economics (elasticities)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:30 PM on 5/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
price elasticity of demand (PED)
measures how much demand for a product will change if the price changes
2
New cards
PED formula
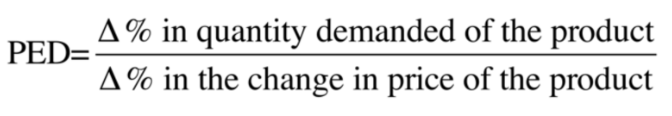
3
New cards
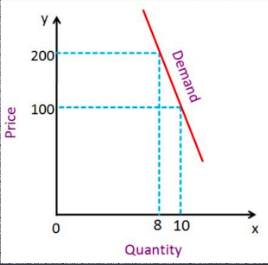
inelastic demand
IF PED IS LESS THAN 1
when a % change in price results in a lower % change in demand
increase in price will cause an increase in total revenue
decrease in price will cause a decrease in total revenue
when a % change in price results in a lower % change in demand
increase in price will cause an increase in total revenue
decrease in price will cause a decrease in total revenue
4
New cards
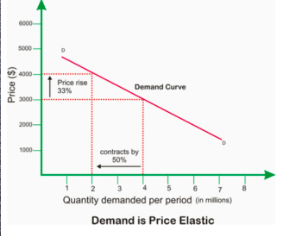
elastic demand
IF PED IS GREATER THAN 1
when a change in % in price results in a greater change in % demanded
firm should NOT raise their prices because a rise in price would result in less revenue
firms should lower their prices
when a change in % in price results in a greater change in % demanded
firm should NOT raise their prices because a rise in price would result in less revenue
firms should lower their prices
5
New cards
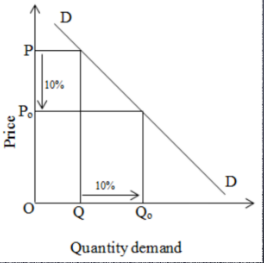
unit elastic demand
IF PED IS = 1
when a % change in price results in an equal % change in demand
a change in price will result in NO change in total revenue$
when a % change in price results in an equal % change in demand
a change in price will result in NO change in total revenue$
6
New cards
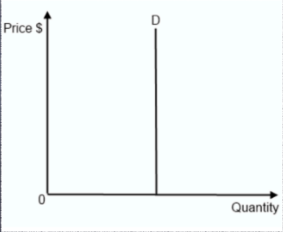
perfectly inelastic demand
IF PED IS = 0
when a change in price results in NO change in quantity demanded
people that need it need it
when a change in price results in NO change in quantity demanded
people that need it need it
7
New cards
determinants of PED
S- substitutes
P- proportion of income
L- luxury or necessity?
A- addictive
T- time
P- proportion of income
L- luxury or necessity?
A- addictive
T- time
8
New cards
substitutes (PED)
determinant of PED
The more substitutes a good has, the more elastic demand is
AND the closer the substitute is, the more elastic demand will be.
The more substitutes a good has, the more elastic demand is
AND the closer the substitute is, the more elastic demand will be.
9
New cards
degree of necessity (PED)
determinant of PED
if a good is a need, then most/many consumers will continue to purchase the good even if prices go up
could be addictive substances
if a good is a need, then most/many consumers will continue to purchase the good even if prices go up
could be addictive substances
10
New cards
proportion of income spent (PED)
determinant of PED
the larger the portion of your income you spend on a good, the more elastic demand will be
luxury goods are very elastic
if a good or service that is a small portion of your income increases in price you will hardly notice
the larger the portion of your income you spend on a good, the more elastic demand will be
luxury goods are very elastic
if a good or service that is a small portion of your income increases in price you will hardly notice
11
New cards
time (PED)
determinant of PED
the longer a consumer takes in making a purchase, the more elastic demand will be
the longer a consumer takes in making a purchase, the more elastic demand will be
12
New cards
income elasticity of demand (YED)
measure of the responsiveness of demand to a change in incomes
13
New cards
YED formula
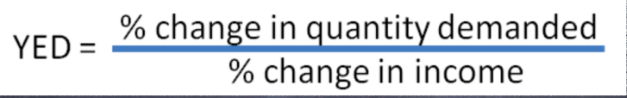
14
New cards
Positive YED
it is a normal good
demand will increase as income increases
demand will increase as income increases
15
New cards
income-inelastic demand
IF YED IS BETWEEN 0 AND 1
good is a necessity
demand will change very little
good is a necessity
demand will change very little
16
New cards
income-elastic demand
IF YED IS GREATER THAN 1
good is a luxury or service
demand will rise noticeably if incomes rise
good is a luxury or service
demand will rise noticeably if incomes rise
17
New cards
inferior good
IF YED IS NEGATIVE
demand decreases as incomes increase
demand will increase as incomes decrease
demand decreases as incomes increase
demand will increase as incomes decrease
18
New cards
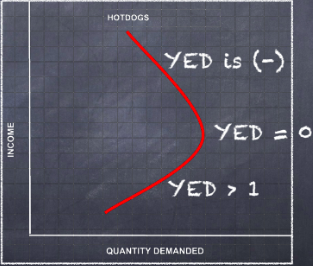
Engel Curve
shows the relationship between demand and income over time
19
New cards
price elasticity of supply (PES)
measure of how much supply will change if prices change
20
New cards
PES formula
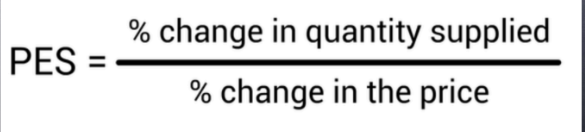
21
New cards
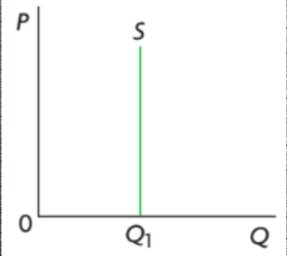
perfectly inelastic supply
IF PES IS ZERO
change in price will have no effect on supply
change in price will have no effect on supply
22
New cards
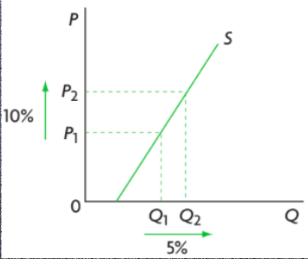
inelastic supply
IF PES IS BETWEEN 0 AND 1
change in the price of a product leads to less change in supply
change in the price of a product leads to less change in supply
23
New cards
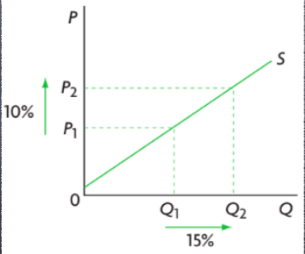
elastic supply
IF PES IS GREATER THAN 1
change in price will lead to a larger increase in supply
change in price will lead to a larger increase in supply
24
New cards
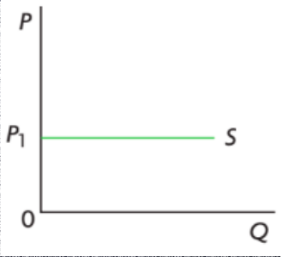
perfectly elastic supply
IF PES IS INFINITY
any change in price will result in no supply
like wheat or other commodities on the world market
any change in price will result in no supply
like wheat or other commodities on the world market
25
New cards
determinants of PES
T- time
R- rate of cost increase
U- unused capacity
M- mobility of factors of production
A- ability to store
R- rate of cost increase
U- unused capacity
M- mobility of factors of production
A- ability to store
26
New cards
time (PES)
determinant of PES
it takes time to reallocate resources and increase supply
over time, if there has been an increase in prices supply will become more elastic
it takes time to reallocate resources and increase supply
over time, if there has been an increase in prices supply will become more elastic
27
New cards
mobility of factors of production (PES)
determinant of PES
the easier it is to change from one line of production to another, the more responsive supply is to a change in price
manufactured goods are more elastic than agricultural products
primary commodities and heavy industrial goods are inelastic supply
the easier it is to change from one line of production to another, the more responsive supply is to a change in price
manufactured goods are more elastic than agricultural products
primary commodities and heavy industrial goods are inelastic supply
28
New cards
unused capacity (PES)
determinant of PES
if a firm can increase production without having to expand its plant size and capital then they can quickly increase supply
if a firm can increase production without having to expand its plant size and capital then they can quickly increase supply
29
New cards
ability to store (PES)
determinant of PES
if a firm can store their goods when demand is low, then they could bring them out of storage when demand increases
if the good is perishable then firms cannot keep it in stock and increase supply when demand shifts
if a firm can store their goods when demand is low, then they could bring them out of storage when demand increases
if the good is perishable then firms cannot keep it in stock and increase supply when demand shifts
30
New cards
rate at which costs increase (PES)
determinant of PES
if the costs of increasing production are high, supply will be inelastic
if the costs of increasing production are low, supply will be elastic
if the costs of increasing production are high, supply will be inelastic
if the costs of increasing production are low, supply will be elastic
31
New cards
PES for manufactured goods
PES values for manufactured goods are generally higher than for commodities
machinery often can be repurposed to respond to a change in demand
machinery often can be repurposed to respond to a change in demand
32
New cards
PES for primary commodities
all natural resources
PES values are very low
it takes months, if not years to change supply
land and resources are limited
environmental destruction, global warming further limits commodities
PES values are very low
it takes months, if not years to change supply
land and resources are limited
environmental destruction, global warming further limits commodities
33
New cards
Sectors of the economy
primary, secondary, tertiary
34
New cards
primary sector
commodities/natural resources
YED values tend to be greater than 1
YED values tend to be greater than 1
35
New cards
secondary sector
manufactured goods
YED values tend to be greater than 1
YED values tend to be greater than 1
36
New cards
tertiary sector
services
YED values tend to be less than 1
YED values tend to be less than 1
37
New cards
developing countries
rely primarily on its primary sector
low PES values make it hard to increase output when prices rise
low YED values mean that as incomes rise, developing countries do not benefit greatly
low PES values make it hard to increase output when prices rise
low YED values mean that as incomes rise, developing countries do not benefit greatly
38
New cards
developed countries
large tertiary sector
benefit as incomes rise in the world
hurt the most when there is a recession
benefit as incomes rise in the world
hurt the most when there is a recession
39
New cards
importance of YED for firms
firms benefit from knowing if they will thrive or struggle in a recession or during economic growth