PPFA 10 - Equilibrium - Buffers
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
understand how buffers resist PH change, apply henderson- hasselbalch equation ,buffer capacity and clinical uses of buffers in pharmacy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the relationship between hydrogen ion concentration and ph ?
At 25 degrees water dissociates into hydroxyl and hydrogen ions bothe present in equal concentrations of 1×10-7 mol/L= balance makes water neutral PH=7
PH is defined as the negative log of H+
𝑝𝐻 = −𝐿𝑜𝑔10 𝐻+
So, when [H⁺] = 1 × 10⁻⁷, the pH = 7 i.e Neutral
What happens if we add an acid or a base?
If we add an acid, it donates protons ⟶ 𝐻+ increases ⟶ ⟶ pH < 7
If we add a base, it accepts protons ⟶ 𝐻+ decreases ⟶ ⟶ pH > 7
How big is the range of H= or PH ?
From about 1 mol/L for a strong acid, down to 1 × 10⁻¹⁴ mol/L for a strong base.
pH range 0-14
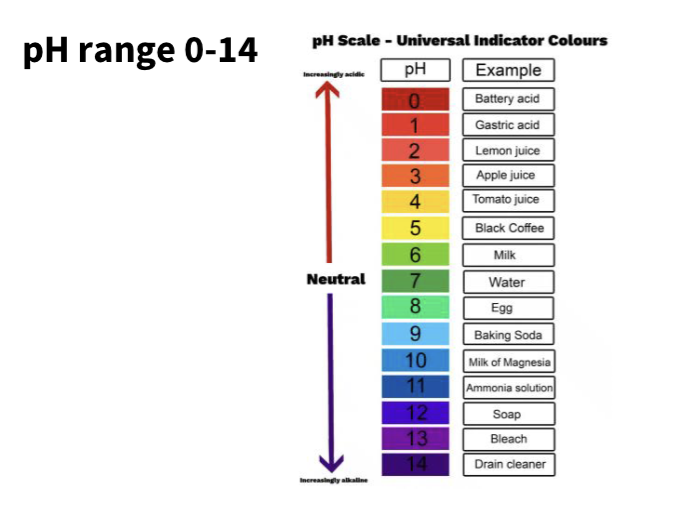
How do we measure PH ?
indicators
ph probe - need calibration
indicator paper
What are the physiological Phs of the body ?
general ph = 7.4 and fluctuates around this
stomach significantly lower- acidic 1-3
small intestine fluctuates
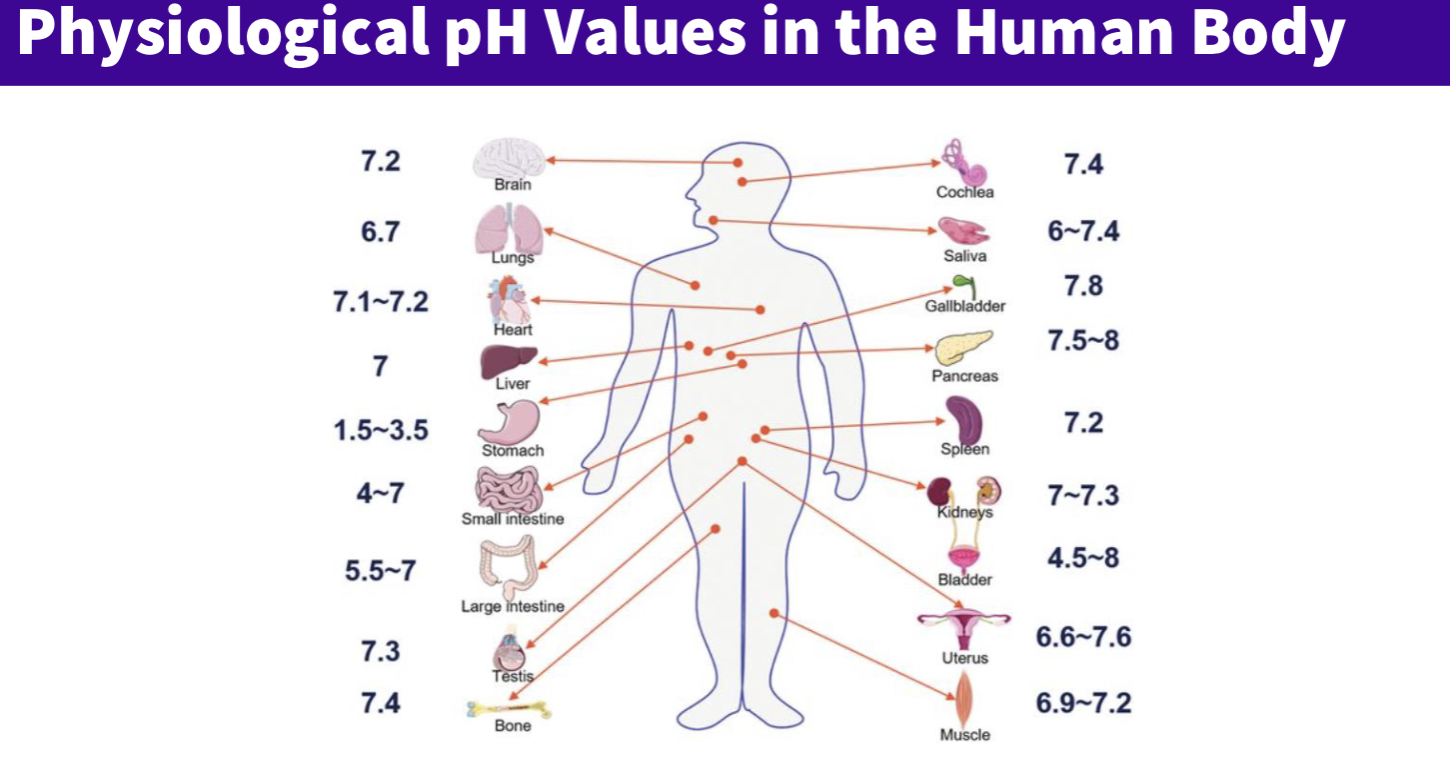
What is the clinical significance with regards to the blood ph ?
Normal arterial blood- 7.4
Venous blood and interstitial fluids - 7.35 ( slightly lower due to more co2 - more carbonic acid )
if blood PH <7.35 ( acidosis) - CNS depression - confusion ,disorientation , coma
if blood PH> 7.45 ( alkalosis ) - CNS hyperexcitability - muscle spasms ,convulsions ,respiratory paralysis
survival limits:
Lower limit ≈ 7.0 (survival for only hours)
Upper limit ≈ 7.7
Fatal range:
< 6.8 or > 8.0 → death occurs quickly
What is the importance of ph in pharmaceutics ?
It affects the ionisation of weak acids and bases, which changes how drugs dissolve and absorb
▪ It influences drug solubility
▪ And importantly, it impacts drug absorption across membranes into the
bloodstream
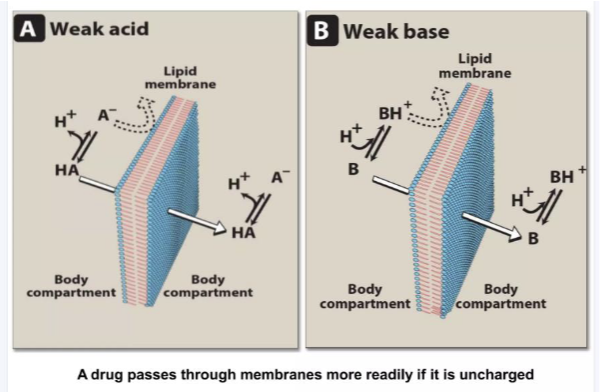
Absorption patterns for weak acid and weak bases ?
For weak acids- needs to be unionised for absorption
For weak bases - needs to be ionised for absorption
What are the dissociation of acids and bases equations and its constant ?
For a weak acid (HA) HA ⇌ H⁺ + A⁻
For a weak base (B) B + H⁺ ⇌ BH⁺
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) measures how much an acid dissociates
To simplify numbers, we use pKa instead;
pKa = -log₁₀Ka
A lower pKa means a stronger acid (it dissociates more easily)
What is the buffer equation - henderson - hasselbalch equation ?
Relationship Between pH, pKa, and Ionisation
From the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation:
For weak acids pH = pKa + log([A⁻]/[HA])
For weak bases pH = pKa + log([B]/[BH⁺])
These equations show how pH and pKa determine the ratio of ionised to unionised
drug
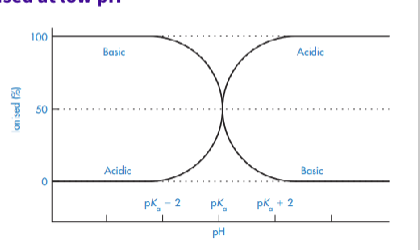
What is the relationship between pKa and Ph ?
The degree of ionisation
When pH = pKa, the drug is 50% ionised and 50% unionised
- If pH > pKa → acidic drugs are mostly ionised at high ph
- If pH < pKa → basic drugs are mostly ionised at low pH
Unionised form = more lipid-soluble and better absorbed
Ionised form = more soluble, less
absorbed
What is a buffer ?
Buffer solutions resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
What is the importance of buffers in their applications ?
Maintain ph
Blood contains acids from metabolism all the time - lactic acid ,carbonic acid - blood ph barely changes
Medications need buffers to resist ph change
What does a buffer consist of ?
They consist of either:
Weak Acid + Conjugate Base (Salt)
HA (weak acid) and A⁻ (from salt like NaA)
• Added H⁺ reacts with A⁻:
A⁻ + H⁺ → HA pH resists change
• Added OH⁻ reacts with HA:
HA + OH⁻ → A⁻ + H₂O pH resists change
Weak Base + Conjugate Acid (Salt)
B (weak base) and BH⁺ (from salt)
Added H⁺ reacts with B:
B + H⁺ → BH⁺ pH resists changeAdded OH⁻ reacts with BH⁺:
BH⁺ + OH⁻ → B + H₂O pH resists change
What is buffer capacity ?
Buffer Capacity (β) measures how well a buffer resists changes in pH when acid or alkali is added.
It is defined as the amount of acid or base (in moles) needed to change the pH of 1 litre of solution by one unit.
If adding 1 mole of alkali changes the pH by 1, then β = 1
The buffer capacity depends on the total concentration of the buffer and the pKa of the weak acid
Key points:
Buffer capacity is highest when pH = pKa
graph - Buffer capacity of acetic acid–acetate
buffer as a function of pH
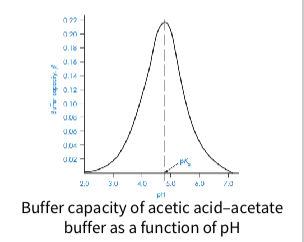
Why is physiological buffer capacity crucial?
To prevents dangerous swings – small pH shifts impair enzymes, large shifts cause coma/death
What is a chemical buffer system ?
Chemical buffer systems in body fluids that quickly neutralise added acids or bases to stabilise pH within second
What is a physiological system ?
Physiological systems that act more slowly:
• Respiratory system: Adjusts breathing rate to control carbon dioxide (CO₂)
levels, which affects blood pH. This takes a few minutes
• Urinary system (kidneys): Removes excess hydrogen ions (acid) through urine, slowly restoring pH over hours
What is bicarbonate buffer - ( major chemical buffer) ?
Bicarbonate buffer:
Made of carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) and bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻).
Neutralizes acids by converting bicarbonate to carbonic acid, which breaks down to water and CO₂ (exhaled).
Neutralizes bases by converting carbonic acid to bicarbonate.
Although its buffering capacity is not maximal at blood pH (~7.4), it’s efficient because it self-regulates via respiration and kidney function
What is a Phosphate buffer- major chemical buffers ?
Phosphate buffer:
In cells, uses dihydrogen phosphate (H₂PO₄⁻) and hydrogen phosphate (HPO₄²⁻) ions to buffer pH near 7.2, closer to physiological pH than bicarbonate, but at lower concentration.
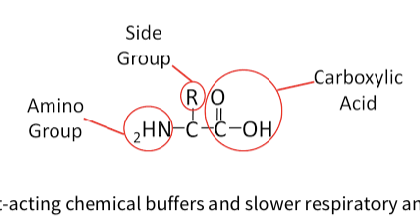
What is a Protein buffer - chemical buffer?
Protein buffer:
The most powerful system, accounting for ~75% of body’s buffering capacity.
Proteins buffer via acidic (–COOH) and basic (–NH₃) groups on amino acids, with pKa values near physiological pH, making them very effective.
Key Points:
The body uses fast-acting chemical buffers and slower respiratory and kidney
mechanisms to tightly regulate pH, crucial for normal function and health.
What is a universal buffer ?
Buffer capacity is highest at a pH near the pKa and drops significantly more than 1 pH unit away from it.
To create a buffer effective over a wide pH range, a mixture of acids with different pKa values (polybasic and monobasic acids) is used. Such mixtures are called universal buffers.
Universal buffers solve this by mixing several acids with different pKa values.
How ?Each acid in the mix has a different pKa. Each acid can buffer (control pH) best near its own pKa. By combining acids with different pKa values, the solution can buffer across a wider pH range.
What are examples of some universal buffers ?
This combination means the solution resists pH changes effectively from ~ pH 2.4 to 12
i.e much wider than a single buffer could handle
summary
Buffers are made from a weak acid and its salt, or a weak base and its salt
You can calculate the pH of a buffer using the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation
Buffers work best at a pH near the weak acid’s pKa, where their ability to resist pH changes (buffer capacity) is highest
Buffers are vital for medicine (e.g formulation for I.V use, eye drops, Nasal sprays