SAM: Exam 3 - Endocrine
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Diabetes Mellitus Pathophysiology
Types
Type 1: dogs, absolute insulin deficiency, requires insulin
B cell destruction / loss → immune system
Transient (dogs): diestrus, glucocorticoids(depo/cats), pancreatitis (may be reversible)
Type 2: cats, relative insulin deficiency, insulin resistance
Might need exogenous insulin
Classic Triad: 7-9y older animals
PU/PD: osmotic diuresis, renal glucose threshold 180–220 mg/dL
proximal tubule → glucose
Polyphagia: insulin needed for satiety → energy use
Weight loss: starvation in the face of plenty
Canine Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1
Et: IM, genetic, chronic pancreatitis, obesity, Cushing’s, diestrus, steroids/progestins
Sig: older, female, Keeshond, Terriers, Mini Schnauzers, Poodles, Beagles
Cs: PU/PD, polyphagia, weight loss, cataracts, hepatomegaly, poor healing, recurrent infections
CBC: ↑ Glucose, ↑ Cholesterol and triglycerides, ↑ Liver enzymes (ALP(higher) and ALT)
UA: Glucosuria, +/- Ketonuria, +/- Pyuria, bacteriuria, hematuria
Dt: fasting hyperglycemia(blood) + glucosuria(urine)
Hyperglycemia only = postprandial(after meal), stress
Glucosuria only = renal tubular dz, artifact
Tx: ↑ fiber, complex carb ↓ fat diet, exercise, Vetsulin, NPH
Minimize CS, avoid hypoglycemia
Most important aspect of treatment: CLIENT Ed!!
Regular Insulin
Short acting → Hospital setting only
Humulin R: DKA
IV, IM
Duration: 1-4 hours
Using Insulin
Syringe: U40
Storage: refrigerate, lasts 4m, roll dont shake (except Vetsulin)
Injection Sites: Rotate between lateral thorax and abdomen
Not scruff, CT makes absorption variable
starting dose → Vetsulin or NPH: 0.25 - 0.5 IU/kg SQ q 12h
Degludec U100 or Glargine U300: 0.6 IU/kg SQ q 24h
Cats: Glargine (lantus) :1U 4kg q 12h
Cats: ProZinc : 1U q 12h
Have owner log into a book daily → better for management/rechecks
Changing dosage:
Dosage increase by 25%
Dosage decrease by 50%

Diabetes Mellitus Therapy
Short-acting: Regular insulin
Use: emergency
Intermediate-acting: Vetsulin (U-40), NPH(U-100, pen)
Use: dogs, first choice, BID, Shake vetsulin
Vetsulin: ~ 14h , NPH: 6-10h
Long-acting: Glargine u-100, Detemir u-100 (levemir), PZI(pro zinc) u-40
Use: Cats, q 12hrs - 1-2U BID total dose
Glargine not peakless in cats
Ultra-long acting: Degludec u-100 (Tresiba), Glargine U-300
Use: dogs, q 24hrs
SGLT2 inhibitors: Bexacat®, Senvelgo®
Use: Never give to sick cats, insulin-treated cats, renal dz
Risk: DKA


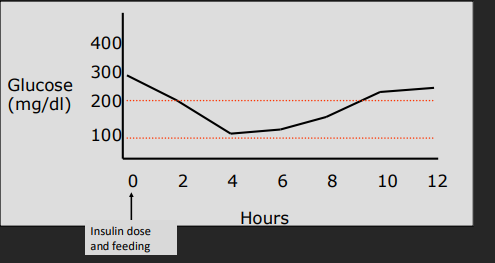
Monitoring Diabetes Mellitus Patients
1st Recheck: 7 days after starting insulin
Target BG: 80-200 (dog), 80-300 (cats)
Watch: Cs + weight (#1), serial glucose curve, log book
When: 2h curve q24h, full PE in 1 week
Don't spot check(only hypoglycemia) or assess before 1w → DO NOT increase dose @ spot check
Check 5-7d after dose change
Tools: Clinical Signs are best
Glucose Curve: goal difference form start to nadir: 80–150 mg/dL
Nadir: lowest glucose / peak
Differential: >100 mg/dl = insulin working
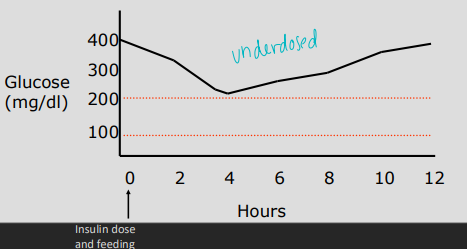
↑ Nadir = underdose
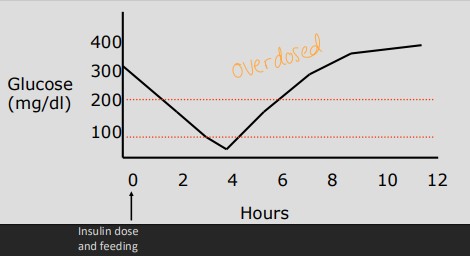
↓ Nadir = overdose on that day
Somogyi effect = overdose rebound hyperglycemia & resistance
Decrease dose by 50% in 1w recheck
INADEQUATE CONTROL = recheck curve
Wrong duration = wrong insulin type
Fructosamine: Glycated proteins: albumin → checks the past 2w glucose maintenance — Not effected by stress!
Confirm adequate Control
Every 2-4m initially, every 4-6m w/no CS!
Flash monitors: FreeStyle Libre
Urine glucose strips: supportive only → not a stand alone test
Glucosuria: poor control
Never glucosuria: over dosed

Feline Diabetes Mellitus
Type 2 - B cell exhaustion (not dead)
Et: obesity, insulin resistance, chronic pancreatitis, amyloidosis (amylin accumulation - antagonizes insulin)
Sig: 9-12y, neutered males, obesity
Cs: PU/PD, polyphagia, weight loss, peripheral neuropathy, plantigrade stance, ± hypokalemia
Dt: hyperglycemia + glucosuria (same as dogs)
Tx: SGLT2 inhibitors, Glargine insulin, ProZinc,
↑ protien ↓ carb diet “catkins” → canned food if no rx diet : change slowly
Resolve signs, Prevent hypoglycemia, GOAL: Remission, treat obesity
Goals: Nadir 80-150, Glucose differential >150
Recheck 5-7 days after ANY dose change
increase dose by 0.5-1U at a time
SGLT2 inhibitor
“healthy cats”
Bexacat – Bexaglifozin - Elanco : pill
Senvelgo − Velaglifozin - BI : liquid
promotes loss of glucose in urine → improves B cell function
Never give to cat that has/is receiving insulin
Never give to cat that is ill
Any signs on medicine → stop drug
Monitoring at 2 d, 1 wk, 2 wk, 1 mo, 3 mo
WATCH for DKA: more severe / life threatening
Unknown if Remission occurs with SGLT2 inhibitor
Remission of Feline Diabetes Mellitus
When: occurs in the 1st 3 months w/ in 1 year of Tx
Cs: Hypoglycemia, excellent control on curve, no glucosuria
Euglycemia for 2w w/o insulin
Suspicious:
1. Hypoglycemia
2. Excellent control on curve
3. No glucosuria
Dt: Cut insulin dose in ½ and recheck in 1w → w/o glucosuria d/c insulin
Recheck glucosuria/furosemide every 3-6m for relapse
Insulin Resistance
What: normal insulin dose has subnormal response
insulin dose >1.5 U/kg BID
inconsistent control
Why: Obesity, Inflam(pancreatitis), Hormone issues, Hyperlipidemia(D)
Insulin problems: under/overdosing, Somogyi
Client problems: poor storage, injection errors, improper handling, dosage in syringe
Patient problems (true): obesity, infection, Cushing’s, acromegaly(cats), neoplasia, hyperlipidemia (Schnauzers), hyper/hypothyroid
Dt: CBC, chem, UA + culture, T4 (cats), imaging, specific endocrine testing (ACTH stim, IGF-1 MRI), CPL
Commonly no clinical signs
Tx: treat underlying disease, Cabergoline, Low fat diet, Bezafibrate, Fenofibrate
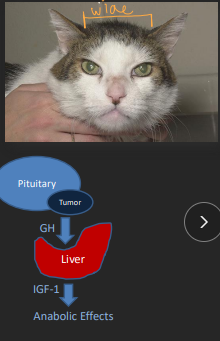
Acromegaly
Cats > dogs
Pituitary adenoma (of somatotrophs)
(IGF-1)
Clinical signs:
– Broad face
– Widened interdental spaces
– Respiratory stridor
– Abdominal organomegally (liver, spleen)
Dx: #1 Blood IGF-1 level → can be normal 1-2m after insulin
Brain MRI → IGF elevated
Tx: external beam radiation
Primary and secondary Hyperlipidemia
commonly hypertriglyceridemia
Fasting (>12h) hypertriglyceridemia
Miniature schnauzer
Secondary hyperlipidemia
Dogs
Protein losing nephropathy
Pancreatitis, severe obesity
Tx: Low fat diet, Bezafibrate or Fenofibrate(best)
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Et: uncontrolled / undiagnosed DM → ketone production → metabolic acidosis + dehydration
Lyte losses: K, P, Mg
Cs: vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, acetone breath(sweet), kussmaul resp, dehydration/shock
Dt: pre-renal azotemia, metabolic acidosis, ketonuria, electrolyte disturbances
Ketometer: blood ketones
Dipstick: acetoacetate and acetone in urine
Tx: Fluids (Norm-R, Plasmalyte, NaCl), K/P/Mg replacement, Regular insulin IM
Dehydration corrected:
Dogs → 6-12h
Cats → 12-24h
Supplement phosphorous to avoid hypophosphatemia (<1.0)
• Provide ½ of K+ as Kpho
May need Magnesium supplement (<0.7)
Sodium bicarb → Anion gap >30, acidosis
Treat hypokalemia before insulin (if K <2.5)
Pathophysiology of Hypothyroidism
Axis: Hypothalamus (TRH) → Pituitary (TSH) → (follicular cells)Thyroid
Hormones: Thyroxine (T4) > Triiodothyronine (T3) negative feedback
Increases metabolic rate.
Bound to plasma proteins.
Only bio active (T3)
Types:
Tertiary: hypothalamus, rare.
Secondary: pituitary, rare.
Primary: thyroid gland, common
Lymphocytic thyroiditis or Idiopathic atrophy.
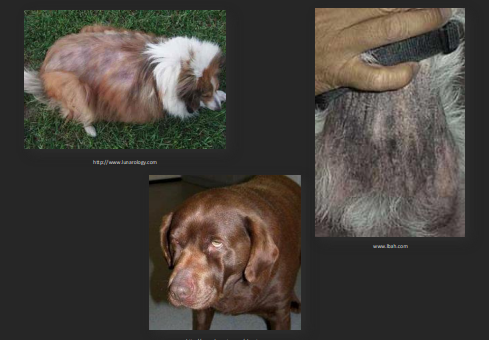
Hypothyroidism
Et: primary; lymphocytic thyroiditis, idiopathic atrophy
Sig: 7 yrs, Doberman, Golden
Cs: lethargy, weight gain, exercise intolerance, neuro deficits (Myasthenia Gravis, LARPAR), poor hair bilateral truncal alopecia , dry skin , hypothemia, bradycardia, Myxedema
Dt: TT4 (↑ sen, ↓ spec), fT4 (↑ spec), TSH ↑ with low T4, non regen anemia, ALP>ALT , ↑ cholesterol & triglycerides, Anti-Thyroglobulin Ab (not diagnostic)
Never ID on TT4 alone → Sick euthyroid can mimic
Always investigate non thyroid dz
TT3 an fT3 not useful
Sighthounds have lower T4 reference interval
Tx: levothyroxine
Recheck 1m, 4-6h post-Tx
Neuro signs do not resolve with Tx
Tx fail try T3 supplemention
Hyperthyroidism
Thyroglobulin stored in follicles
Et: benign thyroid hyperplasia/adenoma
Sig: older cats 12-13y
Cs: weight loss, polyphagia, PU/PD, vomiting, hyperactivity, unkempt coat, thyroid slip, cardio workup
Atypical (apathetic form): anorexia, lethargy → concurrent dz
Dt: TT4 & CS, Thyroid slip, ↑ Hct, ↑ ALT/ALP, ↑ Glucose, ↑ BUN: Creat, proteinuria, dilute urine <1.035 T-99 scan, T3 suppression test
ALT or ALP no work up needed if <500
Monitor: TT4 q2–3w initally, then q 6-12m
Tx: Methimazole, Radioactive I-131, Hill’s iodine restricted y/d diet, Sx (neoplasia)
T3 Suppression Test
Measure T4
Administer T3
Measure T4 &T3
Normal = suppression
HyperT = fails to suppress
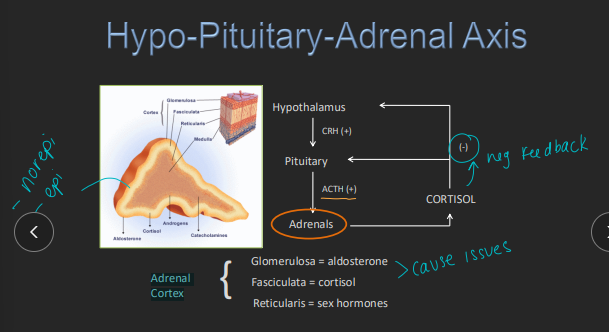
Hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s)
Et: med-giant breeds 2m-16y
Primary adrenal: IM, ↓ cortisol + aldosterone
typical: mineralocorticoid + glucocorticoid
Atypical: only glucocorticoid + normal electrolytes
Secondary pituitary(rare): ↓ cortisol only
Iatrogenic: rapid glucocorticoid withdrawal
Cs: lethargy, vomiting, anorexia, PU/PD, weight loss, shivering, hypoglycemia, non-regen anemia, hypercalcemia
Wax and wane CS
Hypotension, hypoperfusion, shock → Addison crisis
Dt: ACTH stim test (#1), hyponatremia + hyperkalemia, lack of stress leukogram, dilute urine, ECG with hyperkalemia signs (Wide QRS, spiked T, no P)
Lymphocytosis & eosinophilia
Tx:
Emerg: fluids!!! (0.9% NaCl), manage hyperkalemia (insulin, Ca gluconate, bicarb), dex(does not react w/ cortisol), hydrocortisone(reacts w/cortisol)
¼ shock dose (15-22 ml/kg) over 20-30 minutes: crisis treatment
then 90-120 ml/kg/day for 1-2 days
typical: Prednisone + DOCP(percortin) (if lytes are abnormal), fludrocortisone
Atypical: glucocorticoids → prednisone only
stressful events needs to double dose
Px: great
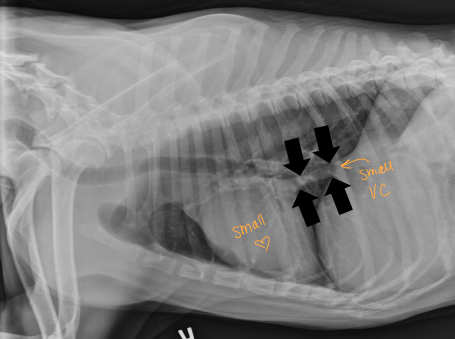
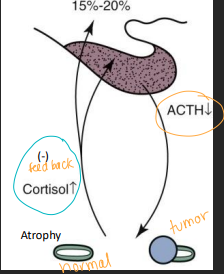
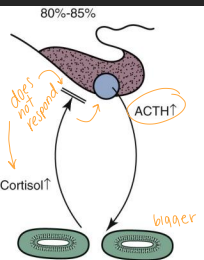
Hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing’s)
Et:
2ndary PDH: fxnal pituitary tumor, bilateral adrenal hyperplasia → pumping ACTH
Adenoma: micro (<3mm) > macro (>10mm)
pars distalis – >70% of dogs
primary FAT: fxnal adrenal tumor, unilateral shrinkage, 50% malignant → pumping cortisol
Iatrogenic: chronic steroids, large dogs
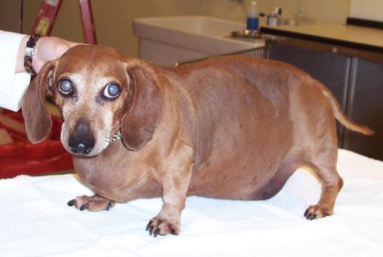
Cs: PU/PD, polyphagia, pot-belly, alopecia, thin skin, panting, infections, calcification of skin, Thromboembolism, renal DZ
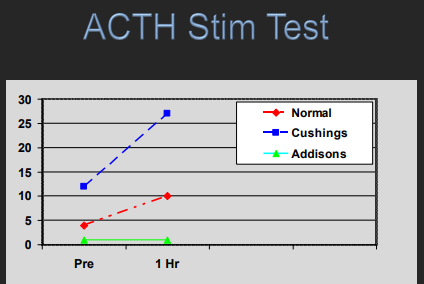
Dt: LDDST (#1, PDH), ACTH stim test (iatrogenic, HAC or monitoring), Urine cortisol:Cr (rule out only!), Endogenous ACTH (PDH vs FAT)
CBC: stress, ↑↑ ALP & cholesterol, UA:1.008-1.025 dilute/proteinuria
Ddx: stress, chronic adrenal dz
FAT not responsive to ACTH or LDDST
Tx: monitor at 2w +4w + q 3-6m with biochem, CBC, ACTH stim or cortisol test
PDH: Trilostane, Ketocazole, Mitotane, Sx
FAT: Trilostane, Mitotane, Sx
Iatrogenic: taper steroids
Cortisol test for cushing’s
<9.0
If clinical signs improving - keep same dose
if no clinical improvement - increase to q 12h dosing
>9.0
increase by 20-25%
<1.5
stop trilostane
If ill administer corticosteroids
Repeat ACTH stim. if CS reappear
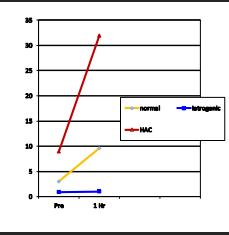
ACTH Testing
Stimulation
Use: monitoring, iatrogenic hyperadrenocorticism
Not sensitive for FAT
Accuracy: specific but less sensitive
Expense: 1h, expensive
Monitoring: 2-4h after pill, recheck 4w after dose changes
Endogenous
Use:
PDH: normal to high
FAT: low
Expense: special handling, must be done ASAP
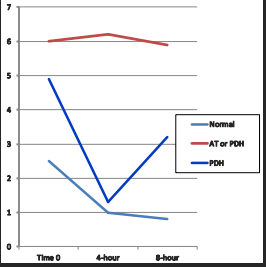
Dex Stimulation Test
Low Dose LDDST
Use: FAT Cushing’s
Cannot diagnose iatrogenic hyperadrenocorticism
Normal: will suppress at 8 hours
Cushing’s: will not suppress at 8h
PDH: suppress and escape
Accuracy: sensitive but less specific
Expense: 8h, extra blood draw, cheaper
High Dose HDDST
Use: PDH, FAT cushings localization
FAT will never suppress
suppressed @ 4 & 8h = PDH
no suppression = 50/50 chance
Expense: 4-8h
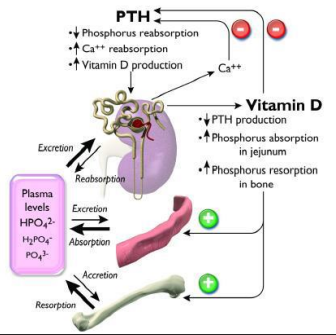
Calcium Disorders
Hormone players: Parathyroid hormone (PTH), Vitamin D (calcitriol) Organs: PT gland, kidney, bone, intestine
PTH: stimulated by low Ca, or high P
Calcitriol: increases Calcium and Phosphorous in blood
Hypercalcemia
Et: Hyperparathyroidism, Addison’s, Renal dz, Vitamin D toxicity, Idiopathic, Osteolysis, Neoplasia, Spurious, Granulomatous dz
“HARD IONS G”
Cs: PU/PD, weakness, vomiting, diarrhea, shivering, kidney tubule injury
soft tissue mineralization if Ca × P product = >70
PTHrP test : Humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy
Dt: ↑ ionized Ca + PTH, low P
Tx: underlying dz, fluids!, furosemide, bisphospates, steriods, Sx
Hypocalcemia:
Et: Hypoparathyroidism, eclampsia, pancreatitis, renal dz, Hypomagnesemia
Cs: tremors, seizures, muscle fasciculations, eclampsia, Facial pruritis, stiff gate
Tx:
Emerg: 10% Ca gluconate IV
Long-term: calcitriol PO
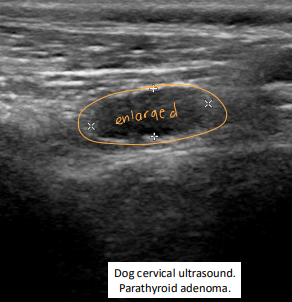
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Et: hypercalcemia
Sig: older dogs 4-17y, parathyroid adenoma → benign fnx
Cs: PU/PD, weakness, Incontinence, vomiting, diarrhea, shivering, Lower UTI signs→ stones, dilute urine(1.004-1.037)
soft tissue mineralization if Ca × P product >70
Dt: ↑ ionized Ca + PTH, low P, PTHrP is negative
Tx: parathyroidectomy, RF ablation, ethanol ablation
Post-tx: risk of hypocalcemia w/in 5 days → calcitriol + Ca
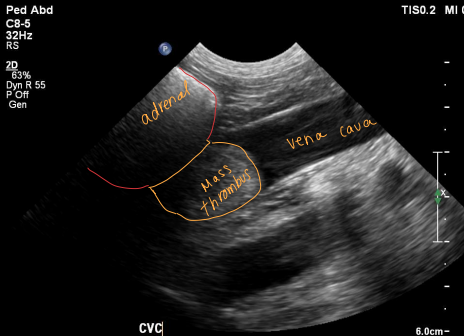
Pheochromocytoma
Medulla = ¼ of adrenal gland
Malignancy of chromaffin cells
local invasion
metastasis
Et: adrenal medulla tumor, excess catecholamines
Epinephrine, norepinephrine
Rare, 12y, dogs>cats
Cs: Restlessness / anxiety / pacing, intermittent collapse, hypertension, PU/PD, tachypnea, Epistaxis, blindness
Dt: CS & PE, imaging, urine normetanephrines
Tx: adrenalectomy (pre-op phenoxybenzamine →α-adrenergic antagonist)
Insulinoma
Et: Functional β-cell tumor, hypoglycemia → Unresponsive to negative feedback
hypoglycemic events: increases
Glucagon – most important
Catecholamines – second line
Sig: Lg breed dogs, 3-14y
Cs: seizures, collapse, weakness
Paired blood insulin & glucose level
– Only submit if BG <60 mg/dL
Dt: low BG + inappropriately high insulin, Hypokalemia, Hypophosphatemia
Imaging low sensitivity
Tx:
Emerg: sugar on gums, IV dextrose, glucagon CRI
Long-term: prednisone, diazoxide, octreotide, multiple meals
surgery → R or L limb = resectable
post op issues: Pancreatitis, Diabetes, Persistent hypoglycemia
Drugs used of Cushing’s Disease (Hyperadrenocorticism)
Trilostane
MOA: Competitive inhibitor of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
SE: hyperkalemia, “steroid withdrawal,” transient or permanent hypoA, death
Mitotane
MOA: Adrenocorticolytic, cytotoxic
SE: GI upset, Addison’s, lethargy, weakness, collapse
Use: send home prednisolone
Ketoconazole
MOA: Inhibits cytochrome P450 enzymes
SE: anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatotoxicity
Use: Not effective in ~33%
L-deprenyl (Selegiline, Anipryl®)
MOA: MAO-B inhibitor
Use: Not effective, for cognitive dysfunction
Drugs used for Thyroid Disease
Methimazole
MOA: Inhibits iodide incorporation
Use: Hyperthyroid
PO or transdermal, monitor CBC/biochem/T4 q2–3w
SE: GI upset, hepatopathy, bone marrow suppression, rare facial excoriation
Radioactive Iodine (I¹³¹)
Use: Hyperthyroid
Definitive treatment, cure with one dose
Requires special facilities, isolation (~1w)
MOA: destroys only thyroid tissue (β + γ radiation)
Levothyroxine
Use: hypothyroid
Monitor TT4 at 1 mo (peak 4–6h post-dose)
MOA: Synthetic T4 replacement
Goal: TT4 upper half of RI or slightly above
Drugs used for Hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s)
Fludrocortisone
MOA: mineralocorticoid + glucocorticoid activity
Use: May need prednisone too
Monitor lytes weekly → monthly → q3-6m
DOCP (Desoxycorticosterone pivalate)
MOA: Mineralocorticoid only
no glucocorticoid effect
Use: Monitor electrolytes @ 2w, then q4–6m
Drugs used for Insulinoma / Hypoglycemia Management
Diazoxide
MOA: K⁺ channel activator
Stimulates gluconeogenesis + glycogenolysis
Octreotide
MOA: Somatostatin analogue
Streptozotocin
MOA: Chemo destroys pancreatic β-cells