3.3 Digestion and absorption
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What happens in digestion?
Large (insoluble) molecules are hydrolysed into smaller (soluble) molecules that are small enough to be absorbed across the cell membrane and into the blood
Describe the digestion of starch in animals
Amylase hydrolyses glycosidic bonds in starch to maltose
Membrane-bound maltase hydrolyses glycosidic bonds in maltose to glucose
Describe the digestion of disaccharides in animals
Membrane-bound disaccharides hydrolyse disaccharides into 2 monosaccharides
Maltase hydrolyses maltose into glucose + glucose
Sucrase hydrolyses sucrose into fructose + glucose
Lactase hydrolyses lactose into galactose + glucose
Describe the digestion of lipids in animals
Bile salts emulsify (break down) lipids, causing them to form smaller lipid droplets
This increases surface area of lipids for increased/faster lipase activity
Lipase hydrolyses lipids into monoglycerides and fatty acids - hydrolysis of ester bond
Describe the digestion of proteins by an animal
Endopeptidases hydrolyse internal peptide binds within a polypeptide to form smaller peptides so more ends/ surface area for exopepidases
Exopeptidases hydrolyse terminal peptide binds at the ends of polypeptides to form single amino acids
Membrane-bound dipeptidases hydrolyse peptide binds between a dipeptide to form two amino acids
Hydrolysis of peptide bonds
Where is amylase produced?
By salivary glands and pancreas
When are membrane-bound maltase found?
Attached to cells lining the ileum
Where are bile salts produced?
By the liver
Where is lipase made?
In the pancreas
Why are membrane-bound enzymes important in digestion?
Membrane-bound enzymes located on cell membranes of epithelial cells lining ileum
They maintain concentration gradients for absorption
Describe the pathway for absorption of products of digestion in animals
Lumen (inside) of ileum → cells lining the ileum (part of small intestine) → blood
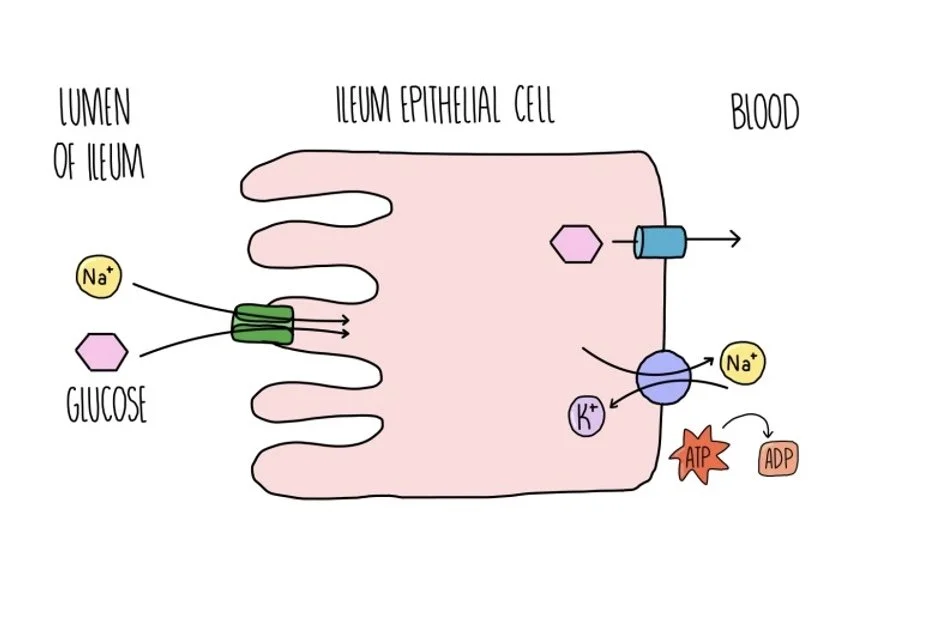
Describe the absorption of amino acids and monosaccharides in animals
Na+ actively transported from epithelial cells lining ileum to blood via sodium potassium pump, establishing a concentration gradient of Na+ (higher in lumen than epithelial cel)
Na+ enters epithelial cell down its concentration gradient with glucose against its concentration gradient via a co-transporter protein
Glucose moves down a concentration gradient into blood via facilitated diffusion
Describe the absorption of lipids in animals
Micelles contain bile salts, monoglycerides and fatty acids - Make monoglycerides and fatty acids more soluble in water, carry/release fatty acids and monoglycerides to lining of ileum and maintain high concentration gradient of fatty acids to cell/lining
Monoglycerides and fatty acids absorbed into epithelial cell by diffusion
Triglycerides reformed in epithelial cell and aggregate (collect) into globules
Globules coated with proteins, forming chylomicrons which are packaged into vesicles
Vesicles move to cell membrane and leave via exocytosis. They enter lymphatic vessels and eventually return to blood circulation