Microbiology Exam 2 Flashcards
1/188
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
Endosymbiotic Theory
eukaryotic cell evolved when larger prokaryotic cell engulfed smaller prokaryotic cells.
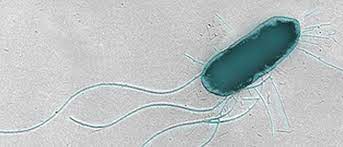
Flagella
-locomotor appendage
-long, cylinder containing microtubules
-covered by an extension of the cell membrane
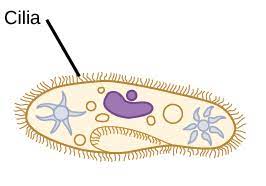
Cilia
-locomotor appendage
-shorter than flagella
- found only in certain protozoa and animal cells
-function: motility, feeding, filtering
Glycocalyx
- outermost boundary that comes in direct contact w/ the environment
-composed of polysaccharides
-functions: adherence, protection, signal reception
Cell Wall
rigid, provides structural support and shape
Cell Membrane
-bilayer of phospholipids and proteins
-serves as a selectively permeable barrier in transport
-functions in interaction and surface adhesion, secretion, and signal transduction
Nucleus
-most prominent organelle of eukaryotic cell
-nuclear envelope composed of two parallel membranes
-contains chromosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
-function: packaging and transport
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
-function: nutrient processing, synthesis, lipid storage
Golgi Apparatus
-”central receiving”
-function: modifies, stores, and packages proteins
-composed of flattened sacs called cisternae
Synthesis and Transport Machine
nucleus → RER → Golgi → vesicles → secretion
Lysosomes
-vesicles containing enzymes that came from the Golgi apparatus
-function: intracellular digestion of food particles, protection against invading microbes
Vacuoles
membrane bound sacs that contain particles for digestion, excretion, or storage
Phagosomes
vacuoles merged with a lysosome
Mitochondria
-function: energy production and storage of ATP
Chloroplasts
-function: convert the energy of sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis
-found in algae and plants
Ribosomes
-function: protein synthesis
-composed of rRNA and proteins
Cytoskeleton
-function: anchoring of organelles, movement of cytoplasm, amoeboid motion, transport, structural support
Fungi
-unicellular or colonial
-heterotrophic
-parasitic fungi = mycoses
-microscopic:
hyphae: long filamentous fungi/molds (vegetative: digest/absorb nutrients; reproductive: produce spores)
yeasts: round ovoid shape, asexual reproduction, have cell wall, lacks locomotor appendages (pseudo hypha: chain of yeasts)
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)
-CA: pneumocystis jiroveci
-Epidemiology: asymptomatic, 30-40% who get it have HIV/AIDS
-Pathogenesis: inhaled spores attach to alveolar walls, they fill with fluid, walls thicken impairing oxygen exchange.
-Symptoms: shortness of breath, slight fever, non-productive cough
-Treatment: trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)
Rose Gardener’s Disease (Sporotrichosis)
-CA: sporothrix schenkii (dimorphic fungi)
-Types:
cutaneous (skin): most common form, occurs on hand/arm after touching plant
pulmonary (lung): rare, inhalation of spores
disseminated (those w/ HIV): infection spreads to another part of the body
-Epidemiology: warmer temp. climates, handlers of thorny plants
-Symptoms: chronic ulcers at site of puncture
-Pathogenesis: spores introduced to wound, pimple develops and enlarges
-Diagnosis: physician obtains swab/biopsy
-Prevention: protective clothing, no vaccine
-Treatment: oral itraconazole (3-6 months); those w/ severity = lipid formulation of amphotericin B, SSKI for cutaneous.
Sporangiospores
formed by successive cleavages called sporangium.
Conidiospores
free spores not enclosed by a sac.
Fungal Identification
-isolation on specific media
-macroscopic and microscopic observation
Roles of Fungi
-adverse:
mycoses, allergies, toxin production
destruction of crops and food storages
-beneficial:
sources of antibiotics, alcohol, organic acids, vitamins
decomposers of dead plants/animals
making food
genetic studies
Valley Fever
-CA: Coccidiodes immitis
-Epidemiology: inhalation of arthrospores, 40% are symptomatic, California/Arizona/S.America,
-Symptoms: resembles TB, coughing, chest pain, fever, weight loss, flu-like, rash
-Pathogenesis: inhalation of spores, tissue damage
-Diagnosis: blood sample, chest x-rays, CT scans, tissue biopsy
-Treatment: clears up on own, oral azoles: ketoconazole (FDA approved), fluconazole (meningitis), IV amphotericin B
Algae
-eukaryotic
-protist
-unicellular, colonial, filamentous
-cell wall
-may or may not have flagella
-photosynthesize w/ chlorophyll
Protozoa
-eukaryotic
-protist
-unicellular
-lack a cell wall
-free living
-heterotrophic
-lack tissues
Algae
-free living
-function: provide basis of food in aquatic habitats, produce oxygen
Protozoa
-have locomotor appendages (flagella, cilia, pseudopods)
-trophozoite: motile feeding stage
-asexual reproduction + sexual reproduction
Giardiasis
-CA: Giardia lamblia
-Facts: lack mitochondria +peroxisomes, has ER, Golgi, cytoskeleton, and flagella, seen by Leeuwenhoek
-Epidemiology: fecal/oral transmission, ingestion of cysts from contaminated water, more prevalent in kids, most frequently diagnosed intestinal parasitic disease in the US.
-Pathogenesis: cysts emerge as trophozoites in colon, attach to bowel, feeds on mucus and reproduce.
-Symptoms: 40% show lactose intolerance, frothy diarrhea, dehydration, weight loss, vitamin deficiencies.
-Treatment: Flagyl (metronidazole), tinidazole, nitazoxanide
-Prevention: boil water, filter water
Malaria
-CA: Plasmodium falciparum
-Epidemiology: “world’s greatest health problem,” 40% are @risk
-Pathogenesis: vector carried (anopheles sp. mosquito), mosquito bites infected person→ picks up gametes → sexual reproduction → bites non-infected person
-Symptoms: flu-like, anemia, jaundice
-Treatment: chloroquinone
Trypanosomes
-pathogenic protozoa
-long, crescent-shaped cell w/ single flagellum
-occur in blood during infection
-transmitted by vectors
Ex:
T. brucei = african sleeping sickness
T. cruzi = chagas disease
Entamoeba
-infective amoeba
-Entamoeba histolytica - amebic dysentery
Symptoms: gastrointestinal disturbances
Parasitic Helminths
-parasitize host tissues
-have mouths for attachment
-have well developed sex organs
Flatworms
Roundworms
Robert Koch
-identified pathogens
Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch
-filterable agent cause of certain diseases
Viruses
-obligate intracellular parasites
-need a host
-ultramicroscopic
-do not independently fulfill characteristics of life
-structure: capsid surrounding nucleic acid core
-Genome is either dna OR rna
-lack enzymes and machinery for protein synthesis
Viral Structure
-no resemblance to cells
-capsid
-envelope (not in all viruses)
-nucleic acid molecule (DNA or RNA)
-matrix proteins
-crystalline appearance
Capsids
- all viruses have capsids
Helical - helix, rod-shaped
Icosahedral - 3D, symmetrical polygon w/ 20 sides (dice), may/may not have envelope
Rotavirus
Norovirus
Envelope
-mostly in animal viruses
-spikes: exposed proteins essential for attachment of virus to host cell
-protects the nucleic acid
-dissolves in alcohol
Poxviruses
-atypical virus
-lack capsid and are covered by lipoproteins and fibrils.
-have bacteriophages
Virus Nucleic Acids
-DNA or RNA, never both
-carries genes necessary to invade host cell
-make new viruses
DNA- ds, ss
RNA- ss, ds
ssRNA ready for translation: postive-sense
ssRNA needing conversion: negative-sense
Enzymes for Viral Replication
-polymerases: synthesize DNA or RNA
-replicases: copy RNA
-reverse transcriptcase: synthesis of DNA from RNA
Influenza
-CA: Influenza A and B
-Facts: enveloped polymers of hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA), mutations: antigenic drift [strain in geo. area)/shift [different strain, same host])
-Symptoms: flu-like
-Pathogenesis: kills epithelial cells, HA binds to host cell, NA hydrolisizes mucus releasing new virions
-Epidemiology: adults shed flu virus from the day before symptoms begin, occur during fall/winter months
-Treatment: Tamiflu, Relenza
-Prevention: nasal mist, intramuscular injection
Naming of Viruses
-type
-microscopic appearance
-anatomical/geographic area
-effects on host
-acronyms blending several characteristics
Adsorption
binding of virus to specific molecules on the host cell.
Penetration
genome enters the host cell
Uncoating
the viral nucleic acid is released from the capsid
Synthesis
viral components are produced
Assembly
new viral particles are constructed
Release
assembled viruses are released by budding (exocytosis) or cell lysis
Rabies
-CA: Rabies virus
-Facts: rod-shaped, negative sense linear RNA genome, zoonotic, exposure through bite from rabid animal
-Pathogenesis: virus → bite → neurons → nervous system to brain → rapid replication → salivary glands
-Symptoms: flu-like, weakness, cerebral dysfunction, anxiety, confusion, agitation, delirium, hallucinations
-Prevention: vaccination of pets/people
Fusion
viral envelope fuses directly with host membrane by lipid rearrangement
Endocytosis
entire virus is engulfed in a vacuole.
Where is DNA generally replicated and assembled?
the nucleus
Where is RNA generally replicated and assembled?
the cytoplasm
Cytopathic effects
cell damage altering microscopic appearance
Persistent Infections
-cell harbors the virus and is not lysed.
herpes simplex virus
herpes zoster virus
Oncogenic
- animal virus enters host cell and permanently alters its genetic material resulting in cancer
papillomavirus - cervical cancer
Epstein-Barr virus - Burkitt’s lymphoma
Bacteriophages
-bacterial viruses (phages)
Steps in Phage Replication
1. Adsorption – binding of virus to specific molecules on
host cell
2. Penetration – genome enters host cell
3. Replication – viral components are produced
4. Assembly – viral components are assembled
5. Maturation – completion of viral formation
6. Lysis & Release
Lytic Cycle
completion of viral infection through lysis and release of virions
Lysogeny
-spread of the virus without killing the host cell
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
vibrio cholerae
clostridium botulinum
Goals of viral cultivation
isolate and identify viruses in clinical specimens
prepare viruses for vaccines
allow for research on structure and effects
In Vitro
test tubes
cell (tissue) cultures
In Vivo
alive
bird embryos
live animal inoculation
Prions
-misfolded proteins, contain no nucleic acid
-resistant to sterilization
-causes transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
-common in animals
Creutzfeldt Jakob Syndrome
Microbial Nutrition
process by which chemical compounds are acquired from the environment to sustain life.
Bioelements
basic requirements of life
What are some examples of bioelements?
-carbon
-hydrogen
-oxygen
-phosphorus
-nitrogen
-sodium
-magnesium
Essential nutrients
substance an organism must get from a source outside its cells
Macronutrients
-required for large amounts (macro)
-plays a role in cell structure and metabolism
ex: proteins, carbohydrates
Micronutrients
-required for small amounts (micro)
-involved in enzyme function and protein structure maintenance
ex: manganese, zinc, nickel
What is an example of organic nutrients?
(must contain carbon and hydrogen atoms)
-methane
-carbohydrates
-lipids
-proteins
-nucleic acids
What is an example of inorganic nutrients?
(combo of atoms that are NOT carbon and hydrogen)
-magnesium sulfate
-sodium phosphate
-O2
-CO2
-H2O
What are the six compounds found in organic compounds?
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
phosphorus
sulfur
nitrogen
Which macromolecule is most prevalent in the cell?
proteins
Heterotrophs
must obtain carbon in an organic form made from other living organisms
Autotrophs
organism uses CO2 as its carbon source
Why can’t organic compounds be synthesized by an organism?
they lack the genetic and metabolic mechanisms to synthesize them.
Chemotroph
gain energy from chemical compounds
Phototrophs
gain energy through photosynthesis
Photoautotrophs
1.oxygenic photosynthesis
-produces O2
-chlorophyll is the primary pigment
ex: plants, algae, cyanobacteria
2.anoxygenic photosynthesis
-production of sulfur
-bacteriochlorophyll is the pigment
ex: purple/green sulfur bacteria
Chemoautotrophs (lithoautotrophs)
survive only on inorganic substances
ex: Venenvibrio
What chemoautotroph produces methane gas under anaerobic conditions?
methanogens
ex: Methanocaidococcus jannaschii
Saprobes
-heterotroph
-free living microorganisms that feed on organic detritus from dead organisms
ex: opportunistic pathogens, facultative parasites
Symbionts
-heterotroph
-obtains nutrients from living or nonliving source
ex: obligate parasites
Passive Transport
-doesn’t require energy
-higher concentration → lower concentration
diffusion
osmosis - diffusion of H2O
facilitated diffusion - solutes requiring a carrier
Active Transport
-requires energy and carrier proteins
-gradient independent
carrier-mediated active transport
group translocation
bulk transport - endo/exo/pino cytosis
Isotonic Solution
water concentration is equal inside and outside the cell
Hypotonic
net diffusion of water into the cell
Hypertonic
-water diffuses out of the cell
-shrinkage if the cell membrane (plasmolysis)
What does it mean for carriers proteins to exhibit specificity?
they bind and transport only a single type of molecule
What does it mean for facilitated diffusion to exhibit saturation?
the rate if transport limited by the number of binding sites on transport proteins
Carrier-Mediated Active Transport
1.membrane-bound transport proteins interact w/ solute-binding proteins
2.ATP is activated and generates energy to pump solute into the cell.
Endocytosis
bringing substances into the cell through a vesicle/phagosome
Phagocytosis
ingests substances or cells (pseudopods)
Pinocytosis
ingests fluids and/or dissolved substances (microvilli)