Macro Lecture - Wk 2 L3
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
L3. What are the 3 essential characteristics of money?
It can be used to settle transactions, it is a store of value and it acts as a commonly accepted use of account.

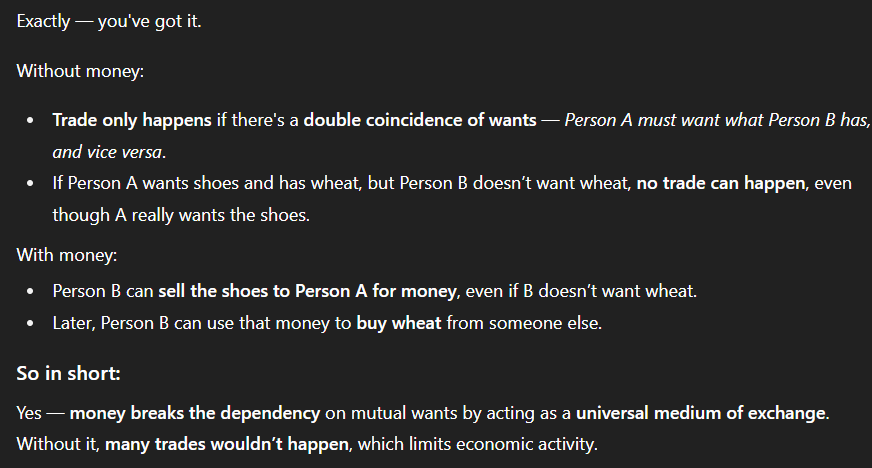
L3. What issue does money overcome that a barter economy can’t address? Explain it.
The double coincidence of wants. Double coincidence of wants is where a trade between 2 people only happens if they both have the good/service that the other wants. With money, they don’t need to both have the good/service that the other wants; one person can be provided the good in exchange for money.
L3. What are the aggregate measures of money?
Currency, Money base, M1, M3, Broad Money
L3. What is currency?
Notes and coins held by the private non-bank sector
L3. What is Money Base as a measure of money?
Currency + banks holding of notes and coins + Reserve Bank liabilities to private banks and non-banks
L3. What is M1 as a measure of money?
Currency + current (cheque) deposits of the private non-bank sector at banks
L3. What is M3 as a measure of money?
M1 + all other private sector deposits at banks except deposits of authorised deposit-taking institutions(ADIs) + all deposits of private non-ADI sector at credit unions and building societies
L3. What is Broad Money?
M3 + other deposit-like borrowings of all financial intermediaries (AFIs) from the non-ADI private sector
L3. Whose behaviour does money creation depend on?
Borrowers, banks, regulators and central bank
L3. How do borrowers affect the creation of money?
They must be willing to borrow, which depends on consumption habits, interest rates and economic conditions
L3. How do banks affect the creation of money?
They must be willing and able to lend. Essentially, they must have sufficient liquidity coverage, sufficient shock-absorbing capital (CET1), and interest rates sufficient to cover costs
L3. How do regulators affect the creation of money?
Australian Prudential Regulation Authority set requirements for liquidity, capital adequacy, and lending standards
L3. How does the Central Bank affect the creation of money?
Reserve Bank of Australia sets the overnight cash rate as well as unconventional monetary policy
L3. What is the formula for Reserves(e.g., ESAs)
R = (r+e)D
L3. What is the formula for the Money Base?
B = C + R = (c + r + e)D
L3. What is the formula for the Total Money Supply?
M = C + D = (c + 1)D
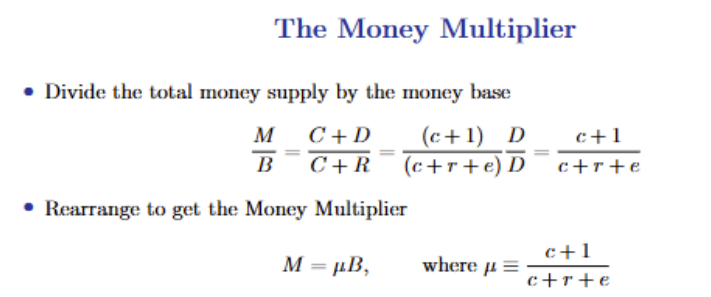
L3. Find the Money Multiplier
L3. How does money supply respond to different policies and behaviours of the private sector?
Decreases when the government increases required reserves, decreases when banks increase their excess reserves, decreases when the private sector hold more currency.
L3. What is usually in the Assets section of the Balance Sheet of a typical commerical bank?
Cash, loan portfolio, investment portfolio, required reserves (if in the US)
L3. What is in the Liabilities section of the Balance Sheet of a typical commercial bank?
Deposits by households and businesses, short-term debt, long-term debt
L3. If Equity is negative, what does it mean about the bank?
It is insolvent
L3. What is liquidity?
How quickly an asset can be bought/sold with minimal impact on its price
L3. What is a core feature of a banking business?
Liquidity intermediation. Bank is funded by short-term liabilities and holds long-term assets

L3. What is the formula for the leverage ratio?
Total assets/equity
L3. What does leverage do?
Magnifies risk and return to shareholders
L3. Why do bank runs happen?
When rumours cause depositors to converge on bank and demand money back
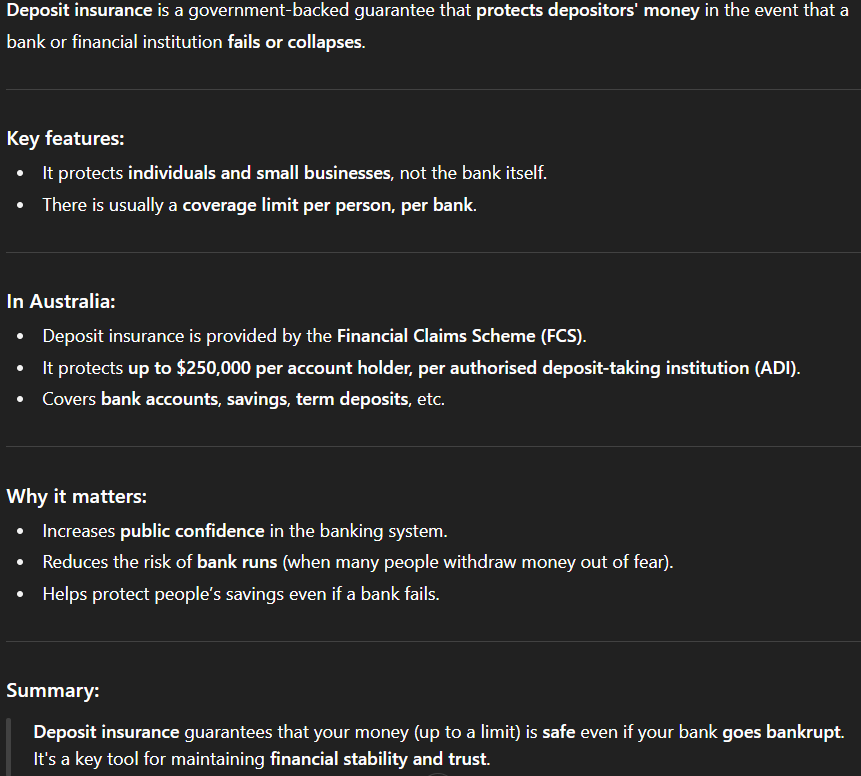
L3. What has been 1 solution to reduce the number of bank failures?
Deposit insurance