Programming Languages
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
How many “ init ()”s are allowed in a Python class declaration?
1
In Java and Python, where are the values of instance variables stored?
heap.
In a Python initializer, what is purpose of the “*args” keyword?
Holds the parameters to be sent to the superclass(s).
In Java, what memory area are class variables stored
static area of memory
Which language ensures that the classes at the top of the hierarchy are initialized first?
Java.
Which language supports multiple inheritance?
Python
Which language requires that the “super()” operator be put in the first line of the constructor/initializer body?
Java.
Which language(s) uses the “new” operator to create class or struct instances?
Java
Which of the following is true of a symbol table?
A programming language can maintain more than one symbol table (namespace) simultaneously.
The environment maintains a symbol table.
Both reference counting and garbage collection make use of symbol tables
In heap maintenance, what does coalesce mean?
merge adjacent blocks of available memory.
The storage reclamation method that Go uses is
garbage collection
In C, new storage on the heap is allocated by the
malloc operator
The indicator field is used in
garbage collection
Which language cannot implement the swap procedure?
Java.
Which language does not support pointer arithmetic?
Java
What was the first language to use garbage collection?
Lisp
How many phases does a mark/sweep garbage collection algorithm have?
3.
In Python, storage management uses
reference counting.
Which of the languages below have nested subprograms?
Python, scheme, javascript
An AR for a lexically scoped language with stack-dynamic local variables and subprograms has how many possible field types (hint: include static and dynamic links)?
5
An AR for a non-recursive language with simple subprograms has how many field types?
3
When drawing diagrams of activation records on a runtime stack,
The bottom of the AR is the front and the stack grows in the upward direction.
For a lexically scoped language with nested subprocedures, the chain offset for the use of a variable is calculated by
obtaining the static depth where the variable is used, obtaining the static depth where the variable is declared, and subtracting the latter from the former.
According to Sebesta, what are the characteristics of a language which allows simple subprograms?
No recursion, no nested subprograms or procedures.
Which of the languages below do not need a stack as part of its runtime environment?
Early versions of FORTRAN
In a C/C++/Java-like language, nested blocks
create a local scope.
can be used to restrict visibility of temporary local variables, thereby increasing program reliability.
are often implemented by placing an AR on the runtime stack.
In a language with stack-dynamic local variables
activation records are stored on the runtime stack
there is one activation record for each procedure activation
activation records are connected by dynamic links
In a lexically scoped language with stack-dynamic local variables and nested subprograms,
the static depth for each procedure is calculated by the compiler and is saved.
In a language with stack-dynamic local variables, when a procedure returns
the AR at the top of the stack is popped and the dynamic link of the popped AR points to the front of the next AR on the stack.
Which is not true of the Rust language.
The default return value of a function is zero.

In the code below, the variable “v1” becomes unbound when Line 3 is executed. Show how to modify Line 3 so that this does not happen.

Rust is a strongly typed language like the Go language. In the above code, the variables v1 and v2 have datatypes. What is the name for the process that determines the datatypes for these variables?
Type inference

The pseudo code below is used for the mark phase of garbage collection. It accepts a pointer to an item on the heap and traverses the entire data structure, marking each memory item as being in use. It assumes all memory blocks are the same size and have two fields that point to other blocks. Supply the names of the two functions with the question marks.
mark, mark
Name the three phases of the garbage collection algorithm described in the textbook and the garbage collection algorithm.
“clear”, “mark”, and “sweep”
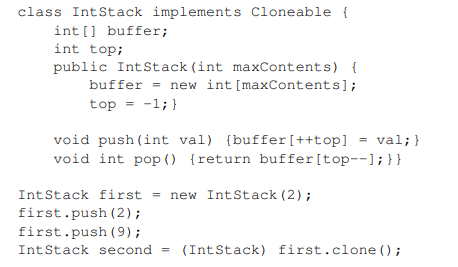
The last line of the Java code below makes a shallow copy of an integer stack given by variable first and assigns it to second. Draw the data structures that are the values of first and second, keeping into account that second is a shallow copy. Also, show what information is on the heap vs the runtime stack.
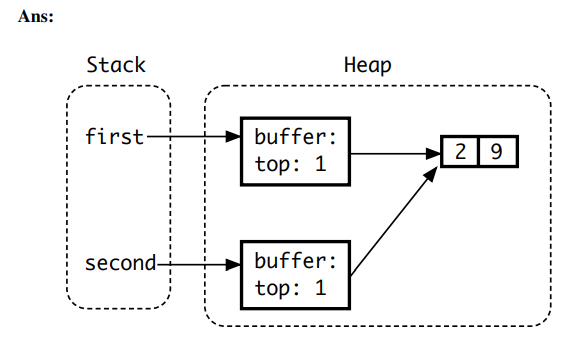
Draw the cons-cell diagram for the Scheme expression below. (( 1 2 ) (5 ( 3 4 )))
True or false? The function below is tail-recursive.
def factorial(n):
if n == 0: return 1
else: return n * factorial(n-1)
False.
True or false? The function below is tail-recursive.
def factorial(n, accumulator=1):
if n == 0: return accumulator
else: return factorial(n-1, accumulator * n)
True.
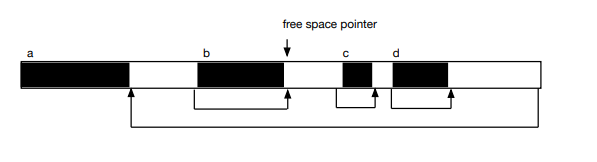
The diagram below shows the free-space list during program execution. We see allocated storage (dark shading), unallocated storage (light shading), variables associated with each allocated storage block, and the pointer structure to maintain the free space.
Show what happens when a block C of allocated memory is reclaimed and returned to the free-space list. Draw a picture that shows how free-space is coalesced.
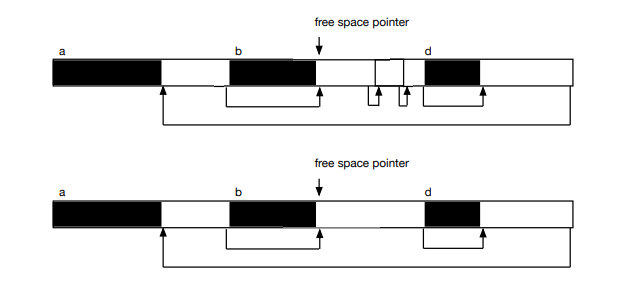
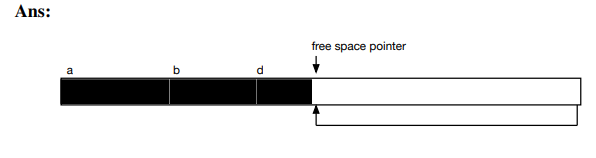
Draw a picture to show what happens when free-space is compacted.
Tail recursion
A recursive function in which the recursive call is the last statement that is executed by the function. So basically nothing is left to execute after the recursion call
Activation Record (AR)
A contiguous block of storage that manages information required by a single execution of a procedure. When you enter a procedure, you allocate it, and when you exit that procedure, you de-allocate it.