BOT 380 Hallucinogens - Anticancer
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Psychoactive plants
Contains compounds that affect the mind or alter the state of consciousness
stimulants
Hallucinogens
Analgesics
Sedatives
Hypnotics
Narcotics
Hallucinogenic Plants
all distort the perception of reality
experience of a dream world
Alter idea of time, space, sound, touch, smell, taste, colour
Affect cognition and moods
Confusions, memory loss, or disorientation rarely occur
Hallucinogen definition
Any agent that causes alterations in perception, cognition, and mood as its primary psychobiological actions in the presence of an otherwise clear sensorium
Psychedelic Greek meaning
Mind manifesting or mind expanding
Psychotomimetics
‘induce psychotic states’
Compared to symptoms of schizophrenia
Traditional use of hallucinogenic plants
Used worldwide but indigenous peoples for magic, medical,a do religious purposes
Used to mediate between man and the supernatural
Albert Hofmann
1949 - interest increases with the synthesis of LSD
Psychoplastogen
Small molecules that produce rapid and sustained structural and functional neural plasticity that are considered therapeutics for depression, addiction and PTSD
ex. Ketamine, MDMA, Scopolomine, LSD, psilocin
MDMA
In conjunction with psychotherapy for PTSD, anxiety and eating disorders
Psilocybin
For treatment of a variety of disorders including anxiety and depression
Use of LSD
cluster headaches and anxiety
Ibogaine
Anti addiction properties
What are monoamine (adrenergic) hallucinogens
Indole and catechol hallucinogens
Indole and catechol hallucinogens properties
target serotonin related pathways
Vivid sensory effects
Perception is altered while maintaining contact with real world
Low toxicity
What type of chemical is indole
Alkaloid with indole component
Sources and compounds of indole
Fungi
Claviceps purpurea (Ergot alkaloids)
Psilocybe mexicana (Psilocybin)
Plant
Turbina corymbosa (lysergic acid)
Claviceps purpurea - Ergot
Parasitic fungus
Fungal spores grow hyphae into ovaries of grain to obtain nutrients
Ergotism
Results from eating infected grain
Symptoms: gangrene,nervous spasms, psychotic delusions, convulsions
Salem witch trials
1692
Maybe have resulted from outbreak of Ergotism
Suggests that the ‘Great Fear’ of peasant revolt in 1789 France where many ‘lost their heads’ may have
occurred due to ingestion of ‘bad flour’
Ergot compounds
*derived from ergoline
ergotamine
Ergine
Lysergic acid
Effects of chemical compounds of Ergot
Show both antagonist and agonist effects of serotonin, dopamine, and adrenergic receptors
Modern uses of Ergot compounds
Uterine contractions
Treats migraines
Reduce prolactin levels resulting from pituitary tumours
Reduce postpartum hemorrhage
Treat senility and Alzheimer’s dementia
What is LSD
d-lysergic acid diethylamide
synthetic compound derived from Ergoloids
Acts as a model for plant derived psychedelics mechanism of action
Effects of LSD
small dose intensify perception
Large dose causes hallucinations
Rapid and complete tolerance develops for behavioural effects after 4-7 days, lasts for 3 days
Not reinforcing (addictive) like other drugs and does not produce withdrawal symptoms
Massive overdose required for lethal effects
LSD mechanism of action
Regulate serotonin pathways
LSD binds to multiple serotonin receptor subtypes (5HT receptors)
Has both agonist and antagonist effects
Tolerance due to down regulation of certain serotonin receptor
LSD: Good Trip
profound perceptual distortions and hallucination
Heightened awareness of sensations and altered sense of self
Effects highly variable
LSD: Bad Trip
panic episode brought on by dislike of drugs effect and fears that the experience will not end
Flashbacks - hallucinogen persisting perception disorders
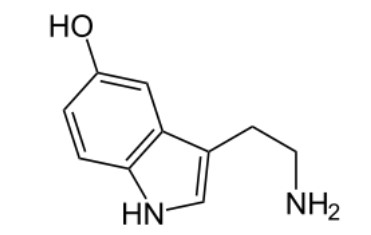
What is this compound?
serotonin
Morning Glories
Turbina produces seeds called ‘Ololiuqui’ (round object)
contains lysergic acid
Where is lysergic acid found in morning glories
Lysergic acid alkaloids are found in these seeds
Psilocybe species: ‘psychedelic mushrooms’ history
religious ceremonies
Mexico and Central America
called Teonanacatl (God’s flesh)
Richard Evans Schultes
First botanist to record rituals and beliefs surrounding this sacred mushroom
Hallucinogenic compounds of Psilocybe mushrooms
structurally similar to serotonin
effects similar to lysergic acid and LSD
Timothy Leary
1960s
invested effects of eating magic mushrooms
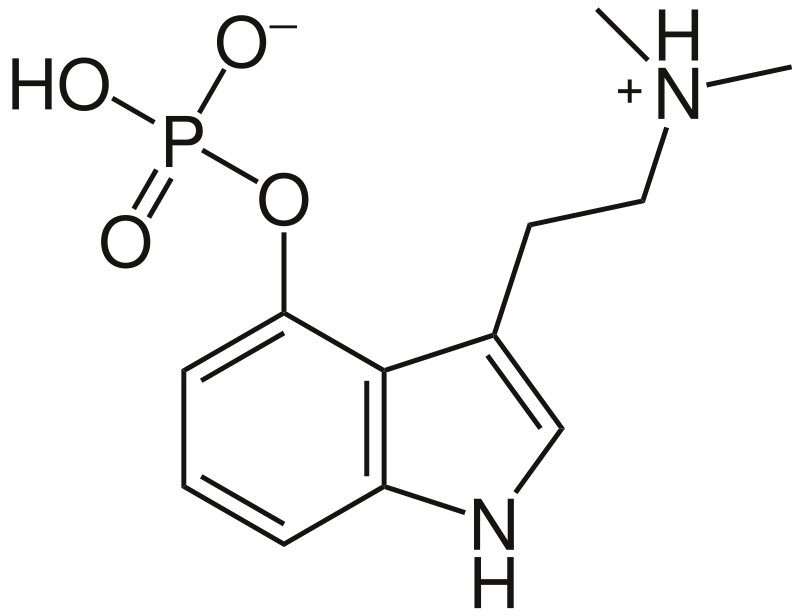
What is this compound?
Psilocybin
Effects of Psilocybe compounds
Timeline of effects
Dizziness, weakness and twitching (30 mins after ingestion)
Visual effects seen (30-60 min after)
Normalcy returns (180 mins after)
Peyote Cactus
Lophophora williamsii
Peyote
small spineless cactus
>56 different alkaloids identified
mescaline is the primary psychoactive alkaloid
Pharmacology of mescaline
similar to indole hallucinogens
contains catechol group
readily absorbed by body
Psychoactive dose of mescaline
Dilation of pupils
Increase in pulse rate and blood pressure
Elevation of body temperaturewas
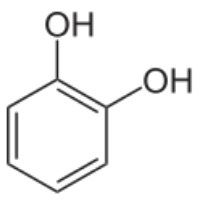
What is this compound
Catechol
Mechanism of action of catechol
Mescaline resembles catecholamine neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine
Effects suggested to mirror mechanism of indole hallucinogens via serotonin actions
pharmacological activity is very similar to LSD
Preparation of Peytote
entire plant is psychoactive
only above ground portion is edible
can be eaten green or made into tea
dried then eaten
dried mescal buttons remain psychoactive indefinitely
Nutmeg
Myristica fragrans
contains catecholamine hallucinogen myristicin
powdered nutmeg was used as a hallucinogen in Old World
aphrodisiac powers (Yemen)
Mace (flesh covering seed) contains different active ingredients with similar effects
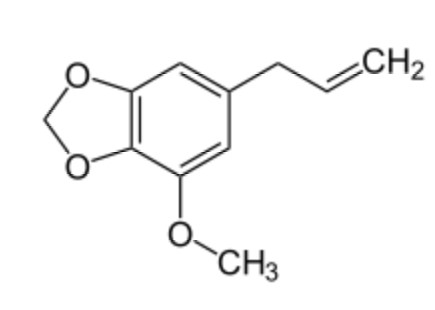
What is this compound
Myristicin
Fly agaric mushroom
Amanita muscaria
amino acid targets
Ibotenic acid, muscimol, muscarine (no psychoactive)
Historical uses of Fly agaric
oldest and most widely used hallucinogenic drug
3500 years ago, the Soma cult of the Indus ValleY
Compounds of Amanita muscaria
muscimol
Muscarine
Ibotenic acid
Ibotenic acid
Ibotenic acid and muscimol produce similar behavioural states despite very different mechanism of action
Activates glutamate receptors
Glutamate is an endogenous excitatory neurotransmitter → binds to receptor that act as ion channels
Muscimol
the most active compound in fly agaric
GABA receptor agonist
Muscimol effects
produces state of confusion, disorientation, sensory disturbances
Fatigue, sedation, sleep
Cognitive ability dimished
Effects of ingesting fly agaric
ingestion for one to four mushrooms for effects
Derangement of senses then manic behaviour
Delirium and altered perceptions of size
General inhibition of motor function
Gauss
German doctor
Uses drug to allow for “twilight sleep” for women during childbirth
Modern scopolamine use
Post-operative Nausea
Motion Sickness
GI Spasms
To aid in GI radiology and endoscopy – Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Eye Inflammation
What kind of compound is scopolamine
Alkaloid
CNS effects of scopolamine
delirium
Mental confusion
Loss of attention
Drowsiness
Loss of memory for recent events
Death
Cordwood Tree
Duboisia myoporoides
leaves have concentration of atropine
Aborigines submerged branches of tree into eel populated pools
Eels become lethargic and easy prey
Other species
Hyoscyamous niger
Atropa belladonna
Colchicine
Mode of action
inhibits mitosis
Disrupts micro tubes
Uses in modern medicine
treat gout
Derivatives used to treat cancer
Side effects
narrow therapeutic index results in overdose
Damage bone marrow
May apple
Podophyllum peltatum
root extract, long history among indigenous peoples of American Northeast in treating skin cancers
Active ingredients
Aliphatic alkaloids, podophyllins
Podophyllotoxin and a-peltatin
Podophyllotoxin
Mode of action
stops replication cellular & viral DNA replication
Destabilizes microtubules to prevent cell division
Uses in modern medicine
treat HPV
Derivatives used to treat cancer
Side effects
Embryotoxic
Autumn Crocus
Colchicum autumnale
extracts inhibit cell division
Colchicine alkaloid
Disrupts spindle formation during mitosis
Red clover
Trifolium pratense
salve made from the flowers
Isoflavone genistein as anti-oxidant
Effective against breast cancer
Taxine
From Taxus
Toxic alkaloid assemblage composed of more than seven alkaloids
Taxol
market name for paclitaxel
Alkaloid
Active anti-cancer agent in pacific yew
Taxol mode of action
blocks cell replication
M phase of cell cycle (mitosis and cytokinesis)
Late anaphase/telophase the spindle structure is lost
Paclitaxel binds to microtubles and prevents disassembly
Cannot complete division
Madagascar periwinkle
Catharanthus roseus
herbal medicine → wasp stings, stop bleeding, eyewash, diabetes treatment
Plant extracts inhibit leukaemia in mice
Active anti-cancer agents
Bloodroot
Sanguinaria canadensis
Indigenous peoples used red sap used to treat breast cancer
Today, used in conjunction with surgery to treat skin cancer
Sanguinarine
used in oral rinses and toothpastes
Effective against oral plaque forming organisms
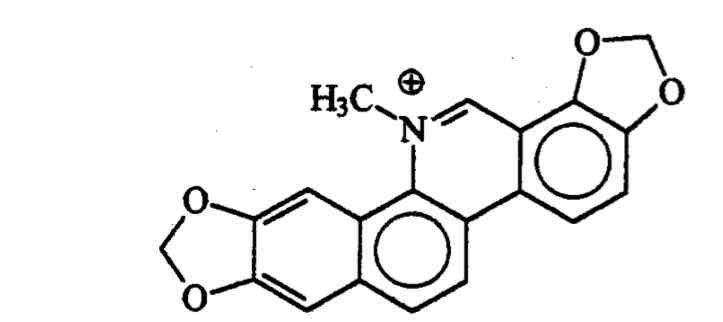
What is this compound
Sanguinarine
Anti-malarial drugs
Quinine and Artemisian
The Dark Ages
1500 years with little knowledge on cause or treatment
spread of malaria in Europe and the New World
Association with swamps and marshes led to believe that malaria was caused by malignant
vapors (miasmas)
Paludisme roughly translate “of the marshes”
Charles Louis Alphonse
discovered malaria parasite (1880)
Noticed parasites in the blood
Causes of malaria
four species of protozoans from the genus Plasmodium cause different forms of disease
Cerebral malaria results in death if untreated
Initiated but bite of female Anopheles mosquito
Symptoms:
reoccurring bouts of fevers, chills, and anemia
Result of merozoites released into bloodstream
sporozoite form of parasite multiples in liver (merozoites are created)
Merozoites invade red blood cells → multiple rapidly, deplete RBC
RBC cell rupture occurs 48-72 hours after invasion → causes fever and chills
Some species can remain dormant for years
Malaria cure
late 16th century/early 17th century
Indigenous people used mark of a mountain rain forest tree to treat fevers (Incas, Cinchona bark)
Quinine
alkaloid
Found in Peruvian tree bark
Odourless white powder
Interferes with merozoite action
Prevents polymerization of heme into hemozoin resulting in toxicity to parasite
Synthetic anti-malarial drugs
Chloroquine, malarone (atovaquone/proguanil), mefloquine
Used to target different Plasmodium life cycle stages and strains
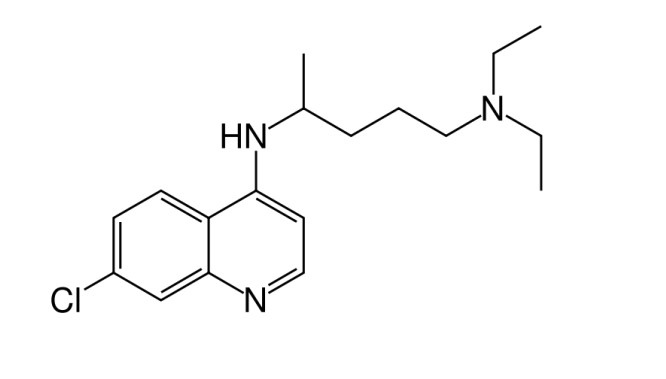
what is this compound
chloroquine
How does quinine work?
degrade hemoglobin to acquire essential amino acids
Digestion carried out in vacuole of the parasitic cell. During this process, the parasite release the toxic
and soluble molecule heme.
the parasite biocrystallizes heme to form hemozoin, a nontoxic molecule
preventing the formation of hemozoin
Wormwood
Artemisia annua
quinine alternative
fever reduction
terpene compound called Artemisinin
produced in trichomes
How is artemisian synthesized
farnesyl diphosphate (FDP) → sesquiterpene intermediate → artemisinic acid → dihydroartemisinic acid → artemisinin
Pathway intermediates of Artemisian
IPP, DMAPP and GPP
Absinthe
Artemisia absinthium
mass produced at the Pernod distillery
originally a cough medicine
thought to infuse the drinker with creativity, intelligence and glamour
Plant mixture
variety of plant extracts including fennel, sweet balm, hyssop, angelica, and anise
most important plant is variety of wormwood
absinthism
Associated with epileptic seizures, orgy behavior, sexual diseases, corrupted artists, criminals
Mimics of absinthe sometimes contain grain alcohol and copper salts (for color)- possibly toxic
Thujone
terpene
responsible for absinthes effects
increased creativity (good)
absinthism (bad)
What does Thujone do?
binds to and blocks GABAA receptors in brain neurons
Release of chloride into postsynaptic neurons reduces synaptic activity
Inhibition of normal GABA activity may lead to the seizures seen when under the influence of thujone
Steps in genetic engineering of Artemisian
Steps 1 and 2:
increase amount of substrate available (FPP)
modify expression of several genes responsible for FPP synthesis
Step 3:
They isolated genes encoding enzymes responsible for oxidizing amorphadiene to artemisinic acid
Toxin
poisonous substance produced by cells or living organisms
Death of Cleopatra
experiments with different plant extracts on slaves
Henbane and Belladonna work quickly, but are painful
Strychnine works quickly, but leaves the face distorted
Supposedly, she decides on Asp’s venom
History of Poisons
Assyrians wrote of plant poisons over 3000 years ago
Greeks attribute discovery of poisonous plants to Hecate
Roman herbalists were often accomplices to murder (readily available)
Arab cultures in 9th century perfect the art of poisoning
How to avoid being poisoned
Avoid eating foods that smell or taste ‘wrong’
Use special goblets → would explode if poison was placed in the drink
Use special stones to neutralize poison → toadstones, bezoar stones
Antidotes and Cures
most cures instruct victim to induce vomiting
Theriaca ( Greek ‘theriakon’ meaning remedies for venomous bites')
Nero poisons his stepbrother to gain the throne
Acetylcholinesterase
quickly removes acetylcholine from synapse
Physostigmine inhibits acetylcholinesterase, resulting in more acetylcholine in the synapse
Cardiac glycoside arrow poisons
Acokanthera, Parquetina, and Strophanthus genera
Produce compounds like Ouabain and Strophanthidin
cardiac glycosides are mixed with a binding agent
Ouabain
cardiac glycosides
used on arrows by hunters in Africa
Mechanism of action
Inhibits the sodium/potassium ATPase that maintains ion gradients in heart muscle cells
Toxic Phenolics
Lignans → Podophyllotoxin
Coumarins → Aflatoxins, Methoxypsoralen
Tannis
Other phenolics → Urushiol
Aflatoxin
Aspergillus sp.
fungus
contaminate corn, cereals, sorghum, peanuts
carcinogenic to humans and animals
• Toxin intercalates and alkylates DNA, inducing mutation
Mithridates Eupator
paranoid of being poisoned
Took small doses of poison to make himself immune
Tried to poison himself but was too tolerant
Slave stabbed him to death
Cyclopamine
Veratrum californicum
alkaloid
Teratogen
Inhibits normal protein patterning in developing organisms
Named after mythical cyclops spoken of in Homer’s Odyssey
Aconitine or Aconite
Aconitum napellus
Monkshood, friar’s cap, auld wife’s huid
Mechanism
reduces ion selectivity if sodium channels
Increase uptake of sodium
Produces cardiac arrhythmias
Traditional medicine
It is the sum total of the knowledge, skill, and practices based on the theories, beliefs, and experiences indigenous to different cultures, whether explicable or not, used in the maintenance of health as well as in the prevention, diagnosis, improvement or treatment of physical and mental illness.
Ethnobotany
indigenously-informed plant identification, foraging, and cultivation in use as food, medicine and shelter