Radioactive Decay: intro to pharm
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Radioactivity is relevant in both
therapeutics and diagnostics
all smoke detectors contain _________________ in small amounts
americium- 241
nuclear pharmacy can document an organ’s ____________________ and _________________
structure and function
when and where was the first radiopharmacy lab set up?
chicago 1950
energy in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves
radiation
radiation with sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule
ionizing radiation
First radiopharmacy lab set up in _______________ in 1950s
• __________ set up a radiopharmacy in 1958
• First monographs for USP radiopharmaceuticals prepared by Dr. Christian from ___________University in 1950s
• Centralized nuclear hospital pharmacies set up in __________________
• First MS degree in Radiopharmacy established at _______ in 1968
• Section on Nuclear Pharmacy established at APhA in __________
chiacago
NIH
Purdue
1969
US
1975
The process by which unstable atoms spontaneously transform to new
atoms* and in the process emit radiation
The new atom may be the same atom in a _____________energy state
radioactivity
lower
Alpha Decay:
_____________ Nucleus —- very massive and __________ ionized
Only a hazard via ingestion or ______________ of alpha emitter
Is it usually an external radiation hazard?
How can it be stopped?
Helium, doubly
inhalation
NO
stopped by paper and dead layer of skin
Uranium, Therium, and Radon
are examples of which type of decay?
Alpha decay
In alpha decay what happens to the atomic number? what happens to mass?
take out helium from atom (subtract 2 from atomic number and 4 from mass) to get NEW element
Beta Decay:
energetic electron —_____________ ionized
external hazard to _____ and ______
internal hazard via ______________ and ___________of beta emitter
a 1 MeV beta aan travel up to 12 ft in air and 1 cm in plastic
singly
eyes and skin
inhalation and ingestion
Phosphorus, Tritium, Carbon, Sulfur
are examples of which type of decay
beta
for beta decay what happens to the atomic number and mass?
take away an electron so add 1 to the atomic number
DONT CHANGE MASS
Gamma Decay:
_____ and ____________ are photons which means they have no charge
external radiation hazard to _______ and __________
internal hazard via ingestion or inhalation of gamma emitter
____________ is good for shielding X and gamma rays because it has __________ electron density
___________125 gamma rays (30 keV) can be easily stopped with 1/8 inch of ________
x-ray and gamma
deep organs and tissues
LEAD high
IODINE stopped with lead
How do gamma rays impact mass and atomic number?
NO CHANGE to mass or atomic number
____________ shieliding material depends on the energy of ________
neutrons
list in order of most dangerous to least dangerous
gamma (most) —beta —- alpha (least)
what can you use to block each particle
alpha = paper
beta = plastic
gamma = lead
_______________used to detect ionizing radiation, usually beta particles and gamma rays, but certain models can detect alpha particles.
Geiger Muller Counter
batter check
range seletion
nal pronbe
GM pancake probe
Typical background of 0.03 mR/hr or 100cpm
Geiger Muller Counter
what do we have THE MOST radiation exposure of
what type of particle is it?
Radon = alpha
in the united states radiation absorbed dose, effective dose, and exposure are measured and atated in units called
rad, rem, roetgen
What is the highest source of radiation that is man-made?
medical xrays
what are different biological effects of exposure to ionizing radiation ?
somatic
genetic
teratogenic
what are some prompt vs delayed somatic effects of radiation exposure
prompt = skin burns + cataracts
how can radiation damage cancer cells?
produce free radicals that can damage DNA
How can you protect yourself from radiation as a pharmacist?
minimize TIME
DISTANCE: double distance = decrease exposure by factor of 4
SHIELDING:
gamma = lead, water, or concrete
beta = thick plastic (lucite)
Radiation levels decrease as the =INVERSE SQUARE of the __________
distance
what is true about the atomic mass, nuclear charge, and mass of isotopes?
same atomic mass (protons)
same nuclear charge
DIFFERENT MASS
radioisotopes are unstable and undergo radioactive transformations also known as
radionuclides
a drug made with a ______________ is a radiopharmaceutical
radionucleotide
What was the first radionuclide used as a pharmaceutical?
radium
who regulates radiopharmaceuticals used for diagnostics and therapeutics?
FDA
Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC)
State Board of Pharmacy
Do all radioisotopes (nuclides) have high half lives?
NO they can range from seconds to years
rate of disintegration (-dN/dt) =
-dN / dt = yN
y= decay constant fraction disentegrating per unit of time
N= # of decomposed atoms and time
how can you find the rate of radioactive decay
N= N0e-yt
N0 = # of original atoms when t=0
half life equation for radioactive decay
t1/2 = 0.693 / y or ln2/k
y= rate of disintegration
what is the scientific vs system international unit for radioactivity? which is used in pharmacy?
scientific = curie
SI = becquerel (USED IN PHARMACY)
how many micro Curies are in one MBq?
27 micro curies = 1 MBq
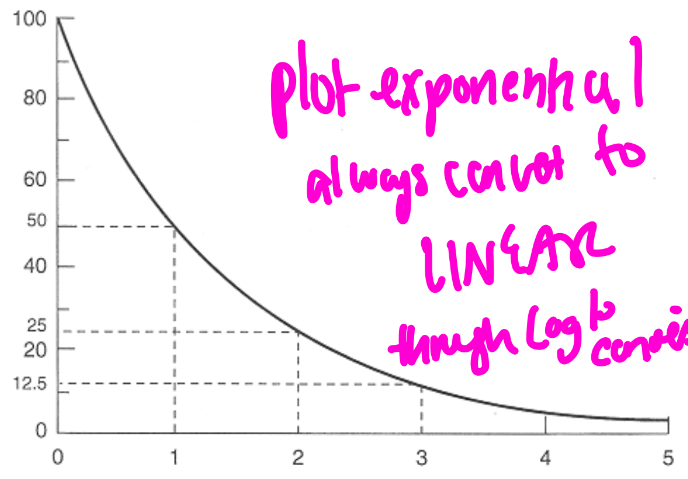
the following is a graph of ____________vs time (in half-lives)
percent initial activity (how much isotope left) vs time
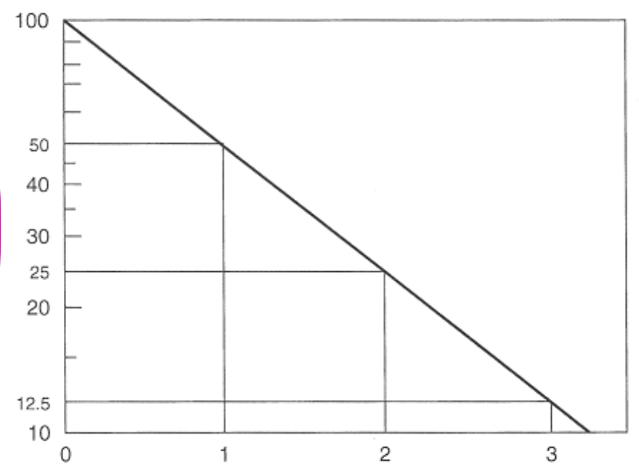
the folllwing is a graph of ____________ vs________________
log (initial activity) / time
log of the concentration of radionuclide / time
chemical compounds containing elements of HIGH atomic number which will stop the passage of X rays
radioisotope contrast medium
many radioactive contrast media contain
barium or iodine
______________is the agent of choice for imaging the GI tract
barium sulfate
why is barium sulfate a good agent for imaging the GI tract? what problems arise?
barium sulfate is INSOLUBLE in acidic gastric juices
side effect = constipation
The USP 27-NF 22 lists _______ official radioactiive pharmaceuticals
70
The most commonly used radiopharmaceuticals are
technetium
strontium
ytrium
Thallous Chloride
Gallium Citrate
Sodium Iodide
Sodium Iodide - 123
_______ capsule and better than I-131 as it delivers _______ radiation and better __________ __________
used to diagnose and treat ____________ function
emits only _________ rays
all drugs that can interfere with _____________ uptake of radionuclide should be withheld prior to I-123 use
oral lower image quality
thyroid
gamma (photon)
thryoid
Iodine- 131:
not as good as ____________ BUT
it is used in diagnostic procedures involving the ________ and also for the treatment of ___________ disorders
can be administered in __________ or ____________ form
requires special precautions to be implemented during administration
sodium iodide - 123
thyroid thyroid
solid capsule of liquid solution
Technetium - 99m
relatively short half life of ____________
offers an abundance of ___________ ________ for imaging without the hazard of ______ particles
can be used as a __________ agent for several pharmaceuticals used for imaging
kits are available to prepare Tc-99m compounds that assist in ___________ imagining (mebrofenin) and ___________ _______ ___________ (sestamibi- cadiolite”, tetrofosmin)
potential use to label ___________ antibodies
is it easy to obtain and inexpensive or hard to obtain and expensive?
6 hours
gamma photons beta
binding
hepatobiliary ischemic heart disease
monoclonal
easy + inexpensive!
Tc- 99m labeled radiopharmaceuticals are easily produced by simply adding _________ to many choices of “cold kits”
TcO4 - 99m
___________ is added to a vial containing a chemical compound that bind to the ___________. The result is a radipharmaceitical which will be taken up in the designated organ for imaging (or analysis) with a _______ camera
TcO4- 99m
radionuclide
gamma
Strontium -89 Chloride (Metastron):
sterile, non-pyrogenic aqueous solution for ____ use and contains NO preservatives
decays _________ emission with half life of 51 days
_______ emission is very harmful to ___________ tissue
used exclusively for ________ scans (tumors, and metastatic lesions)
acts like _________ analogs (clears rapidly from bloodstream and selectively localizes in ______ mineral)
TOXIC: CANT GIVE TO PATIENTS WITH PLATELET COUNTS BELOW __________ and WHITE BLOOD CELL COUNTS BELOW ____________
IV
beta
beta skeletal
bone
calcium bone
RBC = below 60,000 WBC= below 2,400
what does each do (key points only)
Sodium Iodide- 123
Technetium- 99m
Strontium-89 chloride
Yttrium- 90
Thallous - 201 Chloride
Gallium -67 Citrate
thyroid
bind to nuclide for imaging/ gamma photon w/o beta hazard (hepatobiliary imaging + ischemic heart disease)
bone
bind to glass microspheres + target liver
visualize the difference between ischemic and infarcted heart tissues
AIDS, hodgkin’s disease, lymphomas, bronchogenic carcinoma
which radiopharmaceutical : thyroid
sodium iodine - 123 (better alternative)
iodine-131
which radiopharmaceutical: bind to nuclide for imaging/ gamma photon w/o beta hazard (hepatobiliary imaging + ischemic heart disease)
Technetium- 99m
which radiopharmaceutical: bone
Strontium-89 chloride
which radiopharmaceutical: bind to glass microspheres + target liver
Yttrium- 90
which pharmaceutical: visualize the difference between ischemic and infarcted heart tissues
Thallous - 201 Chloride
which pharmaceutical: AIDS, hodgkin’s disease, lymphomas, bronchogenic carcinoma
Gallium -67 Citrate
Yttrium- 90:
a trivalent radioactive metal, pure _______ emitting radionuclide
half-life of 2.8 days
application is in _________________________(RIT) of solid large _______ and _________
TheraSphere are insoluble glass microspheres that are used for hepatocellular carcinoma and BOND TO ______ and target ______________
when injected these stay localized in the _____ and minimize the side effects of the radionuclide
the Y-90 decays to form stable _________-90
beta
radioimmunotherapy tumors and lymphomas
bind to yttrium target liver
liver
zirconium
Thallus-201 Chloride
Sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for ____
Half-life of 73.1 hours
the ______________ analog undergoes rapid transport to the myocardium —useful for visualization of __________________________ ___________ or _______ _______ ________ (helpful in differentiating between the two)
IV
potassium
myocardial infarction or ischemic heart disease
Gallium - 67 Citrate
sterile pyrogen-free from aqueous solution
drug behaves like the _____ ion and has a half-life of 78 hours
can localize in variable primary and metastatic tumors and in focal sites of infection
Useful in __________ , ________, and __________ carcinoma
used for diagnosis and monitoring of “fever of __________ origin” and for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia of _______
Disadvantage: considerable biological variation occurs in patients
ferric
hodgkin’s disease, lymphomas, and bronchogenic
undetermined AIDS
the production of other radionuclides for nuclear medicine (PET) involves the use of a
CYCLOTRON
following administration of the radiopharmaceutical to the patient, a __________ camera is used to image the area of interest
gamma
how are physicians able to check how the radiopharmaceutical distributes itself throughout the body or if it has been taken up by specifically targeted organs
GAMMA CAMERAS
do gamma cameras produce still or dynamic images?
BOTH
which type of camera looks at a patient from many different and is able to demonstrate very precise detail within the patient ?
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT)
information is presented as a series of planes that coorespond to certain depths within the body
the planes presented may be a series of cornal, sagittal, transveres and or oblique slices
which type of imaging?
SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography)
Positron Emission Tomography can be used to map ….
_______ flow and volume
__________ , __________, ____________metabolism
__________ ______________
__________ and ________receptor density
___________ gene expression
pH
_______________ ____________ transport
blood
oxygen, glucose, fatty acids
bone remodeling
tumor and neuroreceptor
reporter
amino acid transport
what is an extremely sensitive technique to image body chemistry and study physiological and biochemical processes within the body
PET (positron emission tomography)
radionuclides which undergo _________ decay usually have very SHORT half lives
positron
PET ______________ are now adjacent to pharamacies
they can be used in ___________ distribution evaluations and one can check if a drug reaches a specific receptor site
longer lived radionuclides are being investigated as radiolabels for __________ antibody based PET
uses in cancer as well as ____________ disorders
cyclotrons
pharmacokinetics
monoclonal
cardiovascular
For any worker who usually works in a controlled area, and
may receive a significant dose from occupational exposure,
_____________________ ______________________ shall be undertaken where appropriate,
adequate and feasible.
individual monitoring
Thermoiluminescent (TLD) or Optically Stimulated Luminescene (OSL) dosimeters are used to detect what types of radiation?
gamma, X, and beta radiation
a film dosimeter can detect
gamma, X, and beta radiation
film badge
electronic dosimeter w or w/o alarm (TLD or OSL)
ring badge
are all forms of
personal monitoring
Assessing Doses for Internal Radiation
______________
whole body monitor: ________ emitting radioisotopes
thyroid monitoring: ________ radioisotipes
urinalysis
gamma
iodine
employers and liscensees shall maintain _____________ ______________ for each monitored worker
records are to be maintain as required by the ____________ _____________
is this information confidential or is it shared?
who has access to records?
exposure records
regulatory body
CONFIDENTIAL
worker, employer, regulatory body, health surveillance professionals