Biochemistry Unit 3
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Stereoisomers
Atoms are connected in the same order but differ in spatial arrangement
Enantiomers
Nonsuperimposable mirror images
Diastereoisomers
Isomers that are not mirror images
Epimers
Differ at one of several asymmetric carbon atoms
Anomers
Isomers that differ at a new asymmetric carbon atoms formed on ring closure
alpha anomers
C6 and Ca point in opposite directions
beta anomers
C6 and Ca point in the same direction
Aldoses
D-Glyceraldehyde, D-Ribose, D-Glucose, D-Mannose, D-Galactose
Beta-D-Glucopyranose
most stable carbohydrate, every group larger than an H is equatorial
D-Glyceraldehyde
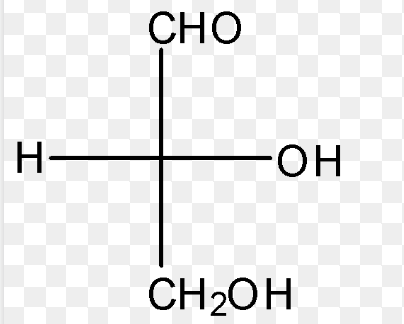
D-Ribose
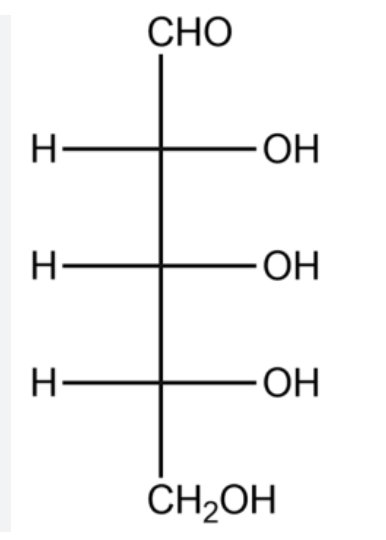
D-Glucose
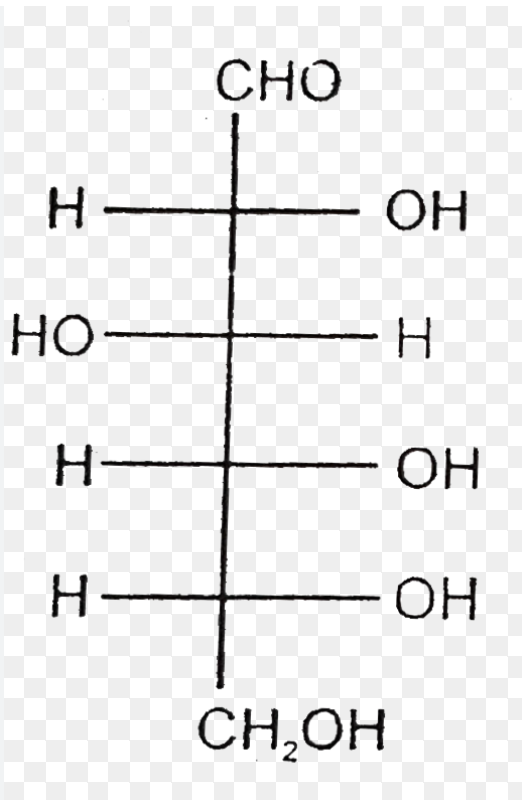
D-Mannose
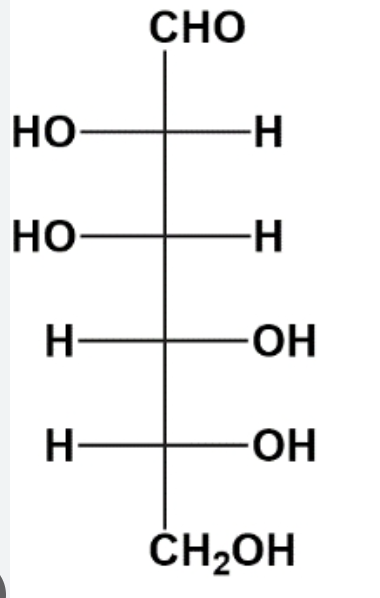
D-Galactose
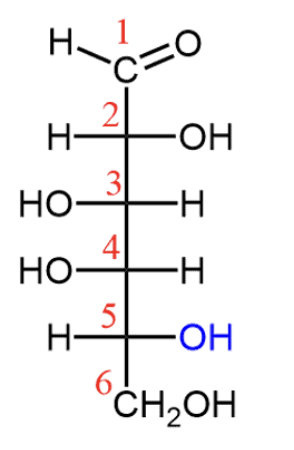
Ketoses
Dihydroxyacetone, D-Fructose
Dihydroxyacetone
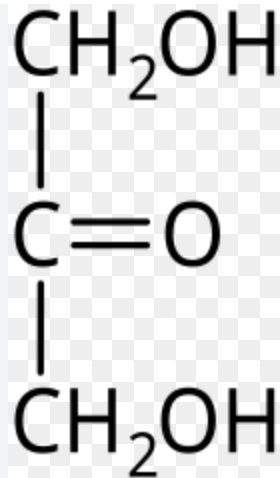
D-Fructose
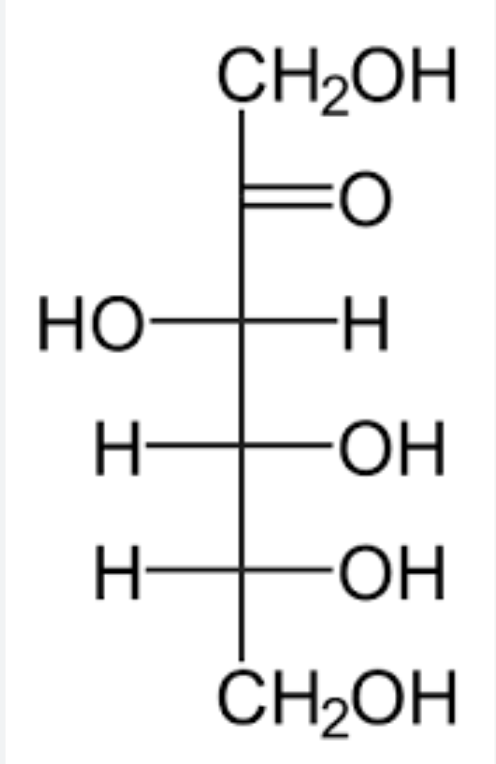
alpha-D-Fructofuranose
cyclic form of fructose
Reducing sugars
need to have a hemiacetal, beta-D-Glucopyranose, Lactose, Maltose (not sucrose), can do mutorotation
Disaccharides
two cyclic carbohydrates connected by a glycosidic bond
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose (not a reducing sugar)
Lactose
Galactose + Glucose (reducing sugar)
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose (reducing sugar)
Glycosidic Bond
Hemiacetal + Alcohol -H2O → Acetal
Cellulose
structural polysaccharide with beta-1,4 linkages
Amylose
unbranched polysaccharide, Starch or Glycogen
Amylopectin
branched polysaccharide, Starch or Glycogen
Starch
coil/ helical shaped homopolymer of glucose with alpha-1,4 linkages, branched every 20-30 residues
Glycogen
coil/ helical shaped homopolymer of glucose with alpha-1,4 linkages, branched every 5-10 residues
Glycoproteins
amino acid residue connected to sugar, connected to acetyl group
N-linked GlcNAc
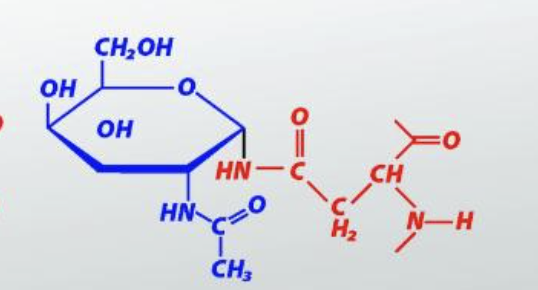
O-Linked GalNAc
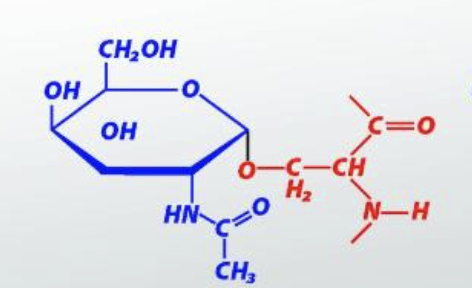
Mutorotation
interconversion of the alpha and beta anomeric forms using the open chain structure as an intermediate
Types of Lipids
free fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, glycolipids, sterols
Fatty Acid
long chain carboxylic acids
omega-3 fatty acid
double bond is on the third carbon, starting on omega carbon atom
Fatty acid nomenclature X:Y (Delta^Z)
X is the number of the carbons, Y is the number of double bonds, Z are the carbon(s) where double bonds are located.
Fatty Acid double bonds are all
cis orientation
Triglyceride
Glycerol backbone with three fatty acid chains, long term storage molecule
Phospholipid
Alcohol bonded to phosphate group bonded to glycerol bond to two fatty acids
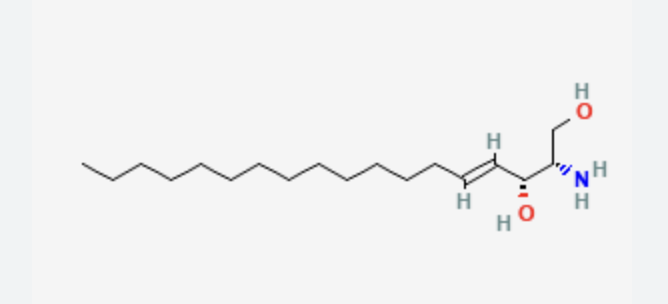
Sphingolipids
Sphingosine and Sphingomyelin
Sphingosine
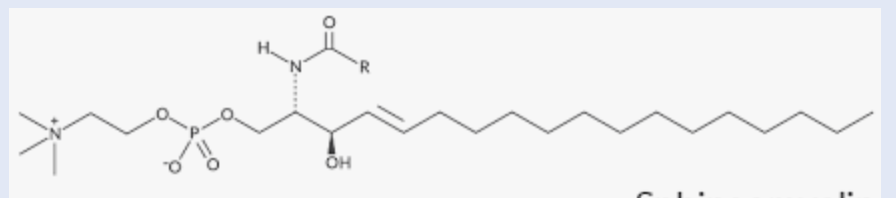
Sphingomyelin
found in myelin sheaths
Glycolipid
Sugar unit bonded to sphingosine backbone that is bonded to a fatty acid unit
ABO blood group antigens are
glycolipids
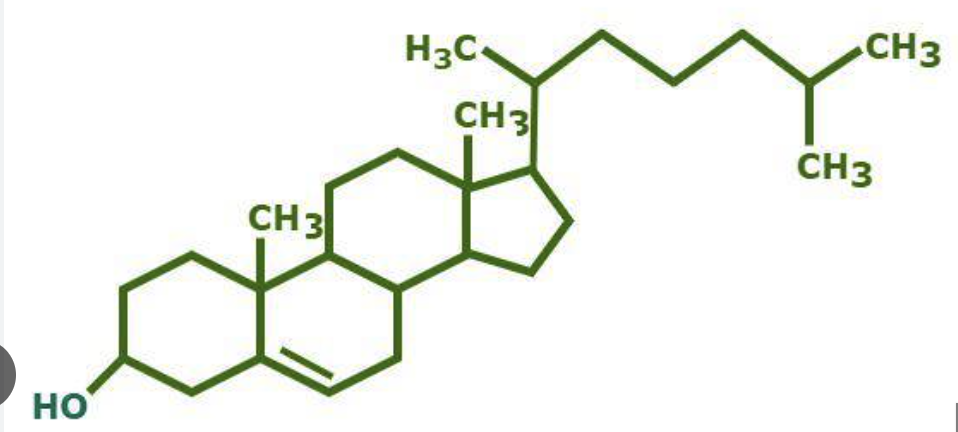
Sterols
cholesterol
Micelle
membrane structure with triangular cross-sections
Phospholipid Bilayer
membrane structure with rectangular cross sections, 30 A long
Transmembrane Proteins
polar aa resides get buried and nonpolar aa residues are near surface of protein
Membrane Associate Protein
nonpolar aa residues are buried and polar aa residues are near surface, interact with polar heads, any anchors would be nonpolar
Anti-Parallel Beta-Sheet Barrel Transmembrane Protein
nonpolar aa residues on outside face and polar aa residues inside
Transmembrane alpha helix proteins must be at least … nonpolar aa long
20
Lateral Diffusion
phospholipids on the same layer flip, rapid
Transverse Diffusion
phospholipids on opp layers flip, very slow
At high temps the membrane is much more..
fluid
Saturated fatty acids
no double bonds, low fluidity, behave like a solid when stacked
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
cis double bonds create a kink in the chain, greater membrane fluidity, lower melting temp
Cholesterol
OH group in near polar head, makes cell membranes more fluid and permeable in low temps
Active Transport
ATP allows movement against a concentration gradient
Passive Transport
no ATP needed, simple and channel/facilitated diffusion
Sodium Potassium Pump
Active Transport, 3 Na+ ount and 2 K+ in, ATP is converted to ADP
Coupled Transport
one concentration gradient is used to power the formation of another using secondary transporters, only made possible by active transport setting up a gradient first
Antiporter
secondary transporter where molecules move in opp directions
Symporter
secondary transporter where molecules move in same direction
Ion Channels
passive transport, holes in the membrane that allow ion movement 1000 x faster than pumps
Potassium Channel
K+ behaves like a lewis acids and uses solvation bonds to pull itself through the channel. Na+ is much smaller than K+ and cannot make the strong bonds needed to pull itself through the channel
Secondary Messengers
Cyclic AMP, phosphate group bonded to ribose bonded to adenine or guanine
7TM Receptors
where the ligand/primary messenger binds on the membrane
Inactive Trimeric G alpha Protein
Bonded to 7TM receptor, GDP, and G beta protein
Active Trimeric G alpha protein
bonded to GTP and adenylate cyclase
Adenylate Cyclase
allosteric enzyme that converts ATP to cAMP
cAMP
binds PKA, release the regulatory pieces from the catalytic pieces so that the catalytic subunits can phosphorylate other proteins
to reset G alpha protein add
H2O
Phosphodiesterase
with water breaks down cAMP into AMP
this type of lipid contains glycerol
phospholipid
cerebroside belongs to which type of lipid
glycolipid
Palmitate
16 carbon saturated fatty acid
Oleic Acid
18 carbon unsaturated fatty acid with double bond at C9
Arachidonic Acid
20 carbon unsaturated fatty acid with double bonds a C5,8,11, and 14
Stearate
18 carbon saturated fatty acid