Organic Chemistry: Exam 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Formula for formal charge
# valence electrons - # of bonds - # unpaired electrons (total number not pairs)
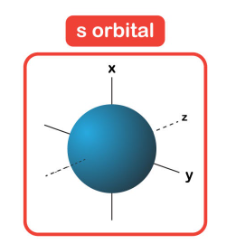
describe s orbital
full circle
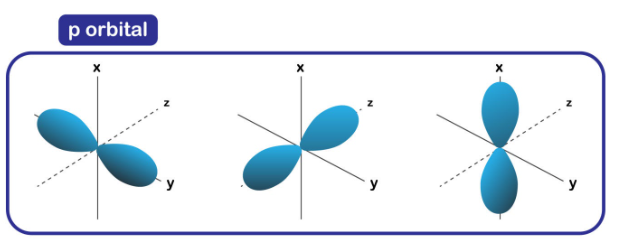
describe p orbital
1 empty orbital, 1 full orbital
always 180* (straight)
how many orbitals in sp orbital?
2 orbitals
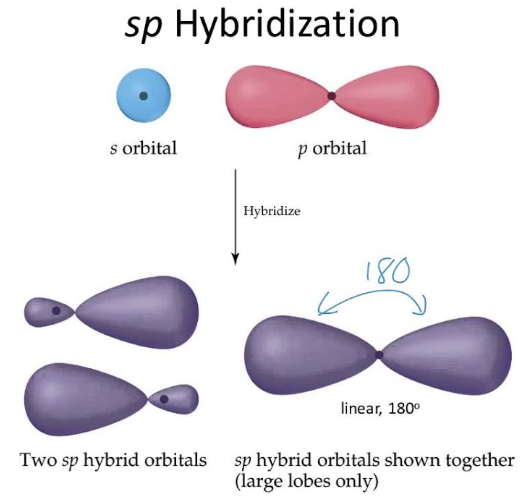
what is the shape of sp orbital
linear
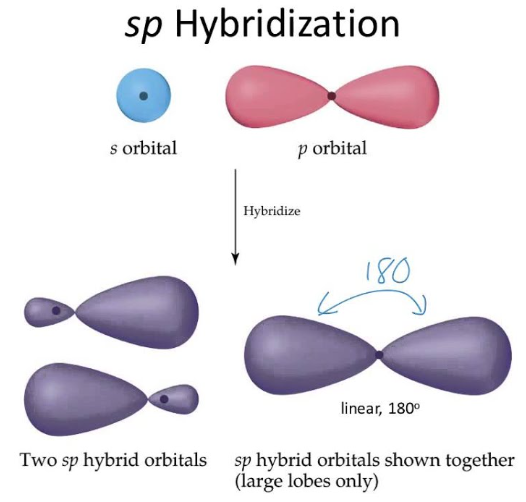
what is bond angle of sp orbital
180 degrees
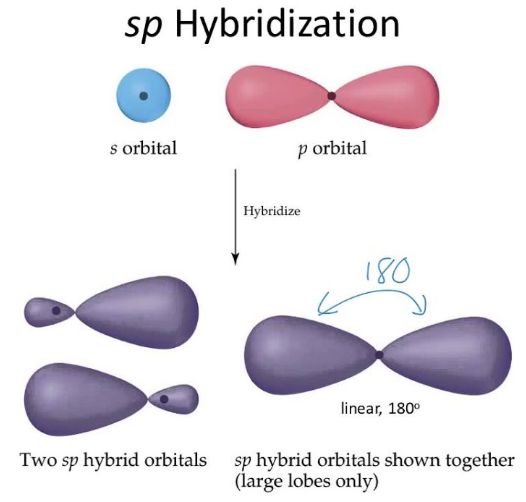
difference between sp and p orbital
p has one empty orbital, both sp orbitals are filled
how many orbitals in sp2
3 orbitals
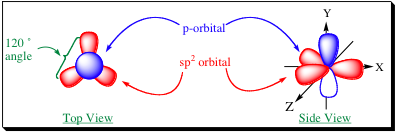
what is shape of sp2
trigonal
what is bond angle of sp2
120
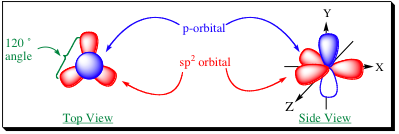
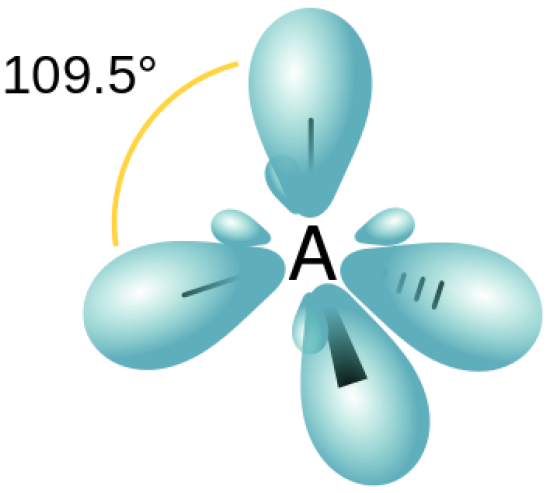
how many orbitals in sp3
4

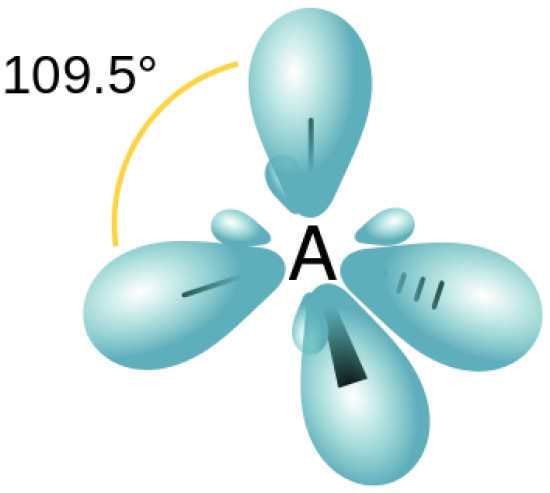
what is shape of sp3
tetrahedral

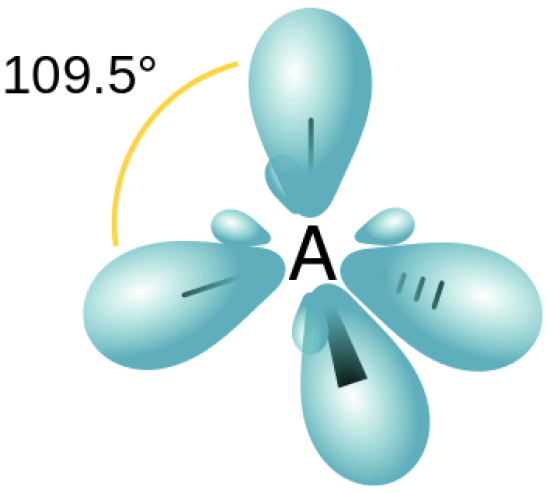
what is bond angle of sp3
109.5

explain C NMR
represnts types of atoms (sp3, sp2, sp, etc)
each line represents unique C signal
In C NMR what does 0-80 range represent
sp3 (4 groups)
single bonds
In C NMR what does 50-80 range represent
left end of sp3 range
represents polar single bonds
4 examples of polar bonds
C-O
N-O
O-H
C-N
2 examples of non polar bonds
C-C
C-H
In C NMR what does 75-100 range represent
sp orbitals
triple bonds
In C NMR what does 100-200+ range represent
sp2 orbitals
double bonds
In C NMR what does 165-200+ range represent
left side of sp2 range
polar double bonds
explain IR spectroscopy
represents types of bonds (single, double, C-H, etc)
where is the fingerprint region in IR spectroscopy
0-1500
region ignored because info not unique to help identify
what does 1500-1700 range represent in IR spectroscopy
C=C
what does 1700-1800 range represent in IR spectroscopy
C=O
ketones
what does 2000-2100 range represent in IR spectroscopy
triple bonds
C≡C
C≡N
what does 2600-2800 range represent in IR spectroscopy
Aldehyde C-H bonds
what does 2800-3000 range represent in IR spectroscopy
sp3 C-H bonds
what does 3000-3200 range represent in IR spectroscopy
sp2 C-H bonds
what does 3300-3400 range represent in IR spectroscopy
sp C-H bonds
what does 3400-3700 range represent in IR spectroscopy
O-H bond in alcohols
N-H bonds in amines
what is the difference between alcohols and amines in 3400-3700 range
alcohols have hill shape
amines have spiked shape and are smaller
What is a single bond
sigma bond
σ
what is a double bond
π + σ
π bond between p orbitals
what is a triple bond
π +π+ σ
2 pi bonds
rules for line-angle structure
C’s not labeled
Other elements labeled
corner represents C
H’s only labeled when not attatched to C
Lone pairs shown
define axial
vertical bond
define equatorial
horizontal bond
is axial or equatorial bonds more stable?
equatorial
steps to determine Z vs E alkenes
split alkene vertically in 2 halves
name compounds on bonds
decide which group gets priority
split horizontally in line with double bond
groups on same side = Z groups on opposite sides = E
How to determine priority in Z or E alkenes?
If lone element: (bigger atomic #)
If compounds: the one with more carbons (ethyl has priority over methyl)
define constiutional isomer
same # of atoms
different arangeent of atoms
define stereoisomer
same atoms
connected same way
different 3D arrangement
examples of stereoisomers
E vs Z
cis vs trans
R vs S
define resonance
all atoms in same place
electrons distributed differently
often “flipped”
4 steps to compare compounds:
same formula? if not compounds are unrelated
same connectivity? if not compounds are constituitonal isomers
same spacial arrangement? if not compounds are stereoisomers
If yes to all, they are identical
Bond order formula
(# bondingg electrons - # antibonding electrons)/2
Do eclipsed or staggered conformations have more energy?
eclipsed
are staggered or eclipsed conformations more stable?
staggered
lower energy is more stable
in staggered conformation, which bonds give off energy?
C-C
C-any element other than H
any involving H give off no energy
how to tell in line-angle structures w/ double bonds the more stable structure?
Structure where double bond is attached to more R groups