AP Bio Unit 6 - Gene expression and regulation
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Macromolecule
Large molecules that build cells

Monomer
A single unit
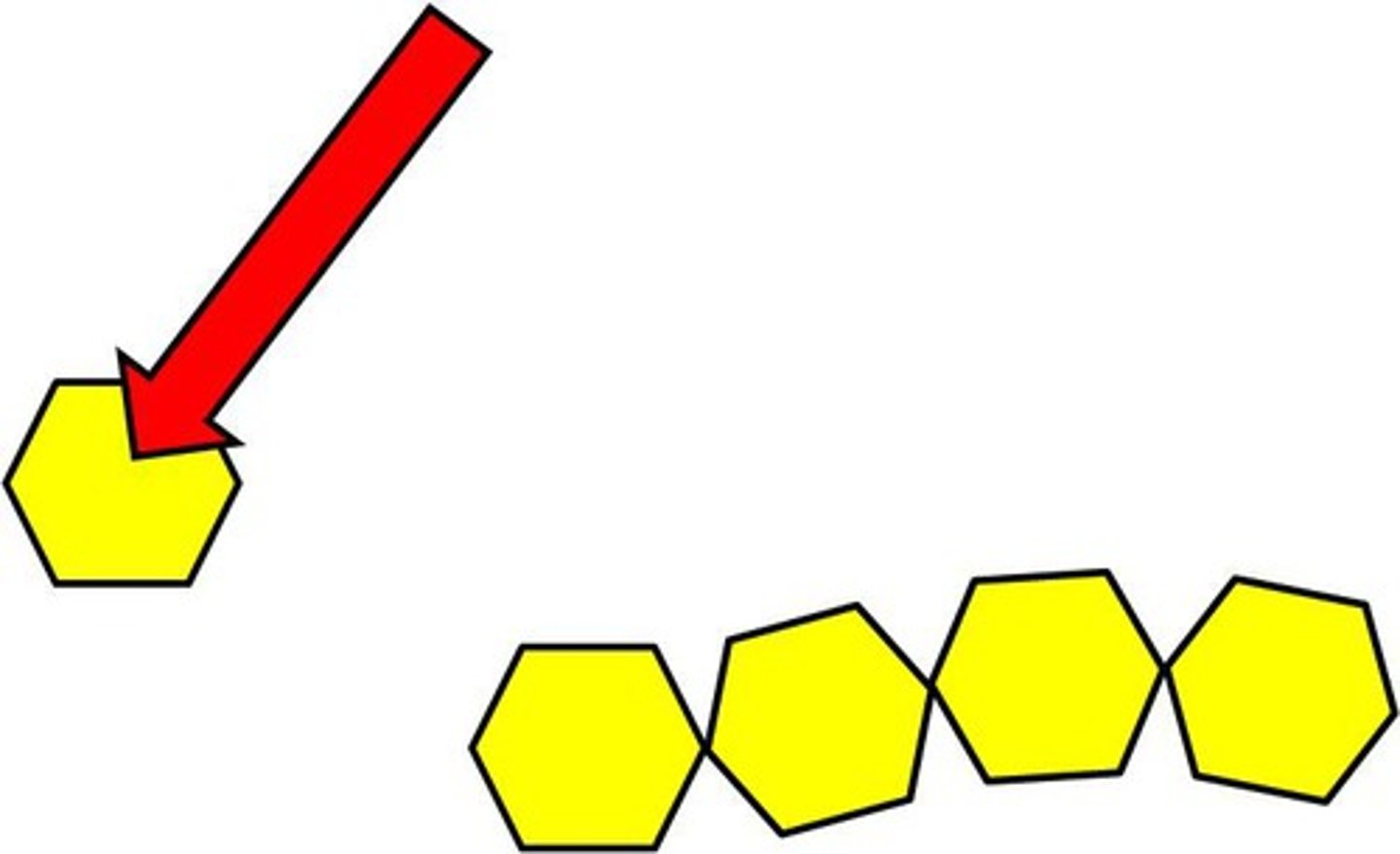
Polymer
Many units (monomers) joined together by covalent bonds
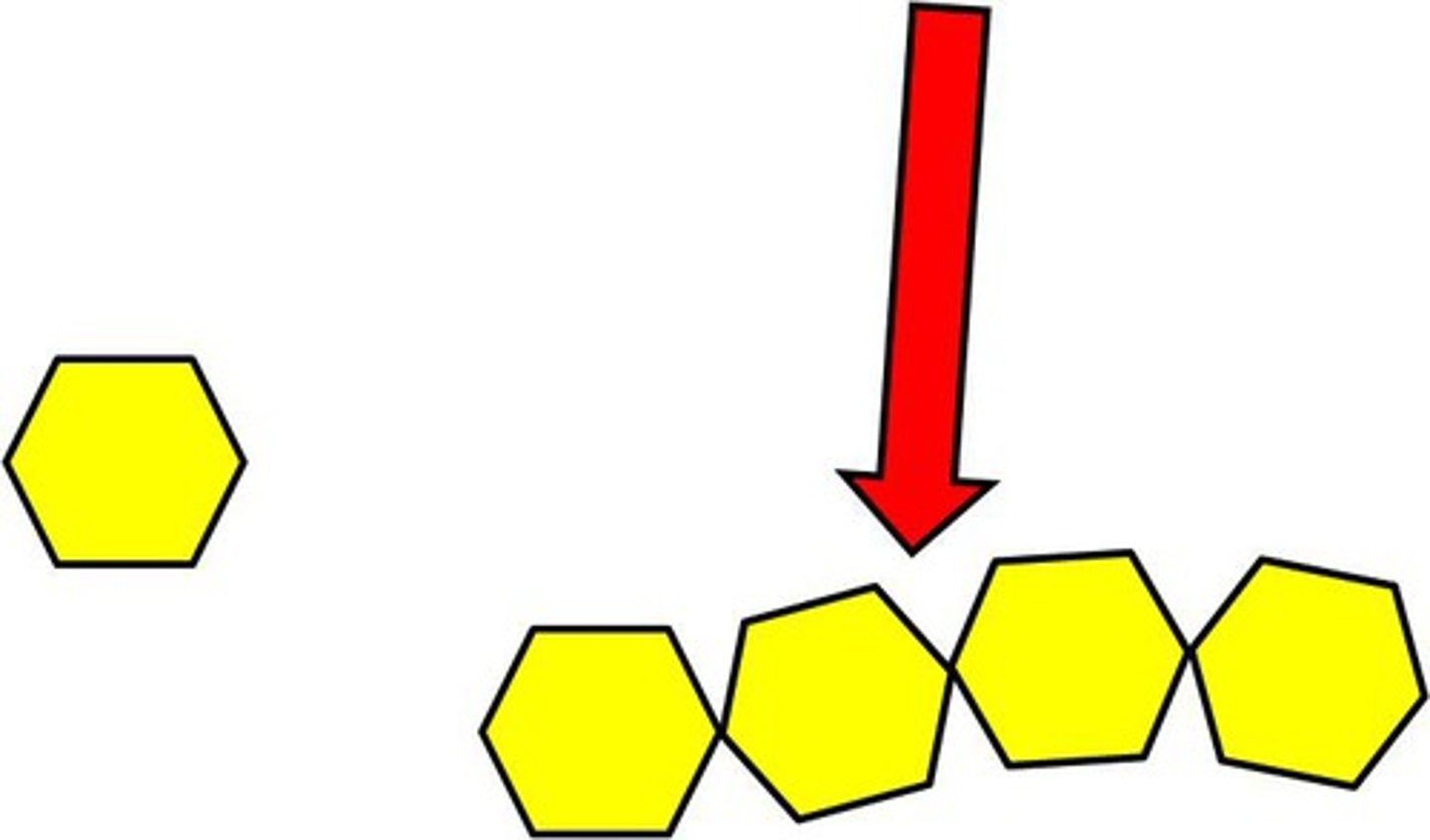
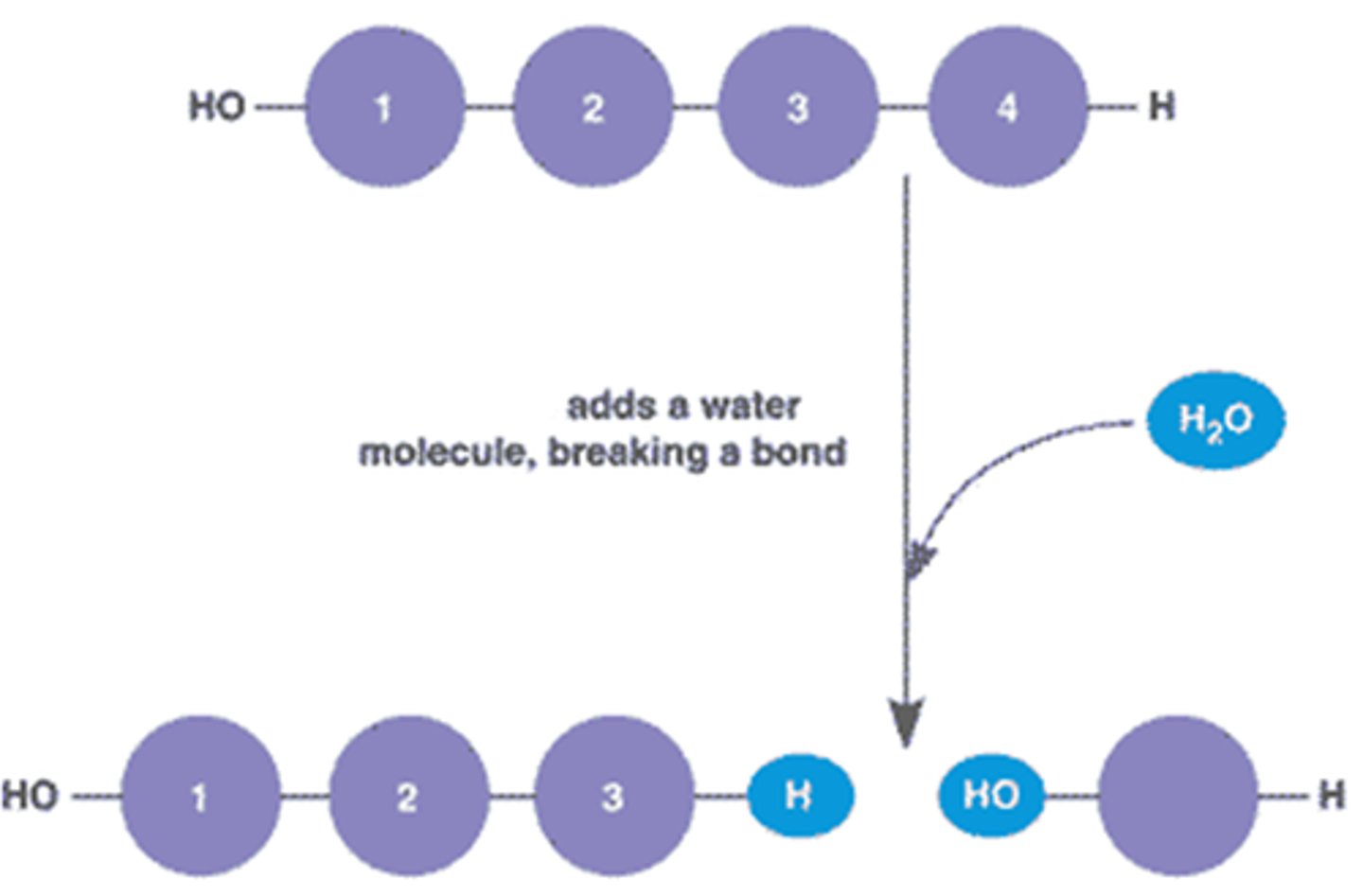
Dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction that makes polymers (water is also produced as a byproduct)
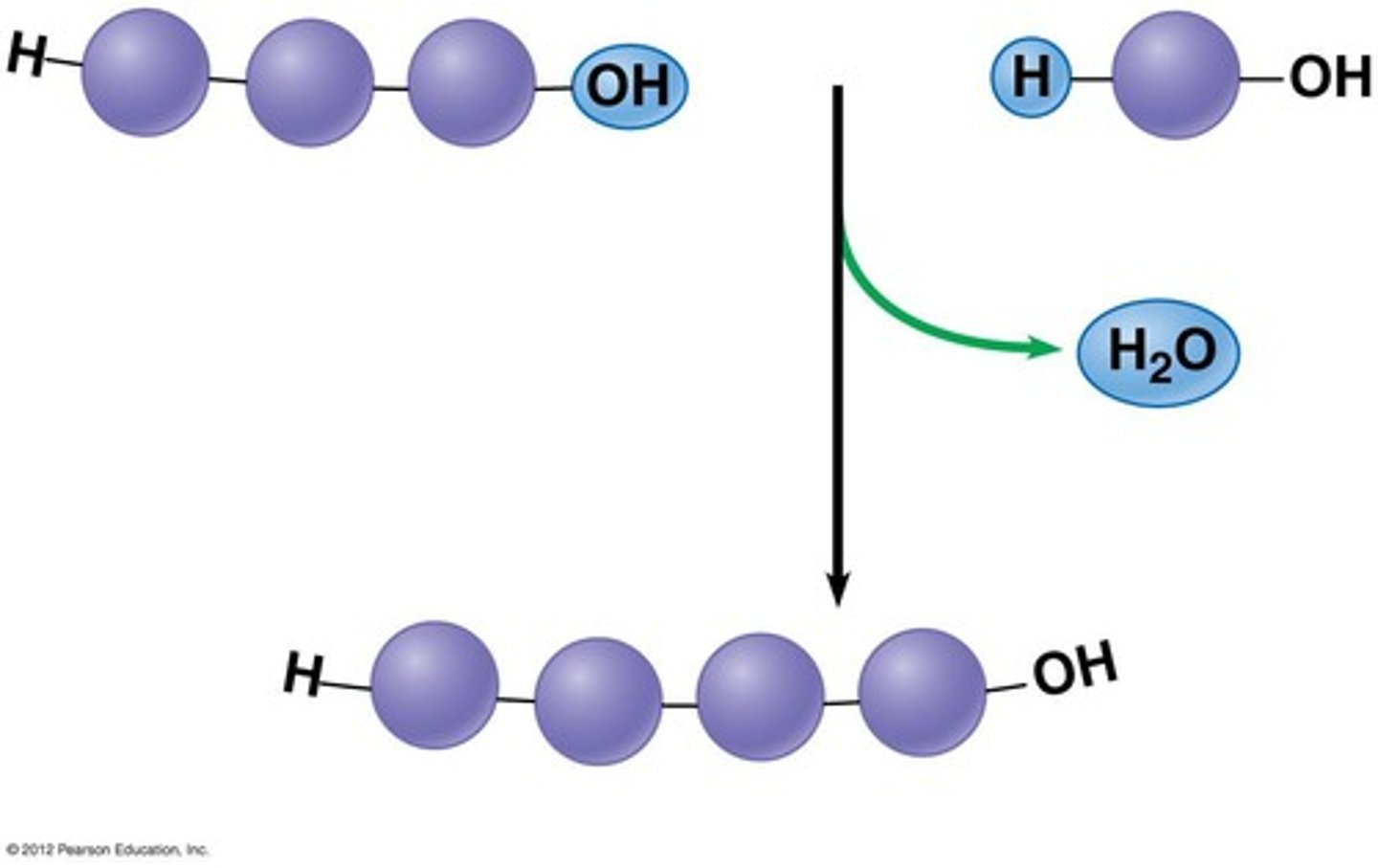
Condensation
A chemical reaction that makes polymers (water is also produced as a byproduct)
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction that breaks polymers into monomers
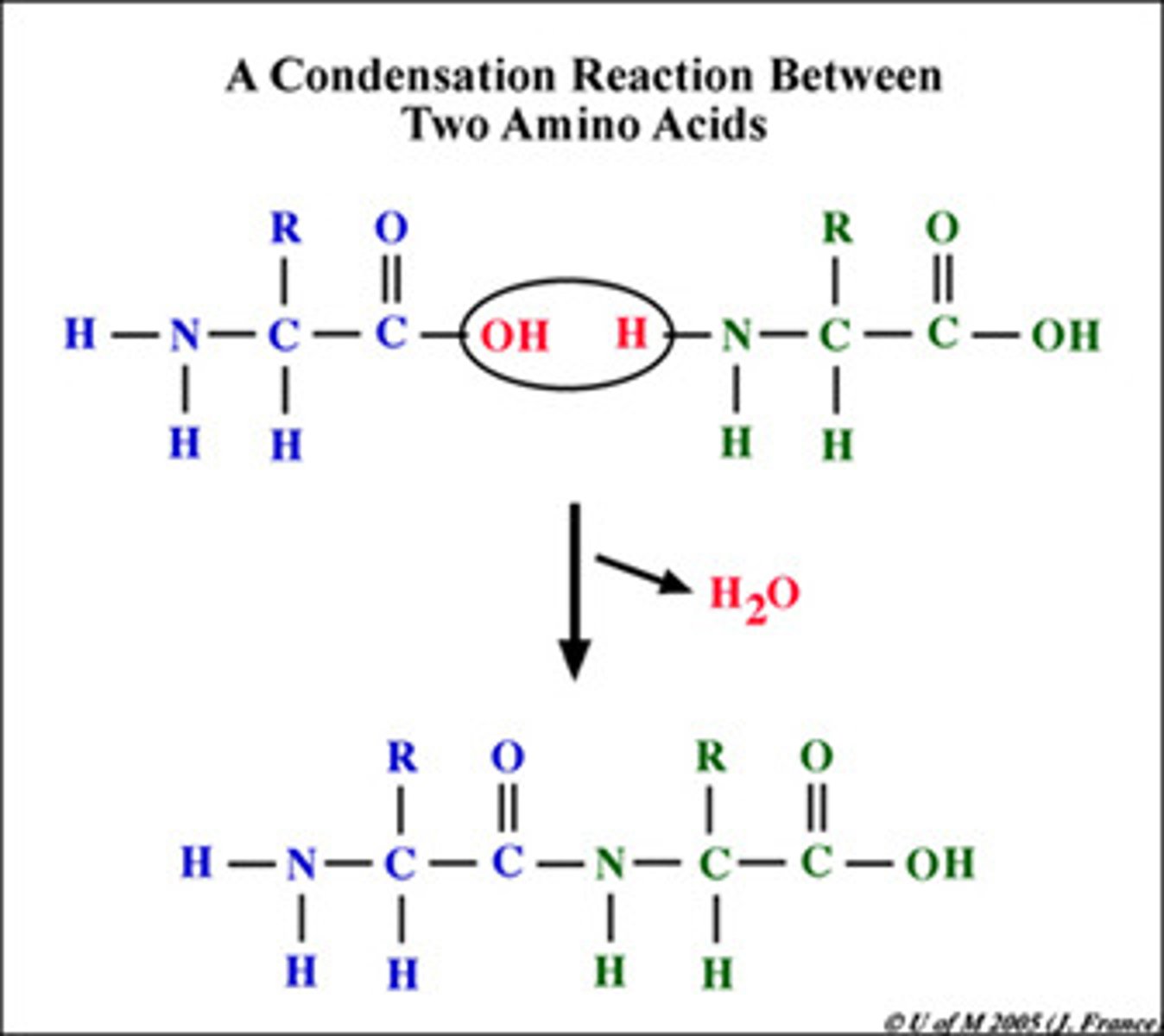
Amino acid
Monomer of proteins
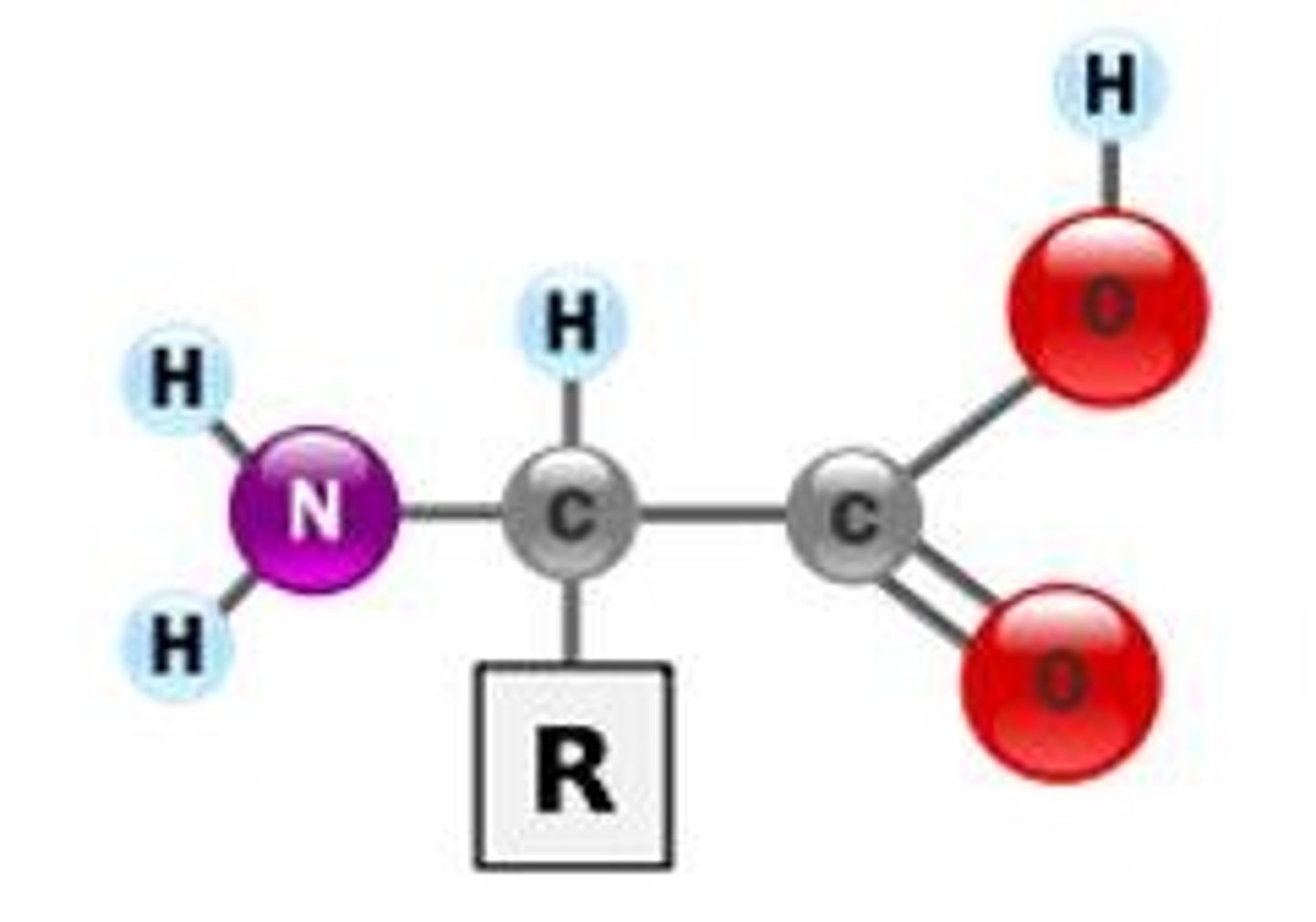
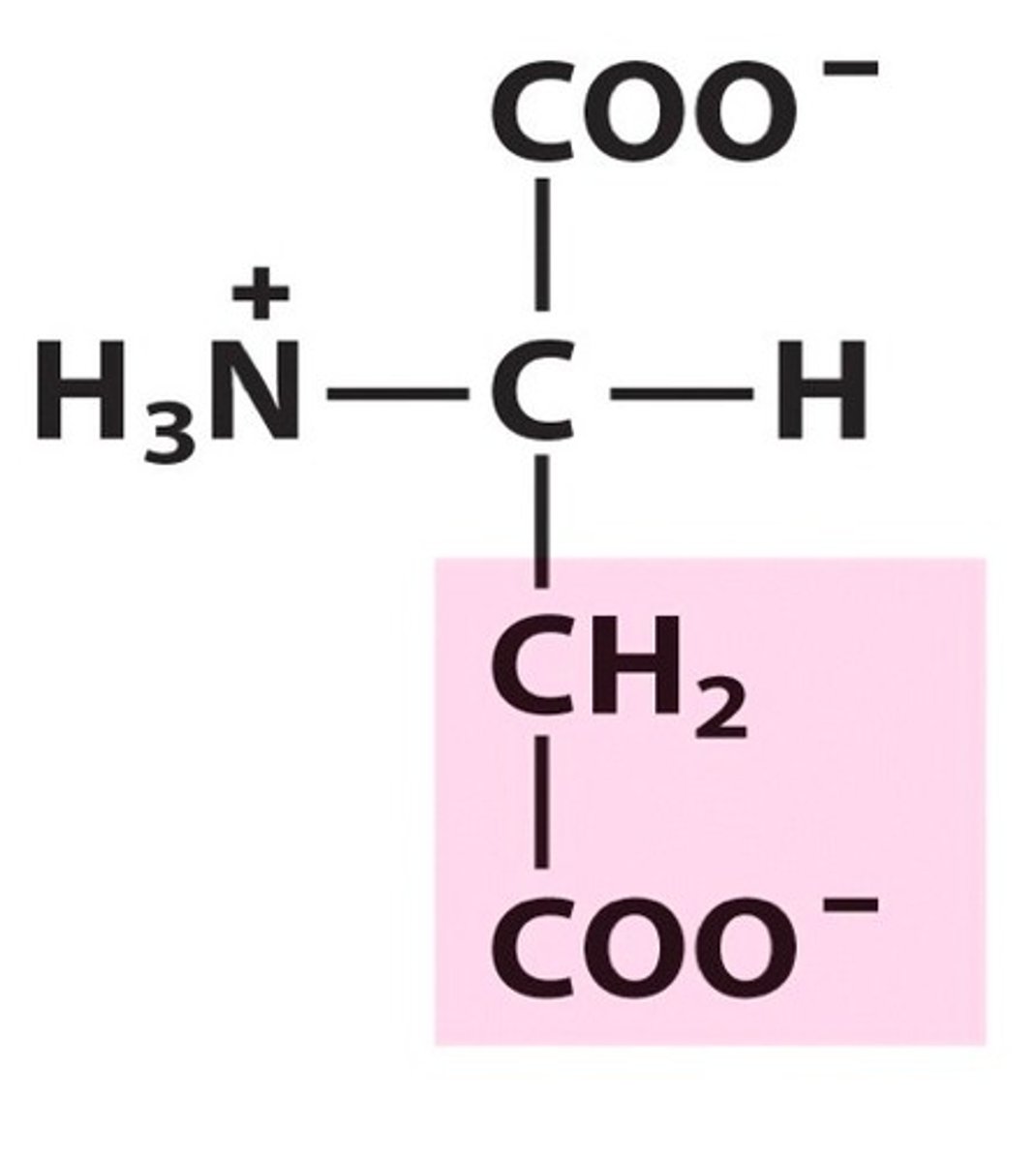
R-group
The part of an amino acid that is different. and gives each amimo acid its unique chemical properties.
Polypeptide
Polymer of proteins (made of many amino acids)
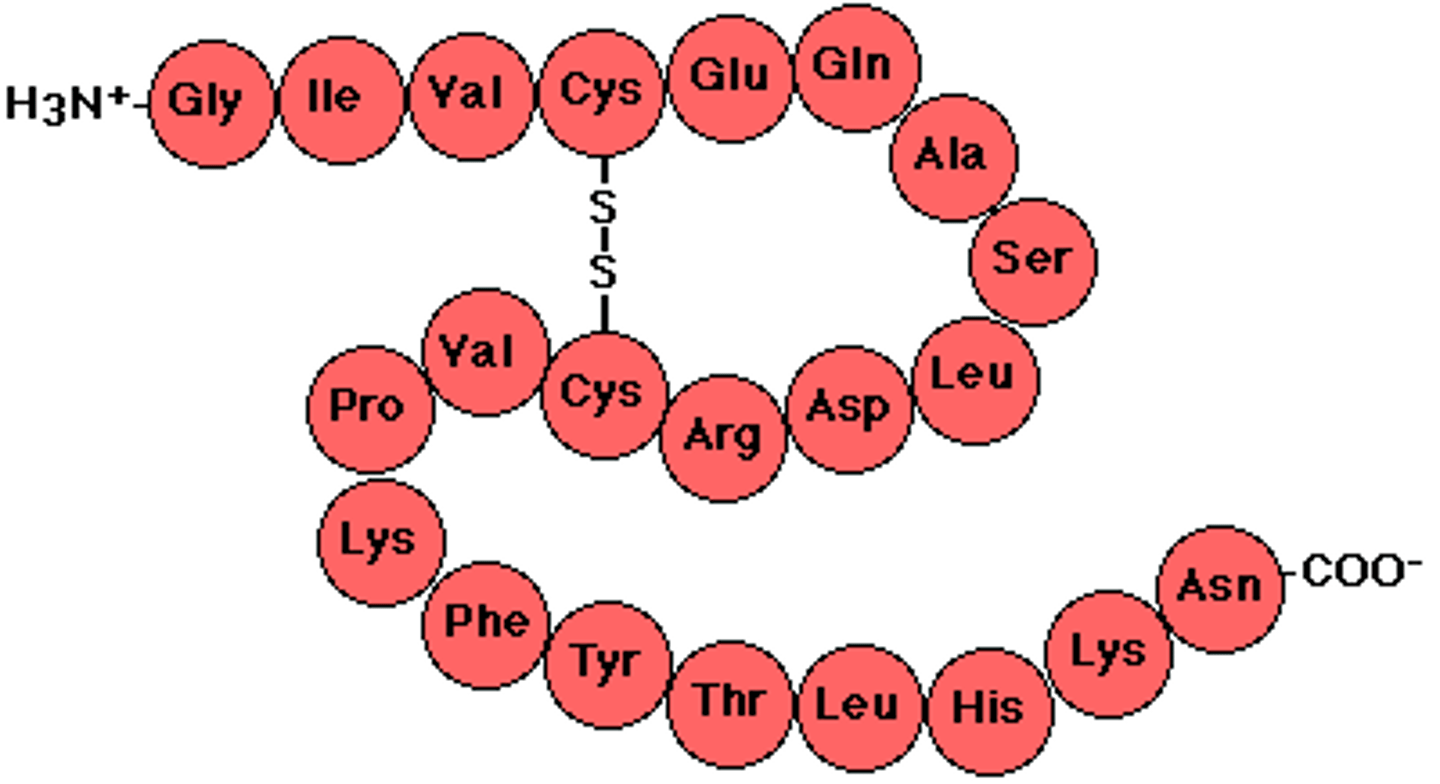
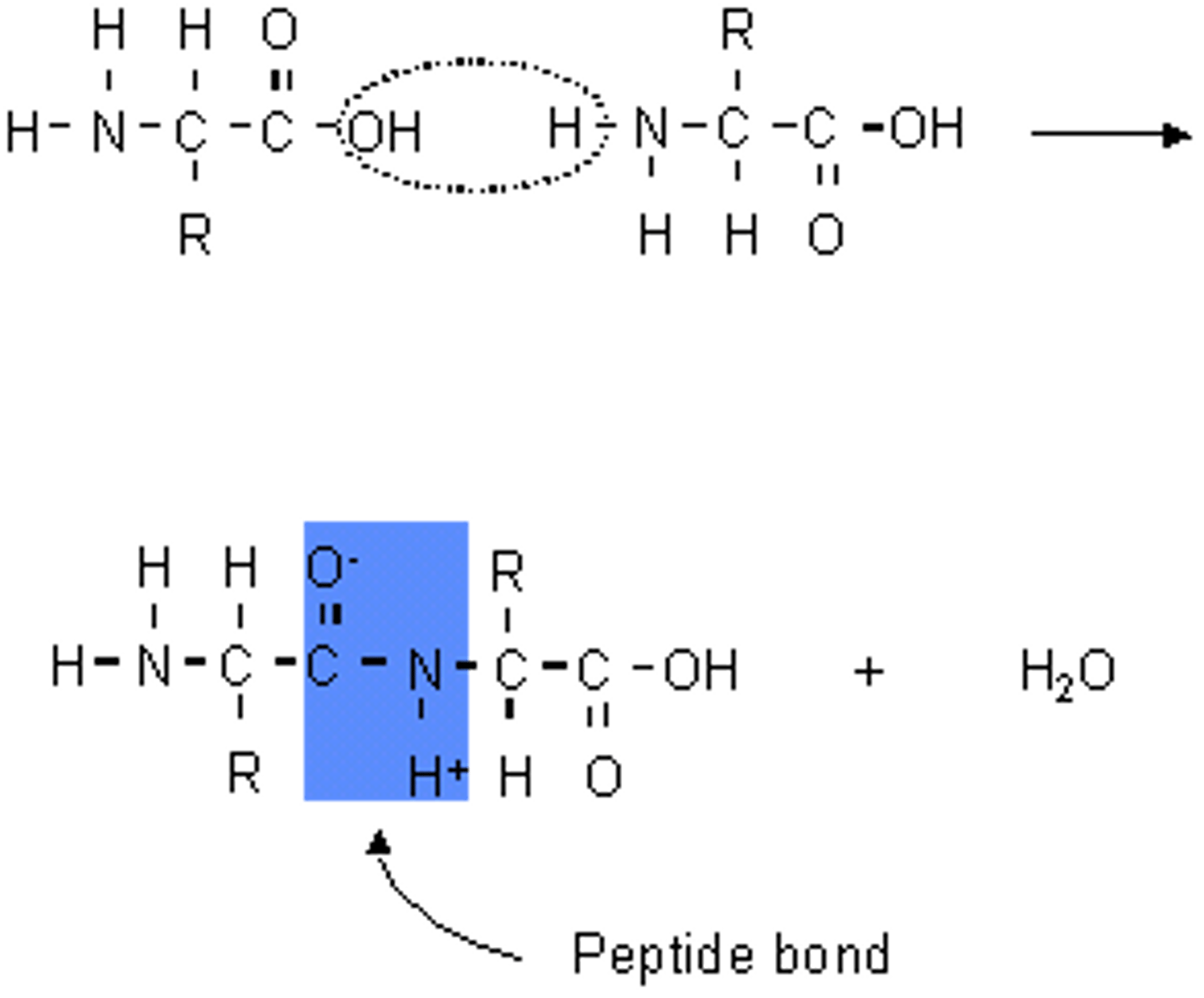
Peptide bond
The covalent bond that joins amino acid monomers together to form a polypeptide.
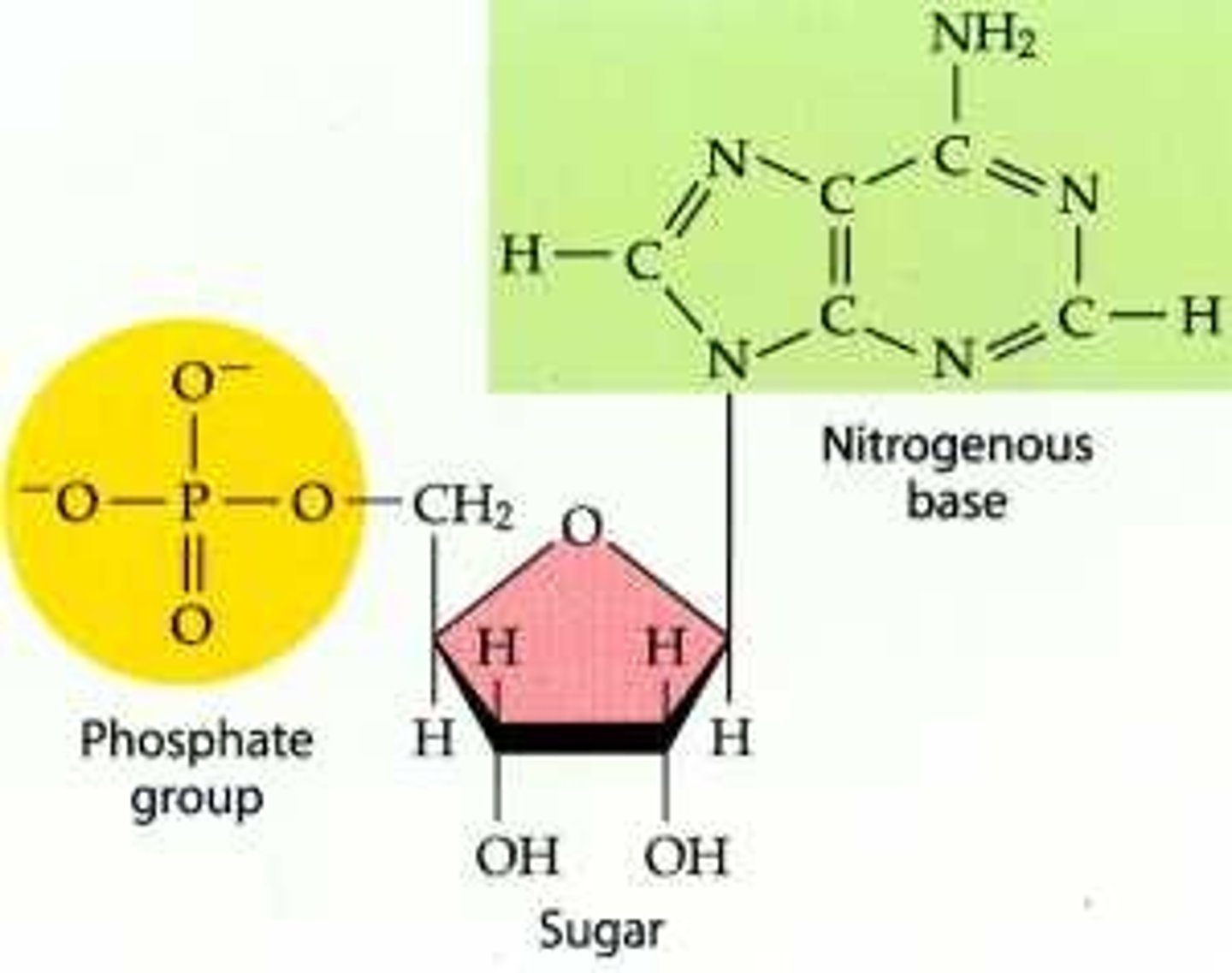
Nucleotide
Monomer of nucleic acids
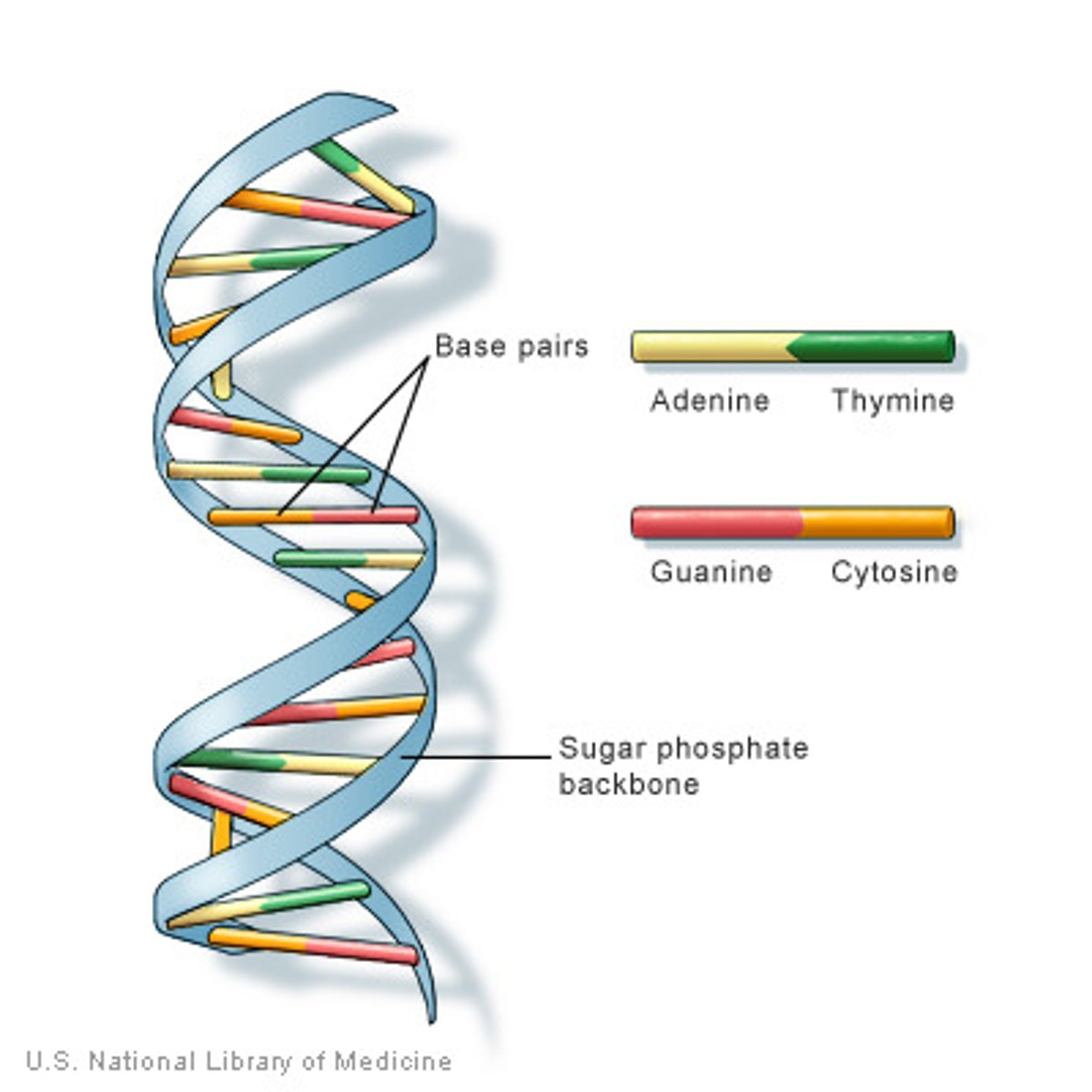
DNA
Polymer of nucleic acids (made of many nucleotides), which is usually present in the form of a double helix.
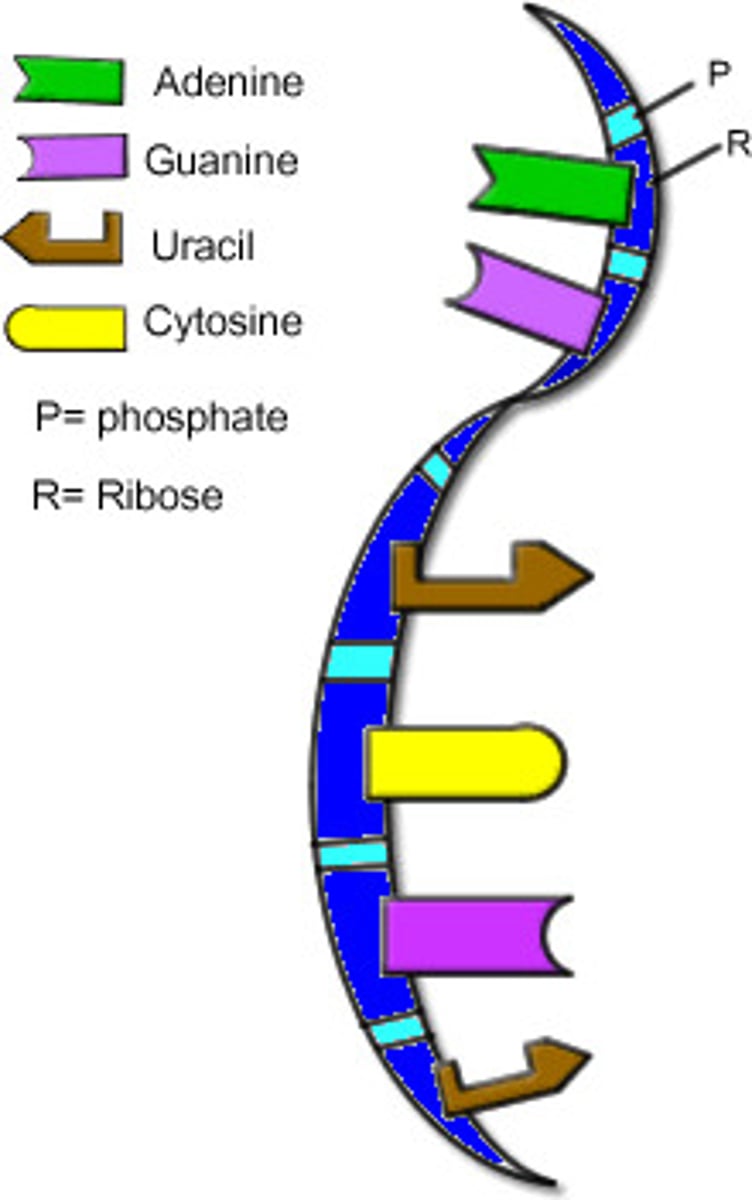
RNA
Polymer of nucleic acids (made of many nucleotides), which is usually single-stranded.
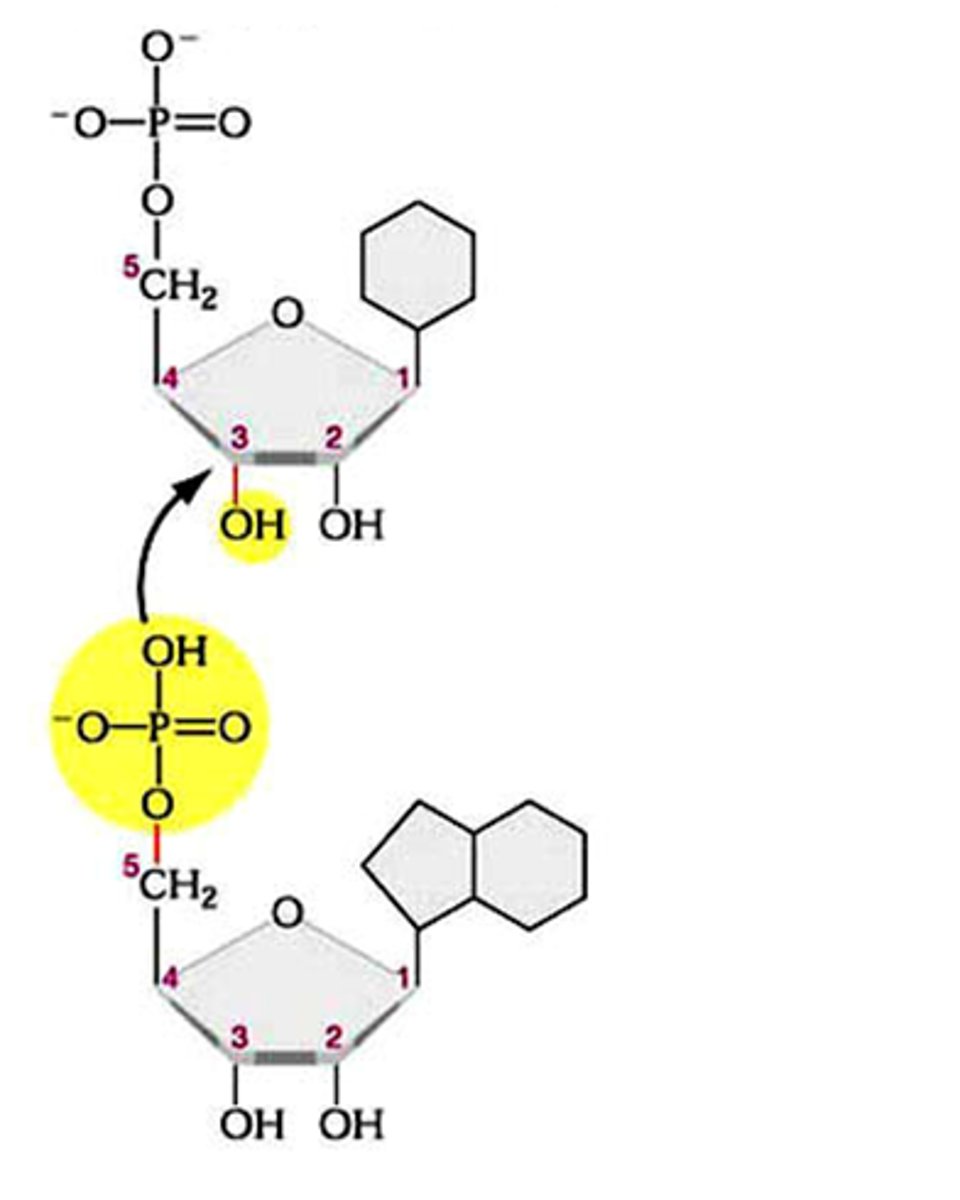
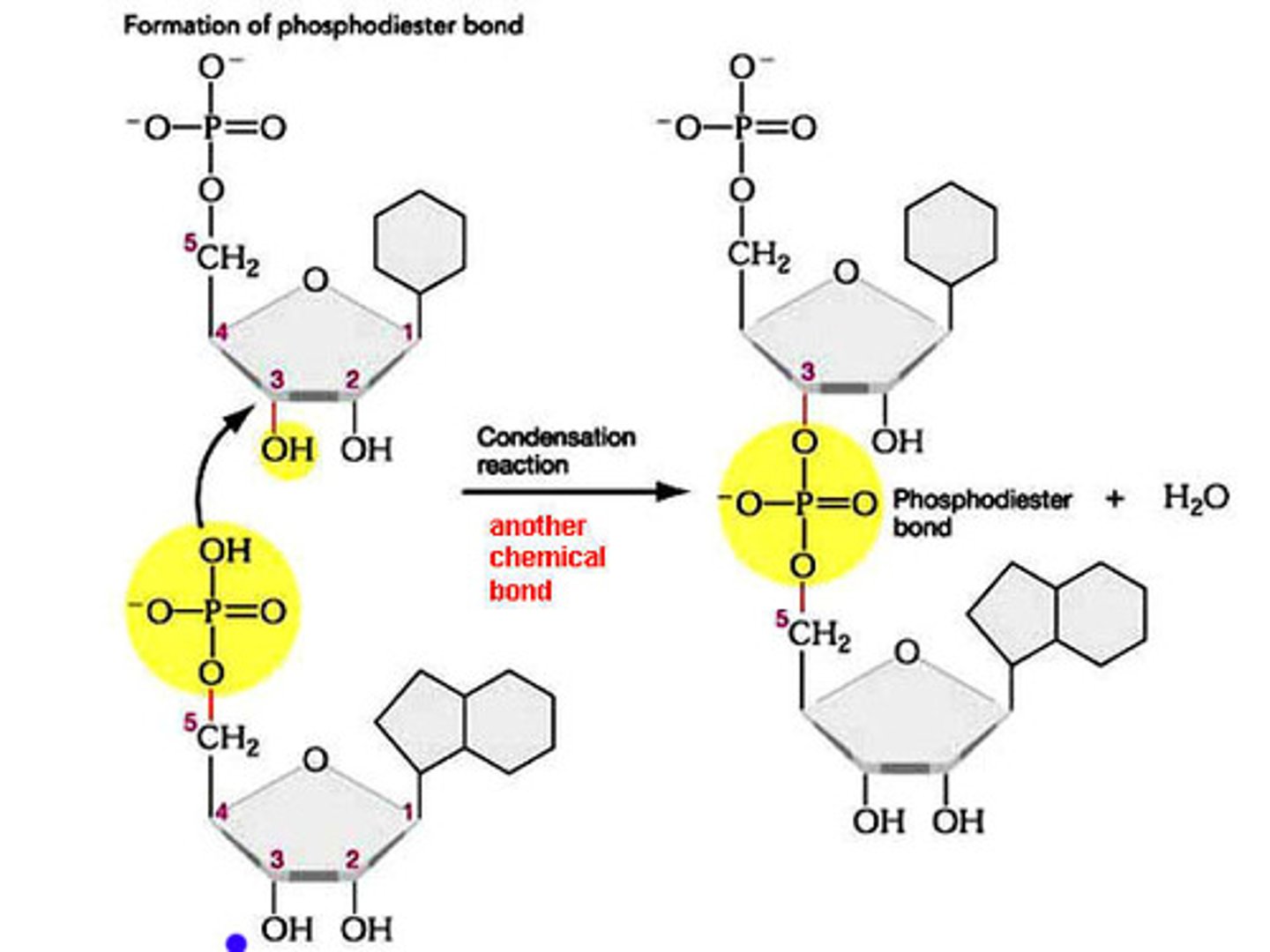
Phosphodiester bond
The covalent bond that joins nucleotides monomers together to form a strand of DNA or RNA.
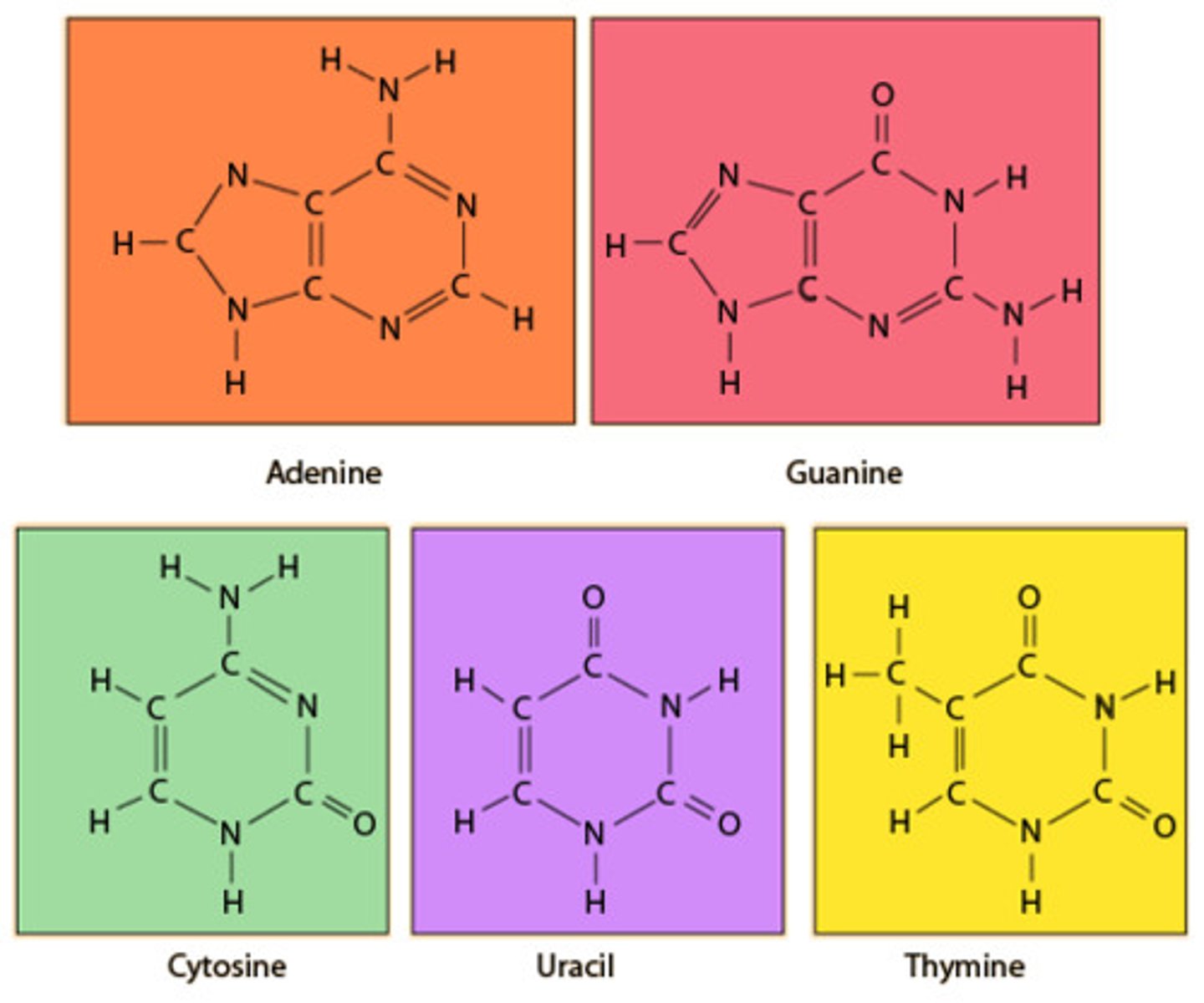
Nitrogenous base
The part of a nucleotide that is different between A, C, T, G.
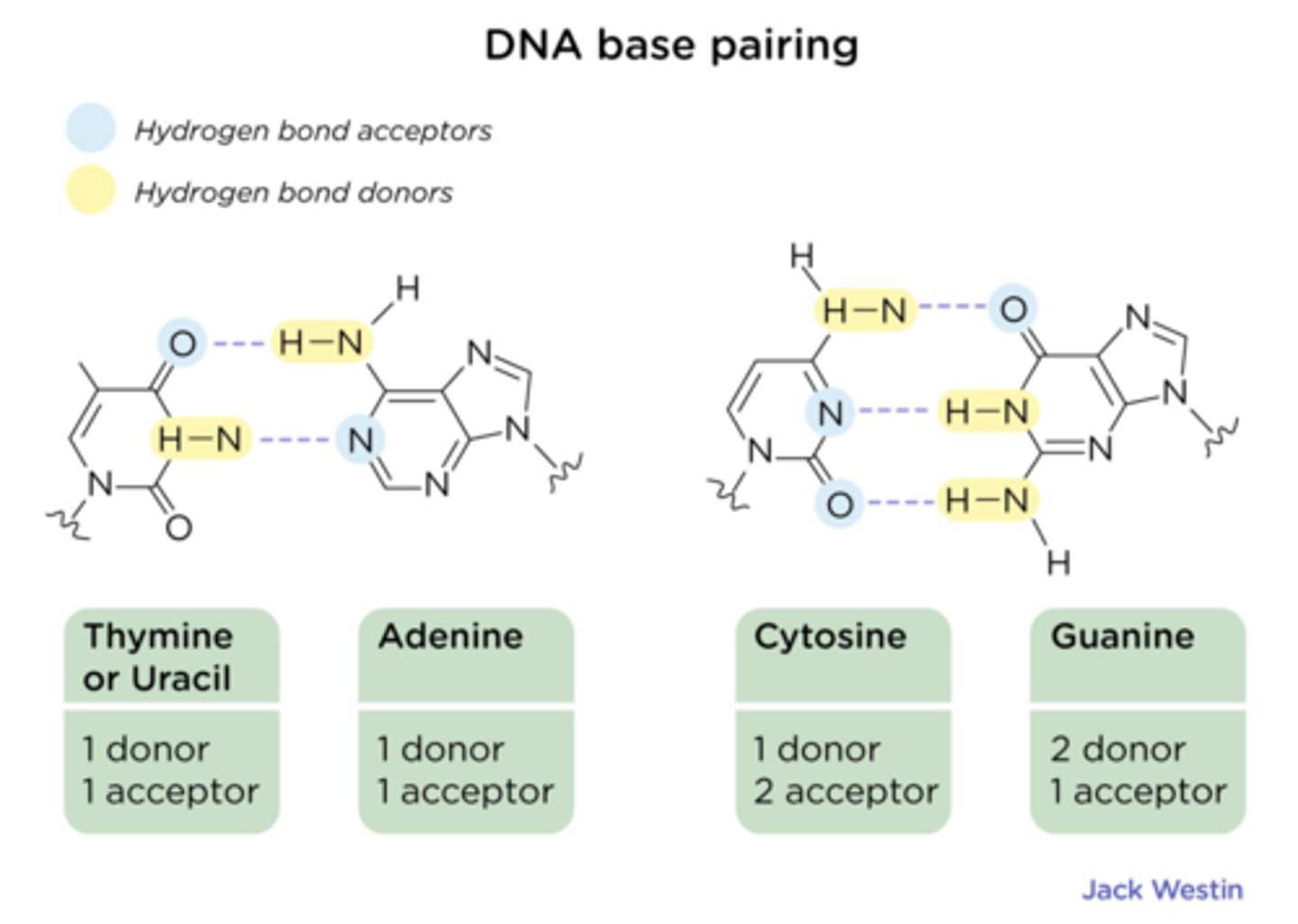
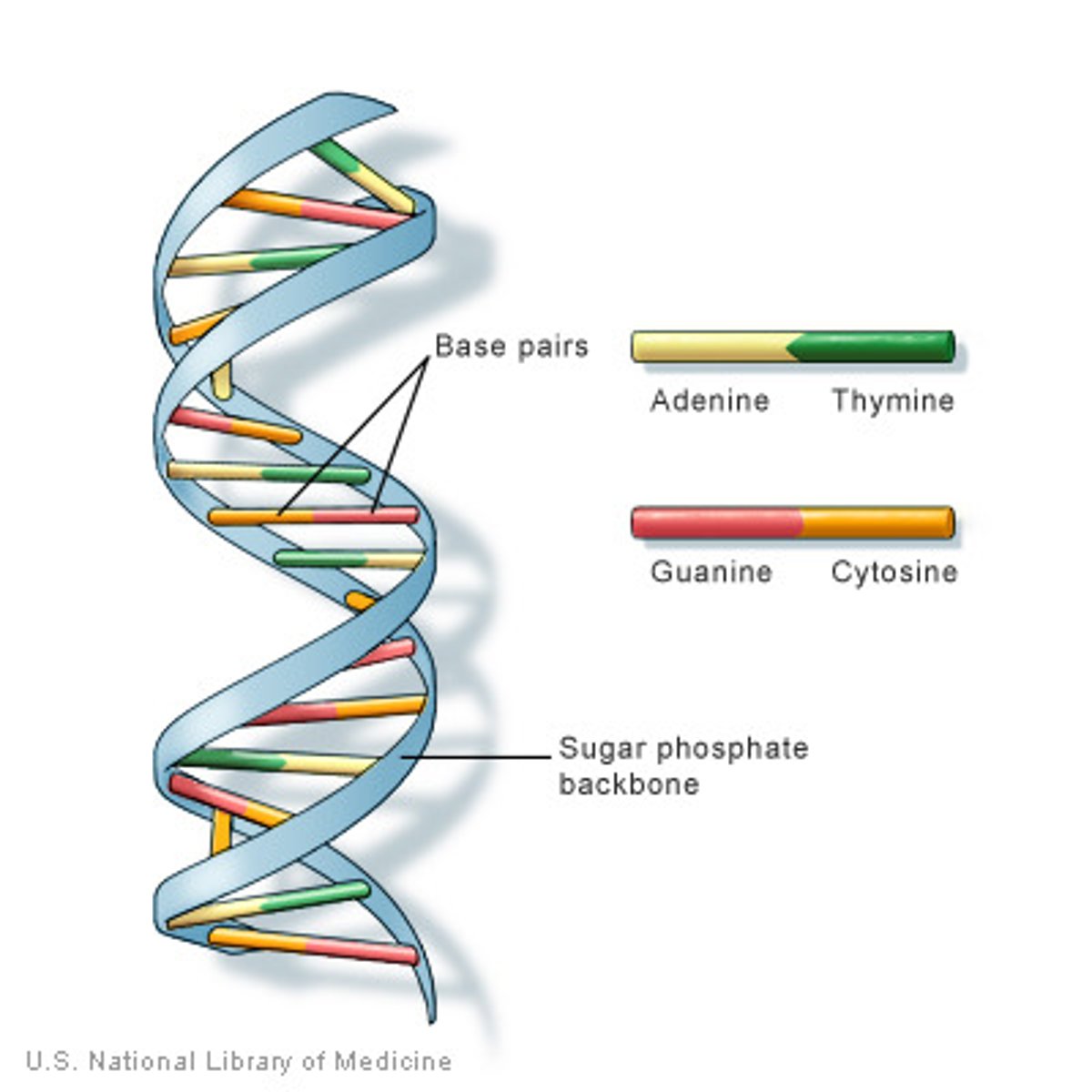
Base pair
A pair of complementary nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds.
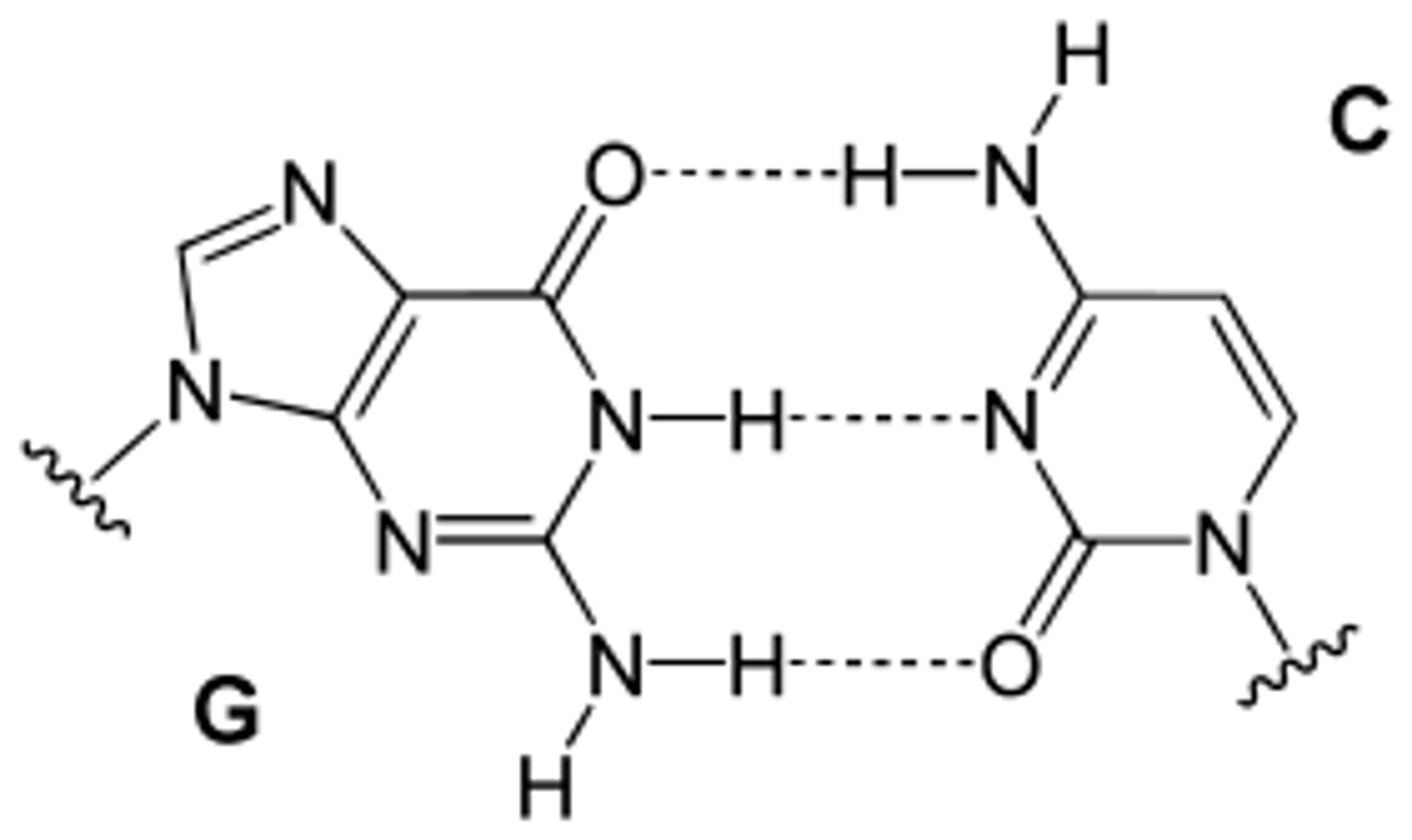
Hydrogen bond
Type of intermolecular force that holds together the two complementary nucleotides in a base pair.
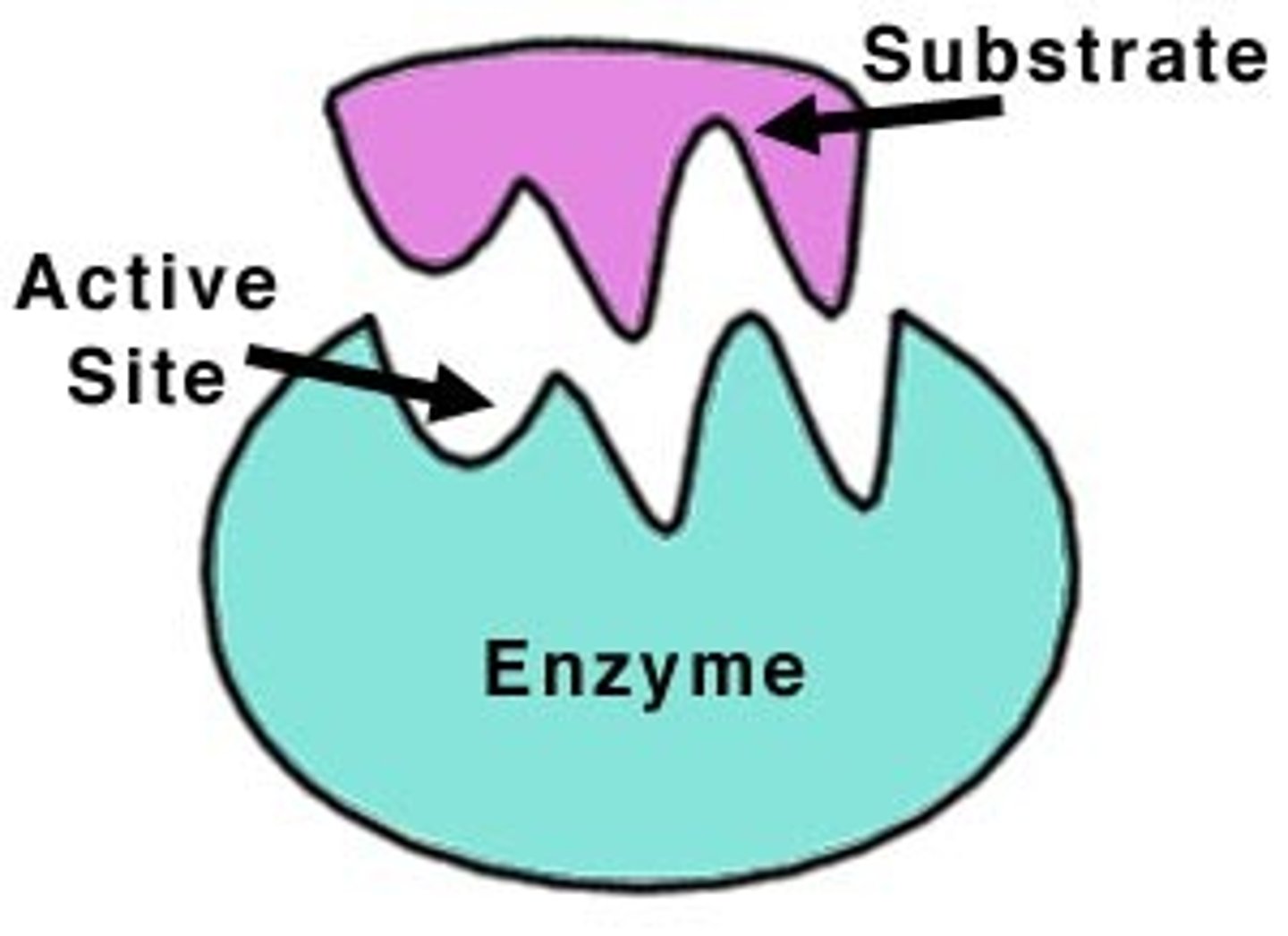
Enzyme
A protein catalyst that speeds up chemical reactions.
Gene
A segment of DNA that codes for a specific protein
Gene expression
DNA -> RNA -> protein.
Production of a protein from a gene (DNA).
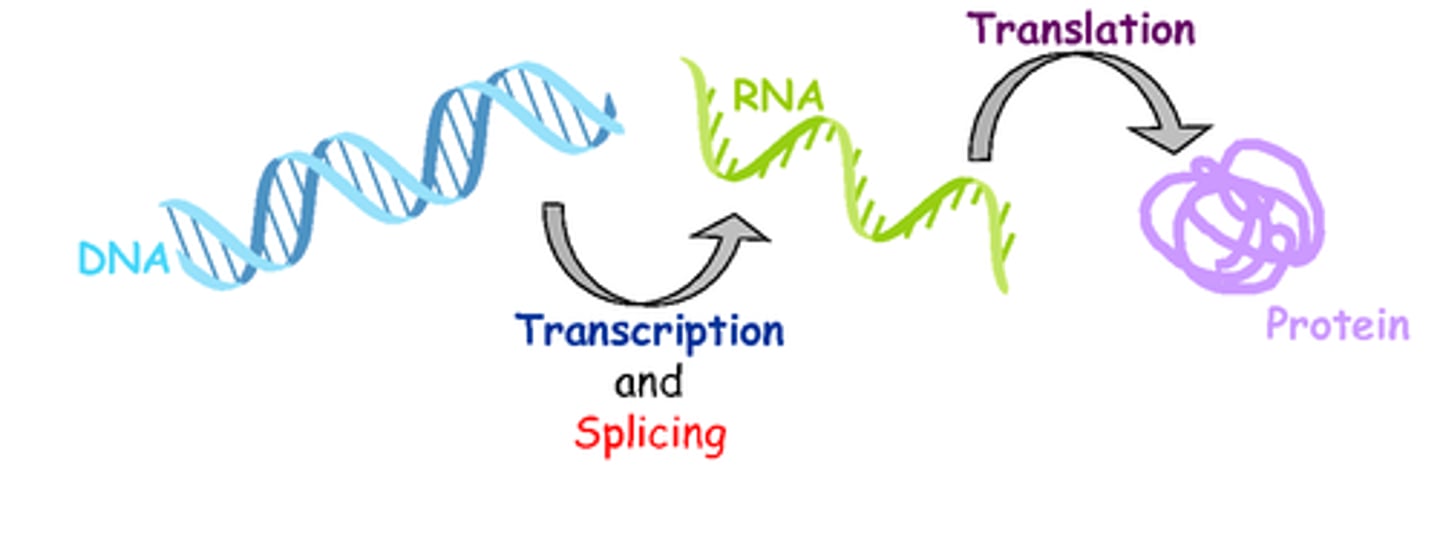
Central dogma
DNA -> RNA -> protein
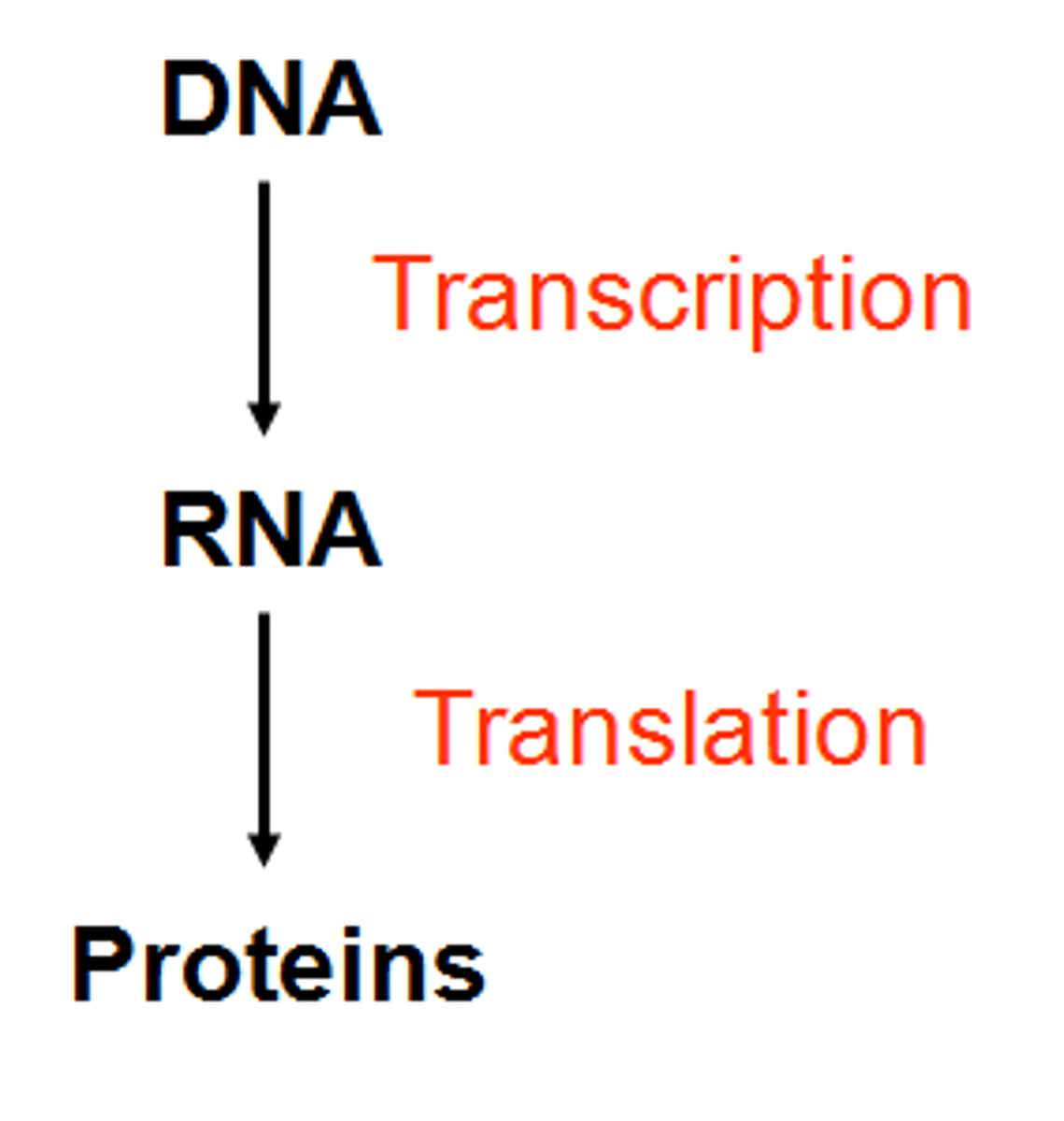
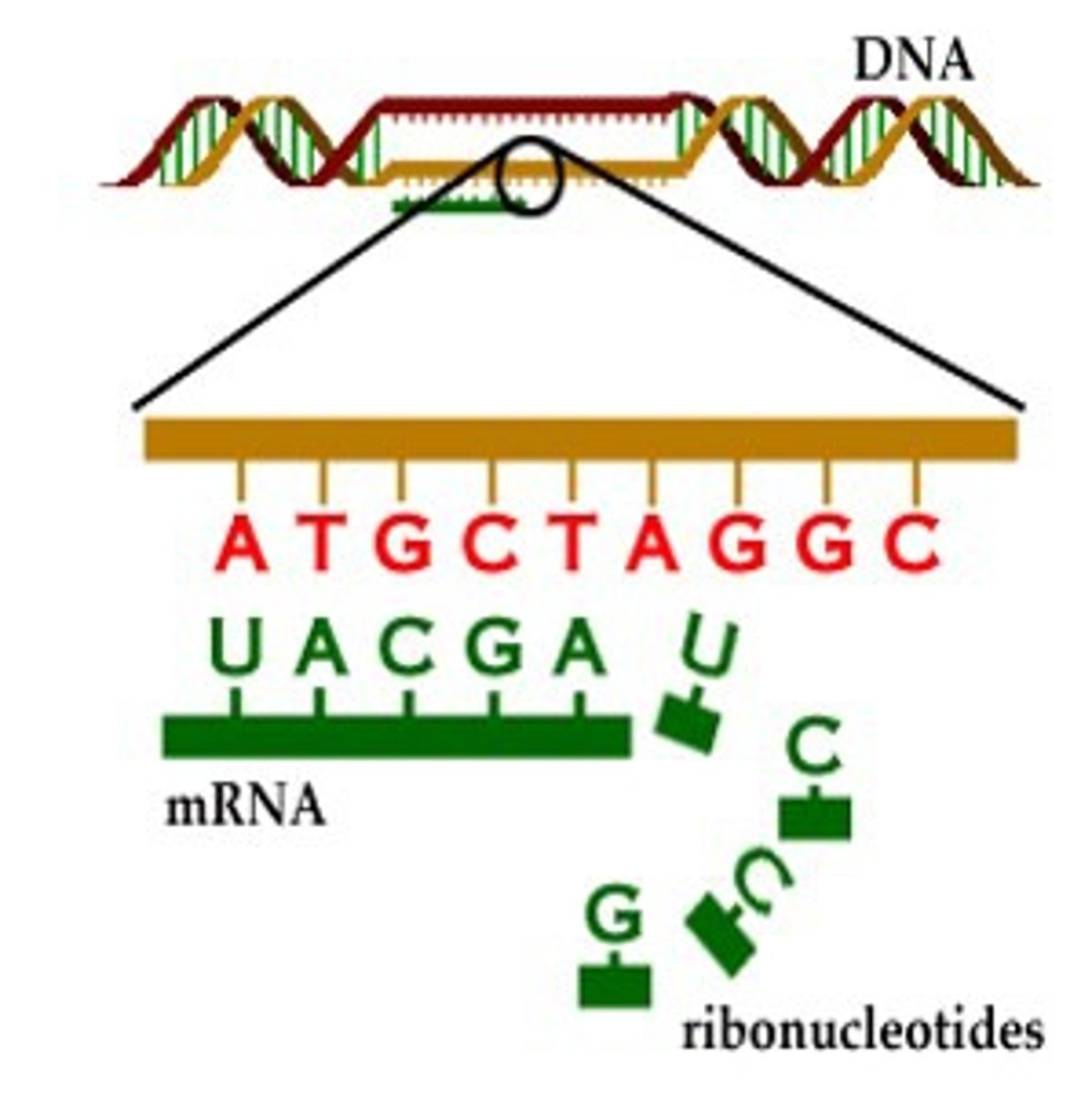
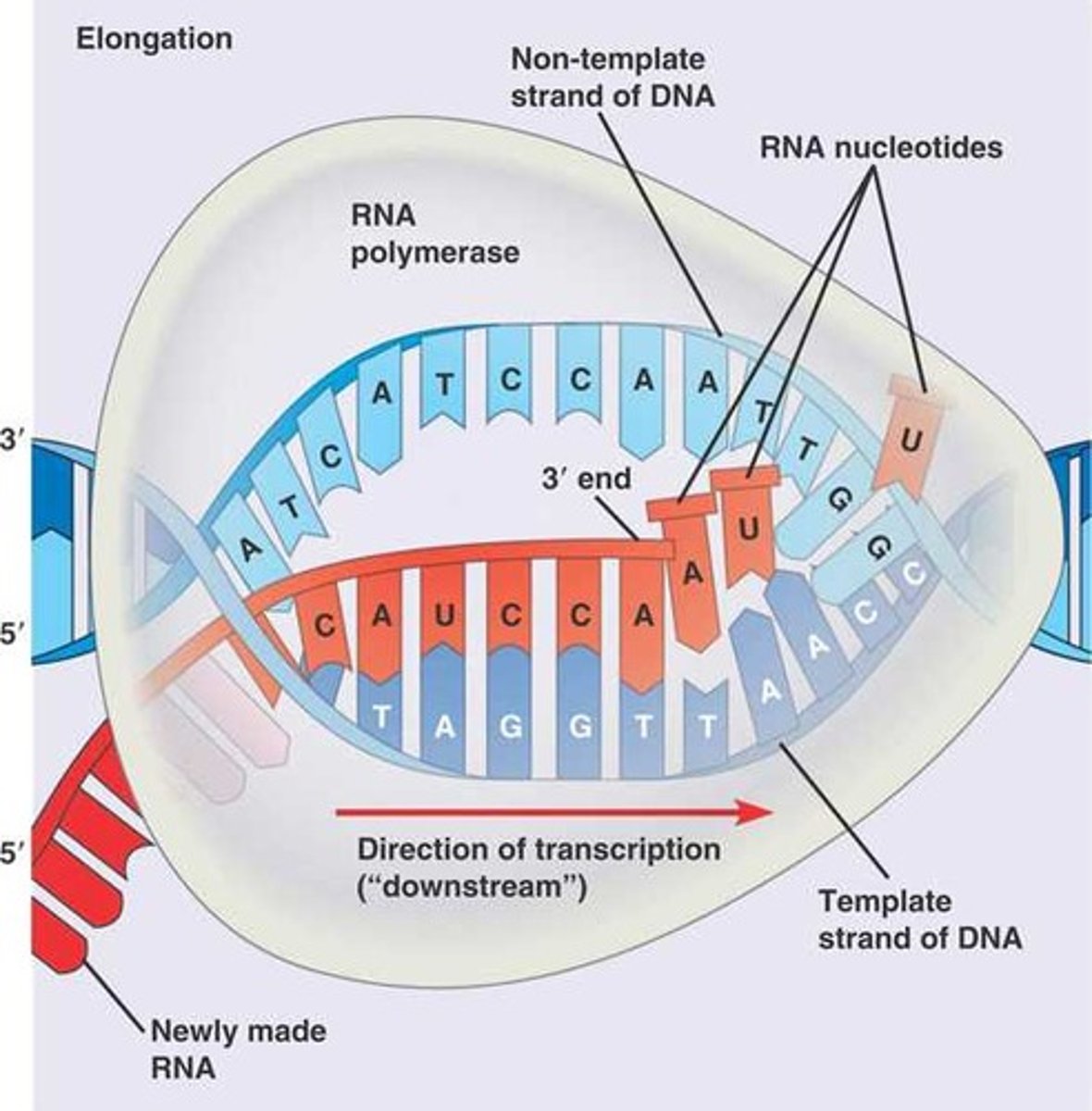
Transcription
Synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
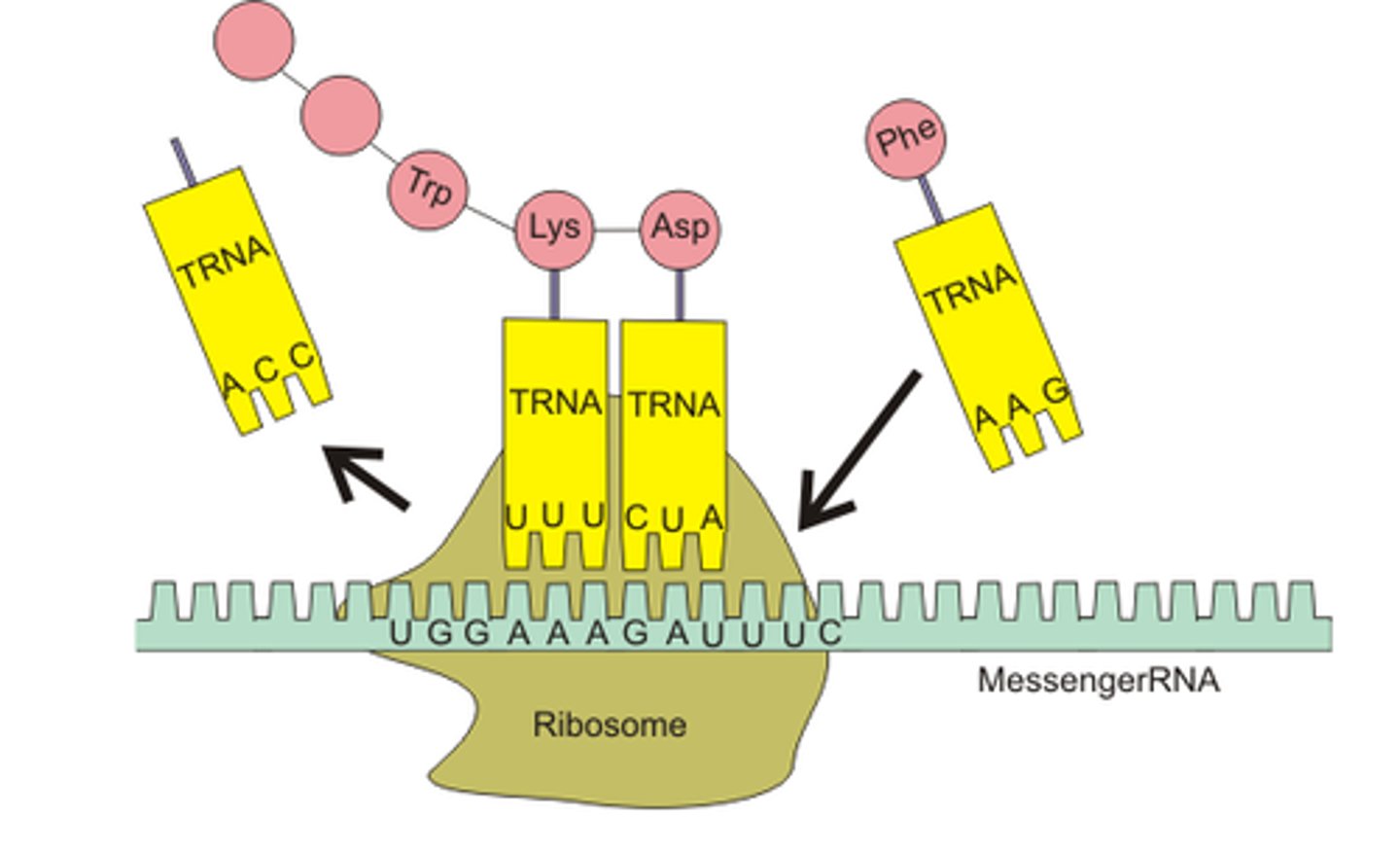
Translation
Synthesis of a protein using the instructions in mRNA
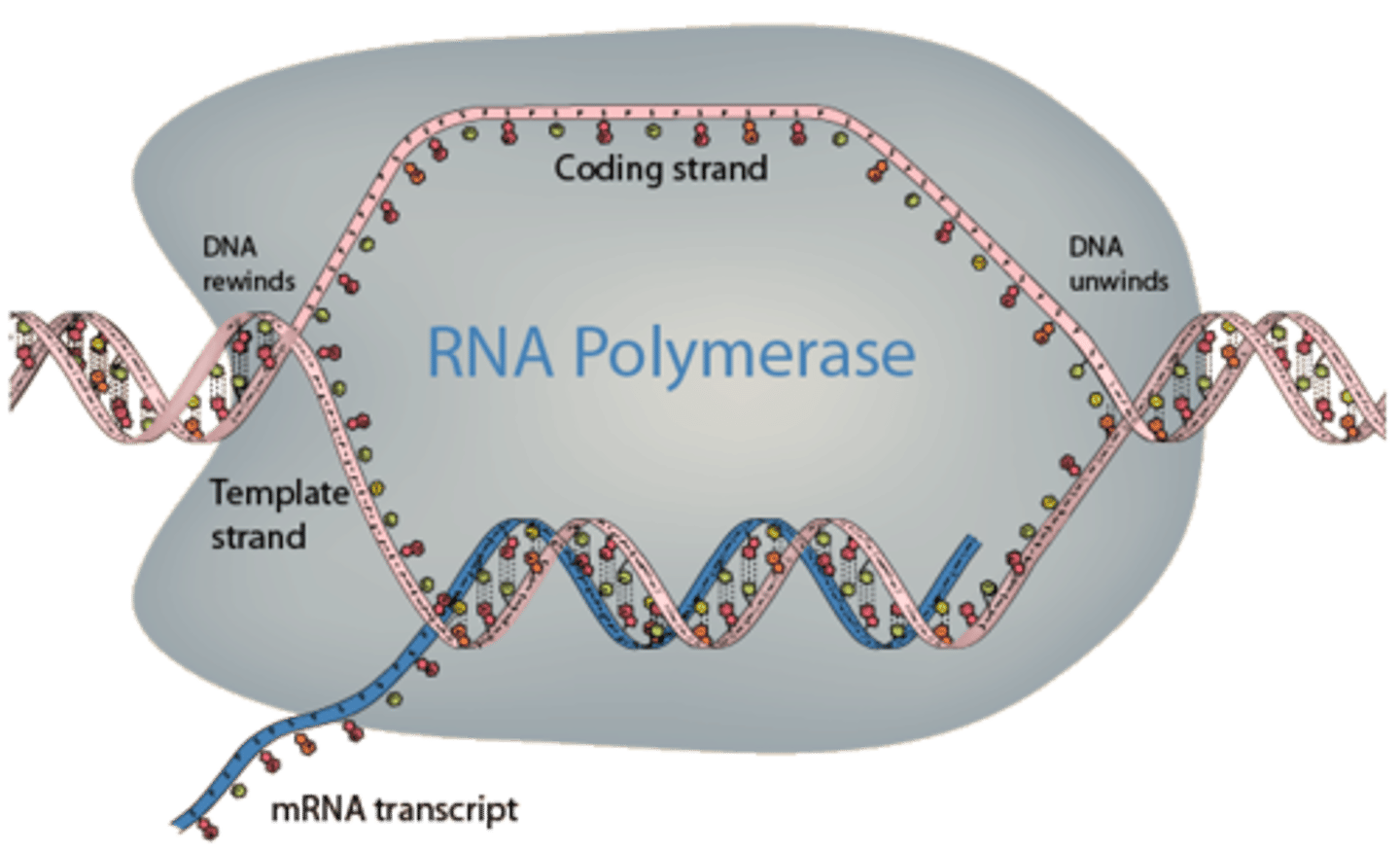
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that catalyzes transcription (makes RNA)
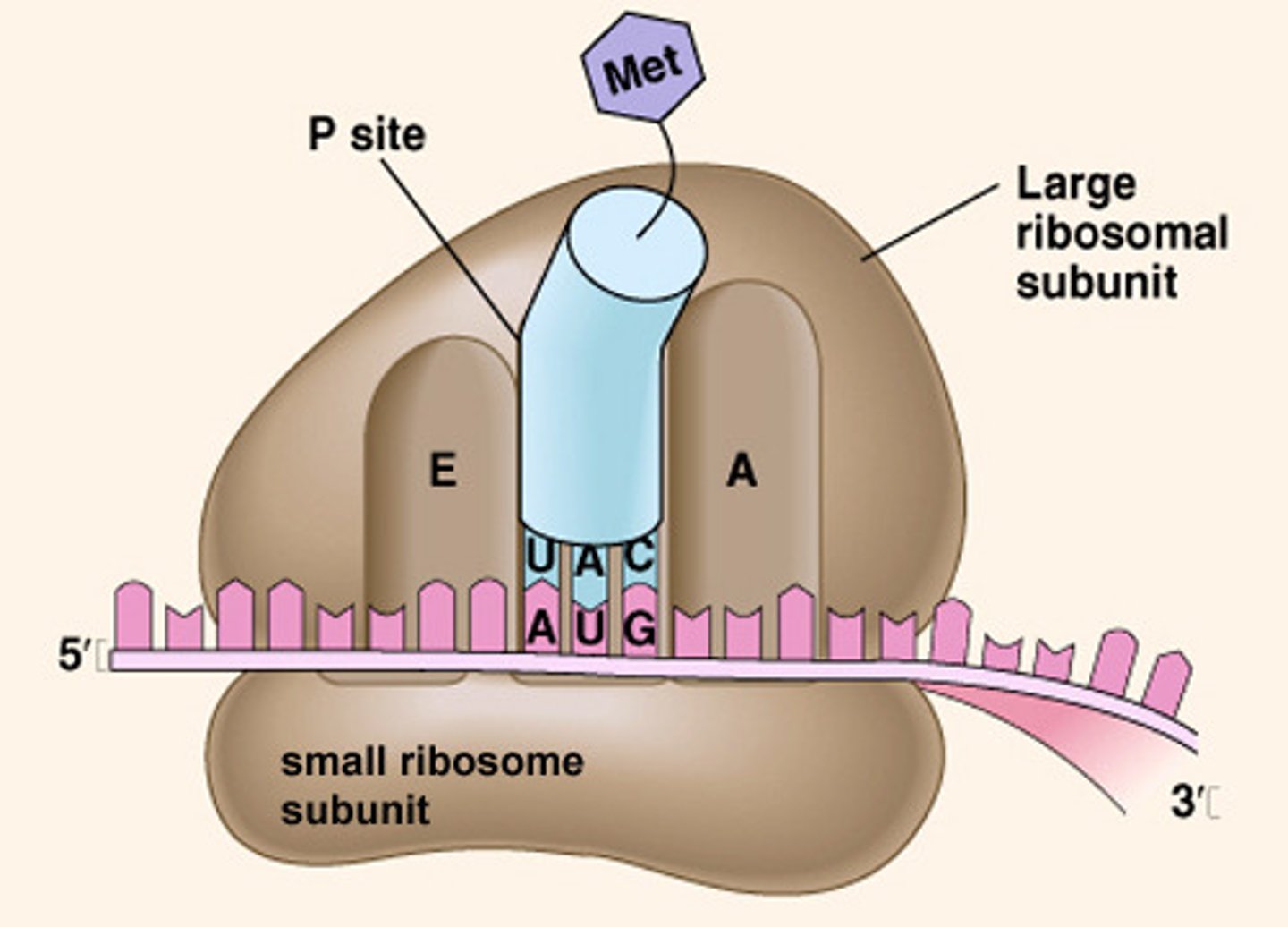
Ribosome
Enzyme complex that catalyzes tranlsation (makes proteins)
mRNA
Messenger RNA; carries information from DNA to the ribosome
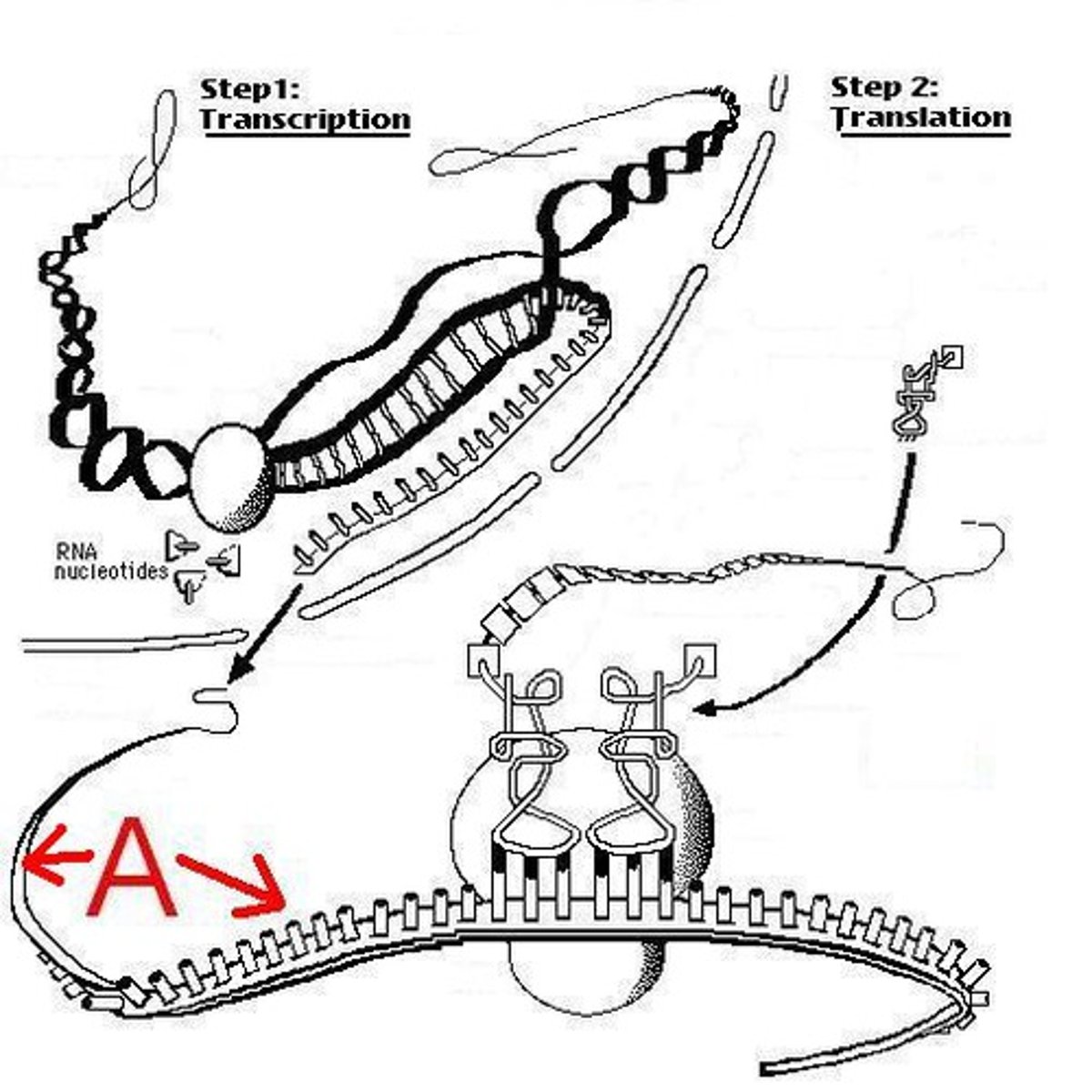
tRNA
Transfer RNA; carries amino acids to the ribosome during translation
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA; a special type of RNA that builds ribosomes
Template strand
DNA sequence that is copied during transcription
Plasmid
Small, circular piece of DNA located in the cytoplasm of many bacteria
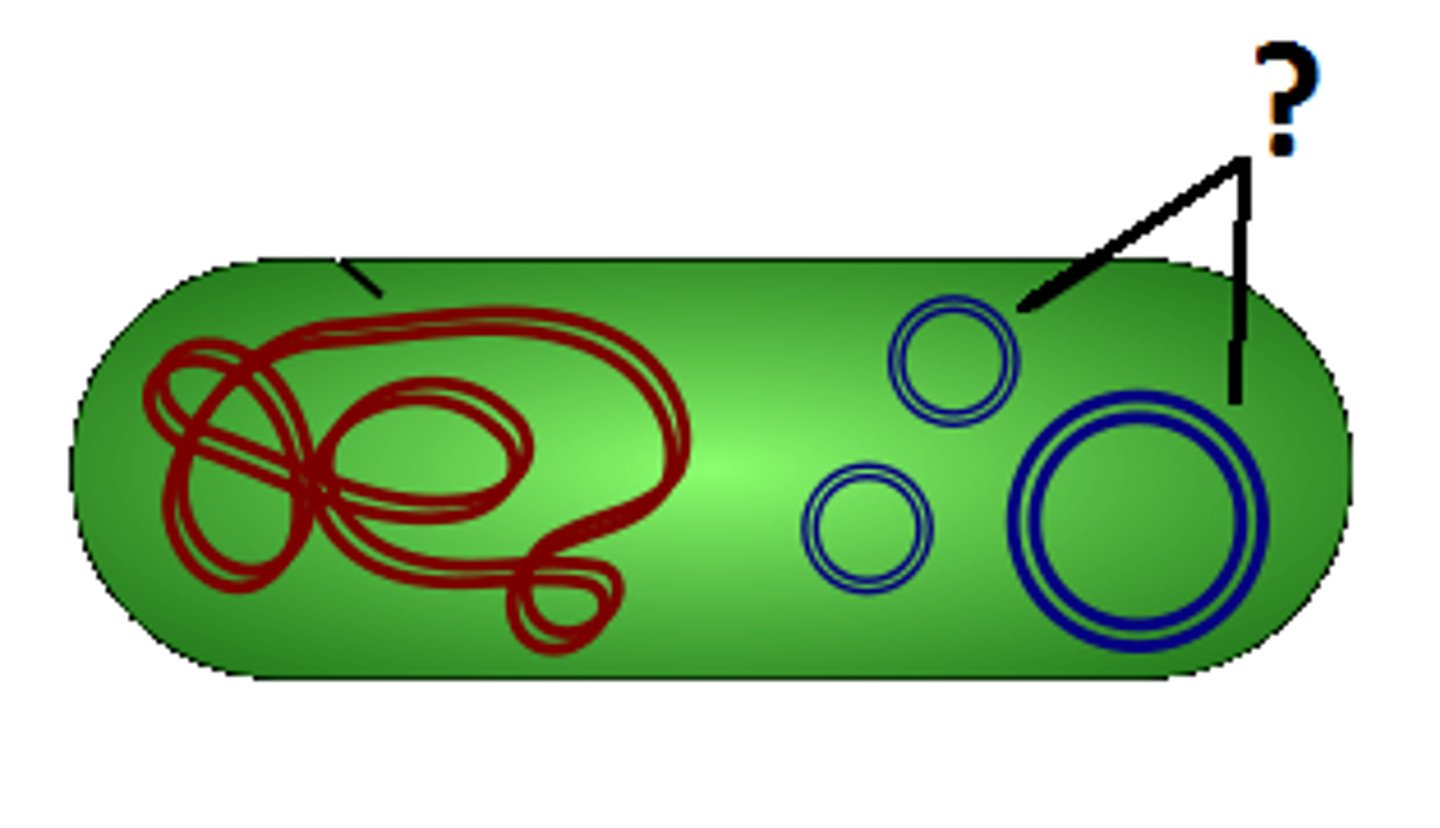
Gene
A segment of DNA that codes for a specific protein
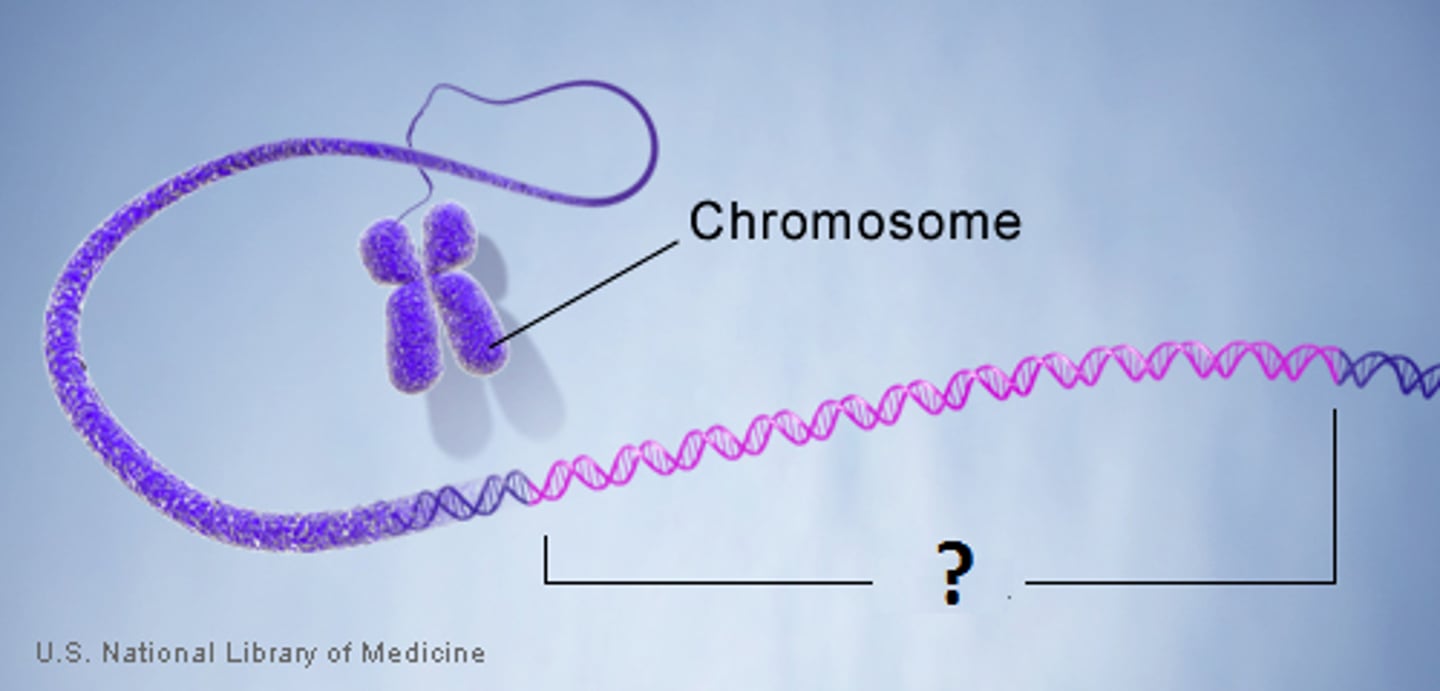
Gene expression
DNA -> RNA -> protein. When a gene is turned "on" and actively producing mRNA and protein.
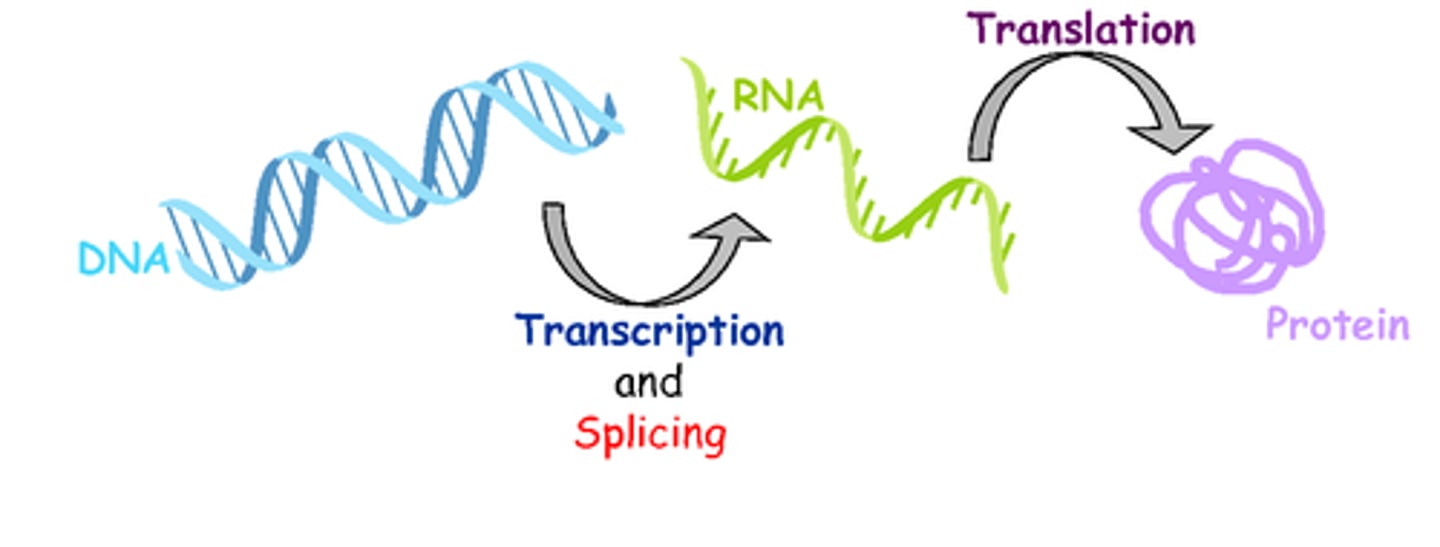
Central dogma of biology
DNA -> RNA -> protein
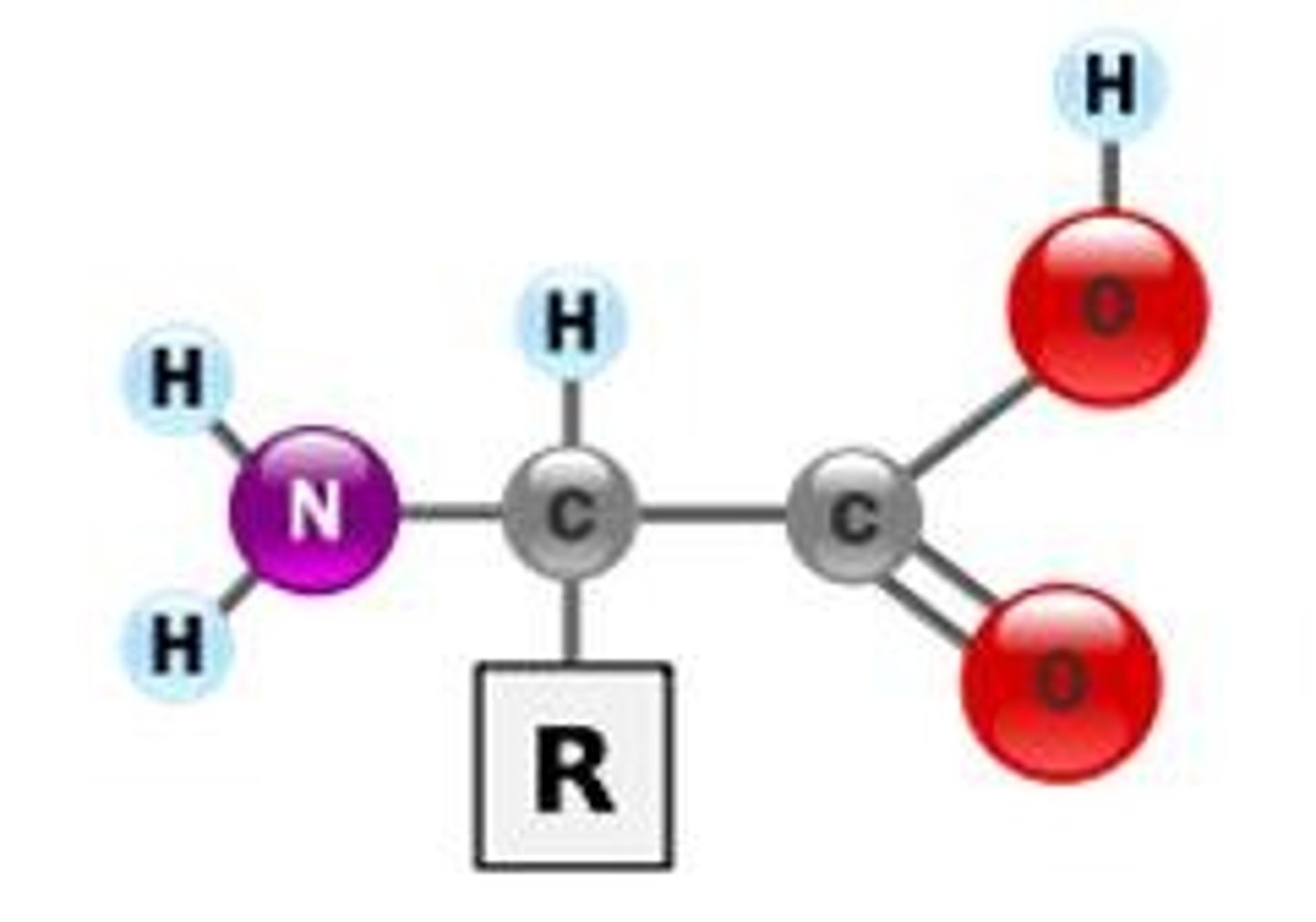
Amino acid
Monomer of proteins
Polypeptide
A single amino acid chain
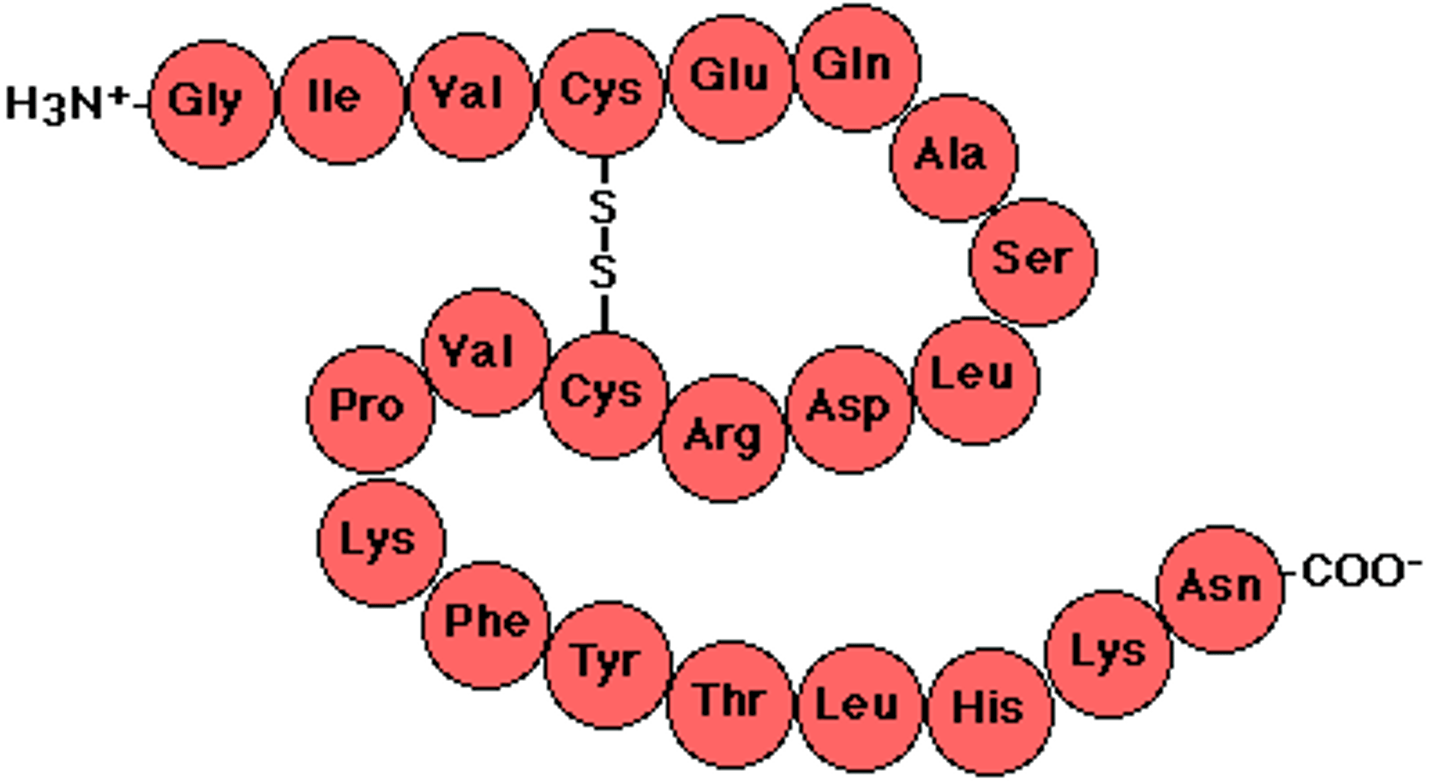
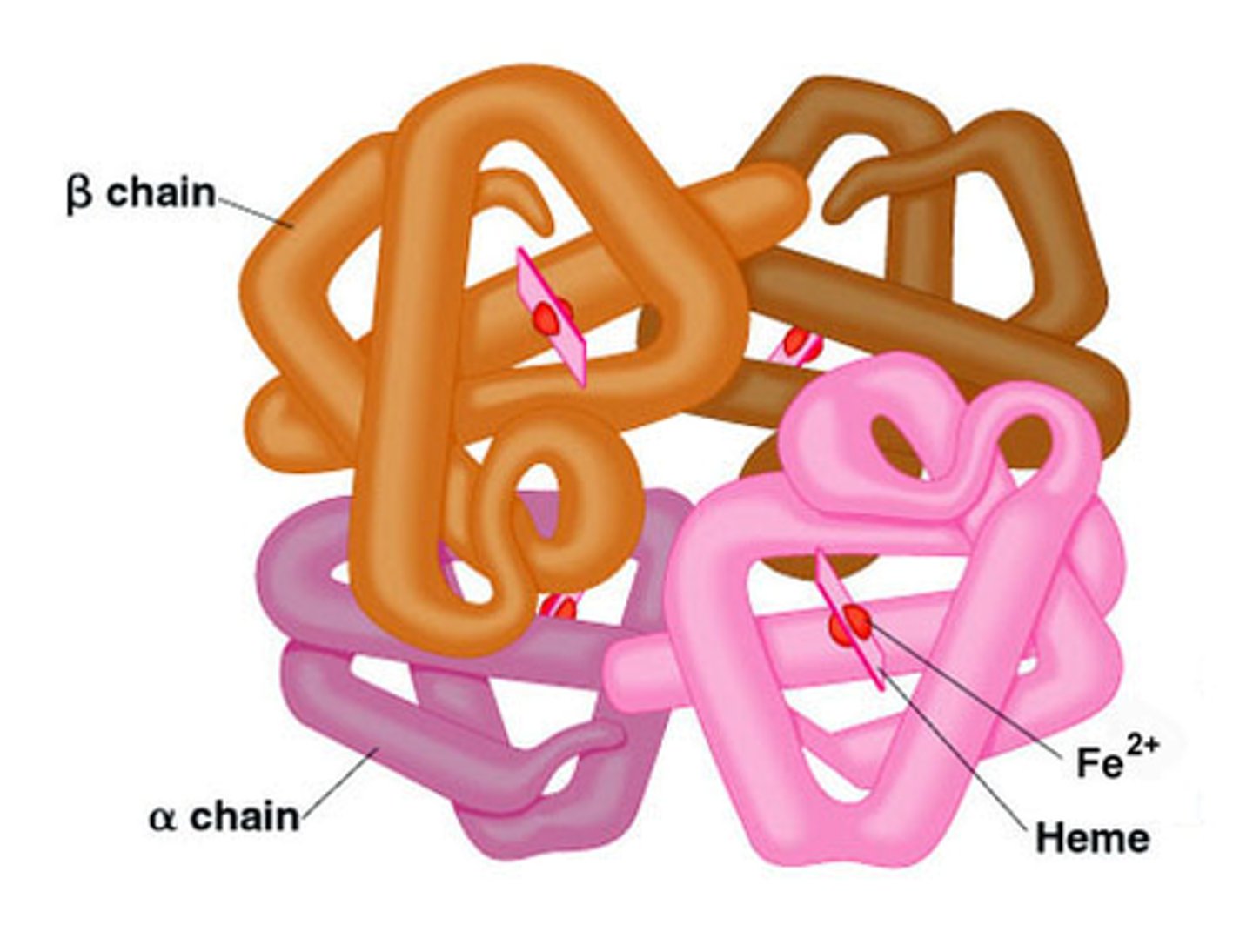
Protein
Functional polymer of amino acids, which can be one or more polypeptide chains folded together; responsible for all of the activities within a cell.
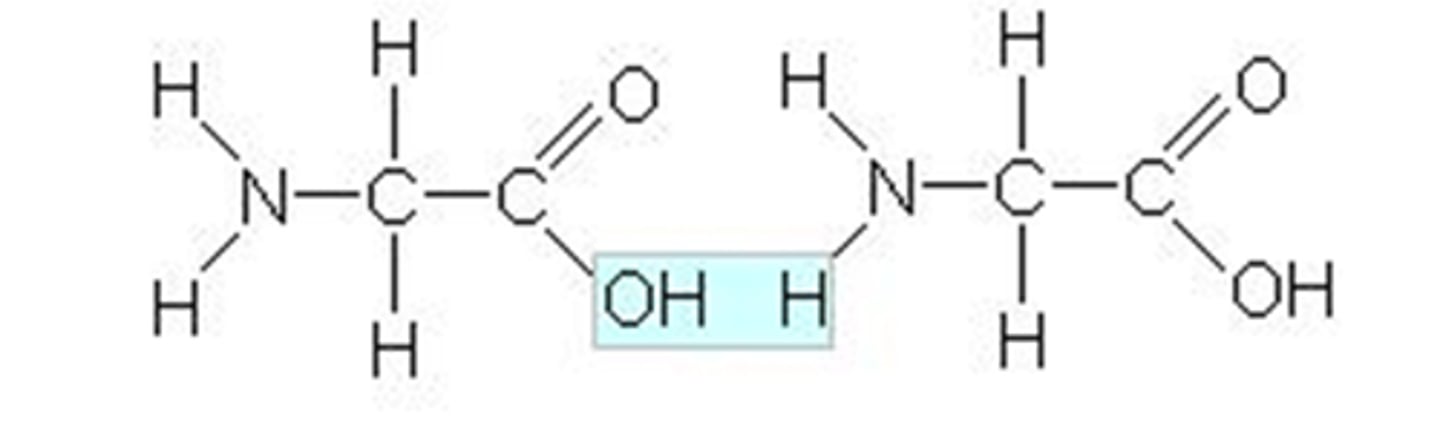
Peptide bond
The covalent bond that joins amino acid monomers together to form a polypeptide.
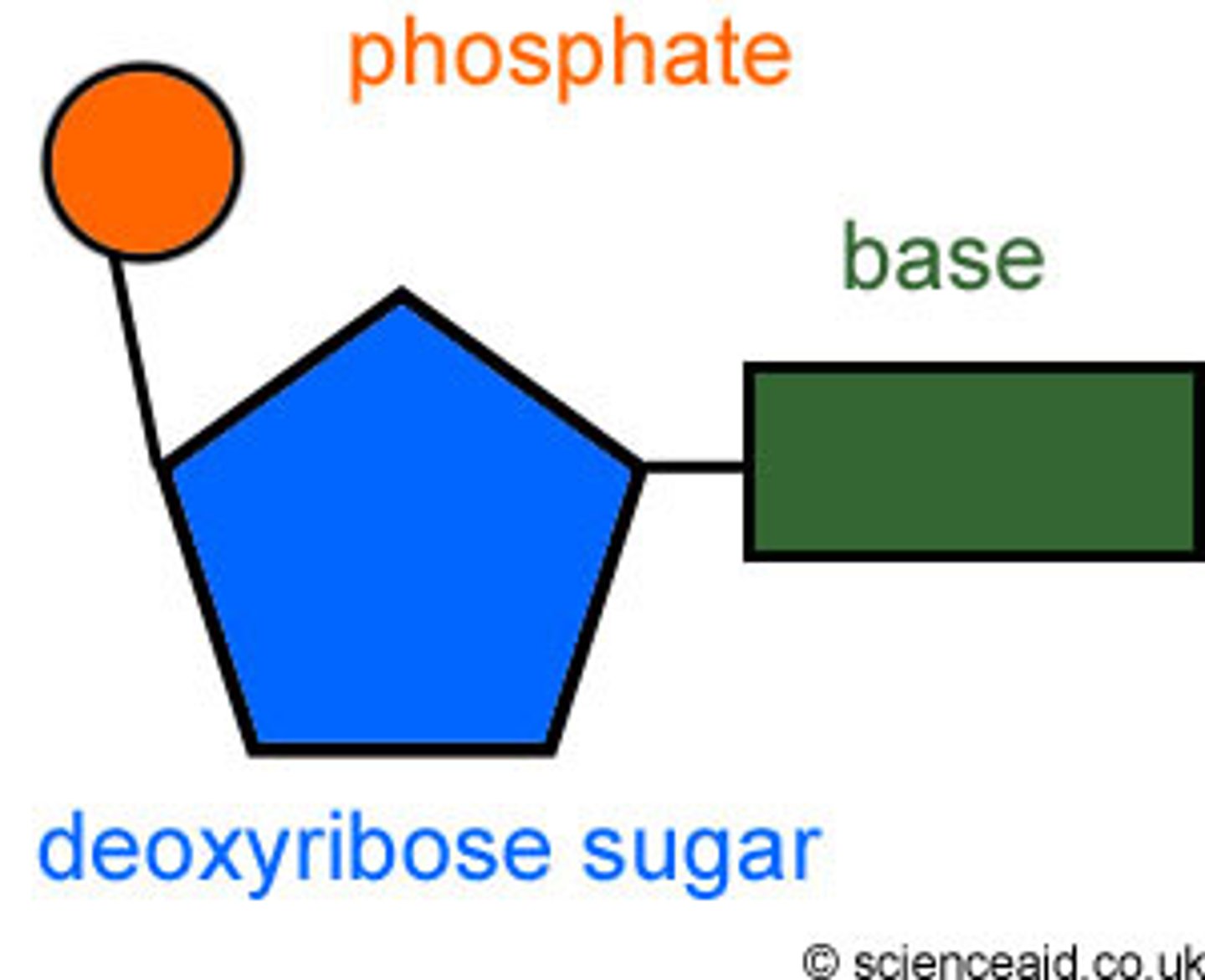
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
DNA
Double-stranded polymer of nucleic acids (made of many nucleotides)
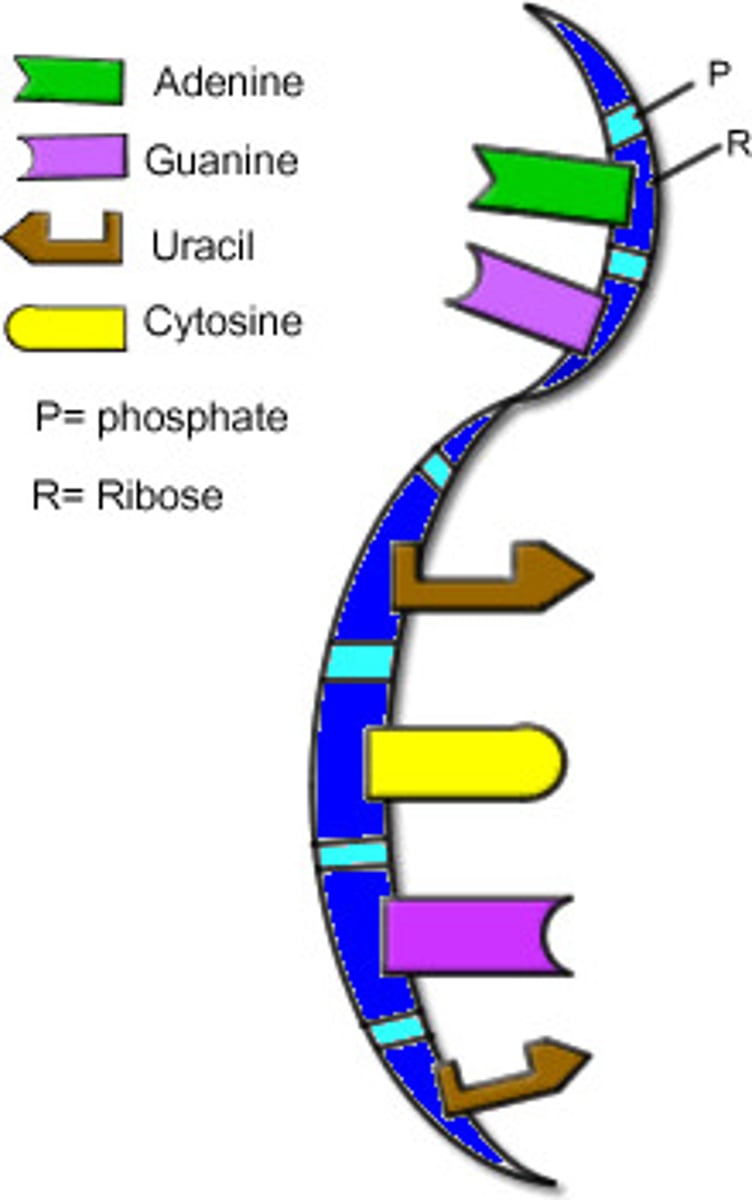
RNA
Single-stranded polymer of nucleic acids (made of many nucleotides)
Base pair
A pair of complementary nucleotides that are held together by hydrogen bonds. Ex: G-C and A-T
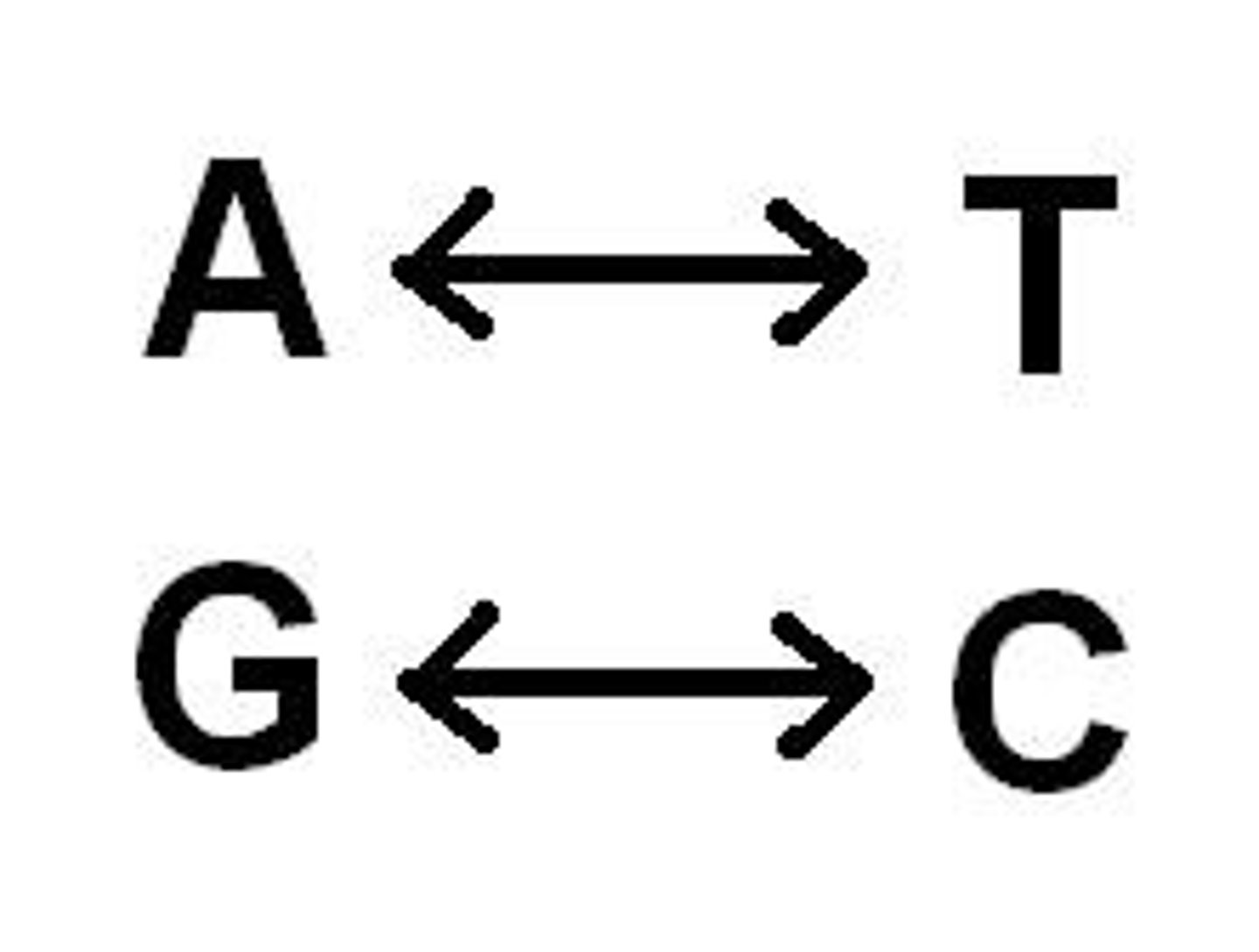
Phosphodiester linkage
Covalent bond that forms between two nucleotide monomers to form a nucleic acid polymer
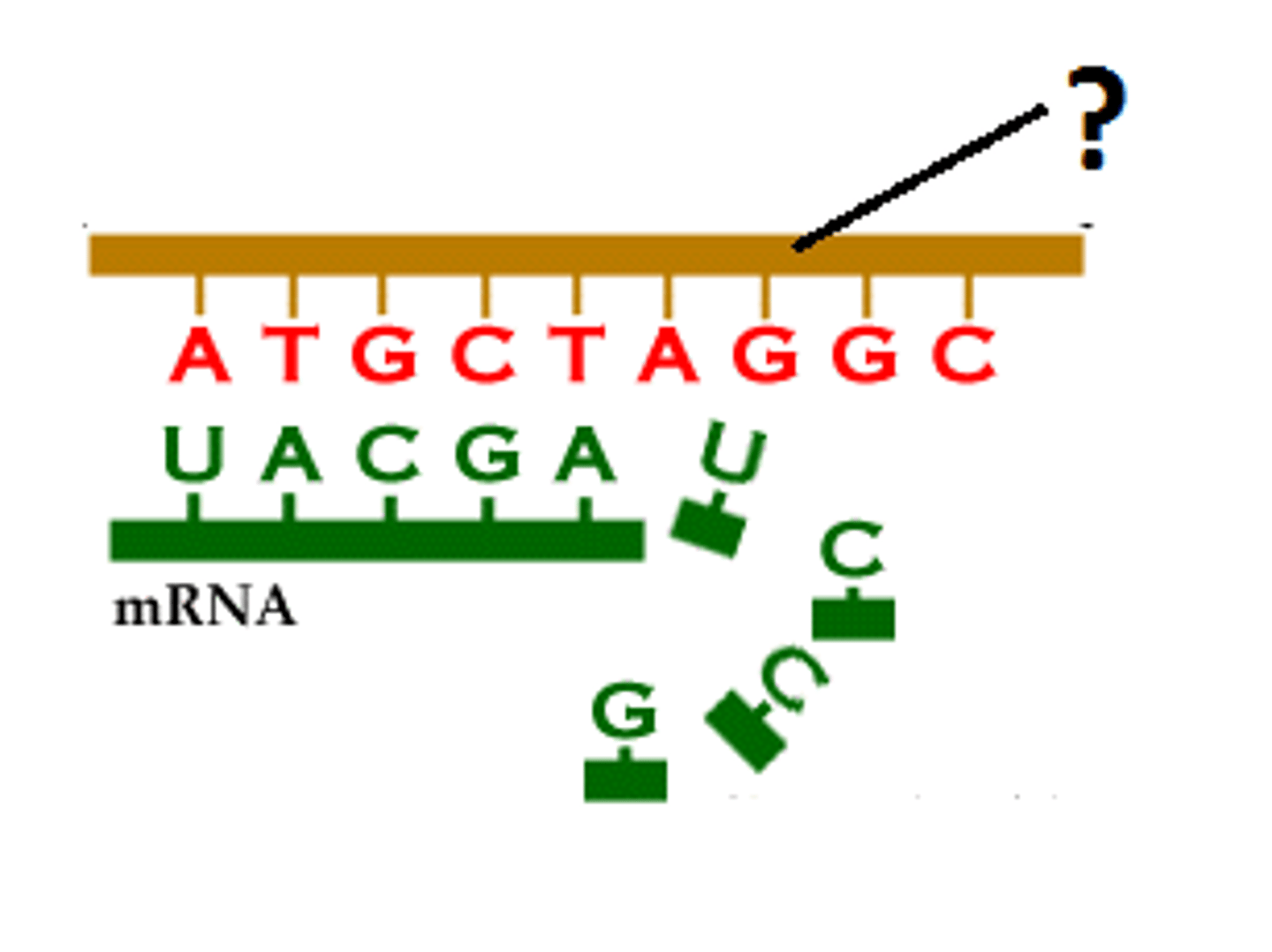
Transcription
Synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
RNA processing
Modification of RNA before it leaves the nucleus that includes addition of a 5' cap, 3' poly-A tail, and splice. This process is unique to eukaryotes.
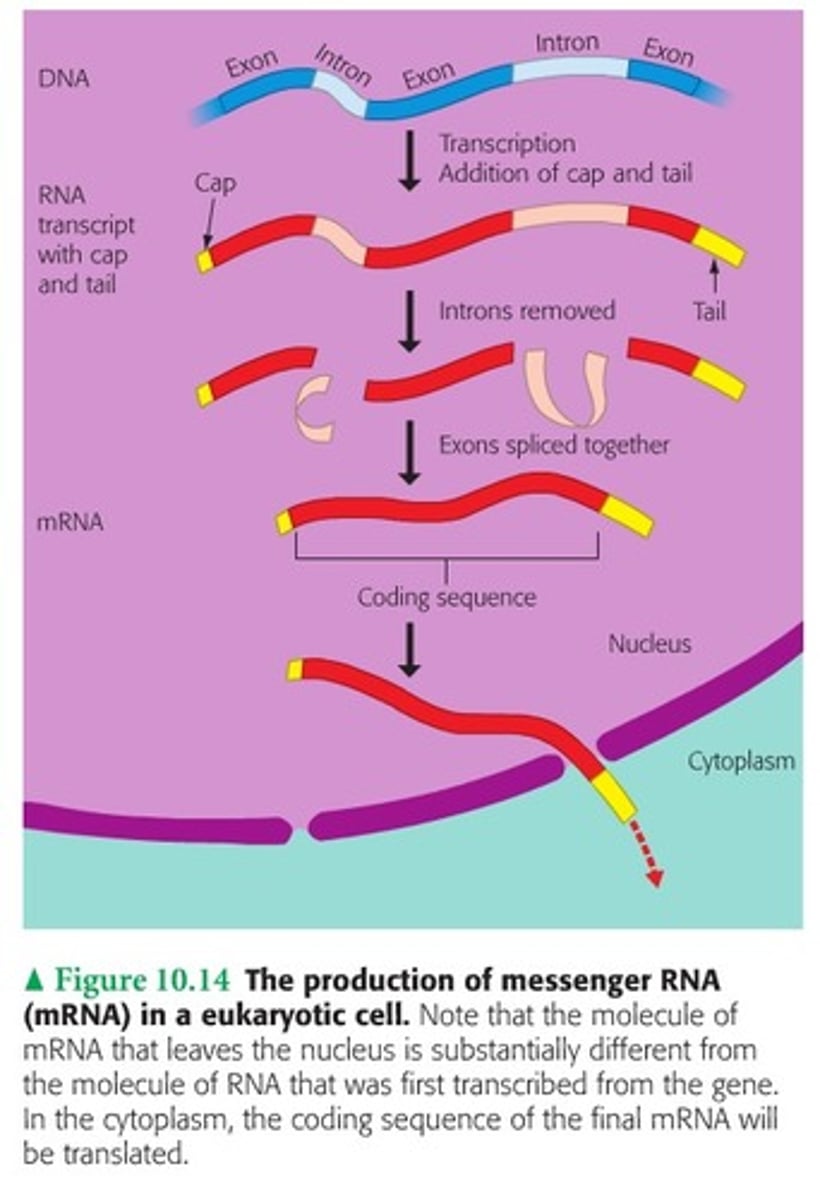
Splicing
Removal of introns and rejoining of exons; happens in the nucleus in eukaryotic cells only
Intron
mRNA sequences that are removed during splicing and do NOT code for a protein
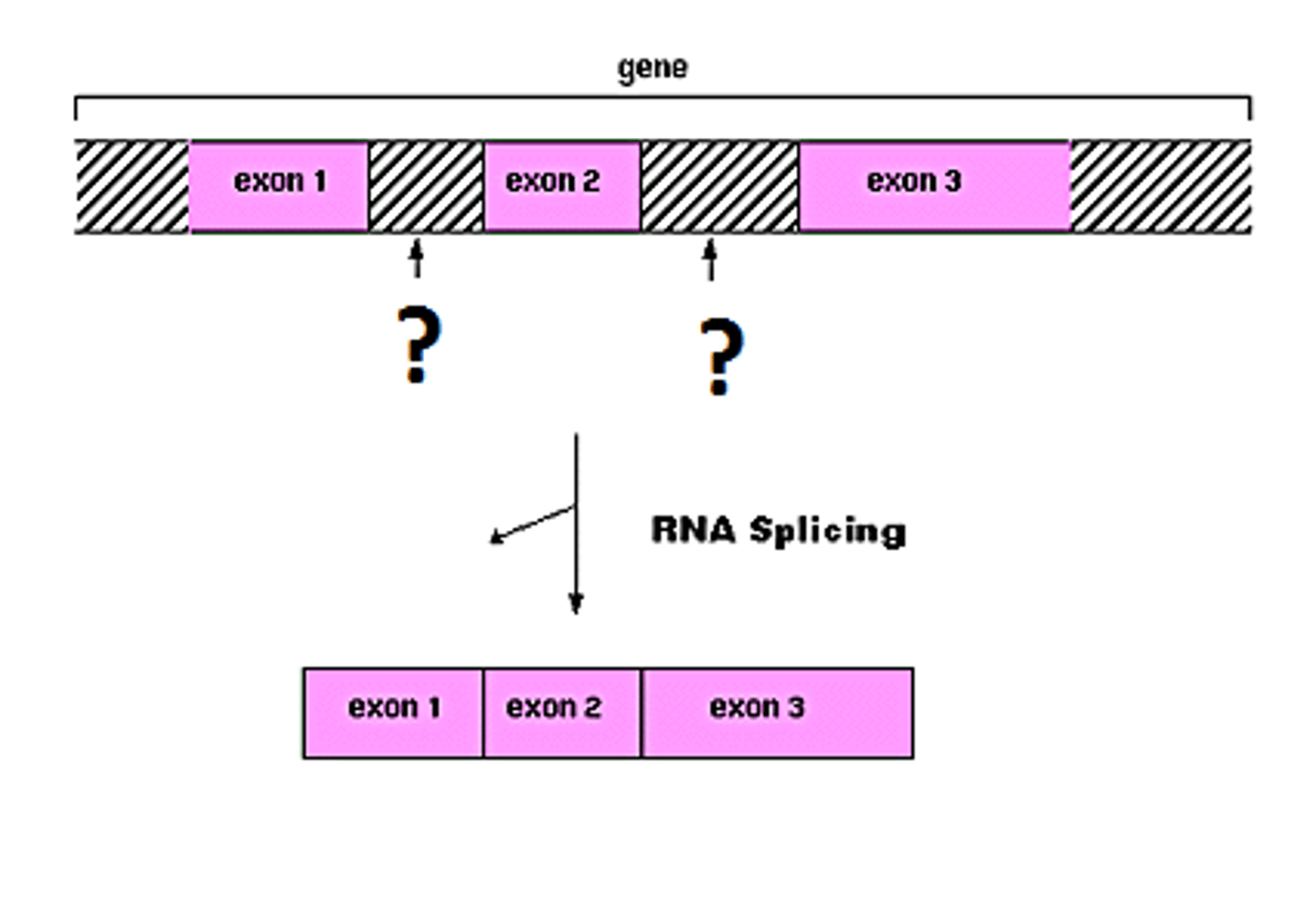
Exon
mRNA sequences that remain during splicing and DO code for a protein
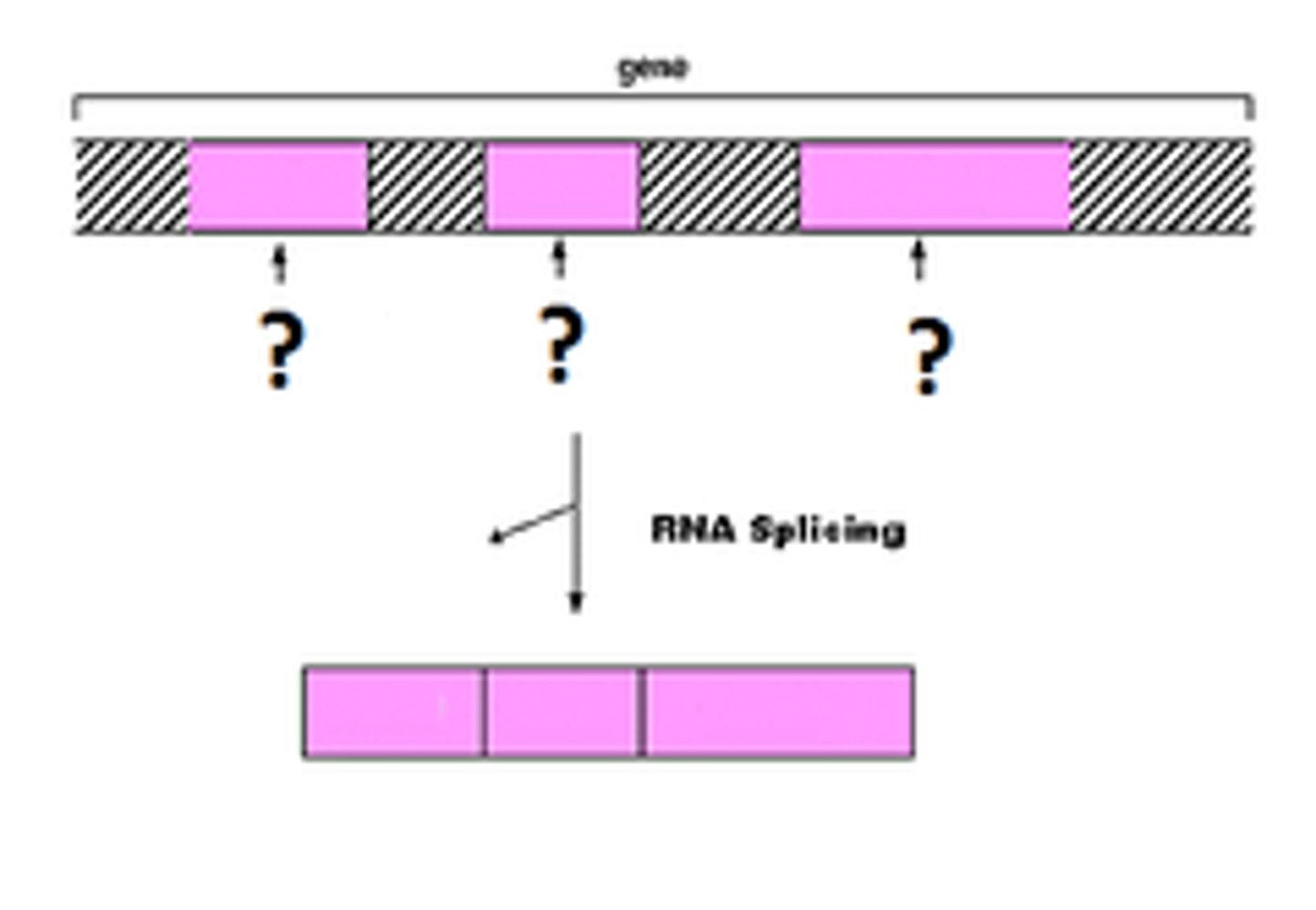
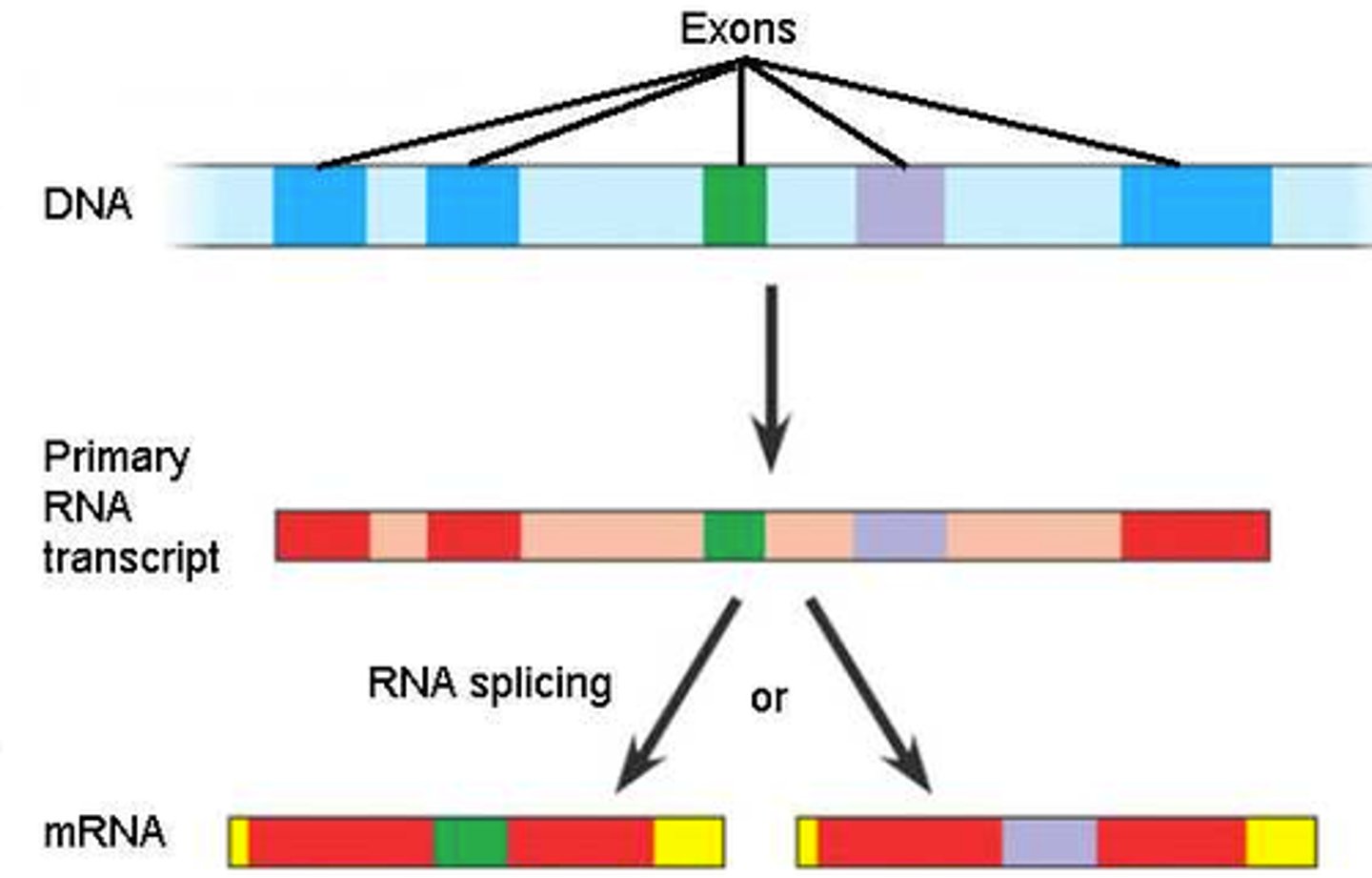
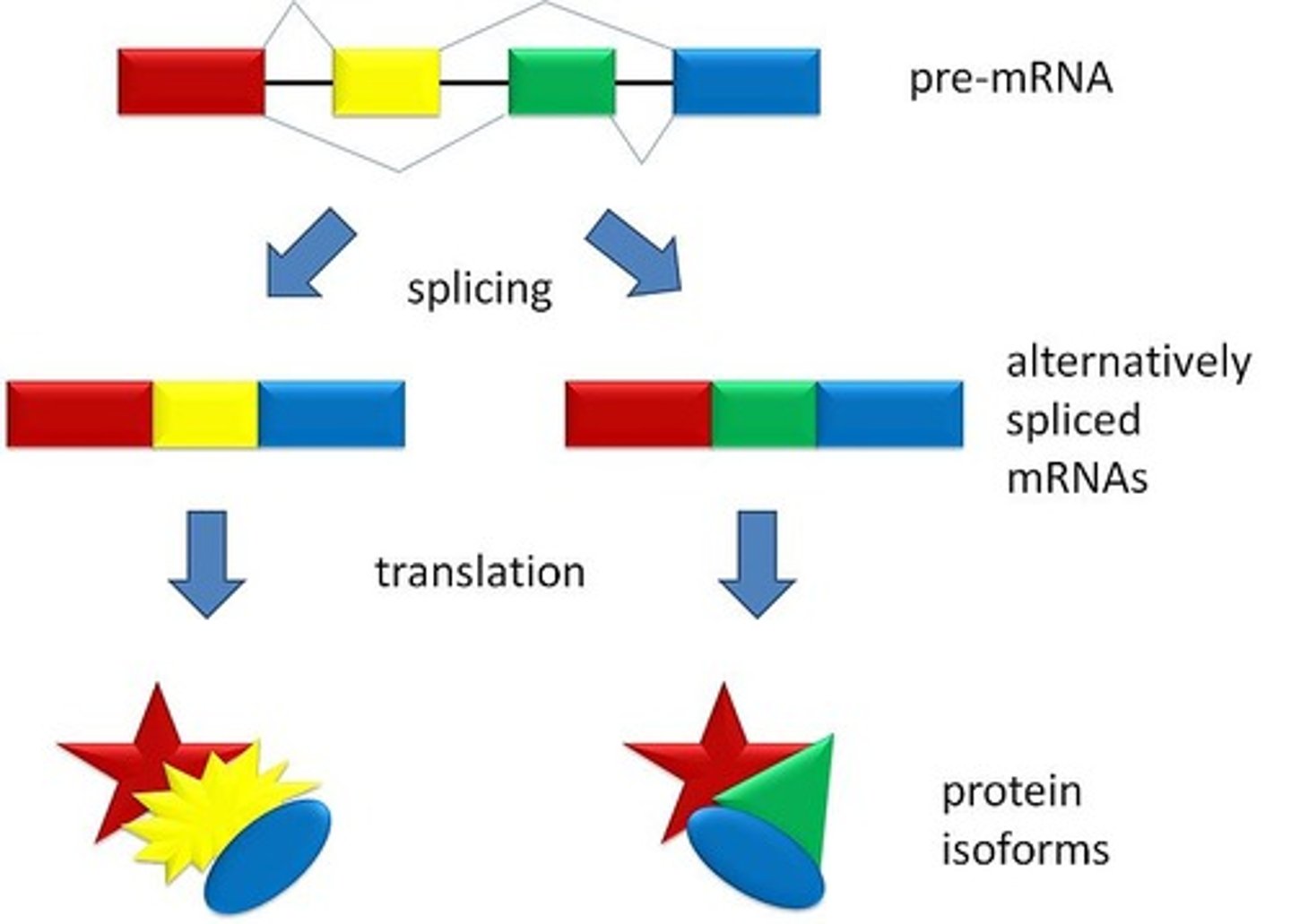
Alternative splicing
Splicing of introns in a pre-mRNA that occurs in different ways, leading to different mRNAs that code for different proteins.
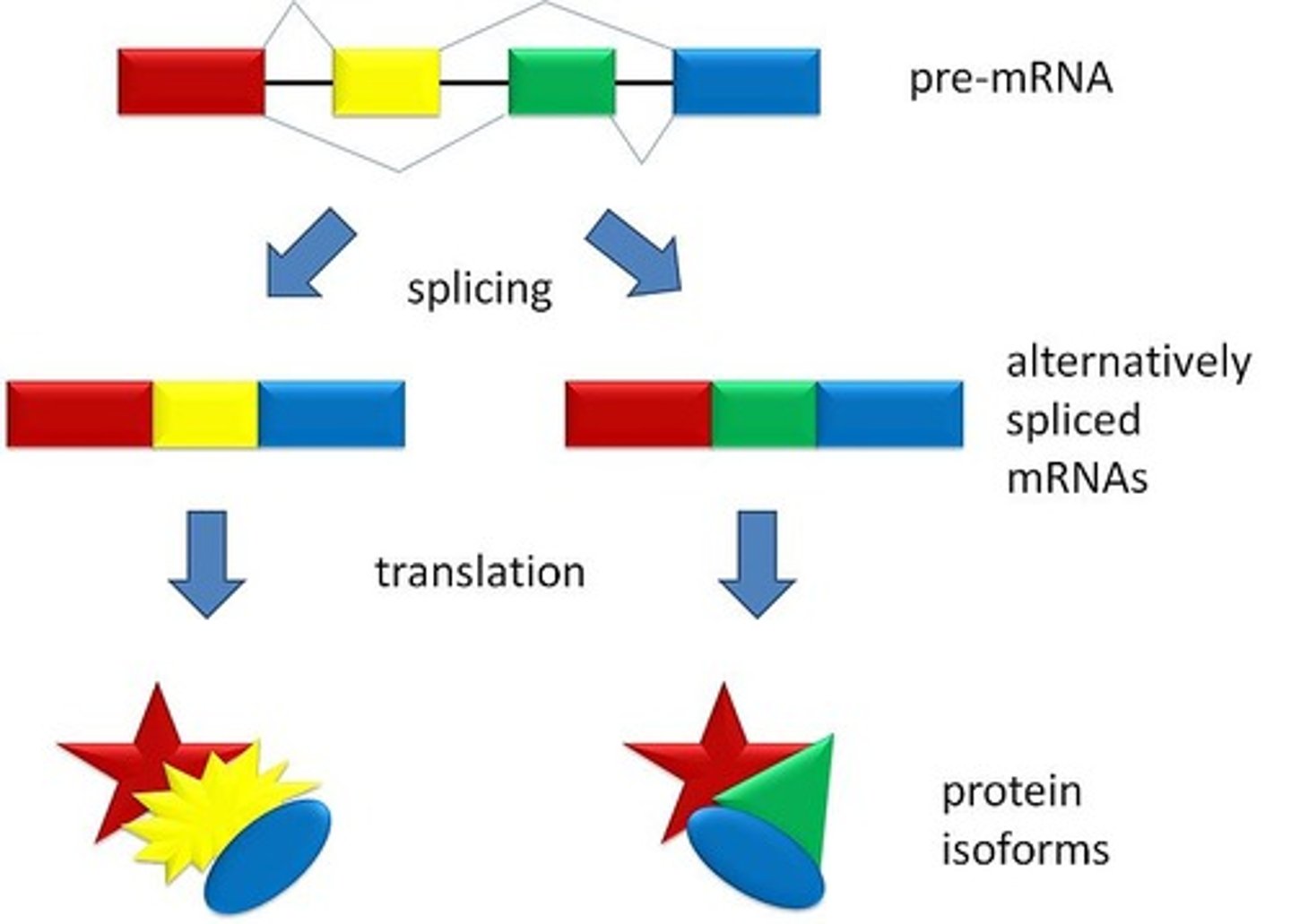
Splice variant
Different versions of a protein encoded by the same gene, but with different splicing.
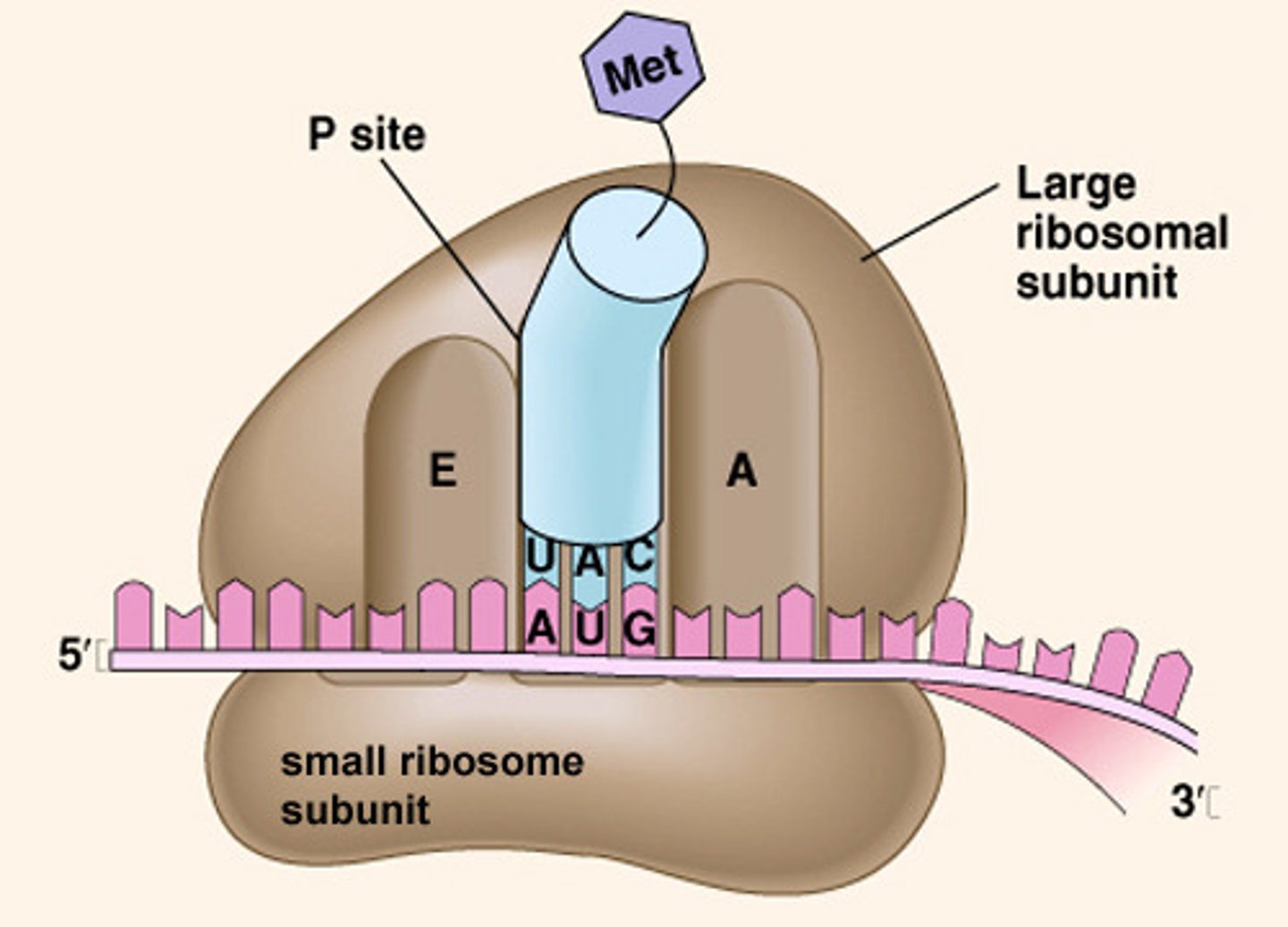
Ribosome
Enzyme complex that catalyzes translation (makes proteins)
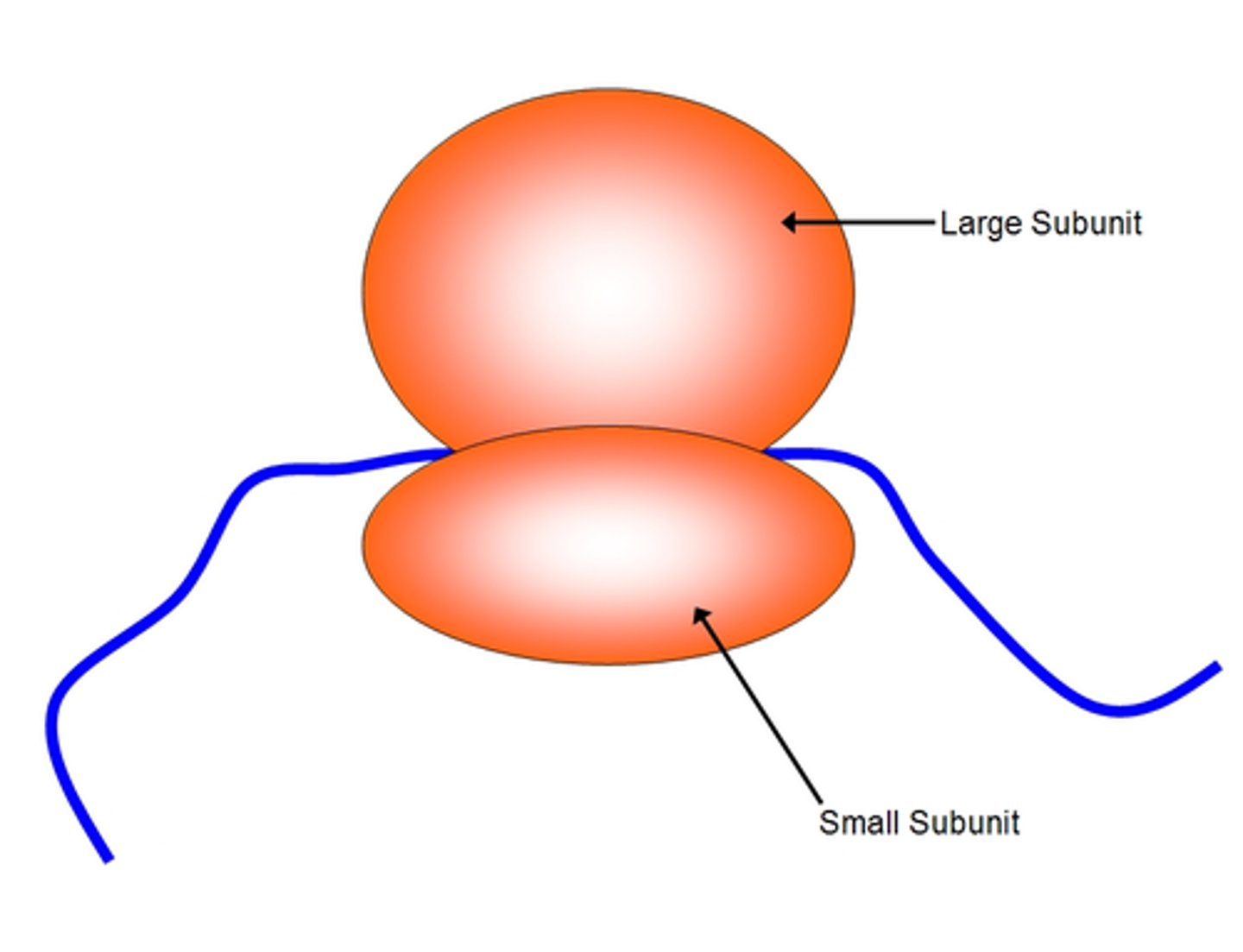
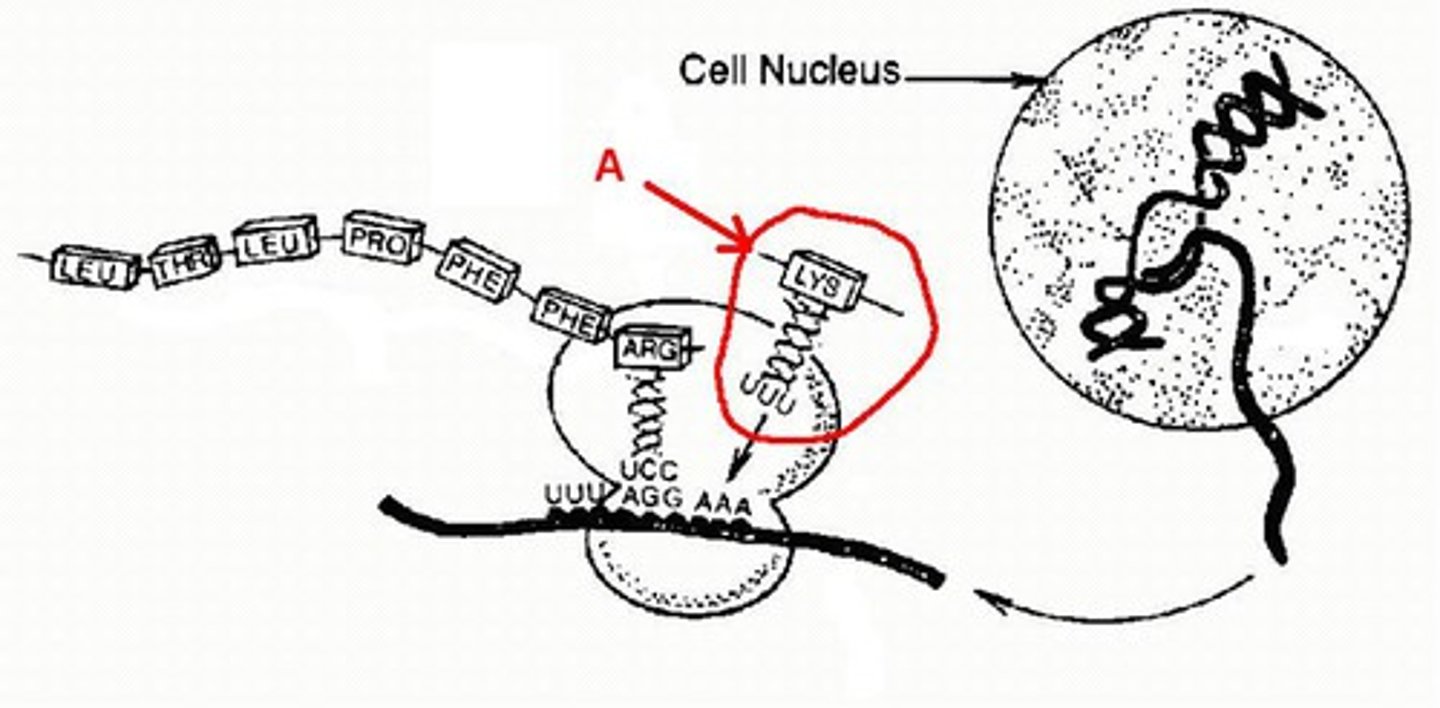
Translation
Synthesis of a protein using the instructions in mRNA
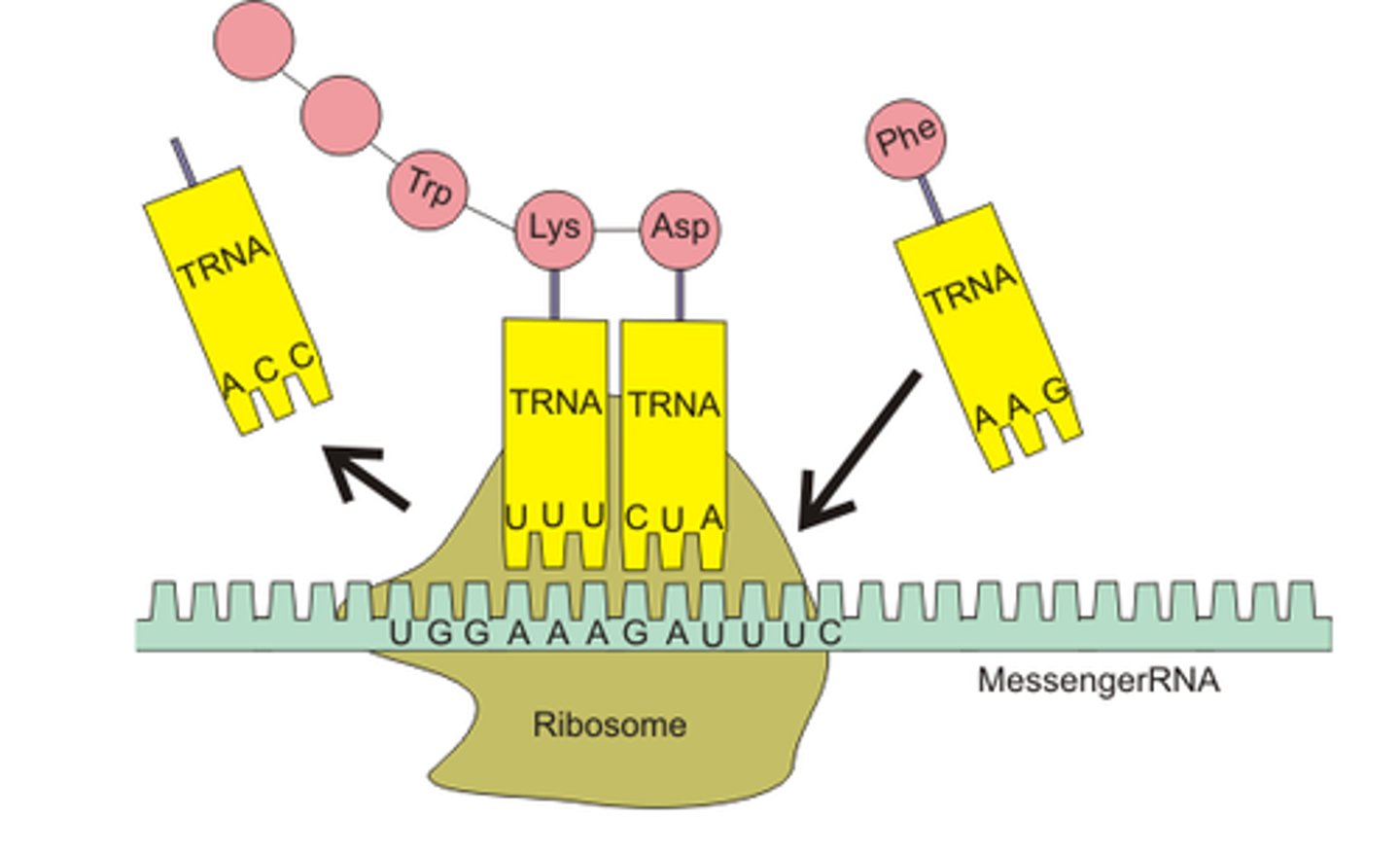
mRNA
Messenger RNA; carries information from DNA to the ribosome
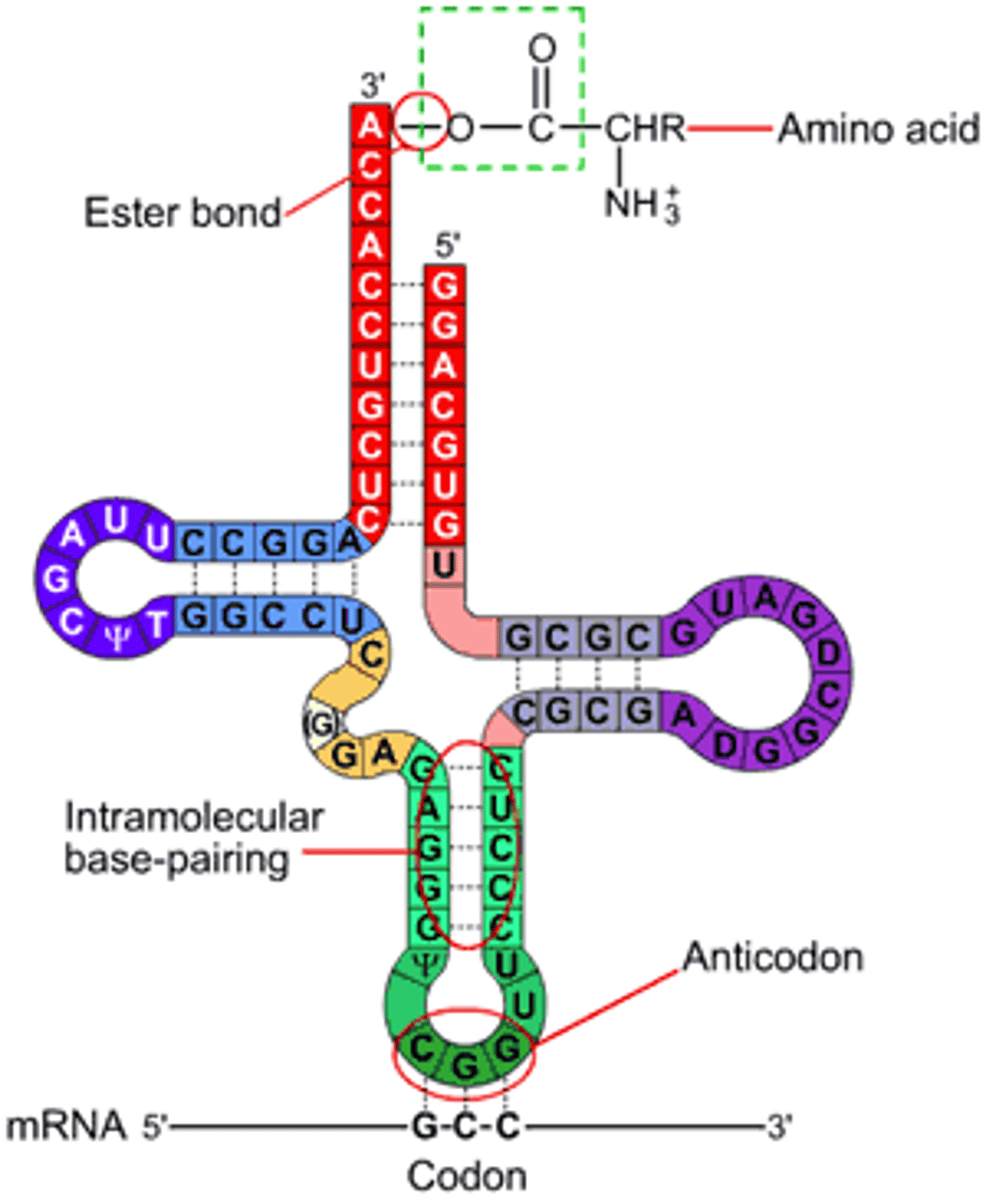
tRNA
Transfer RNA; carries amino acids to the ribosome during translation
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA; a special type of RNA that builds ribosomes
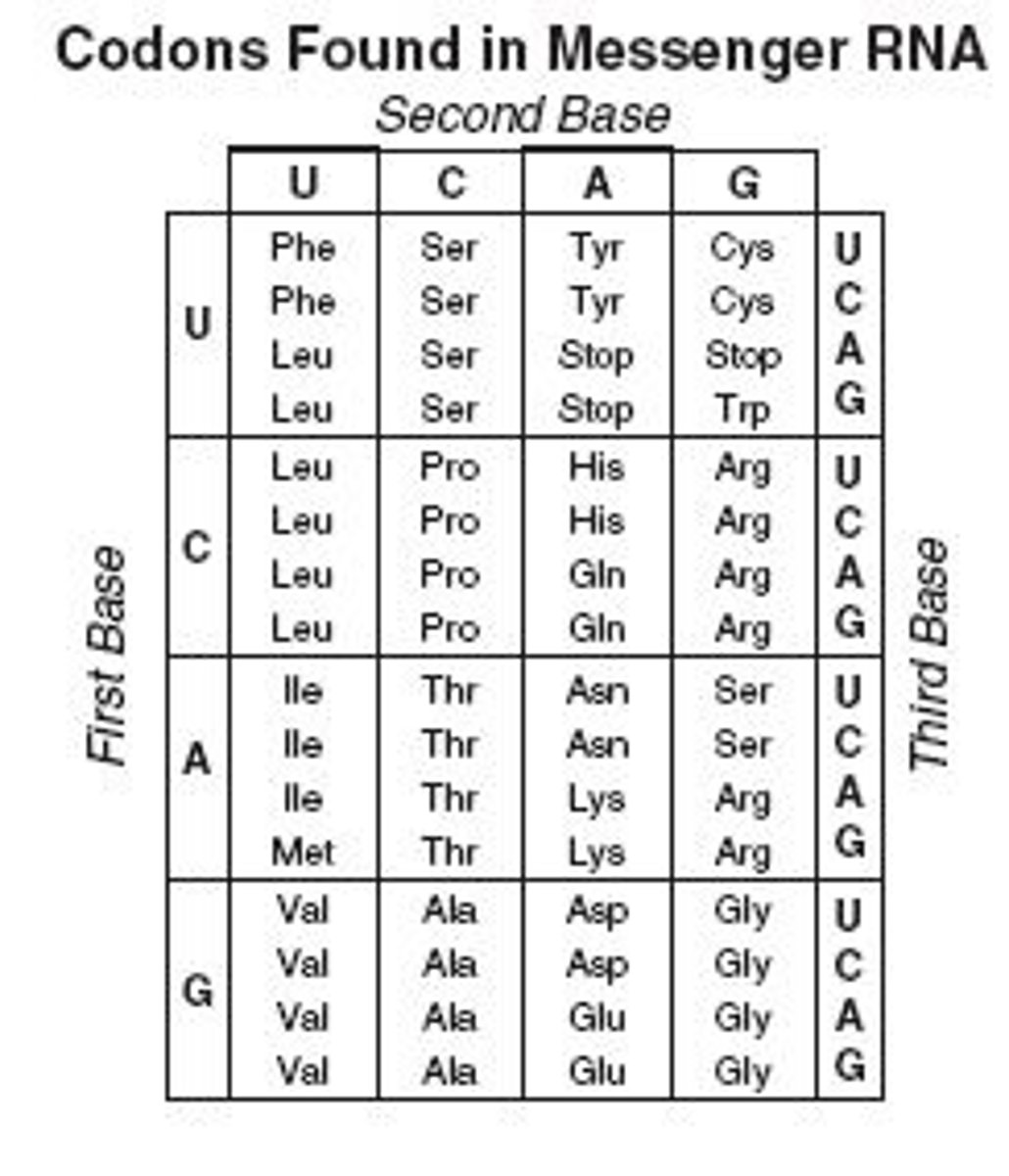
Codon
Three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
Anti-codon
Group of three nucleotides on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
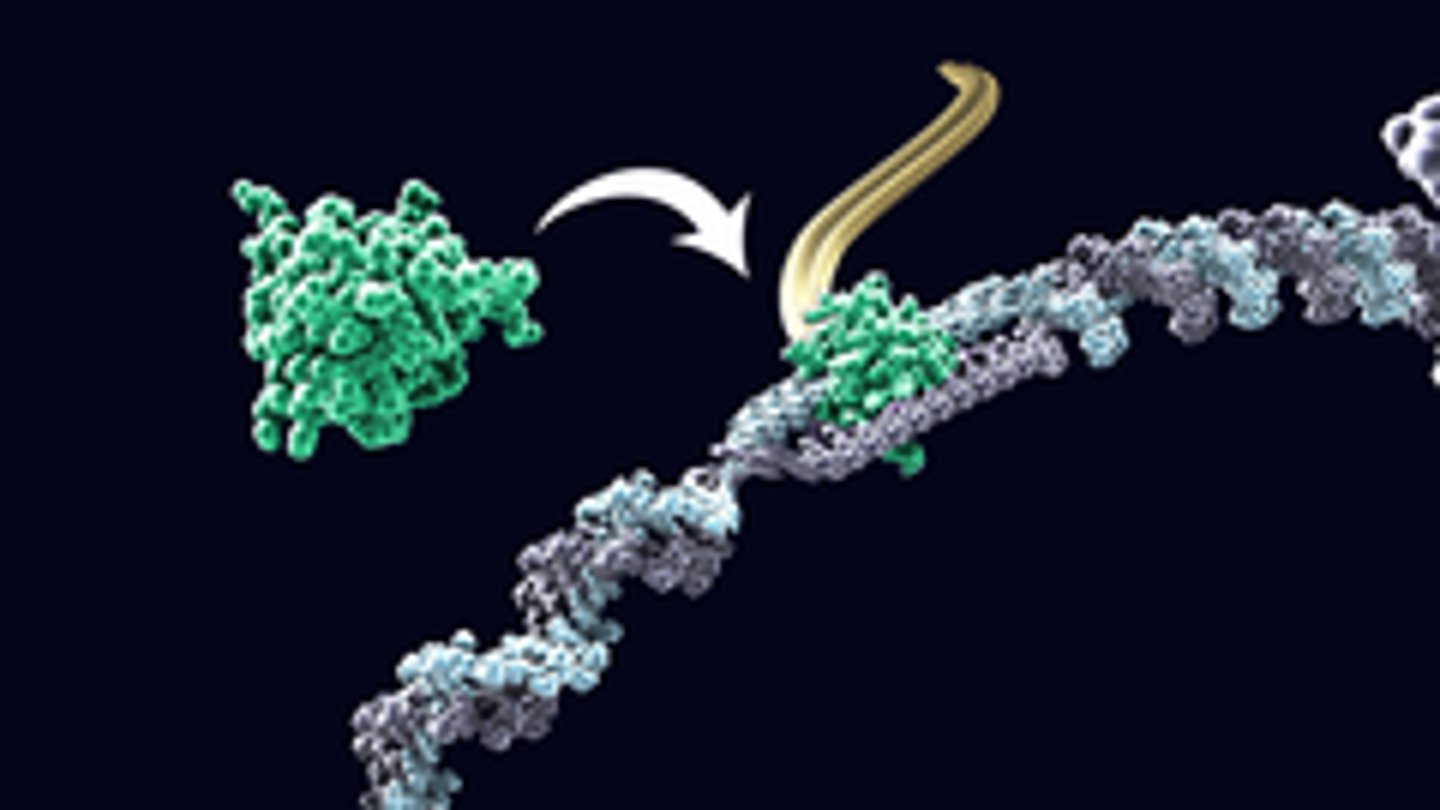
Promoter
Sequence in DNA that binds to RNA polymerase and initiates (starts) transcription
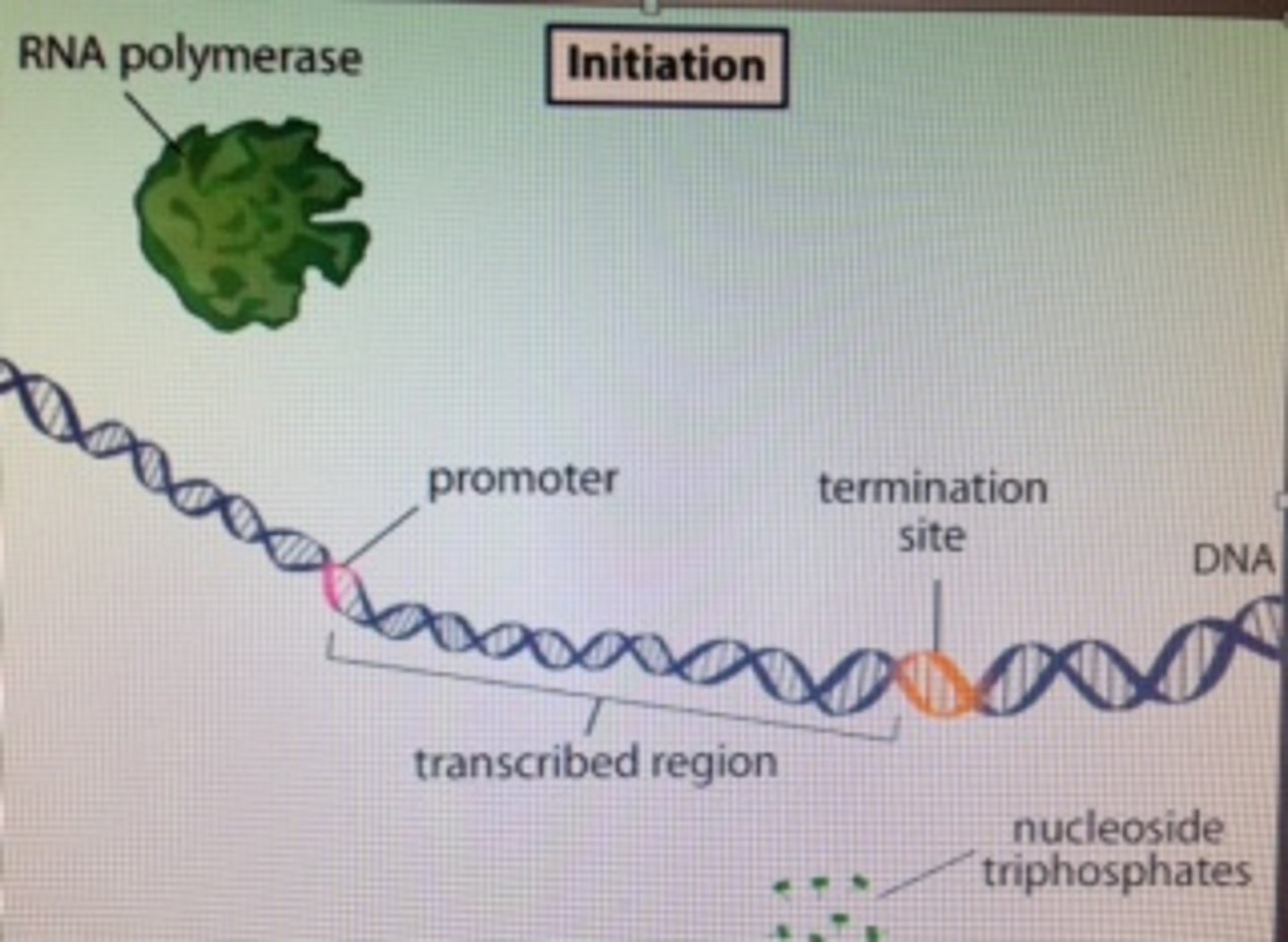
Transcription factor
Protein that helps RNA polymerase find the promoter and initiate transcription
Coding sequence
Part of a gene (DNA) that directly codes for a protein
Termination sequence
Sequence of DNA at the end of a gene that signals the RNA polymerase to stop transcribing

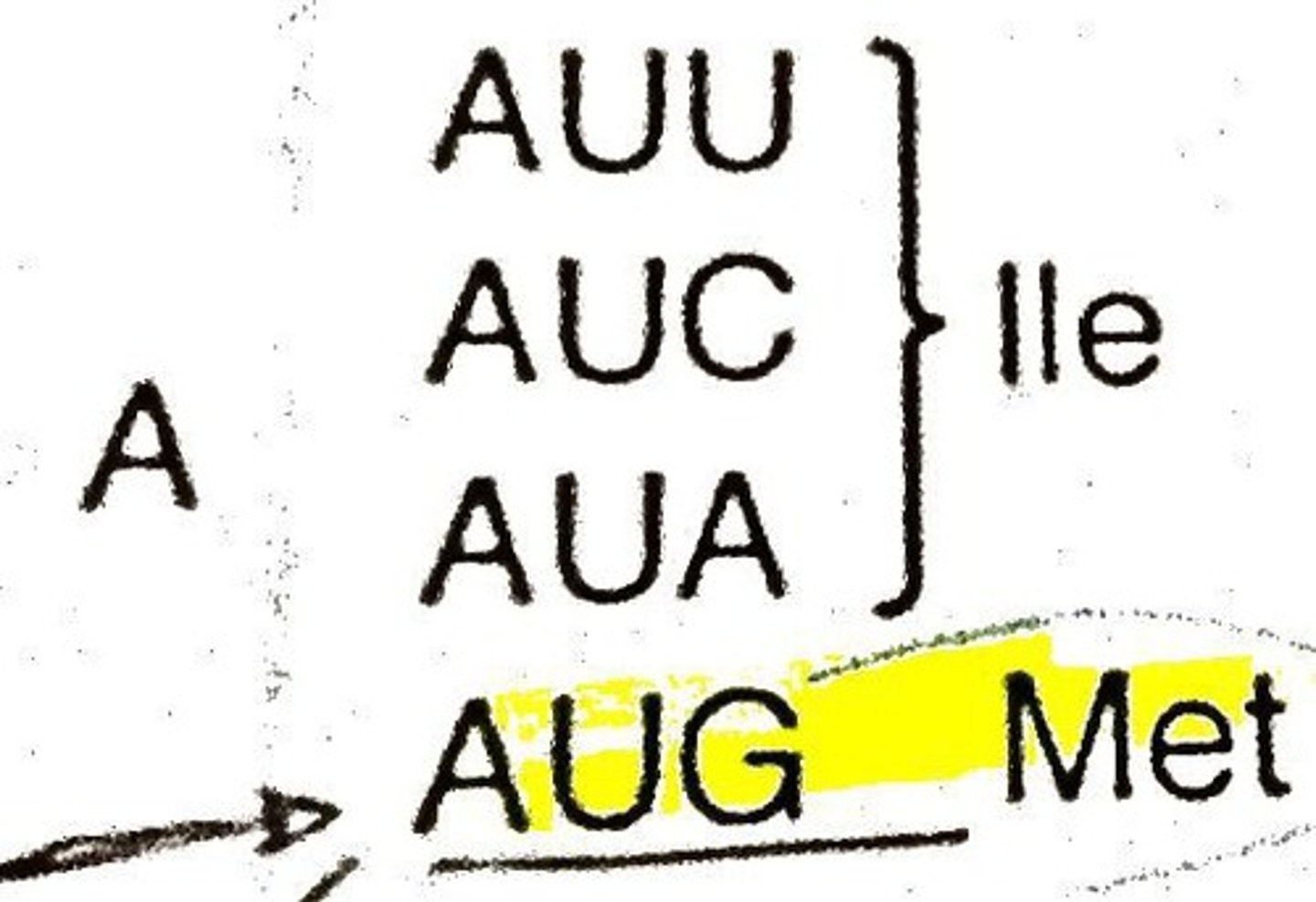
Start codon
AUG; Codon in mRNA that binds to the ribosome and initiates (starts) translation
Stop codon
Codon that signals to ribosomes to stop translation. Does NOT code for an amino acid.

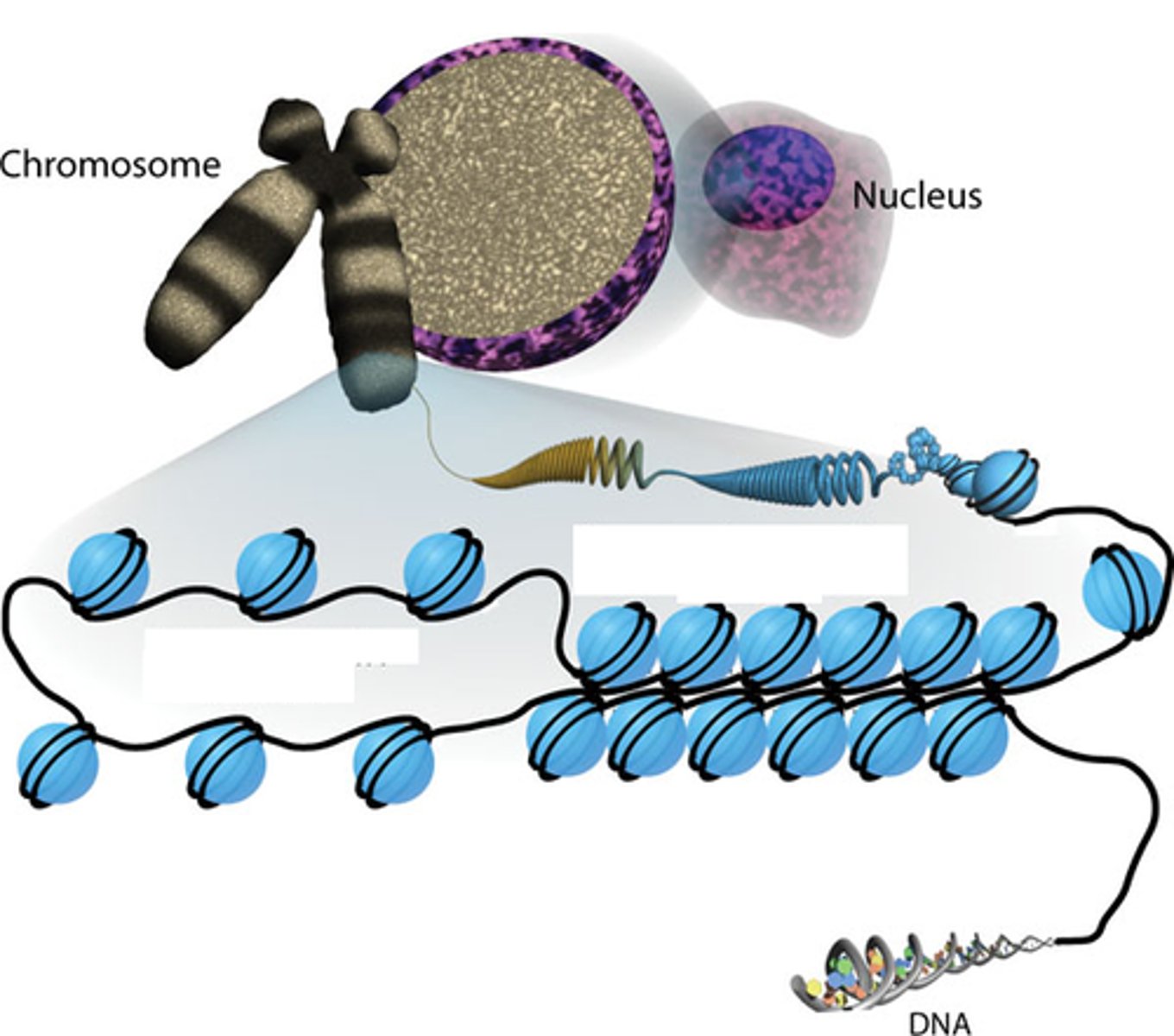
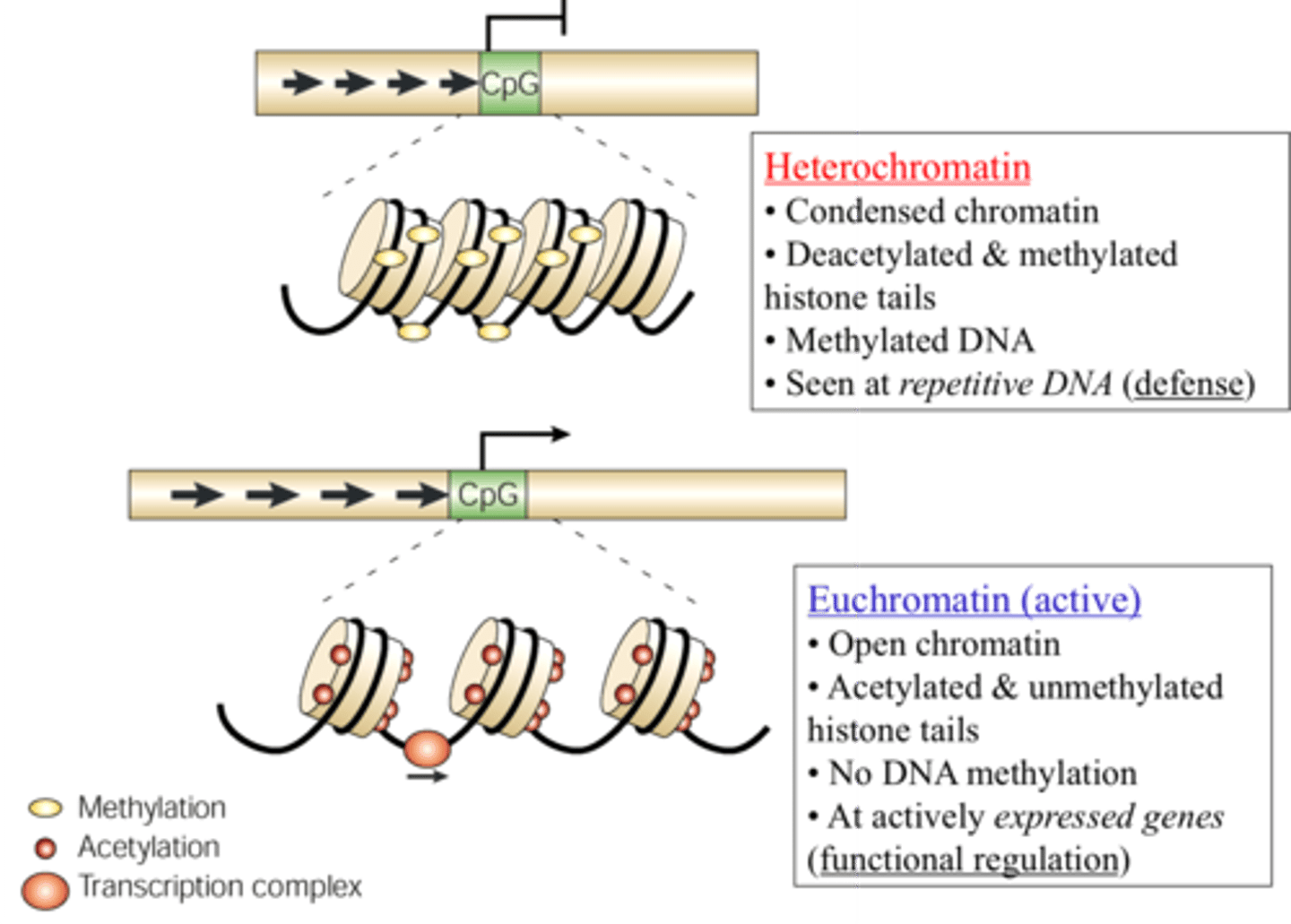
Histone
protein that DNA wraps around in eukaryotic chromosomes
Chromatin
A group of DNA-wrapped histones
Epigenetics
How DNA is organized and packaged
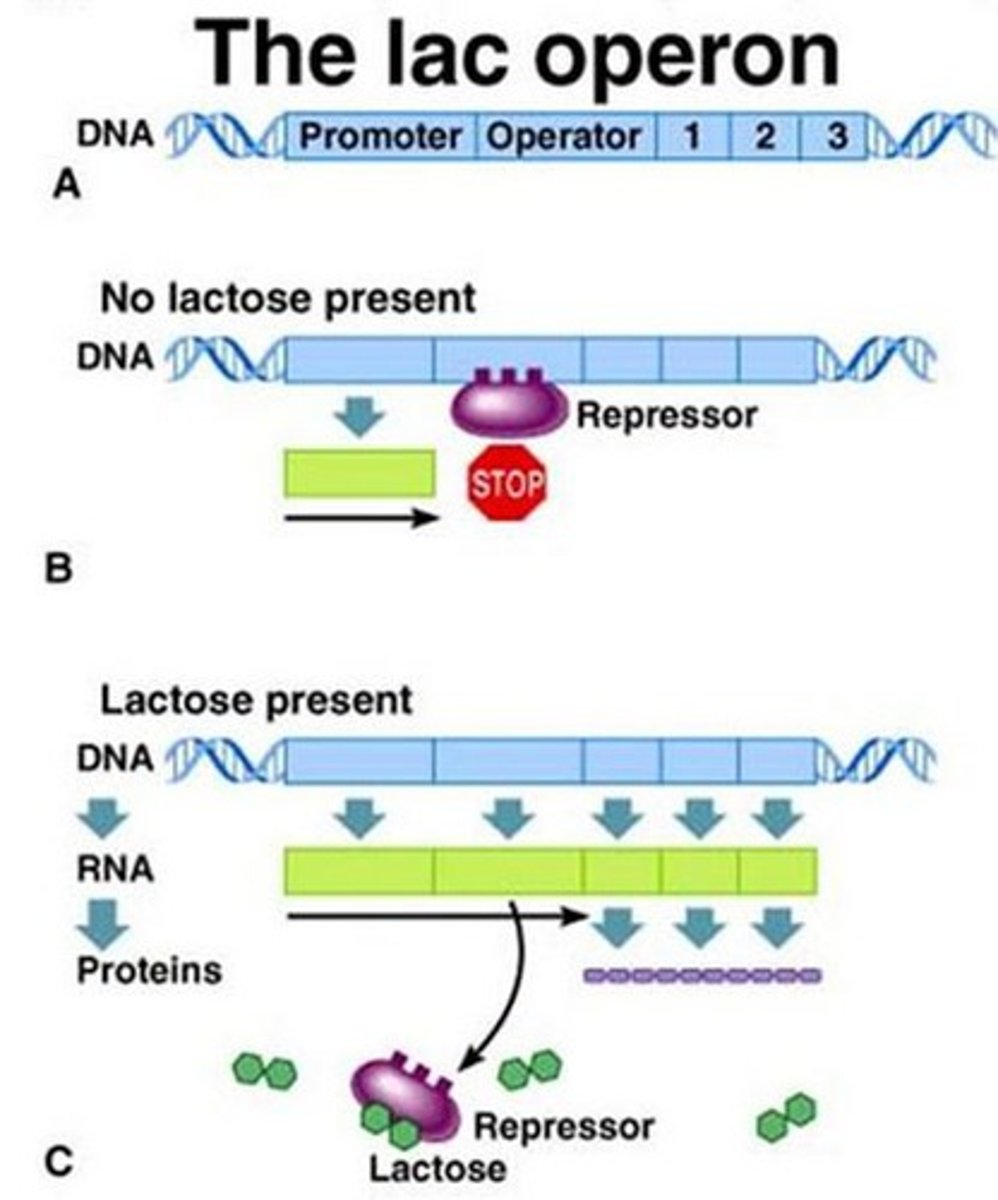
Operon
A group of genes that are all regulated together as a unit; more common in prokaryotic cells
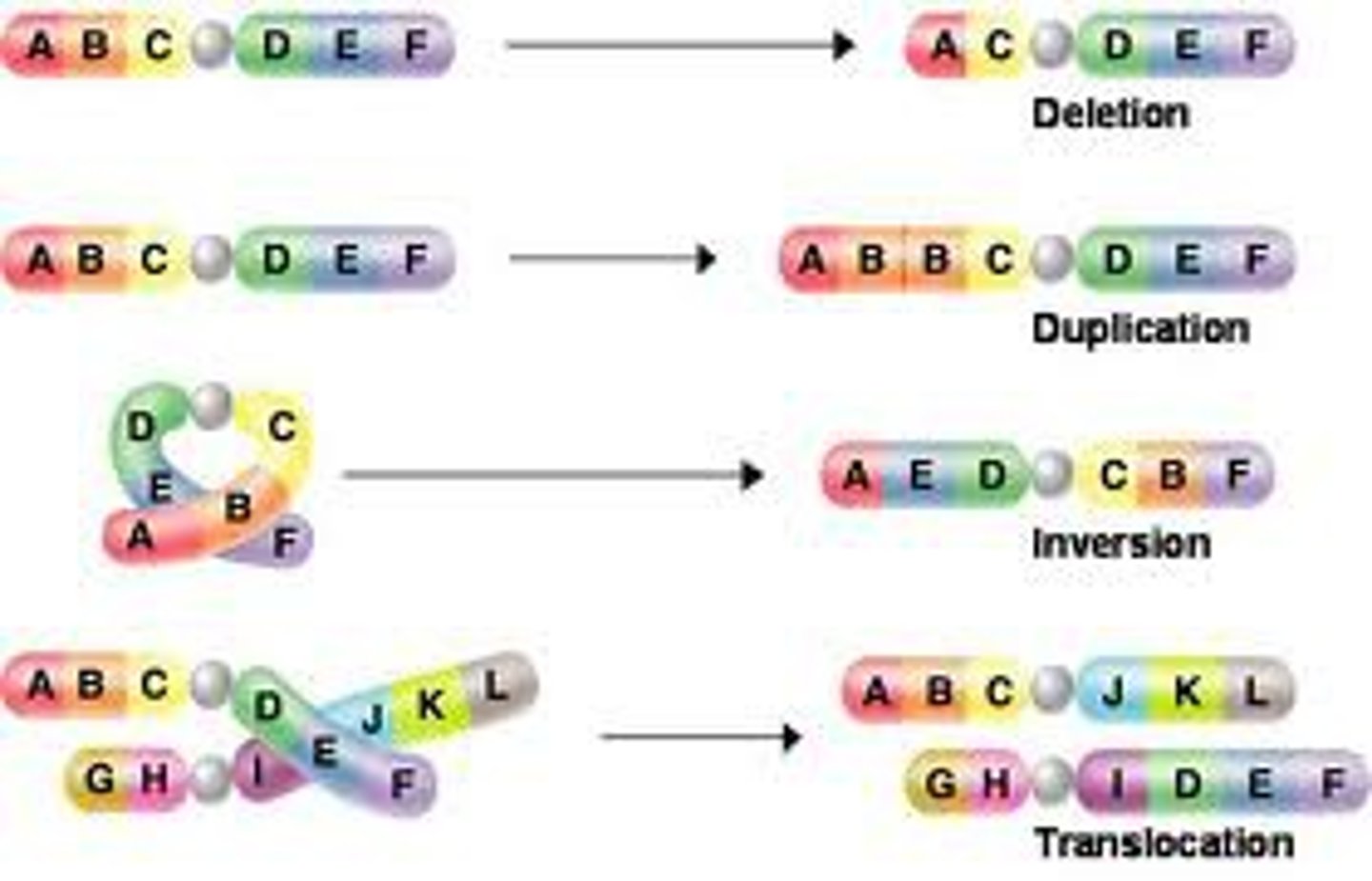
Mutation
Change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA
Point mutation
Gene mutation in which a single nucleotide in DNA is changed

Silent mutation
Mutation that changes a single DNA nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created.
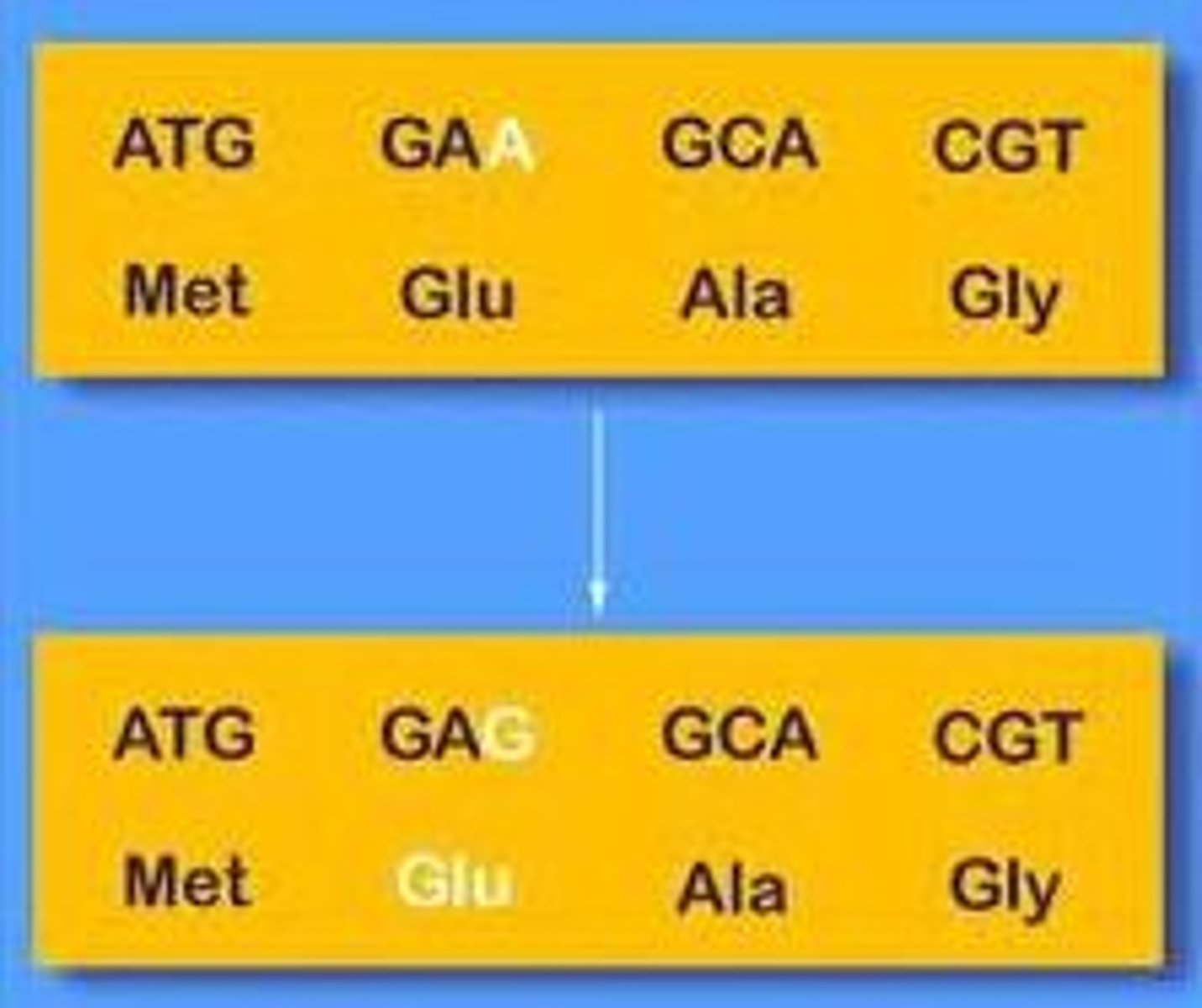
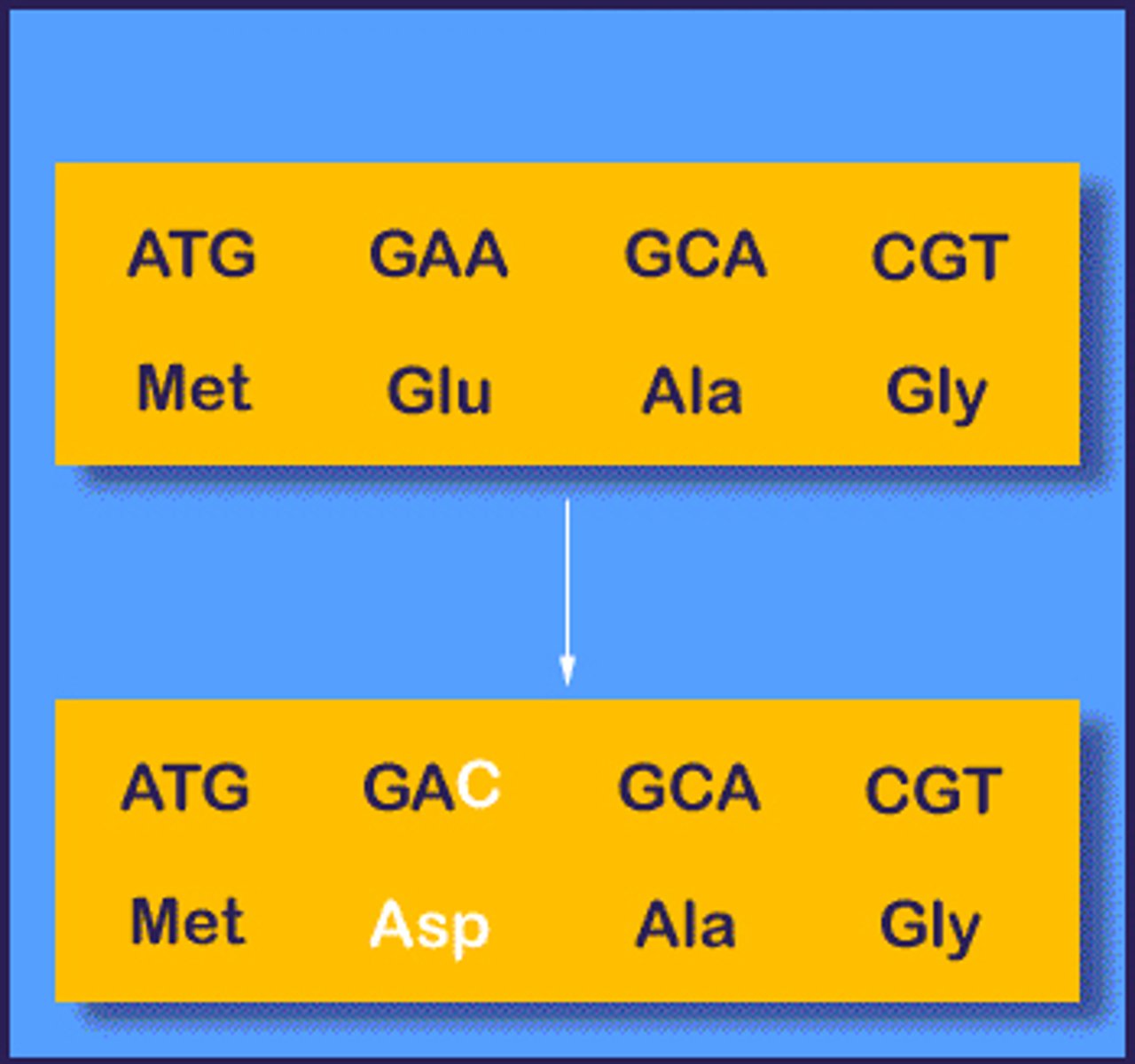
Missense mutation
Mutation that changes a single DNA nucleotide, and the mutated codon specifies a different amino acid.
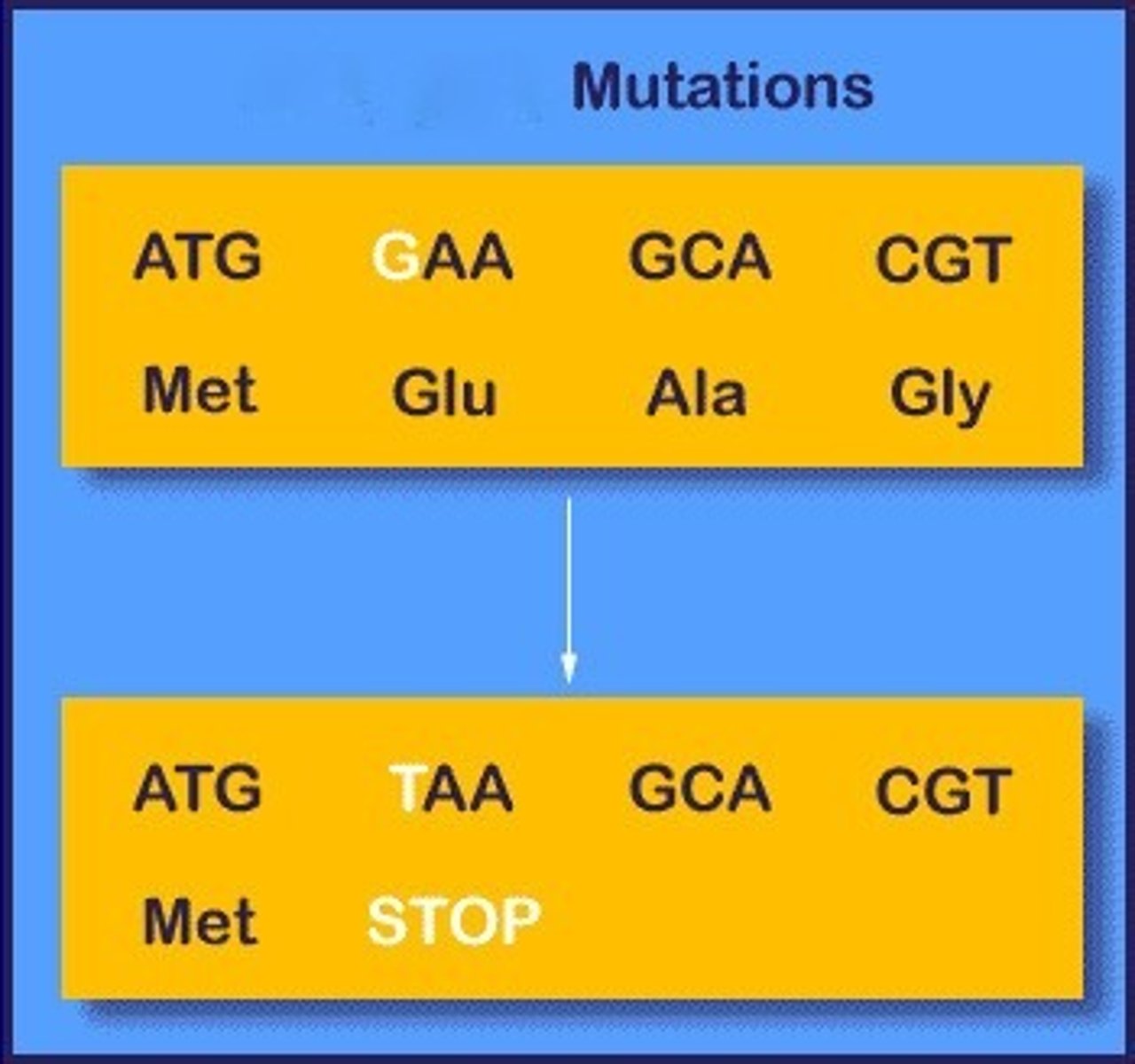
Nonsense mutation
Mutation that changes a single DNA nucleotide, and the mutated codon results in a pre-mature stop codon.
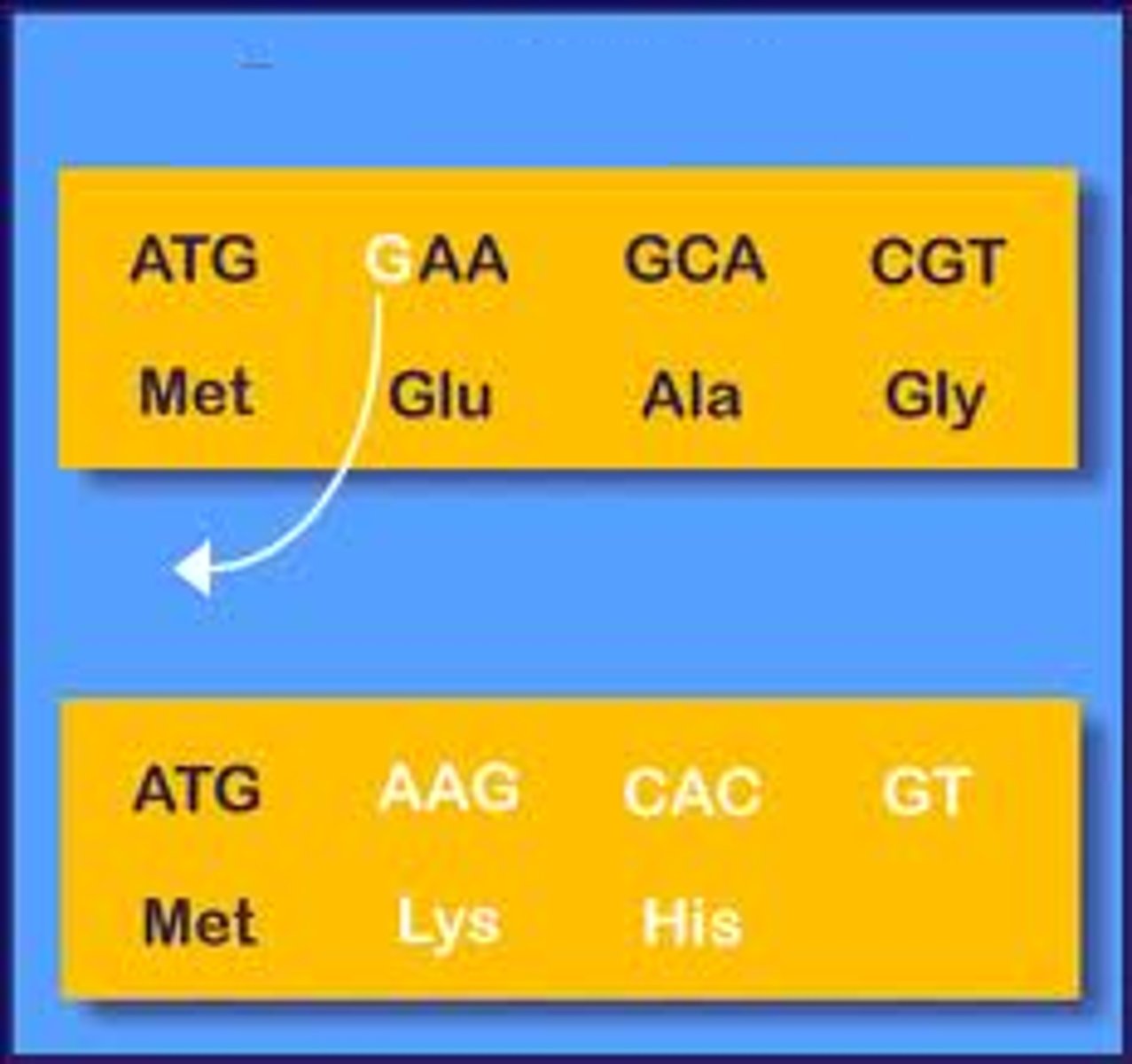
Frameshift mutation
Mutation that involves the insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in the DNA sequence, thus changing the codon reading frame after the mutation
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself.
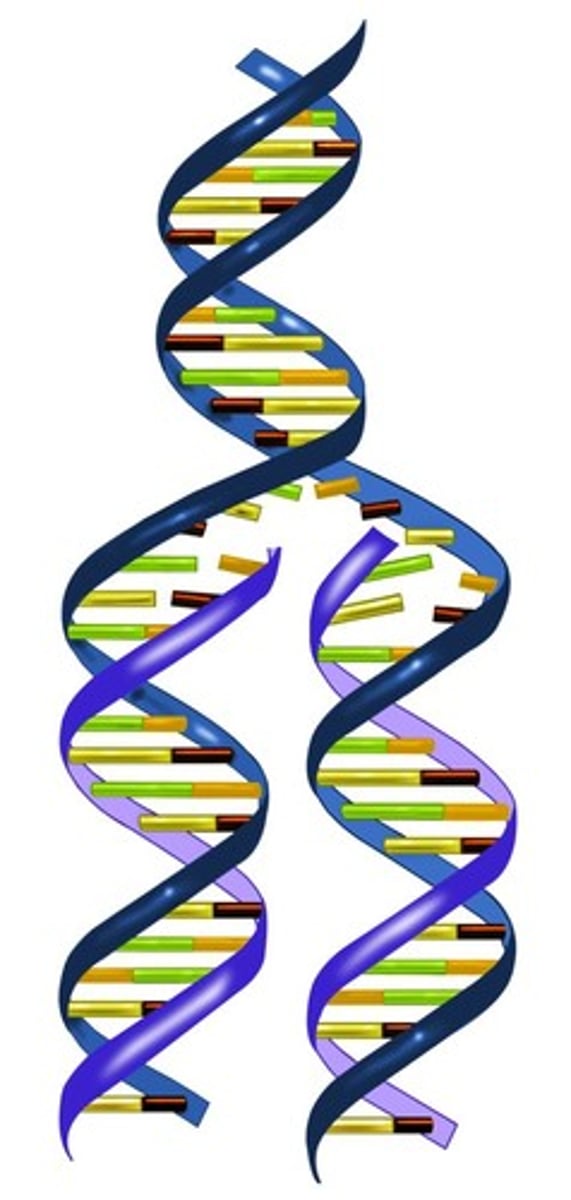

Semi-conservative
In each new DNA double helix made during DNA replication, one strand is from the original DNA molecule and the other strand is newly synthesized.

S phase
Phase of the cell cycle when DNA replication occurs
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that relieves strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork
Helicase
An enzyme that unzips the two strand of DNA, forming a replication fork
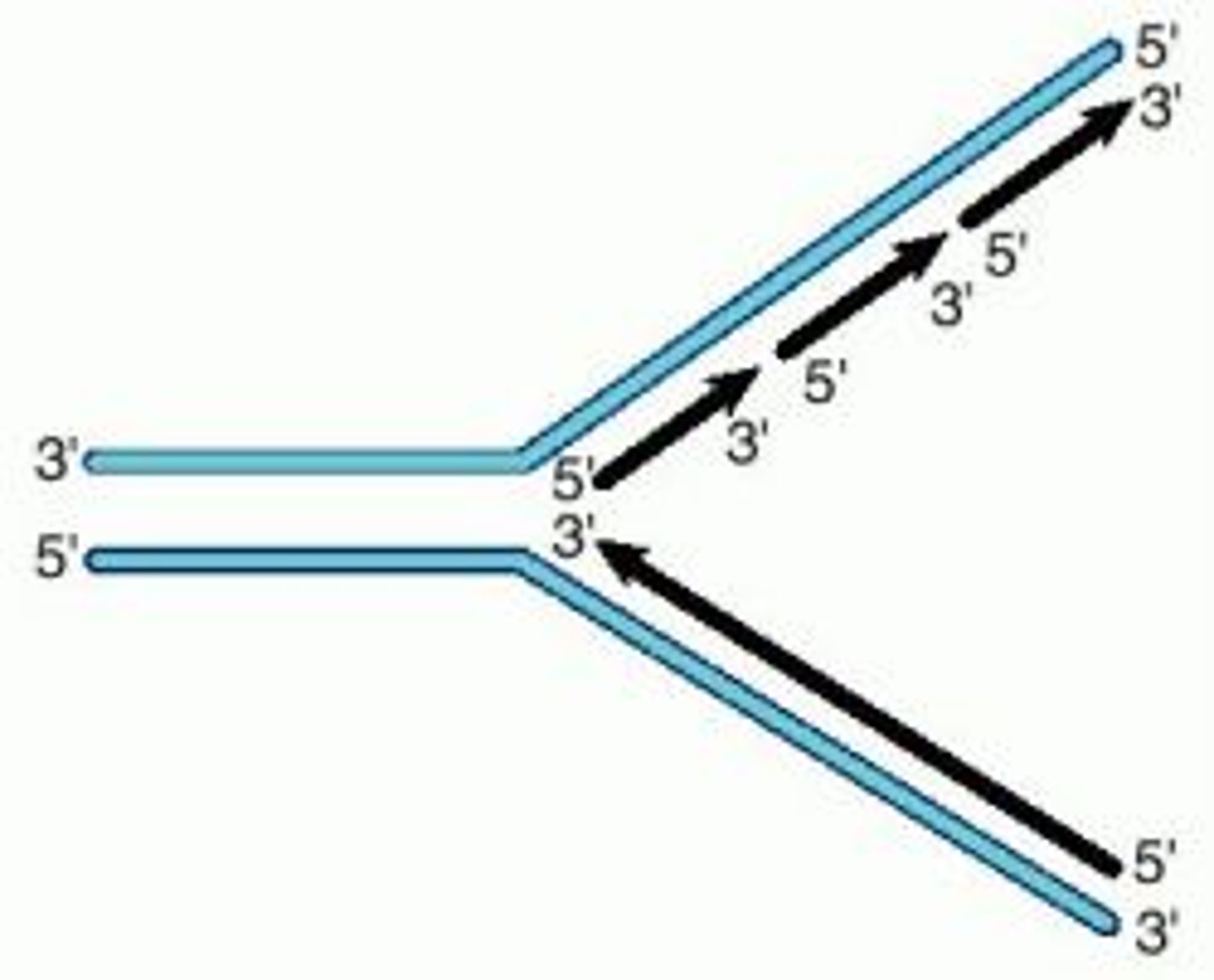
Replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new DNA strand are being formed
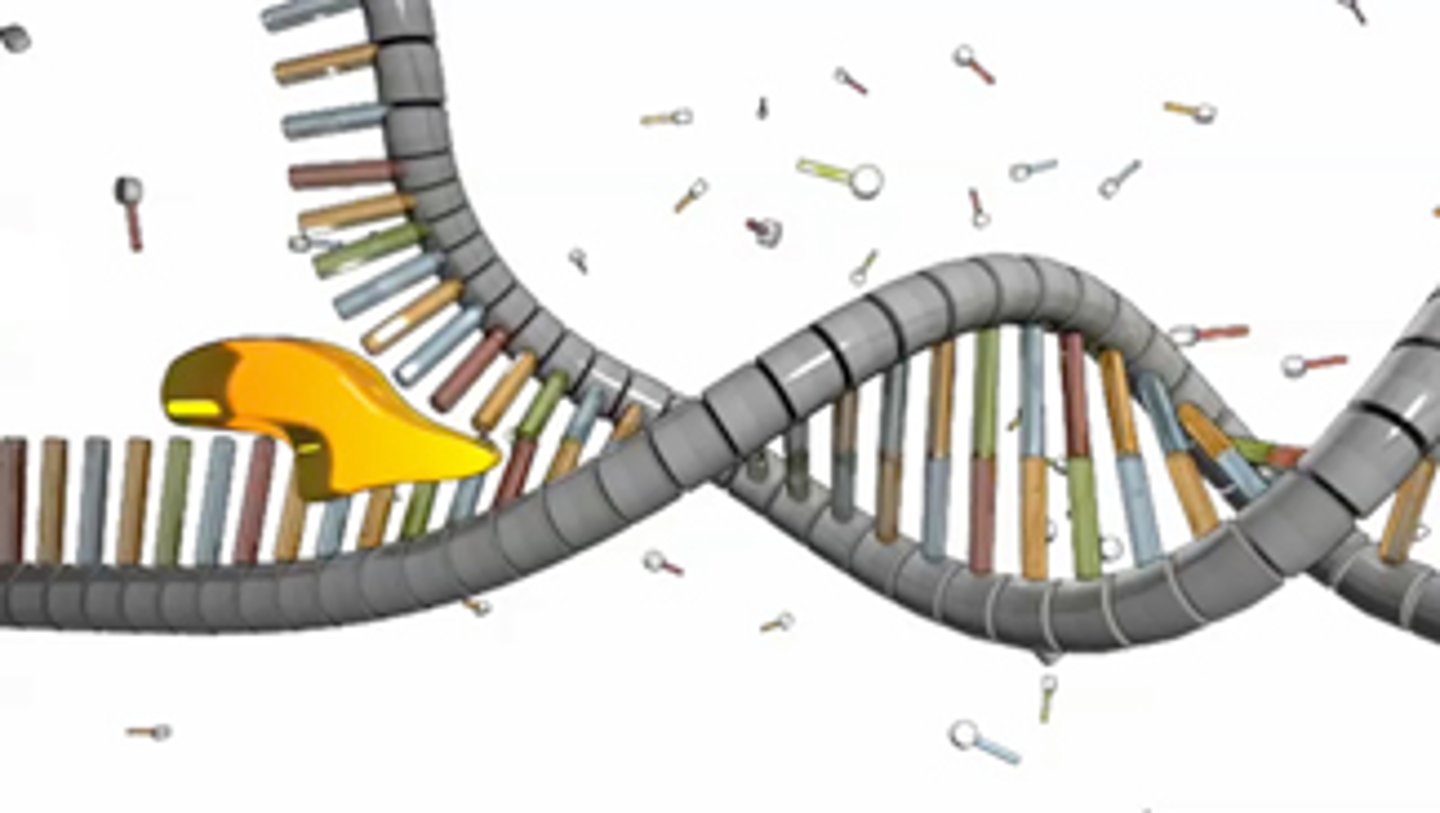
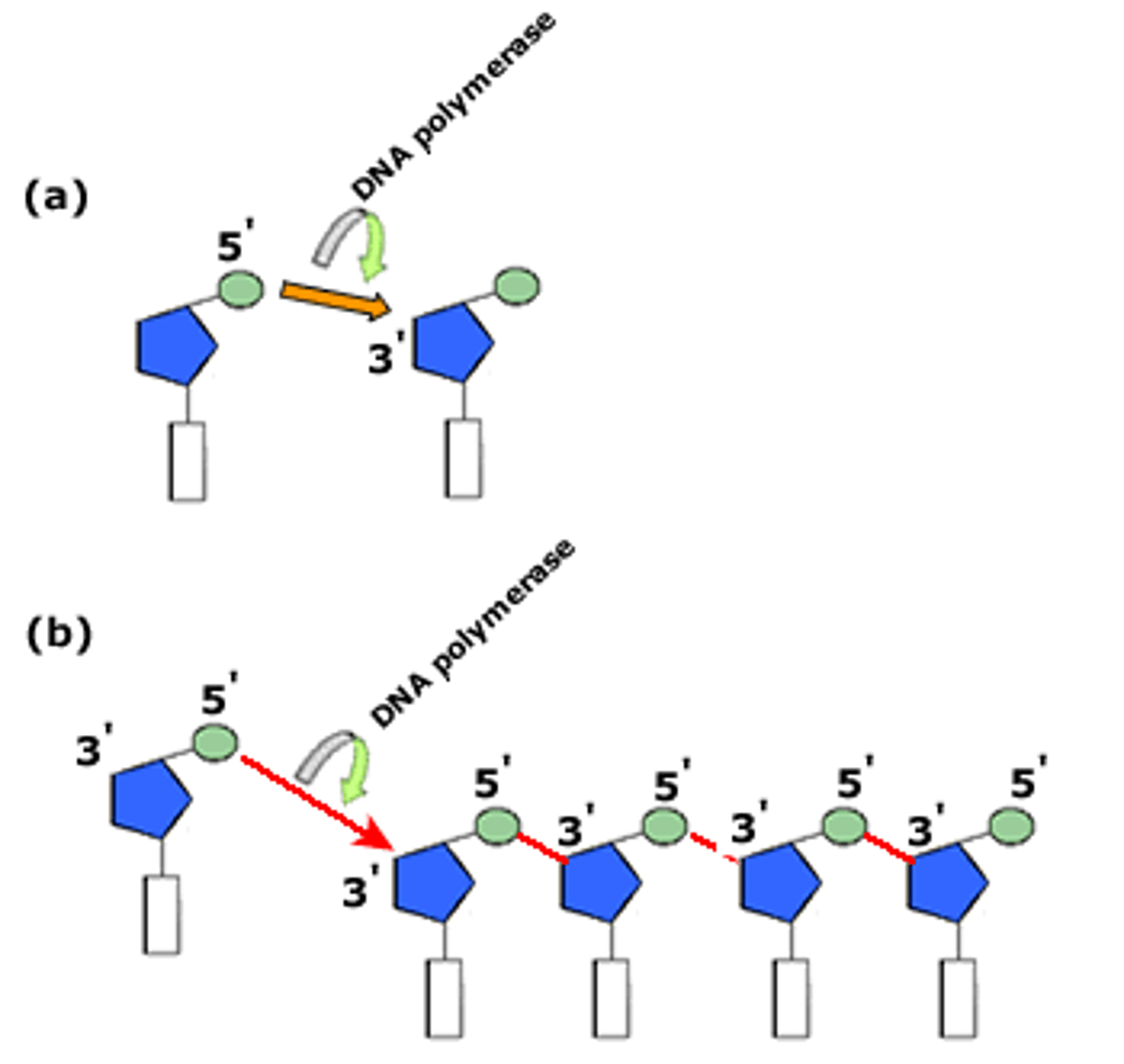
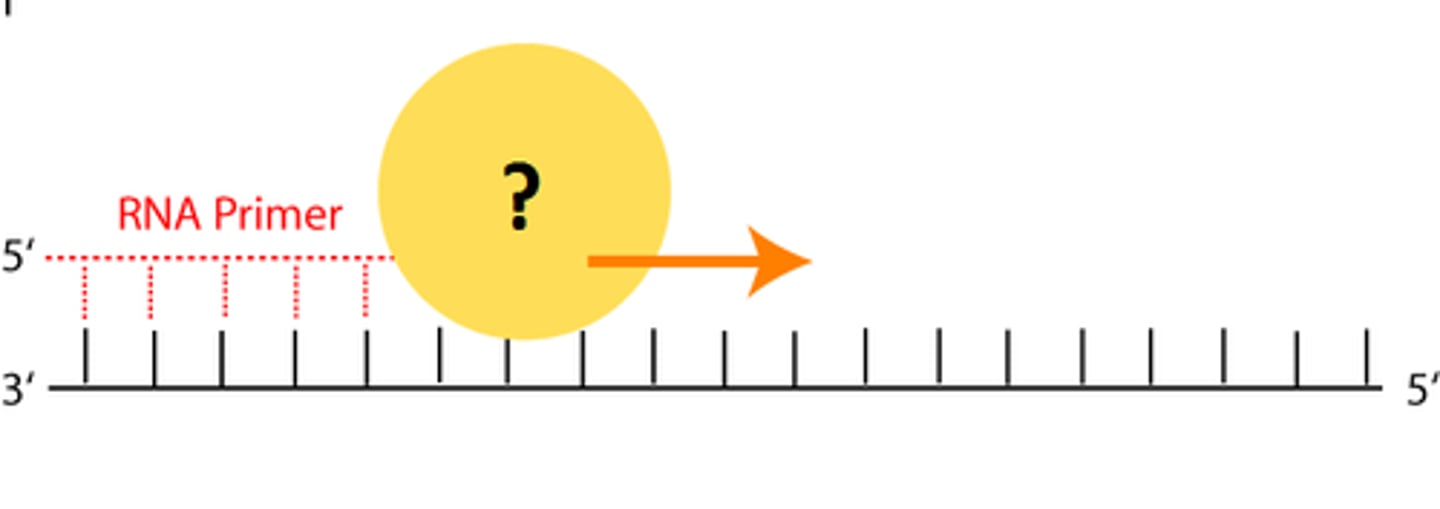
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that joins synthesizes DNA by joining nucleotides together with covalent bonds; always synthesizes DNA in the 5' -> 3' direction
5' to 3' direction
The only direction that DNA polymerase can synthesize DNA; it does so by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a DNA strand.
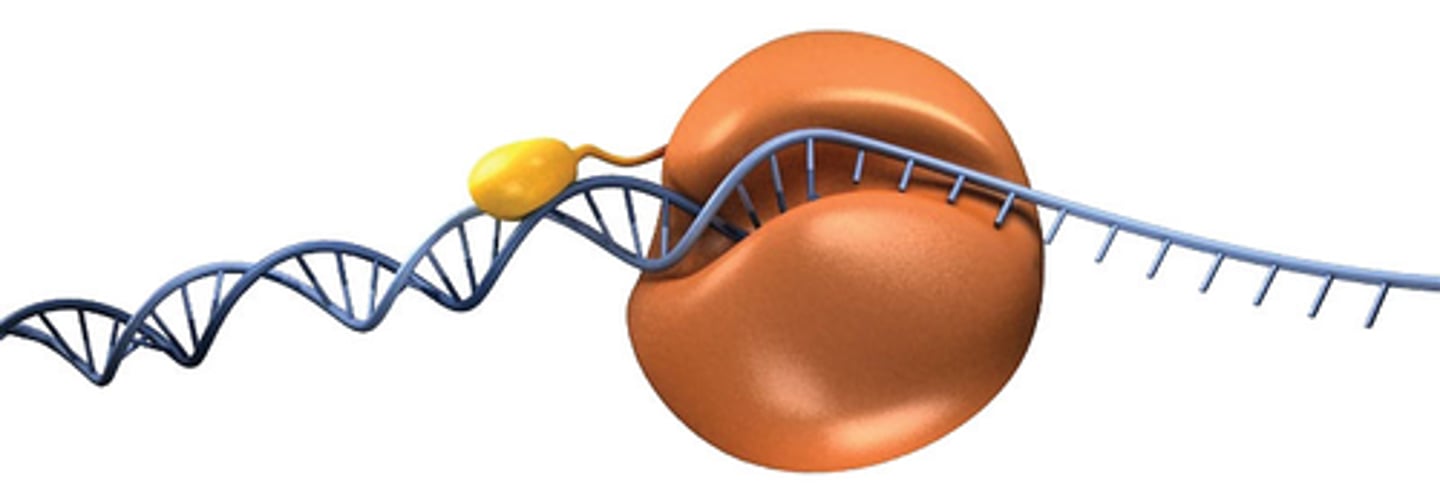
Primase
Enzyme synthesizes an RNA primer that is required for DNA polymerase to begin DNA synthesis
Ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment

Leading strand
Newly synthesized DNA strand that is made in one continuous piece
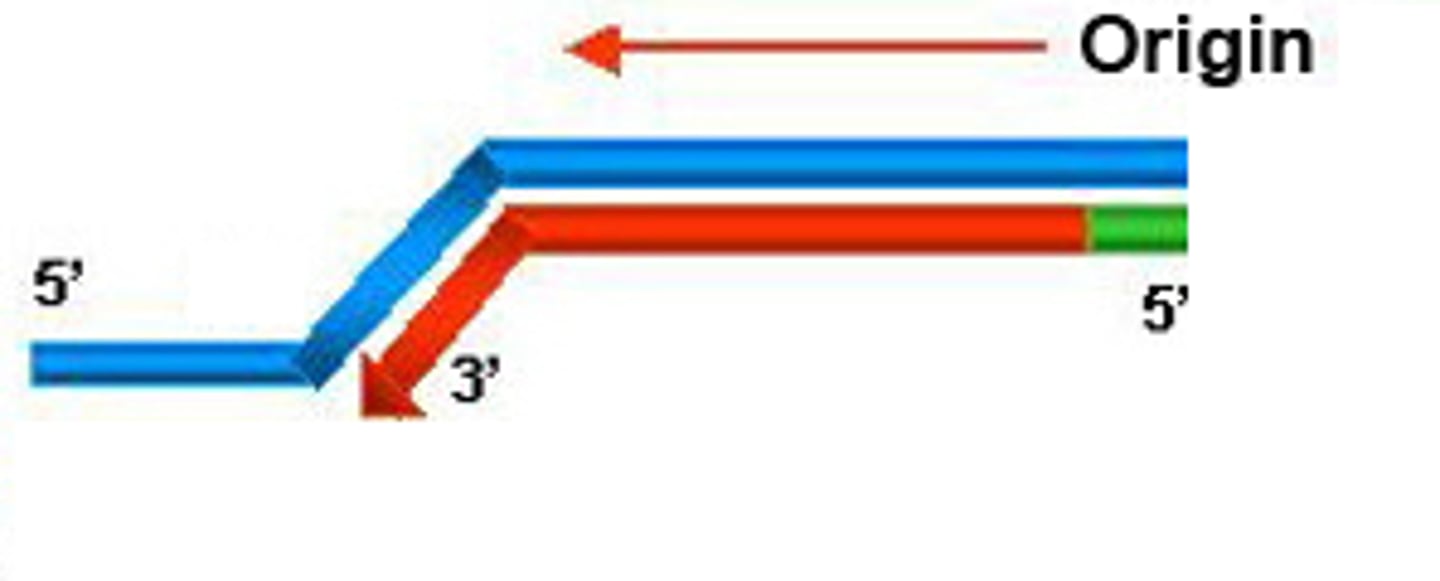
Lagging strand
Newly synthesized DNA strand that is made in multiple sections called Okazaki fragments
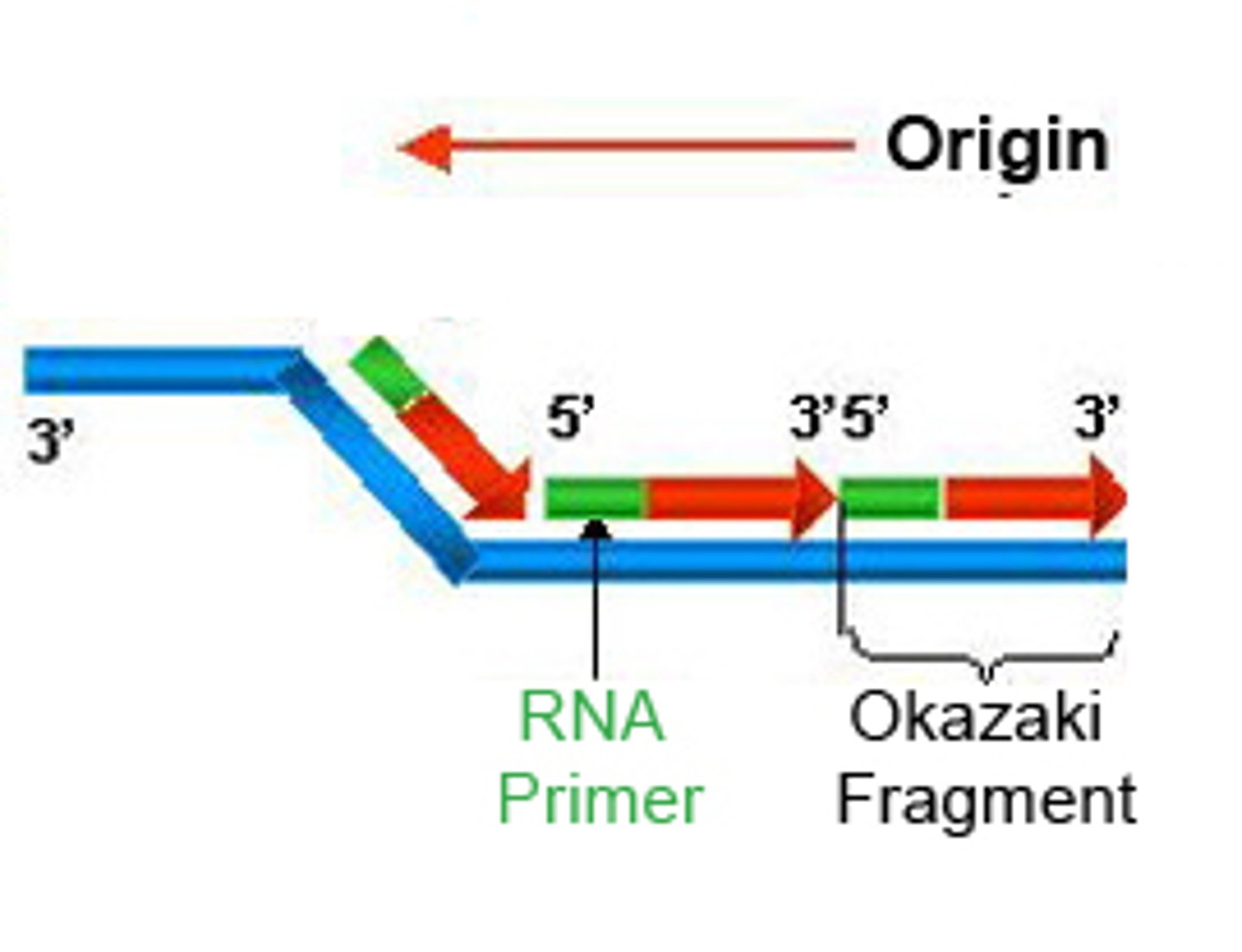
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by ligase to form a complete strand
