MCAT Biology
1/63
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
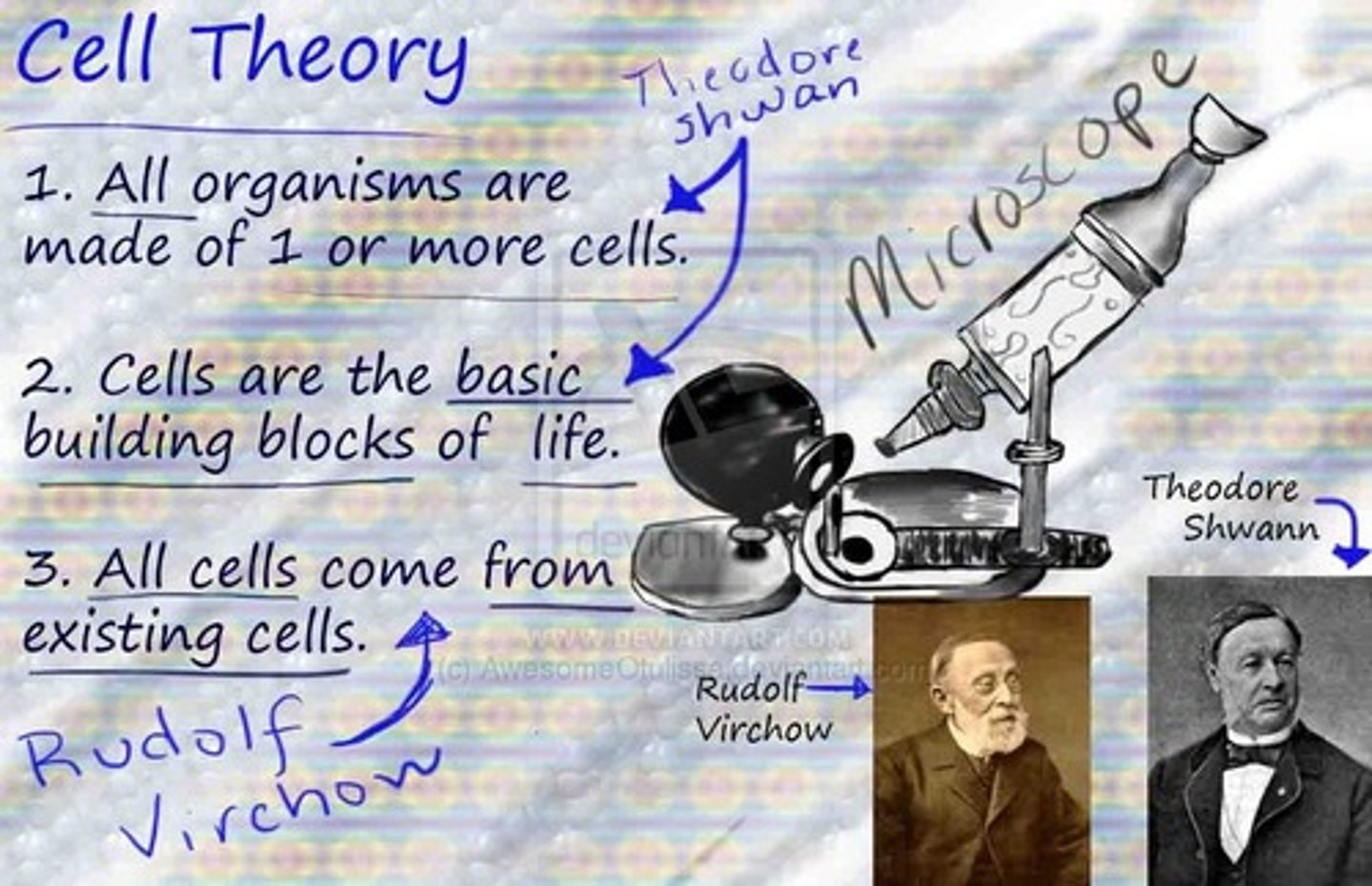
Cell Theory
1. All living things are made up of cells
2. All cells come from pre-existing cells
3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things
Endomembrane System includes
Nuclear Envelope
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Nucleoid Region
DNA region in prokaryotes
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
1. Smooth ER
2. Rough ER
Rough ER
Accept mRNA to make proteins.
Smooth ER
Detox & make lipids.
Gogli Apparatus
Protein Secretion
Modify / distribute proteins. Only in eukaryotes.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
Peroxisomes
Collect and break down material.
Contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals
Lysosomes
Demo & Recycling center. Made by Golgi. Single membrane.
Uses chemicals to break down food and proteins
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Vacuole
a space or vesicle within the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosed by a membrane and typically containing fluid.
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
Centrioles
Located near the nucleus and help to organize cell division
Example: 9 groups of microtubules, pull chromosomes apart
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome.
In prokaryotes. Carry DNA not necessary for survival.
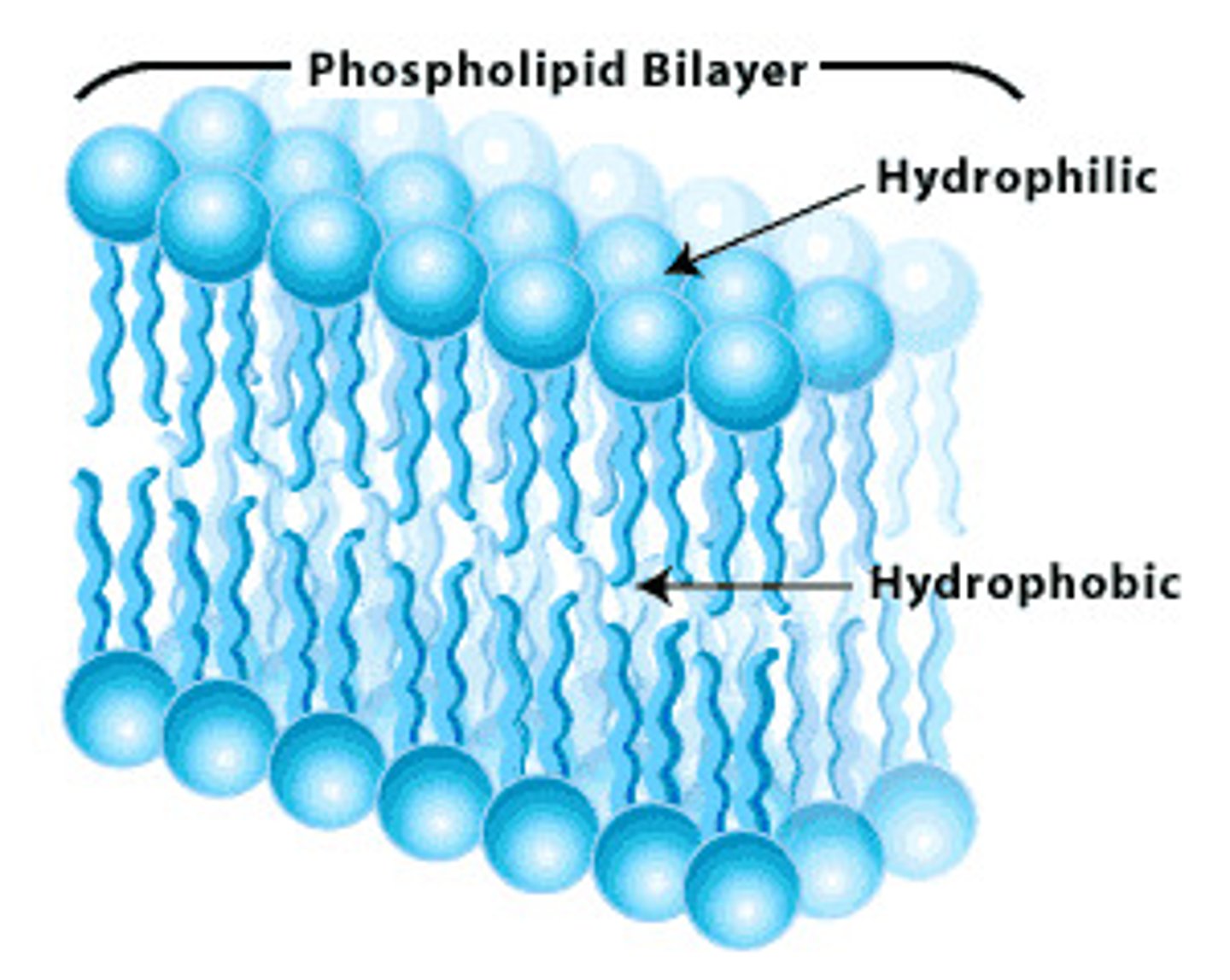
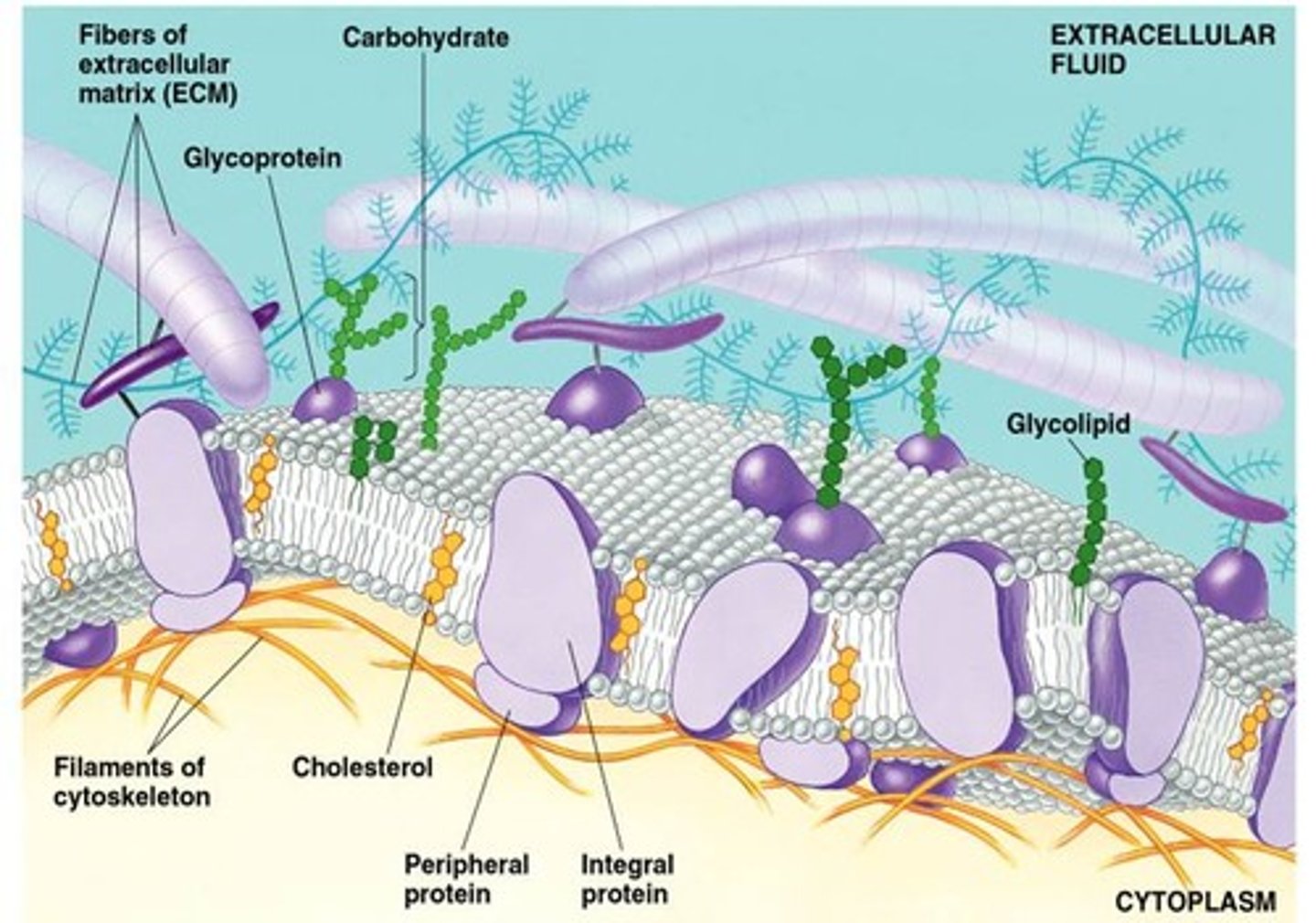
Plasma Membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
Plasma Membrane Parts
Amphipathic - Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic
Phospholipids Bilayer - Phosphate head and two Lipid tail.
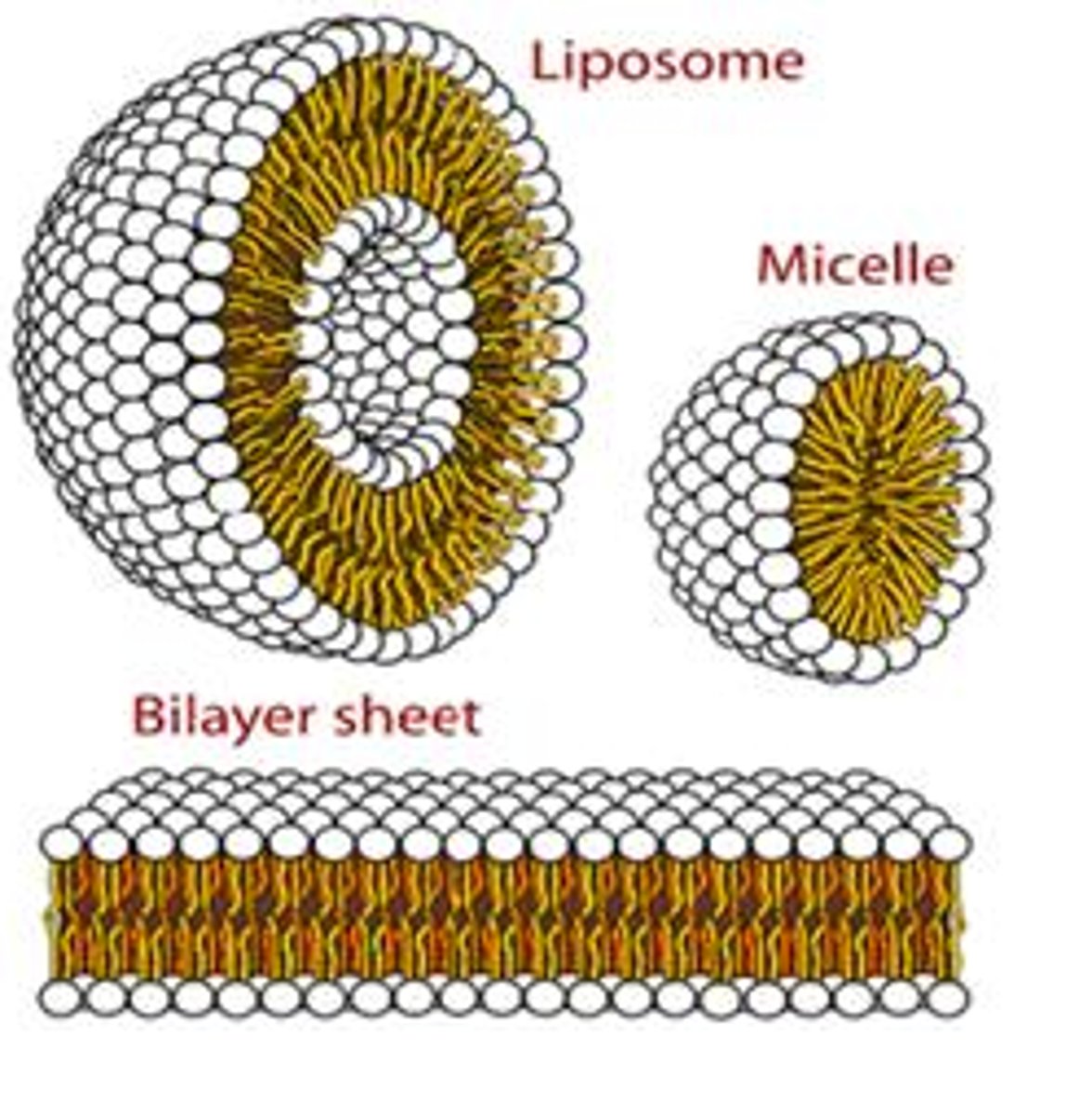
Micelles
Lipid molecules orient with polar (hydrophilic) head toward water and nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails away from water

Liposome
Small membrane bounded transport vesicles
Have been used as a drug delivery recently
Cholesterol
Helps Phospholipid bilayer lubricate when it's cold and glues phospholipid together when its hot.
Glycolipid
A lipid covalently attached to a carbohydrate Plasma membrane
Glycoprotein
A protein with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates in Plasma membrane
Membrane Proteins
Integral proteins and Peripheral proteins
Peripheral Proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; they are appendages loosely bound to the surface of the membrane.
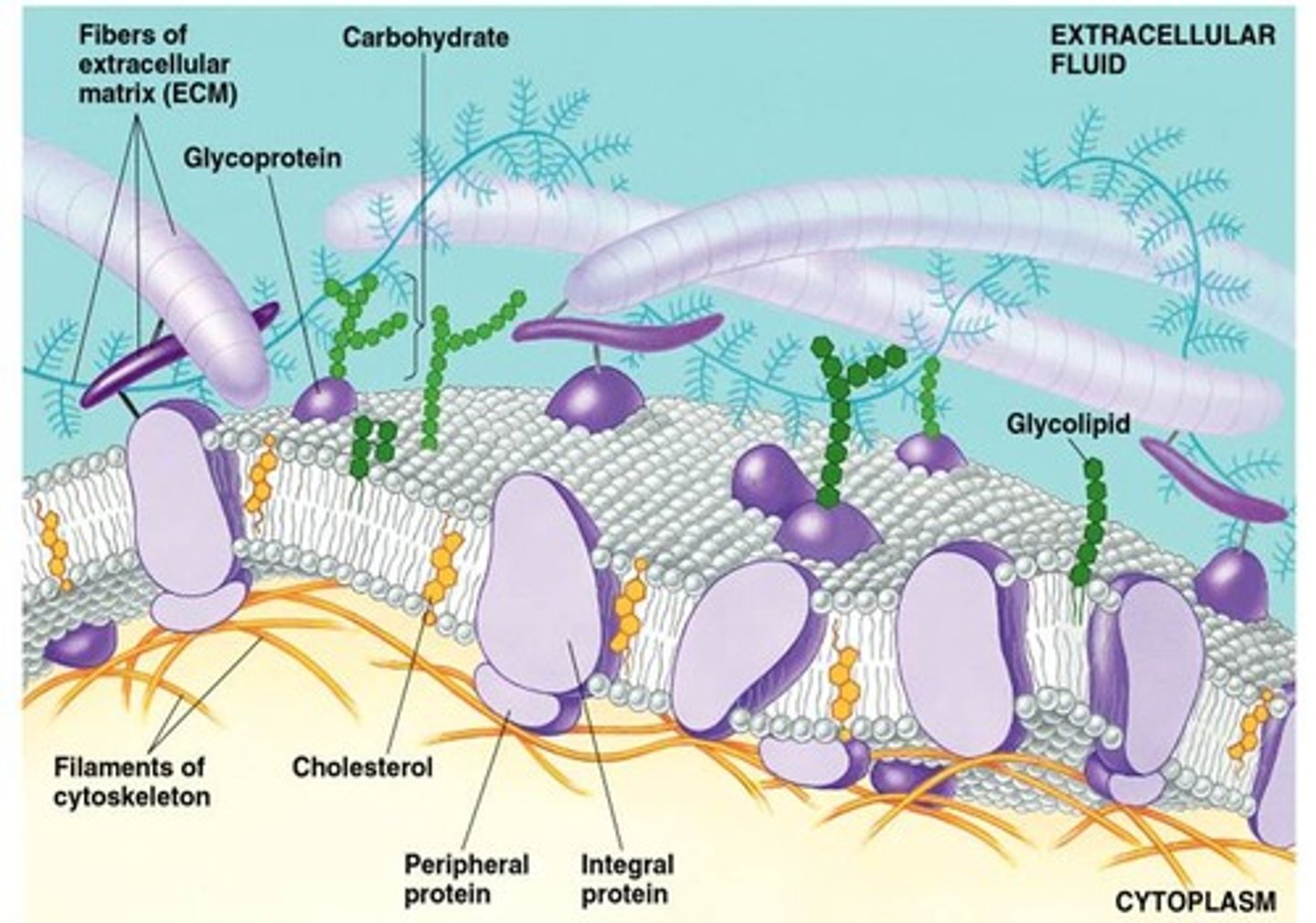
Integral Proteins
Embedded the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
Examples of Hydrophobic Molecules
O2, CO2, N2, benzene, lipids and cholesterol
Example of Small Unchanged Hydrophilic (polar)
Urea, Glycerol H2O
Examples of Large Hydrophilic (Polar) Molecules
Glucose and Sucrose
Examples of Ions
H+, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, Mg2+, HCO3-
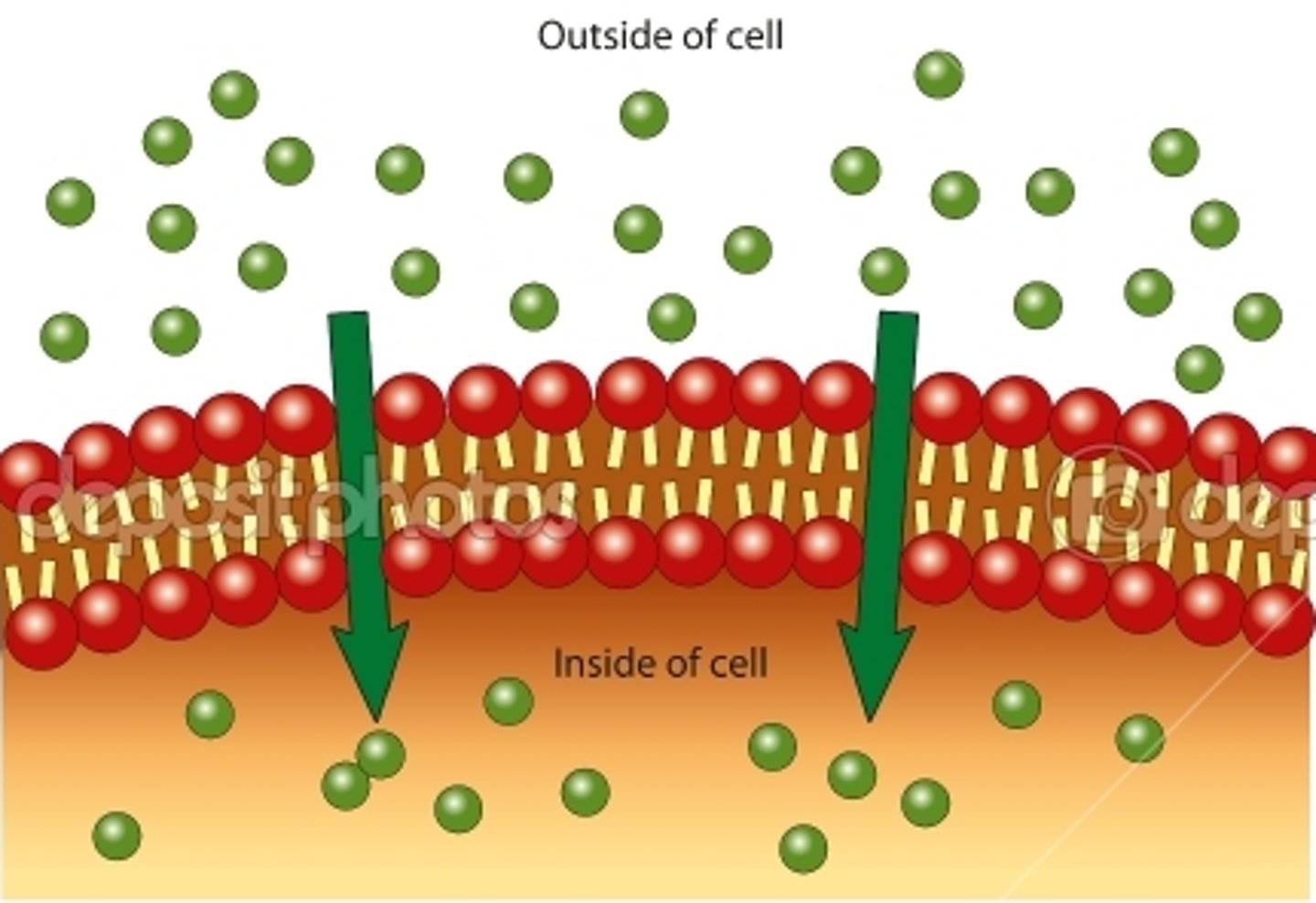
Simple Diffusion
Doesn't require energy, depends on concertation gradient
Direct transport of molecules across the cell membrane
Small uncharged molecules or lipid soluble molecules pass between the phospholipids to enter or leave the cell, moving from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
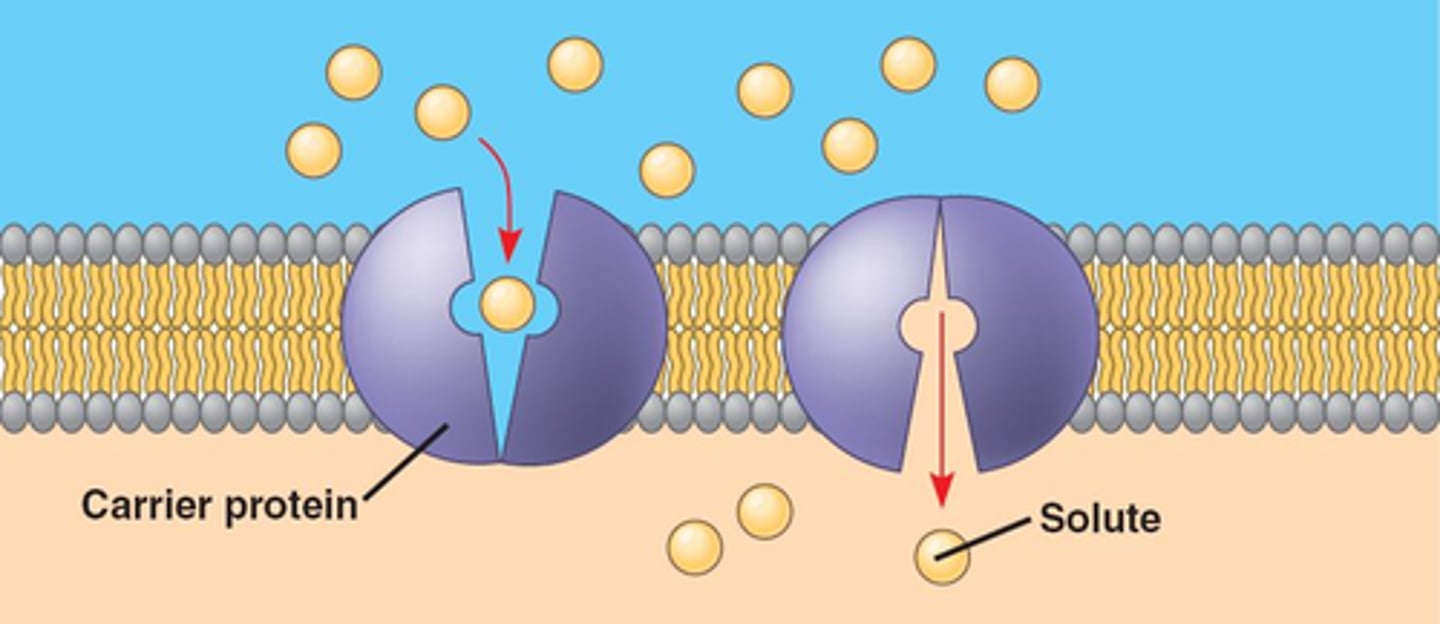
Facilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
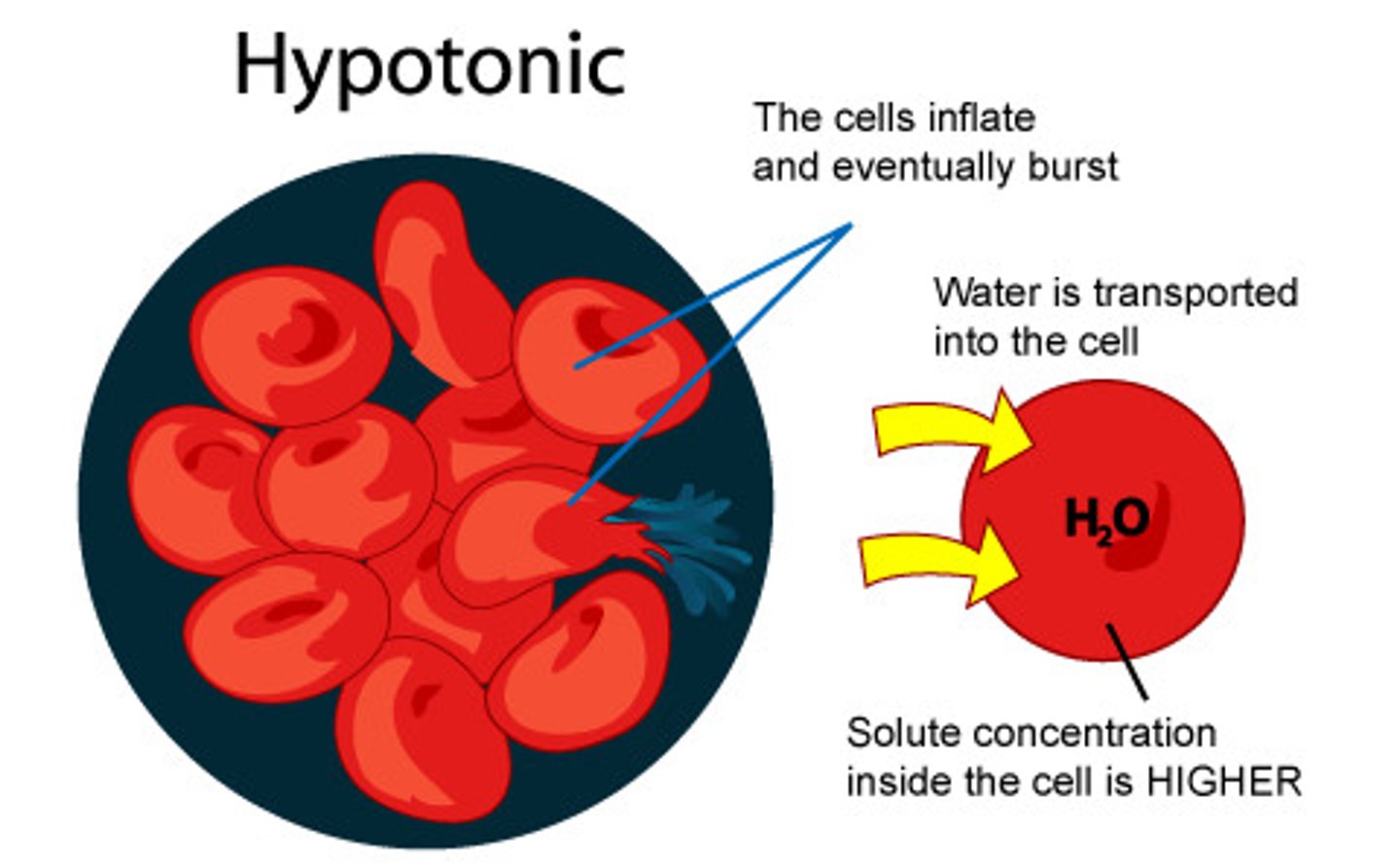
Hypotonic Solution
Cell is in a solution that is less concentrated than it self.
H2O rushes into the cell to neutralize it, cell might burst process called cytolysis OR swell
Isotonic Solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
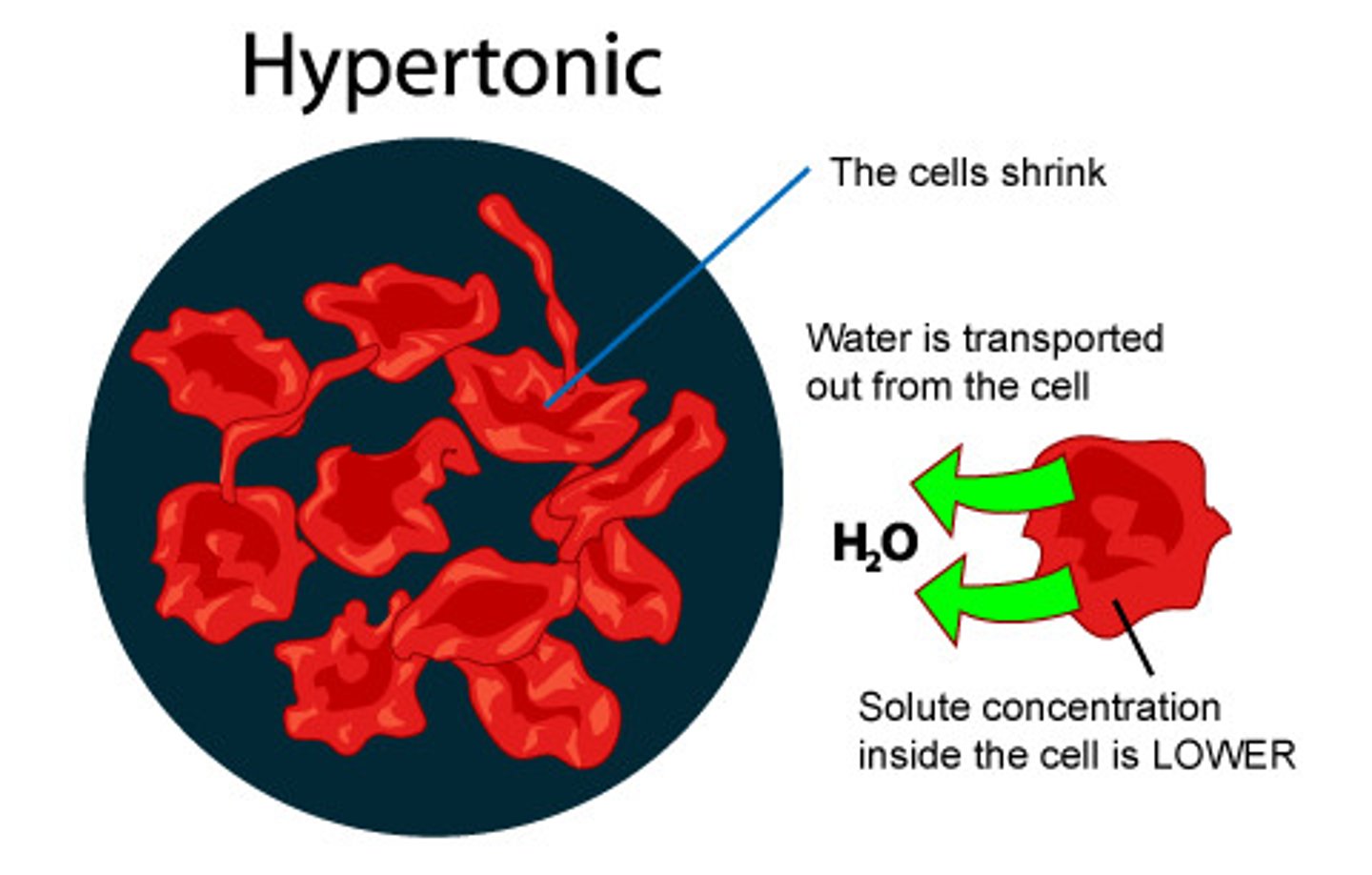
Hypertonic Solution
Cell is in a solution that is more concentrated than it self.
H2O get's out of the cell to neutralize it the outside, resulting cell to shrink
Passive Transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
High to low
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
Low to high
Secondary Active Transport
Form of active transport which does not use ATP as an energy source; rather, transport is coupled to ion diffusion down a concentration gradient established by primary active transport.
We use ATP to create concentration gradient of Na+. Since we used energy to create Na+. We use the energy from this later on to to transport something else like Glucose
Why is it helpful to give Glucose, water and Sodium to someone who is dehydrated? why not just water?
Water alone doesn't get absorbed at a fast enough rate, but with Glucose and sodium they are absorbed together into the cell in the intestines. The concentration of the intestines will be high and now water will rush into the intestines through osmosis.
Solubility of Vitamins
Fat Soluble, Not water Soluble
Vitamin K
Vitamin A
Vitamin D
Vitamin E
Mnemonic: KADE
Vitamin C is not water Soluble, it's found in orange juices
Why is it harmful to drink Salt Water?
Dehydrate you more
Sea water has a high osmatic pressure, causing water to flow out of body cells into the intestines.
Proteins that are used to transport things inside Plasma Membrane
1. Pores
2. Channels
Pores and channels are passive transport
3. Carries - can be Active and Passive Transport
Pores
Holes that allow water to flow through
Can't be open/ closed, They can only be added or remove them
Aquaporins are an examples of pores
Aquaporins
Water channel proteins
Regulated by adding/subtracting the number of pores in membrane.
Example: Add pores if want to make the PM more permeable to water and vice versa.
Channels
Can be opened/ closed
Regulated by
Voltage gated (charge)
Ligand Gated
Mechanically Gated - mostly found in heart
Carries
Change conformation
Can be saturated
Have Enzyme Kinetics - Km and Vmax
Can be inhibited/competitive inhibitors and etc
Can be Active and Passive Transport
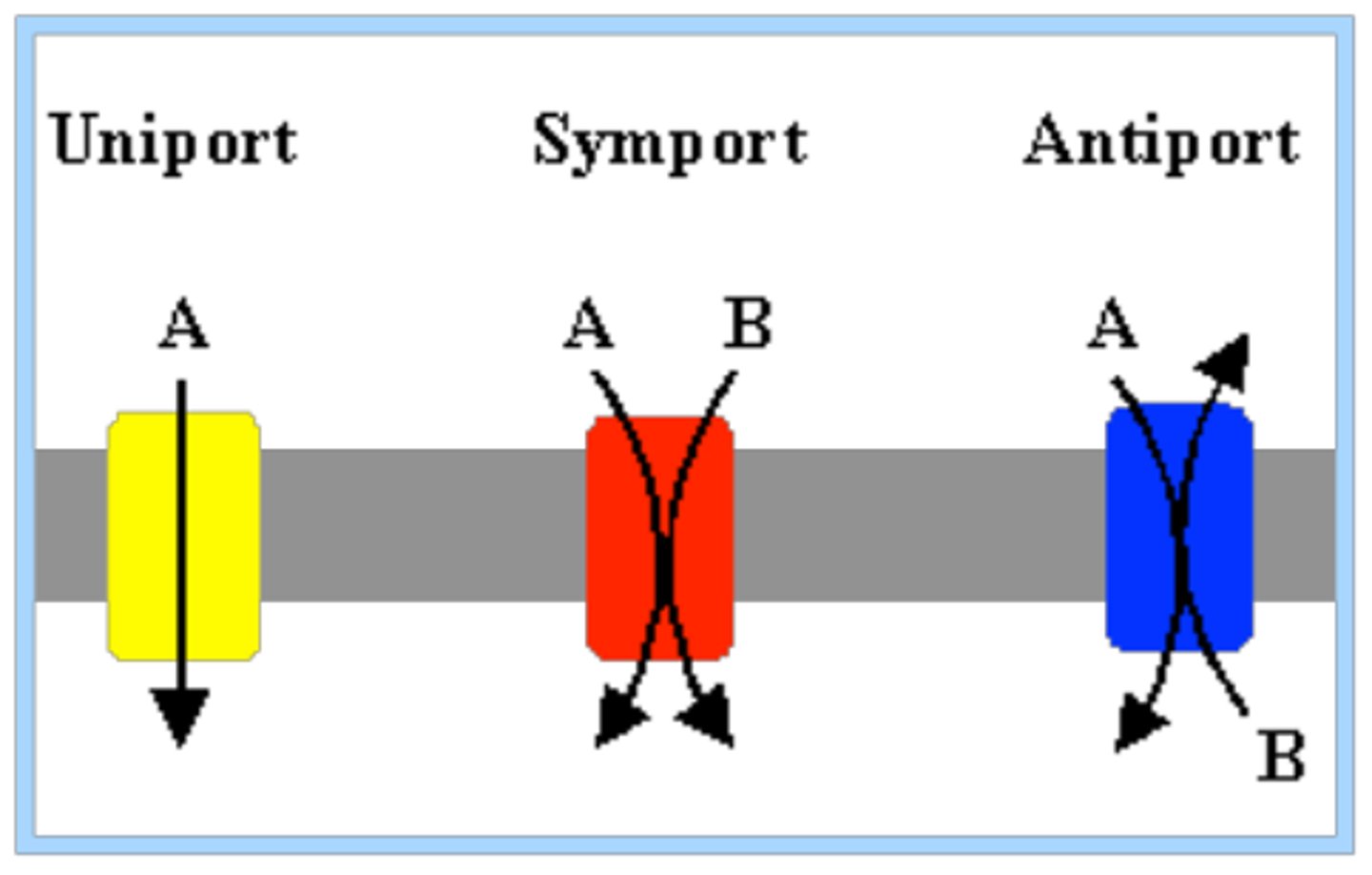
Types of Carries
1. Uniporter
2. Symporter
3. Antiporter
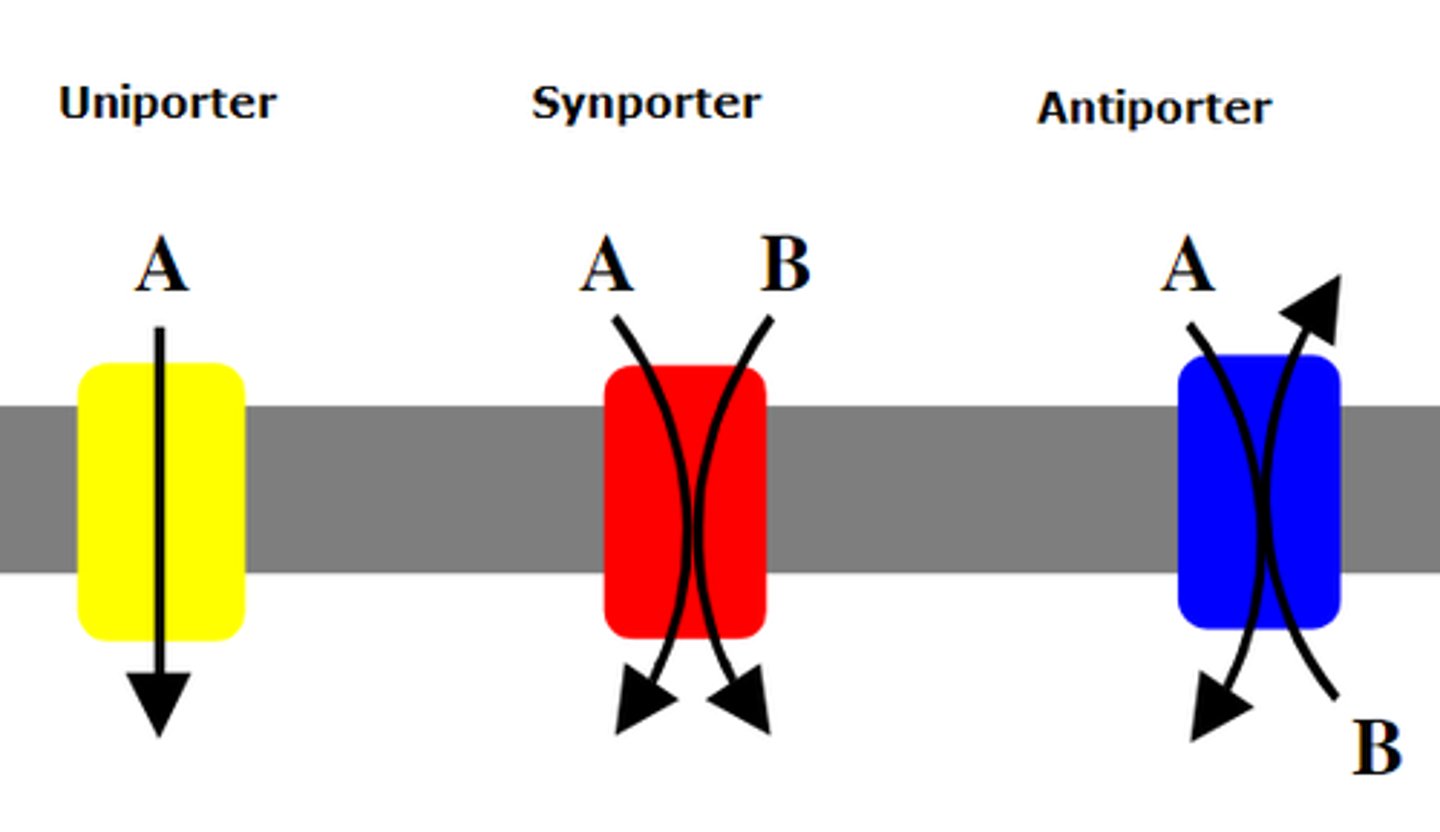
Uniporter
Transport one thing at a time
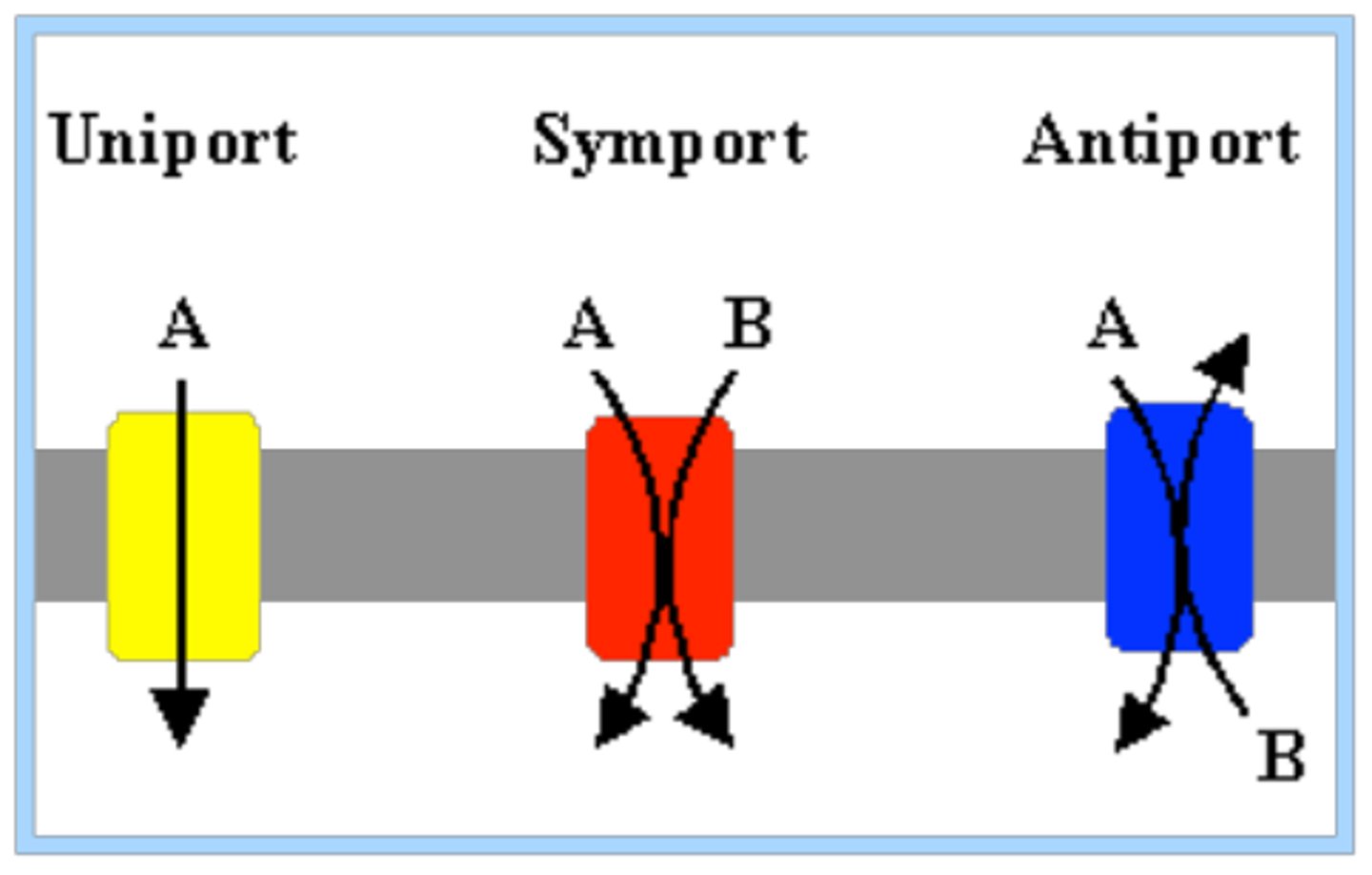
Symporter
Transports two solutes at a time in the same direction
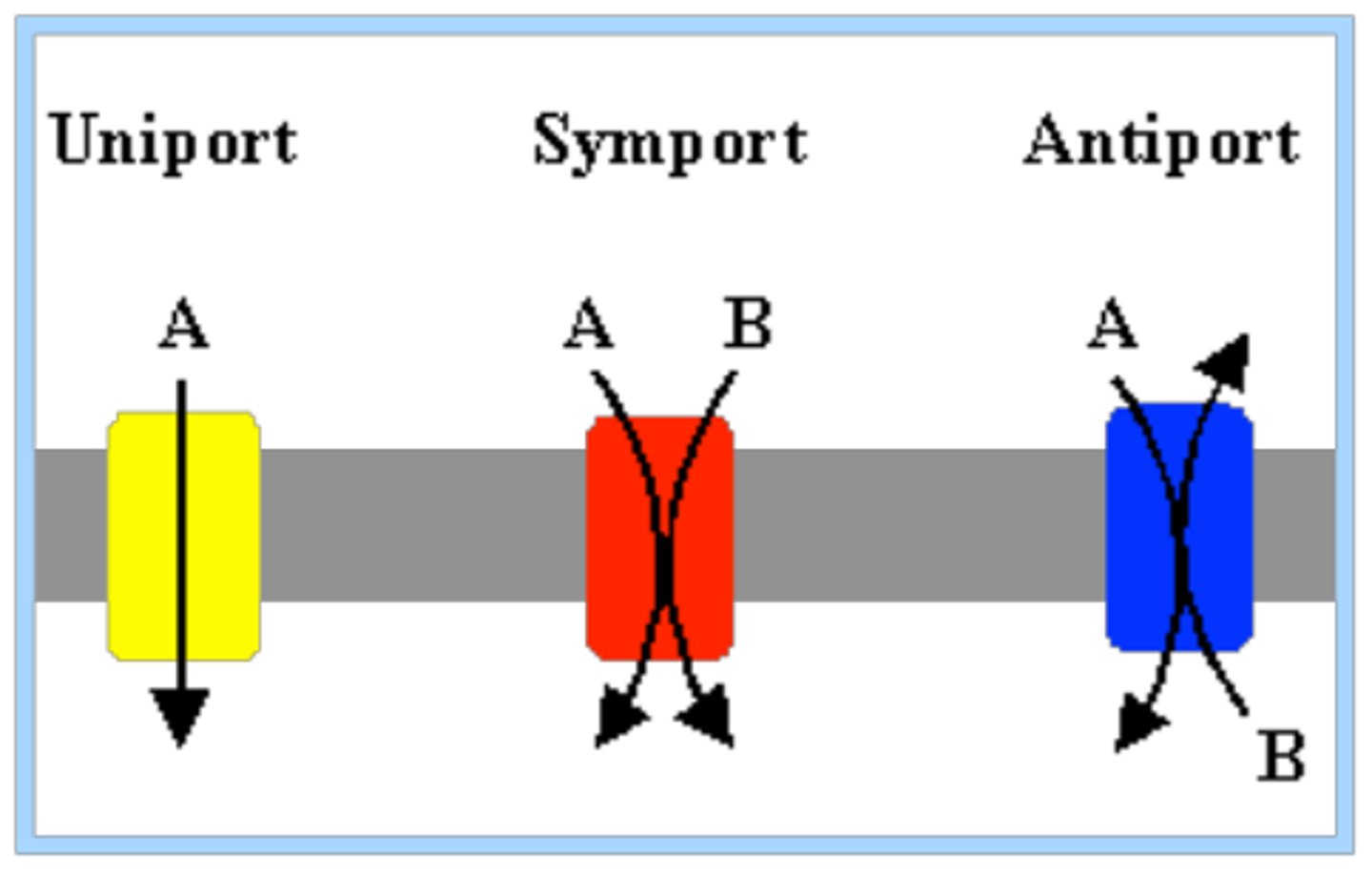
Antiporter
Transports two solutes at a time in the opposite direction. Example: Na+ and K+ ATPase. 2K+ in 3Na+ out. requires energy.
Requires input of energy Uses energy from ATP.
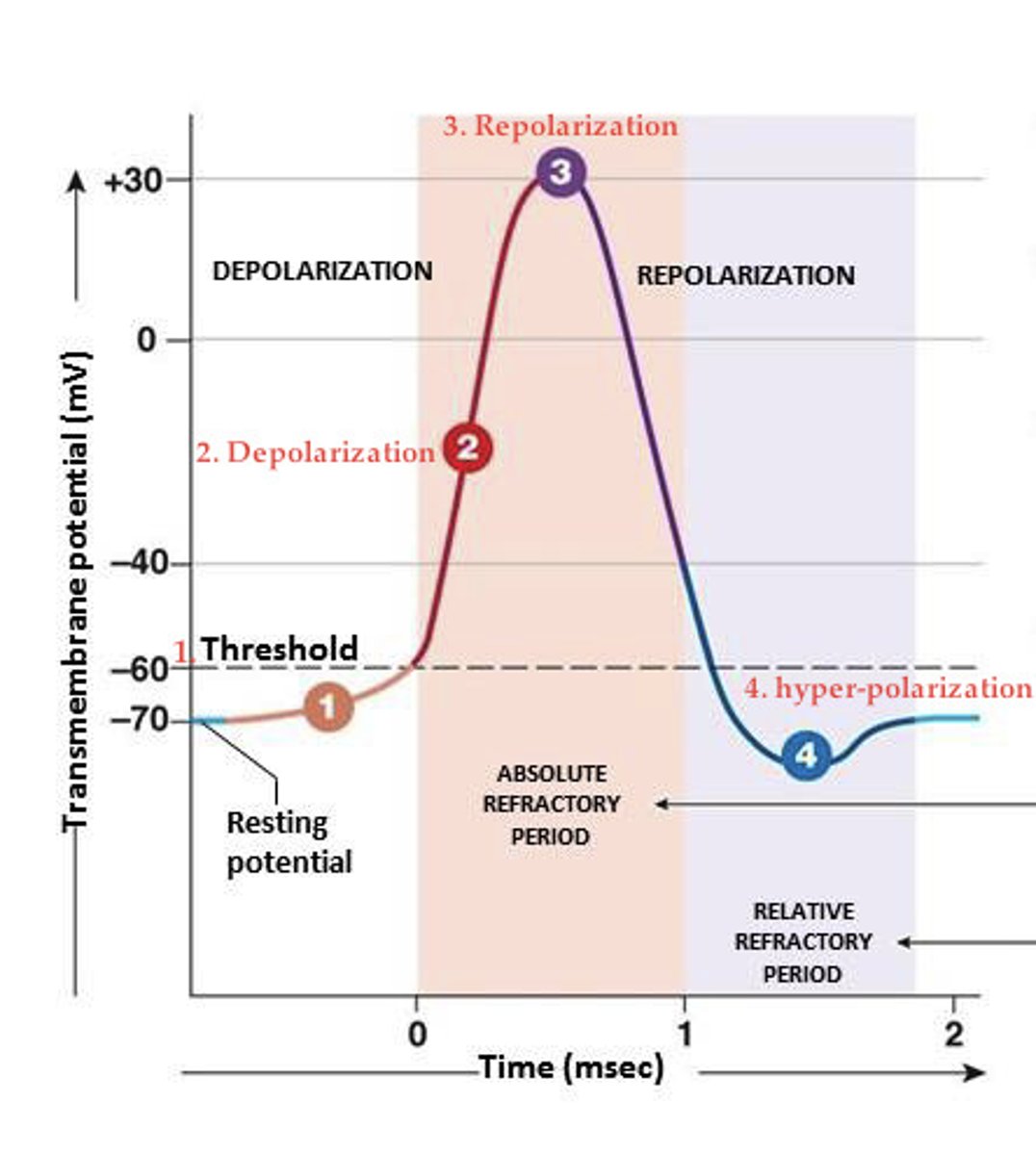
Action Potential
Cell typically hover around -70V
A lot sodium outside and overall charge of the cell is negative
Cells are usually at Resting Potential -70V, it gets a signal. Sodium channels open, more of Sodium Channels open.
Sodium flows into the cell, Na+ channels close and Ka+ opens
Action potential doesn't fire all the time, enough channels must be open in order to fire.
Chloride Channels
Inhibits neuron to fire
Sodium Potassium ATPase
2 K+ In
3 Na+ out
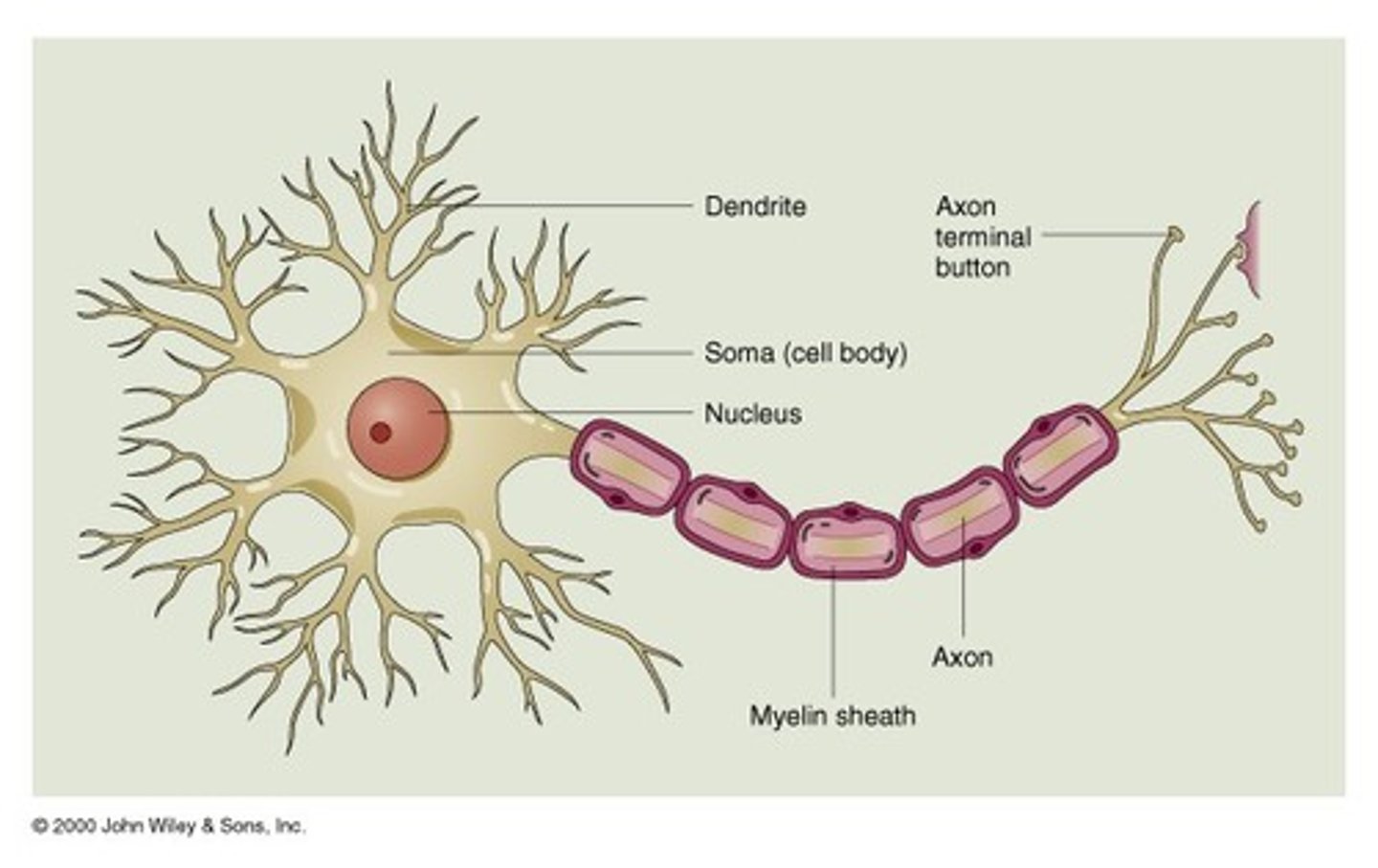
Neuron (Nerve Cell) Structure
Cell Body
Axon
Axon Terminal
Dendrites
Axon Hillock
Myelin sheath
Nodes of Ranvier
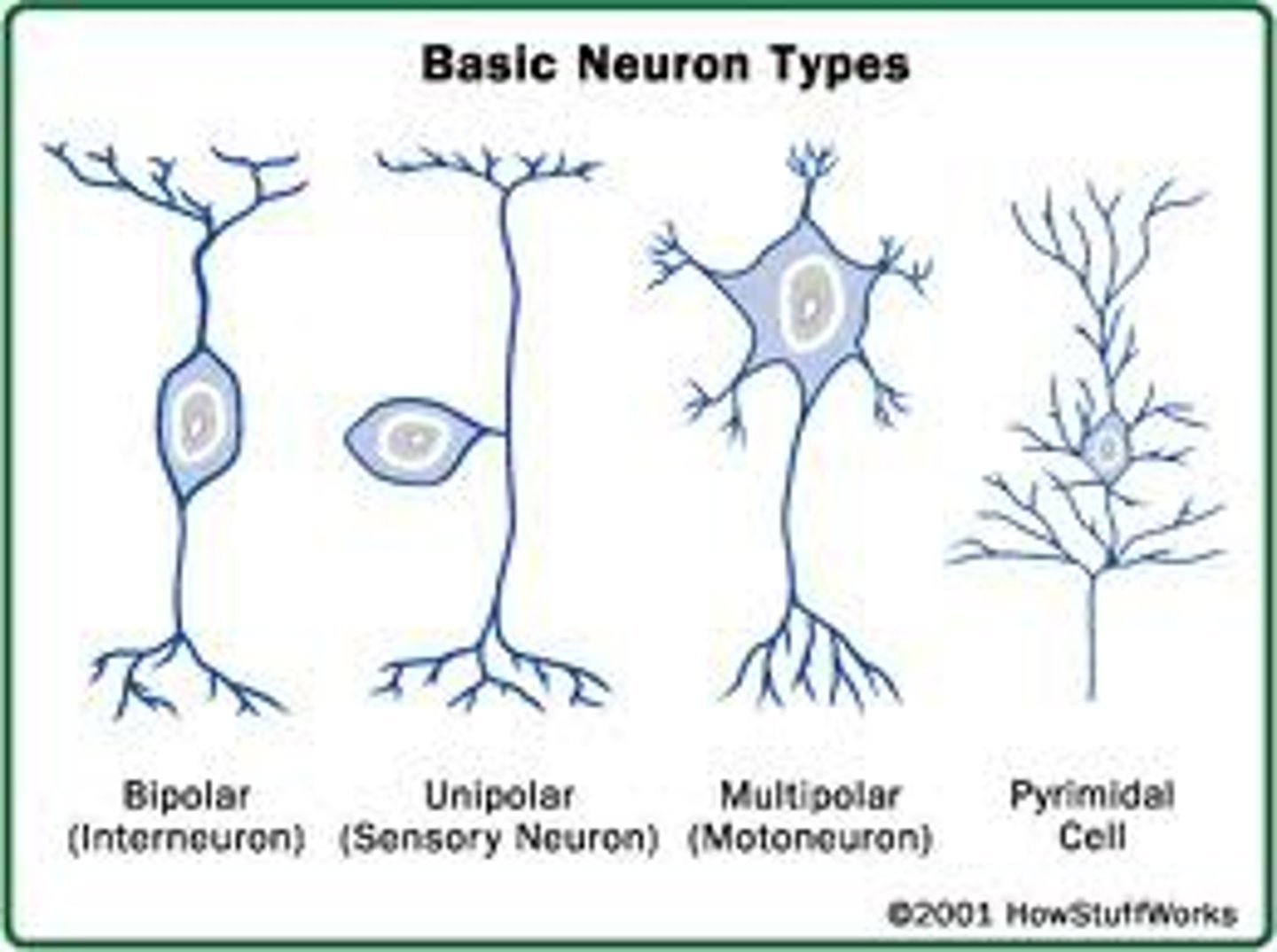
Neuron Types
Multipolar, bipolar, unipolar
At Which part of Neuron are the various excitatory and inhibitory signals summed together.
Axon Hillock
Connections between Neuron
Dendrites - beginning of a Neuron
Axon Terminal is end of old Neuron
Synapses
Dendrites - beginning of a Neuron
Axon Terminal is end of old Neuron
When Dendrites and axon hillock come together it's synapses
Synaptic Cleft
The space between when two Neurons coming together
presynaptic neuron and Post synaptic
Signal Termination
1. Degradation - Degrades neurotransmitter
2. Reuptake - back to presynaptic neuron
3. Diffusion -