ADPR 3850 Exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:44 AM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
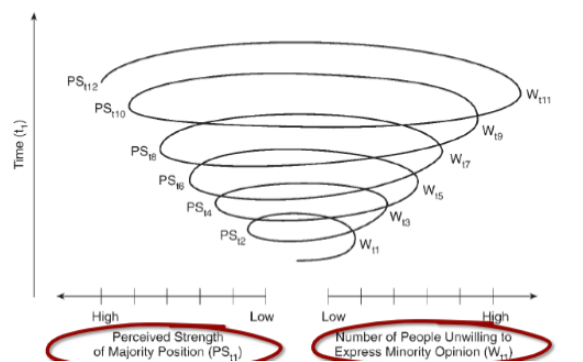
Spiral of Silence
- Society threatens with isolation those people who violate moral consensus
- We fear this isolation and try to prevent it from happening
- Therefore, we constantly monitor our environment and have developed a quasi-statistical sense of the climate of public opinion
- We share our opinions when we believe they are the dominant opinion, or the opinion on the rise (i.e., a bandwagon effect)
- The media often gives a platform to the loudest voices (even though they may represent a minority opinion)
- Together, this results in the spiral of silence ...
- We fear this isolation and try to prevent it from happening
- Therefore, we constantly monitor our environment and have developed a quasi-statistical sense of the climate of public opinion
- We share our opinions when we believe they are the dominant opinion, or the opinion on the rise (i.e., a bandwagon effect)
- The media often gives a platform to the loudest voices (even though they may represent a minority opinion)
- Together, this results in the spiral of silence ...
2
New cards
"Public Opinion”
The collection of views or opinions held by people about issues concerning them
3
New cards
Self-interest
_____________ plays a role in public opinion, including making opinions resistant (or open) to change
4
New cards
elites & major events
But, ______ & ______ ______ can have dramatic impacts on public opinion
5
New cards
+ Ryan Braun accused of steroid use
- My friends (Wisconsin baseball fans) said there should be no punishment; called the report erroneous and accused many of lies and incompetency
- Maintained this stance even as evidence mounted
- After Braun admitted steroid use, many still maintained this stance, or shifted to the “everyone is doing it” argument
+ Johnny Manziel vs. Todd Gurley
- With no interest in the Aggies season and a general dislike of Manziel, my opinion was that rules were (likely) broken and he should be suspended
- One year later and I felt the rule was ridiculous and no suspension warranted
- My friends (Wisconsin baseball fans) said there should be no punishment; called the report erroneous and accused many of lies and incompetency
- Maintained this stance even as evidence mounted
- After Braun admitted steroid use, many still maintained this stance, or shifted to the “everyone is doing it” argument
+ Johnny Manziel vs. Todd Gurley
- With no interest in the Aggies season and a general dislike of Manziel, my opinion was that rules were (likely) broken and he should be suspended
- One year later and I felt the rule was ridiculous and no suspension warranted
Self-interest plays a role in public opinion, including making opinions resistant (or open) to change… EXAMPLES:
6
New cards
Opinion Leaders
_____ _____ are:
- Highly interested in a given subject or issue
- Better informed than most (often college educated)
- Avid consumers of media
- Early adopters of new ideas /technologies
- Have higher income
- Active in the community and with recreation activities
- Good organizers who can galvanize action
- Highly interested in a given subject or issue
- Better informed than most (often college educated)
- Avid consumers of media
- Early adopters of new ideas /technologies
- Have higher income
- Active in the community and with recreation activities
- Good organizers who can galvanize action
7
New cards
Oprah's Book Club
Example of Opinion Leaders
8
New cards
Media
The _____ play a key role in influencing opinion as they are a crucial source for information
9
New cards
Agenda Setting theory
The media don’t tell us what to think, only what to think about
+ Of course, public relations specialists are responsible for anywhere between 50-60% of all media content
+ Of course, public relations specialists are responsible for anywhere between 50-60% of all media content
10
New cards
Agenda Setting
What are the current issues that the media are telling us are important? It probably depends where you look ...
11
New cards
Priming
A memory-based effect whereby exposure to a stimulus influences later thinking
12
New cards
Framing
+ A theory related to the presentation of information
+ Defined a number of different ways by a number of different people
1. As the selection of specific facts or pieces of information that journalists use in a news story (media frames)
2. Different packages of otherwise equivalent information
+ Defined a number of different ways by a number of different people
1. As the selection of specific facts or pieces of information that journalists use in a news story (media frames)
2. Different packages of otherwise equivalent information
13
New cards
Gain Frames and Loss Frames
Two major Frames
14
New cards
Gain Frames
+ Emphasize the advantages of a given action
+ EXAMPLE: “If you quit smoking you will live longer”
+ Work better for motivating prevention behaviors (e.g., using sunscreen)
+ EXAMPLE: “If you quit smoking you will live longer”
+ Work better for motivating prevention behaviors (e.g., using sunscreen)
15
New cards
Loss Frames
+ Emphasize the disadvantages of failing to comply
+ EXAMPLE: “If you do not quit smoking you will die sooner”
+ Work better for motivating detection behaviors (e.g., cancer screenings)
+ EXAMPLE: “If you do not quit smoking you will die sooner”
+ Work better for motivating detection behaviors (e.g., cancer screenings)
16
New cards
Prevention Behaviors; Detection Behaviors
Gain Frames are to _____ as Loss Frames are to ____
17
New cards
Frames
+ _____ are not about offering new facts
+ Rather: ____ differ in how they present issues
- Estate tax vs. Death tax
- Drill for oil vs. Explore for energy
+ In media, _____ help audiences
- determine why an issue is important
+ e.g., Is secondhand smoke a health issue or rights issue?
- efficiently process new information by connecting it to what we already know
+ e.g., Habitual offender laws ... 3-strikes and you’re out!
+ Rather: ____ differ in how they present issues
- Estate tax vs. Death tax
- Drill for oil vs. Explore for energy
+ In media, _____ help audiences
- determine why an issue is important
+ e.g., Is secondhand smoke a health issue or rights issue?
- efficiently process new information by connecting it to what we already know
+ e.g., Habitual offender laws ... 3-strikes and you’re out!
18
New cards
Persuasion
_____ is to:
+ Change or neutralize hostile opinions
+ Crystallize latent opinions and positive attitudes
+ Conserve favorable opinions
+ Change or neutralize hostile opinions
+ Crystallize latent opinions and positive attitudes
+ Conserve favorable opinions
19
New cards
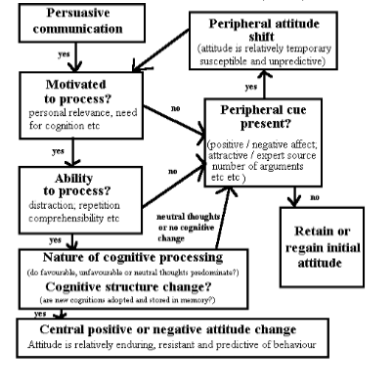
The Elaboration Likelihood Model (ELM)
one Model of Persuasion
20
New cards
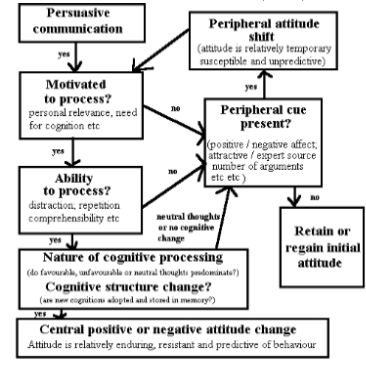
Another model of Persuasion
21
New cards
+ Audience Analysis
+ Source Credibility
+ Making Appeals to Self-Interest
+ Ensure the Clarity of your Message
+ Work in Audience Participation
+ Carefully Determine the Content and Structure of your Message
+ Source Credibility
+ Making Appeals to Self-Interest
+ Ensure the Clarity of your Message
+ Work in Audience Participation
+ Carefully Determine the Content and Structure of your Message
Keys to Persuasion
22
New cards
Audience Analysis
+ Know who you’ll be communicating with
+ How involved are they? What do they think? Etc.
+ How involved are they? What do they think? Etc.
23
New cards
Source Credibility
Who can we have deliver our message? Recall those attributes we just discussed (expertise, sincerity & charisma)
24
New cards
Making Appeals to Self-Interest
+ Structure your message to appeal to your target
+ People also are driven by altruism
+ People also are driven by altruism
25
New cards
Ensure the Clarity of your Message
+ Make the message accessible
+ Have a clear call to action
+ Have a clear call to action
26
New cards
Work in Audience Participation
+ Major growth in user-generated content
+ Participating reinforces their beliefs and adds credibility to the message
+ Participating reinforces their beliefs and adds credibility to the message
27
New cards
Carefully Determine the Content and Structure of your Message
Will you use statistics? Exemplars? Appeals to logic? Appeals to emotion? Testimonials? Celebrity endorsements? Links to normative behavior ...
28
New cards
+ Self-Selection
+ Selective Perception
+ Hostile Media Effect
+ Selective Perception
+ Hostile Media Effect
Limits to Persuasion
29
New cards
Self-Selection
+ Let’s say we get our message to the target audience …
+ We live in an information age and it does not make sense for most of us to:
a) attend to all the messages that come our way
b) process those messages, and
c) develop an in-depth attitude or understanding of the issue in question
- We are “cognitive misers”
+ We live in an information age and it does not make sense for most of us to:
a) attend to all the messages that come our way
b) process those messages, and
c) develop an in-depth attitude or understanding of the issue in question
- We are “cognitive misers”
30
New cards
Selective Perception
+ ... and, we’re biased processors
+ We process information through various perceptual filters, including
- religious beliefs
- Trust
- political ideology
- etc.
+ As a result: Any given “fact” may mean different things to different people …
+ We process information through various perceptual filters, including
- religious beliefs
- Trust
- political ideology
- etc.
+ As a result: Any given “fact” may mean different things to different people …
31
New cards
Hostile Media Effect
+ Another indicator of how we process mediated content
- When we give an equivalent piece of communication to different partisan groups, each group tends to feel that the communication is biased against their point of view
- When we give an equivalent piece of communication to different partisan groups, each group tends to feel that the communication is biased against their point of view
32
New cards
Competition
Two or more groups fighting for the same resource
33
New cards
Conflict
When groups direct their efforts against each other, often through verbal attacks
34
New cards
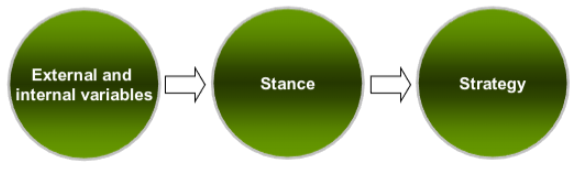
*** Contingency Theory
+ PR professionals monitor for threats, assess those threats, arrive at a desirable stance, and begin communications efforts
- Influenced by Situational demands and Resources
+ The stance is dynamic; It changes as events unfold
- Influenced by Situational demands and Resources
+ The stance is dynamic; It changes as events unfold
35
New cards
Situational demands
nature of crisis, duration, severity, size, complexity; influence of actors, etc.
36
New cards
Resources
time, money, knowledge, expertise, etc.
37
New cards
1. Regret
2. Responsibility
3. Remedy
2. Responsibility
3. Remedy
The three R’s of apologizing:
38
New cards
express empathy ... and do so quickly
Regret
39
New cards
Avoid the blame game and be transparen
Responsibility
40
New cards
be part of the solution
Remedy
41
New cards
+ Pepsi and Syringes
+ Tylenol Poisonings
+ Tylenol Poisonings
Examples of Contingency Theory In Action
42
New cards
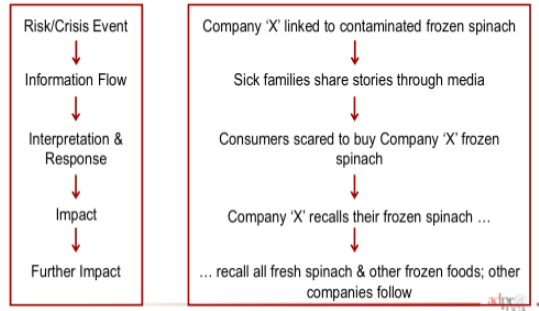
Further complicating this process: public concern can be difficult to predict or disproportional to the actual risk..
The Amplification (Or Attenuation) Of A Crisis
43
New cards
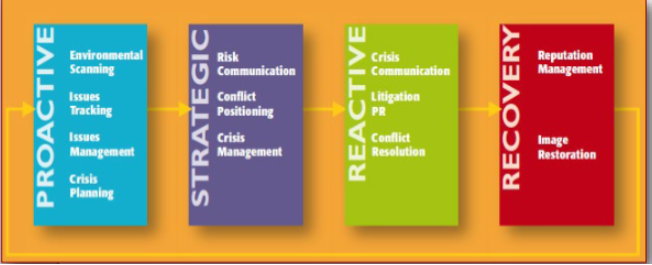
The Conflict Management Life Cycle
1. Proactive
2. Strategic
3. Reactive
4. Recovery
5. Repeat
2. Strategic
3. Reactive
4. Recovery
5. Repeat
44
New cards
The Conflict Management Life Cycle: The Proactive Phase
+ To prevent a conflict from arising or spreading
- Environmental scanning: reading, watching, paying attention to matters of interest to organization
- Issues tracking: a more narrowed version of above
- Issues management: create strategic plans or begin modifying behavior to address emerging issues
- Crisis plan: preparing for the worst
- Environmental scanning: reading, watching, paying attention to matters of interest to organization
- Issues tracking: a more narrowed version of above
- Issues management: create strategic plans or begin modifying behavior to address emerging issues
- Crisis plan: preparing for the worst
45
New cards
The Conflict Management Life Cycle: The Strategic Phase
+ Emerging conflict is identified as needing action
- Crisis management: filling in the current logistics for your specific crisis plan
- Risk communication: communicating the risk to vulnerable publics
- Conflict positioning strategies: how can the organization best position itself in the “court of public opinion” and in preparing for possible litigation?
- These two areas may be in conflict with one another
- Crisis management: filling in the current logistics for your specific crisis plan
- Risk communication: communicating the risk to vulnerable publics
- Conflict positioning strategies: how can the organization best position itself in the “court of public opinion” and in preparing for possible litigation?
- These two areas may be in conflict with one another
46
New cards
The Conflict Management Life Cycle: The Reactive Phase
+ Must react when conflict reaches a critical level of impact
- Crisis communication: putting that planning into effect; help victims; communicate plans through media
- Conflict resolution techniques: reduce the conflict and/or bring about resolution
- Litigation public relations: preparing for legal actions
- Crisis communication: putting that planning into effect; help victims; communicate plans through media
- Conflict resolution techniques: reduce the conflict and/or bring about resolution
- Litigation public relations: preparing for legal actions
47
New cards
The Conflict Management Life Cycle: The Recovery Phase
+ Strategies employed in the aftermath to bolster or repair reputation
- Reputation management: Research-based approach to understand and bolster reputation
- Image restoration strategies: An extreme form of reputation management when damage to an organization is large
- ValuJet acquires AirTran and takes their name
- Reputation management: Research-based approach to understand and bolster reputation
- Image restoration strategies: An extreme form of reputation management when damage to an organization is large
- ValuJet acquires AirTran and takes their name
48
New cards
Eighty-six percent of business crises are “smoldering crises,” meaning there are clear warning signs
Smoldering crises vs. sudden crises
49
New cards
Crisis Communication Management: Filling The Void
+ Principle 1: when a crisis occurs, an information vacuum is created
+ Principle 2: when a vacuum exists, it will be filled
- By whom? With what?
+ Principle 2: when a vacuum exists, it will be filled
- By whom? With what?
50
New cards
Crisis Management: How To Communicate During A Crisis
+ Set up a central information center
- Monitor news coverage and the phone
+ Designate a (strong) spokesperson
+ Be accessible and honest
+ Communicate with key publics
+ Provide information often (understand the needs of media)
+ Be careful about saying, “no comment”
+ Put the public first
+ Take responsibility – Ryan Braun vs. Roger Clemens
- Monitor news coverage and the phone
+ Designate a (strong) spokesperson
+ Be accessible and honest
+ Communicate with key publics
+ Provide information often (understand the needs of media)
+ Be careful about saying, “no comment”
+ Put the public first
+ Take responsibility – Ryan Braun vs. Roger Clemens
51
New cards
1. Control or Efficacy
2. Complexity
3. Familiarity
4. Message consistency
5. Consequences
2. Complexity
3. Familiarity
4. Message consistency
5. Consequences
Risk Communication: Five Variables Affecting Risk Perception
52
New cards
Control or Efficacy
how much control do you have over risk avoidance? (e.g., smoking versus chemicals in my water)
53
New cards
Complexity
How hard is it to avoid the risk (e.g., flu shots vs. changing my diet and exercise habits)?
54
New cards
Familiarity
How familiar is the risk and the behavior required to avoid the risk (e.g., hurricane preparation)?
55
New cards
Message consistency
Are your messages consistent?
56
New cards
Consequences
Do your audiences believe the consequences apply to them?
57
New cards
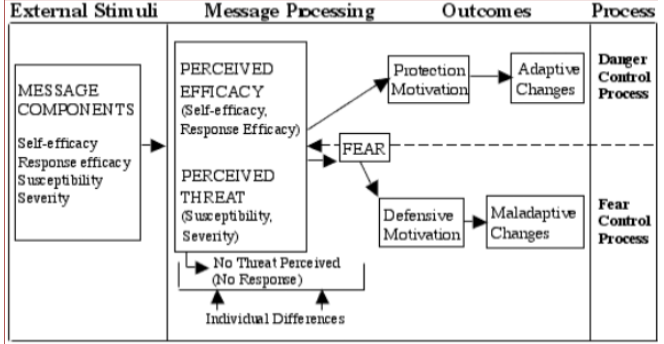
Risk Communication: Extended Parallel Processing Model
+ Fear & Smoking
+ Four factors are believed to influence the outcome a fear appeal message:
- Self-Efficacy
- Response Efficacy
- Susceptibility
- Severity
+ Four factors are believed to influence the outcome a fear appeal message:
- Self-Efficacy
- Response Efficacy
- Susceptibility
- Severity
58
New cards
Self-Efficacy
Can I perform the tasks needed to control the threat/risk?
59
New cards
Response Efficacy
If I perform those tasks, will it prevent the threat/risk?
60
New cards
Susceptibility
Does the threat/risk impact me?
61
New cards
Severity
Is the threat/risk large enough to worry about?
62
New cards
Important Factors Related to the Public Relations Audience
1. Diversity
+ Geography, history, culture, religion, etc.
2. Expanding international audiences
3. Use of technology
+ Used to segment audiences and compile data (e.g., Google AdWords)
+ Formation of online communities … like the nerds I play (online) hockey with!
4. Support for single issues
+ Finding like-minded others through technology often leads to singular focus on issues for people ... but what about other important issues?
+ Bill Gates vs. Filter bubble
5. Visual orientation
+ Compounded by smart phones, tablets, etc.
+ Shortened attention spans and the importance of the “sound bite”
6. Emphasis on personality and celebrity
+ Who is a “celebrity”? Can we trust “celebrity” tweets? Or are these just paid advertisements?
7. Distrust of authority & polarization
+ Makes PR crucially important, but also difficult
+ Geography, history, culture, religion, etc.
2. Expanding international audiences
3. Use of technology
+ Used to segment audiences and compile data (e.g., Google AdWords)
+ Formation of online communities … like the nerds I play (online) hockey with!
4. Support for single issues
+ Finding like-minded others through technology often leads to singular focus on issues for people ... but what about other important issues?
+ Bill Gates vs. Filter bubble
5. Visual orientation
+ Compounded by smart phones, tablets, etc.
+ Shortened attention spans and the importance of the “sound bite”
6. Emphasis on personality and celebrity
+ Who is a “celebrity”? Can we trust “celebrity” tweets? Or are these just paid advertisements?
7. Distrust of authority & polarization
+ Makes PR crucially important, but also difficult
63
New cards
Generation Z (born ~ 1997 to 2015)
- a.k.a., the Post-Millennial Generation, iGen
- Make up 26% of the U.S. population – slightly more than Millennials or Boomers
- Spend only 8 min. per day online via PC
- Online time is almost exclusively mobile
- Less accepting of the idea of the “American Dream”
- Self-identify as loyal, compassionate, open-minded, and determined, but see others in their generation as competitive, spontaneous, adventuresome, and curious
- More risk-averse than previous generations
- Lower alcohol and drug use rates
- Interested in “making the world a better place”
- Make up 26% of the U.S. population – slightly more than Millennials or Boomers
- Spend only 8 min. per day online via PC
- Online time is almost exclusively mobile
- Less accepting of the idea of the “American Dream”
- Self-identify as loyal, compassionate, open-minded, and determined, but see others in their generation as competitive, spontaneous, adventuresome, and curious
- More risk-averse than previous generations
- Lower alcohol and drug use rates
- Interested in “making the world a better place”
64
New cards
Millennials (born ~ 1981 – 1996)
- a.k.a., Generation Y, E-Generation
- 80 million Millennials in U.S. equals high buying power
- Spend 1/4 to 1/3 of their lives online
- Foster relationships online
- (Some) trends among Millennials:
- Are not influenced by advertising
- Review blogs before making a purchase
- Value authenticity
- Want to engage with brands on SNS
- Want to co-create products with companies
- Use multiple tech devices
- Brand loyal
- Expect brands to give back to society
- 80 million Millennials in U.S. equals high buying power
- Spend 1/4 to 1/3 of their lives online
- Foster relationships online
- (Some) trends among Millennials:
- Are not influenced by advertising
- Review blogs before making a purchase
- Value authenticity
- Want to engage with brands on SNS
- Want to co-create products with companies
- Use multiple tech devices
- Brand loyal
- Expect brands to give back to society
65
New cards
Generation X (born 1965 – 1980)
- Independent
- A generation of latch-key kids
- Tech savvy & resourceful
- Work to live rather than live to work
- Not particularly employer loyal
- Value freedom in the workplace
- Disdain being micro-managed
- Generally tolerant of “alternative” lifestyles
- A generation of latch-key kids
- Tech savvy & resourceful
- Work to live rather than live to work
- Not particularly employer loyal
- Value freedom in the workplace
- Disdain being micro-managed
- Generally tolerant of “alternative” lifestyles
66
New cards
Baby boomers (born between 1946-64)
- Came of age during advent of TV, giving them appreciation for visual advertising
- Question authority & take a strong positions on social issues (60s mentality)
- May retire later than their parents due to improved health and financial uncertainty
- Competitive in their careers and define themselves according to their profession
- Great appreciation for leisure time
- Educated & take pride in accomplishment
- Question authority & take a strong positions on social issues (60s mentality)
- May retire later than their parents due to improved health and financial uncertainty
- Competitive in their careers and define themselves according to their profession
- Great appreciation for leisure time
- Educated & take pride in accomplishment
67
New cards
Seniors
- Approximately 13% of today’s population
- Are less easily convinced than young adults
- Active in voting, reading media (senior women flocking to Facebook)
- Excellent source of volunteers given free time and strong health
- Extremely health conscious
- Nintendo Wii/Norwegian Cruise Lines partnership
- Savings eroded since the 2008 economic crisis
- Are less easily convinced than young adults
- Active in voting, reading media (senior women flocking to Facebook)
- Excellent source of volunteers given free time and strong health
- Extremely health conscious
- Nintendo Wii/Norwegian Cruise Lines partnership
- Savings eroded since the 2008 economic crisis
68
New cards
Women
- Have significant purchasing power
- Traditionally “male” businesses trying to capitalize on this by campaigning to women
- Harley Davidson: Female-only garage parties and instructional videos
- Exercise great influence as opinion leaders
- Large networks of friends
- Have been labeled “multi-minded”
- Able to balance roles as professionals, mothers, wives, etc.
- e.g., NFL marketing
- Traditionally “male” businesses trying to capitalize on this by campaigning to women
- Harley Davidson: Female-only garage parties and instructional videos
- Exercise great influence as opinion leaders
- Large networks of friends
- Have been labeled “multi-minded”
- Able to balance roles as professionals, mothers, wives, etc.
- e.g., NFL marketing
69
New cards
The LGBTQ+ (Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer/Questioning Community)
+ Brand loyal and tend to support companies and brands that reflect their views
+ Disposable income:
- 29% of same-sex households have median incomes over $90,000
- 20 million LGBTQ adults have buying power of ~ $1 trillion / year
+ Disposable income:
- 29% of same-sex households have median incomes over $90,000
- 20 million LGBTQ adults have buying power of ~ $1 trillion / year
70
New cards
Religious groups
- Growing in market & political power (e.g., Catholics; Evangelicals)
- Movie studios developing projects in the aftermath of the success of “The Passion of the Christ”
- Notes on the film Noah:
- Paramount hired a faith-based consultant
- Special trailers screened at Christian conferences & high-profile pastors invited to screenings
- “You're going to see Russell Crowe as a superhero, a guy who has this incredibly difficult challenge put in front of him and has to overcome it.”
- Movie studios developing projects in the aftermath of the success of “The Passion of the Christ”
- Notes on the film Noah:
- Paramount hired a faith-based consultant
- Special trailers screened at Christian conferences & high-profile pastors invited to screenings
- “You're going to see Russell Crowe as a superhero, a guy who has this incredibly difficult challenge put in front of him and has to overcome it.”
71
New cards
Diversity media
- The number of options for reaching minority audiences has increased
- Research concerning these publics has also shown impressive growth
- And we’re seeing a growth in targeted info based on race/ethnicity
- Research concerning these publics has also shown impressive growth
- And we’re seeing a growth in targeted info based on race/ethnicity
72
New cards
Hispanic Audiences
- Fastest-growing ethnic group in U.S.
- Heavy use of social media and texting
- Heavy consumers of radio and TV
- e.g., Spanish-language KLAX #1 during L.A. morning drive time
- Traditionally passionate and brand loyal demographic that is skeptical when they believe campaigns have simply been translated into Spanish
- Heavy use of social media and texting
- Heavy consumers of radio and TV
- e.g., Spanish-language KLAX #1 during L.A. morning drive time
- Traditionally passionate and brand loyal demographic that is skeptical when they believe campaigns have simply been translated into Spanish
73
New cards
Black Audiences
- Rise in affluence
- Buying power reached $1.2 trillion in 2016 and jumped to ~$1.5 trillion by 2020
- Black audiences recognized as pop culture trendsetters
- e.g., The evolution of Mountain Dew:
- Heaviest TV consumers ... and networks (finally) taking notice
- Buying power reached $1.2 trillion in 2016 and jumped to ~$1.5 trillion by 2020
- Black audiences recognized as pop culture trendsetters
- e.g., The evolution of Mountain Dew:
- Heaviest TV consumers ... and networks (finally) taking notice
74
New cards
Asian Audiences
- Relatively small, but educated and affluent group
- Often ignored by communicators due to issues of complexity
- Small group with much diversity
- Heavy reliance on digital communications
- Smart products, gaming, streaming services
- Multi-generational homes where families watch content together
- Often ignored by communicators due to issues of complexity
- Small group with much diversity
- Heavy reliance on digital communications
- Smart products, gaming, streaming services
- Multi-generational homes where families watch content together
75
New cards
Mediasphere
- Top-down
- Controlled by gatekeepers
- Expensive
- One-way communication
- Controlled by gatekeepers
- Expensive
- One-way communication
76
New cards
Blogosphere
- Widespread or horizontal
- Meritocracy
- Inexpensive
- Mobile, two-way communication
- Meritocracy
- Inexpensive
- Mobile, two-way communication
77
New cards
Social media
Blogosphere is synonymous with
78
New cards
Leveraging the Power of the Internet: Risks
- You lose control of your content ... can support or destroy a reputation
- A half-hearted attempt will hurt business
- Social media works when you listen to consumers, facilitate conversations, engage in those conversations, otherwise it alienates
- There is a need to be on multiple platforms that evolve quickly
- A half-hearted attempt will hurt business
- Social media works when you listen to consumers, facilitate conversations, engage in those conversations, otherwise it alienates
- There is a need to be on multiple platforms that evolve quickly
79
New cards
Leveraging the Power of the Internet: Benefits
Is convenient (easy to use and update, cost-effective), interactive, no space constraints, can be targeted, casual, less sanitized, & accepted with less cynicism
80
New cards
Real-Time Content & Casual Content
Social Media Promotes _____________ & __________
81
New cards
Dangers of Social Media
+ Do corporations have a place on social media?
+ How can we leverage real-time communications while avoiding these mishaps?
+ But further, have we given proper consideration to how others might respond?
+ How can we leverage real-time communications while avoiding these mishaps?
+ But further, have we given proper consideration to how others might respond?
82
New cards
Facebook
The most popular Social media platform
83
New cards
~70%
Facebook is used by ~ __% of American adults overall
84
New cards
Facebook
+ Organizations establish a presence on Facebook for:
- Audience engagement and involvement
- Because they feel they have to
+ Public relations materials will need to stand out in a sea of content
+ ***It is inclusive in demographics though users tend to be older
- Audience engagement and involvement
- Because they feel they have to
+ Public relations materials will need to stand out in a sea of content
+ ***It is inclusive in demographics though users tend to be older
85
New cards
Misinformation (EXAMPLE: Zika virus)
What goes viral on Facebook? False information, apparently
86
New cards
Twitter
+ Used by about 22% of American adult internet users and 20% of all American adults
+ In PR, Twitter is a distribution platform for:
- late-breaking news,
- to refute a viral rumor,
- or to provide real-time updates on developing situations
+ Also used for marketing and promotional purposes
+ Using ____ can put out PR fires
+ *** Younger than Facebook, more Urban/Suburban than rural
+ In PR, Twitter is a distribution platform for:
- late-breaking news,
- to refute a viral rumor,
- or to provide real-time updates on developing situations
+ Also used for marketing and promotional purposes
+ Using ____ can put out PR fires
+ *** Younger than Facebook, more Urban/Suburban than rural
87
New cards
- Make direct appeal for others to share (e.g., “retweet”)
- Imitate news headline style
- Produce longer, more informative tweets
- But, keep vocabulary simple
- Produce messages with commonly used words in the target community. Authors write: “Although distinctive messages may attract attention, messages that conform to expectations might be more easily accepted and shared”
- Imitate news headline style
- Produce longer, more informative tweets
- But, keep vocabulary simple
- Produce messages with commonly used words in the target community. Authors write: “Although distinctive messages may attract attention, messages that conform to expectations might be more easily accepted and shared”
Best practices for getting read on Twitter
88
New cards
Viral Marketing
+ “Buzz” or awareness about a product or service, particularly those with limited budgets
- e.g., Dumb ways to die
- e.g., Dumb ways to die
89
New cards
Internet Memes
+ Organizations increasingly attempting to build interactive content for sharing in social spaces
+ The marketing team behind Straight Outta Compton produced the “Straight Outta Somewhere” meme generator, which allowed users to insert their hometown into the film’s logo
+ The marketing team behind Straight Outta Compton produced the “Straight Outta Somewhere” meme generator, which allowed users to insert their hometown into the film’s logo
90
New cards
Pinterest
+ Strong interest in _______ from a PR perspective because the format often pushes users toward goods
- Used by ~ 30% of American adult internet users and 25% of American adults overall
+ Dominated by women in their 30s ... a group that does a disproportionate amount of the shopping
- Strong links from Pinterest to company websites (second to Facebook)
+ Pinterest presence must incorporate high quality visuals to be successful
- Used by ~ 30% of American adult internet users and 25% of American adults overall
+ Dominated by women in their 30s ... a group that does a disproportionate amount of the shopping
- Strong links from Pinterest to company websites (second to Facebook)
+ Pinterest presence must incorporate high quality visuals to be successful
91
New cards
Snapchat
+ Has emerged as arguably the most important platform for reaching young Millennials/Gen Z
+ Audience: ~62% of 18-29 yr. olds are on the platform
+ There’s actually a divide within that age range:
- Nearly ¾ of 18-24 yr. olds vs. a little less than half of those 25-29
- Only ~3% of those 65+ are on the platform
- Roughly 1/3 of users between the ages of 13 and 24 claim to use it, “because their parents did not”
+ Reports more than 200 million daily active users
+ The platform reports approximately 18 billion video views per day
+ 61% of users are female
+ Young audiences are especially engaged and a strong majority use the platform everyday and multiple times a day
+ Audience: ~62% of 18-29 yr. olds are on the platform
+ There’s actually a divide within that age range:
- Nearly ¾ of 18-24 yr. olds vs. a little less than half of those 25-29
- Only ~3% of those 65+ are on the platform
- Roughly 1/3 of users between the ages of 13 and 24 claim to use it, “because their parents did not”
+ Reports more than 200 million daily active users
+ The platform reports approximately 18 billion video views per day
+ 61% of users are female
+ Young audiences are especially engaged and a strong majority use the platform everyday and multiple times a day
92
New cards
Instagram
+ Recently eclipsed 500 million users
- Used by 28% of American adult internet users
- Used by 24% of American adults overall
+ Users tend to be quite active
- Nearly 60% of users go on everyday
- About 35% use it multiple times per day
+ Teens list it as their second most important social media platform (Snapchat is #1)
+ Emphasis on quality images, but also quality captions to contextualize your message
+ *** Lot of POCs and young people
- Used by 28% of American adult internet users
- Used by 24% of American adults overall
+ Users tend to be quite active
- Nearly 60% of users go on everyday
- About 35% use it multiple times per day
+ Teens list it as their second most important social media platform (Snapchat is #1)
+ Emphasis on quality images, but also quality captions to contextualize your message
+ *** Lot of POCs and young people
93
New cards
Virtual Reality
+ Virtual reality is poised to be an integral part of future PR efforts
+ Some are already taking advantage of the technology …
- Jurassic World Apatosaurus app
- Time Magazine and the March on Washington
+ Some are already taking advantage of the technology …
- Jurassic World Apatosaurus app
- Time Magazine and the March on Washington
94
New cards
Dark Patterns
tricks in websites/apps that make you do things that you didn't mean to
95
New cards
Sneak into Basket
A website sneaks an additional item into your basket, often through an opt-out button or checkbox on a prior page
96
New cards
Roach Motel
You find it hard to get out of a situation that was easy to get into (e.g. a premium subscription)
97
New cards
Privacy Zuckering
Being tricked into publicly sharing more information about yourself than you intended to
98
New cards
Hidden Costs
When unexpected charges appear at the last step of the checkout process, e.g. delivery charges, tax, etc
99
New cards
Disguised Ads
Advertisements that are disguised as other kinds of content or navigation
100
New cards
Confirmshaming
Decline options worded to shame user into compliance