Diuretics
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
diuretics
-drugs that diminish NaCl reabsorption at different sites in the nephron, thereby increasing sodium and H2O losses
-used to treat edematous states (CHF, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, advanced CKD)
-used to treat hypertension
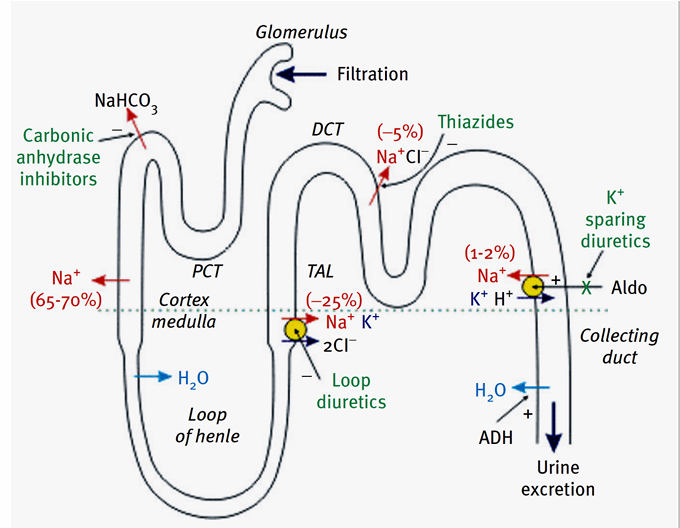
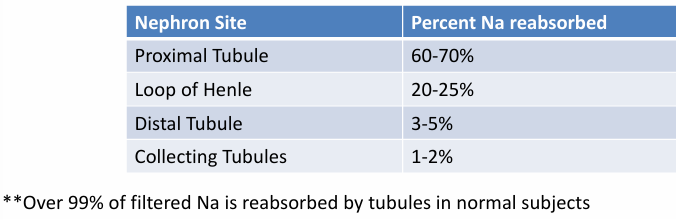
site of action of diuretics
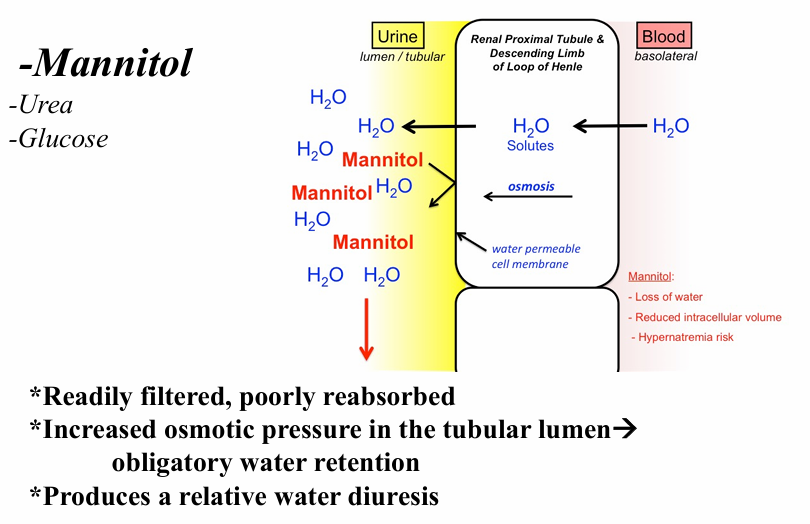
osmotic diuretics
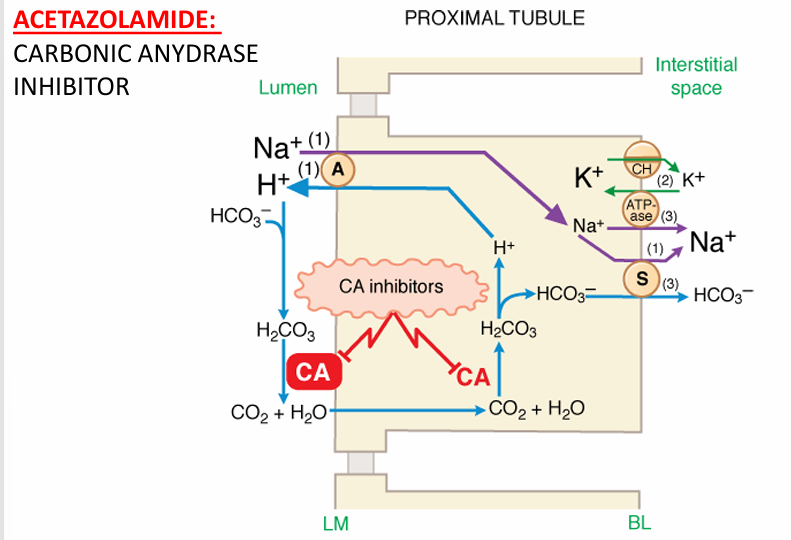
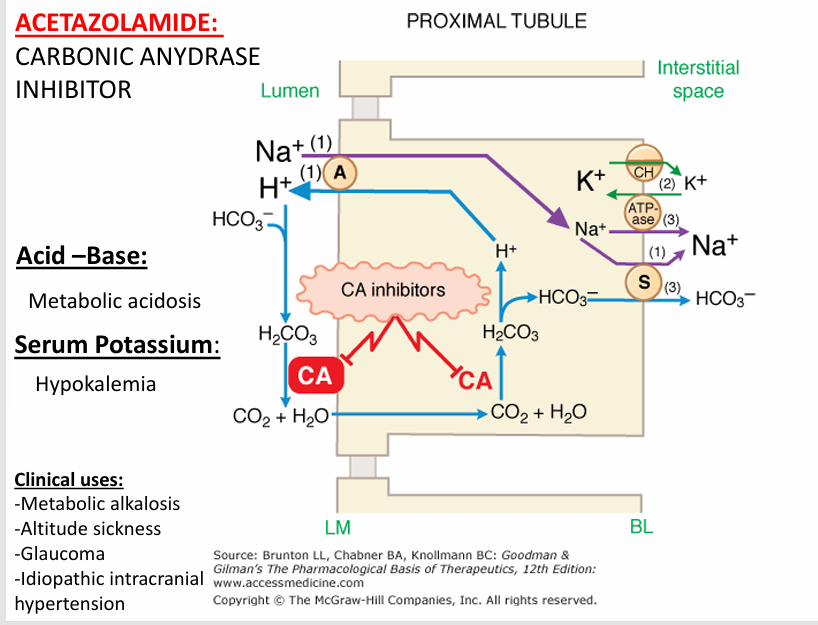
acetazolamide
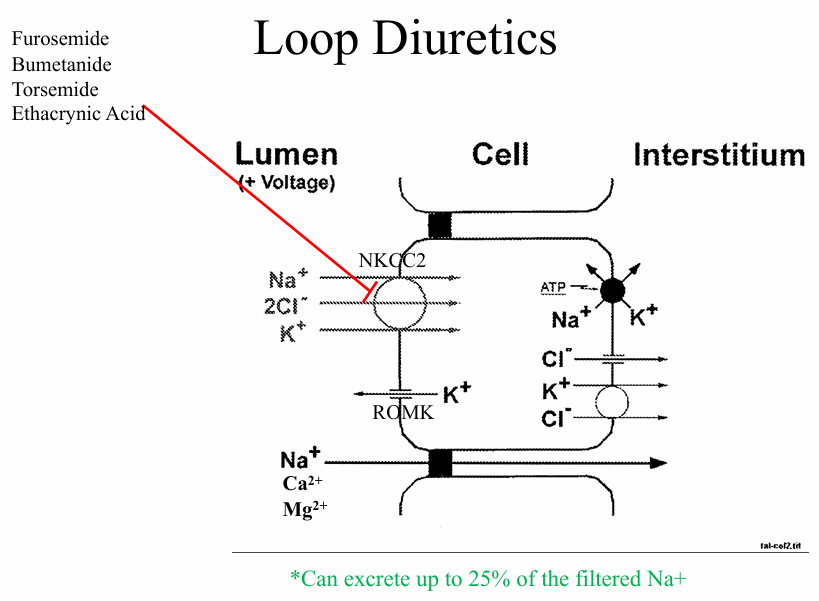
loop diuretics
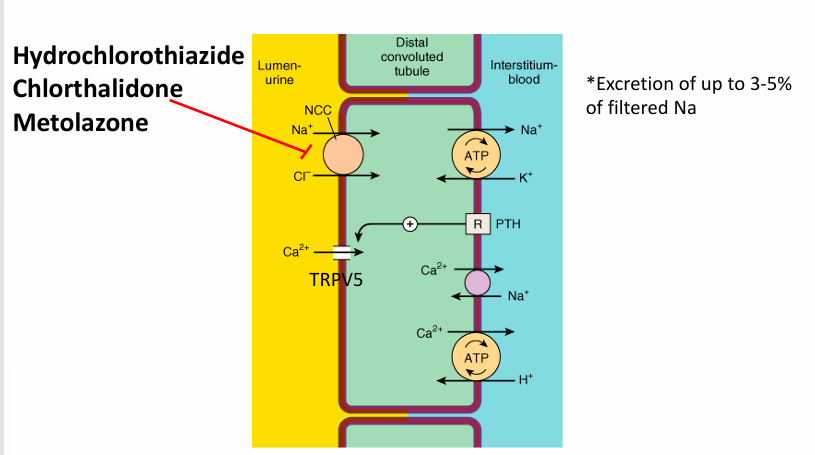
thiazide-type diuretics
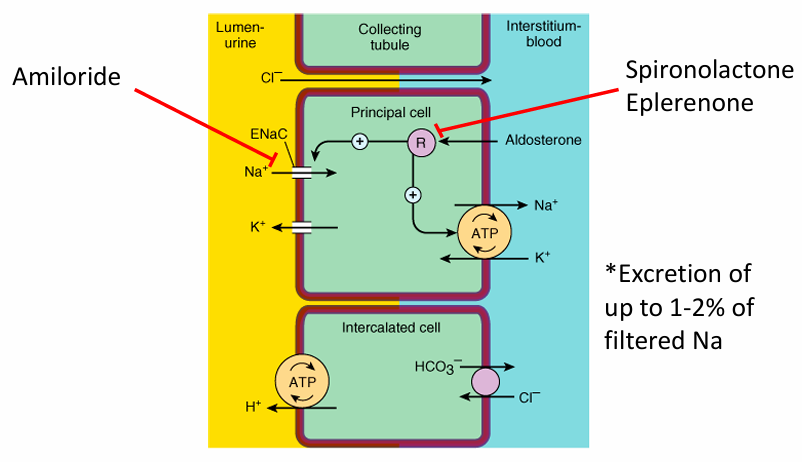
potassium-sparing diuretics
determinants of diuretic potency
-diuretic dose
-quantity of Na normally reabsorbed at the diuretic-sensitive site
-ability of more distal segments to reabsorb excess sodium
re-establishment of the steady state
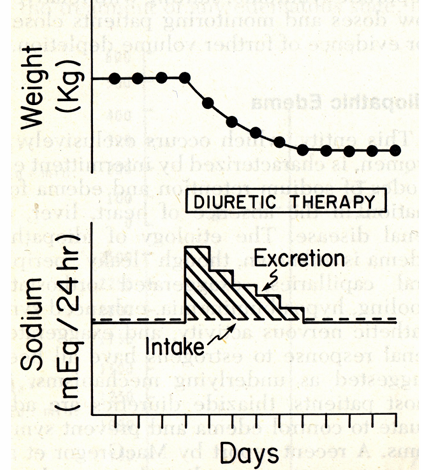
re-establishment of the steady state: counter-regulatory responses
-volume depletion → increased SNS, renin, ATII, aldosterone: increased filtration fraction → increased proximal tubular reabsorption, direct stimulation of Na reabsorption in the proximal tubule and collecting duct
-nephron remodeling: hypertrophy of distal nephron
loop diuretic infusion increases
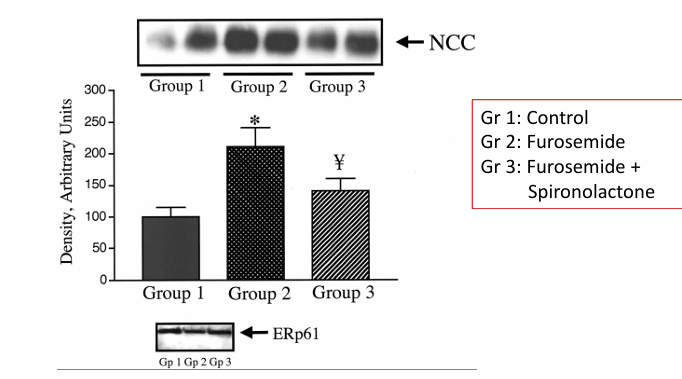
-thiazide-sensitive Na/Cl cotransporter abundance: role of aldosterone
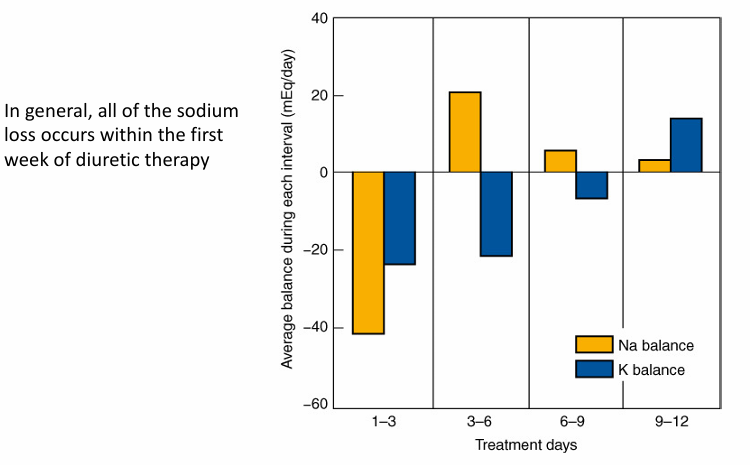
reestablishment of steady state after administration of high-dose thiazide to normal subjects
diuretics affect…
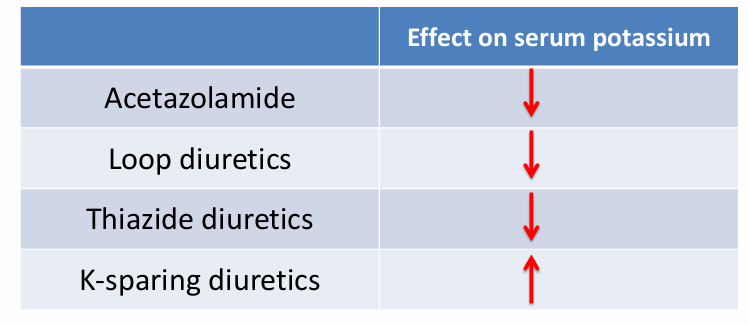
-potassium balance
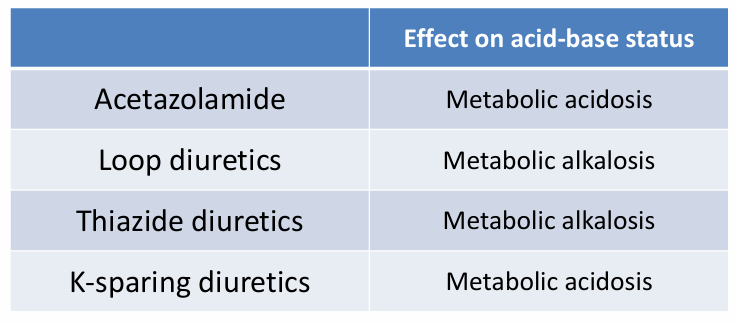
-acid-base balance
-other electrolytes (Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+)
-uric acid
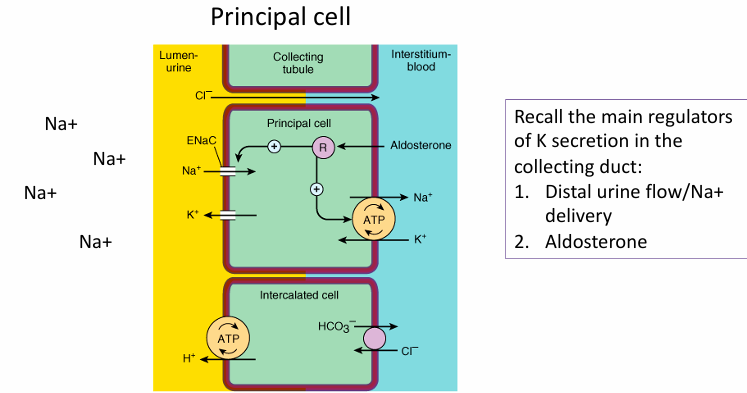
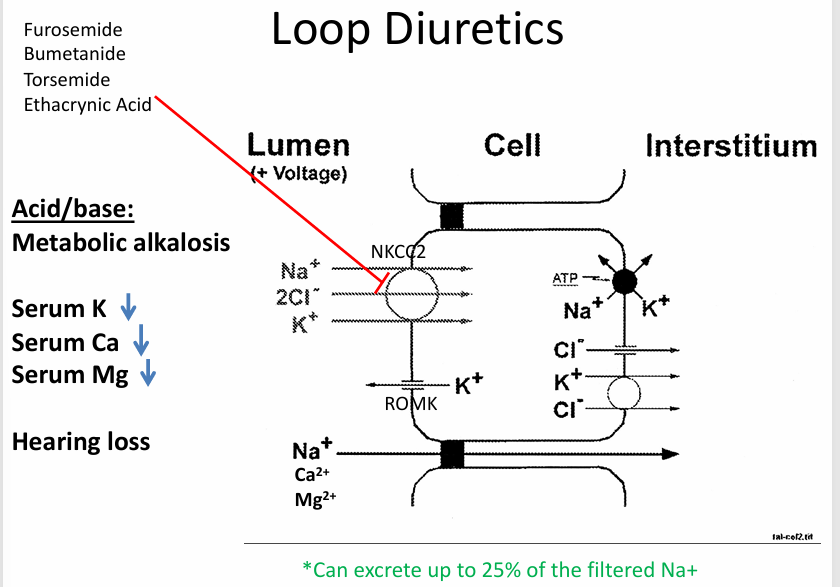
understanding loop and thiazide diuretic-induced hypokalemia
understanding loop and thiazide diuretic-induced metabolic alkalosis
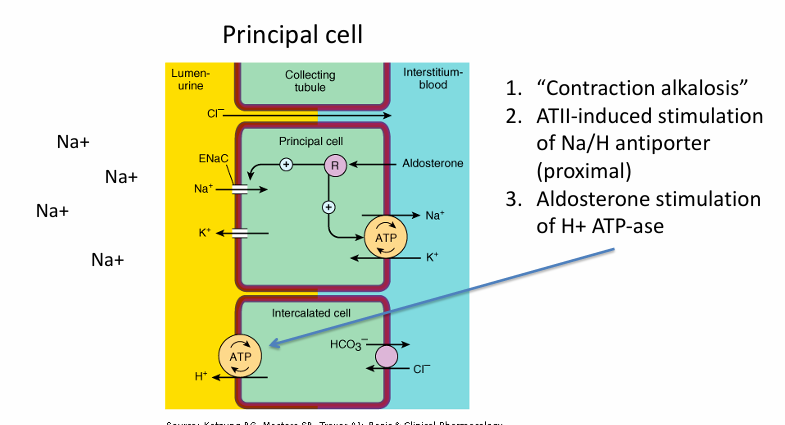
loop diuretics- acid/base
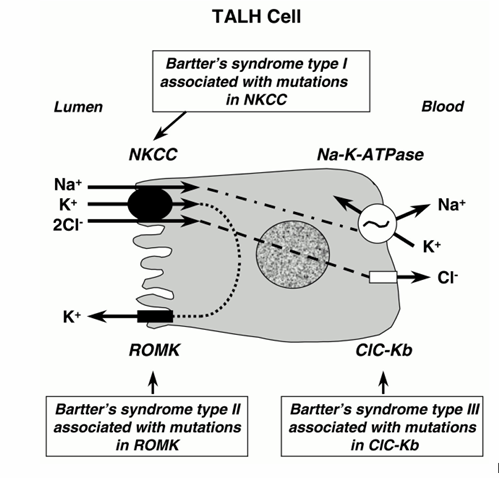
Bartter syndrome
-genetic disease resembling chronic furosemide use
thiazide-type diuretics- acid/base
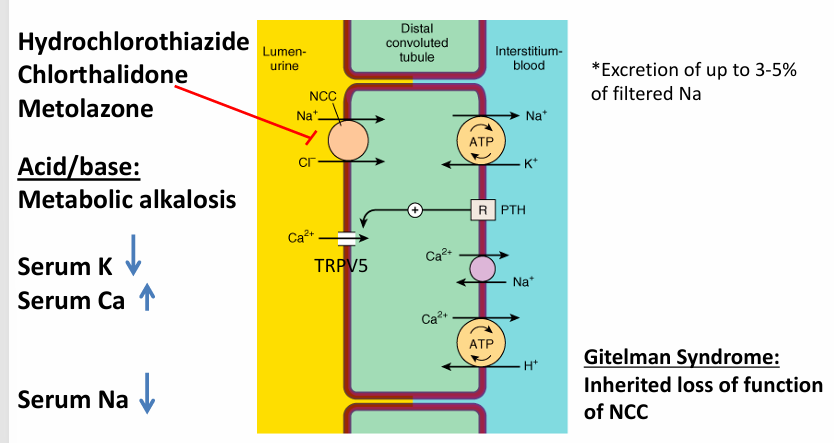
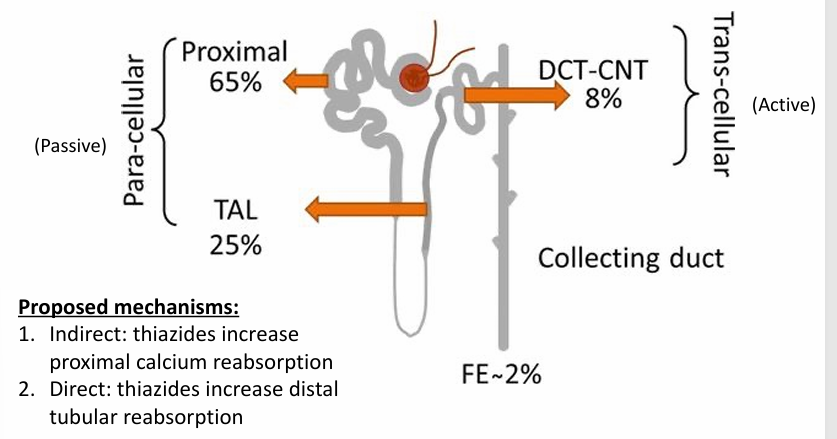
thiazides and hypercalcemia
thiazide-associated hyponatremia
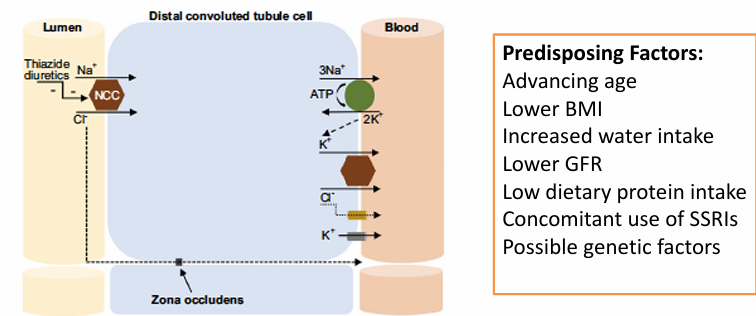
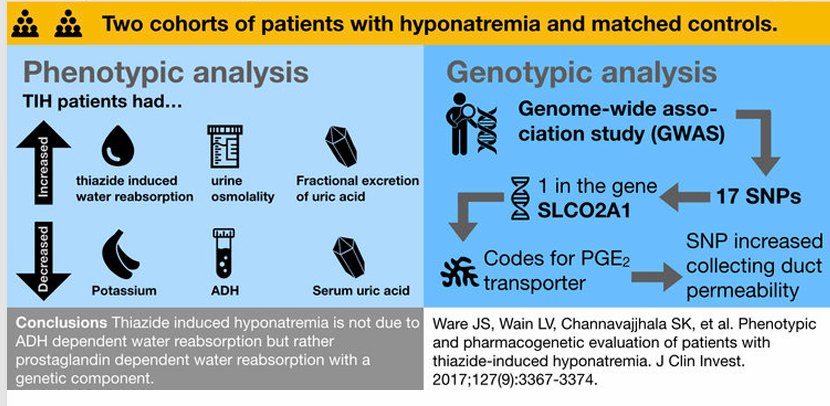
thiazide-induced hyponatremia- physiologic and genetic analysis
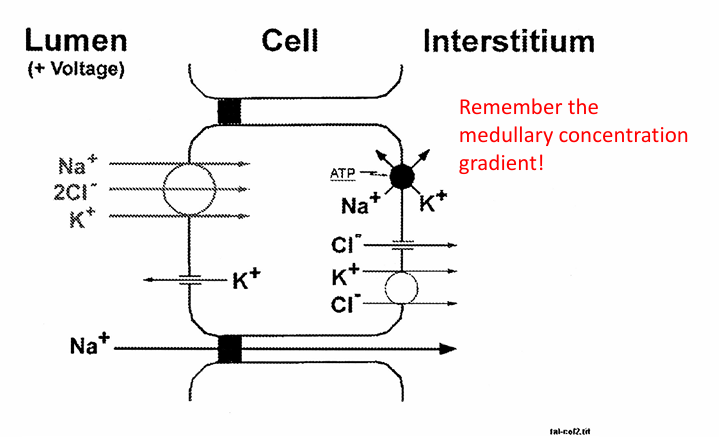
why is hyponatremia less common with loop diuretics?
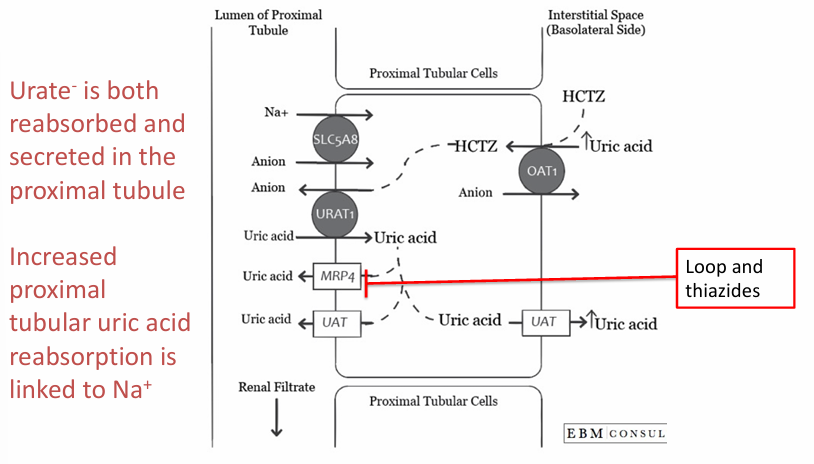
loop and thiazide diuretics may both cause
-hyperuricemia
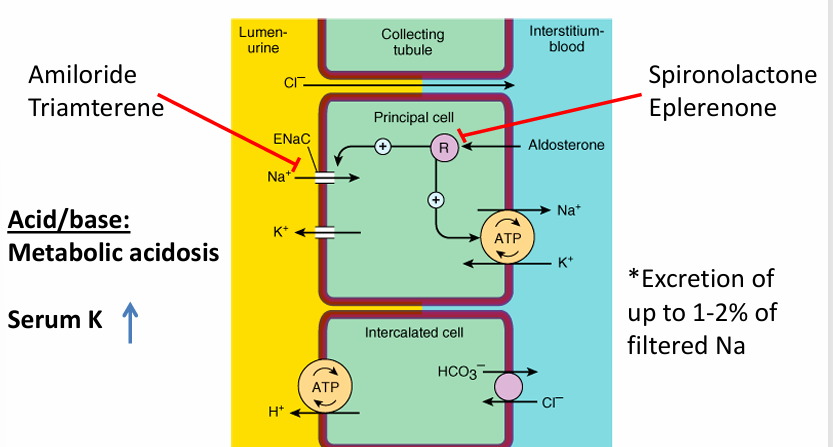
potassium-sparing diuretics- acid/base
acetazolamide- acid/base

effect on serum potassium
-urinary K excretion depends on distal delivery of Na and aldosterone

effect on acid-base status
loop and thiazide diuretics enter the lumen by
-proximal tubular secretion
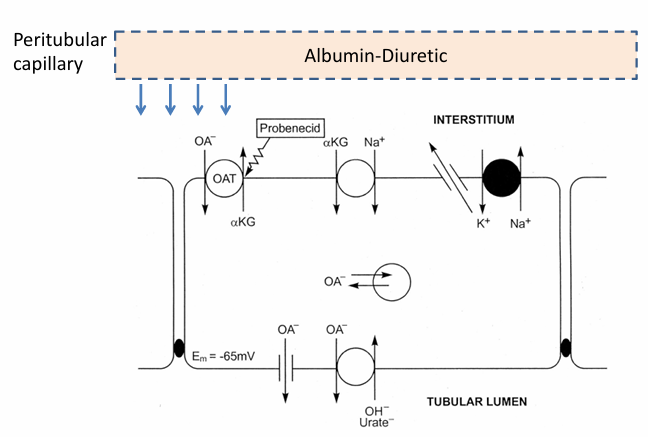
mechanisms of diuretic resistance/refractory edema
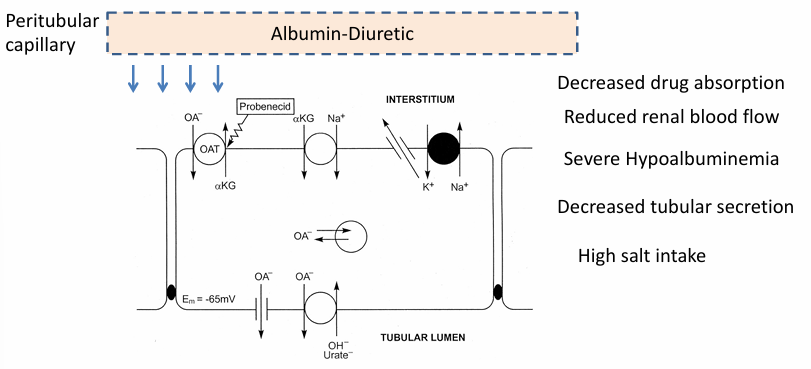
overcoming diuretic resistance
-change to a more bioavailable drug
-increase diuretic dose
-increase diuretic frequency (BID dosing)
-attempt more rigorous dietary Na restriction
-combine different classes of diuretics (“sequential nephron blockade”)
sequential diuretic use
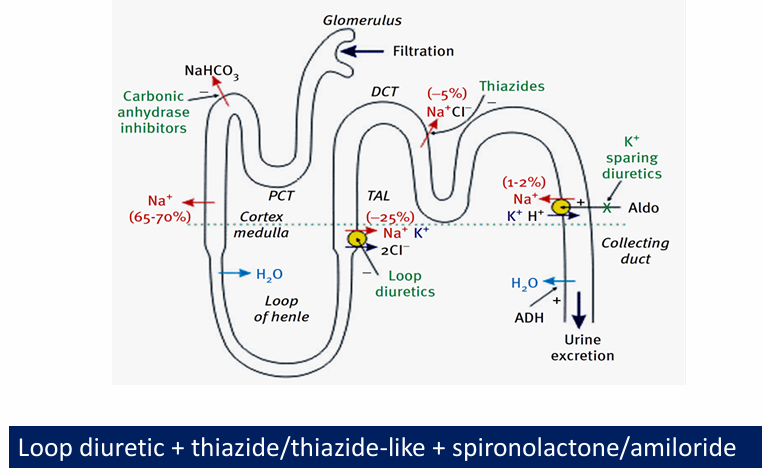
which diuretic class used to treat: SIADH, hypercalcemia, calcium stones, loop-diuretic-induced metabolic alkalosis, loop-diuretic-induced hypokalemia
-SIADH: loop
-hypercalcemia: loop
-calcium stones: thiazide
-loop-diuretic-induced metabolic alkalosis: acetazolamide or K-sparing diuretic
-loop-diuretic-induced hypokalemia: K-sparing diuretic
conclusions
