THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Water is a ____ molecule because the oxygen atom carries a slight ____ charge, while the hydrogen atoms carry a slight ____ charge
Polar, negative, positive
What do you call the attraction between the hydrogen of one water molecule and the oxygen of another?
Hydrogen Bonds
Where do you find Acids on the pH scale?
0 to just below 7
Where do you find Bases on the pH scale?
Just above 7 to 14
List some unique properties of water
High surface tension due many Hydrogen bonds
High Specific Heat- take water longer than the air to fluctuate temperature
Less dense when frozen
Cohesion- easily bonds to other water molecules
Adhesion- easily bonds to other molecules (inside of a plant stem)
Universal Solvent- Water is able to dissolve many important molecules (for example, bloodstream)
What substances do not dissolve easily in water?
Polar substances like lipids (hydrophobic)
What do you call water molecules sticking to other WATER molecules?
Cohesion
This is the most common solvent in a cell
Water
In order to be considered organic, a molecule must contain this element
Carbon
How many electrons does carbon have in its outermost energy level?
4
Molecules that are long chains and large rings can be made in cells because carbon loves to bond with what?
Other carbon atoms and many atoms of other elements, such as Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfer
What kind of covalent bonds can carbon make with other atoms?
single, double , triple bonds
The formation of polymers from monomers occurs as a result of this type of reaction
dehydration synthesis (WATER IS REMOVED TO MAKE THE BIGGER MOLECULE)
The breakdown of polymers into smaller monomers occurs as a result of this type of reaction
Hydrolysis (WATER IS ADDED BACK WHEN THE MOLECULE IS BROKEN APART)
What are the four groups of macromolecules
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
Give examples of carbohydrates
Mono (glucose), di (sucrose), and polysaccharides (starch)
How do plants store glucose? (a molecule)
Starch
How do you store glucose? (a molecule)
Glycogen
Give examples of lipids
fats, oils , waxes, pigments, steroids
Where would you find long chains of amino acids, linked by peptide bonds?
Proteins
What piece of an amino acid makes it unique from other amino acids?
R group
Give examples of nucleic acids
DNA, RNA
What is the function of DNA?
Store genetic information, direct cell activities
In a chemical reaction, these are the substances that get changed (the “ingredients”)
Reactants
In a chemical reaction, these are the new substances formed
Products
The amount of energy needed to initiate a chemical reaction
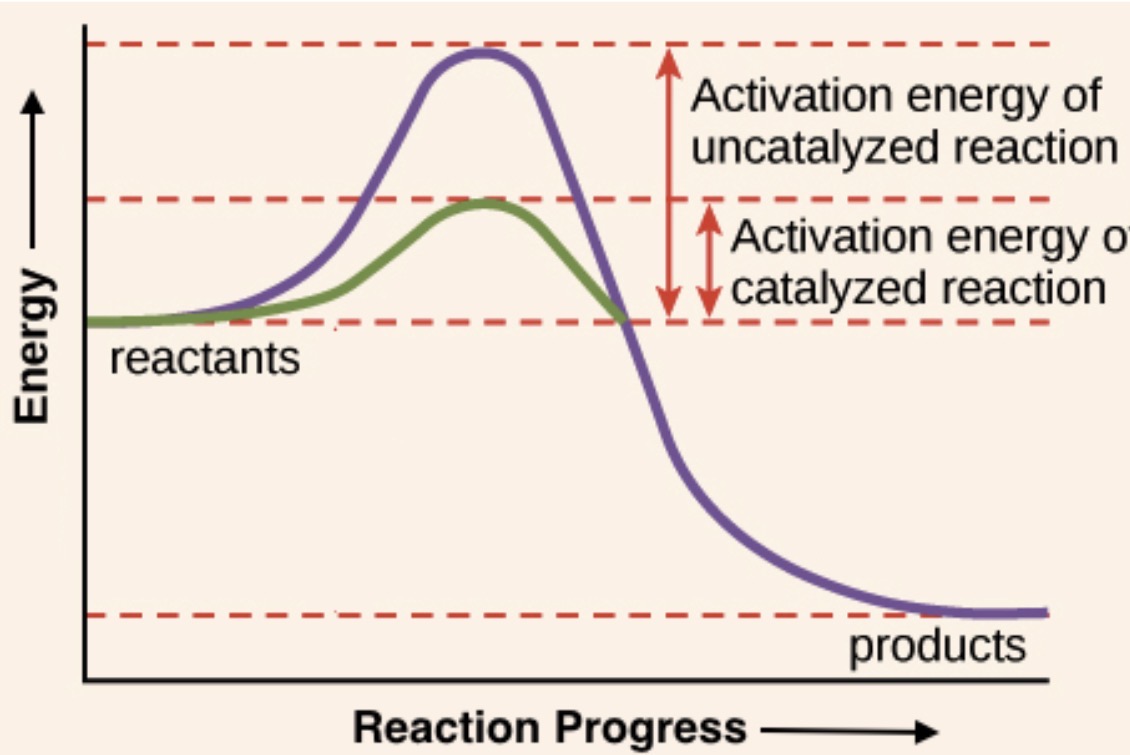
Activation Energy
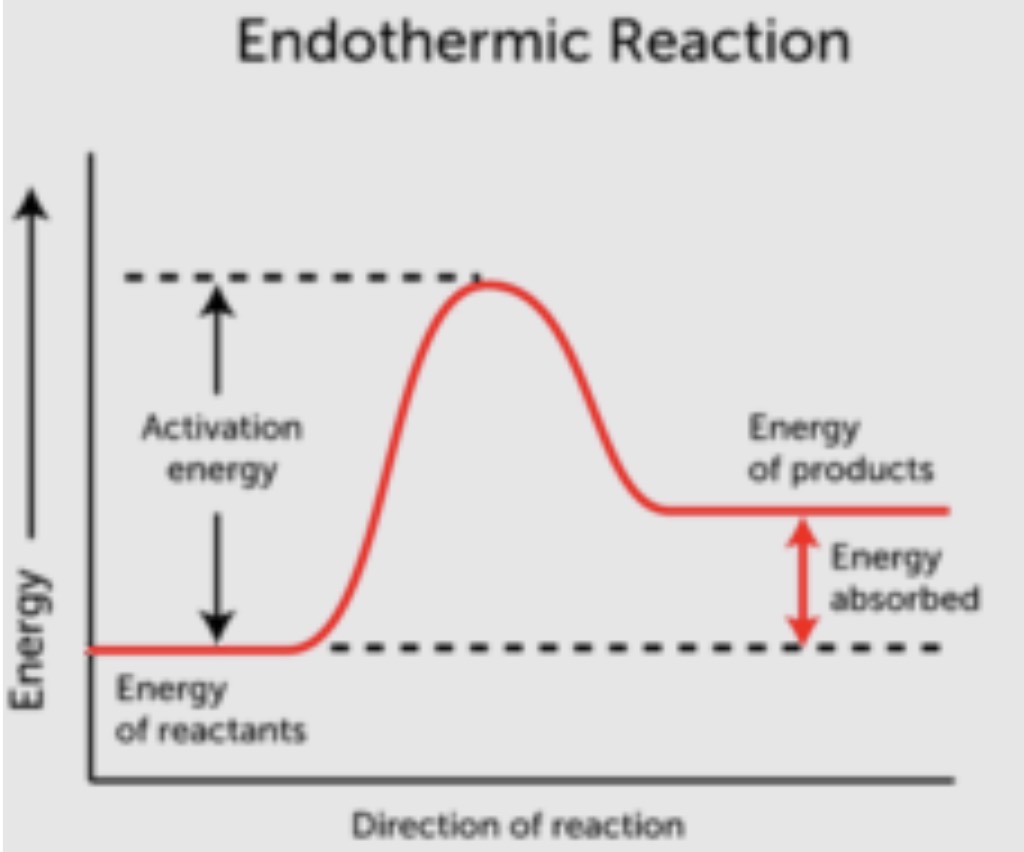
These reactions absorb energy overall. Draw a picture of the energy of this reaction.
Endothermic reaction
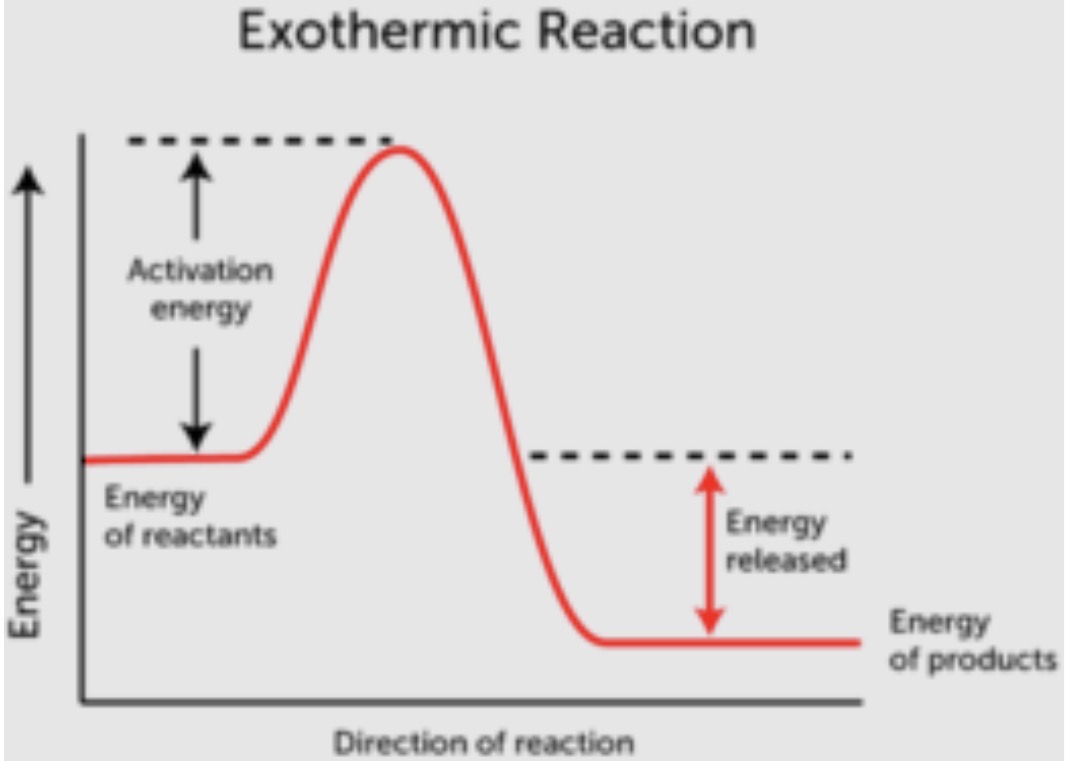
These reactions release energy overall. Draw a picture of the energy of this reaction.
Exothermic Reactions
Without these, the chemical reactions in your cells would occur too slowly to support life’s processes
Enzymes
Reactants in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction are called
Substrates
What is the name of the place on an enzyme where the substrate binds?
Active site
List two factors that can impact the activity of an enzyme
pH and temperature
If any of your answers to #32 above changes too drastically, what happens to the enzyme?
Enzyme can become denatured, changing the shape of the active site, causing the substrate to not fit, and subsequently, the reaction to not occur
Draw a graph comparing the energy pathways of a reaction without an enzyme and one with an enzyme