Antiarrhythmics- Austin and his student
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What adrenergic receptor controls the heart?
b1
T/F The atria and ventricles contract independently of each other.
T
What is the missing step in the following conduction pathway?
SA nodes serves as pacemaker
atria contract
signal _________________
conduction then spreads rapidly/uniformly
ventricular contraction
signal delayed at AV node
Answer the following about electrolyte channels and cardiac APs:
Electrolyte | in or out of the cell | depolarize or polarize |
|---|---|---|
K+ | ||
Na+ | ||
Ca2+ |
Electrolyte | moves in or out of the cell | depolarize or polarize |
|---|---|---|
K+ | out | polarize |
Na+ | in | depolarize |
Ca2+ | in | depolarize |
T/F: All muscle cells in the body contain a plateau phase in their AP.
F- cardiac myocytes ONLY MUSCLE W/ plateau
What node is the most important for normal heart rate control?
SA node
SA node is influenced primarily by the slope of phase ___ depolarization.
4
How does sympathetic activation effect heart rate, threshold potential, action potentials, and depolarization?
Heart rate= INCREASE
Threshold potential= DECREASE
Action potential duration= SHORTER
Depolarization= FASTER
Arrhythmias may be caused by…
anatomical defects
electrolyte imbalances
ischemia
stress
caffeine, smoking, decongestants
What are the symptoms of arrhythmias?
Dyspnea (SOB)
Dizziness
Fatigue
Syncope
Angina
Palpitations
What is the difference between a tachyarrhythmia and a bradyarrhythmia?
tachyarrhythmia- increased firing rate (>100 bpm)
bradyarrhythmia- decreased firing rate (<60 bpm)
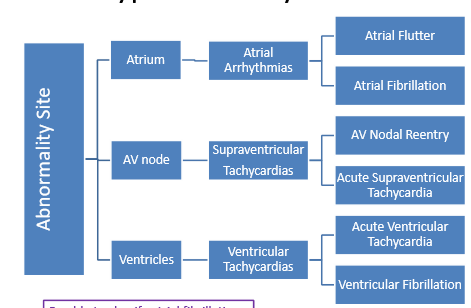
Be familiar with this chart
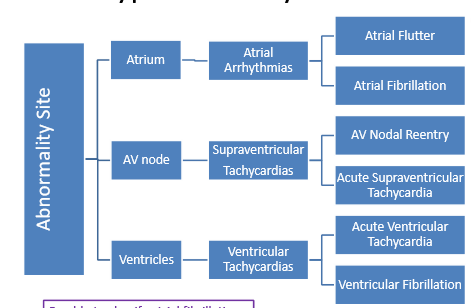
Example Q using the chart:
If I had acute supraventricular tachycardia, the arrhythmia would stem from the _____________.
a. atria
b. SA node
c. AV node
d. ventricle
c
What is the importance of the QT interval?
represents ventricular depolarization
fastest way to die
Above what QTc level would cardiac arrest or a lethal arrhythmia like Torsades de pointes occur?
a. QTc > 510 mS
b. QTc >470 mS
c. QTc >450 mS
d. QTc >525 mS
a. QTc > 510 mS
What classes of drugs can cause a prolonged QT interval?
antipsychotics
antidepressants
antibacterials
antiarrhythmics
What 3 things can you use to treat arrhythmias?
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICD)
used in high death risk
constant monitor for v-fib and v-tach
Catheter ablation
catheter heat destroys abnormal tissue
Drugs
The Vaughn-Williams classification system is used for antiarrhythmic drugs. Fill in the following table:
Classification of Drug | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
Ia | ____ channel blocker |
Ib | ____ channel blocker |
Ic | _____ channel blocker |
II | _______ blocker |
III | _____ channel blocker |
IV | _____ channel blocker |
Classification of Drug | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
Ia | Na+ channel blocker |
Ib | Na+ channel blocker |
Ic | Na+ channel blocker |
II | b-adrenergic blocker |
III | K+ channel blocker |
IV | Ca2+ channel blocker |
What drugs belong to class II antiarrhythmics?
b-blockers
B-blockers inhibit phase ___ depolarization.
4
What structure of the heart do beta-blockers effect?
SA and AV nodes
What arrhythmias are b-blockers particularly useful for?
exercise-induced arrhythmias
stress-induced arrhythmias
post-MI arrhythmias
Common ADRs of Class II antiarrhythmics/ b-blockers:
bradycardia
hypotension
bronchospasm in non-selective bb’s
heart block
insomnia, depression
Can Class II and Class IV antiarrhythmics be combined to treat arrhythmias?
For example, can I combine diltiazem and metoprolol?
NO!
increases risk of HF= too much shutdown
Which class of antiarrhythmics inhibits sympathetic input to pacing regions of the heart?
II
Which class of antiarrhythmics block open calcium channels to slow conduction in tissues dependent on Ca2+ current?
IV
What structure of the heart do non-DHP CCBs effect?
SA and AV nodes
What are the ADRs of Class IV antiarrhythmics aka non-DHPs?
AV nodal block
HA, fatigue, dizzy
nausea, constipation
Which of the following is true regarding Class II and Class IV antiarrhythmics?
SATA
a. both effect the SA and AV nodes
b. both decrease CO
c. dangerous if used together
d. both decrease the slope of phase 0 depolarization
a, b, c
d is false- only Class IV decreases the slope of phase 0 depolarization
What drugs belong to class Ia antiarrhythmics?
Disopyramide
Quinidine
Procainamide
What drugs belong to class Ib antiarrhythmics?
Lidocaine
Mexiletine
Phenytoin (Ochs has this one on hers so i just added it here)
What drugs belong to class Ic antiarrhythmics?
Flecainide
Propafenone
What drugs belong to class III antiarrhythmics?
Amiodarone
Dronedarone
Dofetilide
Ibutalide
Sotalol
Class I antiarrhythmics effect phase ___ of the cardiac action potential.
0
Which classes are effective for supraventricular AND ventricular arrhythmias?
SATA
a. Class Ia
b. Class Ib
c. Class Ic
a, c
Which classes are effective ONLY for ventricular arrhythmias?
SATA
a. Class Ia
b. Class Ib
c. Class Ic
b
Which Class I subgroup has MODERATE Na+ channel blockage?
Ia
Which Class I subgroup has WEAK Na+ channel blockage?
Ib
Which Class I subgroup has STRONG Na+ channel blockage?
Ic
What is the main ADR of the class Ia antiarrhythmic Disopyramide?
anticholinergic side effects

What are the contraindications for each class Ia antiarrhythmic?
disopyramide
quinidine
procainamide
IN ALL: 2nd/3rd heart block
disopyramide- cardiogenic shock, QT prolongation
quinidine- thrombocytopenia, myasthenia gravis
procainamide- systemic lupus erythematous, torsade de pointes
Which class Ia agent is an IV injection not an oral capsule?
Procainamide
When is lidocaine, a class Ib agent, used?
IV injection used for refractory ventricular tachycardia and cardiac arrest
What are the contraindications of Class Ib agents?
Lidocaine
Mexiletine
BOTH: 2nd/3rd degree heart block
Lidocaine- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, corn allergy, amide-allergy
Mexiletine- cardio shock,
What is a warning with Mexiletine?
Severe skin reactions (DRESS)
What class I agent has some beta blocker activity?
propafenone
Flecainide should be avoided in what?
chronic a-fib
Class IC agents are contraindicated in what?
HF
MI
Class III antiarrhythmics block K+ channels at phase ___ of the cardiac action potential.
3
What class III antiarrhythmics are ONLY effective for supraventricular arrhythmias?
dronedarone
ibutilide
dofetilide
What class III antiarrhythmics are effective for BOTH supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias?
amiodarone
sotalol
What element does amiodarone contain that could potentially cause thyroid problems?
iodine
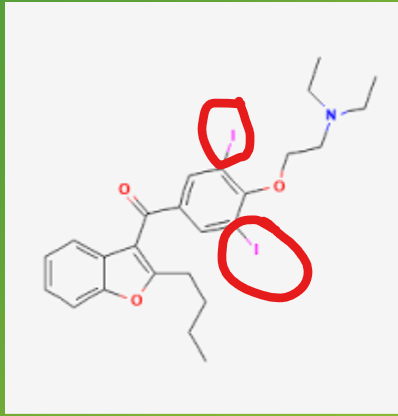
Amiodarone and Dofetilide are the drugs of choice with what comorbidity?
HF
What are the BBW for amiodarone?
pulmonary toxicity
hepatotoxicity
proarrhythmic affects
In addition to the the BBW for amiodarone, what are some of the other warnings?
thyroid dysfunction
visual impairment
photosensitivity
neuropathy
When starting amiodarone what do we do to digoxin?
decrease dose by 50%
When starting amiodarone what do we do to warfarin?
decrease warfarin dose by 30-50%
Amiodarone is inhibitors of what CYP enzymes?
CYP2C9
CYP2D6
Pgp
What are the boxed warnings of Dronedarone?
a-fib: increased risk of death, stroke, HF
HF: increased risk of death
What are the contraindications of Dronedarone?
permanent a-fib
HF
QTC >500
bradycardia
use of CYP3A4 inhibitors
Although Sotalol is a class III agent, it has some class ___ activity since it’s a nonselective beta-blocker.
II
Ibutilide is an IV formulation only indicated for what?
cardioversion to normal sinus rhythm
What must be corrected before beginning Ibutilide?
hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia
Dofetilide must be initiated with continuous monitoring for ____ hours.
72
Dofetilide is contraindicated in…
QTc>440
CrCl <20
Initiation of which drugs must be done under observation?
dofetilide and sotalol
Does Digoxin deal with rate or rhythm control?
RATE
What does digoxin block?
Na-K-ATPase Pump
How do Digoxin and Adenosine effect the heart?
slow conduction through AV node