UAMS Hematology Exam 6 - part 2
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is the calculation for INR?
(Patient PT/PT Normal Mean)^ISI
What does aspirin do to platelets?
irreversibly suppresses platelet function. It inhibits thromboxane which is needed for platelet aggregation. The platelets will not aggregate. It is an irreversible reaction.
What are thrombolytic agents? List two.
Clot busters that break up existing clots. Streptokinase or Tissue Plasminogen Activator (TPA) are a couple of them.
What population is most affected by Vitamin K Deficiency?
Preemie newborns
- due to newborns having an immature liver, no GI bacteria, and no vitamins in mother's milk
What other things can cause Vitamin K deficiency?
antibiotics and poor diet
What coagulation test is elevated in Vitamin K Deficiency?
The PT is elevated since Factors II, VII, IX, and X are deficient. Factor VII is most significantly affected.
What are some other names for Inhibitors?
circulating anticoagulants, lupus anticoagulants, and anti-phospholipid antibodies
A defect in which factors will cause thrombosis?
Protein C, Protein S, or ATIII (anti-thrombin III)
Which factor deficiency will cause clotting instead of bleeding?
Factor XII
What factors are found in absorbed plasma?
I, V, VIII, XI, XII (all but the vitamin K factors)
What factors are found in aged serum?
VII, IX, X, XI, XII (contain all but the consumed factors)
Bernard-Soulier Disease is a defect of what?
glycoprotein Ib - GPIb
- it is a defective receptor that binds vWF
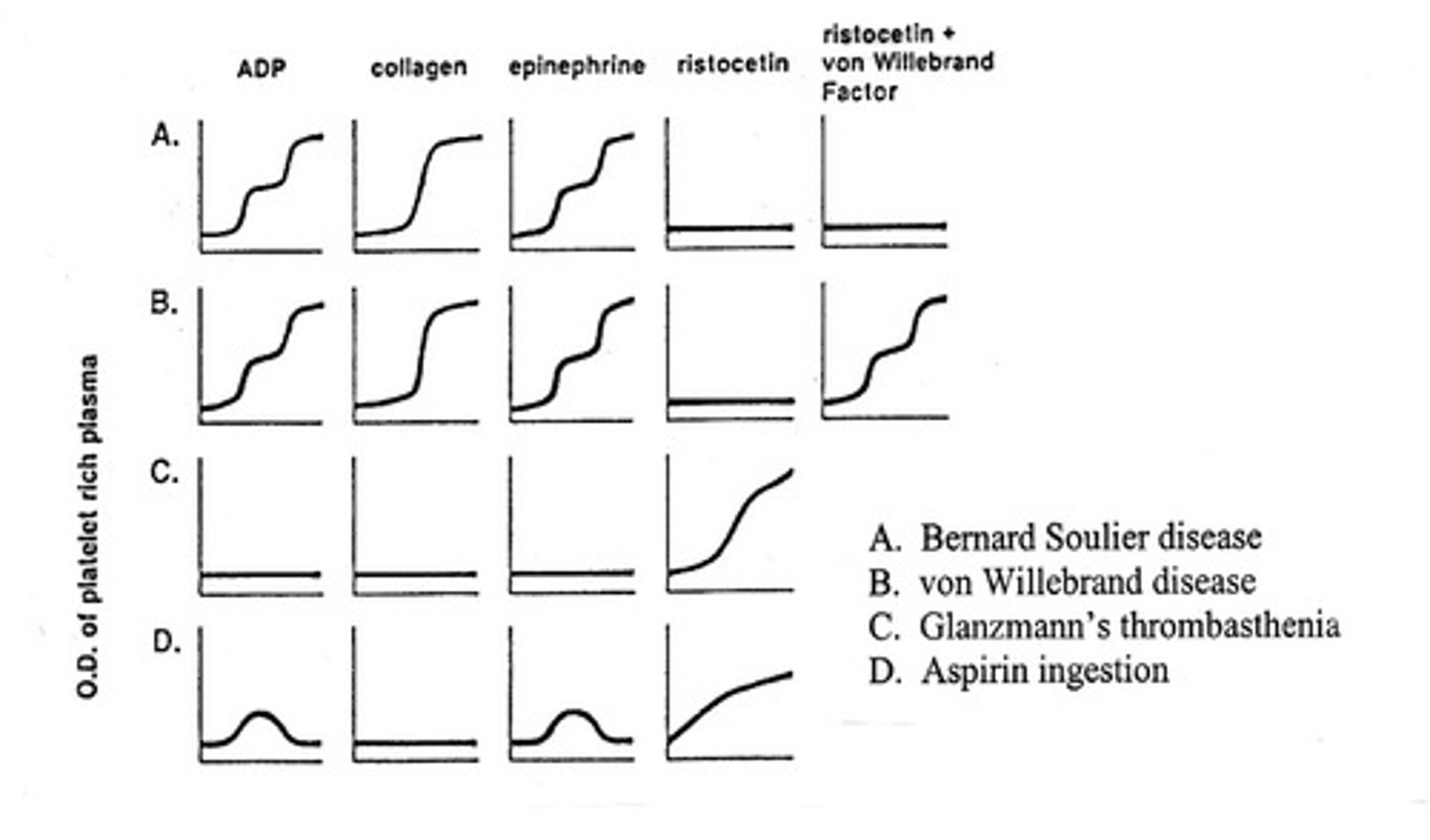
Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia is a defect of what?
platelet membrane GPIIb/IIIa
- receptor of binding fibrinogen and vWF
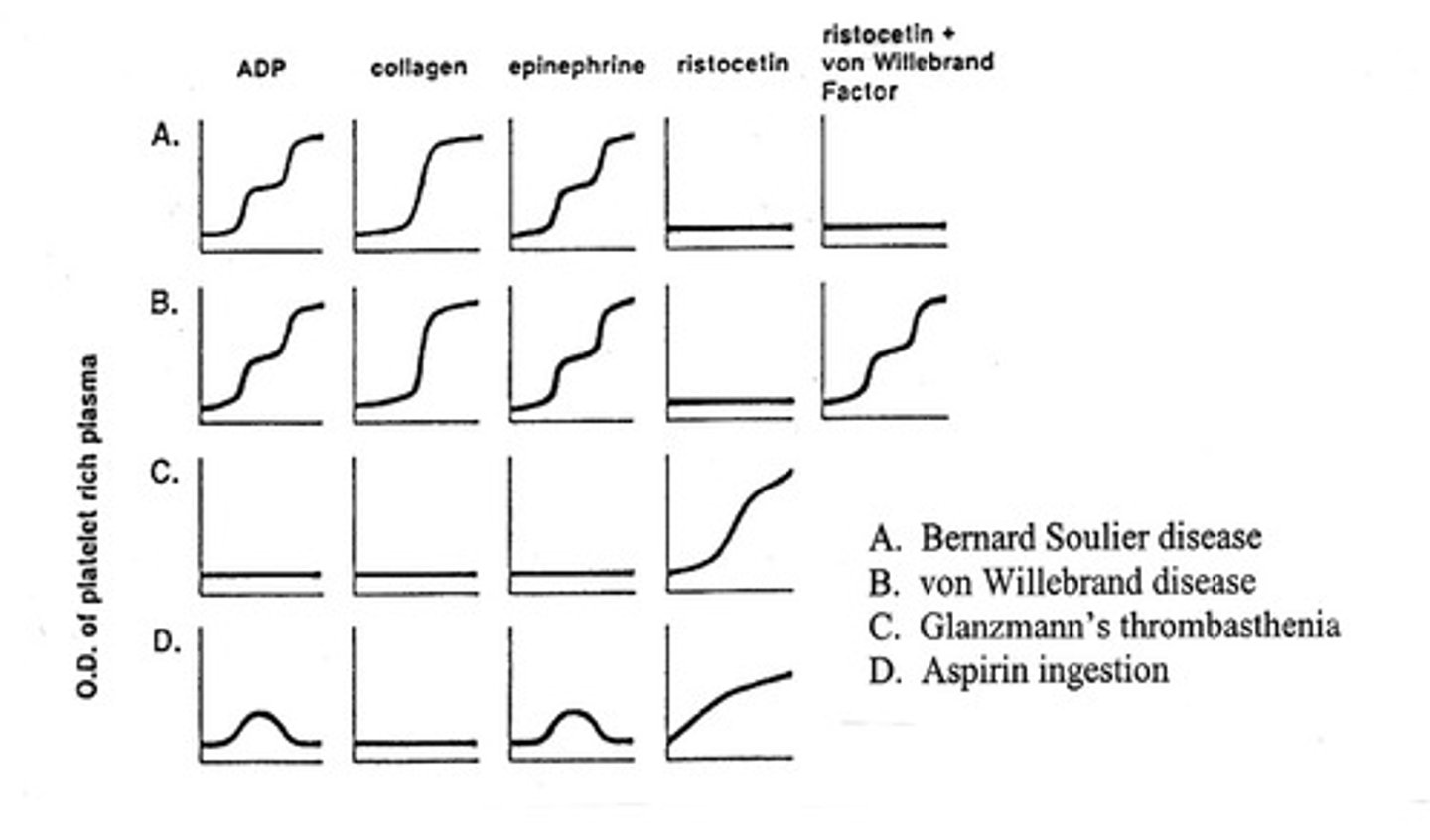
What tests measure the common pathway?
thrombin time and fibrinogen test
- thrombin is factor II, and fibrinogen is factor I
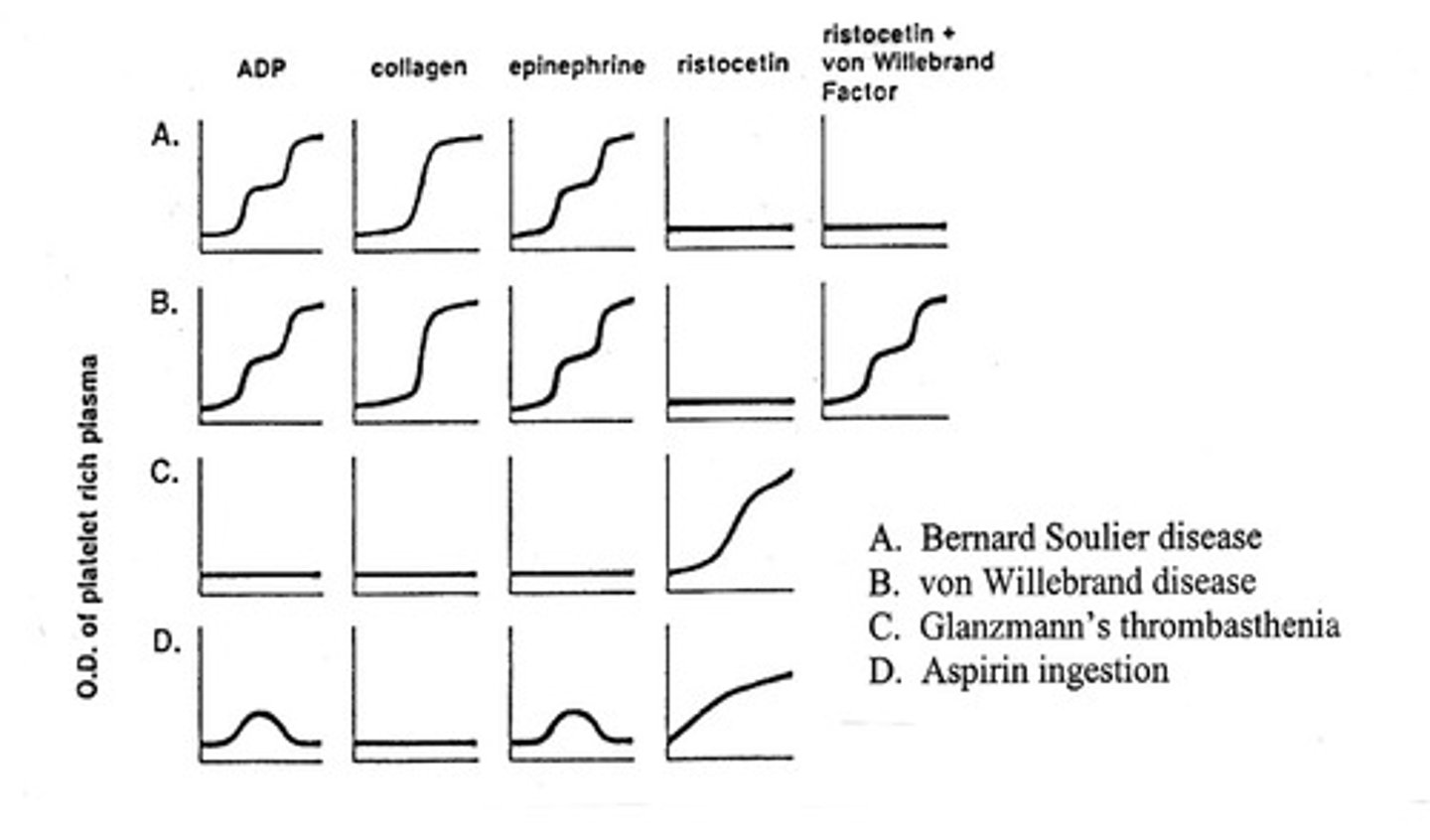
What deficiency does the urea solubility test test for?
Factor XIII
What disease states is the PT elevated in?
vitamin K deficiency, liver disease, and Factor VII deficiency
What therapy does the PT monitor?
Coumadin therapy
What reagent is used for the PT test?
thromboplastin combined with CaCl
What reagent is used in the PTT test?
Actin and CaCl
- actin contains phospholipids and a negatively charged activator
What therapy does the PTT monitor?
heparin therapy
What does the PT, PTT, and TT NOT measure?
platelet function
What has the bleeding time test been replaced with?
platelet count and aggregation studies
What does the Thrombin Time (TCT) test measure?
Measures the time it takes to convert fibrinogen to fibrin.
What is the normal range for TCT, and how do you interpret the results?
Normal range: 15-20 seconds
The longer the TCT, the less fibrinogen is present
What does the fibrinogen test measure?
measures the amount of fibrinogen
What is the normal range for Fibrinogen, and how do you interpret the results?
Normal range: 220-498 mg/dL
The time is takes for detection of a clot is inversely proportional to the amount of fibrinogen.
What is the normal range for D-Dimer?
110-240 ng/dL
A patient with a Hct of >55% has a coag tube drawn on them. No correction is made to the anticoagulant to blood ratio. What will the coagulation results look like?
Causes falsely prolonged results. The decrease in plasma volume relative to whole blood unacceptably raises the anticoagulant-to-plasma ratio.
What happens to coag results if there is a traumatic phlebotomy collection?
Tissue factor (factor III) is activated which falsely decreases the coag results.
What happens to coag results if there is prolonged tourniquet use?
There will be an increase in vWF and Factor VIII which will cause blood stasis and falsely decrease clot based assays.
What happens to coag results if there is a short draw?
increases the concentration of anticoagulant which falsely increases coag results.
What does a fibrometer do?
mechanically searches for clots. If not clots, then sample is most likely lipemia. PT and PTT will be falsely elevated.
Which test is abnormal in factor XIII deficiency?
urea solubility
Why must blue tops be centrifuged for a specified time and speed?
to get platelets out of the plasma
what is the action of thrombin?
cleaves A and B peptides from fibrinogen
If PT, PTT, PLT count are all normal and BT (bleeding time) is increased, what is the problem?
qualitative platelet or vascular disorder
what is the major activator in the fibrinolytic system?
TPA (tissue plasminogen activator)
Which substance starts the clotting process?
exposed collagen
At what platelet count could one have a spontaneous bleed?
<10,000/uL
what is the principle of the FSP/D-dimer test?
antibodies to FSP are attached to latex particles
how do you select platelet satellites?
examine platelet smear
What is the cause of the highest number of serious health threats?
arterial thrombosis
If factor VIII assay had a value of 55% activity, would the patient have bleeding?
no
what is the function of the kinin system?
Vasoactivity, inflammation, activates intrinsic system
What will the PT and PTT results look like if: Blood clot in leg with no treatment?
normal
What will the PT and PTT results look like if: ITP?
normal
What will the PT and PTT results look like if: DIC?
abnormal - elevated
What will the PT and PTT results look like if: Heparin therapy?
increased
What will the PT and PTT results look like if: Hemophiliac carrier?
normal
What will the PT and PTT results look like if: Child scheduled for out-patient surgery?
normal
What will the PT and PTT results look like if: Bleeding time after aspirin ingestion?
increased