Eukaryote Structures
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
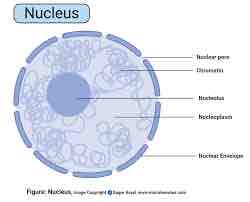
Give the structure of the nucleus (3)
Double membrane (nuclear envelope)
Nuclear pores
Nuclear envelope
What is the function of the nucleus (2)
Controls activities of the cell
Contains genetic material
What is the nucleolus
A dense area of chromatin
What does the nucleolus do
Produces ribosomes
What is the role of the cell surface membrane (3)
Controls exchange between cell and surrounding environment
Cell receptors for recognition
Contains fluid for endo/exocytosis
How big is the cell surface membrane
7nm
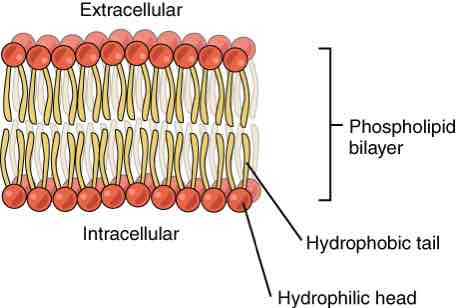
What is the cell membrane made of (2)
Phospholipid bilayer
Glycoprotein complex
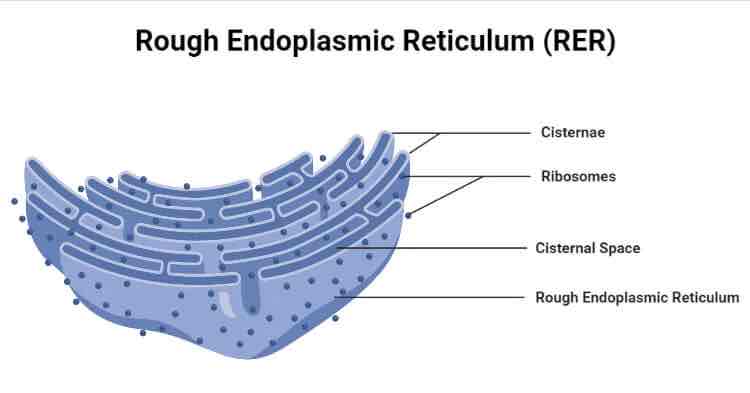
What is the role of protein the rough endoplasmic reticulum (2)
Protein synthesis
Transport
Give the structure of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (2)
Flattened sacs (cisternae)
Studded with ribosomes
Where is the endoplasmic reticulum found and why (2)
Continuous with the outer membrane of the nucleus
Close to DNA
Role of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Lipid synthesis
Transport
What’s the difference in structure between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum
There are no ribsomes on the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
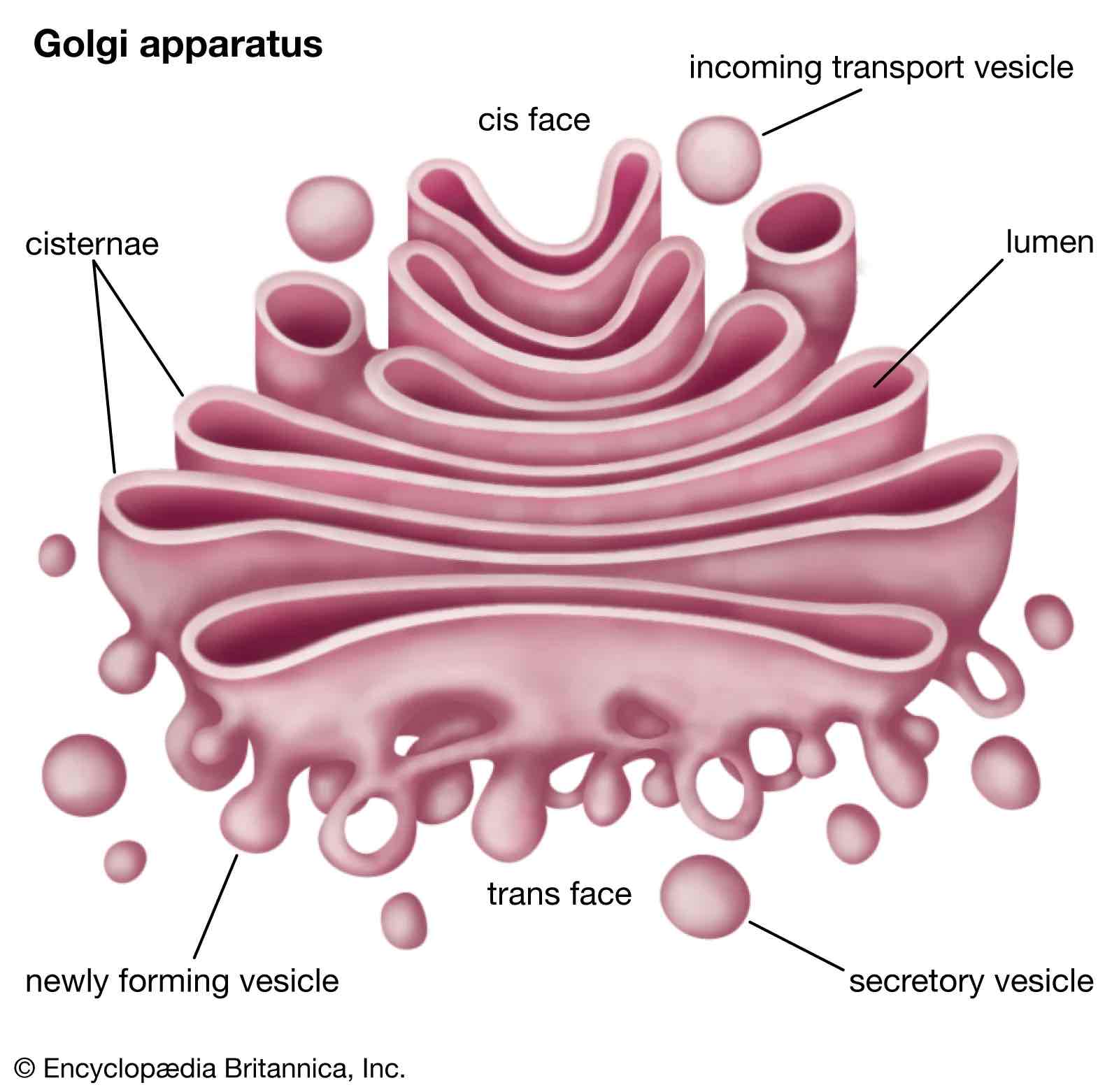
Whats the role of the golgi body (3)
Collects and processes proteins
Transports molecules in secretory vesicles
Lysosome formation
Give the faces of the golgi body (2)
Cis face
Trans face
What is the role of the mitochodria and how (2+3)
Site of respiration
Synthesis of lipids
Produces ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
ATP broken down to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) to release energy in hydrolysis
ADP can be stored and converted back to ATP
Give the size and shape of the mitochondria (2+1)
3-10μm long
0.5-1μm wide
Rod shaped
Describe the structure of mitochondria and what it contains (2+2)
Double membrane
Inner membrane folded to form cristae
Ribosomes (70S)
Circular DNA
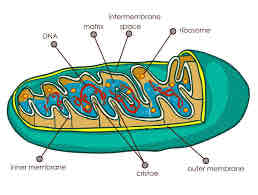
Explain the role of the matrix
Where respiration reaction takes place (+cristae)
Contains enzymes in solution
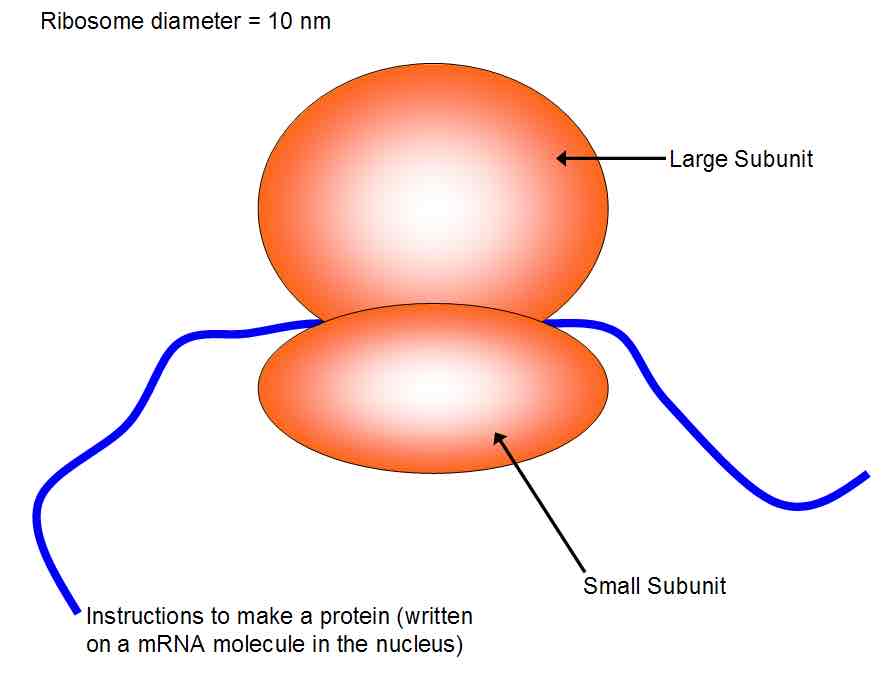
Give the role of a ribosome and what it is made of
Allows interaction for protein synthesis
Made protein and rRNA
Describe the structure and size of a ribsosome (2+1)
Two subunits
Groove for mRNA attachment
25nm
Describe the structure and size of a lysosome (2+1)
Little, spherical sacs
Single membrane bound vesicle (prevents self digestion)
0.1-0.5μm
Explain the role of the lysosome (2)
Breaks down unneeded substances
Self digestion (enzymes released into cytoplasm)
Optimal condition for lysosome and why (2)
Acidic conditions
Optimal pH for hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes
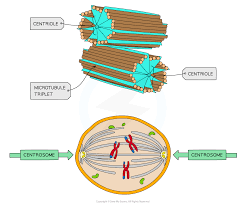
Give the role of centrioles (3)
Cell division
Separates chromosomes to opposite ends of cell (moved by spindle fibres)
Produces cilia
Give the arrangement of centrioles (2)
9+2 arrangement
At right angles to each other (in pairs called centrosomes) outside nucleus (till ready to split)
What is the role of the microtubules (3)
Gives cell structure (cytoskeleton)
Moves stuff around in cell
Spindle fibres separate chromatids/chromosomes
What are microtubules made of
Tubulin
What do microtubules make up (4)
Centrioles (general)
Specialised structures
Flagella
Cilia
Spindle fibres
Give the size and structure of microtubules
25nm (diameter)
Long, rigid, hollow tubes
Give the role of the cilia
Movement (eg gas exchange moves mucus in airways)
How long are cilia
10μm
Role of microvilli
Increases surface area for absorption at brush border
How big are microvilli
1μm
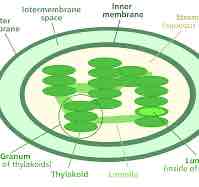
How big are chloroplasts
4-10μm
Describe the structure of a chloroplast (7)
Double membrane
Inner membrane folded into stacks called grana (granum)
Grana made of thylakoids studded with chlorophyll
Thylakoid centre is the lumen
Grana linked with lamelle
Intermembrane space is fluid called stroma
Contains 70S ribosomes
What is the tonoplast
A single membrane that surrounds the vacuole/cell sap
What is the role of the tonoplast
Controls exchange between vacuole and cytosplasm
What is the role of the cell wall (2)
Provides structure and support for the cell
Prevents bursting due to water entering via osmosis (turgid pressure against membrane)
Describe the structure of the cell wall
Cellulose microfibrils held together by hemicellulose
What is the role of the vacuole (3)
Contains cell sap
Maintains water potential of cell
Regulates turgid pressure
What does the cell sap contain (3)
Salts
Sugars
Water
What is a starch grain
Storage area
What is the plasmodesmata
Part of symplasmic pathway
Inorganic ions to pass through between cells
Cytoplasmic connection through cell wall