ABA Final Exam
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
Parsimony
The idea that simple, logical explanations must be ruled out, experimentally or conceptually, before more complex or abstract explanations.
Determinism
Scientists presume that the universe, or at least the part of it they intend to probe with the methods of science, is a lawful and orderly place in which all phenomena occur as the result of other events. In other words, things happen for a reason.
Replication
The repetition of experiments to determine the reliability and usefulness of findings and the repetition of independent variables within experiments.
Empiricism
What all scientific knowledge is built upon; the practice of objective observation.
Philosophic Doubt
The continuous questioning of the truthfulness and validity of all scientific theory and knowledge.
Experimentation
The basic strategy of most science. Controlled comparison of some measure of the phenomena (dependent variable) under two or more different conditions in which only one factor at a time (independent variable) differs from one condition to the next.
Effective
Improves behavior sufficiently to produce practical results for the client.
Technological
The written description of all procedures used in the study is sufficiently complete and detailed to enable others to replicate.
Applied
Investigates socially significant behaviors with immediate importance to the subject.
Behavioral
Entails precise measurement of the observable behavior in need of improvement and documents that it was the subject's behavior that changed.
Analytic
Demonstrates experimental control over the occurrence and nonoccurrence o f
the behavior; a functional relation is demonstrated.
Generality
Produces behavior changes that last over time, appear in other environments,
or spreads to other behaviors.
Conceptually Systematic
Behavior change interventions are derived from basic principles of behavior.
Behavior analysts analyze behavior by making inferences about behavior
based on what their clients tell them about the behavior.
False
Applied behavior analysis i s not a type of psychotherapy.
True
Rather than focus on theories of behavior, and other similar concepts,
behavior analysis i s data based.
True
The primary job of Board Certified Assistant Behavior Analysts
(BCaBA) and Registered Behavior Technicians (RBT is to work directly
with clients.
True
The overarching purpose o f applied behavior analysis, as a field of study,
is to concentrate on socially important behaviors.
True
Applied behavior analysis is both a science and a form of therapy.
True
A good behavioral definition requires you to make inferences about
internal states or motivation of the individual.
False
Behavior analysis places emphasis on current environmental events as
important causes of behavior.
True
Behavior analytic treatments can be implemented by people in everyday
life.
True
Behavior analysis emphasizes hypothetical underlying causes of behavior.
False
Behavior analysts search for the maintaining variables ("the cause") of
behavior in the environment.
True
Evidence-based treatments are treatments that have been proven effective in scientific studies and clinical practice including consumer preference.
True
The best predictor of future behavior i s past behavior.
True
"Some Current Dimensions of Applied Behavior Analysis" is the most
widely cited study in ABA
True
The philosophy of behavior described by Skinner is referred to a s radical
behaviorism.
True
Behavior observed and recorded by another individual.
B. Overt
Walking through the parking lot to get to your car.
B. Overt
Writing your answers to these test questions.
B. Overt
Behavior that is labeled a "private event" and cannot be observed by others.
A. Covert
Running laps on an indoor track.
B. Overt
Thinking about what you will eat for lunch.
A. Covert
Feeling confident about your answers to test questions.
A. Covert
Behavior is defined as …
B. what a person says and does.
Which two events marked the formal beginnings of ABA?
A. The formation of the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis and the publication of "Some Current Dimensions of Applied Behavior Analysis"
Who is/are considered the founder(s) of the experimental analysis of behavior (EAB)?
A. Skinner
Mary's parents are trying to figure out why she constantly screams at her sister. The process of trying to identify the functional relationship between a behavior and the environment is referred
to as:
B. analysis
In applied behavior analysis, measurement of behavior is taken …
D. All of these
Behavior analysis is the field of psychology concerned with the _____
and _____ of human behavior.
C. analysis, modification
The philosophy of the science of behavior is referred to as …
B. Behaviorism
In applied behavior analysis, the people who develop behavior modification plans and analyze the data are generally …
D. Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBAS)
12. List three areas of application (i.e., areas of work) where behavior analytic principles have been applied.
• RBTs, BCBAs, BCaBAs
• Education, parent training, business, etc.
Who is/are considered the founders) of applied behavior analysis (ABA)?
Wolf, Baer, and Risley.
Wolf (1978) introduced the term social validity to describe the social significance of ____, ____, and ____
in behavior analytic research and practice.
Goals; procedures; results
List four dimensions of behavior that can be measure (and were discussed in Ch. 1) and describe a behavior that could b e measured with each dimension.
• Frequency ➡ how many times someone speaks every 5 minutes
• Duration ➡ how long someone takes to answer a question from start to finish
• Latency ➡ how long it takes someone start a task after a timer goes off
• Intensity ➡ how much force someone uses to hit a buzzer
List the three primary branches of behavior analysis:
• Behaviorism
• EAB
• ABA
A runner records how many minutes she jogs each evening.
Duration
A fitness trainer measures changes in a client's waist size across the semester.
Permanent product
A soccer coach counts every goal scored by a player during practice.
Frequency
Parents begin tracking how loud their child yells when told "no."
Intensity
Checking at the end of each minute to see i f the student is reading versus daydreaming.
Time sample recording
A track coach records the number o f seconds between the starting gum and the athlete's first stride off the blocks
Latency
A baseball player records the force with which he hits the ball.
Intensity
Recording how long it takes an athlete to begin stretching after the coach gives the signal.
Latency
What is involved in determining the logistics of recording?
D. all of these
A researcher cannot observe aggression in a child's home, so they set up a playroom that resembles the child's living room. This is an example of a ___ setting.
C. analogue
A teacher checks the number of spelling words correctly written on a worksheet to
assess learning. The teacher is using ____ recording.
D. permanent product
Which of the following can be used as a recording instrument?
D. all of these
An observation period i s broken into 10-second segments. The observer marks whether the child's target behavior occurred at least once in each segment. This is called:
C. interval recording
The horizontal axis (x-axis) on a graph is used to record:
A. time
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an A-B design?
It demonstrates a functional relationship
Before using a reversal design, one must ask:
D. all of these
In an A-B-A-B design, B refers to ___
and A refers to ___.
C. treatment; baseline
A critical feature of a multiple-baseline design is that:
C. A and B
In an ___ research design, baseline and treatment conditions are conducted in a rapid succession and compared to each other.
D. alternating treatments
The research design that adjusts the required performance up or down in gradual steps is called:
C. changing criterion
Another name for a reversal design is a(n) …
a) A-B-A-B design
Another name for an alternating treatments design is a(n)
D. multielement design
One advantage o f a multiple baseline design is that:
B. It does not require a reversal to demonstrate experimental control
A parent records each time a child refuses to pick up toys as it happens.
A. Direct
At the end of the day, a caregiver writes down how many tantrums occurred that day.
B. Indirect
On a survey, a teenager reports how often she yells at her sibling.
B. Indirect
A psychologist tallies each time a client interrupts during a counseling session.
A. Direct
A teacher observes and immediately records when a student blurts out answers.
A. Direct
The child's nail biting usually occurs in his bedroom. The bedroom is an analogue setting.
False
The units of behavior are shown on the y-axis of a graph.
True
Each plotted data point reflects the level of behavior at one moment in time.
True
IOA must be 100% to be acceptable.
False
Data points are not connected across phase-change lines.
True
Replication in single-subject research i s not necessary to show a functional relation (i.e., experimental control).
False
A disadvantage of the changing criterion design is that it requires control over both the direction and level of behavior change
True
Behavior analysts avoid labels and look for measurable aspects of behavior.
True
In single-subject research, behavior is measure across conditions for one or a few individuals.
True
When two observers record the same behavior during the session and compare, it's called interobserver agreement.
True
A child only completes math problems when the teacher is watching. This illustrates reactivity.
True
To decide whether an intervention caused a change in behavior, we need to compare the behavior in the ___ phase to the behavior in the ___ phase.
Baseline; treatment
In ABA, the main tool used for displaying behavior change is a ___.
Graph
List three types of multiple baseline graphs.
• multiple baseline across participants
• across settings
• across behaviors
An intervention can affect a behavior's ___, ___, and ___. Therefore, these factors must be evaluated when interpreting treatment results.
Level; trend; variability
Describe the difference between whole-interval and partial-interVal recording.
• Whole-interval: behavior is scored if it occurs throughout the event
• Partial-interval: behavior is scored if it occurs at any point in the interval
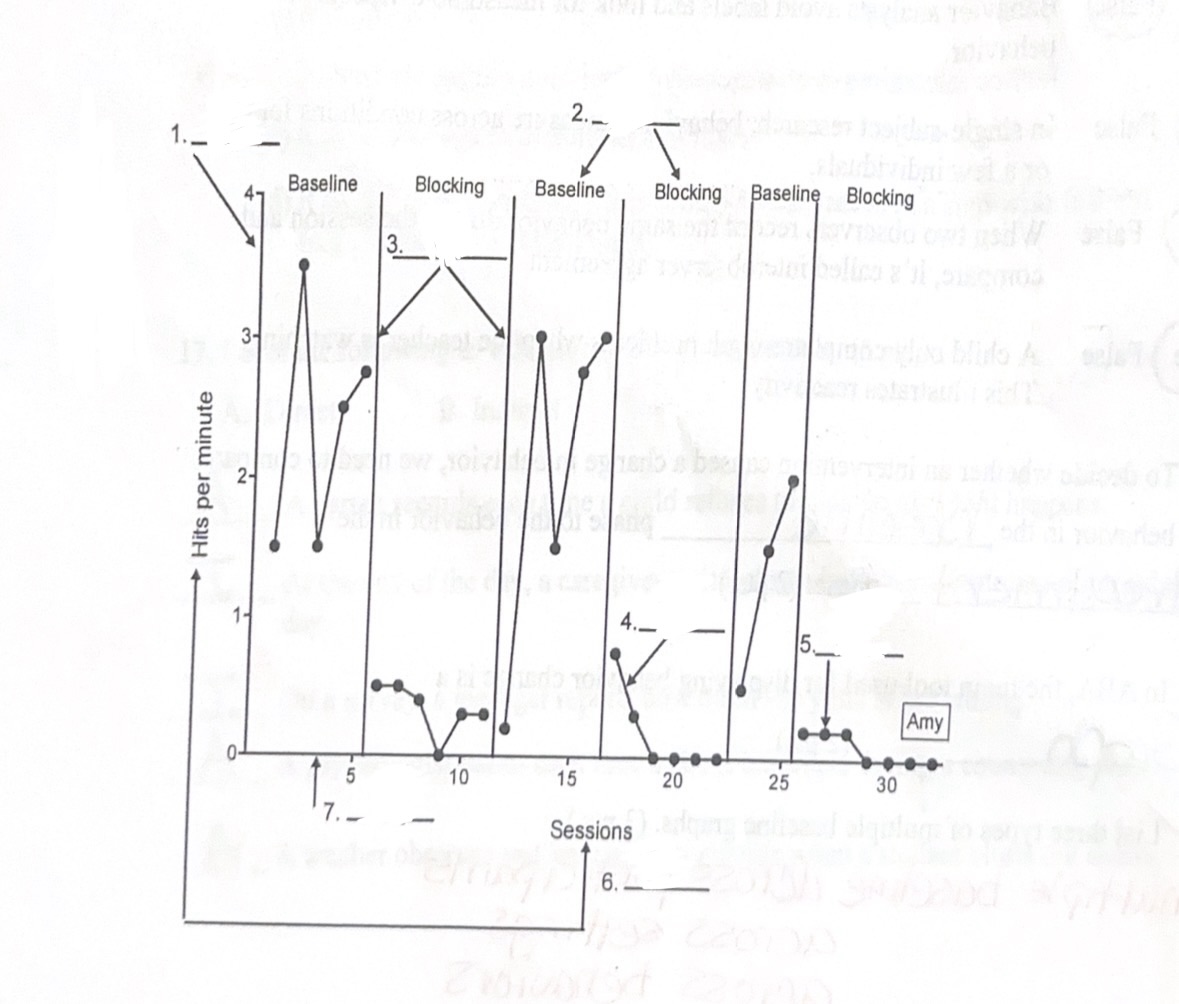
1) B. Vertical axis (y-axis)
2) G. Phase label
3) E. Phase-change labels
4) D. Data path
5) C. Data point
6) F. Axis labels
7) A. Horizontal axis (x-axis)
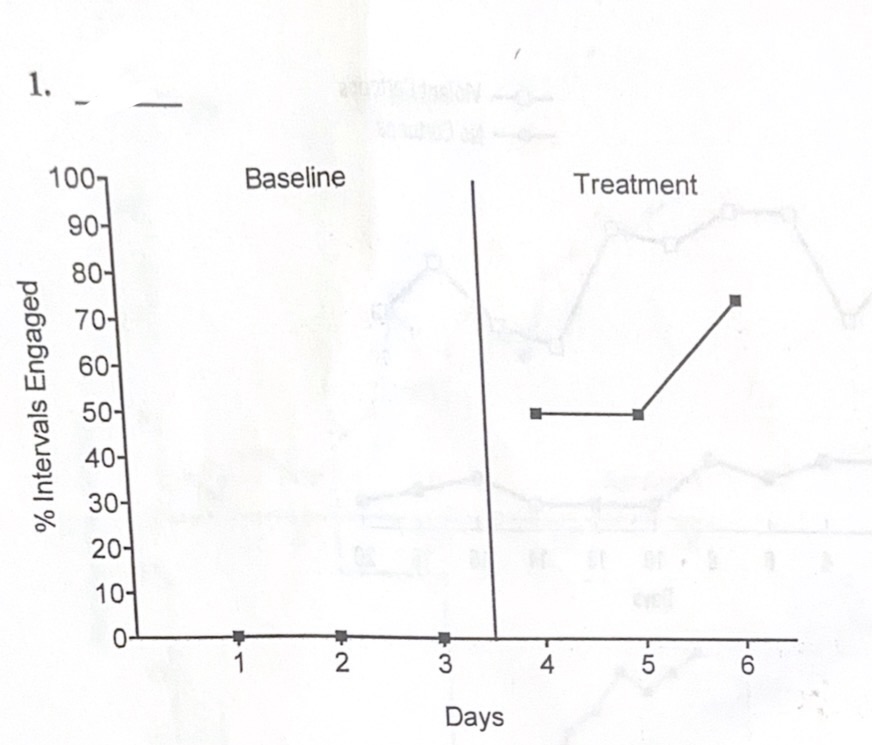
C. A-B
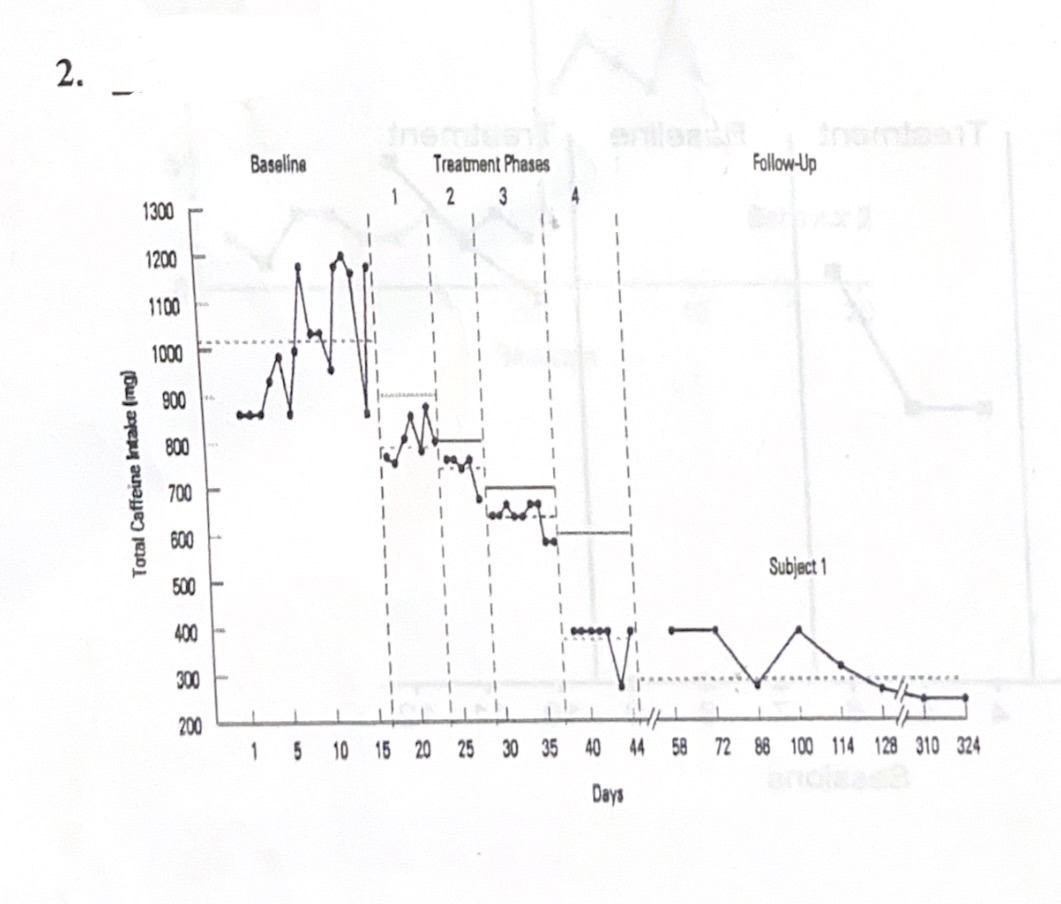
D. Changing criterion

E. Alternating treatments
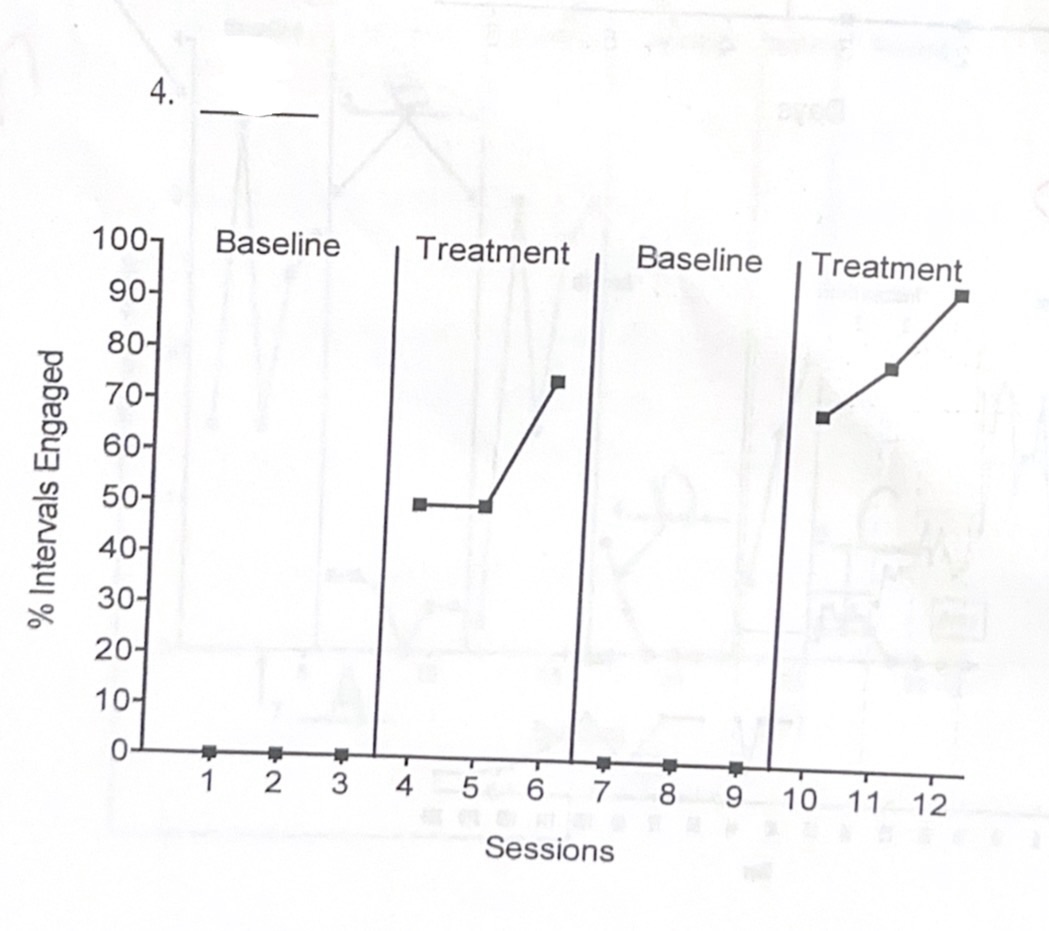
B. Reversal A-B-A-B
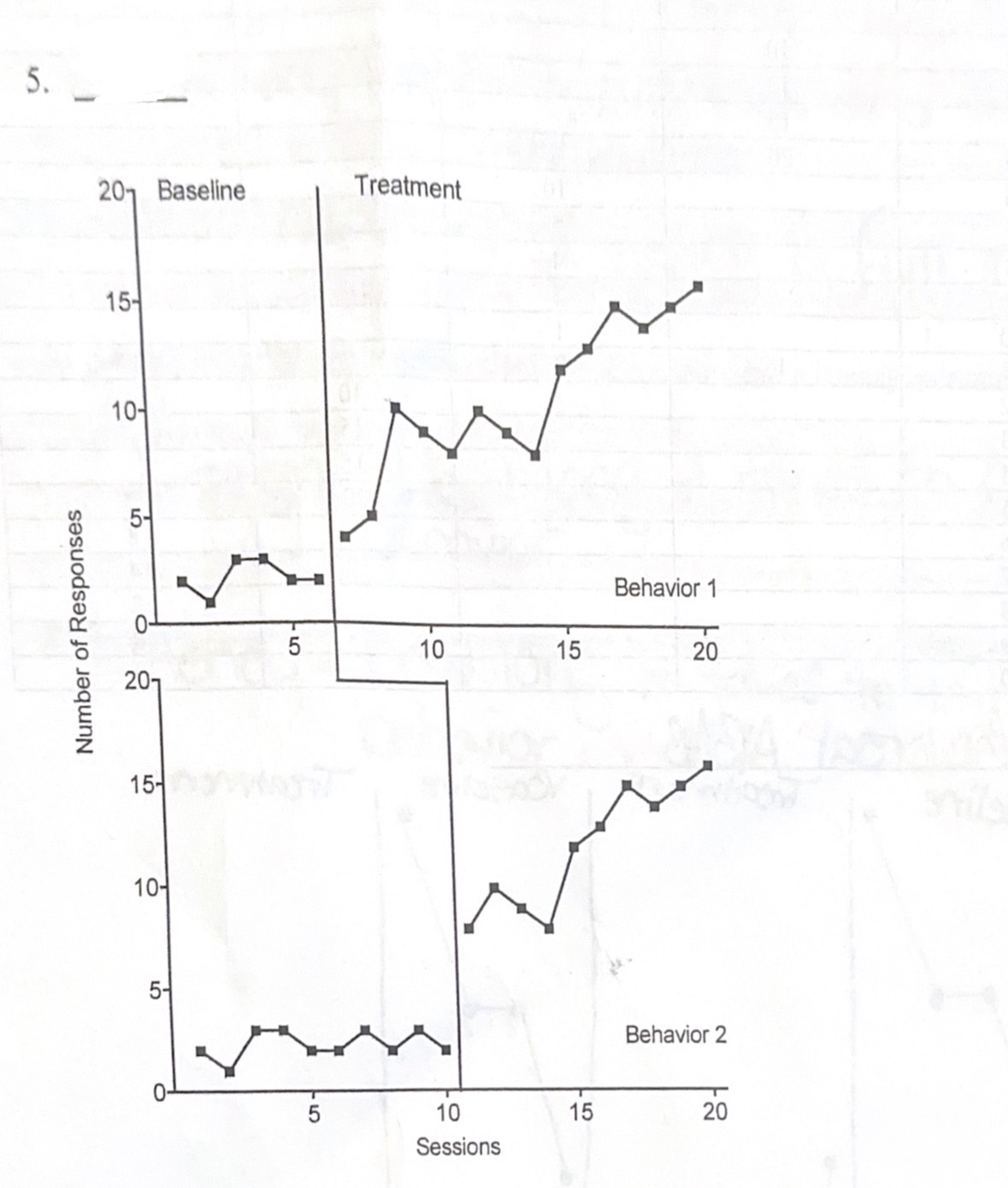
A. Multiple baseline
Which of the following processes increase the likelihood of a behavior occurring again?
E. A and C