5 - Indirect restorations
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Can teeth fully recover their strength with ceramic inlays/onlays and composite cements?
Yes
What materials are used for direct and indirect restorations?
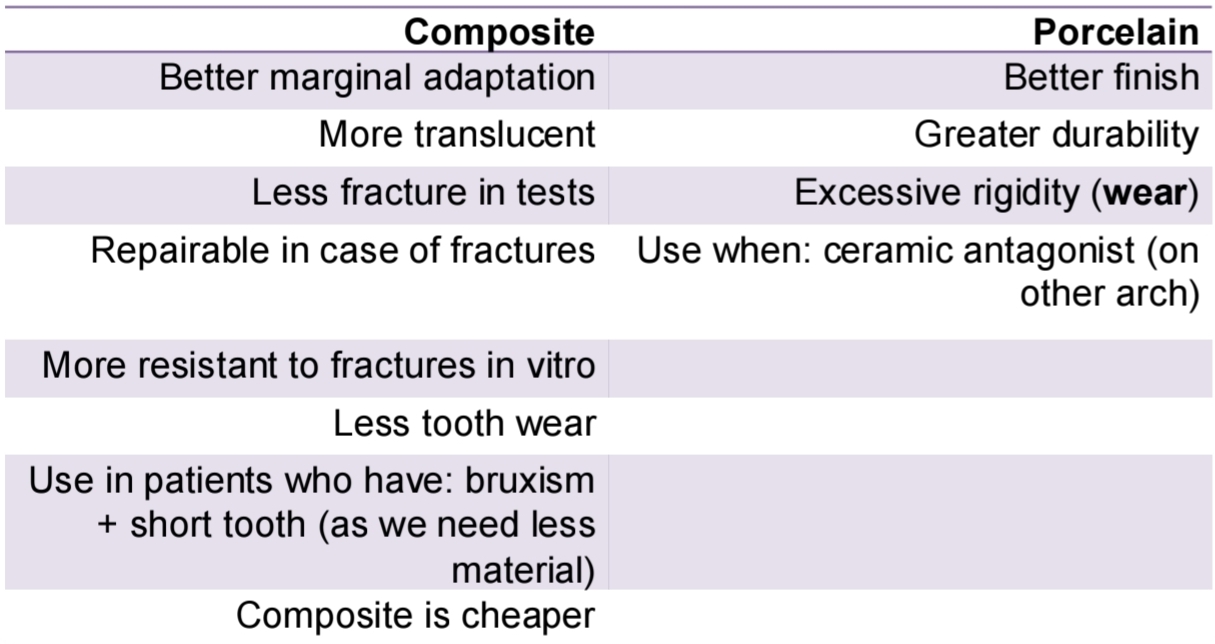
What are the diferences between composite and porelain as a restoration material?
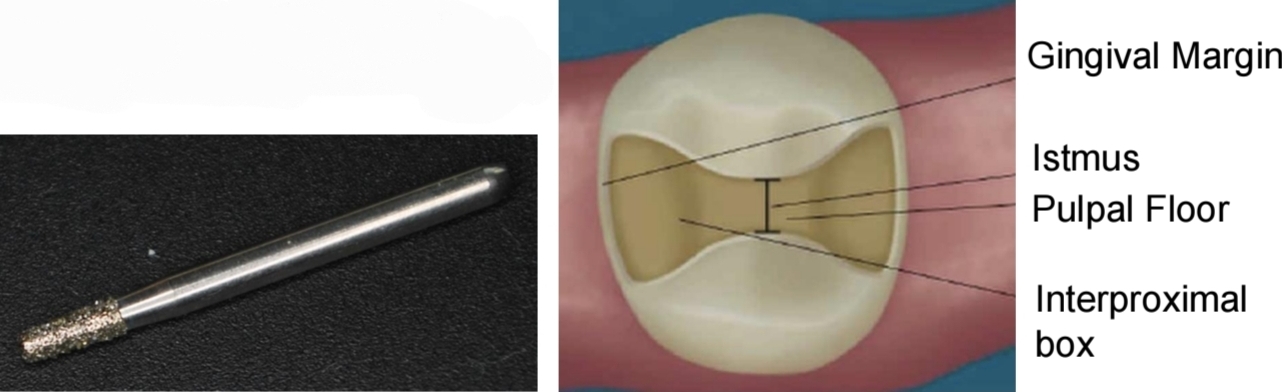
Inlay vs Onlay vs Overlay vs Veneers vs Crown
Inlay - doesnt cover any cusps (intracoronary)
Onlay - covers any cusp
Overlay - covers entire occlusal surface
Veneers - Vestibular surface
Crown - covers entire tooth incl. cervical portion
What are indications of Indirect restorations? (learn 5)
Weakened teeth
Widely destroyed tooth
Correct malocclusion and abrasions
RCT teeth (m + pm cusp protection)
Partial denture support
Fixed prostheses pillar
Subgingival restorations
Large Class 1 or MOD (class 2)
Close diastema and improve contacts
What are contraindications of indirect restorations?
Small defects
High caries activity
Inadequaate retention
Short clinical crown
Young teeth (large pulp chamber)
Deciduous teeth
What are disadvantages of indirect restorations?
Retention by adhesive cement
Complex cementation
Mutiple clinical laboratory phases
Higher cost
Agressive cavity prep
More detailed prep required
Less retention than full crowns
What are the advantages of indirect restorations?
Save tooth structure
Colour stability
Visible and accessible margins to cavity prep for cleaning
Indirect materials have less tendency to stress and wear
Anatomical reproduction and good finish
Lower rate of volumetric changes
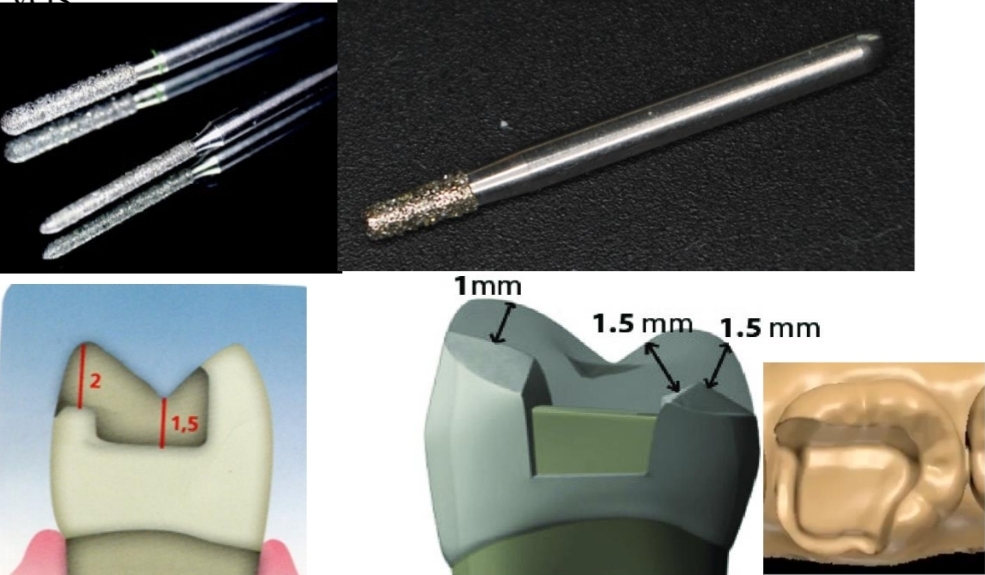
How do you prepare a tooth for an Inlay?
Class 1 or 2 cavity preparation
Diamond bur, taperd flat head and rounded tips
Divergent walls 10-15°
Isthmus max width 1.5-2mm
Occlusal plane 1.5mm depth and perpendicular to path of insertion
Proximal boxes more that 1mm axial depth, and 2mm b/l
Remove contact points
No bevel
What is a good restoration option for large restorations of posteriors after RCT that still have healthy walls?
Onlay
How is a tooth prepared for an onlay?
Conical diamond bur with rounded tip
No contact point between cavity margin and adjacent tooth
Axial reduction with conical flathead and round tip bur, with deep chamfer
No sharp angles
No bevels
90° cavosurface angle
At least 0.5mm gingival enamel (good marginal seal)
No occlusal contact on restoration - tooth interface
1.5 - 2mm thickness for cusp coating
How is an overlay made?
CAD/CAM in lab
(note that chamfer margin is needed in overlay prep, similar to onlay)
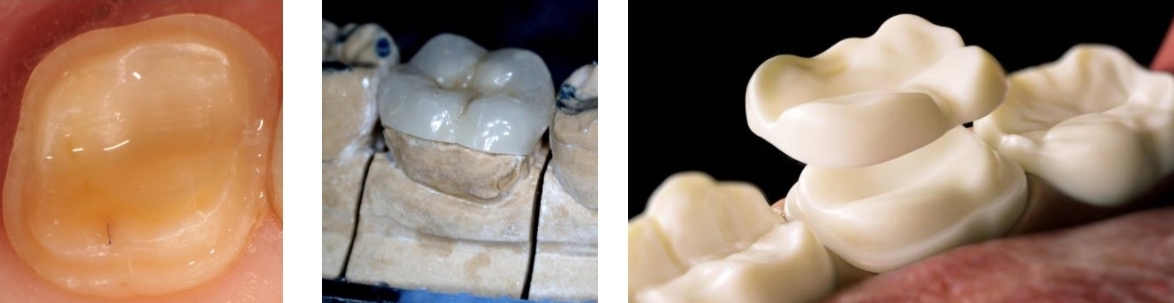
How are provisional restorations made for inlays?
Temp filling cement (e.g. Fermit).
Impression not needed
How are provisionals made for onlays
Use Protemp, direct technique
Alginate/silicione impression needed
Cement provisionals without eugenol (temp-bond)
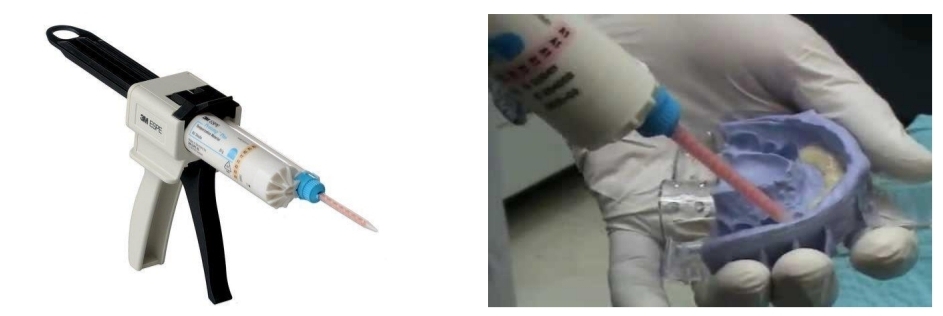
What does the first clinical session consist of?
Xray, impressions for provisionals, remove caries and prep tooth.
Definitive impression for lab to make indirect restoration
Wax occlusal register
Cement provisional restoration
What does the second clinical session consist of?
Remove provisional and clean the tooth
Insert and cement restoration
Consider contact points, marginal adjustment, stability, aesthetics, Occlusion
How do we complete absolute isolation before cementation?
Apply a resin barrier (the same type used in tooth whitening) to protect the gums
Cure for 20 seconds
Use Teflon tape on adjacent teeth to prevent bonding
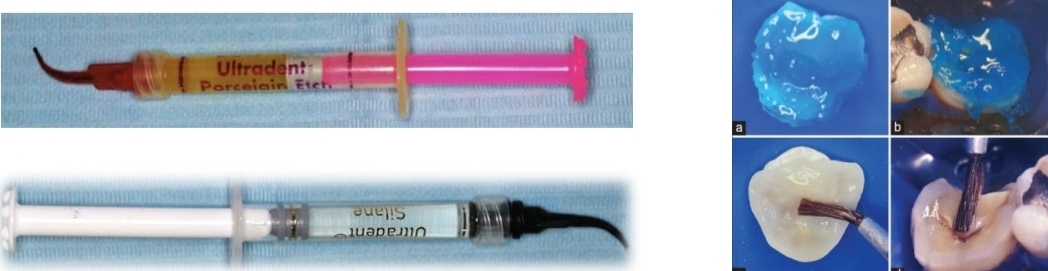
Different ceramics need different etching times and acids- what is used for the inner side of ceramic vs silicate porcelain?
9.6% (yellow) hydrofluoric acid for 2 minutes (ceramic)
4.9% (red) hydrofluoric acid for 20 seconds (silicate porcelain)
After HF etching- etch with orthophosphoric acid for 30 seconds, apply silane for 1 minute
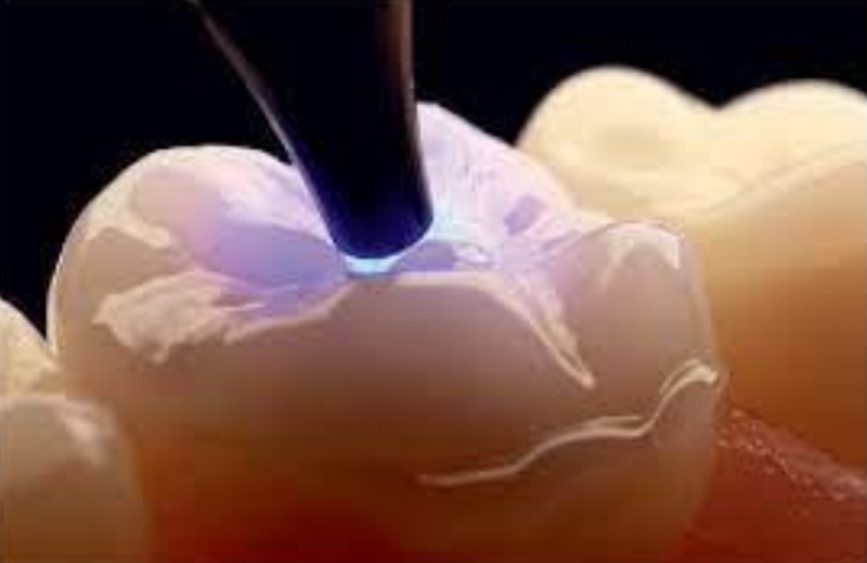
What does the total etching of enamel and dentin, and the adhesive application consist of.
Etch enamel with 37% orthophosphoric acid for 30 seconds, etch dentin for 20 seconds, rinse and gently air dry
Apply dual adhesive on tooth and restoration on inner surface
What adhesive should you use for what cement?
Dual cement - Dual adhesive
Photo cure cement - Photo cure adhesive (otherwise wont bond)
Dual cement will fully cure with time
How do you conduct bonding of an indirect restoration?
Fill tooth and restoration with dual cement
Place tooth with pressure occlusally
Polymerise for 5 secs then remove excess cement
Cure each surface for 1 minute
What should we use to adjust occlusion and polish?
Occlusion - Fine grain turbine (yellow), Arkansas slow speed
Polish - Silicone tips (for porcelain)
What are the reccomendations within the first 24 hours of treatment?
Soft diet, avoid dyed food
Book 48hr revision (adjust occlusion)
Book 7-15 day revision (assess gingiva and eliminate cement traces)
Avoid usual mouthwashes
Warn about hypersensitivity (several weeks)
What should the patient do for maintenance?
Usual hygeine
Medium hard brush
What should the dentist do for maintenance?
3,6 and 12 month checkup (check tartar build up aswel)
Avoid ultrasonic instruments (can create fissures on ceramics)
Avoid abrasive polishing systems (remove glaze)
Polish marginal stains with silicon cups