Plant Systems
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
How do guard cells control the opening and closing of stomata?
To regulate the rate of gas exchange and transpiration
What does the anther of a flower produce?
Pollen, which contains male gametes (sperm cells)
Seed dispersal for animals
eats fruit and defecates seed out; some seeds stick to animals
seed dispersal for wind
seed is moved by wind
seed dispersal for water
seed is moved by water
What is the purpose of seed dispersal?
to increase gene flow and allows new plants to grow away from their parent plant
phototropism
the directional growth or movement of a plant or part of a plant in response to light
thigmotropism
a plant's directional growth response to physical contact or touch with an object
gravitropism
a plant's directional growth or change in the direction of its growth in response to gravity
What plant hormone is responsible for phototropism?
auxin
Which part of the stem produces the hormone?
the tip of the stem
Which side of the stem does the hormone accumulate (build up)?
the shaded side
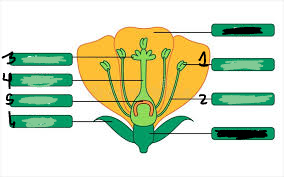
pistil
3,4,5
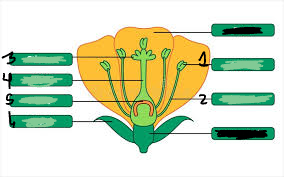
stigma
3
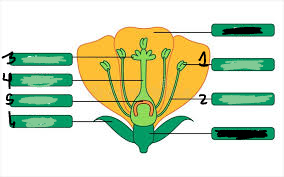
style
4
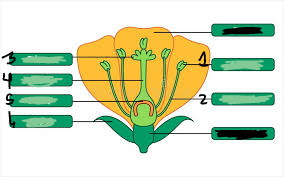
ovary
5
ovule
underneath 5
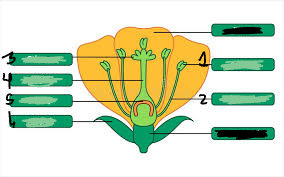
anther
1
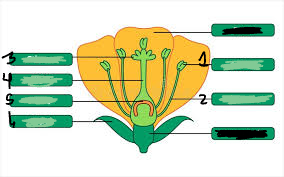
filament
2
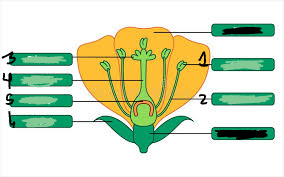
stamen
1&2
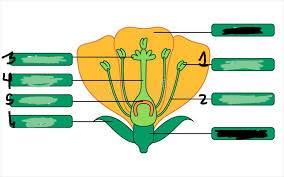
sepal
6
Can some flowers self-pollinate
yes
The part of the flower that the pollen must enter for fertilization
stigma
Purpose of root hairs on the roots of plants
they increase the surface area for absorption of water and essential nutrients from the soil
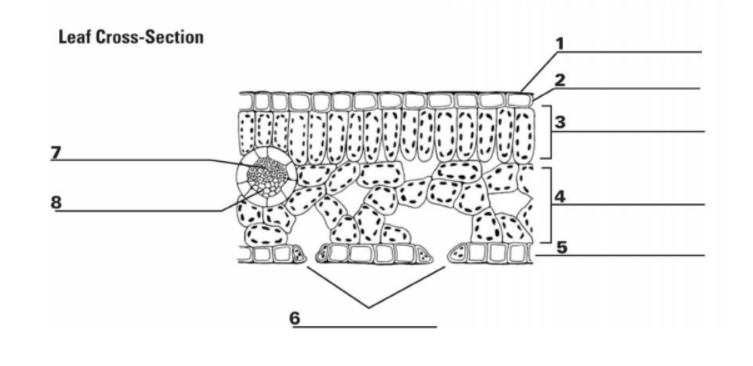
1
Cuticle: the waxy outer layer that protects the leaf from water loss
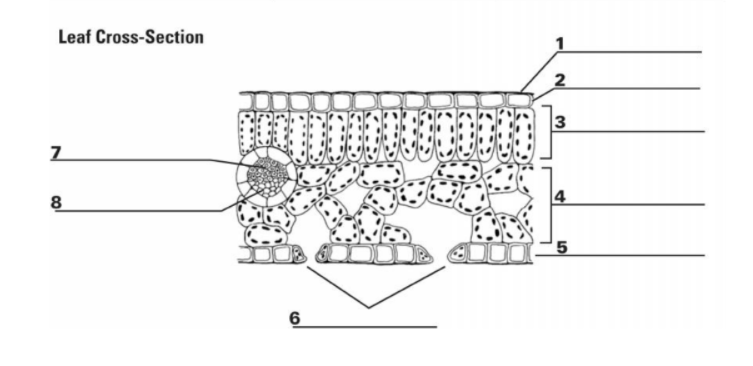
2
Upper Epidermis: A protective layer of cells regulates gas exchange through stomata (tiny pores) allows for light transmission
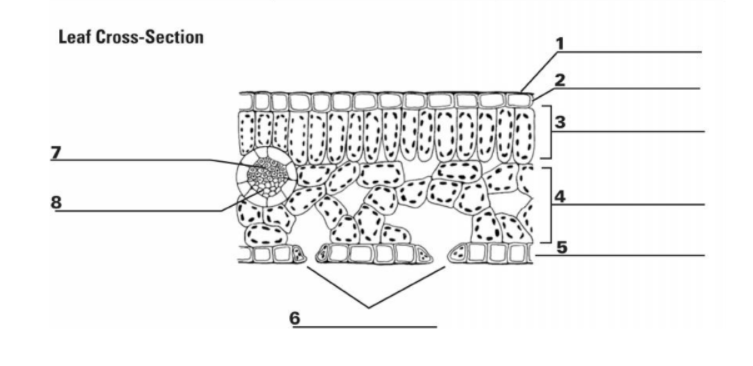
3
Palisade Mesophyll Cell: the primary photosynthetic tissue, composed of palisade and spongy cells
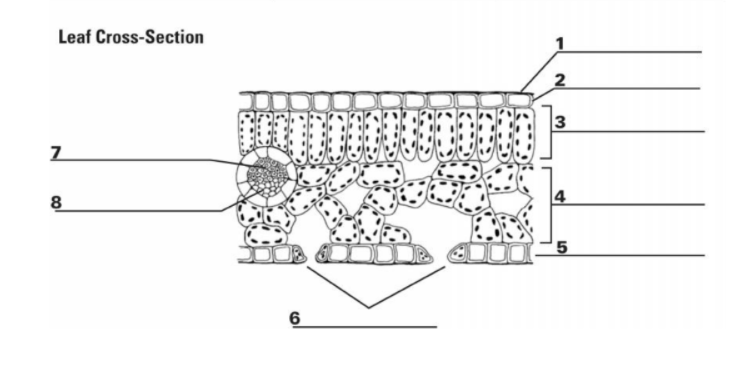
7&8
Vascular Bundle (Xylem & Phloem): x-transports water, p-transports nutrients
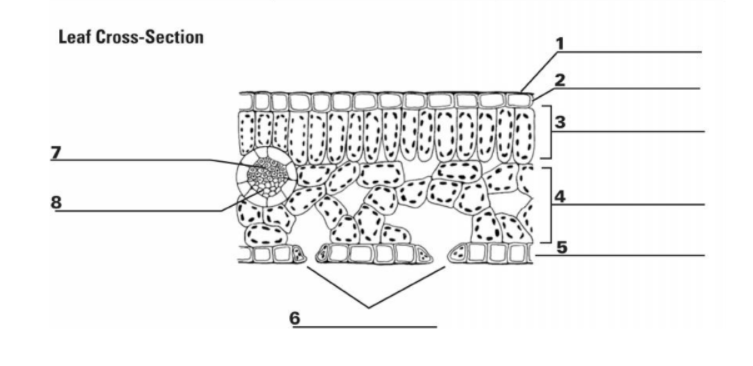
5
Guard Cell: regulates the opening and closing of stomata, tiny pores on the leaf surface
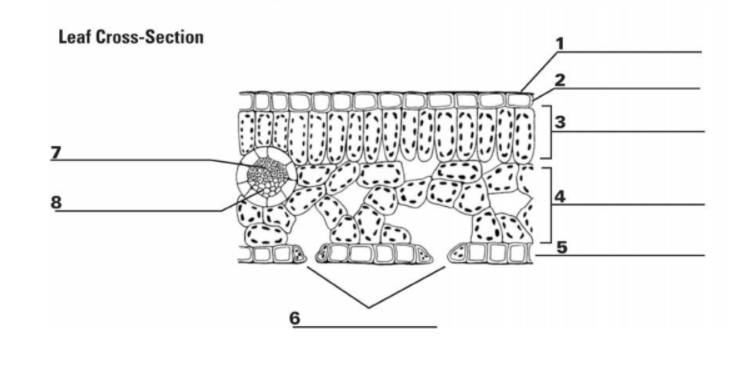
6
Stomata: pores on the underside of the leaf that facilitate gas exchange (carbon dioxide uptake and oxygen release) during photosynthesis
Where does the most photosynthesis occur in a leaf?
the mesophyll (C)
Why do carnivorous plants have the adaptation of ingesting insects if they still use photosynthesis to make their own food?
They live in nutrient poor (low nitrogen) environments. Insects provide the nitrogen.
What is the purpose of the vascular tissue?
To transport water, minerals, and sugars throughout the plant. Two types are xylem and phloem.
Xylem/Phloem
xylem: conducts water and dissolved nutrients upward from the roots of the plant
phloem: conducts carbohydrates (sugars) and other metabolic products downward from the leaves
Where in the plant does photosynthesis take place?
chloroplast