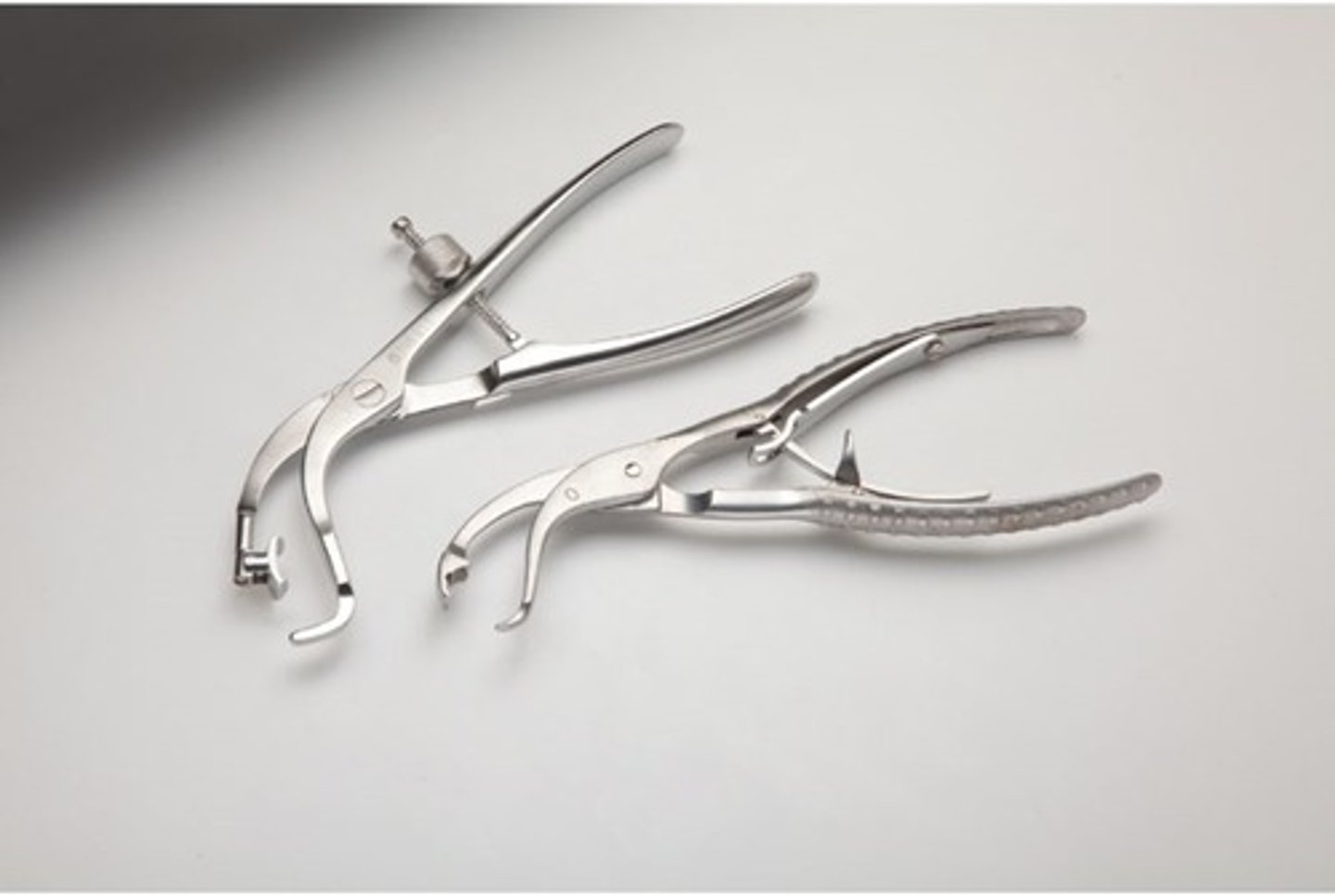
Plate Forceps
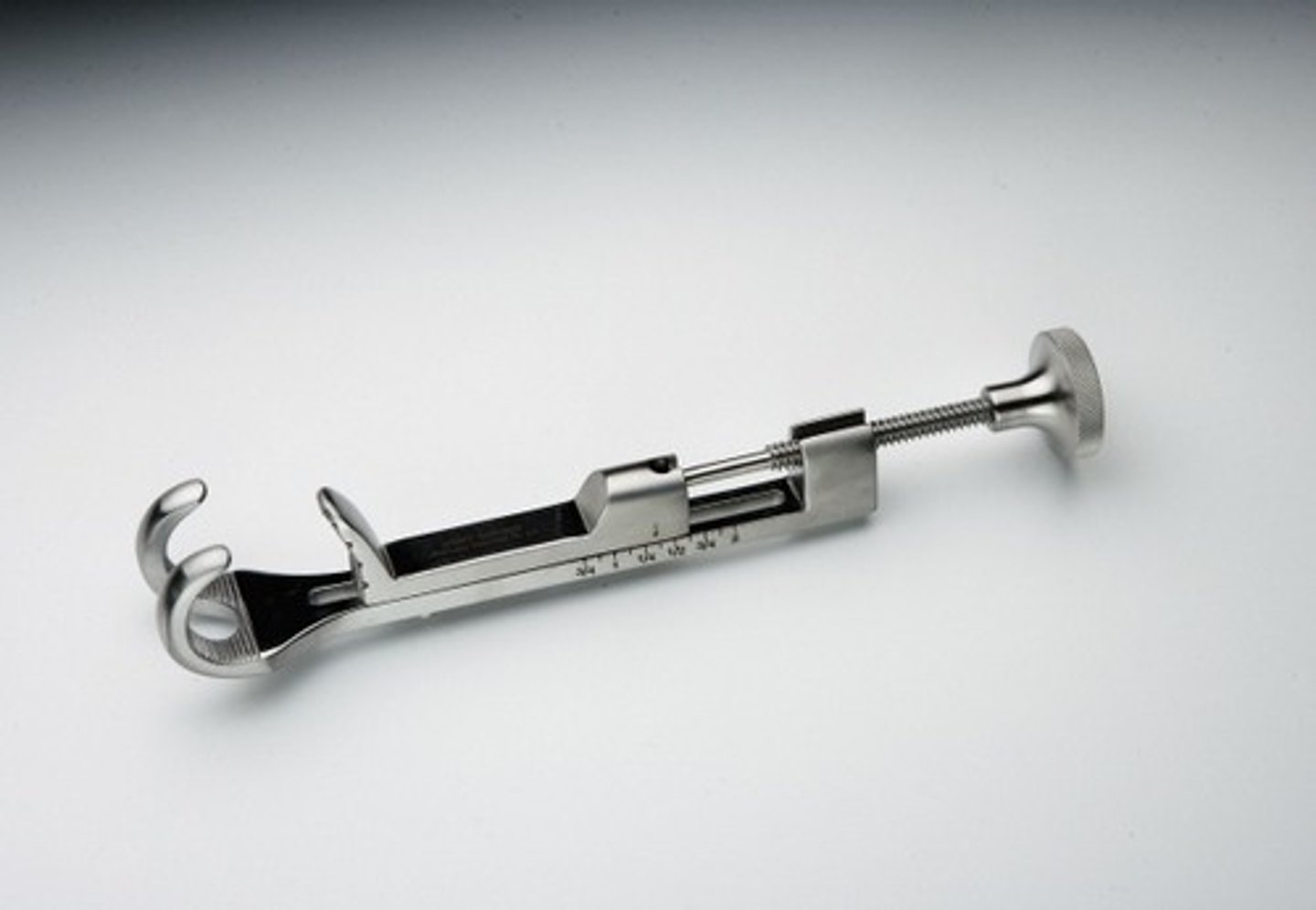

Lowman Bone Clamp
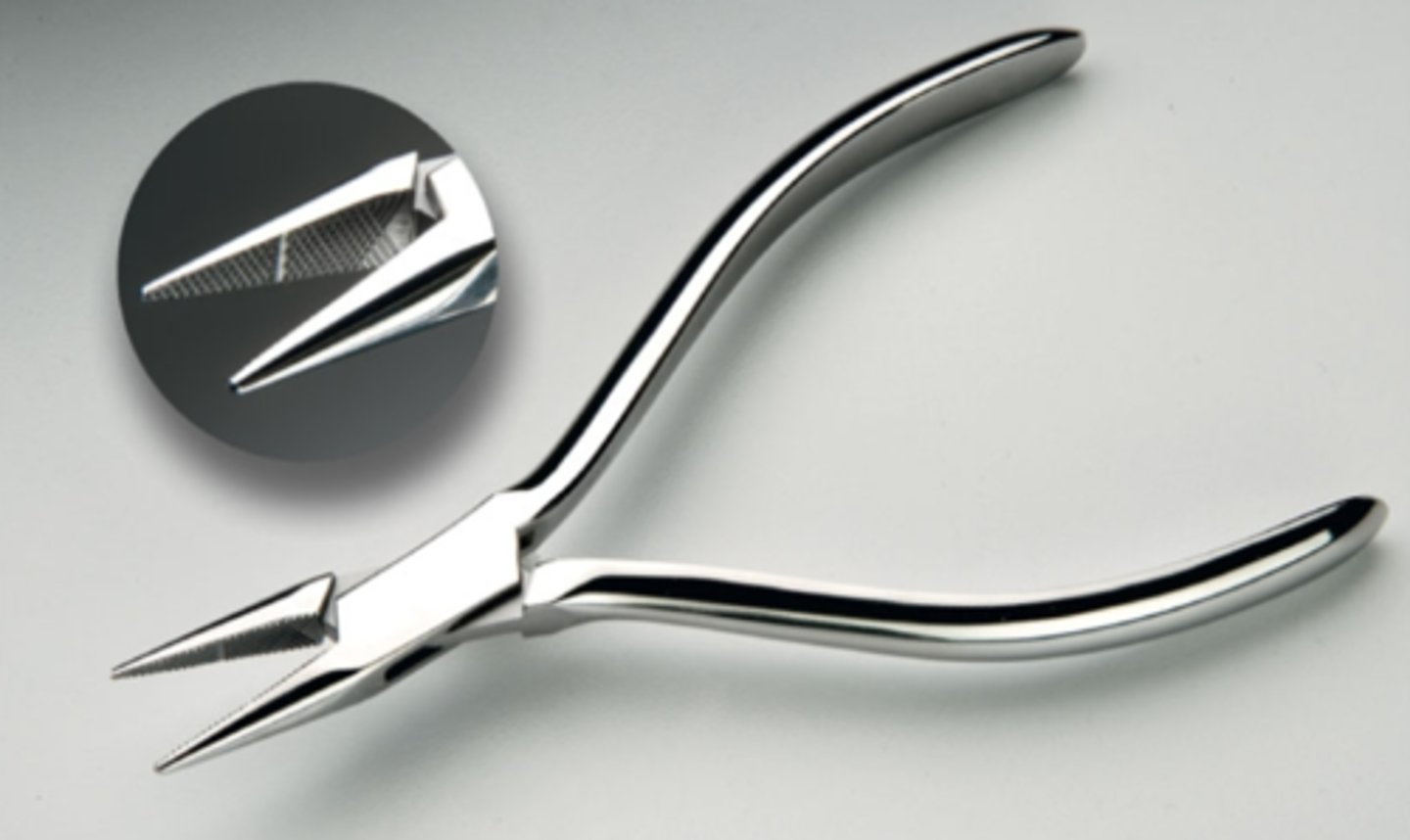

Needlenose Pliers
Pliers
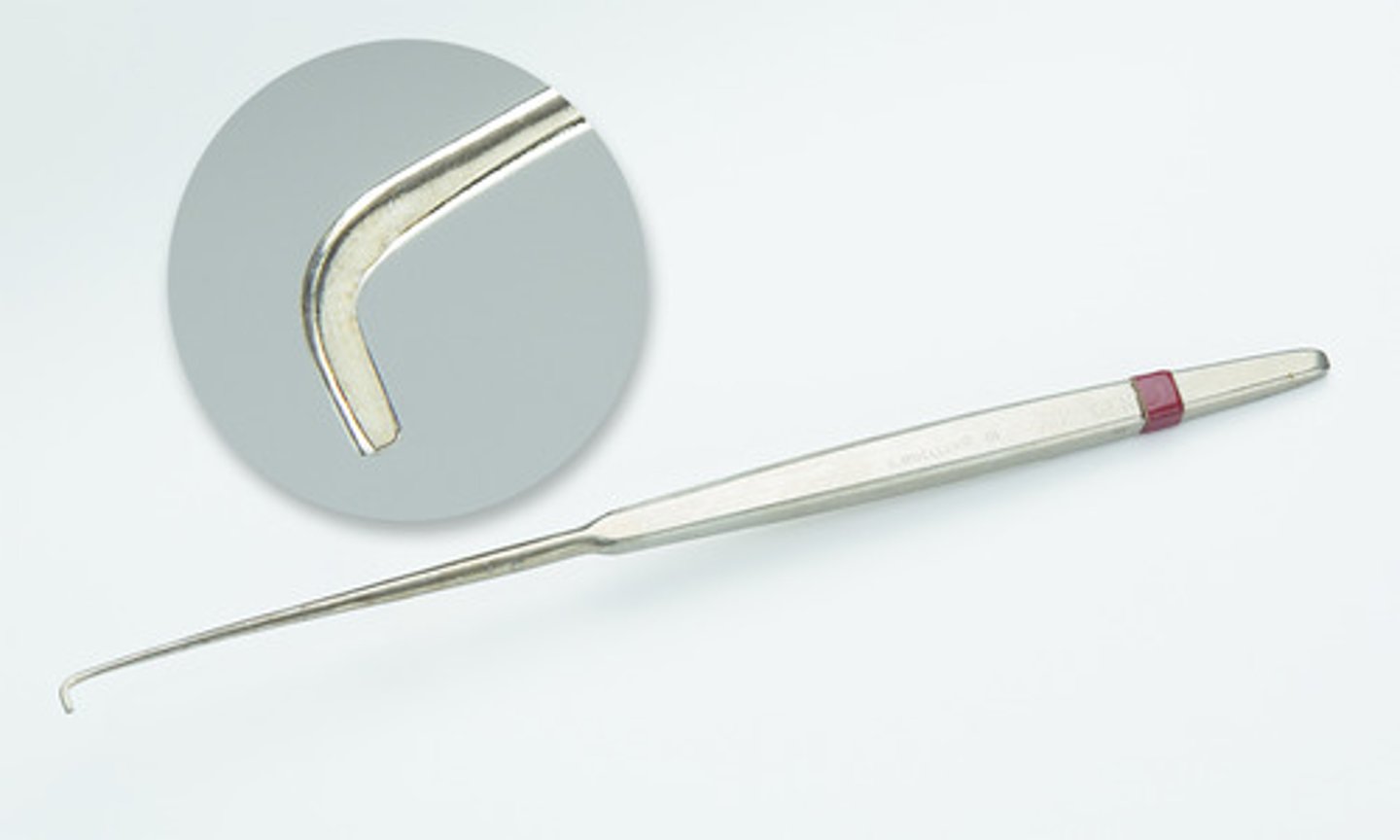

Arthroscopy Probe
Bennett Retractor
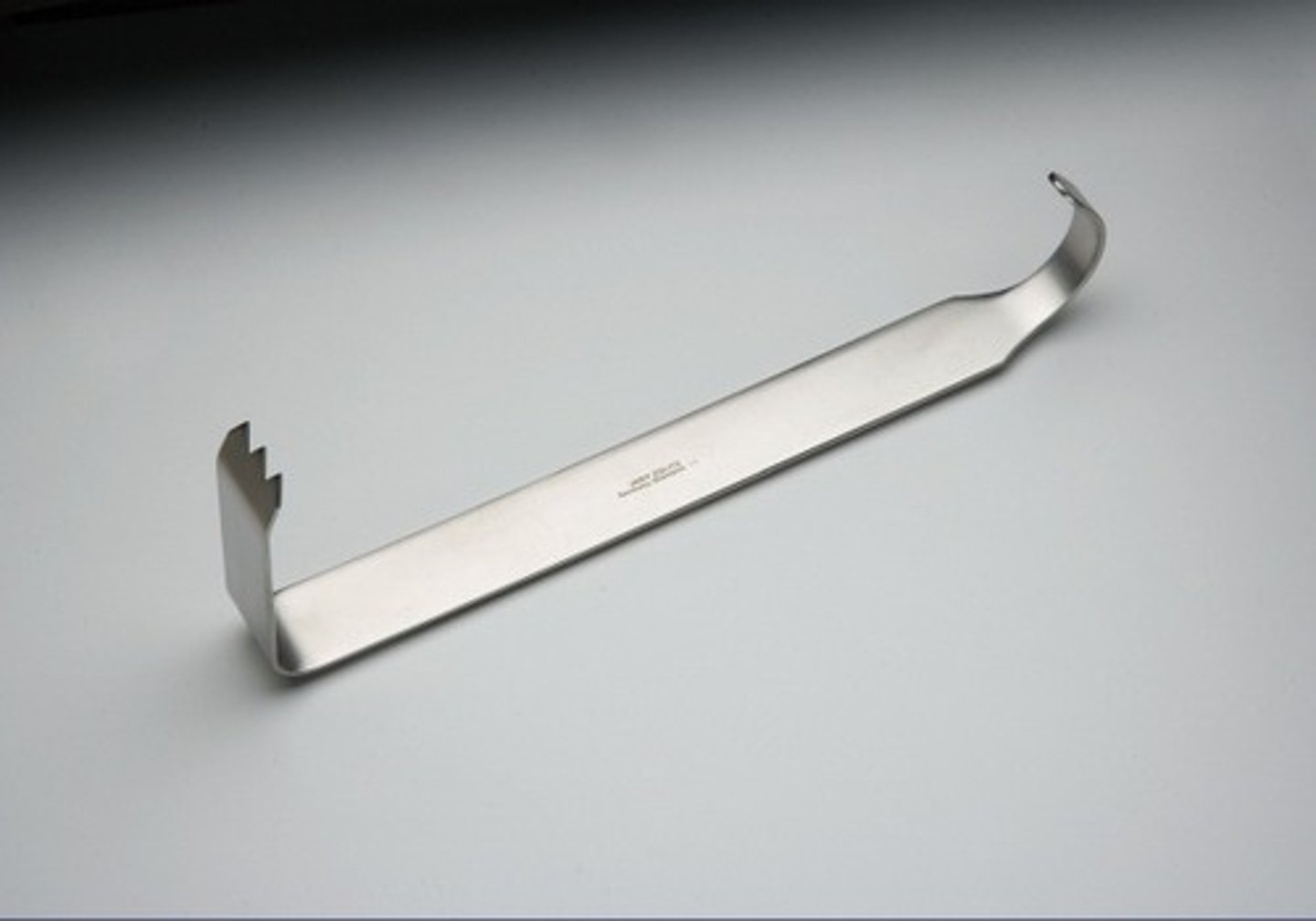

Hibbs Retractor
Beckman Retractor
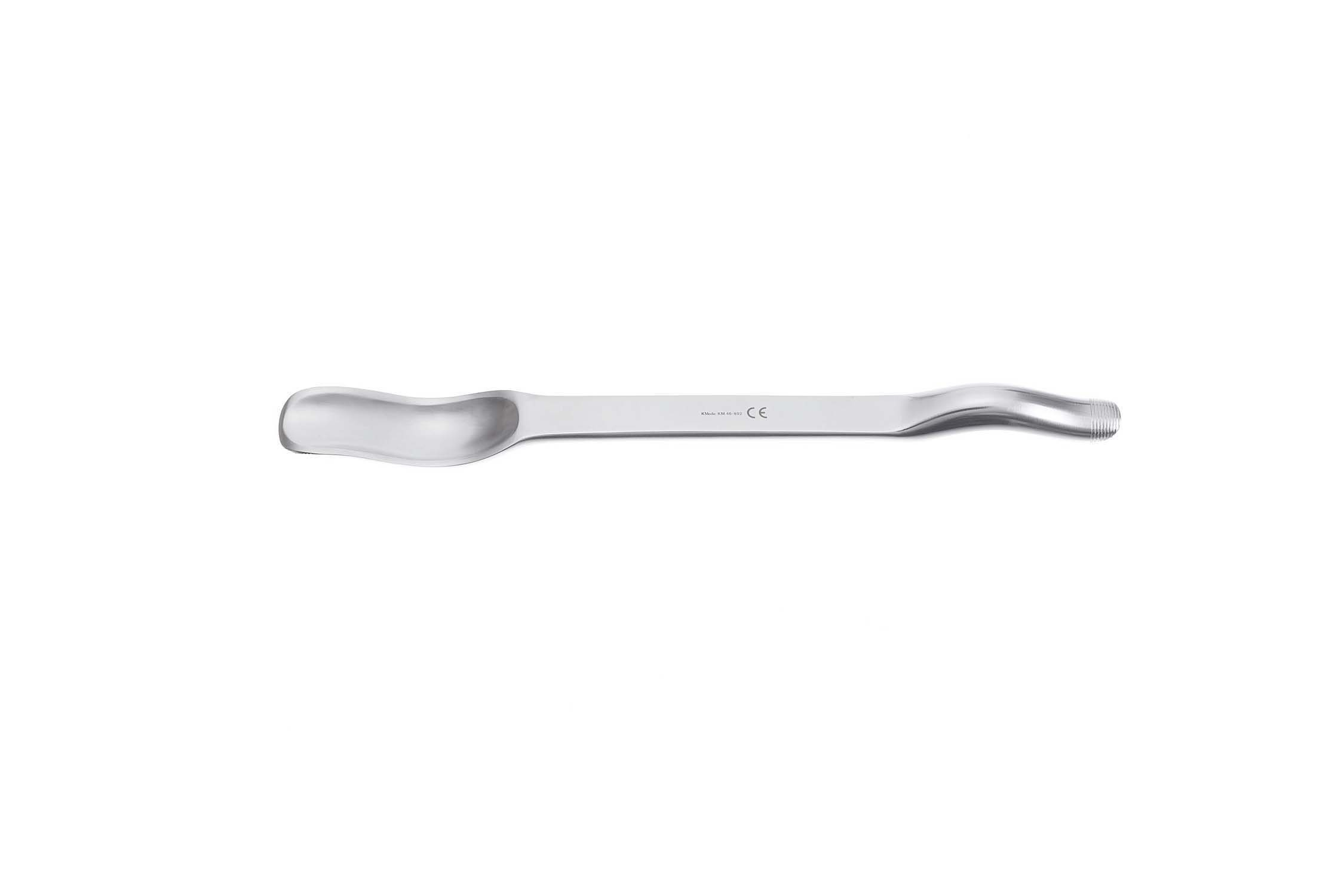

Murphy-Lane Bone Skid
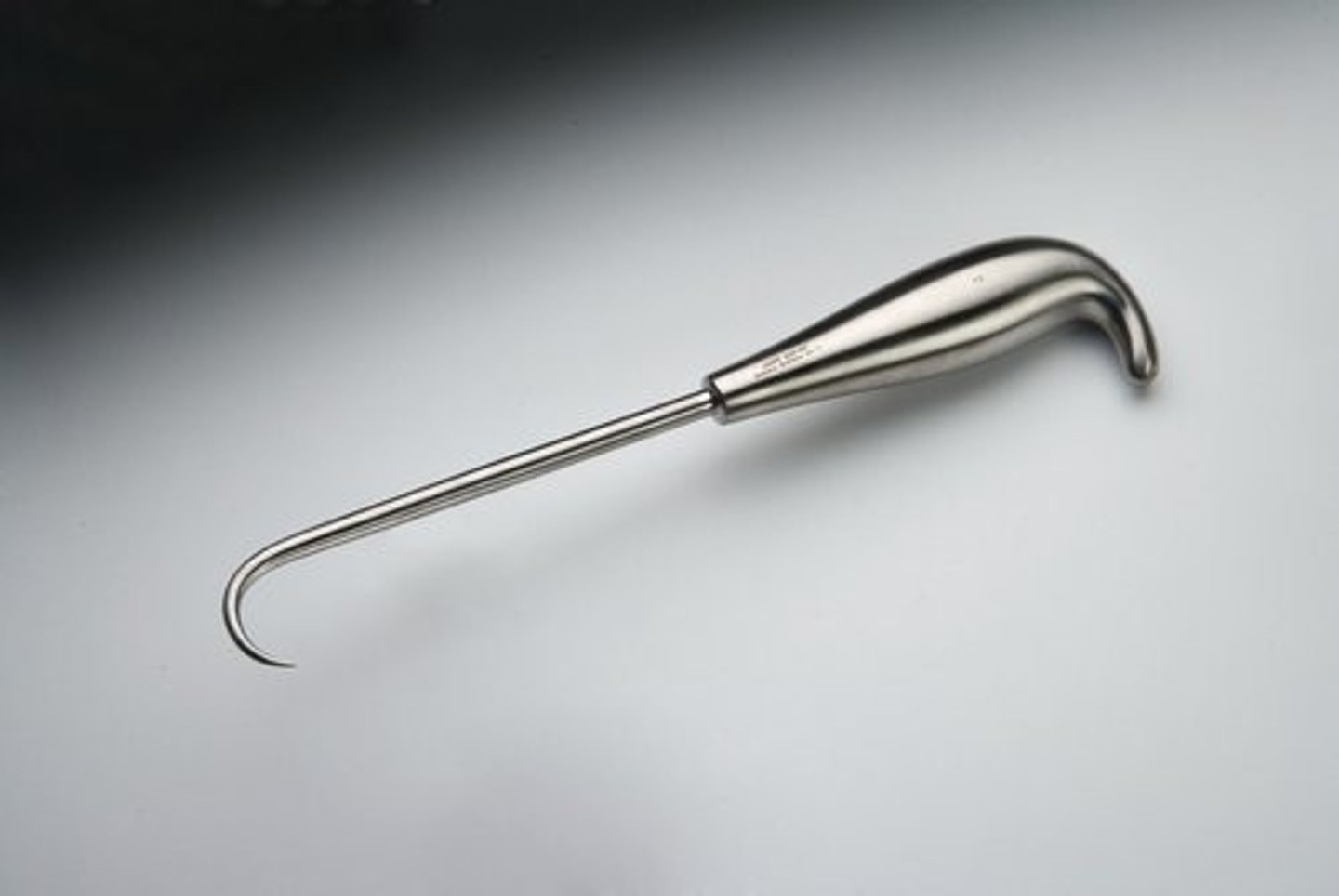

Bone Hook
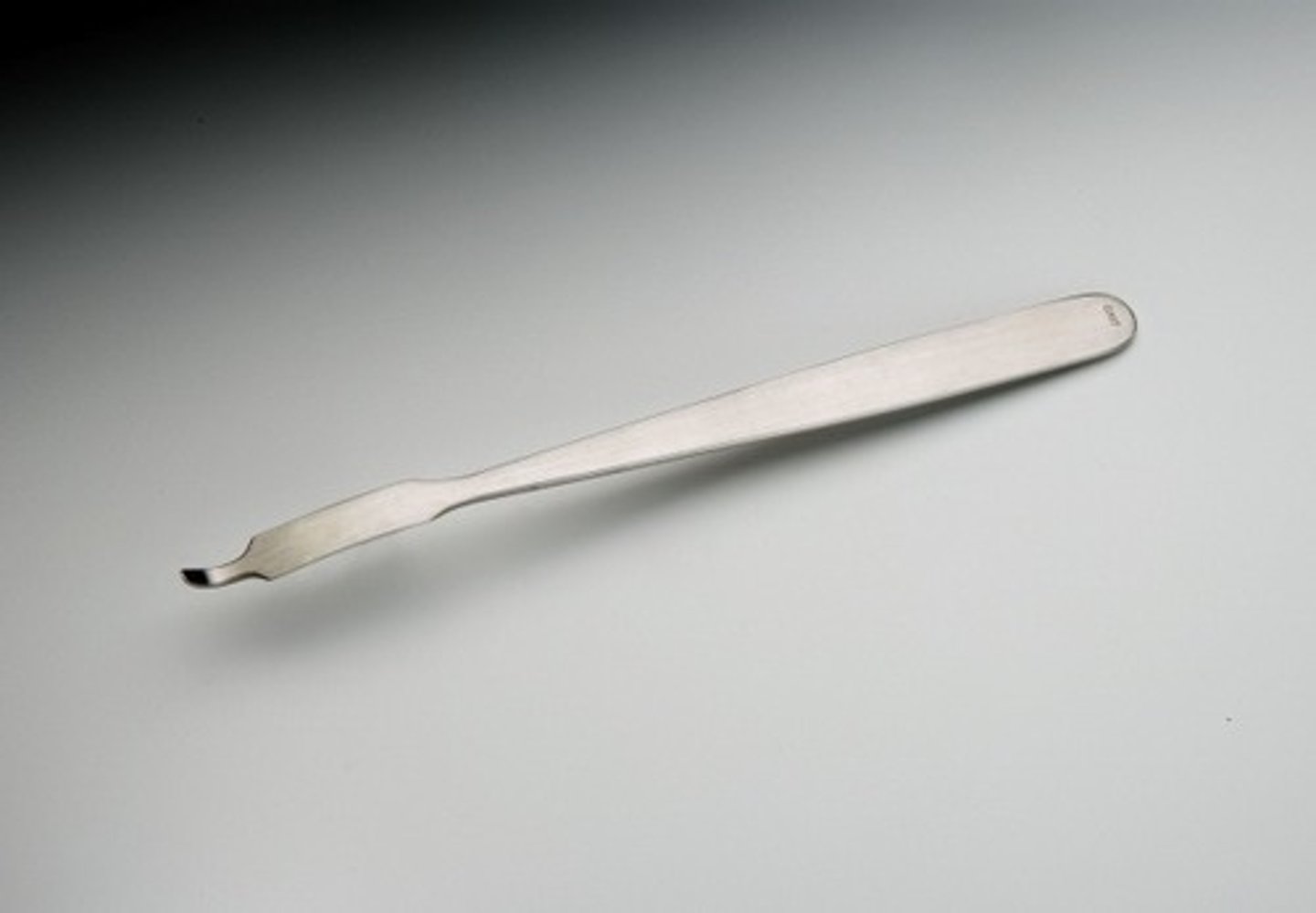

Mini Hohmann Retractor
Charnley Retractor
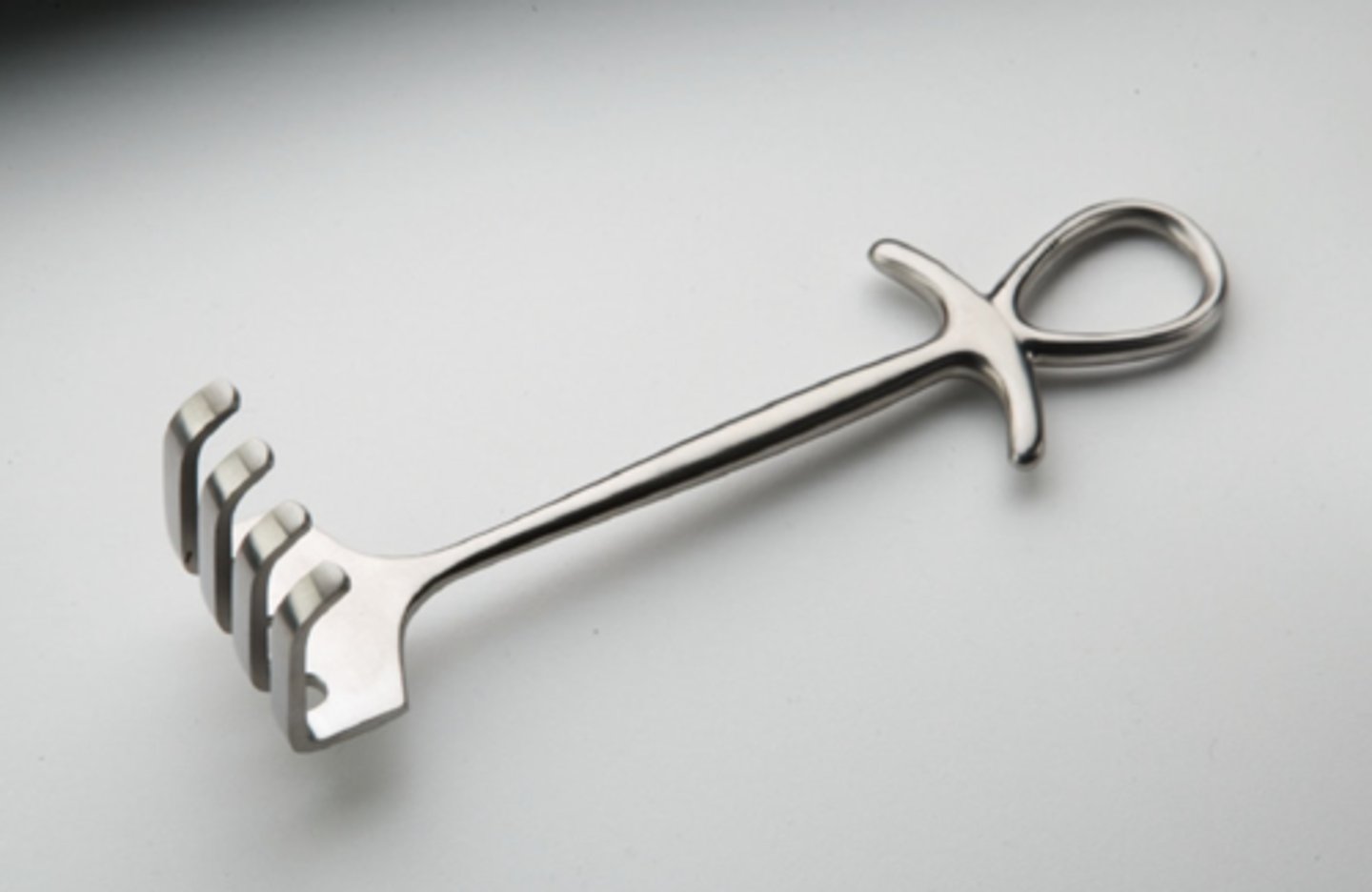

Israel Rake Retractor
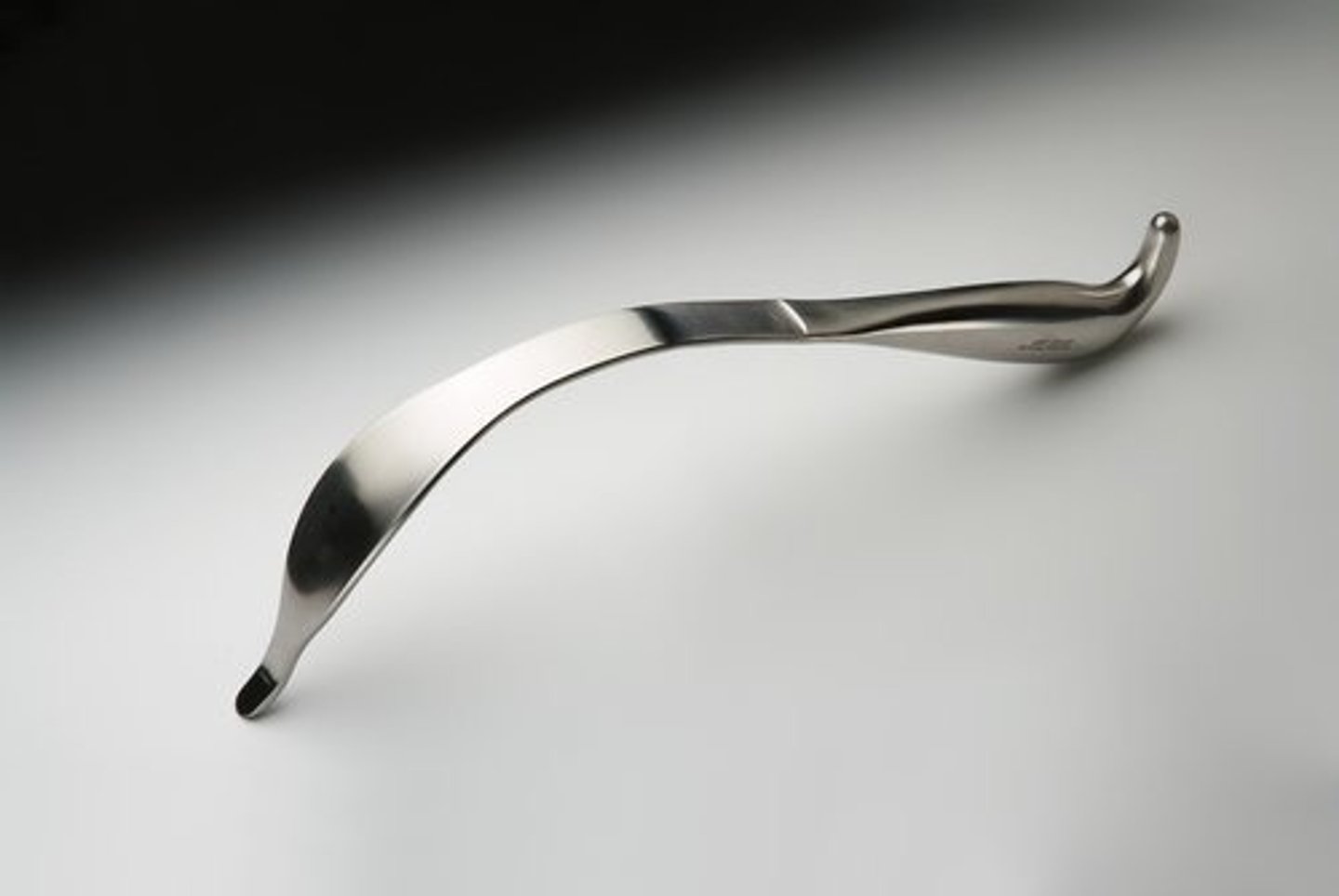

Cobra Retractor
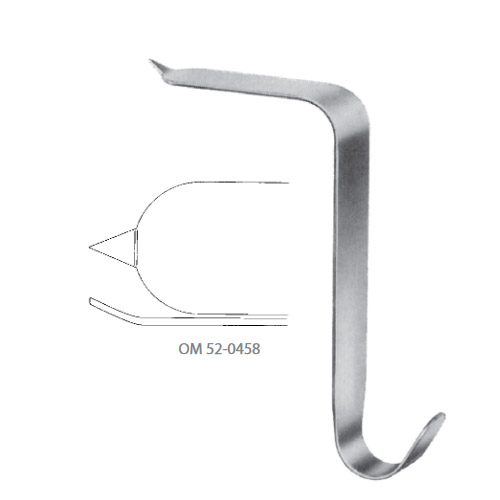
Taylor Hip Retractor
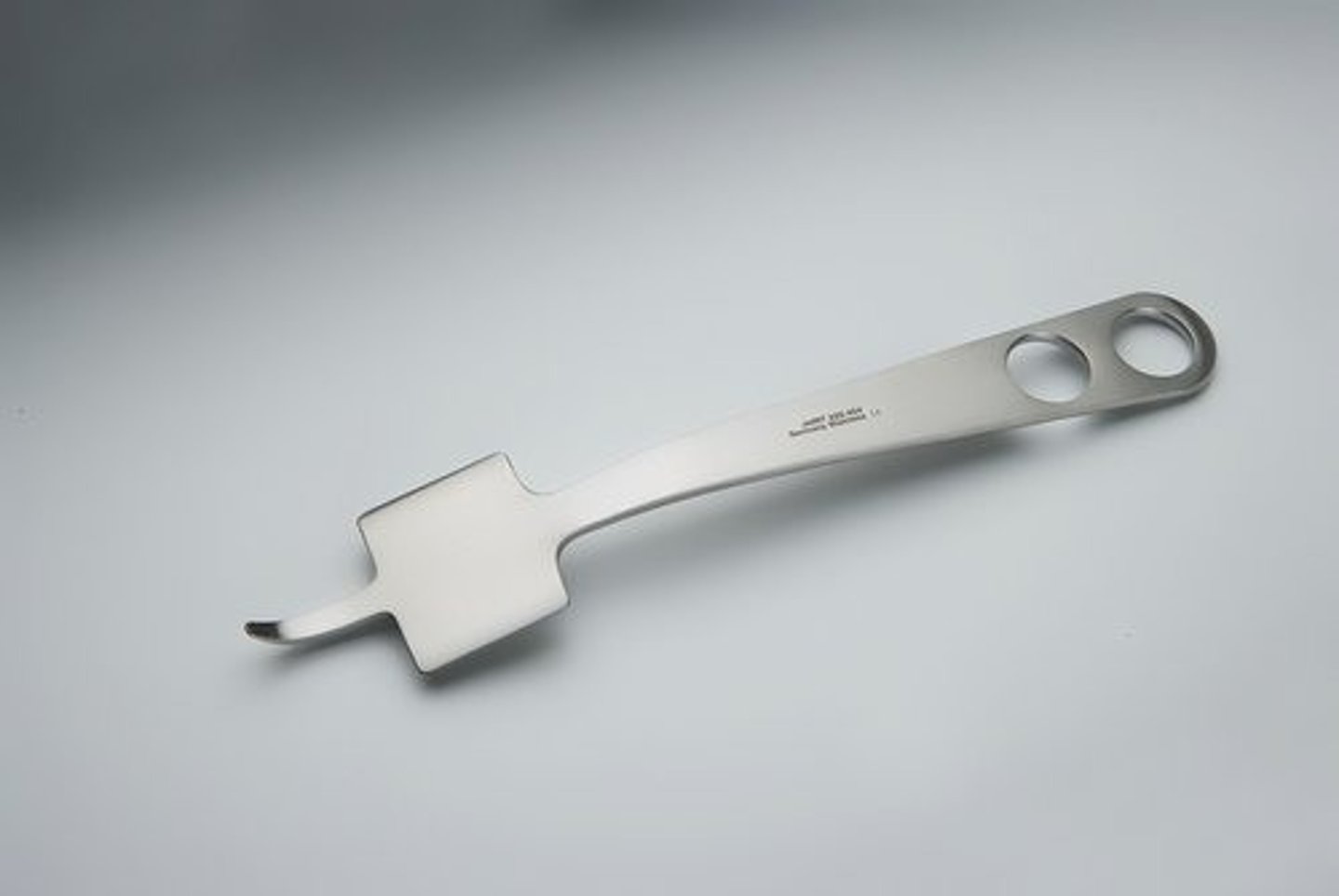

Sharp hohmann retractor
the surgical reconstruction or replacement of a joint
Arthroplasty
pain in a joint
Arthralgia
inflammation of a join
Arthritis
degenerative disease of the joint and is a normal part of aging
Osteoarthritis
autoimmune disease resulting in abnormal stiffness and fixation of joints
Rheumatoid arthritis
abnormalities of the internal structures of the knee joint. The torn edge resembles a bucket handle
Bucket handle tear
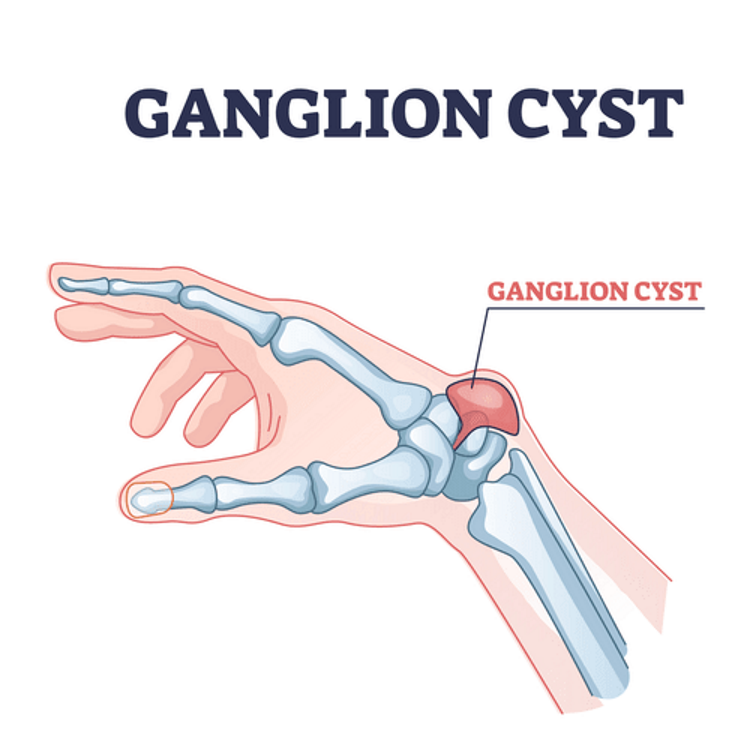
cystic growth commonly occurring on the dorsum of the wrist
Ganglion of tendon sheath
inflammation of bone and cartilage
Osteochondritis
tumor of the bone
Osteoma
a softening of bone caused by loss of calcification
Osteomalacia
Inflammation and infection of the bone and bone marrow, usually caused by bacteria. Staphylococci are the most common causative bacteria
Osteomyelitis
Staphylococci
BLANK are the most common causative bacteria
Destruction and death of bone tissue. Frequently occurs in the head of the femur due to a disease process or trauma that obstructs or destroys the blood supply to the femoral head
Osteonecrosis [Avascular Necrosis]
decreasing bone mass causing the bones to become brittle and fragile
Osteoporosis
A bony protuberance on the medial aspect of the first metatarsal. Associated with a hallux valgus deformity
Bunion
A bony prominence projecting from a bone is called an exostosis
Hallux Valgus
Outward turning of the hip joint
Coxa Valga
Inward turning of the hip joint
Coxa Vara
The knees are in close position and the space between the ankles is increased
Genu Valgum – “Knock-kneed”
The space between the knees is abnormally increased and the lower leg bows outwardly.
Genu Varum – “Bowlegged”
outward turning of the foot away from the midline
Talipes valgus
inward turning of the foot toward the midline
Talipes varus
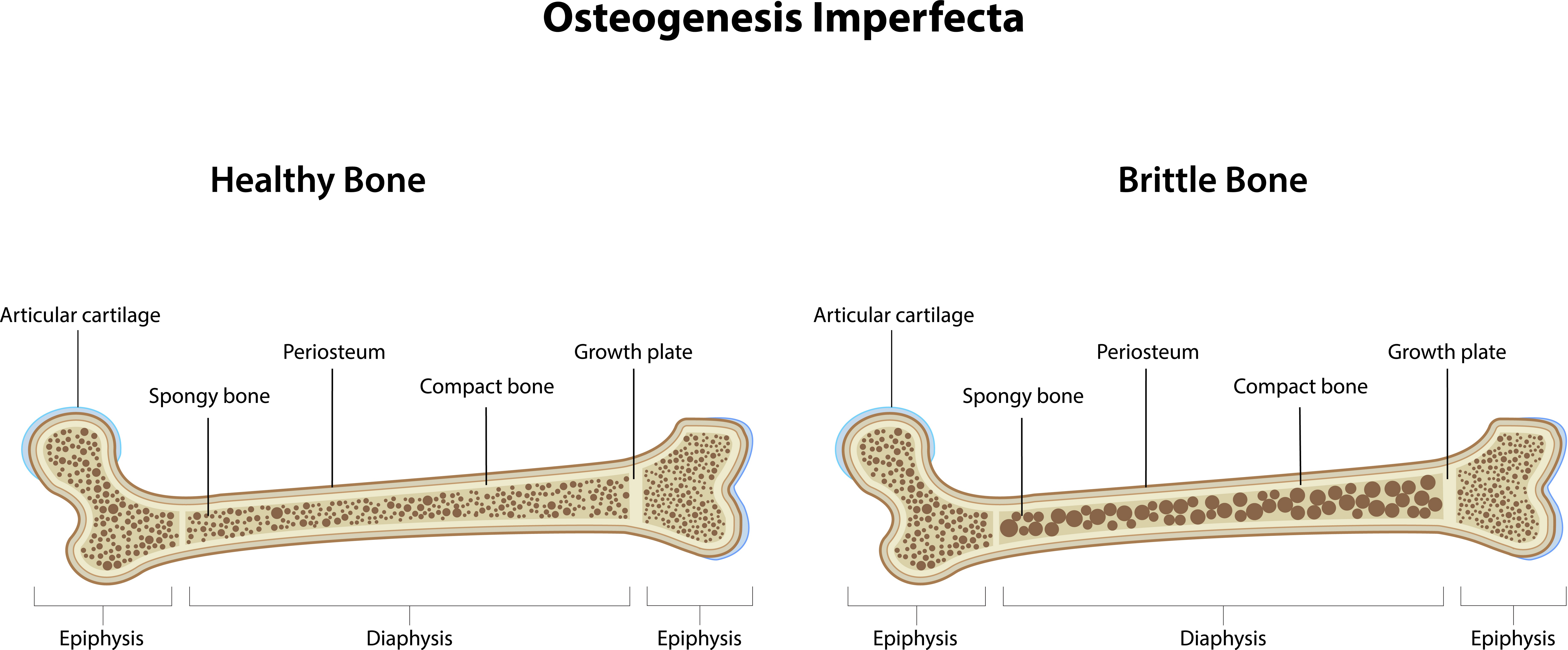
genetic and congenital condition that involves defective development of connective tissue, resulting in deformed and abnormally brittle bones that are easily fractured
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
displacement of bone from its socket, usually caused by trauma.
Dislocation
discontinuity of the normal alignment of bone. Most fractures are caused by accidents, although some are pathological (fractures caused by diseased bones)
Fracture
compound or open fracture
If the bone pierces the skin, it is called a BLANK
[Time limit for surgery to decrease risk of infection.]
simple or closed fracture
If it does not pierce the skin, it is called a BLANK
complete
Continuous through the bone is called BLANK
(Whether or not the bone pierces the skin)
incomplete or partial
Not continuous is called BLANK
runs parallel to the axis of the bone
Linear fracture
curves around the bone
Spiral fracture
is across the bone
Transverse fracture
is on the joint surfaces
Intra-articular fracture
Ewing’s Tumor
Multiple Myeloma
Osteosarcoma
Malignant Neoplasms
Chondroma
Giant Cell Tumor
Osteoma
Benign Neoplasms
a bone fragment is pulled away from its main body by soft tissue that is attached to it
Avulsion fracture
an injury to the metaphysis which is the growing plate at each end of a long bone
Bucket Handle fracture
large, triangular fracture fragments seen commonly in comminuted long bone fractures
Butterfly fracture
when the ends of the bone have come out of alignment
Displaced fracture
approx. 2 days
Stages of Normal Bone Healing
Inflammation
begins on 2nd day
Stages of Normal Bone Healing
Cellular Proliferation
3 - 4 weeks
Stages of Normal Bone Healing
Callus Formation
2-3 weeks following injury and can last 3-4 months
Stages of Normal Bone Healing
Ossification
maintenance state of normal bone
Stages of Normal Bone Healing
Remodeling
8 – 12 weeks
When a bone fracture occurs, complete bone healing is expected in BLANK. The site of injury should be completely immobilized (internal or external fixation) and in proper alignment
An increase in the healing time of fractures
Delayed Union –
bone fragments that are separated so that bone contact does not occur
Distraction –
When circulation cannot be reestablished after a decreased blood supply to the bone may lead to irreversible necrosis
Avascular Necrosis – (traumatic injury or vascular system)
Compromises the integrity of the skin, allowing microorganisms to enter that may cause a bone infection. (Osteomyelitis)
Compound fracture –
When the fractured bone ends do not meet
Nonunion -
When the fracture heals in a position that does not resemble the original form of the bone
Malunion –
An increase in pressure within a closed space that leads to neurovascular vascular compromise
Compartmental Syndrome –