Electronegativity and Ionization Energy
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold electrons in a chemical bond.
How does electronegativity change across the periodic table?
Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom in a group.
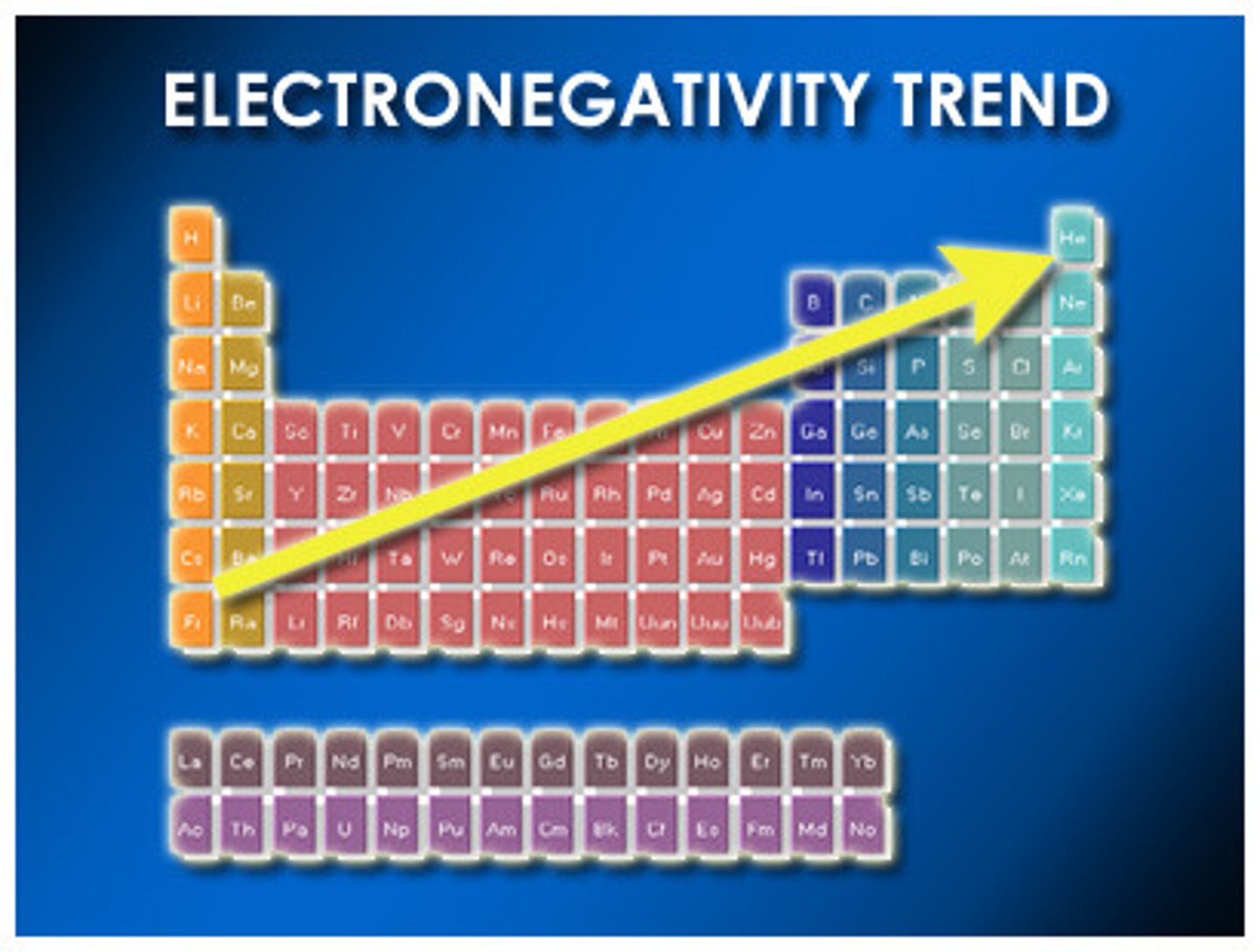
Examples of elements with high electronegativity?
Fluorine and oxygen are examples of elements with high electronegativity.
What is ionization energy?
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state.
How does ionization energy change across the periodic table?
Ionization energy generally increases from left to right across a period and decreases from top to bottom in a group.
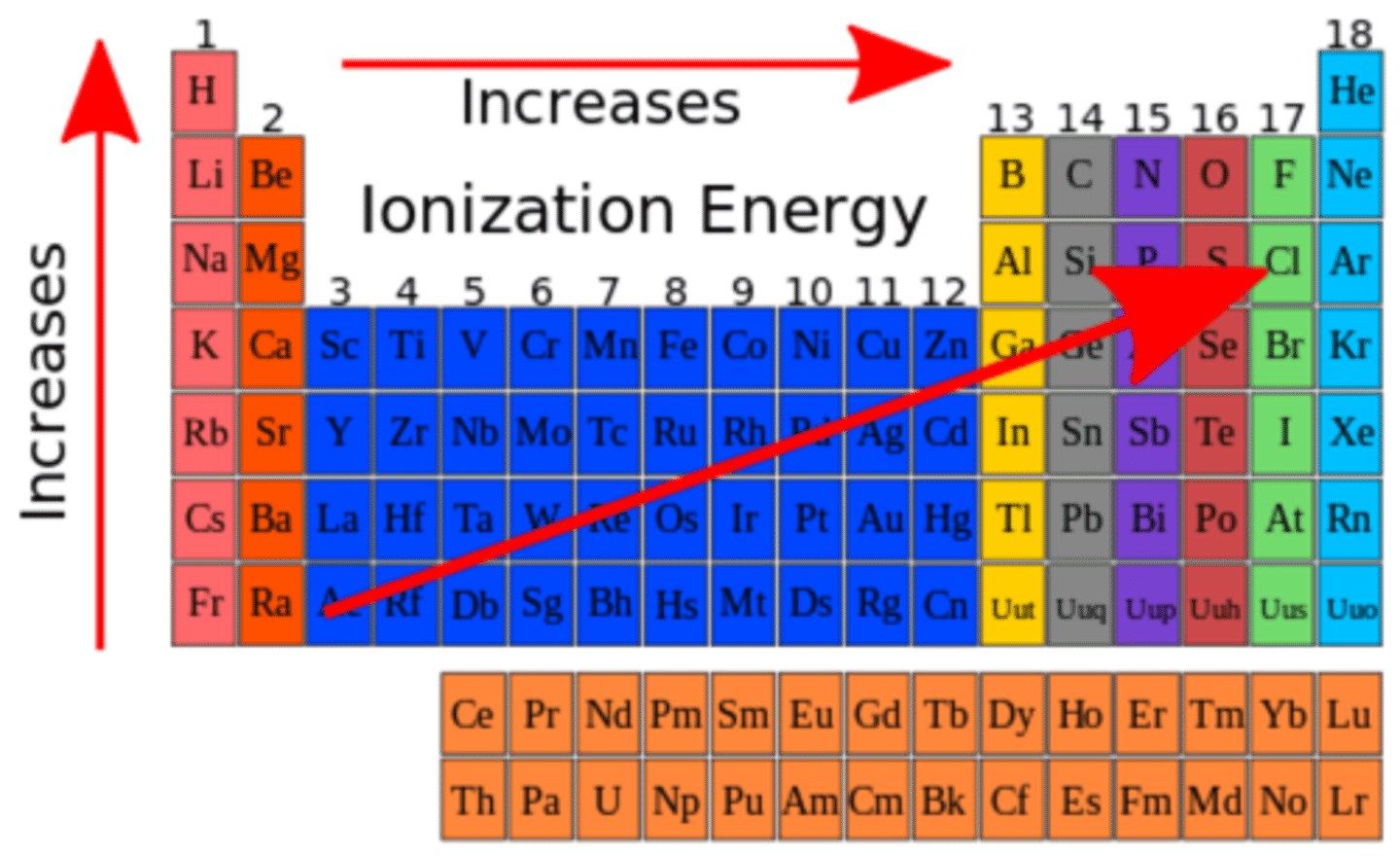
The relationship between ionization energy and atomic size.
There is an inverse relationship between ionization energy and atomic size. As atomic size increases, ionization energy decreases.
Why does fluorine have a higher electronegativity than other elements?
Fluorine has a higher electronegativity because it has a strong attraction for electrons due to its small atomic size and high effective nuclear charge.
How can electronegativity and ionization energy be used to predict chemical reactivity?
Elements with high electronegativity and high ionization energy tend to be less reactive, while those with low electronegativity and low ionization energy are more reactive.