Radiology lab practical
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Radiographic positioning
- Lateral thorax
- Measure: caudal border of the scapula
- Beam: caudal border of the scapula
- Borders: spine, sternum, cranial point of shoulder, caudal to last rib
Radiographic positioning
- VD thorax
- Measure: caudal border of scapula
- beam: midline and caudal border of scapula
- Borders: cranial point of shoulder, caudal to last rib
Radiographic positioning
- lateral abdomen
- Measure: caudal aspect of 13th rib
- Beam: dog - caudal aspect of 13th rib/ cat - 2-3 fingers with caudal to last rib
- Borders: 1 inch cranial to xiphoid and caudally to the greater trochanter
Radiographic positioning
- VD abdomen
- Measure: caudal aspect of 13th rib at the level of the umbilicus
- Beam: dog - midline and caudal aspect of the 13th rib/ cat - 2-3 finger widths caudal to last rib
- Border: 1 inch cranial to xiphoid and caudal to the greater trochanter
Radiographic positioning
- Lateral pelvis
- Measure: at the level of the greater trochanter
- Beam: greater trochanter
- Borders: cranial to the wing of the ilium and caudal to the ischium, 1/3 of femur distally
Radiographic positioning
- VD pelvis extended view
- Measure: thickest part of the pelvis
- Beam: midline between the caudal pubis/ ischia
- Borders dorsally to the tip of the iliac wing and caudal to include the patellas
Radiographic positioning
- VD pelvis frog leg
- Measure: thickest part of the pelvis
- beam: midline between the caudal pubis/ischia
- Borders: dorsally to the tip of the iliac wings, caudal to the caudal border of the ischium, include 1/3 of each femur
Radiographic positioning
- Lateral elbow
- Measure: thickest part of the elbow at the distal humerus
- Beam: distal humeral condyles
- Borders: distal 1/3 of the humerus and proximal 1/3 of the radius and ulna
Radiographic positioning
- Lateral flexed elbow
- Measure: thickest part of the elbow at the distal humerus in a flexed position
- Beam: distal humeral condyles
-Borders: distal 1/3 of the humerus and proximal 1/3 of the radius and Una
Radiographic positioning
- Craniocaudal elbow/AP
- Measure: thickest part of the elbow at the distal humerus
- Beam: distal humeral condyles
- Borders: distal 1/3 of the humerus and proximal 1/3 of the radius and ulna
Radiographic positioning
- Lateral stifle
- Measure: distal end of the femur
- beam: intercondylar fossa
- Borders: proximal 1/3 of the tibia and distal 1/3 of the femur
Radiographic positioning
- Craniocaudal stifle/AP
- Measure: distal end of femur
- Beam: on the stifle joint
- borders: proximal 1/3 of the tibia and distal 1/3 of the femur
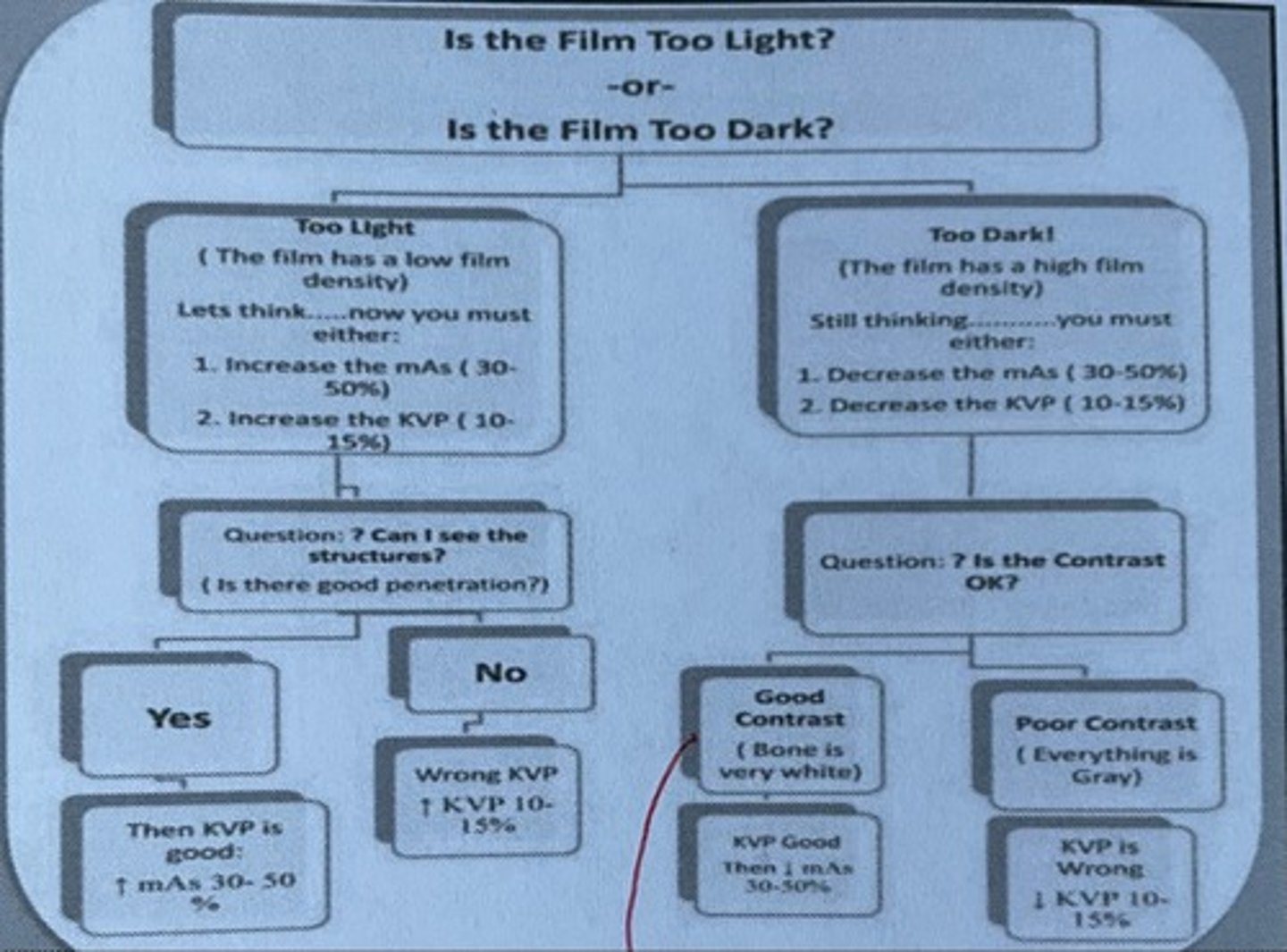
How would you proceed if your radiograph is too light and you can see structures?
Increase MAS 30-50%
How would you proceed if your radiograph is too light and you cannot see structures?
Increase KVP 10-15%
How would you proceed if your radiograph is too dark and the contrast is good (bone is very white)
Decrease MAS 30-50%
How would you proceed if your radiograph is too dark and the contrast is poor? (Everything is gray)
Decrease KVP 10-15%
Is the film too light or too dark chart
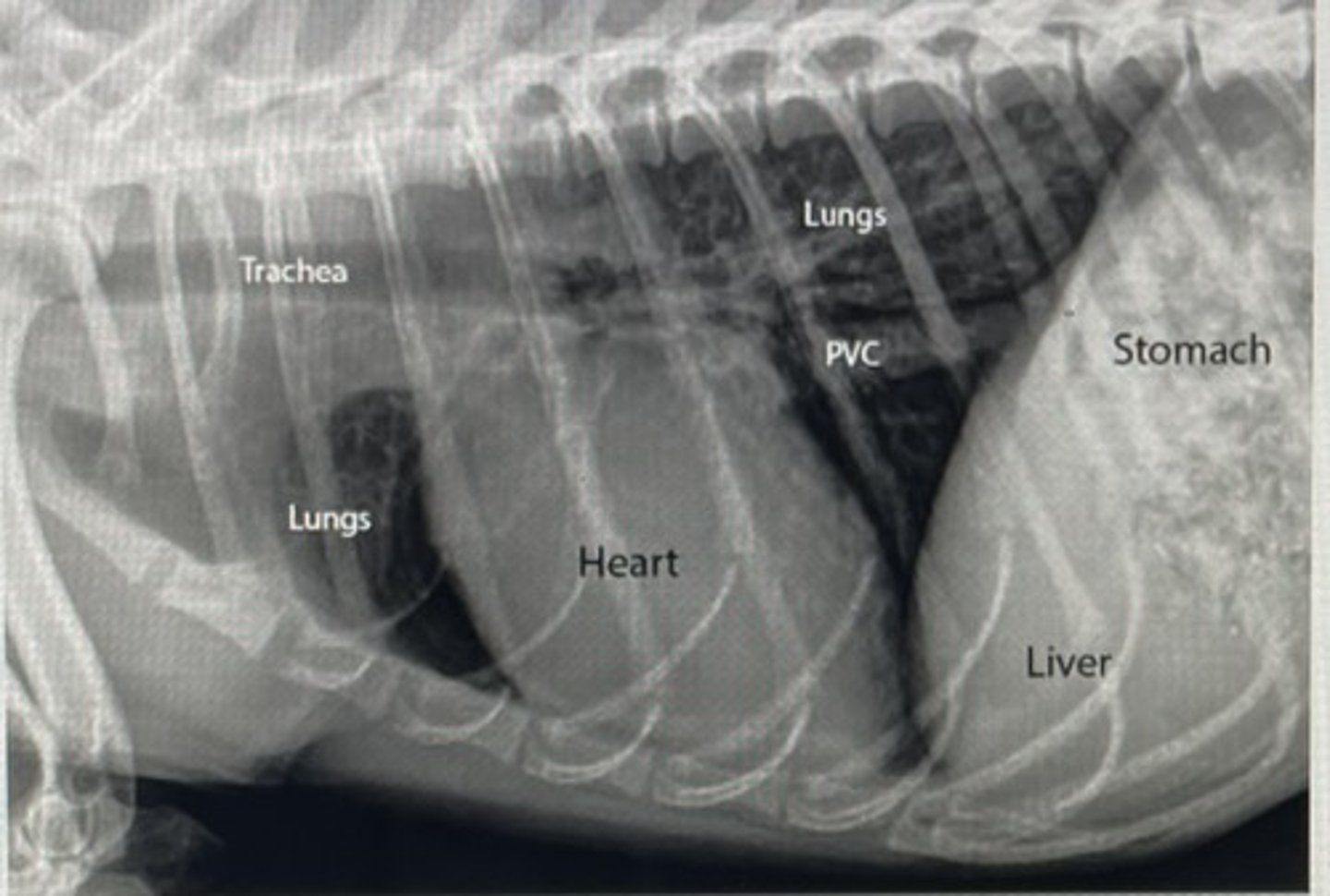
X-ray anatomy chest picture
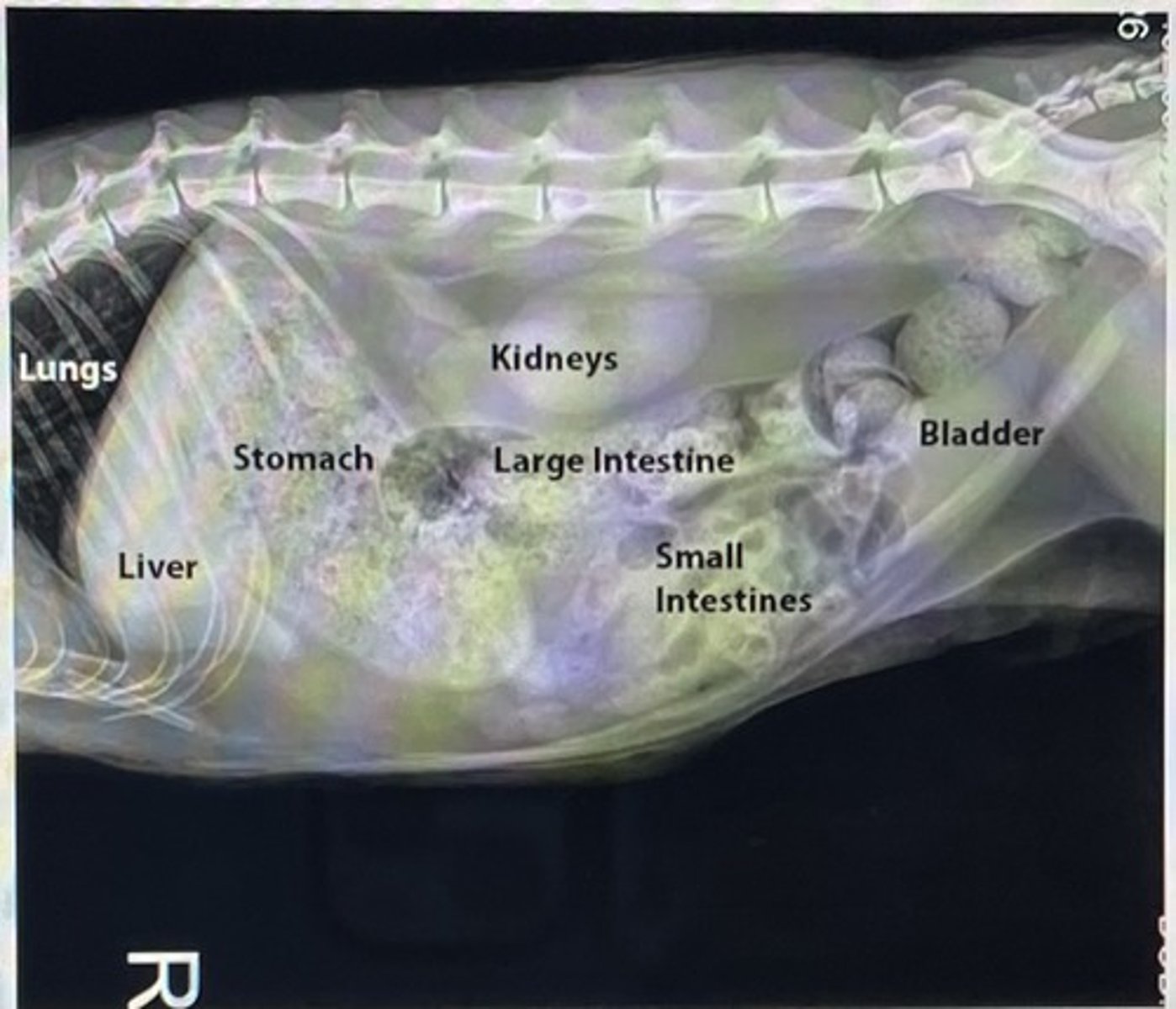
X-ray anatomy abdomen picture
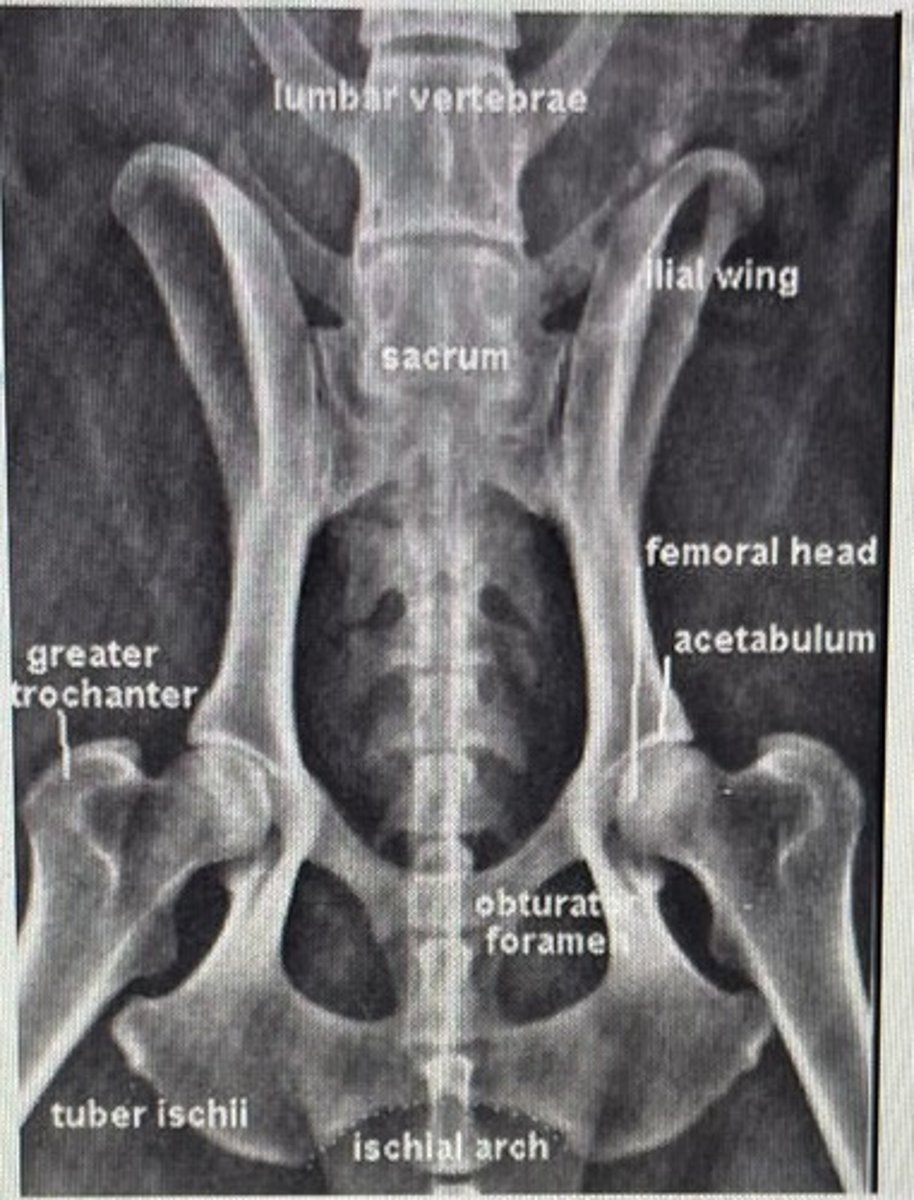
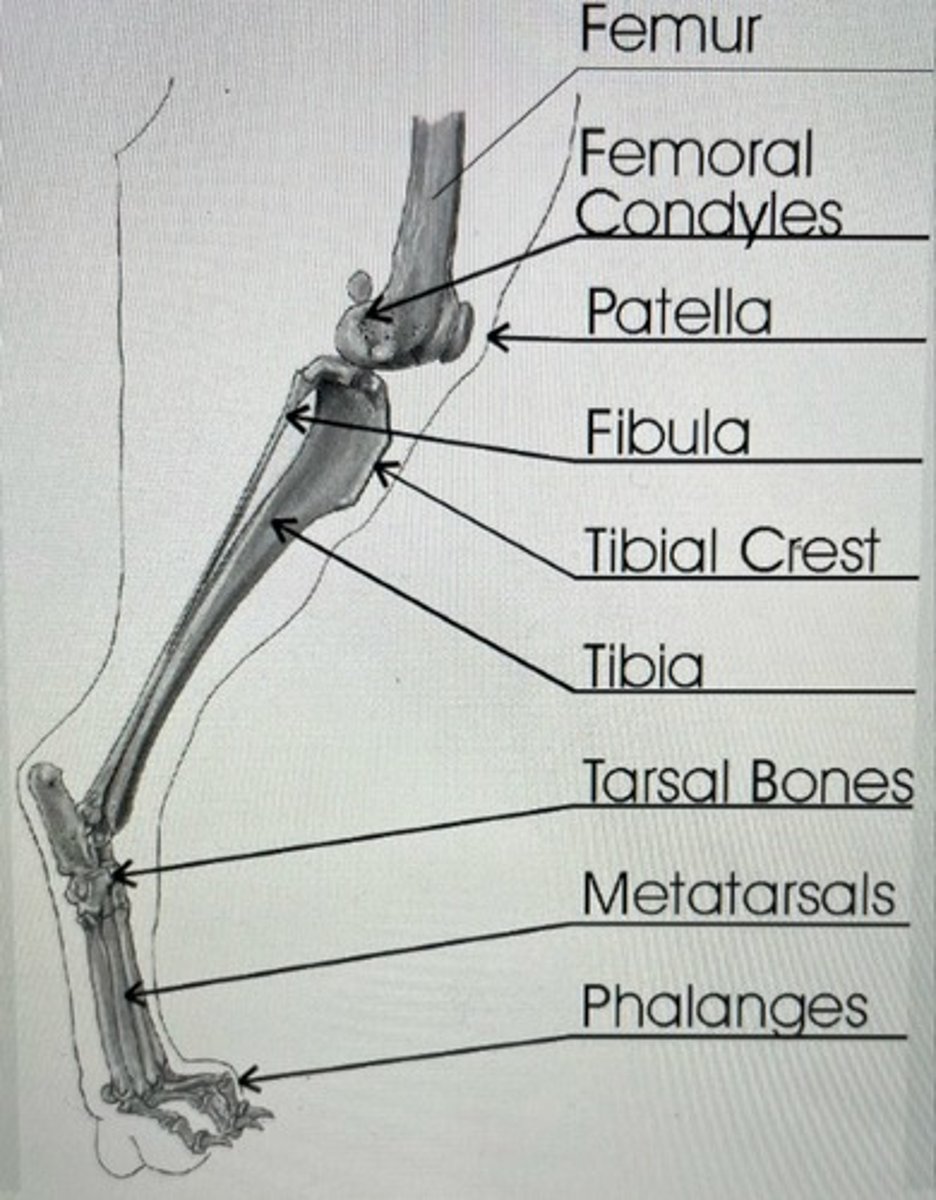
X-ray anatomy pelvis picture
X-ray anatomy front leg picture
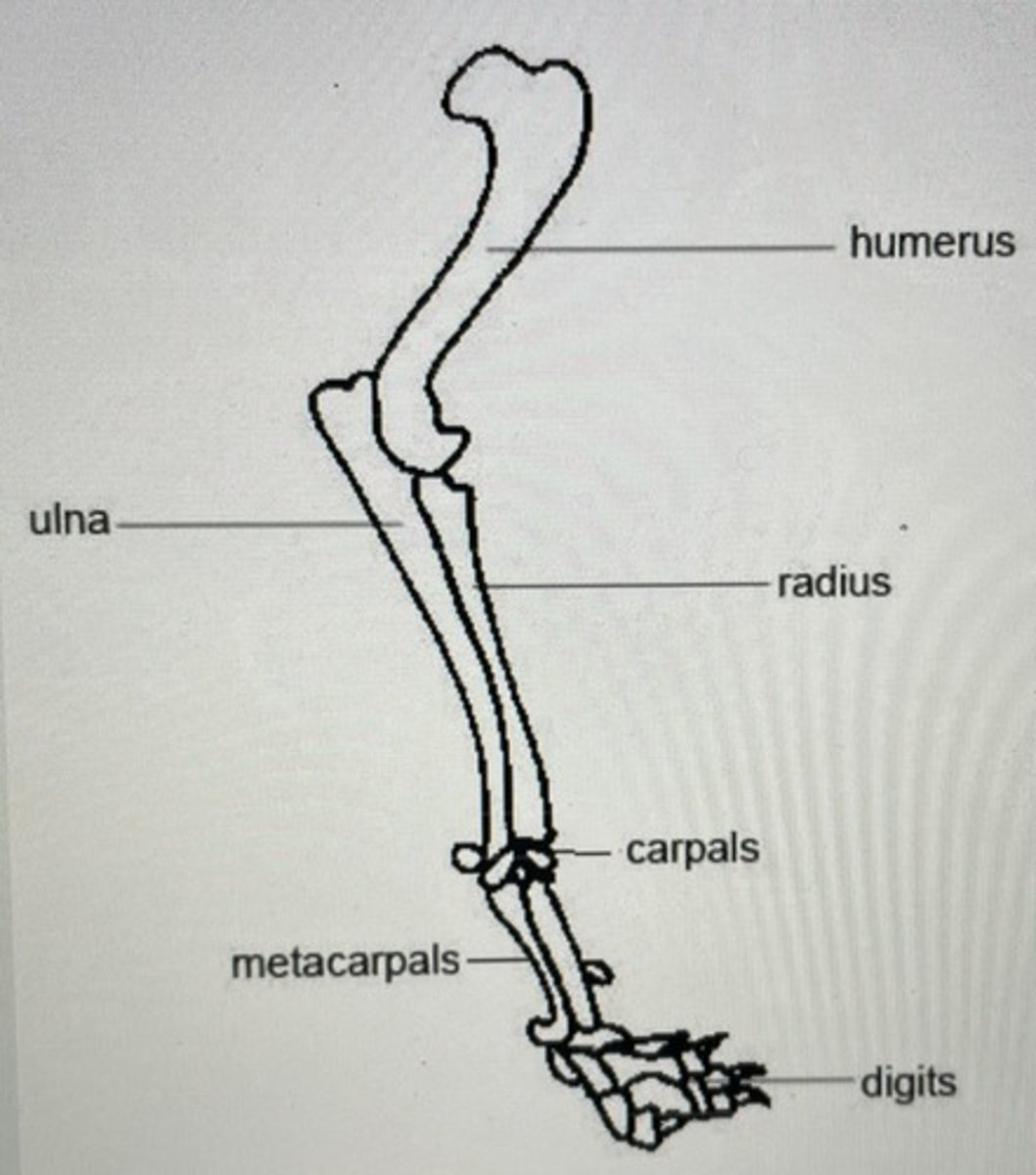
X-ray anatomy hind leg picture
Why do we take x-rays on inhalation for chest views?
To show full lung fields
Why do we take expiration for abdominal views
Pushes diaphragm up, which causes the organs to decompress
If you want to look at the left side of the lungs, how would you position the patient?
Right lateral
If you wanna look at the right side of the lungs, how would you position the patient?
Left lateral
If you wanna look at the left side of the patient for abdomen, how would you position the patient?
Left lateral
If you wanna look at the right side of the patient for an abdomen, how would you position the patient?
Right lateral
What are the positive types of contrast media?
- Barium sulfate
- Water soluble organic iodines
- BIPS
What contrast medias would be used for G.I. series?
- Barium sulfate
- Oral organic iodine
- BIPS
What is the agent of choice for suspected G.I. preparation/obstruction?
Oral organic iodine
What are the types of negative contrast medias
- Room air
- 02
- CO2
- NO2
Double contrast procedures are commonly used in
- Bladder
- Stomach
- colon
Why must you give the negative contrast before the positive contrast for a double contrast procedure?
Decrease air bubbles, which may be mistaken for lesions/artifacts
What are the indications for G.I. studies?
- V/D
- Melena/hematochezia
- FBO/FBI
- Acute abdomen/pain
-enteric mass
- Assesses G.I. transit time
What are the contraindications for G.I. studies?
- Fluid/gas filled esophagus or stomach
- GDV
What are the indications for a lower G.I. study?
- Abnormal defecation
- Stricture
- Obstruction
- colon/Rectal neoplasia
What are the indications for esophagram?
- Dysphasia
- Megaesophagus
- Chronic gagging/retching
- Foreign bodies
- Abnormal swallowing
Towards the tongue
lingual
Towards the palate
Palatial
Surface of incisors that face the lip
Labial
Lateral surfaces of all teeth, except the incisors
Buccal
Direction towards the last tooth in each quadrant
Distal
Direction towards the anterior or first tooth of each quadrant
Mesial
Used for grasping and cutting food
Single rooted
Incisors
Used for grasping and holding
Single rooted
Canines
Designed for cutting/shearing
Single to three rooted
Premolars
Often flattened occlusal services used for grinding
Double to three rooted
Molars
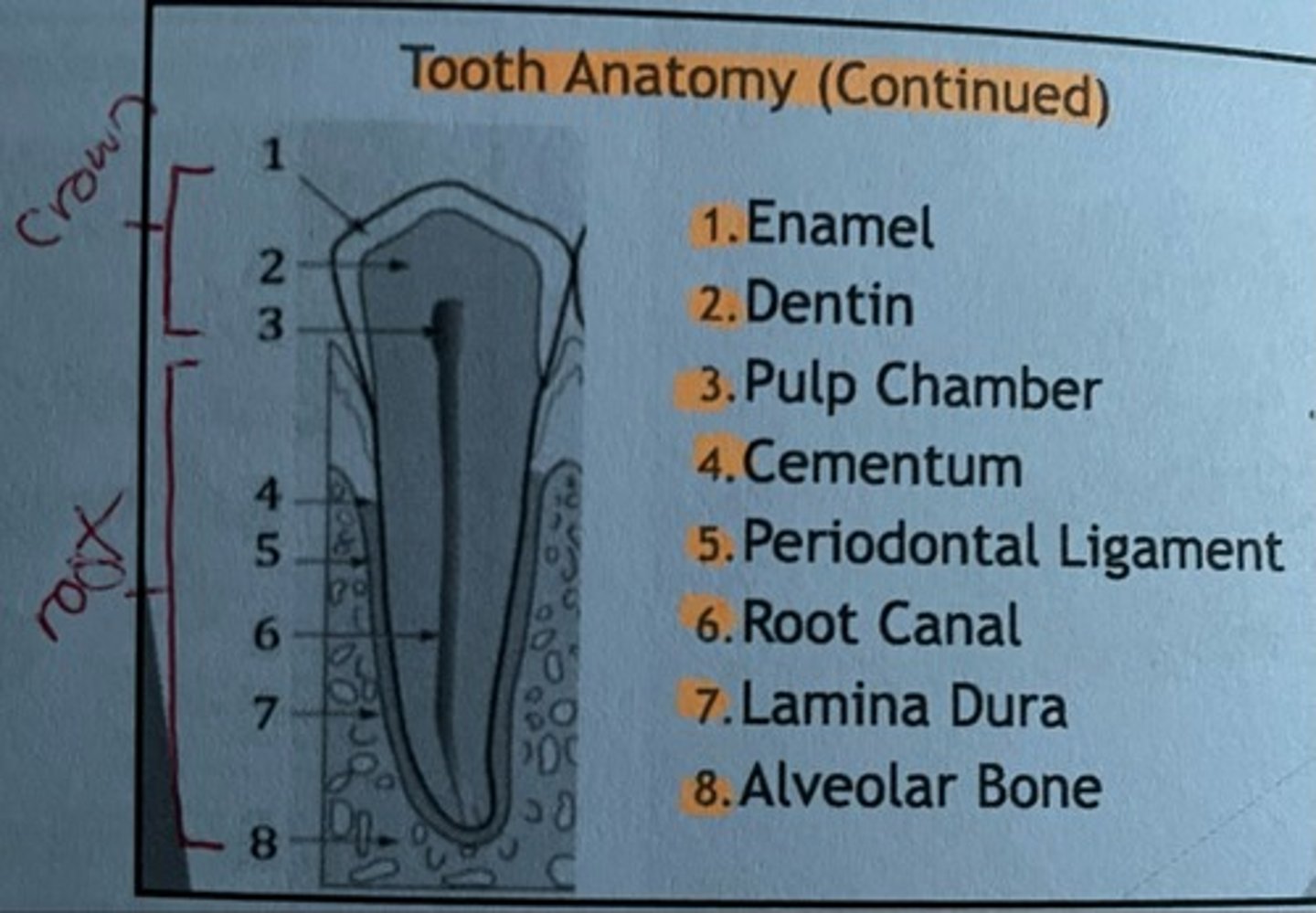
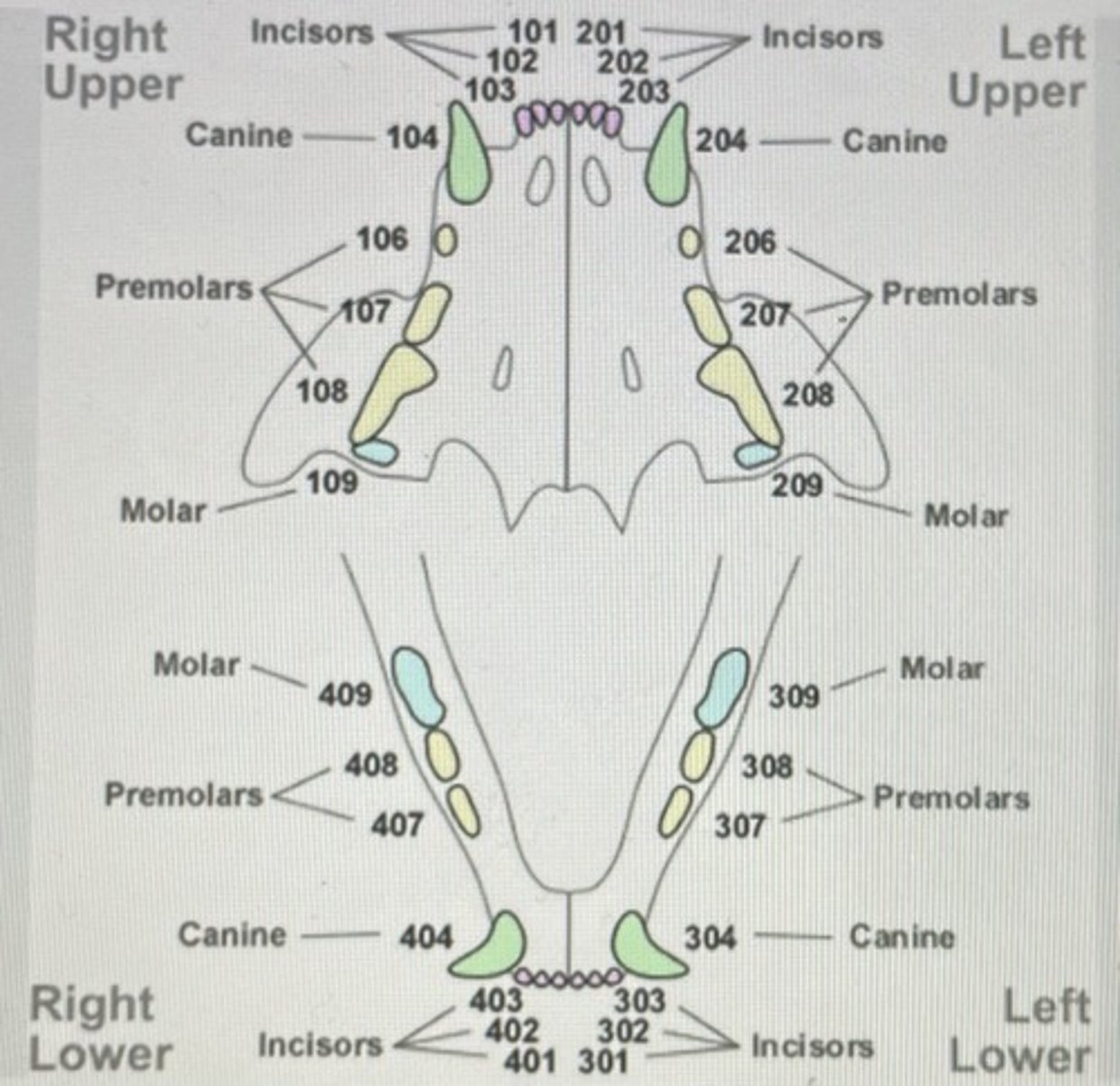
Tooth anatomy picture
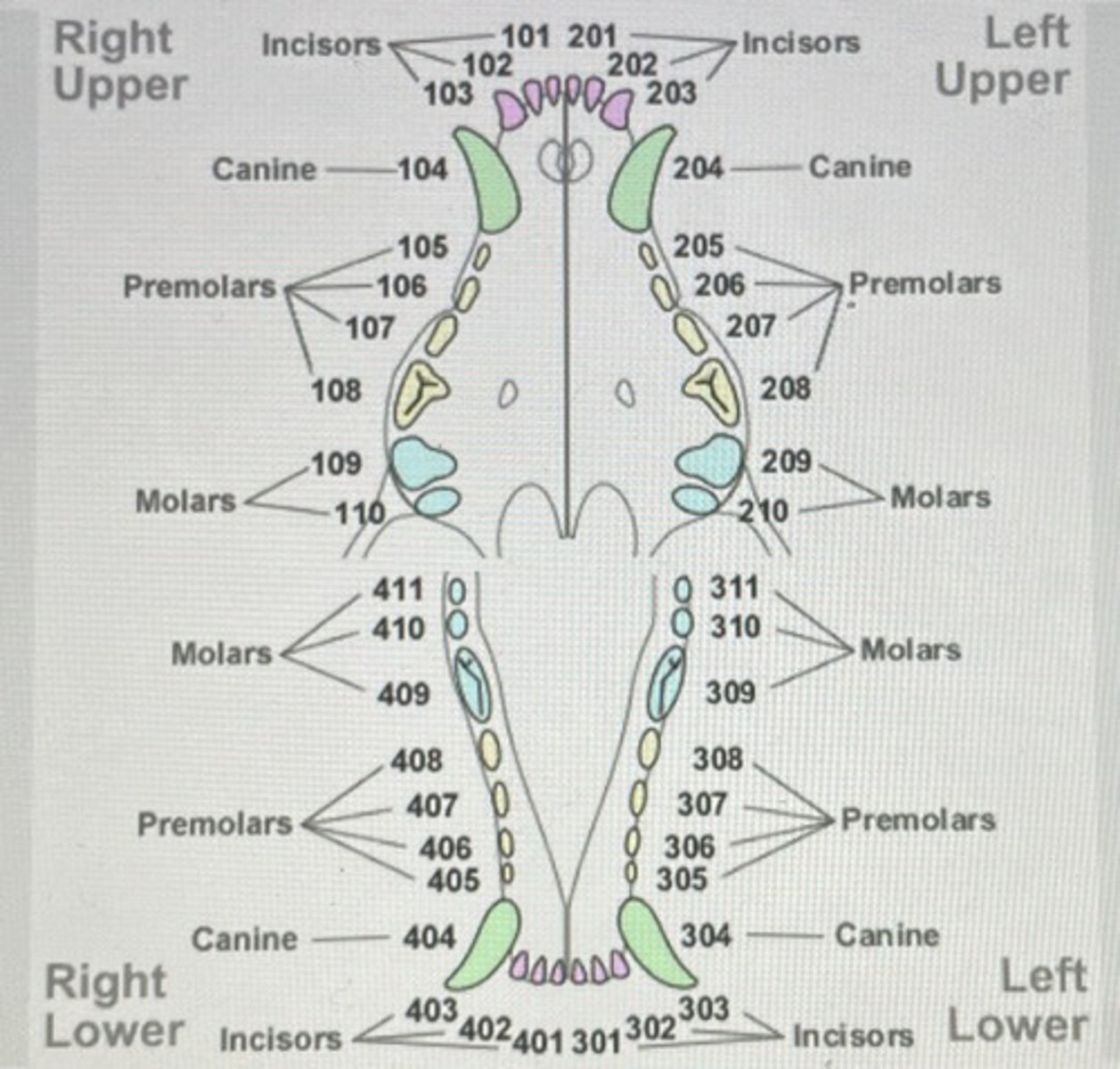
Modified triadan system dog picture
Modified triadan system cat picture
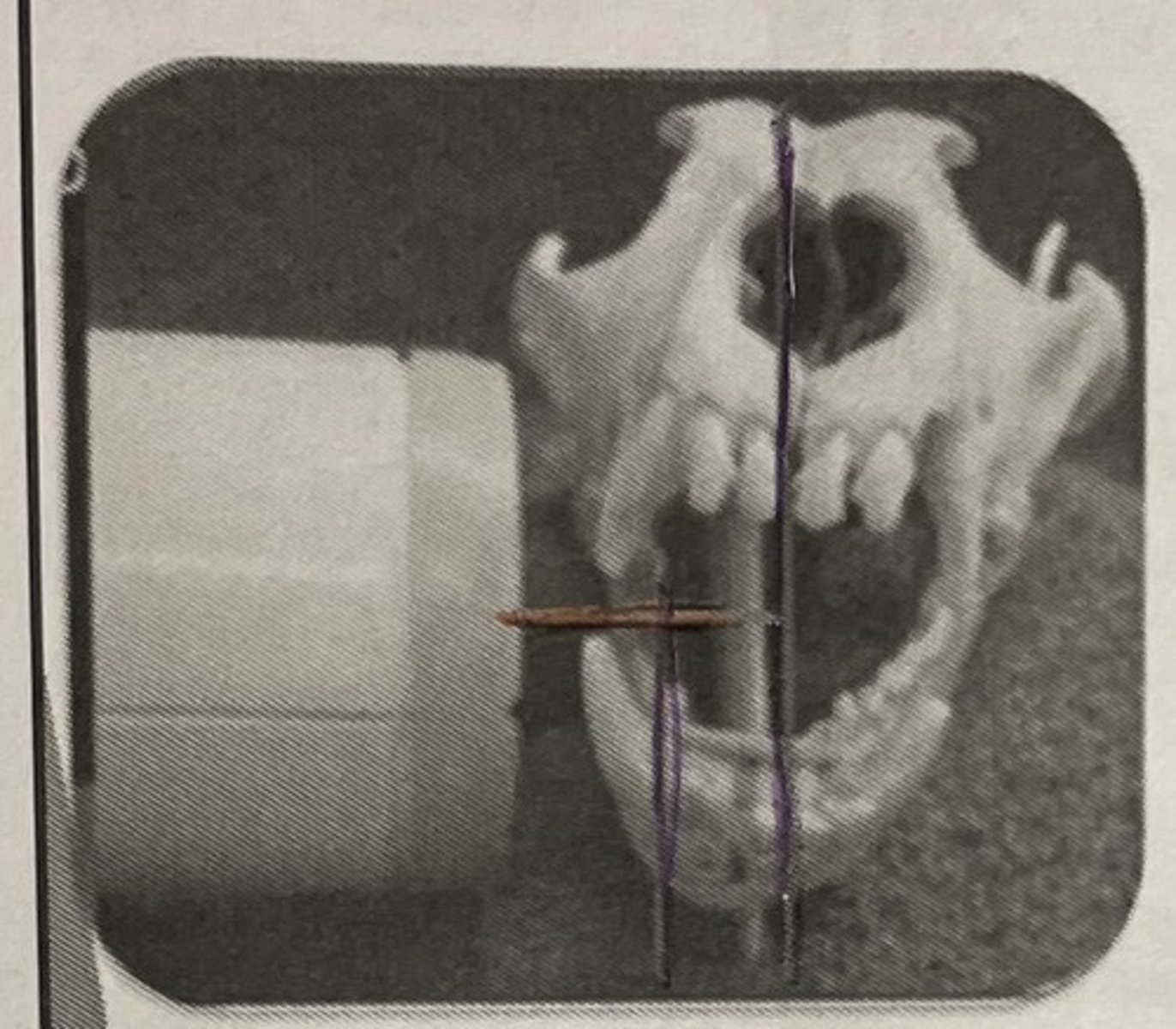
- The plate/film sensor in long axis of the tooth/teeth are parallel to each other
- Tube head/beam will be perpendicular to the plate and tooth
Parallel angle technique
Parallel angle technique photo
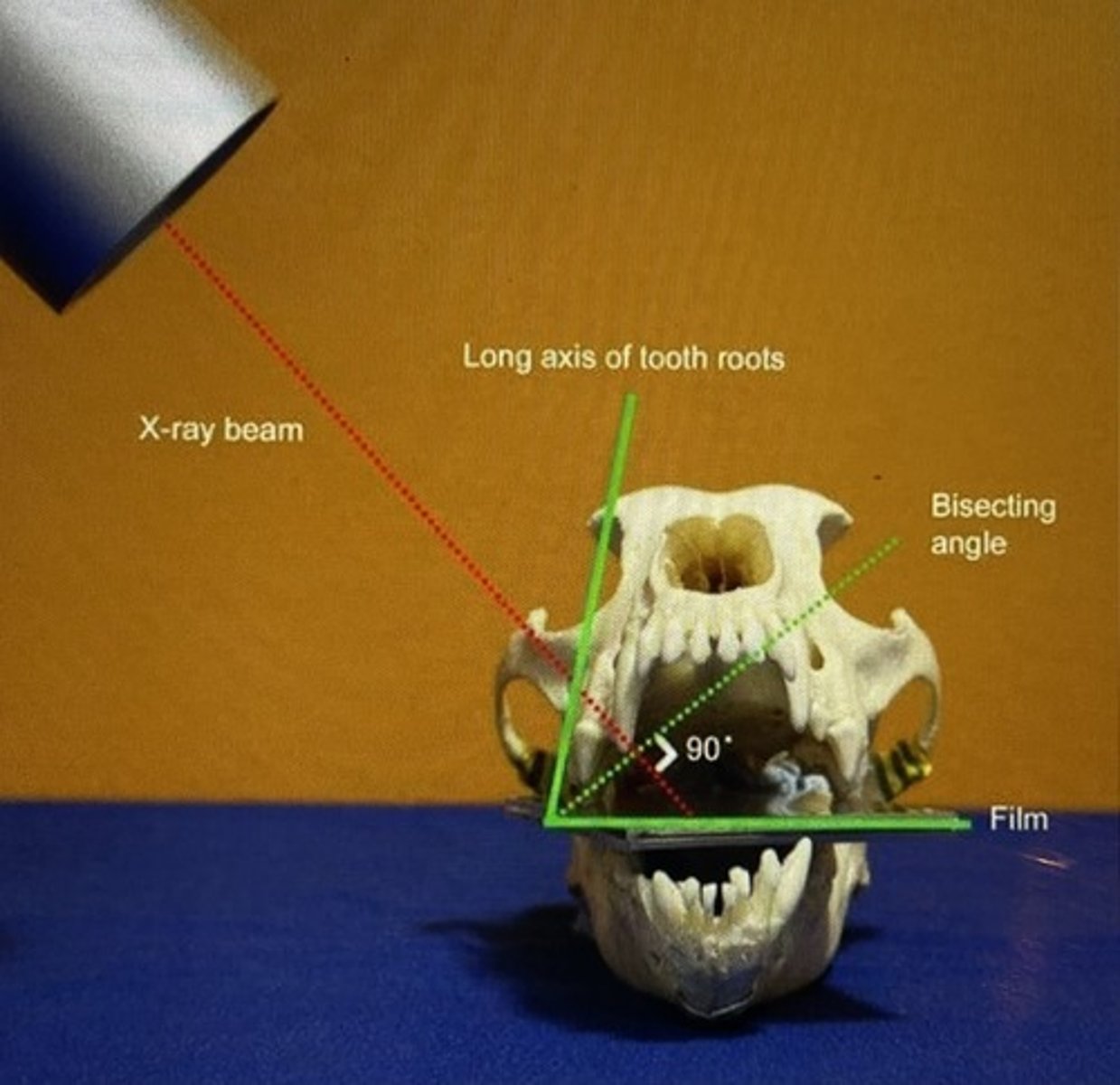
Is formed by the intersection of the film plane and the long axis of the tooth
The tube head is perpendicular to the BA
Bisecting angle technique
Bisecting angle technique photo
Simplified technique canine/incisors
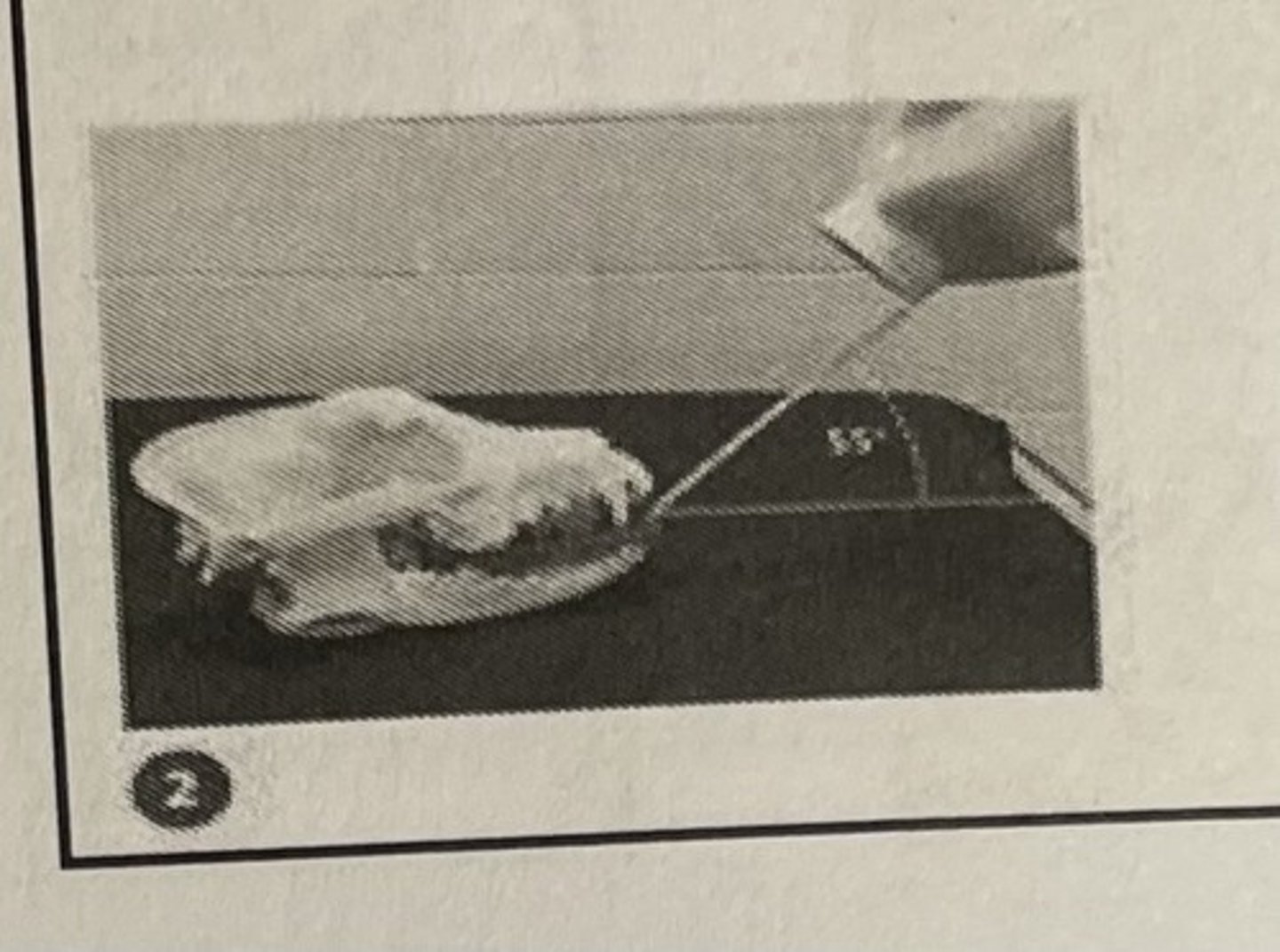
Simplified technique: maxillary pre-molars/molars
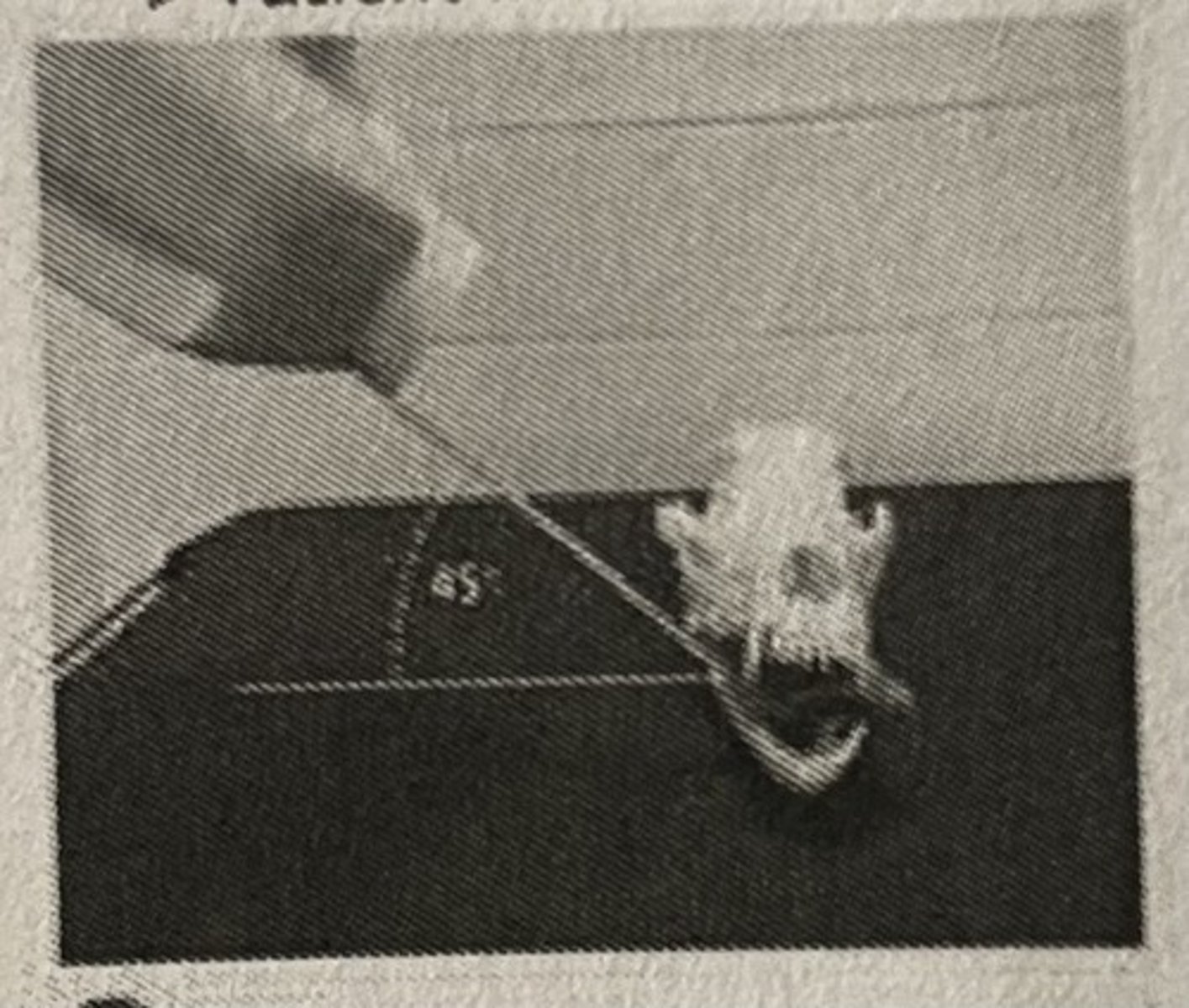
Simplified technique: Mandibular incisors/canines
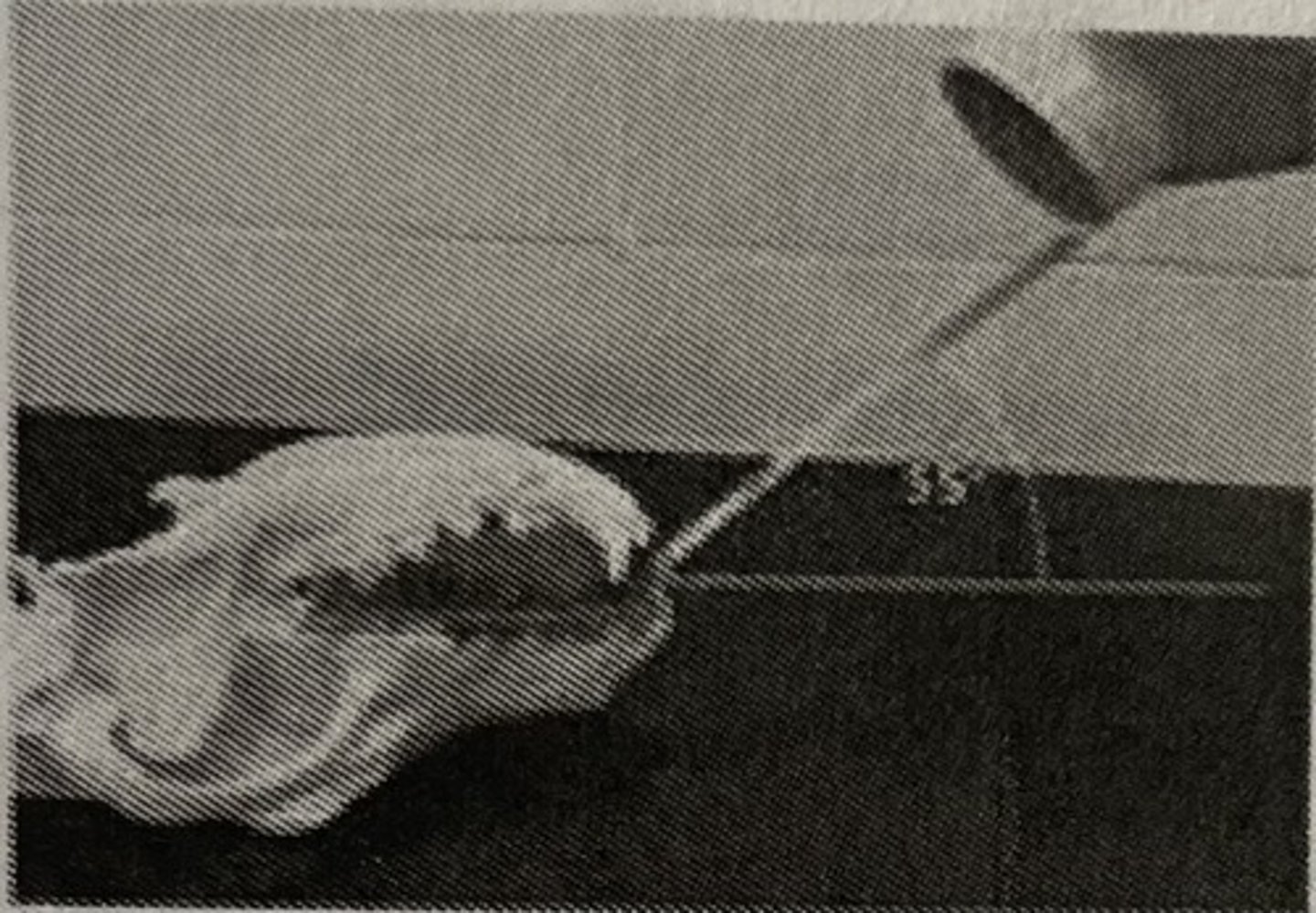

Simplified technique: mandibular premolars/molars
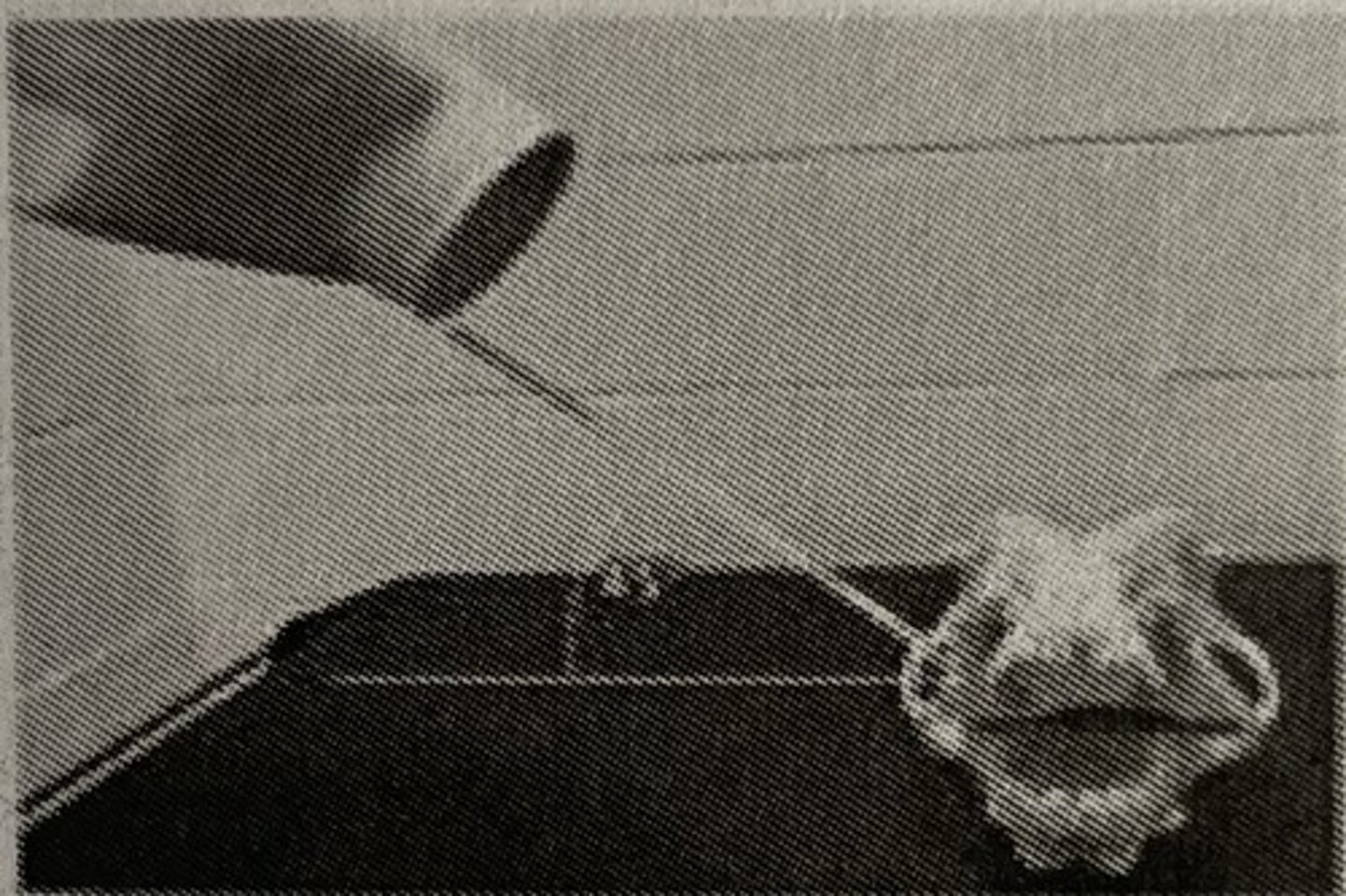
What are the two methods to diagnose hip dysplasia?
- OFA
- Pennhip
What does OFA stand for?
Orthopedic Foundation for Animals
What does PennHIP stand for?
Pennsylvania Hip Improvement Program
- Focus primarily on detecting the presence of hip dysplasia
- provides certification on overall appearance of hips
- Often used to determine if a dog is suitable for breeding
- Dog must be two years of age
- VD and lateral pelvis views required
OFA
- Measures joint laxity to predict future development of hip dysplasia
- Dogs must be 16 weeks of age
- Extension, distraction, compression views required
- a score is calculated to predict a dog's potential for developing hip dysplasia
Pennhip
What must you do before taking x-rays on horses?
- Clean the entire leg of debris
- Pick hoof
What are some indications for x-rays on horses?
- Laminitis
- Arthritis
- Hole/Derogation
- Fractured splint bones
- Slab fracture
When taking x-rays on horses, what should you be aware of?
- No sudden movements
- Keep a hand on them at all time
- Never stand behind them
- Let the horse examine x-ray equipment before starting
The ability of various tissues to return a sound wave
Echogenicity
Tissues, that generally do not have the ability to bounce back sound waves, usually appear black on scans
Anechoic tissue
Tissues that have limited ability to reflect sound waves back to the source, will appear various shades of gray
Hypochoic tissue
Tissues, that easily bounce back waves back to the transducer, produce image that are brighter in appearance
Hyperchoic tissue
Weakening of the sound waves as it moves through tissue
this is one of the factors that limits the depth of perception
Attenuation
Process where sound waves are not reflected back, but instead converted into heat
Absorption
Redirection of the beam back to the transducer
Reflection
Inter-Tissue reflection of the sound wave
Scattering
What should face the head when using the ultrasound probe
The little notch on the transducer
What is the most important component of a ultrasound machine?
Piezoelectric crystals
How would fluid appear on ultrasound?
Black/Anechoic
How would soft tissues appear on ultrasound?
Grey/Hypochoic
How would bone/air look on an ultrasound?
White/Hyperchoic
What does FAST ultrasound stand for
Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma
A rapid ultrasound examination often performed in emergency situations, used to assess for free fluid in the abdominal cavity, pericardial spaces, and/or plural spaces, which can indicate trauma
FAST ultrasound
What does POCUS ultrasound stand for
Point of care
A bedside diagnostic imaging technique used to quickly assess a patient's condition
POCUS
Back of four limbs from the carpet and distal
Palmar
Back of hind limbs from the hock distal
Plantar
Towards the head
cranial
Away from the head end or toward the end hind of the body
Caudal
Nearest to the point of origin of a structure
Proximal
Farther from the point of origin
distal
Laying on side
recumbent
Top of back
dorsal
Bottom of stomach
ventral
Closest to the midline
medial
Farther from the midline
lateral
Anterior posterior
AP
DV
Dorsal ventral
VD
ventral dorsal
These films will always appear black
- Totally black: no patient or really bad technique
- Black with an image: you did something right
Exposed and processed
These are always clear
Unexposed and processed