Biochemistry Exam 3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
What is the prosthetic group of dihydrolipoyl transacetylase?
lipoamide
2
New cards
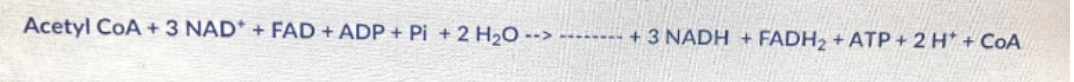
In a net chemical reaction the TCA cycle, what is the missing stoichiometry?
\
**2 carbon-dioxide**
**4 carbon dioxide**
**Pyruvate**
**6 carbon dioxide**
**Carbon dioxide**
\
**2 carbon-dioxide**
**4 carbon dioxide**
**Pyruvate**
**6 carbon dioxide**
**Carbon dioxide**
4 carbon dioxide
3
New cards
In the TCA cycle, which of the following enzymatic step is linked to the formation of NADH
\
**Fumarase**
**Succinate dehydrogenase**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
**Aconitase**
**Citrate synthase**
\
**Fumarase**
**Succinate dehydrogenase**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
**Aconitase**
**Citrate synthase**
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
4
New cards
True or Falce
The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules
The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules
True
5
New cards
The "only substrate-level phosphorylation" enzymatic step in the TCA cycle forms the following the product
\
\
**Fumarate**
**L-malate**
**Alpha-ketoglutarate**
**succinyl CoA Synthase**
Succinate
\
\
**Fumarate**
**L-malate**
**Alpha-ketoglutarate**
**succinyl CoA Synthase**
Succinate
succinate
6
New cards
In TCA, aconitase catalysis involves rapid dehydration followed by a quick hydration step
True
False
True
False
True
7
New cards
Most fuel molecules enter the TCA cycle as
\
**pyruvate**
**Acetyl coenzyme A**
**Oxaloacetate**
**citrate**
\
**pyruvate**
**Acetyl coenzyme A**
**Oxaloacetate**
**citrate**
Acetyl coenzyme A
8
New cards
The conversion of pyruvate into acetyl CoA consists of three steps
List them
\
\
List them
\
\
Decarboxylation, oxidation, and transfer of acetyl group to CoA
9
New cards
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex cannot complete another catalytic cycle until the dihydrolipoamide is oxidized to…
\
TPP
**FAD**
**Acetyl CoA**
**Lipoamide**
**NAD**
\
TPP
**FAD**
**Acetyl CoA**
**Lipoamide**
**NAD**
Lipoamide
10
New cards
In bacteria, the TCA cycle could be regulated by inhibition at the aconitase enzymatic step
\
True
false
\
True
false
False
11
New cards
The following TCA cycle enzyme involved rapid dehydration followed by quick/rapid hydration step
\
**Fumarase**
**Succinate dehydrogenase**
**Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
**Aconitase**
\
**Fumarase**
**Succinate dehydrogenase**
**Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
**Aconitase**
Aconitase
12
New cards
The following enzyme can inhibit the TCA cycle only in bacteria but not in other eukaryotes
\
**Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
**None of the above**
**Aconitase**
**Malate dehydrogenase**
\
\
**Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
**None of the above**
**Aconitase**
**Malate dehydrogenase**
\
None of the above
13
New cards
Which of the following TCA enzymes is not linked to the decarboxylation and oxidation processes?
\
**Malate dehydrogenase**
**Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**
**Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
\
**Malate dehydrogenase**
**Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**
**Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
Malate dehydrogenase
14
New cards
Following the TCA cycle biomolecule is closely linked to "The gluconeogenesis pathway.
\
**pyruvate**
**Citrate**
**Oxaloacetate**
**Malate**
**succinats**
\
**pyruvate**
**Citrate**
**Oxaloacetate**
**Malate**
**succinats**
Oxaloacetate
15
New cards
In TCA cycle, formation of Lmalate by enzyme fumarase involve
\
**Hydration**
**Oxidation reduction**
**Reduction**
Oxidation
**Dehydration**
\
**Hydration**
**Oxidation reduction**
**Reduction**
Oxidation
**Dehydration**
Hydration
16
New cards
Participation of the three enzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and five coenzymes is required for acetyl CoA formation. What are the 5 coenzymes required for this complex?
\
\
\
\
FAD
NAD+
Coenzyme A
ATP
lipoamide
NAD+
Coenzyme A
ATP
lipoamide
17
New cards
The Citric Acid cycle (Krebs or TCA cycle ) takes place in mitochondrial Inner membrane space Essentially in TCA cycle the Electrons removed form acetyl CoA to from citrate and FADH2
\
True
False
\
True
False
False
18
New cards
**In TCA, isocitrate dehydrogenase enzyme involves rapid dehydration followed by a quick hydration step**
**True**
**False**
**True**
**False**
False
19
New cards
This allosteric enzyme is the first control point fo the TCA cycle
\
**Citrate synthase**
**Malate dehydrogenase**
**fumarase**
**Alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**
**Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
\
**Citrate synthase**
**Malate dehydrogenase**
**fumarase**
**Alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**
**Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex**
**Isocitrate dehydrogenase**
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
20
New cards
Following TCA cycle biomolecule is closely linked to "Pyrimidine" biosynthetic pathway.
\
**glutamate from a-ketoglutarate**
**glutamate from succinate CoA**
**Aspartate from oxaloacetate**
**Asparate from citrate**
**Asparate from glutamate**
\
**glutamate from a-ketoglutarate**
**glutamate from succinate CoA**
**Aspartate from oxaloacetate**
**Asparate from citrate**
**Asparate from glutamate**
Aspartate from oxaloacetate
21
New cards
in glycerol 3 phosphate shuttle electrons from ........can enter the Mitrochondrial electron transport chain by being used to reduce dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glycerol 3 phosphate
\
NADH+
FAD
NADH
QH2
FADH2
\
NADH+
FAD
NADH
QH2
FADH2
NADH
22
New cards
During "Malate -Aspartate Shuttle ", in cytoplasm , aspartate is deaminated to form glutamate and the cycle is restarted
\
**True**
**False**
\
**True**
**False**
False aspartate makes oxaloacetate by aminating alphaketoglutarate
23
New cards
in the Chemiosmotic hypothesis model, the transfer of electrons through the respiratory chain leads to the pumping of electrons from cytoplasmic side of the inner mitochondrial membrane to the matrix
\
**True**
**false**
\
**True**
**false**
false it pumps electrons from the matrix to the cytoplasmic side to create the gradient that ATP synthase uses to creat ATP
24
New cards
ATP synthase is composed of a proton conducting unit and catalytic units. The F1 subunit consists of five types of polypeptide chains are?
alpha3, beta3, Gamma, Delta and epsilon
25
New cards
ADP enters the mitochondrial matrix only if ATP exits, and vice versa.
\
True
False
\
True
False
True
26
New cards
The coenzyme Q is also known as ubiquinone.
\
Which is NOT correct relating to coenzyme Q
\
**ubiquinone is a hydrophilic quinone**
**ubiquinone is a hydrophobic quinone**
**Fully oxidized state (Q), coenzyme Q has 2 keto groups**
**Quinones can exist in three oxidation states**
**Scmquonine penetrates ubiquinol (QH3)**
**the fully reduced form of coenzyme o**
\
Which is NOT correct relating to coenzyme Q
\
**ubiquinone is a hydrophilic quinone**
**ubiquinone is a hydrophobic quinone**
**Fully oxidized state (Q), coenzyme Q has 2 keto groups**
**Quinones can exist in three oxidation states**
**Scmquonine penetrates ubiquinol (QH3)**
**the fully reduced form of coenzyme o**
ubiquinone is a hydrophilic quinone
27
New cards
Cyanide reacts with the ferric form ....... whereas carbon monoxide inhibits the ferrous form
\
**Heme bH**
**HEME BL**
**HEME A3**
**FE-SE CLUSTER**
**HEME**
\
**Heme bH**
**HEME BL**
**HEME A3**
**FE-SE CLUSTER**
**HEME**
HEME A3
28
New cards
Most Electron Transport Chain \[ETC\] complex contains Fe-cluster, except this one
\
NADHQ oxidoreductase
Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
Cytochrome c reductase
Succinate Q reductase
\
NADHQ oxidoreductase
Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
Cytochrome c reductase
Succinate Q reductase
Succinate Q reductase (Complex ll)
29
New cards
when second electron and proton to the semiquinone generate ubiquinol ( QH2) the..... From the coenzyme Q which holds its protons more tightly
\
**Both oxidized and reduced**
**Fully oxidized**
**Partially reduced**
**Partially oxidized**
**Fully reduced**
\
**Both oxidized and reduced**
**Fully oxidized**
**Partially reduced**
**Partially oxidized**
**Fully reduced**
fully reduced
30
New cards
Which of the following ETC complex does not involve coenzyme Q in the membrane core \[Reflecting oxidant or reductant role\]?
\
**Only ETC I**
**Only ETC II**
**Only ETC Iii**
**all Only ETC I,ii and III**
**Only ETC IV**
\
**Only ETC I**
**Only ETC II**
**Only ETC Iii**
**all Only ETC I,ii and III**
**Only ETC IV**
Only ETC Il (succinate Q dehydrogenase)
31
New cards
Cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV) catalyzes the ……. of molecular oxygen to water
\
**Oxidation**
**First oxidation then reduction**
**Reduction**
**Reduction of coQ**
\
**Oxidation**
**First oxidation then reduction**
**Reduction**
**Reduction of coQ**
reduction
32
New cards
In oxidation-reduction reactions, the donor of electrons in model case x is called the reducing agent, whereas the acceptor of electrons H+ here is called the
\
**Oxidant**
**Partially reductant**
**Both as redox**
**Reductant**
**Partially oxidant**
\
**Oxidant**
**Partially reductant**
**Both as redox**
**Reductant**
**Partially oxidant**
Oxidant
33
New cards
A......potential difference between NADH and molecular oxygen drives electron transport through the chain and favors the formation of a proton gradient.
\
1\.14 mV
0\.82V
0\.32V
1\.14
1\.14V
\
1\.14 mV
0\.82V
0\.32V
1\.14
1\.14V
1\.14V
34
New cards
The regulation of the rate of oxidative phosphorylation by the ..... level is called …. or……..
\
**FADH2**
**ADP**
**NADH**
**Cytochrome C**
**ATP**
\
**FADH2**
**ADP**
**NADH**
**Cytochrome C**
**ATP**
ADP, respiratory control or acceptor control
35
New cards
FADH2 enters the electron transport chain at the second protein complex of the chain. FADH2 does not leave the complex; rather, its electrons are transferred to Fe-S centers and then finally to Q to form QH2.
True
False
True
False
True
36
New cards
Which molecule mediates the electroneutral exchange of H2PO4- for ADP in concert with the ATP\* ADP translocase?
\
**hydroxide (OH-)**
**pyruvate,**
**phosphoric acid (H3PO4)**
**ATP**
**ADP**
\
**hydroxide (OH-)**
**pyruvate,**
**phosphoric acid (H3PO4)**
**ATP**
**ADP**
hydroxide (OH-)
37
New cards
In the heart and liver, electrons from ....... are brought into mitochondria by the malate- aspartate shuttle , which is mediated by two membrane carriers and four enzymes
\
**Mitochondrial matrix NADH**
**Mitochondrial matrix NAD+**
**Mitochondrial matrix FADH2**
**Cytoplasmic NAD+**
**Cytoplasmic NADH**
\
**Mitochondrial matrix NADH**
**Mitochondrial matrix NAD+**
**Mitochondrial matrix FADH2**
**Cytoplasmic NAD+**
**Cytoplasmic NADH**
Cytoplasmic NADH
38
New cards
The electrons of NADH enter the chain at NADH- Q oxidoreductase. which is not true for this complex ETC 1?
\
**None of them ( all are correct statements)**
**It is the largest ETC complex**
**It has 46 subunits**
\
**None of them ( all are correct statements)**
**It is the largest ETC complex**
**It has 46 subunits**
None of them ( all are correct statements)
(46 subunits, M.W.>900 kD, FMN pros group, Largest\*)
(46 subunits, M.W.>900 kD, FMN pros group, Largest\*)
39
New cards
mitochondria have two membrane systems and outer membrane in an extensive high folded inner membrane the outer membrane is folded into a series of external ridges called cristae
\
True
False
\
True
False
False
40
New cards
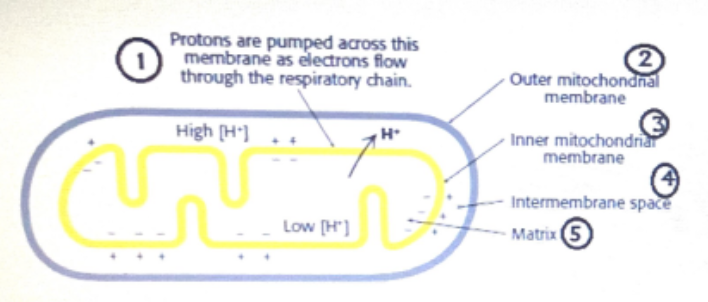
according to the chemiosmotic hypothesis which location will have basic pH
( higher than neutral such as 9.5 or so) after the pumping process?
\
\
( higher than neutral such as 9.5 or so) after the pumping process?
\
\
5 matrix
41
New cards
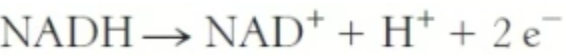
What is the net potential of the reduction of NADH?
0\.32V
42
New cards
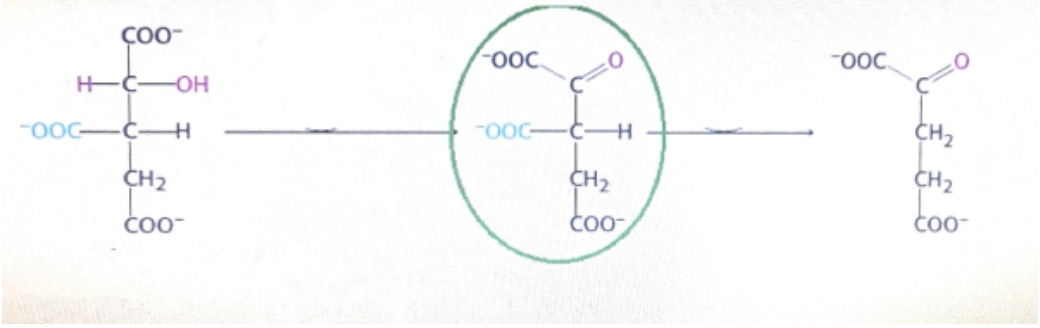
name the intermediate shown in circle during the TCA cycle
Oxalosuccinate, intermediate between isocitrate(left) and alpha-ketoglutarate(right)
43
New cards
among the following which one is not a product after the end of the oxidation step in the TCA Cycle?
\
A-ketoglutarate
Sycccinyl CoA
Fumarate
Oxaloacetate
Succinante
\
A-ketoglutarate
Sycccinyl CoA
Fumarate
Oxaloacetate
Succinante
Succinante
44
New cards
Oligomycin and dicyclohexylcarbodimide (DCCD) prevent the influx of protons through .....
\
**NADH Q Oxidoreductase**
**Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase**
**Cytochrome c oxidase**
**Sussinate Q reductase**
**ATP synthase**
\
**NADH Q Oxidoreductase**
**Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase**
**Cytochrome c oxidase**
**Sussinate Q reductase**
**ATP synthase**
ATP synthase
45
New cards
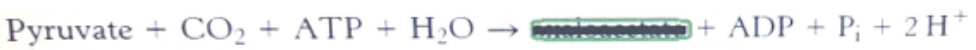
This enzyme converts pyruvate into oxaloacetate by oxidizing ATP in gluconeogenesis
pyruvate carboxylase
46
New cards
The pyruvate complex cannot complete another catalytic cycle until dihydrolipoamide is oxidized to ……... Afterward, it is regenerated by dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3) when it is oxidized to its original form.
\
\
lipoamide
47
New cards
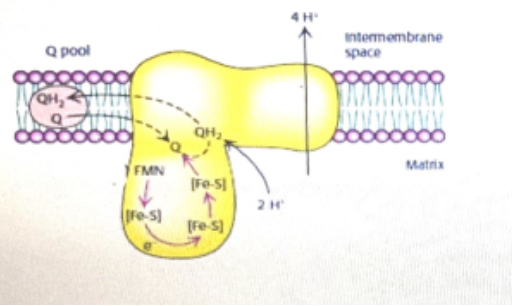
based on the electron flow of the respiratory chain and the given picture competent, name the related ETC (electron transport complex) enzyme
NADH Q oxidoreductase (complex 1)
48
New cards
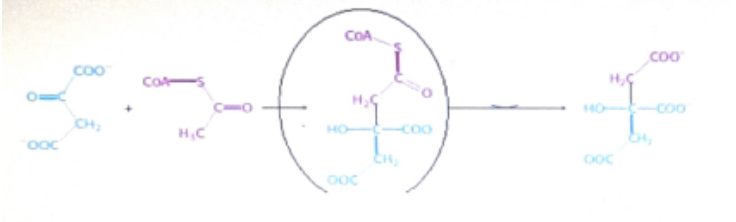
name the intermediate shown in circle during the TCA cycle
Citryl CoA is the intermediate. Oxaloacetate reacts with acetyl coats to make citric coA before producing citrate as the product
49
New cards
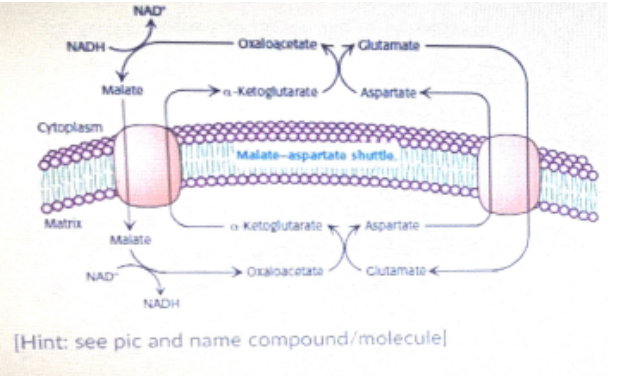
in the heart And liver electrons from cytoplasmic NADH are brought into mitochondria by the Malate aspirate shuttle in the cytoplasm the aspirate is then deaminated to form ..... and the cycle is restarted
oxaloacetate