L6: Lithosphere, Weathering, and Soil Formation Overview
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
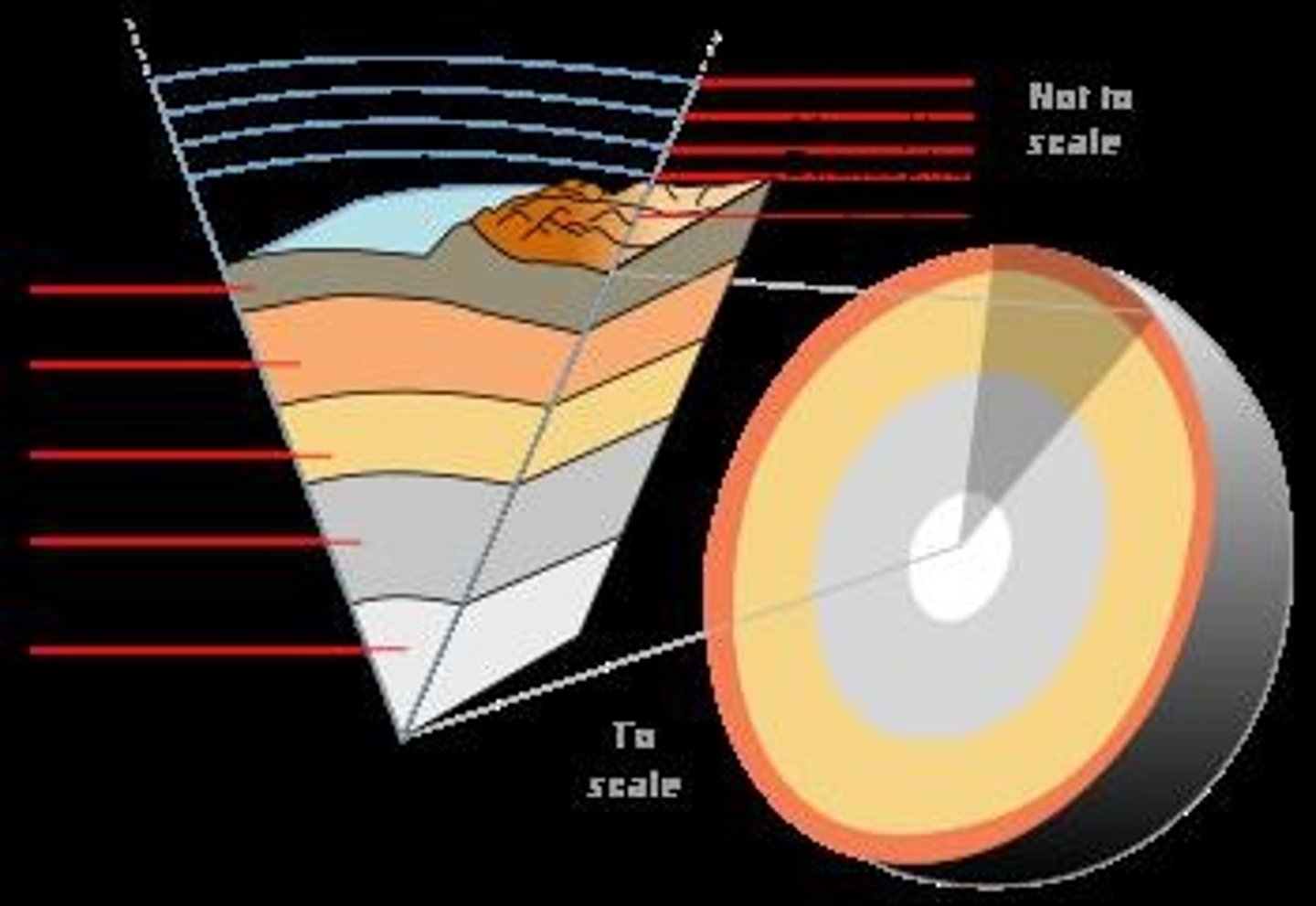
Lithosphere
Solid outer layer of Earth, includes crust and upper mantle.
Mechanical Weathering
Physical breakdown of rocks without chemical change.
Chemical Weathering
Breakdown of rocks through chemical reactions.
Role of Organisms in Weathering
Biological activity contributes to soil formation and rock breakdown.
Formation of Soils
Process involving weathering, organic matter, and mineral accumulation.
Aluminosilicate Minerals
Primary minerals forming Earth's crust, containing aluminum and silicon.
Minerals
Natural compounds with specific chemical structures and properties.
Rock
Aggregate of one or more minerals, forming solid mass.
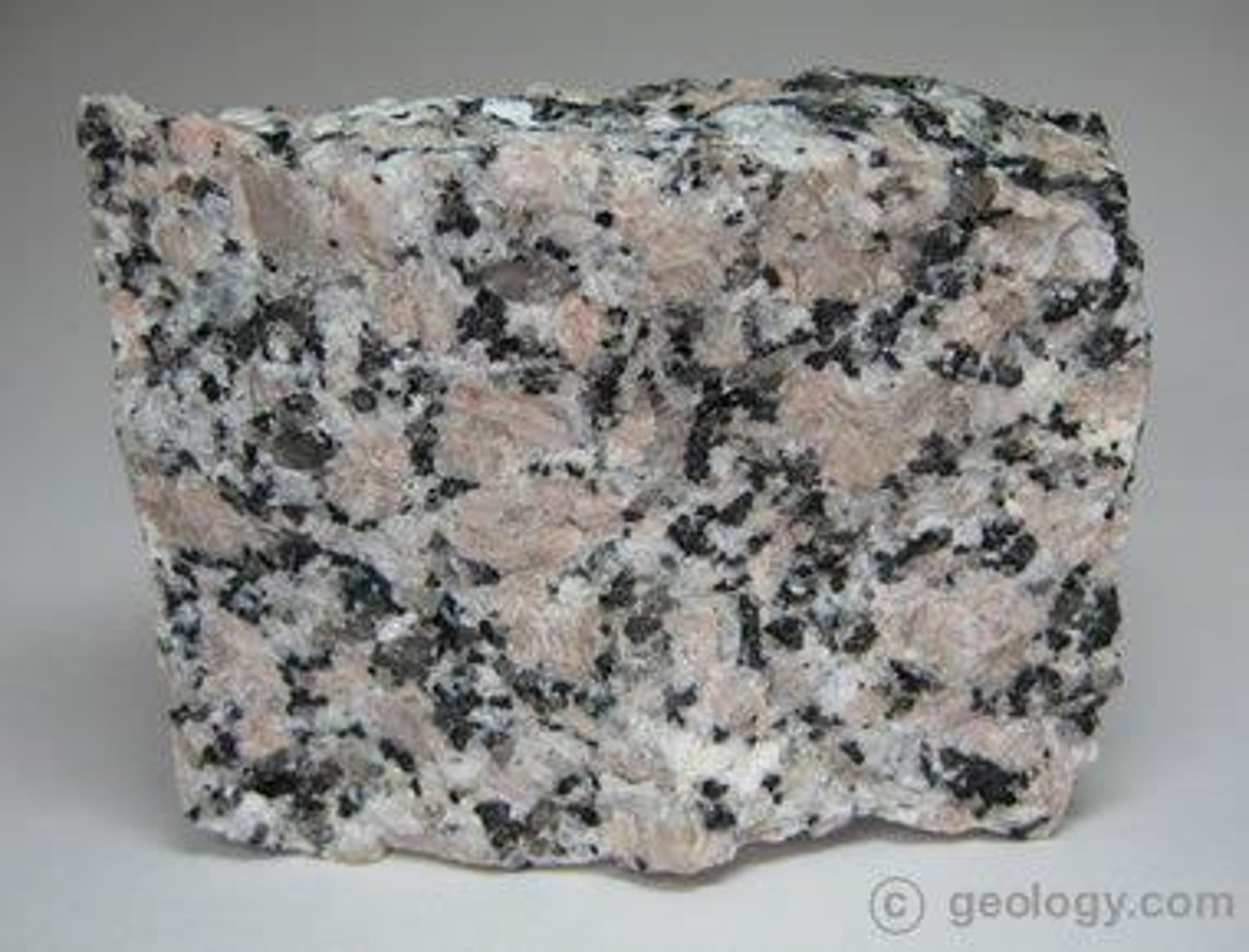
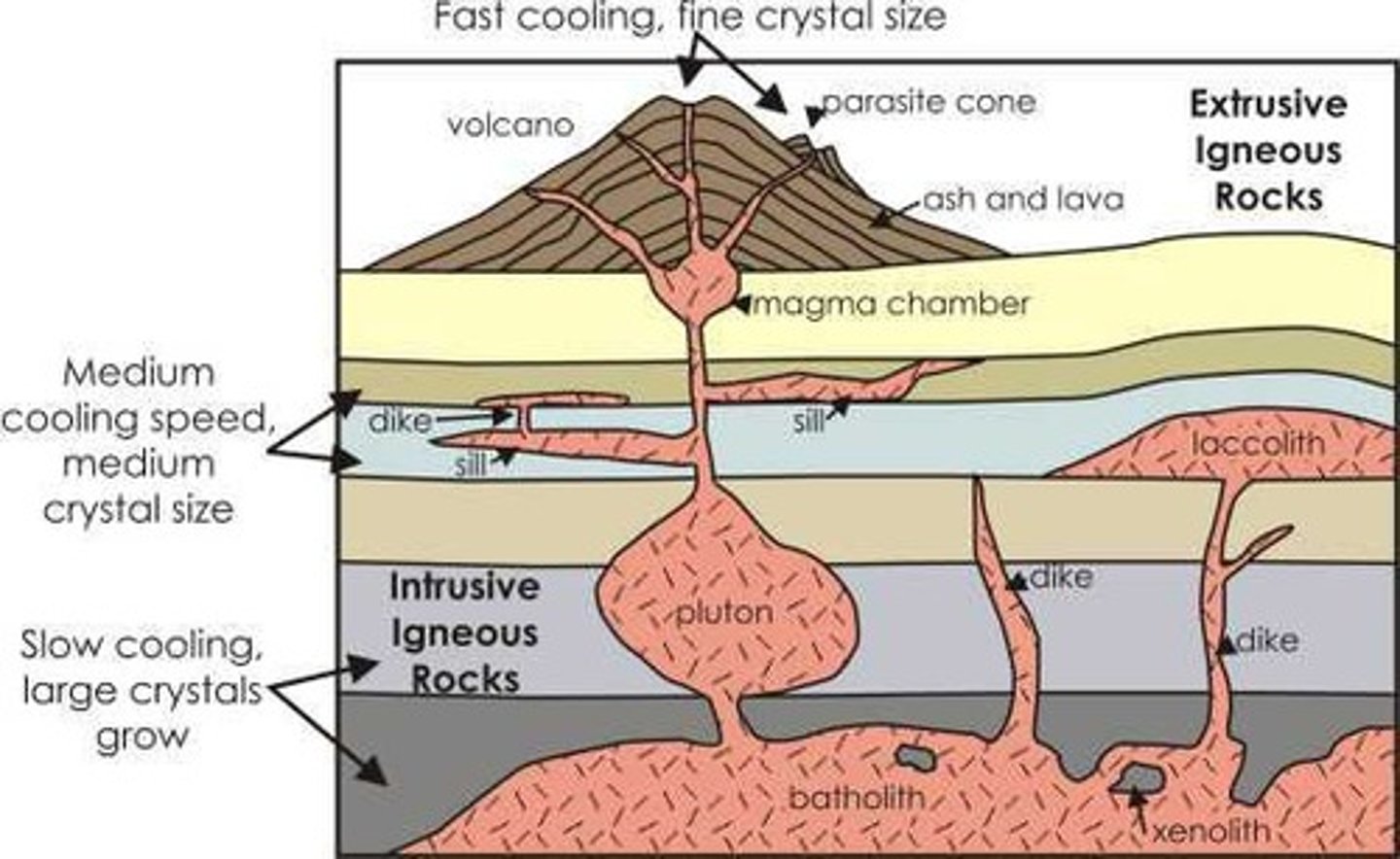
Granite
Igneous rock composed mainly of feldspar and quartz.

Igneous rock
Formed from cooling molten rock at various depths.
Oceanic crust
Denser, thinner crust primarily composed of basalt.
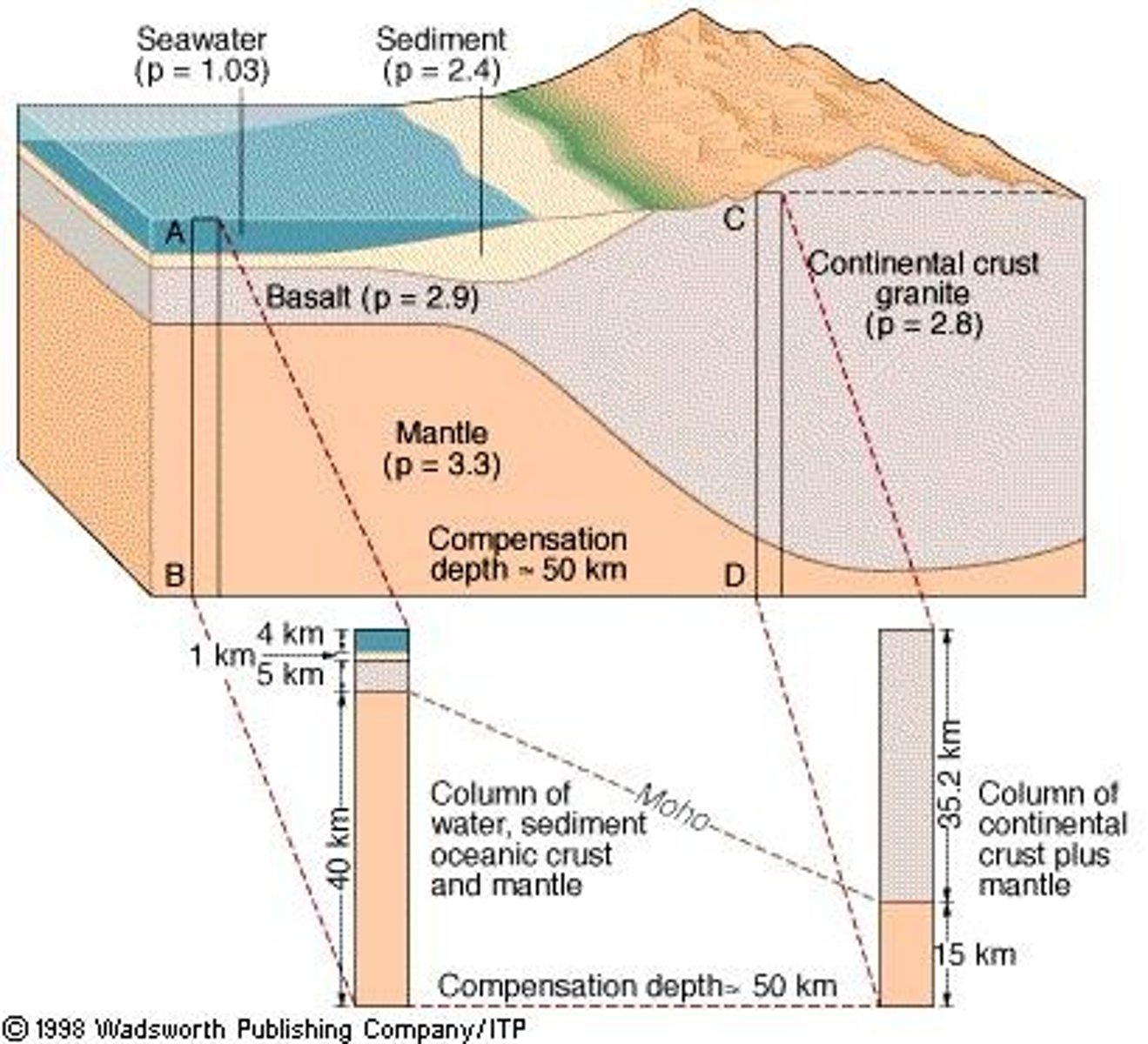
Continental crust
Thicker crust primarily composed of granite.
Alumino-silicate materials
Primary components of both oceanic and continental crust.
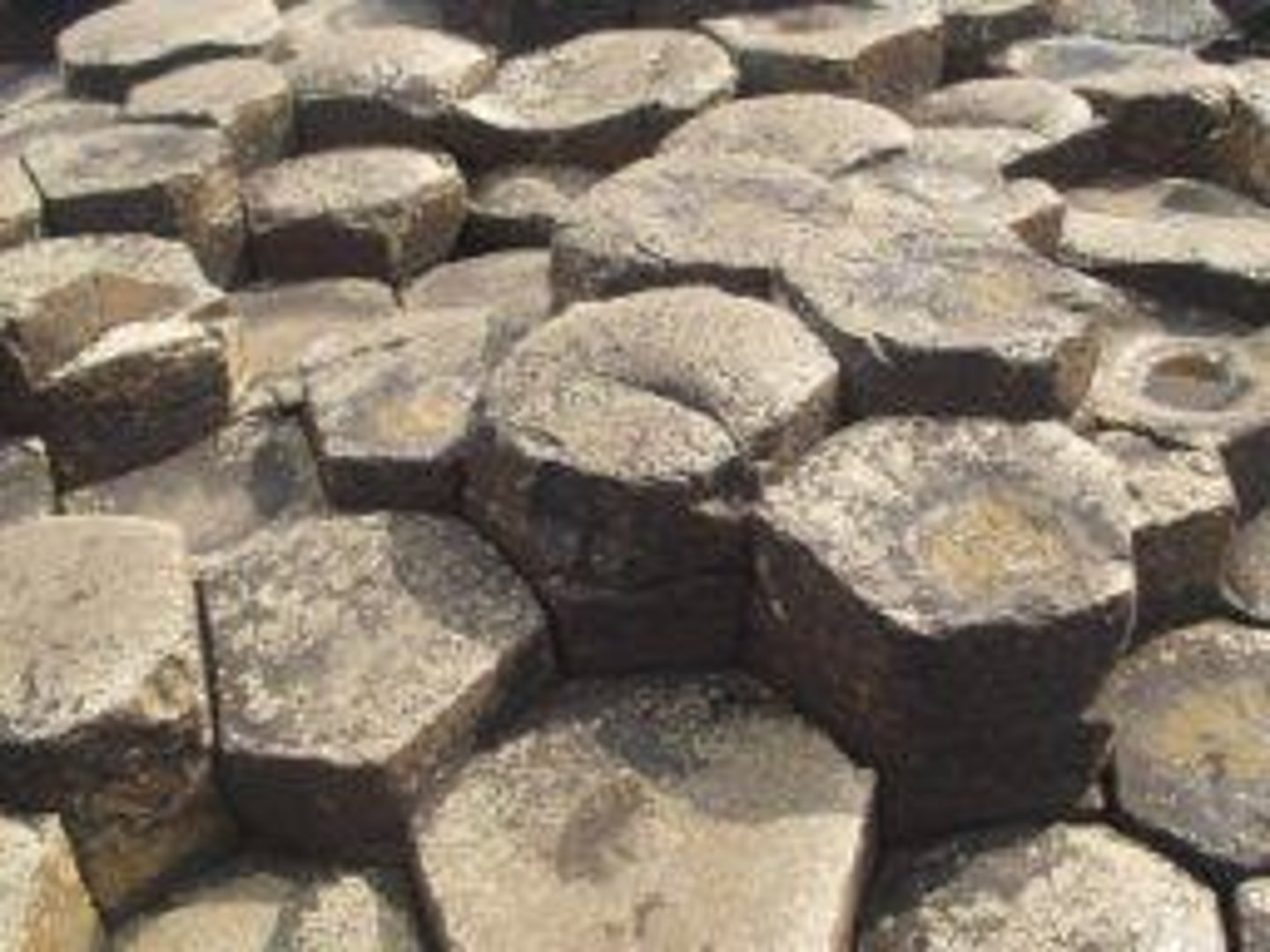
Basalt
Igneous rock, dense, forms oceanic crust.

Granite
Igneous rock, less dense, forms continental crust.
Plagioclase feldspar
Common mineral in igneous rocks.
Subduction
Oceanic crust sinks beneath continental crust.
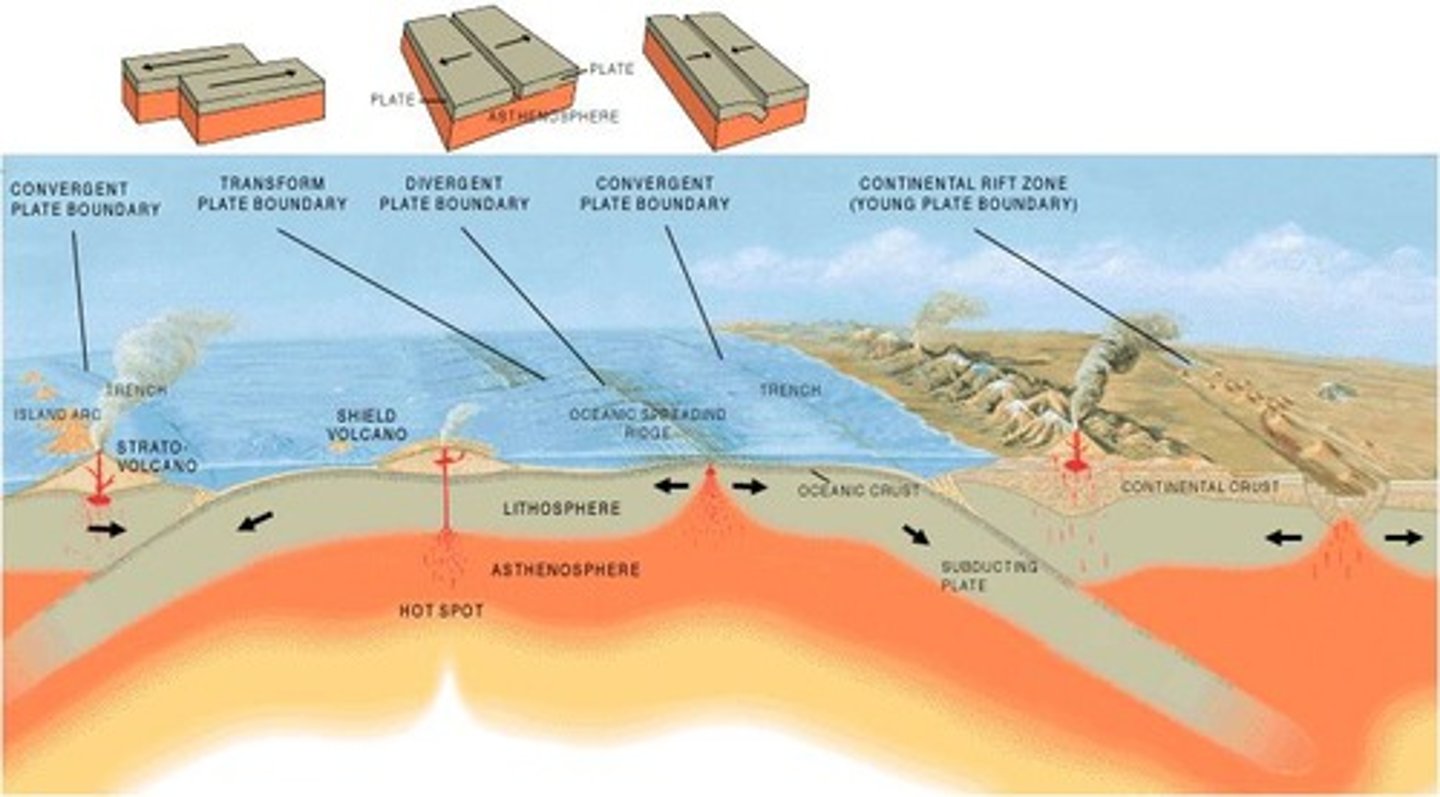
Asthenosphere
Layer where melted subducting crust is added.
Accretion
Process of adding material to continents.
Metamorphosis
Alteration of rocks due to heat and pressure.
Spreading zones
Locations where new crust is created.
Rift zones
Continental areas where crust is formed.
Mechanical weathering
Physical breakdown of rocks by natural forces.
Chemical weathering
Alteration of rocks through chemical reactions.
Sedimentary rock
Formed from sediments settling in low-energy areas.
Sandstone
Sedimentary rock formed from sand particles.
Shale
Sedimentary rock formed from clay particles.
Chert
Sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline quartz.
Metamorphic rocks
Rocks altered by pressure and temperature.
Gneiss
Metamorphic rock with banded texture.
Marble
Metamorphic rock formed from limestone.
Congruent dissolution
All components of a mineral dissolve completely.
Incongruent dissolution
Forms secondary minerals during the dissolution process.
Secondary minerals
Minerals formed from weathering processes.
Chemical weathering
Process releasing ions into water from minerals.
Evaporites
Sedimentary rocks formed from evaporated water.
Halite
Mineral formed from evaporated sodium chloride.
Calcite
Calcium carbonate mineral from evaporated water.
Gypsum
Calcium sulfate mineral from evaporated water.
Role of organisms
Catalysts for weathering and sedimentary rock formation.
Carbon dioxide in soils
Produced by respiring plants, animals, microbes.
Organic acids
Acids from plants that enhance mineral weathering.
Chelators
Substances preventing metal precipitation, aiding breakdown.
Biogenic minerals
Minerals formed by biological processes.
Hermatotypic corals
Corals that deposit calcium carbonate.
Coccolithophores
Algae that produce calcium carbonate shells.
Foraminifera
Amoeboid protists contributing to sedimentary rock.
Diatomaceous earth
Silica shells from diatoms, used in various applications.
Cation exchange capacity (CEC)
Soil's ability to retain and exchange cations.
Sesquioxides
Minerals like geothite and hematite in soils.
Clay minerals
Degraded aluminosilicates controlling soil chemistry.
Carbonate formation
Occurs when calcium concentration increases in soil.
Soil structure
Arrangement of soil particles affecting its properties.
Chemical characteristics of mineral soil
Influence retention and loss of substances in soil.
Evaporation
Process concentrating calcium, forming solid carbonate.
Calcium Carbonate
Solid formed from concentrated calcium during evaporation.
Arid Conditions
Dry environments where evaporation is common.
Phosphate Availability
Influenced by soil pH levels.
Neutral Soils
Optimal for phosphate availability.
Low pH
Causes PO43- to co-precipitate with Fe and Al.
High pH
Causes PO43- to co-precipitate with carbonate.
Phosphorus
Critical nutrient for plant growth.
Igneous Rock
Source of easily erodable phosphorus forms.
Fe and Al Sesquioxides
Traps phosphorus through weathering processes.
Soil Formation
Combination of mineral and biological particles.
Vertical Soil Structure
Result of water and plant interactions.
Soil Horizons
Distinct layers of soil with varying composition.
O Horizon
Organic matter layer at the soil surface.
A Horizon
Topsoil rich in organic material.
E Horizon
Heavily leached layer beneath topsoil.
B Horizon
Subsoil containing minerals from leaching above.
C Horizon
Parent material from which soil develops.
Sesquioxides
Iron and aluminum oxides formed in soils.
Chernozem
Soil type found in dry grasslands.
Spodosol
Soil type found in wet conifer forests.
Permafrost
Layer of permanently frozen soil.
Glacial Scouring
Soil removal process caused by glaciers.
Long Island Morraine
Landform created by glacial deposits.
Weathering Types
Includes mechanical and chemical processes.
Soil Profiles
Vertical cross-section showing soil layers.