electrical energy
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
actually kms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is electricity?
Electricity is the flow of electric charge that powers various devices and systems through circuits.
What are switches for ?
An open switch creates a gap in the circuit, preventing the current from flowing. A closed switch allows electrons to flow around the whole circuit, carrying energy to all parts of the circuit.
Why are metals useful for electrical energy transfer?
Metals have a regular arrangement of tightly packed atoms. Each atom carries one or more valence electrons that move freely in the metal.
direction of electrical energy
Electrons from the negative terminal of a power supply go through the metal to go to the positive terminal.
why do current only flow in closed circuits?
Electrons need a complete, uninterrupted pathway linking both terminals of the power source. Open circuits have a gap through which electrons cannot flow.
What is a current?
Current is the flow of electrical charge. Current is measured in amps (A). The ammeter will always be connected in series with the component to measure the current.
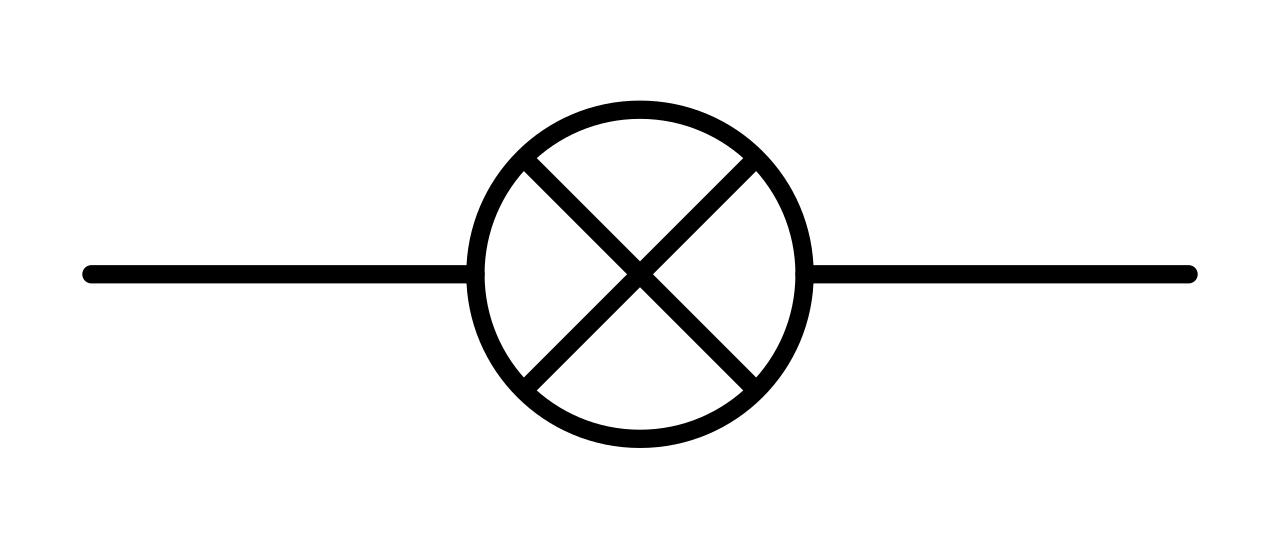
what symbol is this
bulb
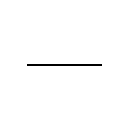
what symbol is this
wire
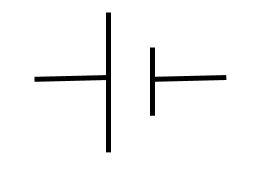
what symbol is this
cell
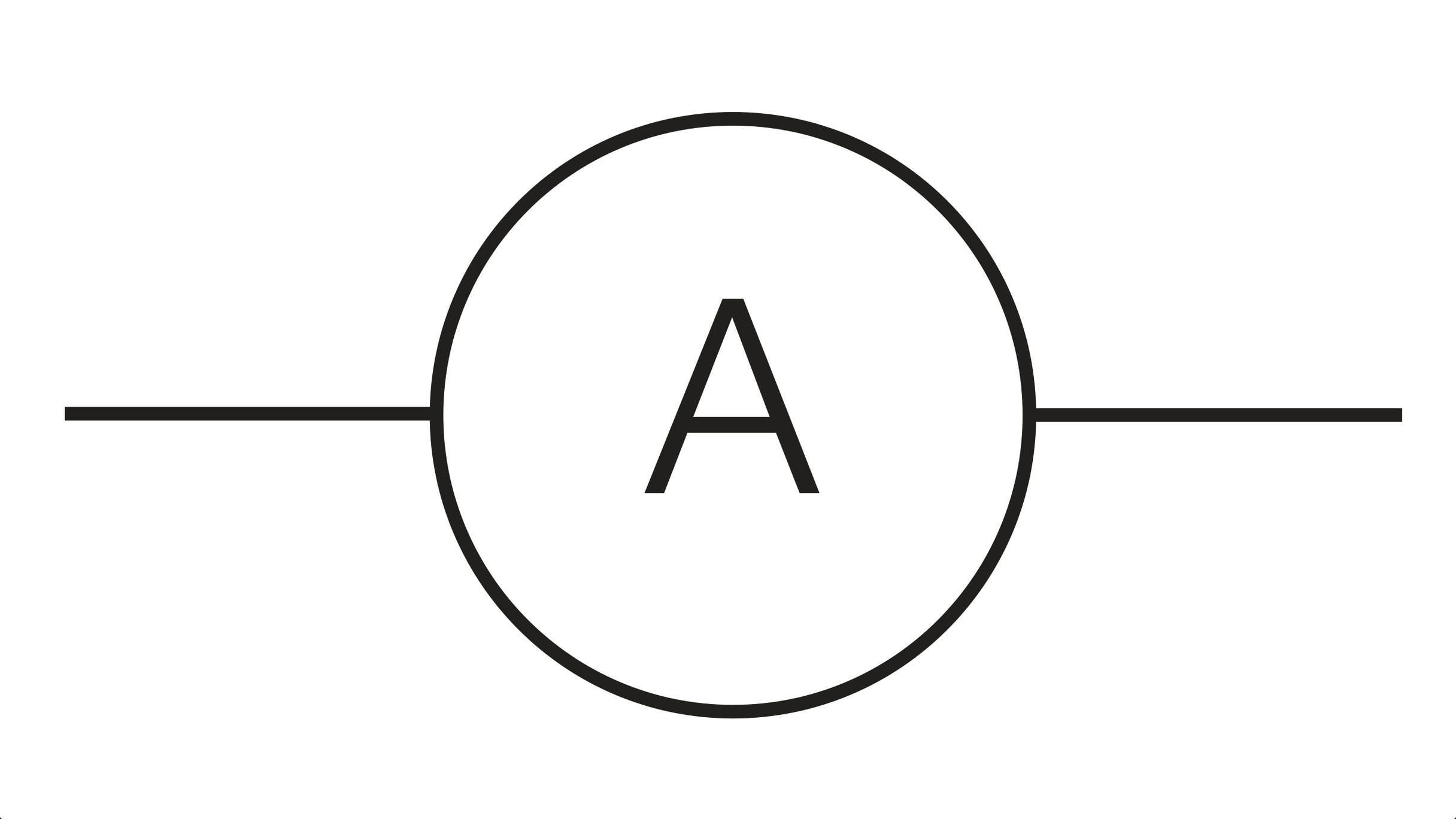
what symbol is this
ammeter
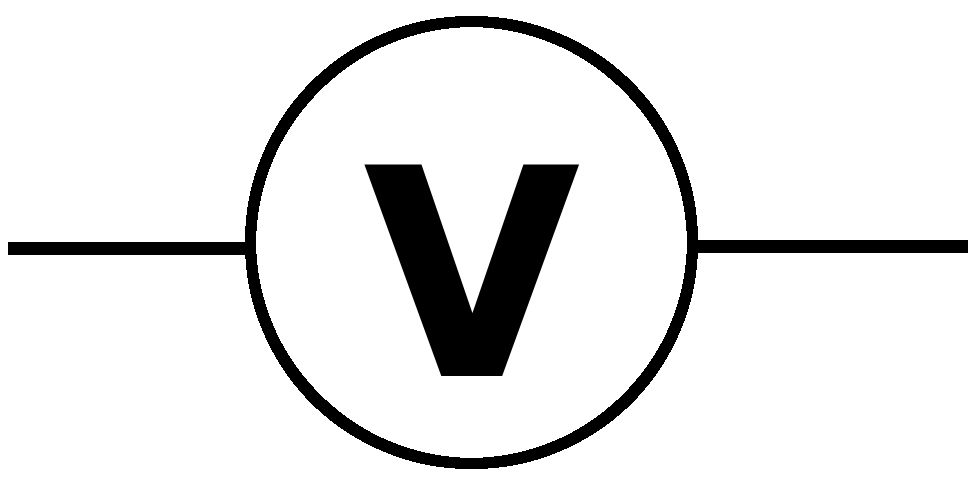
what symbol is this
voltmeter
what symbol is this
fuse
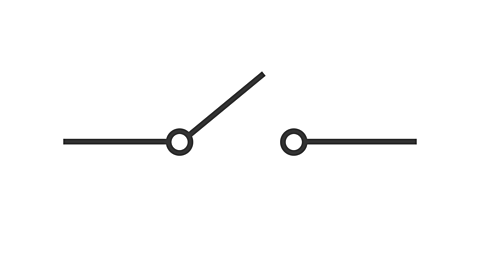
what symbol is this
open switch
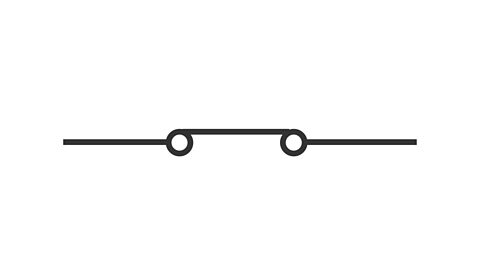
what symbol is this
closed switch
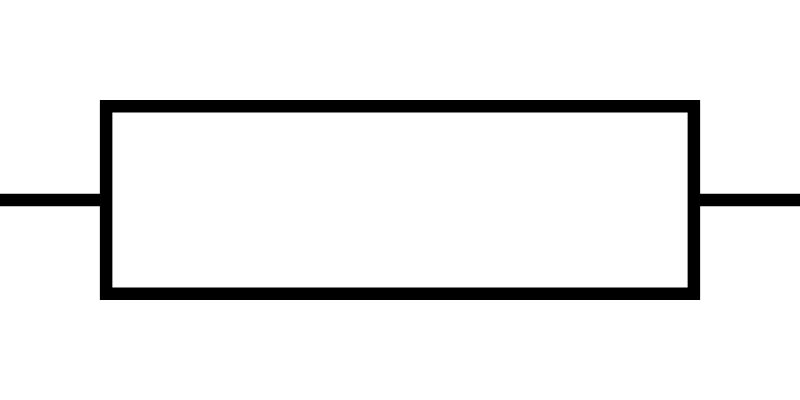
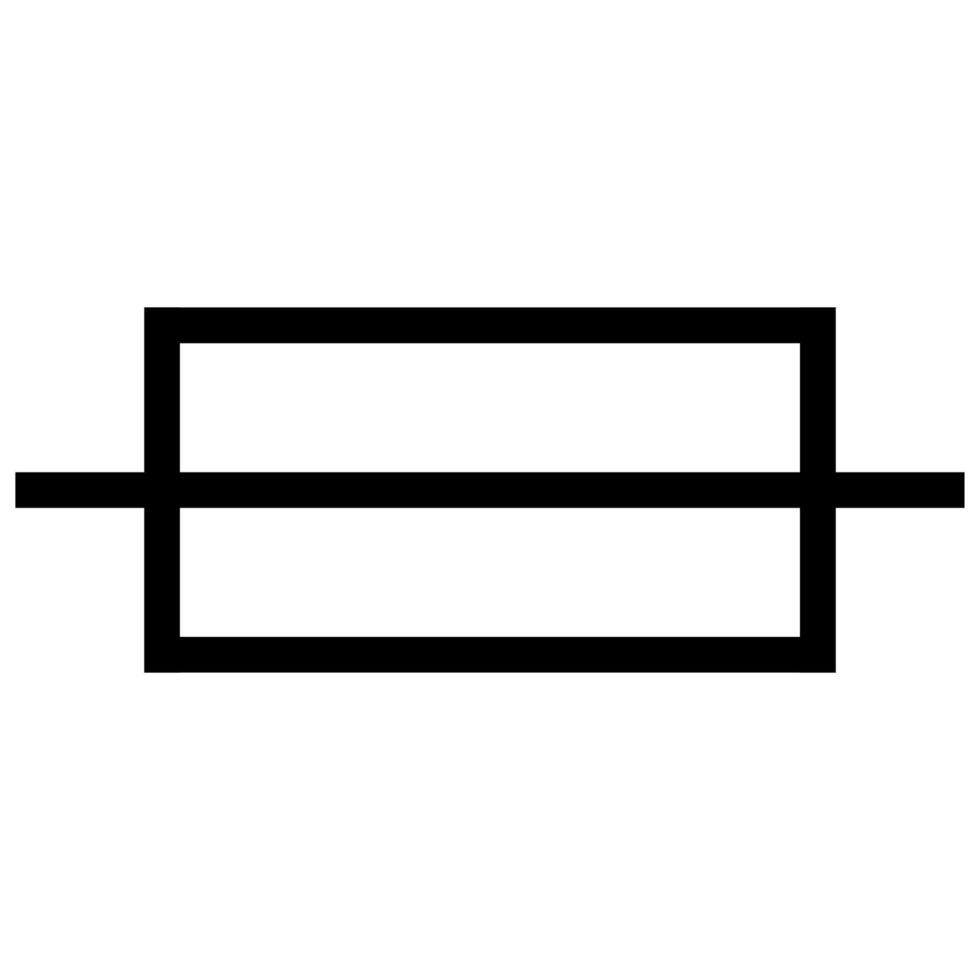
what symbol is this
resistor
draw the power supply symbol
idk why google won’t show up with the scipad one but it should look like two ends with a positive sign on the left and a negative sign on the right.
just watch for those signs and you’ll know it’s a power supply
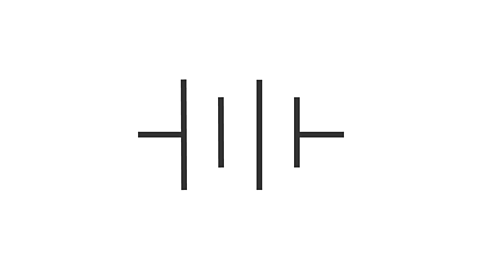
what symbol is this
battery
it’s literally just a bunch of cells.
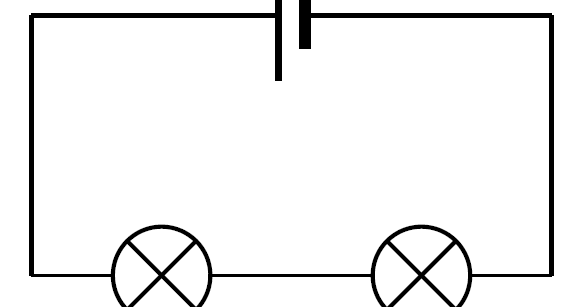
series circuit
All the components are connected one after the other. If one of the bulbs in the circuit fails (breaks), then the current in ALL the bulbs will STOP.
draw a series circuit (just have a general idea)
smth like this
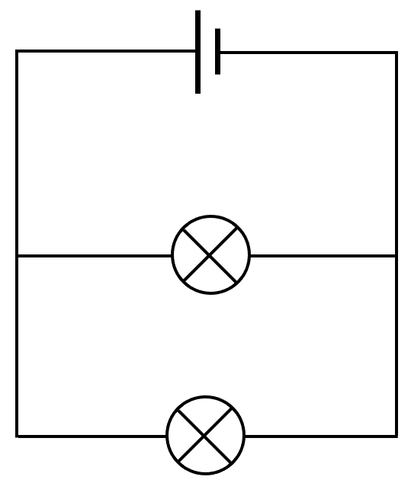
parallel circuits
the components in the circuit are parallel to each other. If one bulb fails, the other two still have a current through them and will still glow.
draw a parallel circuit
smth like this
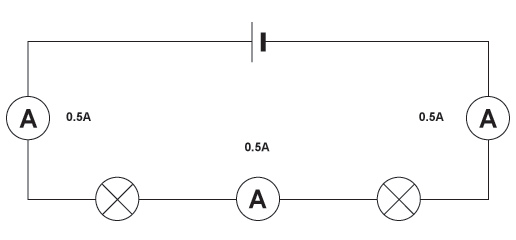
current in a series circuit + resistance
When all bulbs are identical, the current is same. The total resistance is the sum of individual resistances.
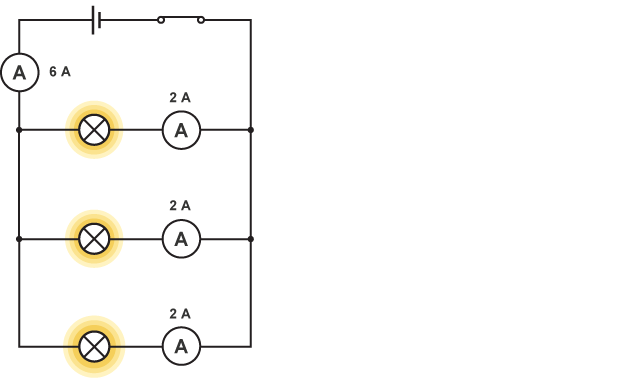
current in a parallel circuit + resistance
The current is shared out among the branches. The sum of the currents in the branches is equal to the current in the main part of the circuit. Ammeters are still connected in series with the components.
basically, if an ammeter in the branch read 3A, the other ammeter in the branch would read 3A, and the ammeter in the main circuit would read 6A.
JUST DIVIDE THE AMMETER CURRENT IN THE BRANCHES TO MATCH THE CURRENT IN THE MAIN CIRCUIT.
The total resistance is less than the smallest individual resistance.
Voltage
The potential difference between two points in a circuit. It is the force from an electrical power source that pushes the current through a circuit, allowing them to do work. Expressed in volts (V). The higher the voltage, the stronger the push on electrons, meaning they carry more electrical energy.
voltmeter
used to measure voltage. they are always connected in PARALLEL with the component whose voltage is being measured.
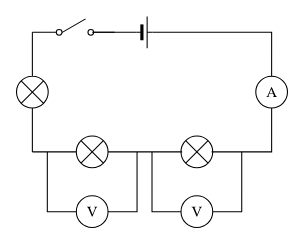
Voltage in a series circuit
The voltage in a series circuit is divided among the components. Changing the amount of components in the circuit will alter the voltage each component gets to use, however it will not alter the supply voltage.
Voltage in parallel circuit
BASICALLY EVERYTHING IS THE SAME AS LONG AS THE BULBS ARE IDENTICAL.
The voltage is the same across all parallel branches to the supply voltage. Adding/removing parallel components will not change the voltage in the other parallel branches.
Power
Electrical components usually convert energy from one form to another. Electric power is a measure of the rate at which energy is TRANSFORMED in an electrical circuit. It is measured in watts (W).
Power formulas
P = IV
P = power (W)
I= Current (A)
V= Voltage (V)
P=E/t
P= power (W)
E= change in energy (J)
t= time (s)
How does the power of the bulbs affects their brightness?
Bulbs that glow brighter are converting more electrical energy. They are using more power.
Energy transformed
One watt is equal to one joule of energy being transformed each second.
1 W = 1 J/s
Energy transformed formal
E = P x t
E= change in energy (J)
P= power (W)
t= time (s)
Resistance
Resistance is a quantity that describes how much an electrical component restricts the flow of current.
Resistance/voltage formula
Voltage:
V = IR
V= Voltage (V)
I= Current (A)
R= Resistance (Ω)
Resistance:
R= V/I
what happens to the current when the voltage is doubled?
When the voltage is doubled, the current doubles along with the voltage.
what happens to the current when the resistor is halved?
When the resistor is halved, the current doubles.