Lab 4 - Contractility and Fatigue of Skeletal Muscle
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Objective
to observe and measure muscle contraction, and to understand the effects of fatigue on muscle strength
Equipment Required
PC
IXTA ROAM
C-AAMI-504 ECG cable and lead wires
disposable electrode stickers
FT-220 Hand Dynamometer
bathroom scale + large pail
string
metric ruler
The strength of a striated muscle contraction is ____ to the amount of electrical activity in the muscle.
directly proportional
Which channel does the FT-220 hand dynamometer plug into?
A2 input
Placement of Lead wires
Red (+1) - near the elbow
Black (-1) - middle of the forearm
Green (G) - on the wrist
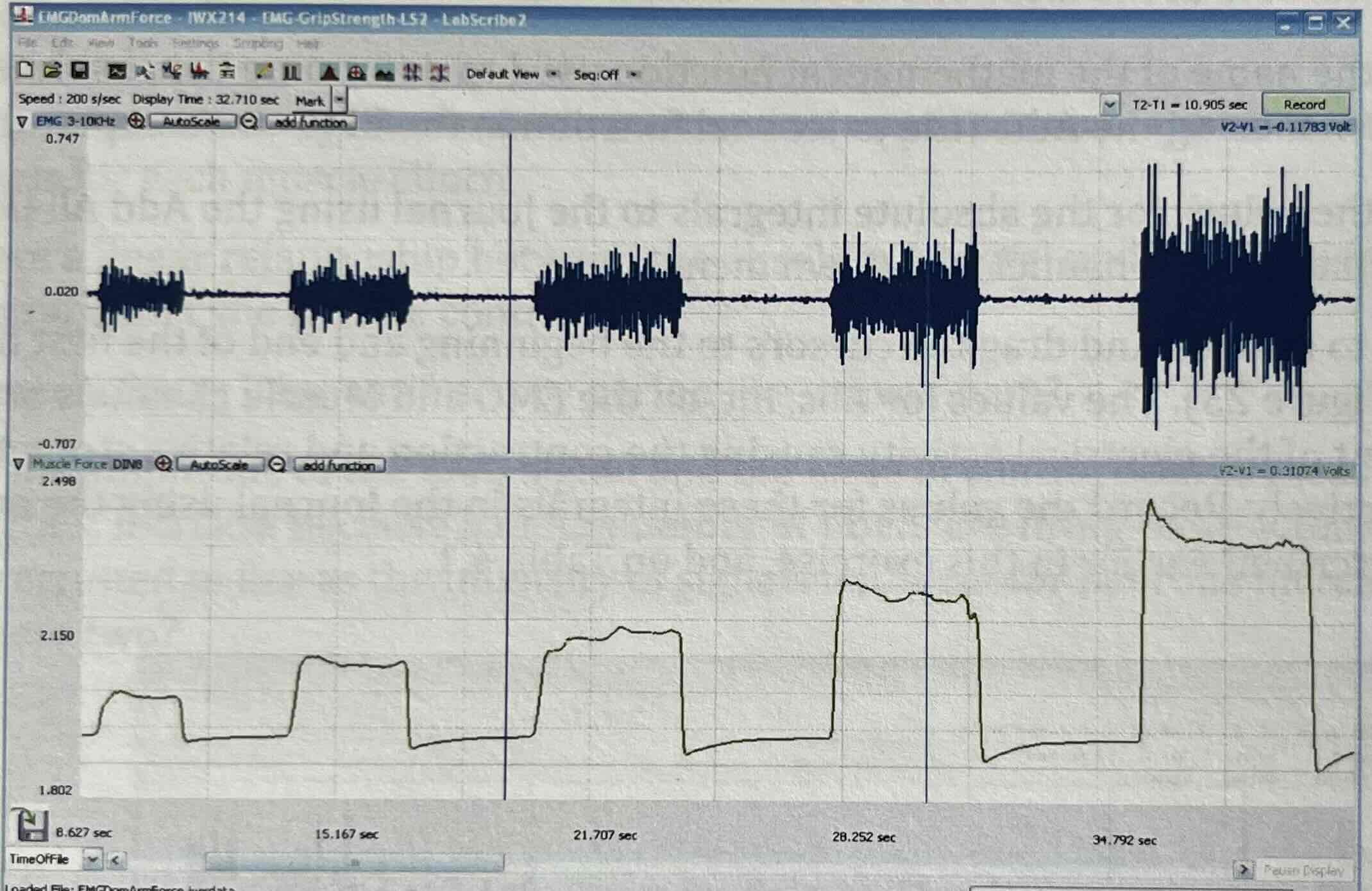
EMG Intensity and Force in Dominant Arm (Exercise 1)
to determine the relationship between the intensity of EMG activity and the force of a muscle contraction in the subject’s dominant arm
Expected Results from Exercise 1
Cursor Placements to measure abs int
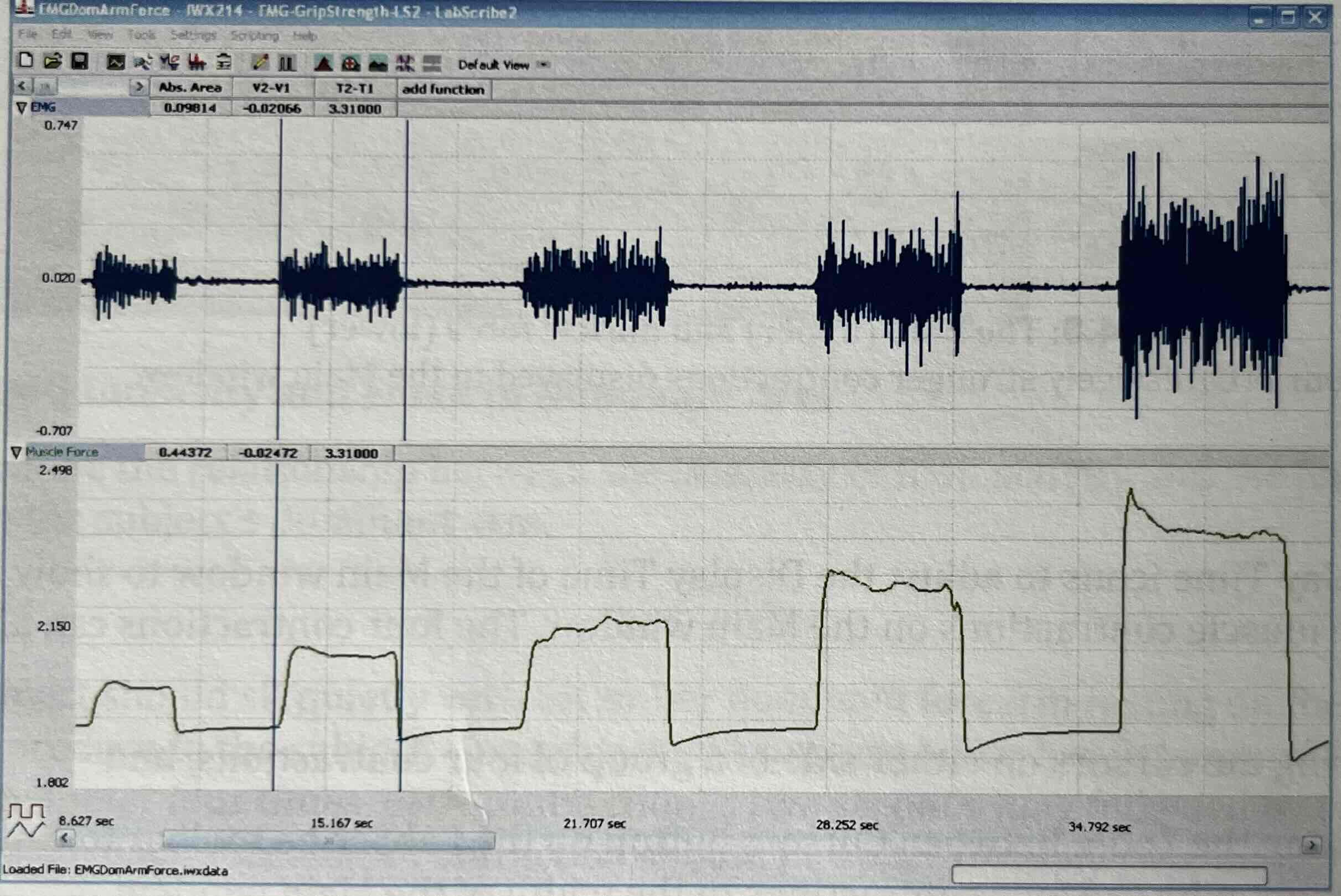
Is there a linear relationship btw the abs int under EMG signals and the abs int under the muscle contraction?
Yes as they are directly proportionate of one another
Do muscle fibers have a refractory period like nerve fibers?
No, instead they go through a twitch and relaxation cycle where they cannot be re-stimulated to contract immediately after a contraction
Why does the amplitude of the EMG signal and the force of contraction increase?
a finite number of fibers are firing more often AND more fibers are recruited to fire as the intensity of signals in the motor neurons increases
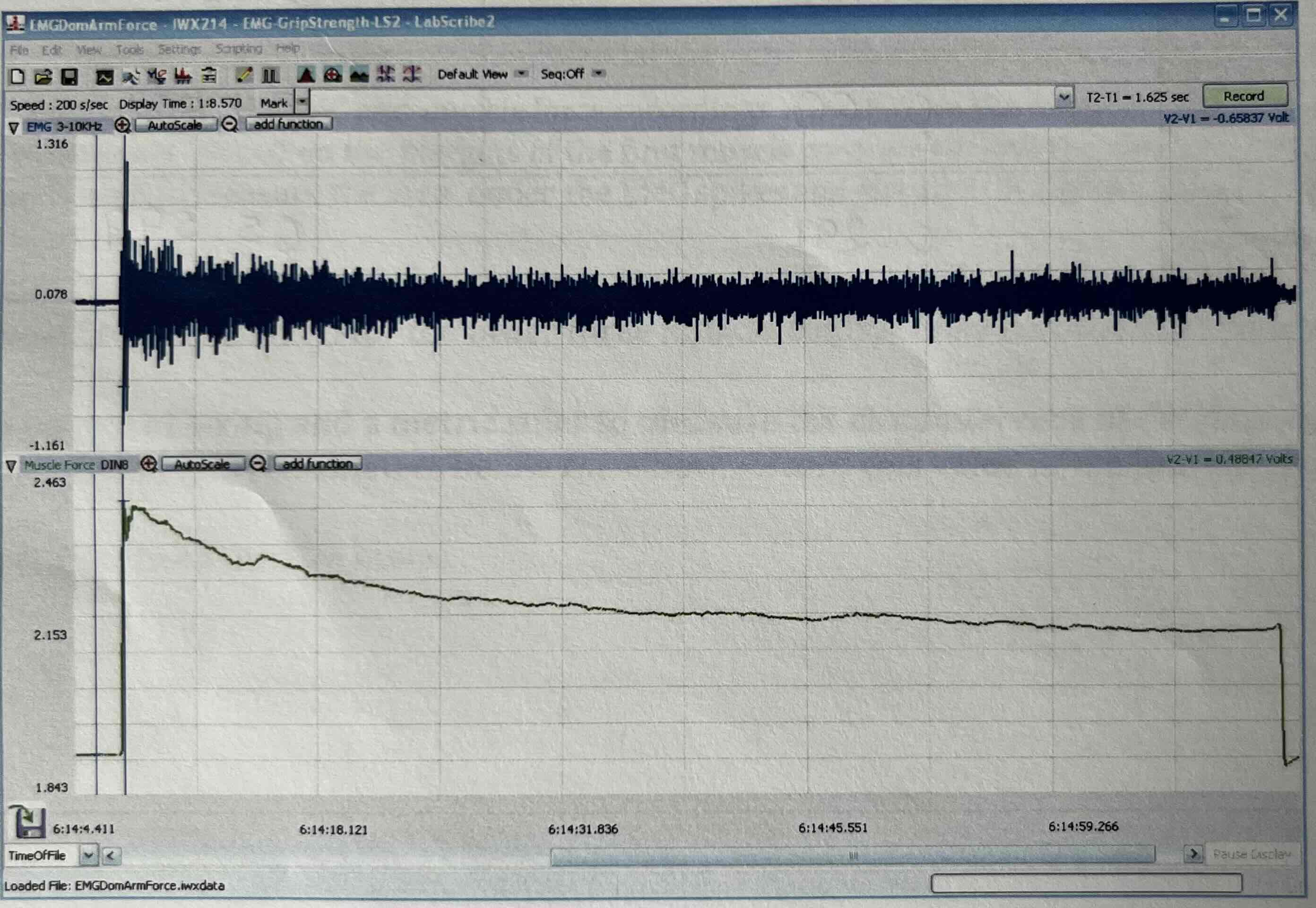
EMG Intensity and Fatigue in Dominant Arm Aim (Exercise 2)
to observe the relationship between the length and strength of a muscle contraction and EMG activity in the dominant forearm
Expected Results of Exercise 2
EMG Intensity and Force in the Non-Dominant Arm Aim (Exercise 3)
to determine the relationship between the intensity of EMG activity and the force of a muscle contraction in the subject’s non-dominant arm
EMG Intensity and Fatigue in Non-Dominant Arm Aim (Exercise 4)
to observe the relationship between the length and strength of a muscle contraction and EMG activity in the non-dominant forearm
Is there a difference in maximum forces generated by the dominant and non-dominant forearms?
Yes, dominant generates greater max force
Is there a difference in the forearm circumference of dominant and non-dominant forearms?
Yes, dominant is greater
Is there a relationship between the circumference of the forearm and the maximum force developed?
Yes, there is a positive relationship between the two
How does the time to fatigue to half-strength in the dominant and non-dominant forearms compare?
Dominant arm takes longer to fatigue, muscles in the dominant arm have been trained to be more resistant through simple everyday tasks
If there is a difference in the circumference of the forearms what is it caused by?
It is caused by an increase in the circumference of each muscle fiber, NOT by an increase in the number of muscle fibers